LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:通过大型模型进化、视觉语言和多模态任务统一模型、用Internet规模知识构建开放具身智能体、基于Dixit游戏的grounded语言模型特定化、面向同质空间等变网络的统一的基于傅里叶的核和非线性设计、快速有限宽度神经切线核、面向人眼逼真合成动画和重打光的混合表示、图像自举自监督视频表示学习、无模板可动画体演员
1、[LG] Evolution through Large Models
J Lehman, J Gordon, S Jain, K Ndousse, C Yeh, K O. Stanley
[OpenAI]
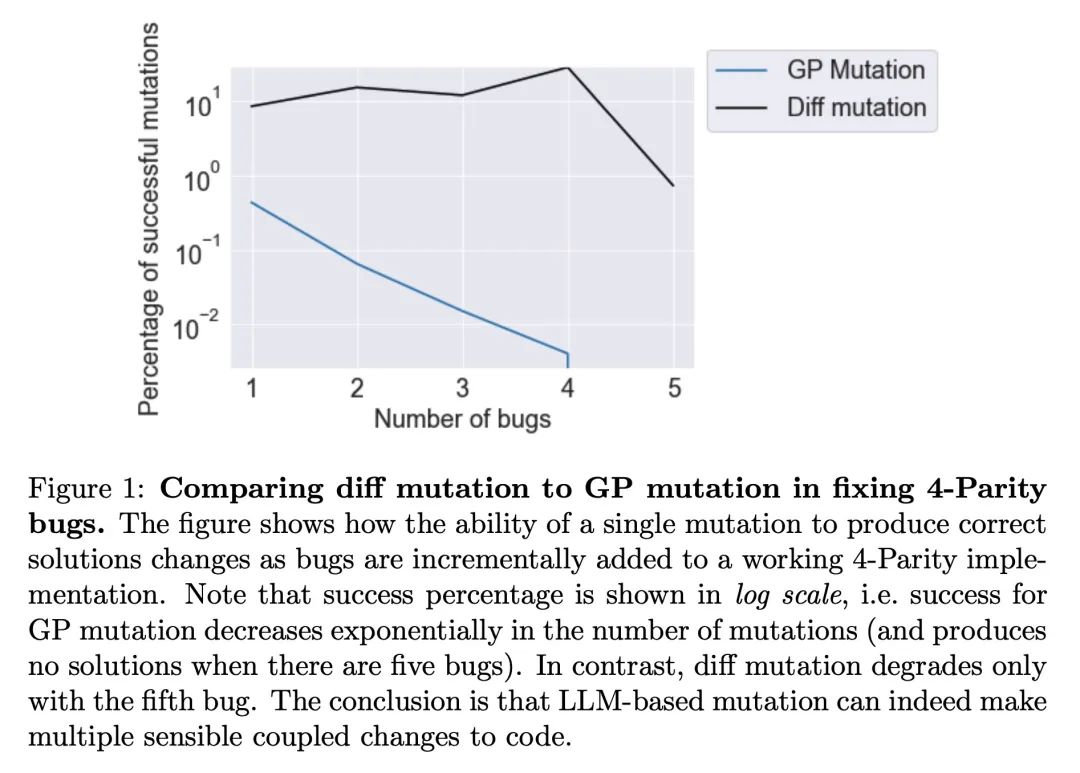
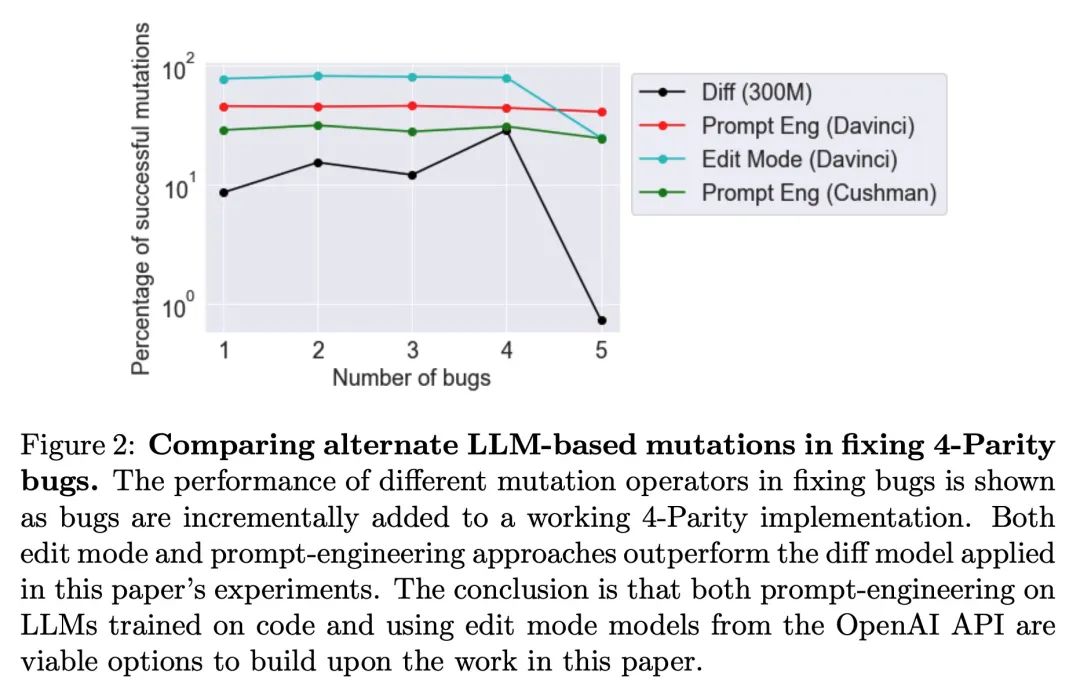
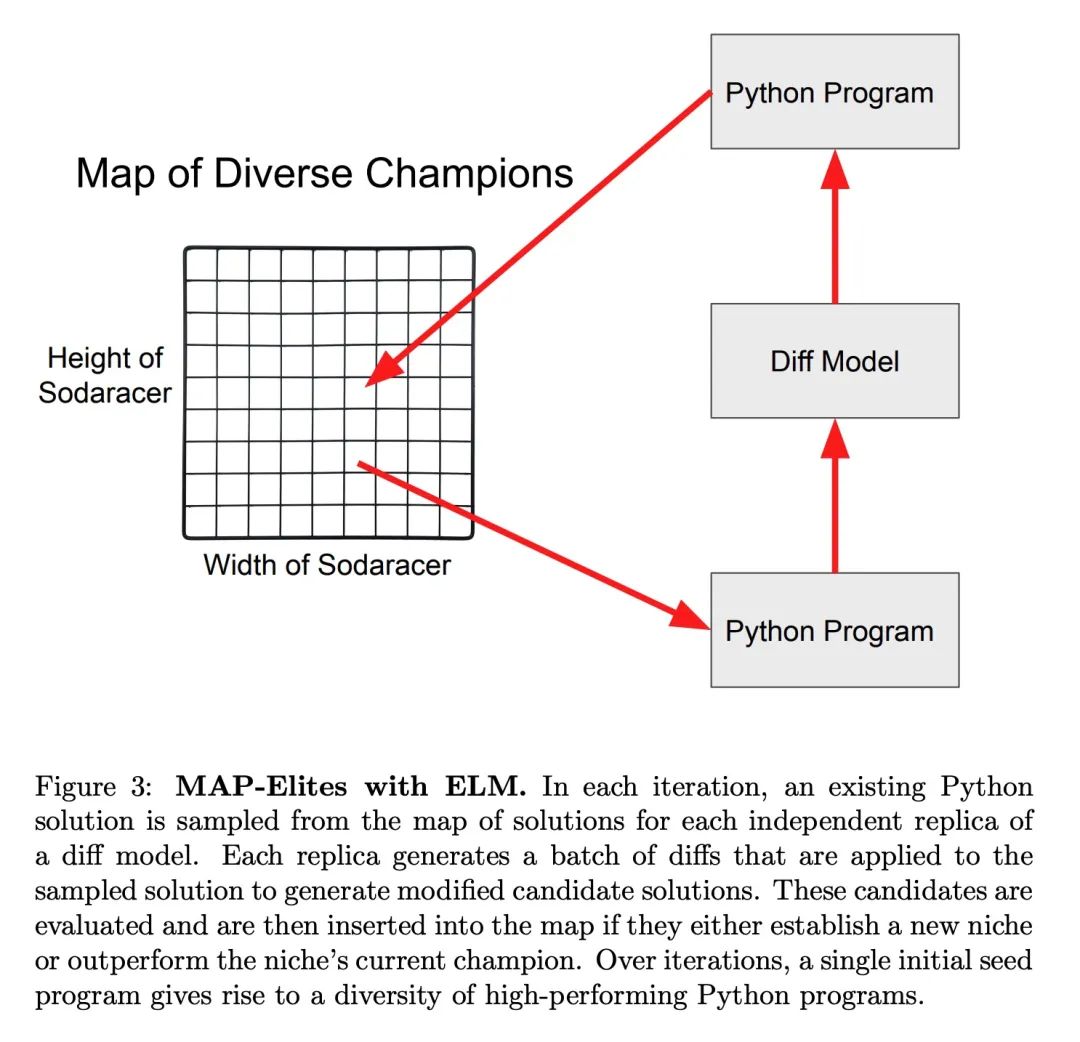
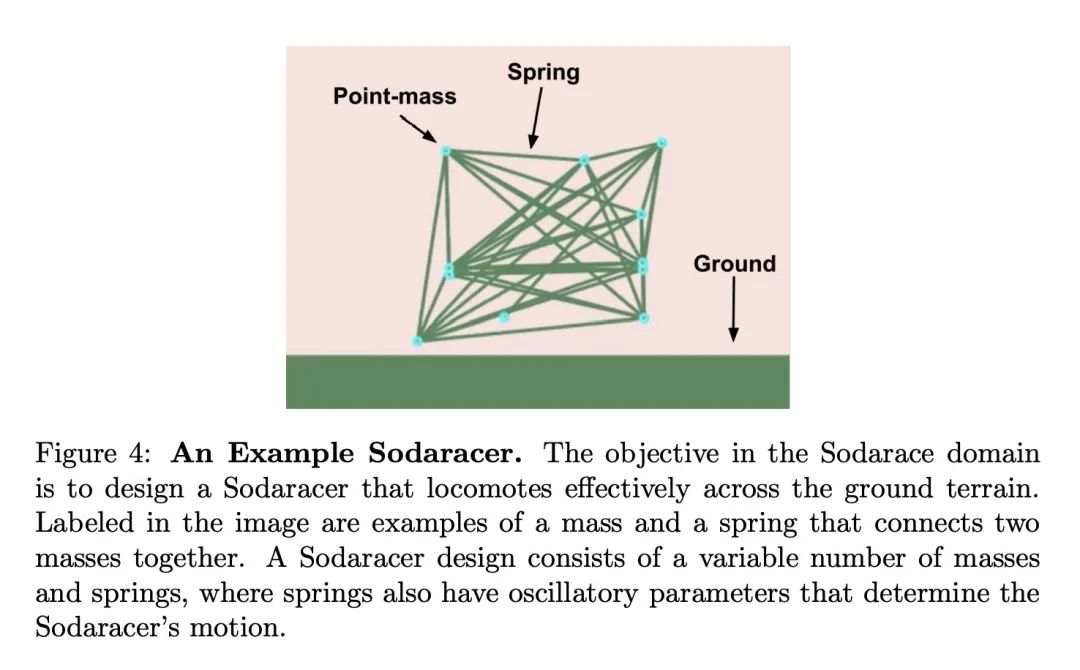
通过大型模型进化。本文提出的见解是,经过训练以生成代码的大规模语言模型(LLM)可以极大地提高应用于遗传编程(GP)程序变异算子的有效性。由于此类LLM受益于包含序列变化和修改的训练数据,因此可以近似人类可能做出的更改。为了突出这种通过大规模模型进化(ELM)的广泛影响,在实验中,ELM与MAP-Elite相结合,生成了数十万个Python 程序的函数示例,这些示例输出到Sodarace域的工作行走机器人,这些数据是原始LLM在预训练中从未见过的。这些示例有助于自举训练一个新的条件语言模型,该模型可以为特定地形输出正确的步行器。在之前零训练数据可用的域中,引导新模型为给定上下文输出适当输出的能力,对开放性、深度学习和强化学习产生了影响。本文深入探讨这些影响,希望能激发由ELM开辟的新研究方向。
This paper pursues the insight that large language models (LLMs) trained to generate code can vastly improve the effectiveness of mutation operators applied to programs in genetic programming (GP). Because such LLMs benefit from training data that includes sequential changes and modifications, they can approximate likely changes that humans would make. To highlight the breadth of implications of such evolution through large models (ELM), in the main experiment ELM combined with MAP-Elites generates hundreds of thousands of functional examples of Python programs that output working ambulating robots in the Sodarace domain, which the original LLM had never seen in pre-training. These examples then help to bootstrap training a new conditional language model that can output the right walker for a particular terrain. The ability to bootstrap new models that can output appropriate artifacts for a given context in a domain where zero training data was previously available carries implications for open-endedness, deep learning, and reinforcement learning. These implications are explored here in depth in the hope of inspiring new directions of research now opened up by ELM.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08896

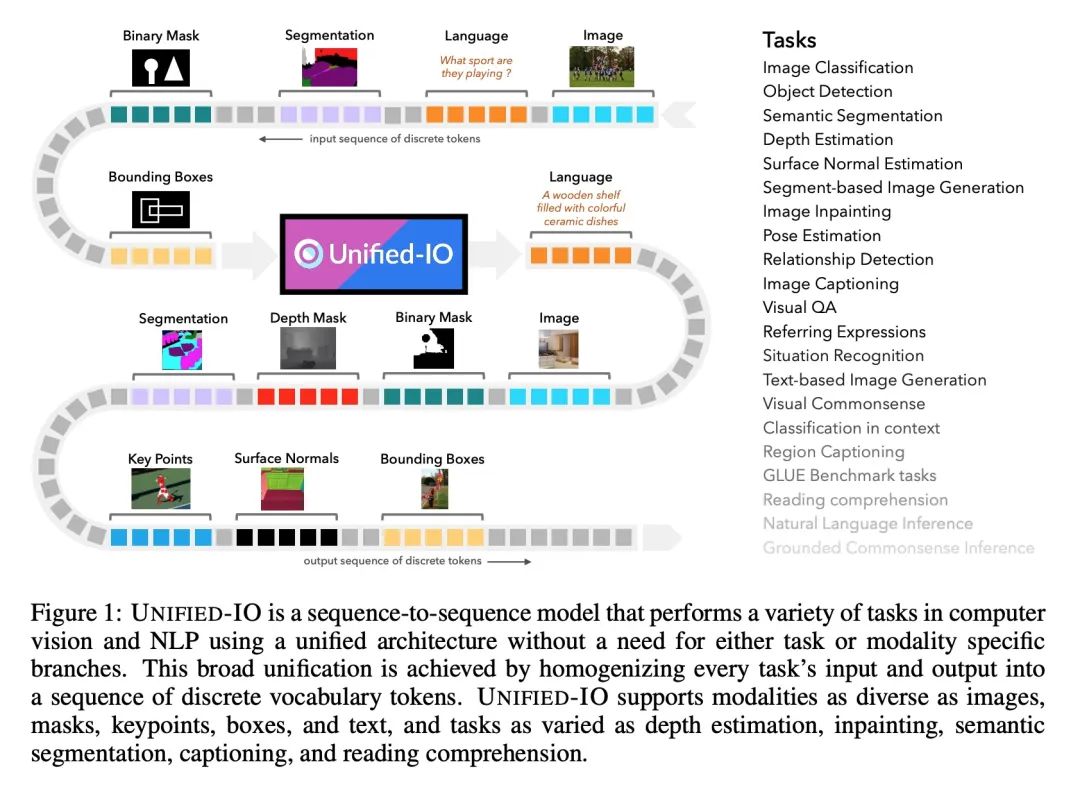
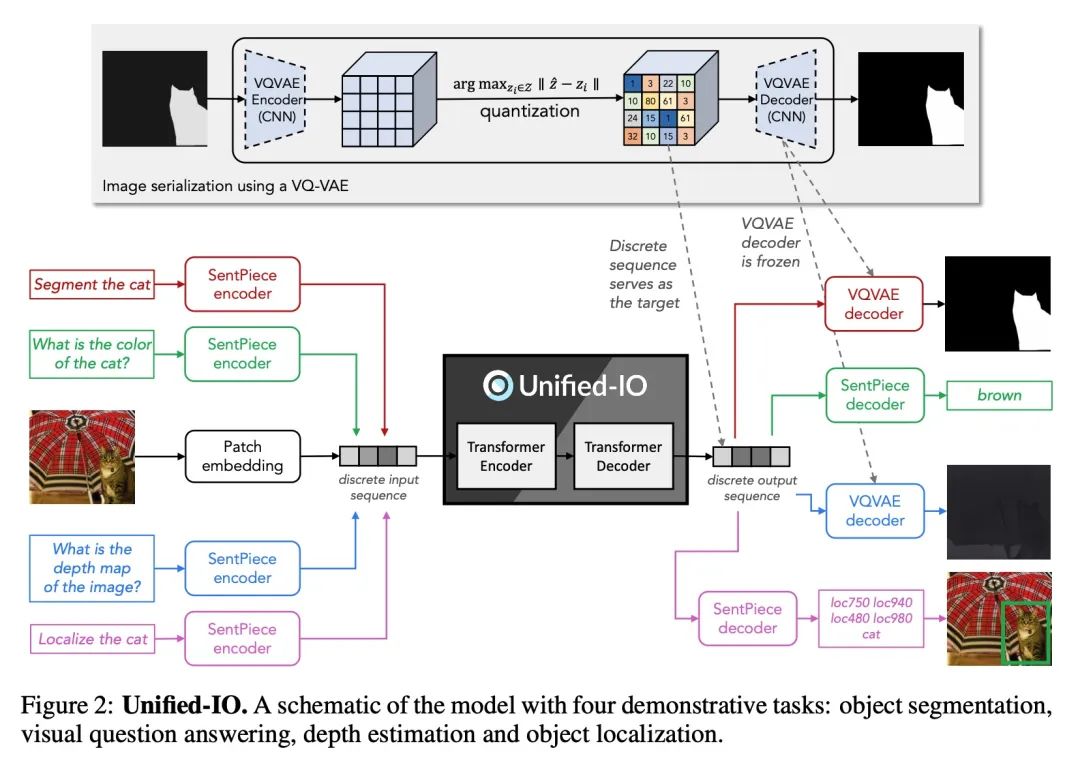
2、[CV] Unified-IO: A Unified Model for Vision, Language, and Multi-Modal Tasks
J Lu, C Clark, R Zellers, R Mottaghi, A Kembhavi
[Allen Institute for AI]
Unified-IO:视觉、语言和多模态任务统一模型。本文提出UNIFIED-IO,一个能执行大量人工智能任务的模型,涵盖了经典的计算机视觉任务,包括姿态估计、目标检测、深度估计和图像生成,视觉-语言任务,如区域描述和参考表达的理解,以及自然语言处理任务,如问答和转述。由于与每个任务相关的输入和输出都是异质的,包括RGB图像、每像素映射、二进制掩码、边框和语言,因此为如此多的任务开发一个统一的模型带来了独特的挑战。本文通过将每种支持的输入和输出同质化为一串离散词汇token来实现这种统一。这种跨越所有任务的共同表示法,能在视觉和语言领域的80多个不同的数据集上共同训练一个基于Transformer的架构。UNIFIED-IO是第一个能够在GRIT基准上执行所有7项任务的模型,在16个不同的基准上产生了强大的结果,如NYUv2-Depth、ImageNet、VQA2.0、OK-VQA、Swig、VizWizGround、BoolQ和SciTail,无需进行基准微调或特定任务的修改。
We propose UNIFIED-IO, a model that performs a large variety of AI tasks spanning classical computer vision tasks, including pose estimation, object detection, depth estimation and image generation, vision-and-language tasks such as region captioning and referring expression comprehension, to natural language processing tasks such as question answering and paraphrasing. Developing a single unified model for such a large variety of tasks poses unique challenges due to the heterogeneous inputs and outputs pertaining to each task, including RGB images, per-pixel maps, binary masks, bounding boxes, and language. We achieve this unification by homogenizing every supported input and output into a sequence of discrete vocabulary tokens. This common representation across all tasks allows us to train a single transformer-based architecture, jointly on over 80 diverse datasets in the vision and language fields. UNIFIED-IO is the first model capable of performing all 7 tasks on the GRIT benchmark and produces strong results across 16 diverse benchmarks like NYUv2-Depth, ImageNet, VQA2.0, OK-VQA, Swig, VizWizGround, BoolQ, and SciTail, with no task or benchmark specific finetuning. Demos for UNIFIED-IO are available at: unified-io.allenai.org
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08916


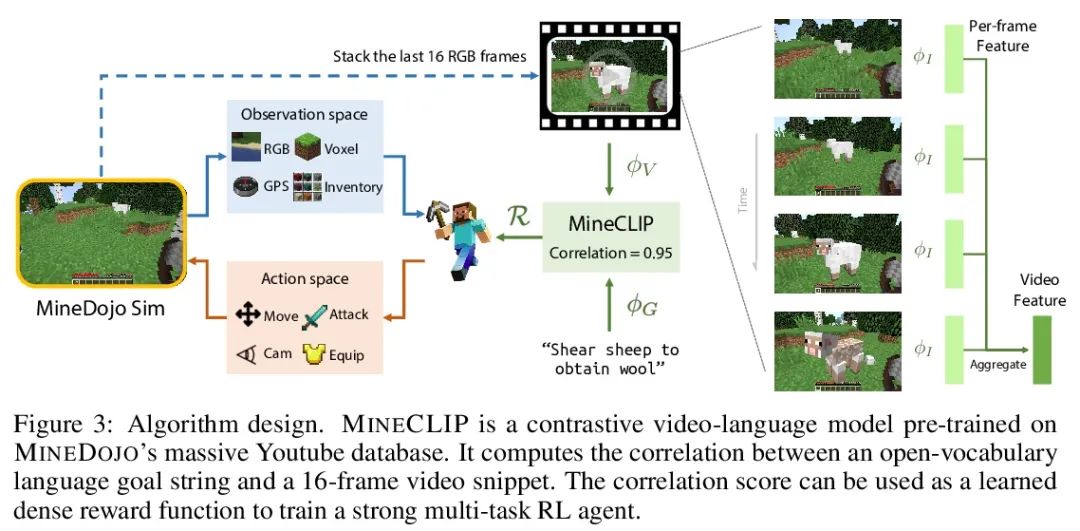
3、[LG] MineDojo: Building Open-Ended Embodied Agents with Internet-Scale Knowledge
L Fan, G Wang, Y Jiang, A Mandlekar, Y Yang, H Zhu, A Tang,...
[NVIDIA & Caltech & Stanford & Columbia & SJTU & UT Austin]
MineDojo:用Internet规模知识构建开放具身智能体。自主智能体在诸如Atari游戏和围棋等专业领域取得了巨大进步。然而,它们通常是在孤立环境中以有限的、人工设想的目标进行学习,无法在广泛的任务和能力方面进行推广。受到人类在开放世界中不断学习和适应的启发,本文提倡建立三位一体的通用智能体:1)支持多种任务和目标的环境,2)大规模的多模态知识数据库,以及3)灵活可扩展的智能体架构。本文提出MINEDOJO,一个建立在流行的Minecraft游戏基础上的新框架,其特点是具有数千种不同的开放式任务的模拟套件和一个具有Minecraft视频、教程、维基页面和论坛讨论的Internet规模的知识库。利用MINEDOJO的数据,本文提出一种新的智能体学习算法,利用大型预训练的视频语言模型作为学习奖励函数。该智能体能解决各种用自由形式的语言指定的开放任务,而不需要任何人工设计的密集的设计奖励。
Autonomous agents have made great strides in specialist domains like Atari games and Go. However, they typically learn tabula rasa in isolated environments with limited and manually conceived objectives, thus failing to generalize across a wide spectrum of tasks and capabilities. Inspired by how humans continually learn and adapt in the open world, we advocate a trinity of ingredients for building generalist agents: 1) an environment that supports a multitude of tasks and goals, 2) a large-scale database of multimodal knowledge, and 3) a flexible and scalable agent architecture. We introduce MINEDOJO, a new framework built on the popular Minecraft game that features a simulation suite with thousands of diverse open-ended tasks and an internet-scale knowledge base with Minecraft videos, tutorials, wiki pages, and forum discussions. Using MINEDOJO’s data, we propose a novel agent learning algorithm that leverages large pre-trained video-language models as a learned reward function. Our agent is able to solve a variety of open-ended tasks specified in free-form language without any manually designed dense shaping reward. We open-source the simulation suite and knowledge bases (https://minedojo.org) to promote research towards the goal of generally capable embodied agents.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08853




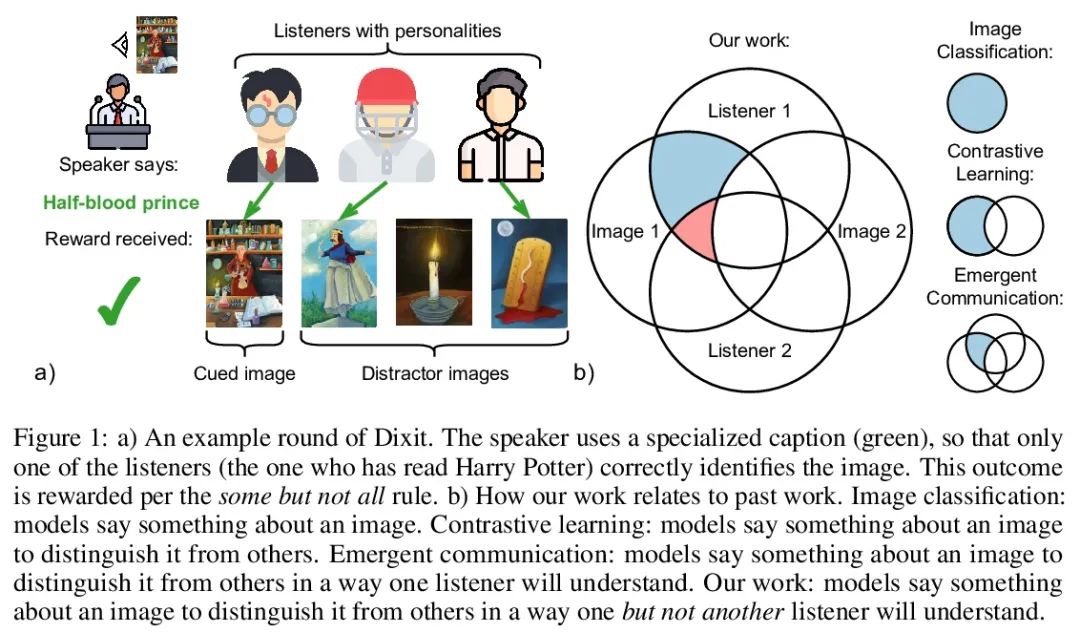
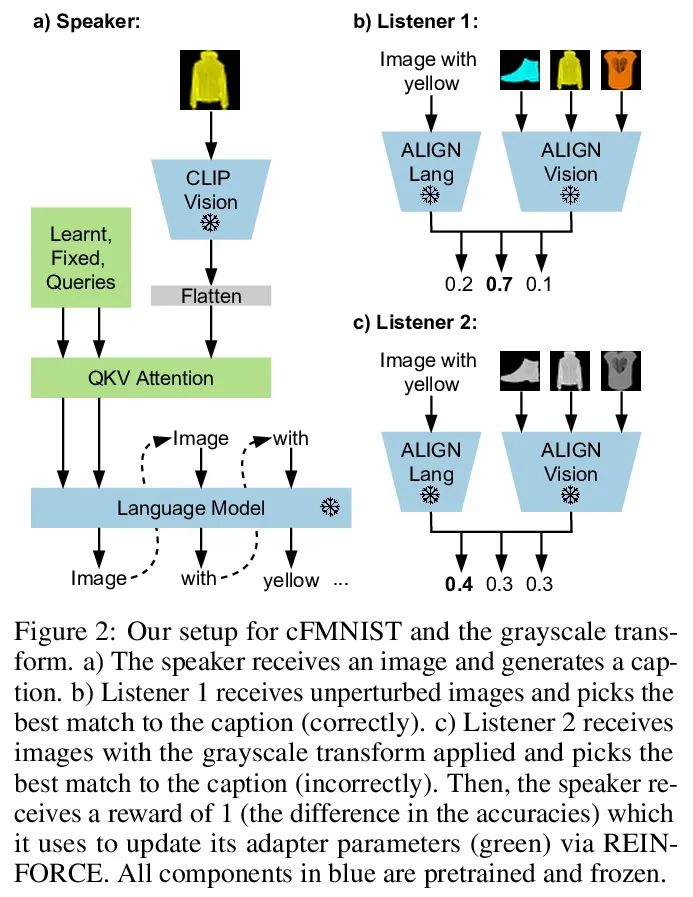
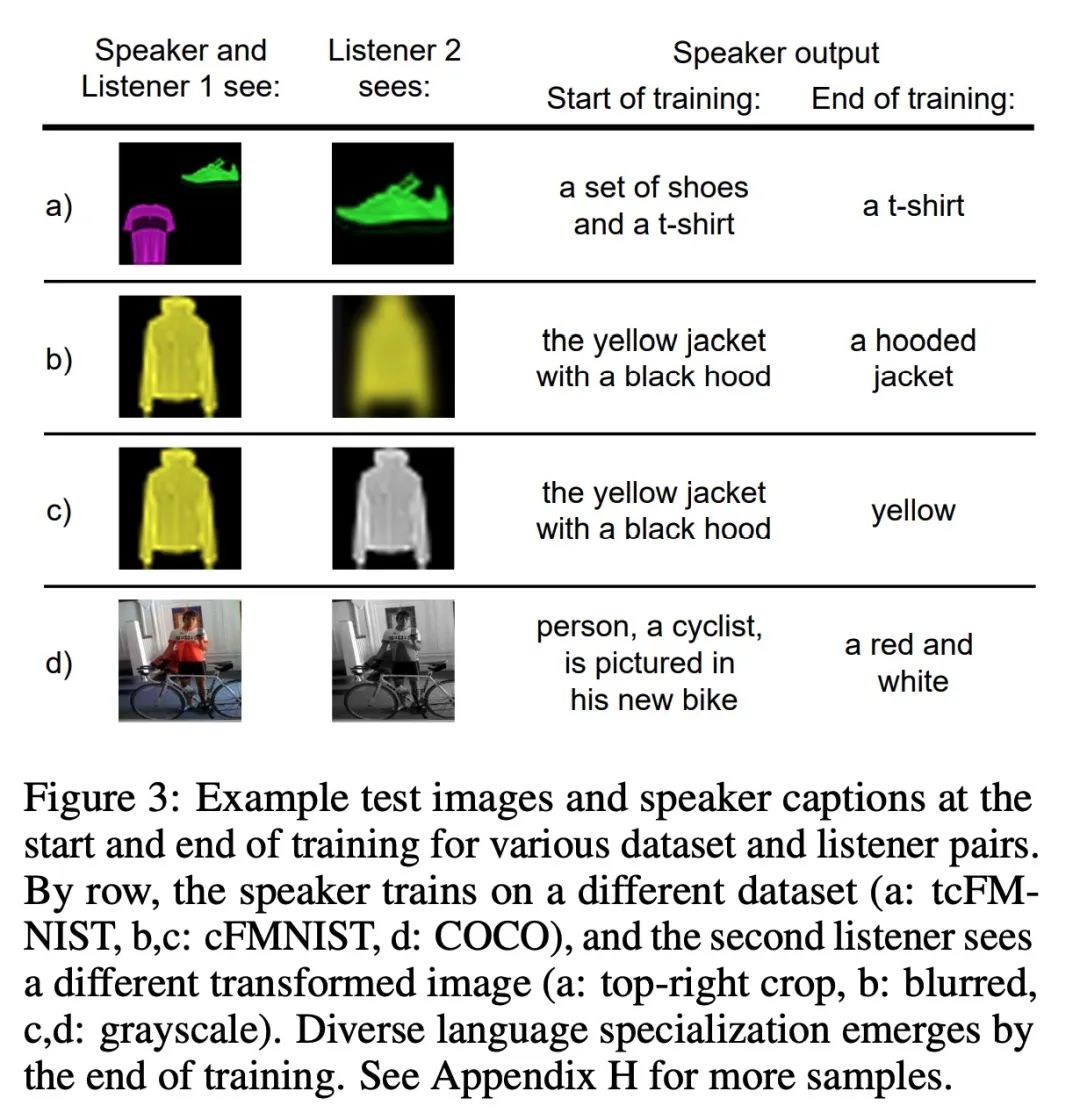
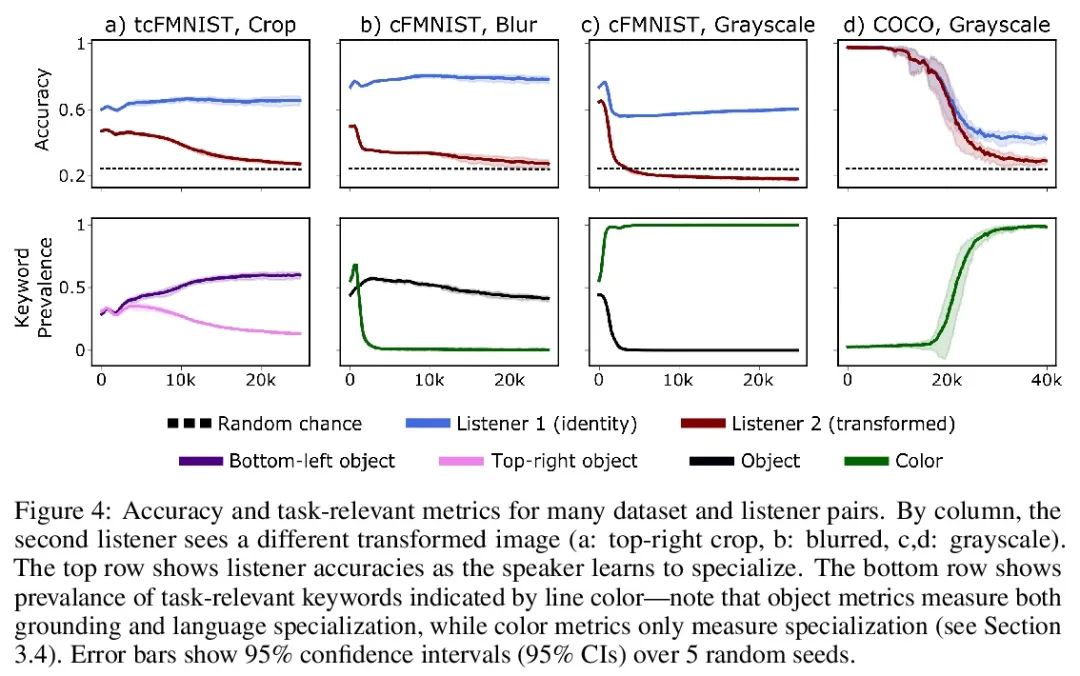
4、[LG] Know your audience: specializing grounded language models with the game of Dixit
A K. Singh, D Ding, A Saxe, F Hill, A K. Lampinen
[University College London & DeepMind]
了解你的听众:基于Dixit游戏的grounded语言模型特定化。有效的交流需要适应与每个交流伙伴共享的特异性的共同点。本文研究该问题的一个特别具有挑战性的实例:流行的游戏Dixit。将一轮Dixit游戏制定为一个多智能体的图像参考游戏,其中一个(经过训练的)说话者模型因描述一个目标图像而得到奖励,这样一个(经过预训练的)听话者模型可以从一个干扰者池中正确地识别它,但另一个听话者不能。为了适应这种环境,说话者必须利用它与不同听众的共同点的差异。本文表明,在这种对比性的多智能体环境中,对CLIP视觉编码器和大型语言模型之间的基于注意力的适配器进行微调,会产生仅来自奖励的上下文依赖的自然语言特定化,而无需直接监督。一系列受控实验表明,说话者可以根据各种不同听众对的特异性优势和劣势进行自适应。本文还展示了说话人的特定化向未见过的真实世界数据的零样本迁移。所述实验为在复杂的多伙伴环境中实现自适应交流提供了一步,并强调了像Dixit这样的游戏所带来的有趣的研究挑战。
Effective communication requires adapting to the idiosyncratic common ground shared with each communicative partner. We study a particularly challenging instantiation of this problem: the popular game Dixit. We formulate a round of Dixit as a multi-agent image reference game where a (trained) speaker model is rewarded for describing a target image such that one (pretrained) listener model can correctly identify it from a pool of distractors, but another listener cannot. To adapt to this setting, the speaker must exploit differences in the common ground it shares with the different listeners. We show that finetuning an attention-based adapter between a CLIP vision encoder and a large language model in this contrastive, multi-agent setting gives rise to context-dependent natural language specialization from rewards only, without direct supervision. In a series of controlled experiments, we show that the speaker can adapt according to the idiosyncratic strengths and weaknesses of various pairs of different listeners. Furthermore, we show zero-shot transfer of the speaker’s specialization to unseen real-world data. Our experiments offer a step towards adaptive communication in complex multi-partner settings and highlight the interesting research challenges posed by games like Dixit. We hope that our work will inspire creative new approaches to adapting pretrained models.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08349

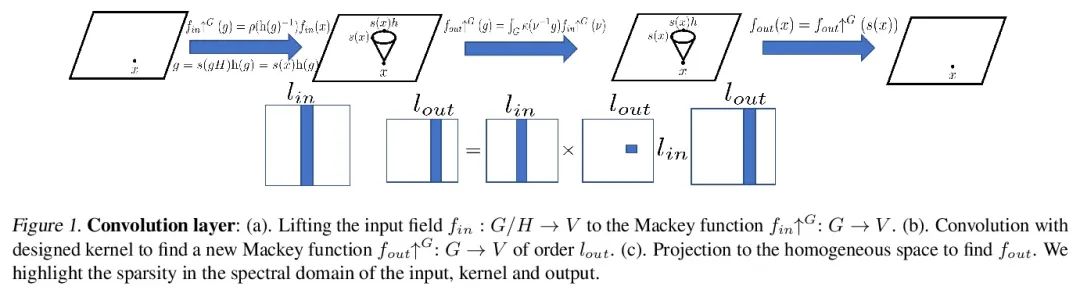
5、[CV] Unified Fourier-based Kernel and Nonlinearity Design for Equivariant Networks on Homogeneous Spaces
Y Xu, J Lei, E Dobriban, K Daniilidis
[University of Pennsylvania]
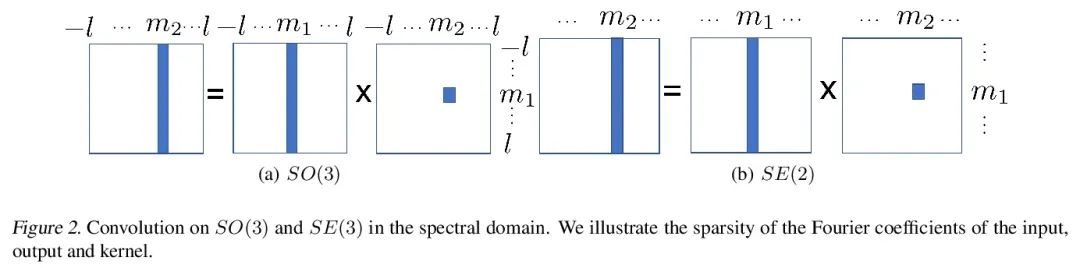
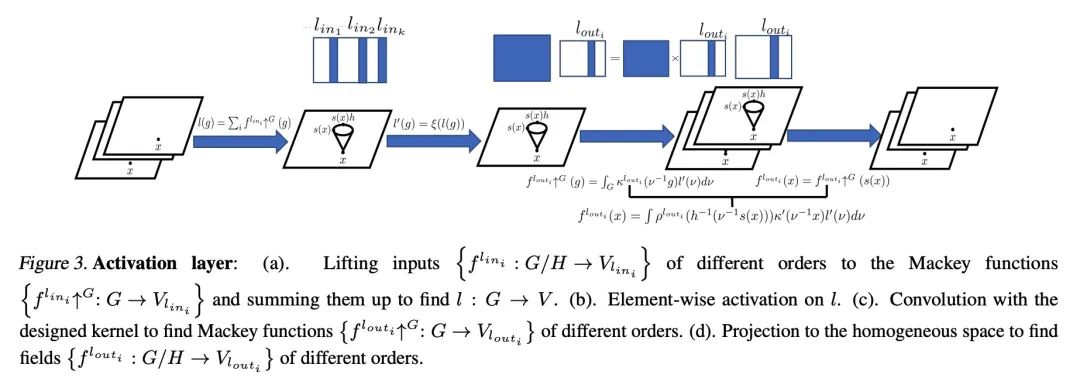
面向同质空间等变网络的统一的基于傅里叶的核和非线性设计。本文介绍了一个统一框架,用于从傅里叶角度衍生出的同质空间上的群等变网络。本文研究了卷积层前后的特征场被张量估值的情况。通过傅里叶域提出一个统一的内核推导,利用提升的特征场的傅里叶系数的稀疏性。当同质空间的稳定器子群是一个紧凑的李群时,稀疏性就出现了。本文进一步提出一种激活方法,通过等变卷积提升和投射回场后,通过元素非线性对常规表示进行激活。本文表明,其他将特征视为稳定器子群中的傅里叶系数的方法是所提出激活方法的特例。在SO(3)和SE(3)上的实验显示了在球面向量场回归、点云分类和分子补全方面最先进的性能。
We introduce a unified framework for group equivariant networks on homogeneous spaces derived from a Fourier perspective. We address the case of feature fields being tensor valued before and after a convolutional layer. We present a unified derivation of kernels via the Fourier domain by taking advantage of the sparsity of Fourier coefficients of the lifted feature fields. The sparsity emerges when the stabilizer subgroup of the homogeneous space is a compact Lie group. We further introduce an activation method via an elementwise nonlinearity on the regular representation after lifting and projecting back to the field through an equivariant convolution. We show that other methods treating features as the Fourier coefficients in the stabilizer subgroup are special cases of our activation. Experiments on SO(3) and SE(3) show state-of-the-art performance in spherical vector field regression, point cloud classification, and molecular completion.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08362


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
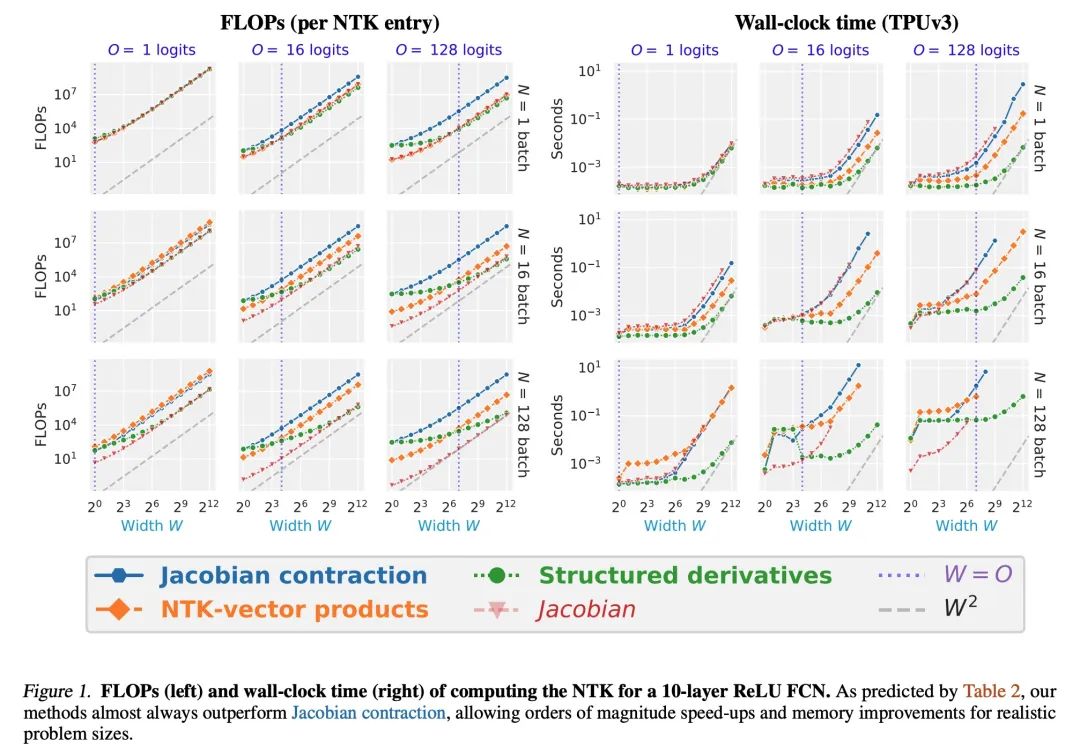
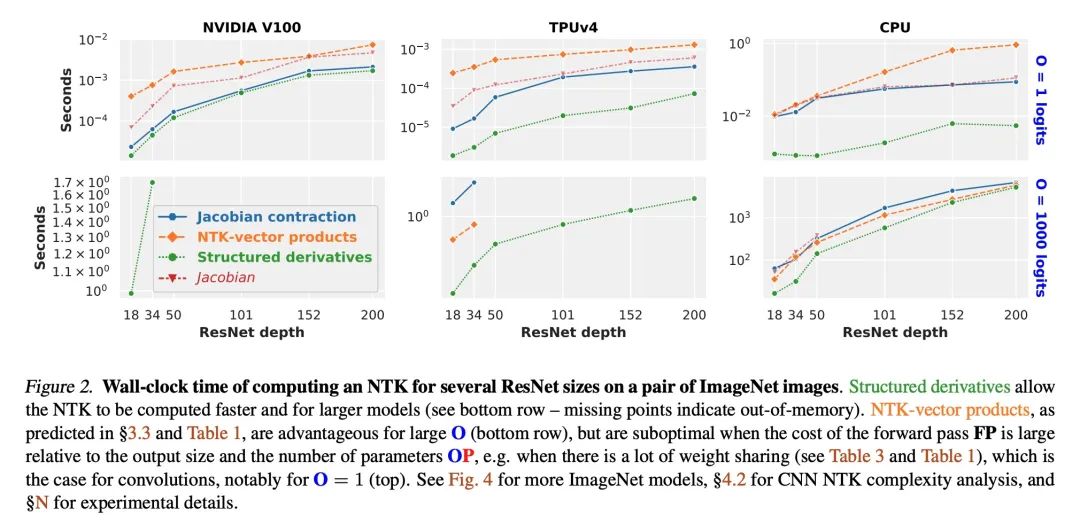
[LG] Fast Finite Width Neural Tangent Kernel
快速有限宽度神经切线核
R Novak, J Sohl-Dickstein, S S. Schoenholz
[Google Brain]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08720

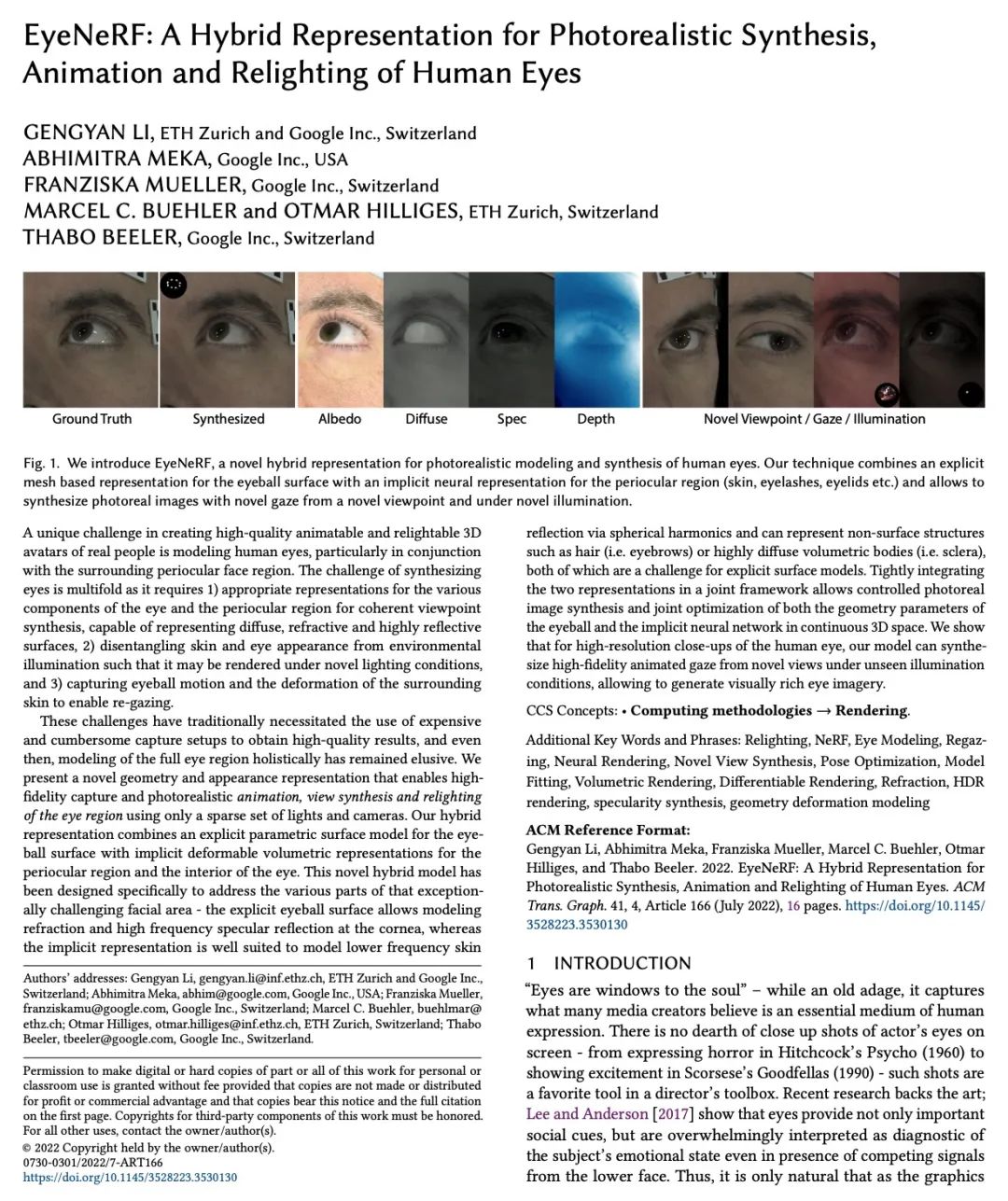
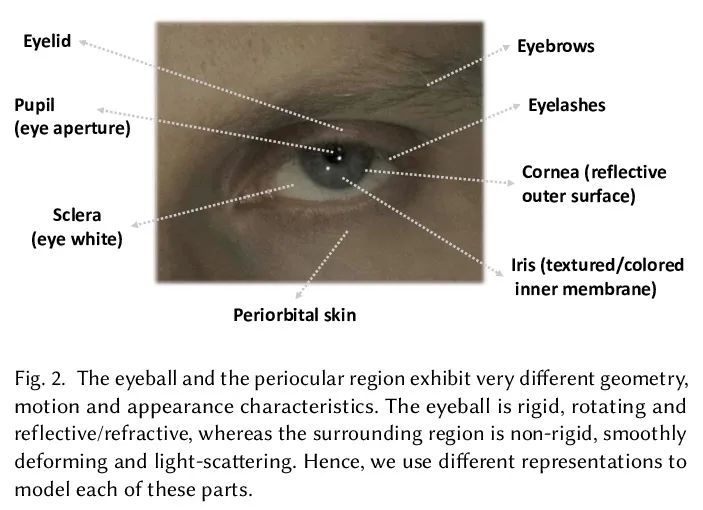
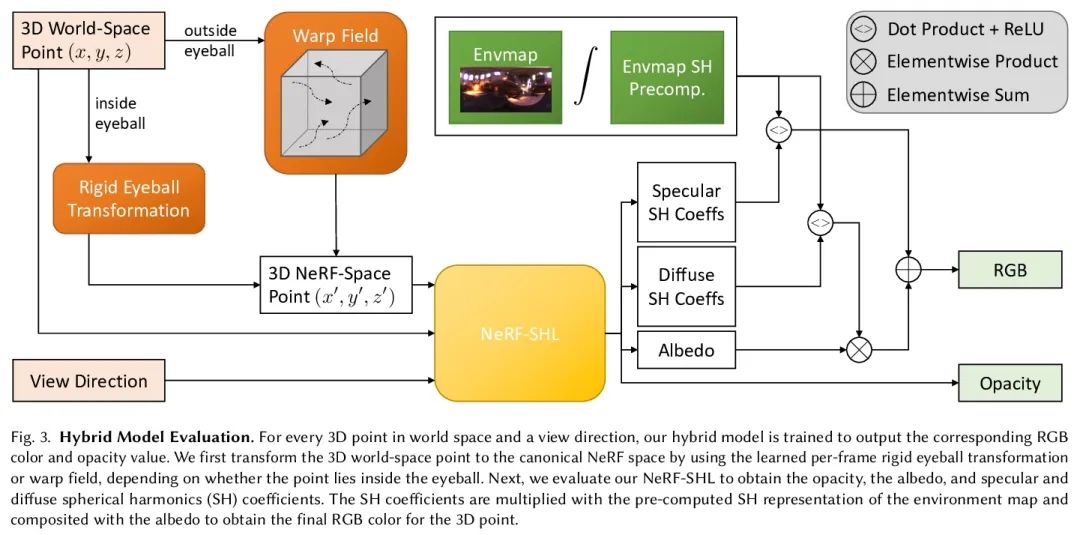
[CV] EyeNeRF: A Hybrid Representation for Photorealistic Synthesis, Animation and Relighting of Human Eyes
EyeNeRF:面向人眼逼真合成、动画和重打光的混合表示
G Li, A Meka, F Muller, M C. Buhler, O Hilliges
[ETH Zurich & Google]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08428

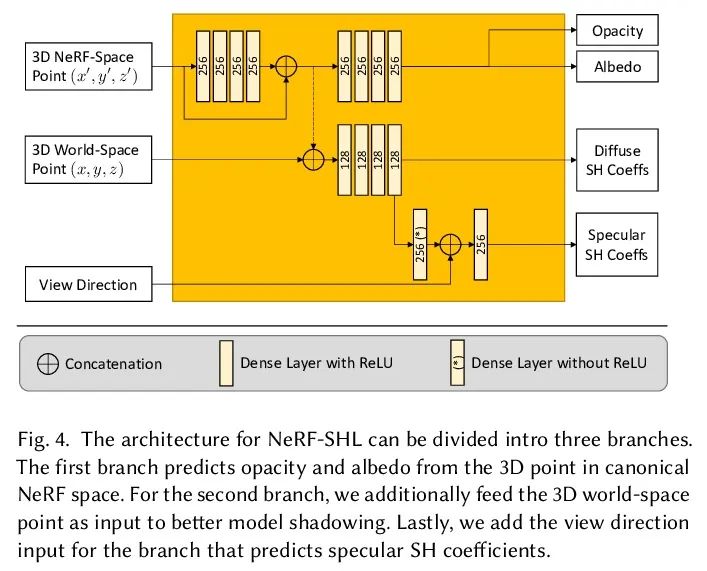
[CV] iBoot: Image-bootstrapped Self-Supervised Video Representation Learning
iBoot:图像自举自监督视频表示学习
F Saleh, F Tan, A Bulat, G Tzimiropoulos, B Martinez
[Samsung AI Cambridge]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08339

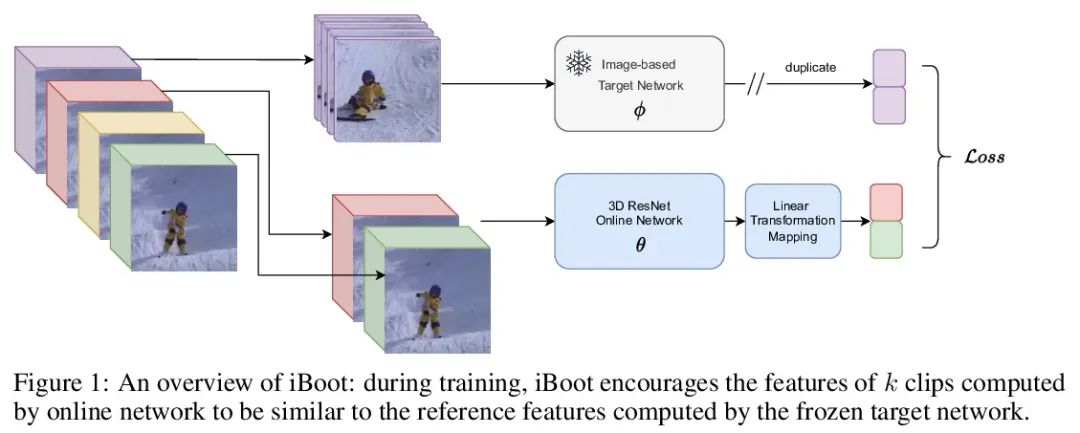

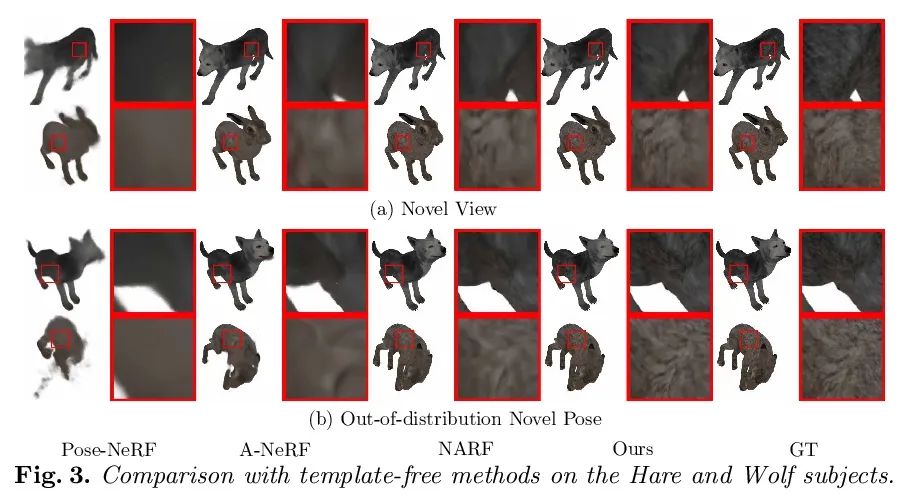
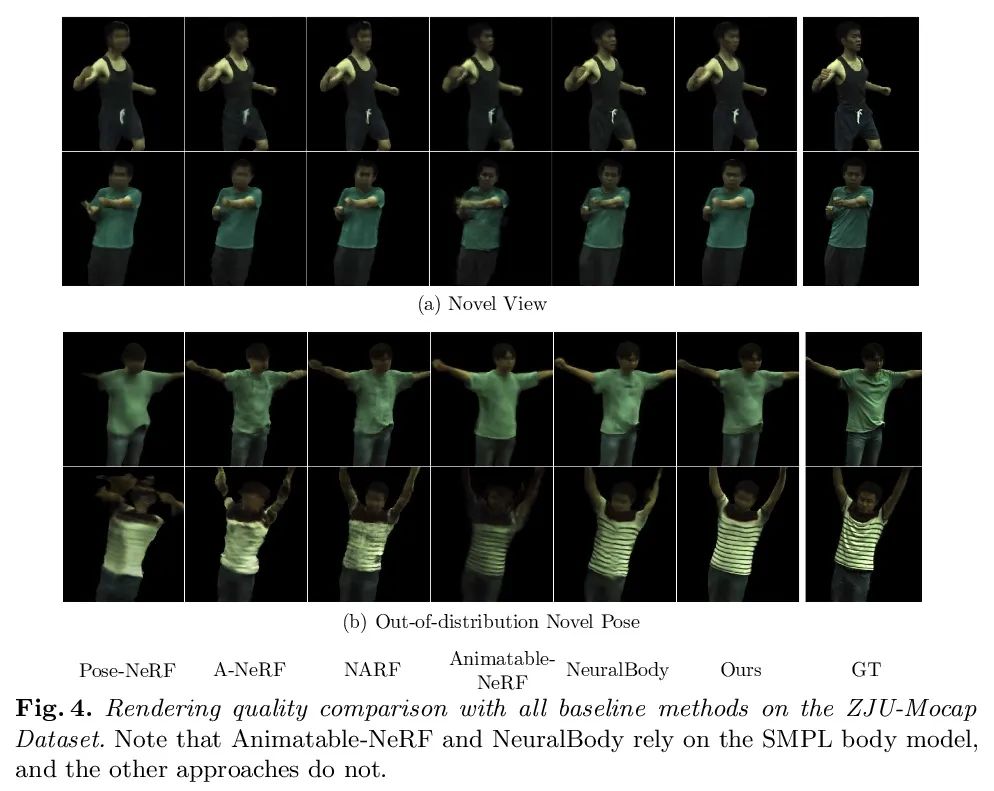
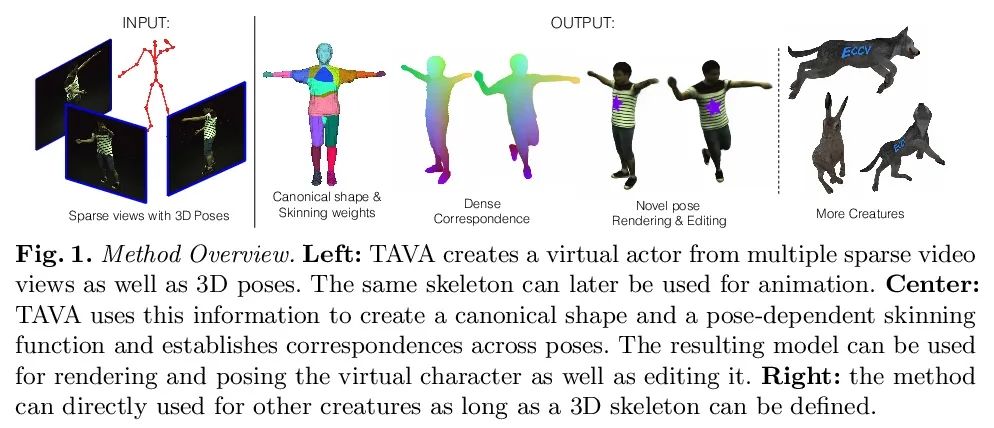
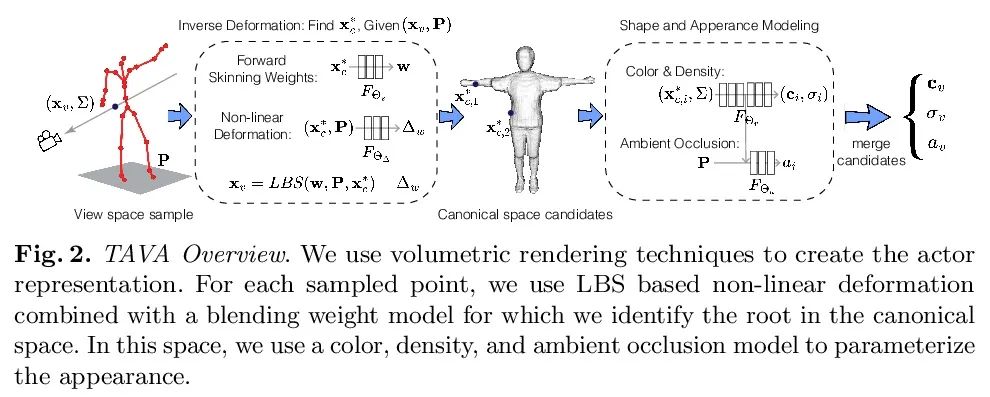
[CV] TAVA: Template-free Animatable Volumetric Actors
TAVA:无模板可动画体演员
R Li, J Tanke, M Vo, M Zollhofer, J Gall, A Kanazawa, C Lassner
[UC Berkeley & University of Bonn & Meta Reality Labs Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.08929



内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢