论文 Paradigm Shift in Natural Language Processing 用范式(paradigm)这一概念总结了NLP领域今年的发展大趋势。一作是黄萱菁和邱锡鹏老师的博士生孙天祥。
摘要
In the era of deep learning, modeling for most NLP tasks has converged to several mainstream paradigms. For example, we usually adopt the sequence labeling paradigm to solve a bundle of tasks such as POS-tagging, NER, Chunking, and adopt the classification paradigm to solve tasks like sentiment analysis. With the rapid progress of pre-trained language models, recent years have observed a rising trend of Paradigm Shift, which is solving one NLP task by reformulating it as another one. Paradigm shift has achieved great success on many tasks, becoming a promising way to improve model performance. Moreover, some of these paradigms have shown great potential to unify a large number of NLP tasks, making it possible to build a single model to handle diverse tasks. In this paper, we review such phenomenon of paradigm shifts in recent years, highlighting several paradigms that have the potential to solve different NLP tasks.
在深度学习时代,大多数 NLP 任务的建模已经收敛到几种主流范式。 例如,我们通常采用序列标注范式来解决诸如 POS-tagging、NER、Chunking 等一组子任务,而采用分类范式来解决诸如情感分析之类的任务。 随着预训练语言模型的快速发展,近年来出现了范式转变的上升趋势,即通过将一个 NLP 任务重新构建为另一个 NLP 任务来解决它。 范式转变在许多任务上都取得了巨大的成功,成为提高模型性能的一种很有前途的方法。 此外,其中一些范式已显示出统一大量 NLP 任务的巨大潜力,使得构建单一模型来处理不同任务成为可能。 在本文中,我们回顾了近年来这种范式转变现象,重点介绍了几种有可能解决不同 NLP 任务的范式。
论文中发现:
(1)近年来范式转变的频率正在增加,尤其是在预训练语言模型(PTM)出现之后。为了充分利用这些 PTM 的力量,更好的方法是将各种 NLP 任务转为 PTM 擅长的范式。(2) 越来越多的 NLP 任务已经从 Class、SeqLab、Seq2ASeq 等传统范式转向更通用、更灵活的范式:(M)LM、Matching、MRC 和 Seq2Seq。
其中(M)LM是指(Masked) Language Model,MRC指Machine Reading Comprehension。目前(M)LM非常火,作者认为其他几个范式值得更多关注。
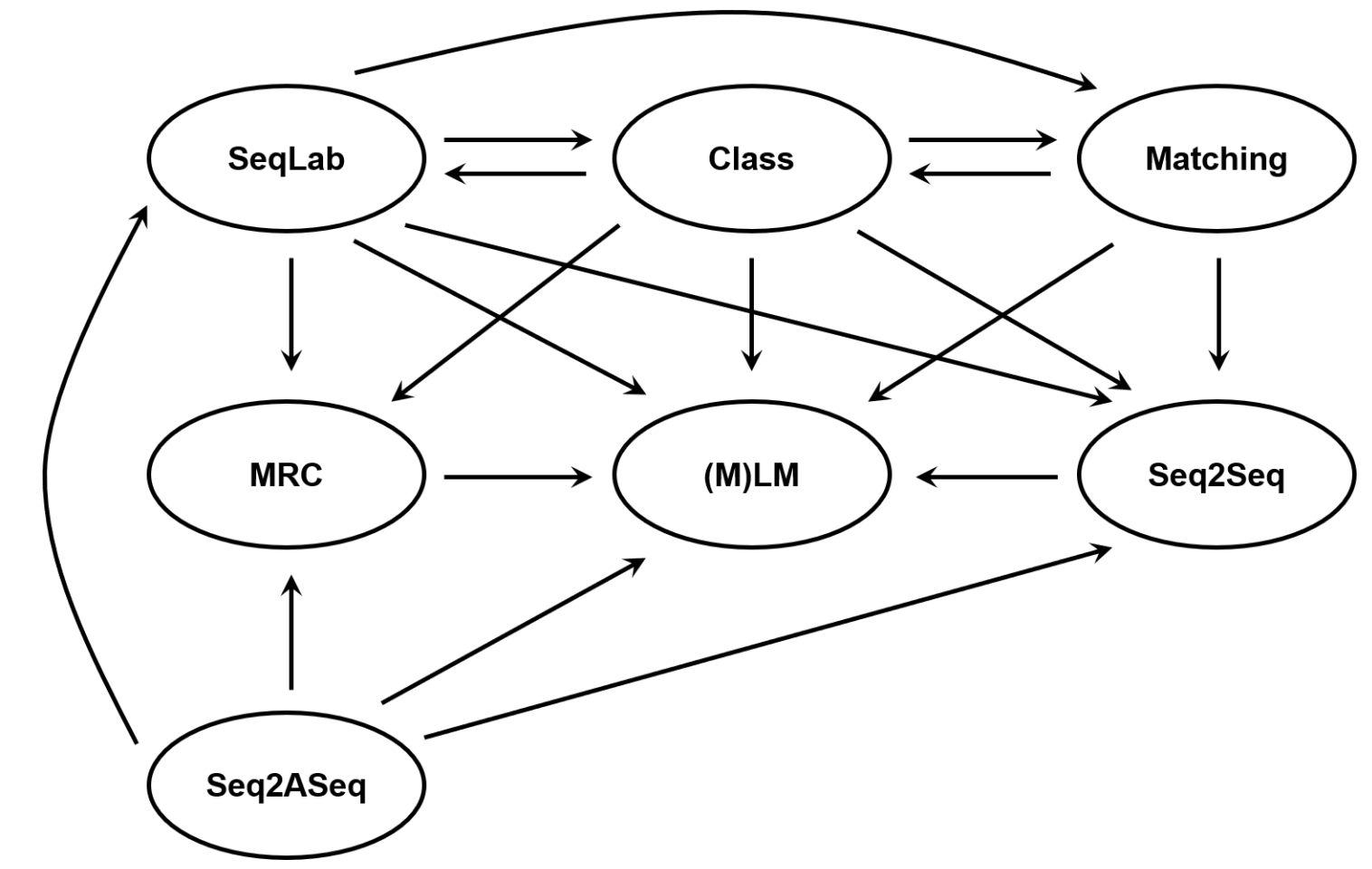
图片出自孙天祥个人网站
也可以参考孙天祥的介绍Slides。
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢