LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
摘要:作为正则化器的Mixup可以出人意料地提高精度和分布外鲁棒性、物理机器人学习的世界模型、通过分支定界验证对抗鲁棒性的IBP正则化、视觉问答自监督视觉预训练探索、通过纯文本和半监督训练提高推敲能力、3D感知视频生成、步行系统地形感知运动优化、概念抽象基准理解评估、面向文档检索的神经语料库索引器
1、[LG] RegMixup: Mixup as a Regularizer Can Surprisingly Improve Accuracy and Out Distribution Robustness
F Pinto, H Yang, S Lim, P H.S. Torr, P K. Dokania
[University of Oxford & Meta AI]
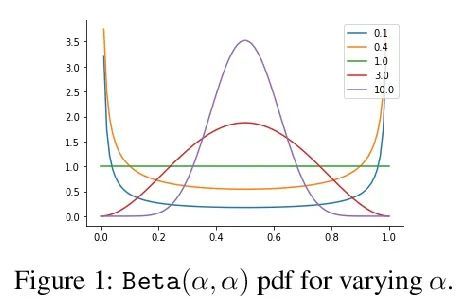
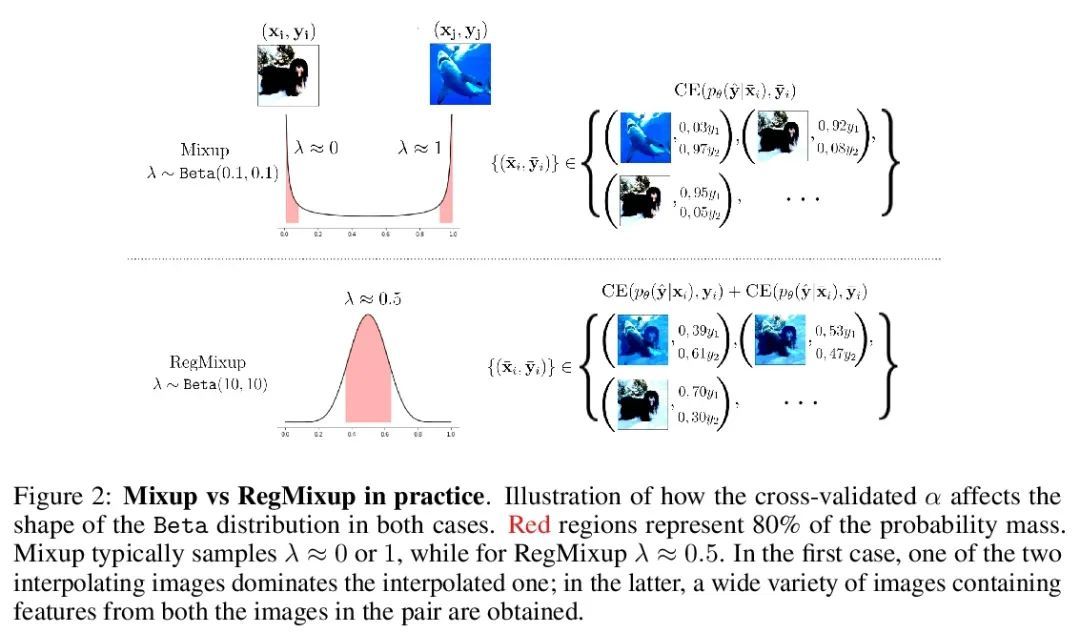
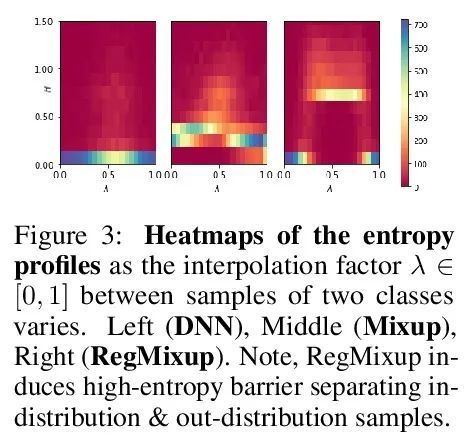
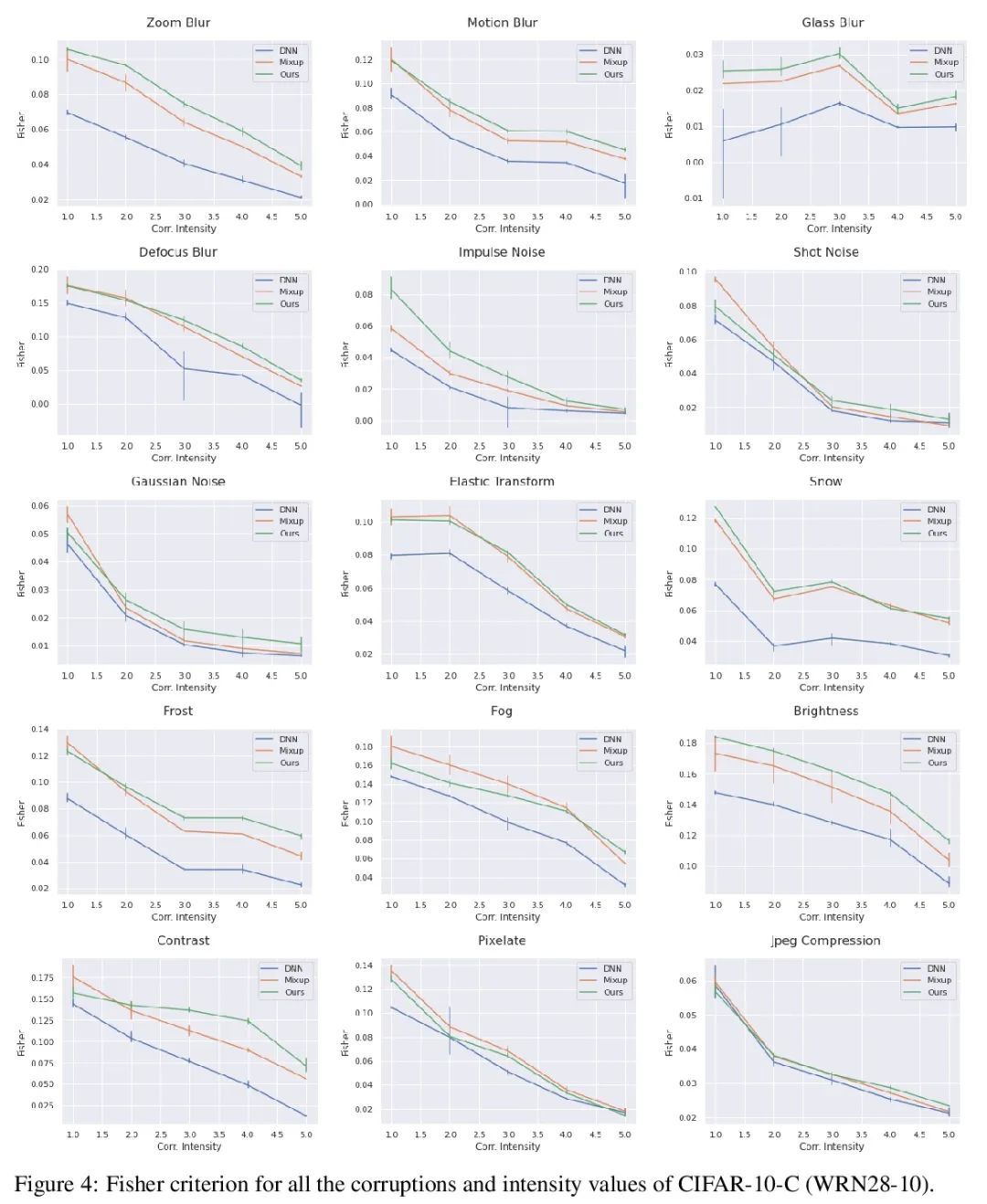
RegMixup:作为正则化器的Mixup可以出人意料地提高精度和分布外鲁棒性。本文表明,如果不把Mixup作为唯一的学习目标,而把它作为标准交叉熵损失的额外正则化器使用,那么著名的Mixup的有效性可以进一步提高。这个简单的改变不仅提供了更高的精度,而且在各种形式的协变量迁移和分布外检测实验下,Mixup的预测不确定性估计的质量也得到了明显的改善。Mixup在检测分布外样本方面的性能大大降低,这可能是由于它倾向于学习自始至终表现出高熵的模型;使得它难以区分分布内样本和分布外样本。为了证明所提出方法(RegMixup)的功效,对视觉数据集(ImageNet和CIFAR-10/100)进行了全面的分析和实验,并将其与最近的一套可靠的不确定性估计方法进行了比较。
We show that the effectiveness of the well celebrated Mixup [Zhang et al., 2018] can be further improved if instead of using it as the sole learning objective, it is utilized as an additional regularizer to the standard cross-entropy loss. This simple change not only provides much improved accuracy but also significantly improves the quality of the predictive uncertainty estimation of Mixup in most cases under various forms of covariate shifts and out-of-distribution detection experiments. In fact, we observe that Mixup yields much degraded performance on detecting out-of-distribution samples possibly, as we show empirically, because of its tendency to learn models that exhibit high-entropy throughout; making it difficult to differentiate in-distribution samples from out-distribution ones. To show the efficacy of our approach (RegMixup2), we provide thorough analyses and experiments on vision datasets (ImageNet & CIFAR-10/100) and compare it with a suite of recent approaches for reliable uncertainty estimation.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.14502

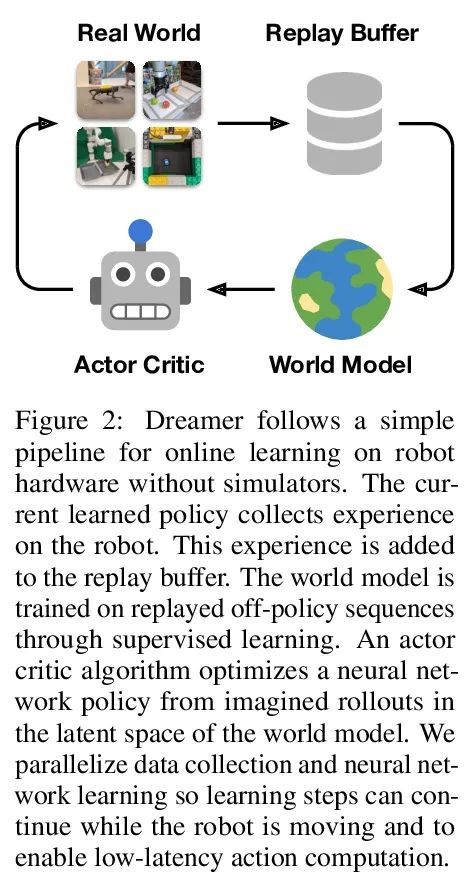
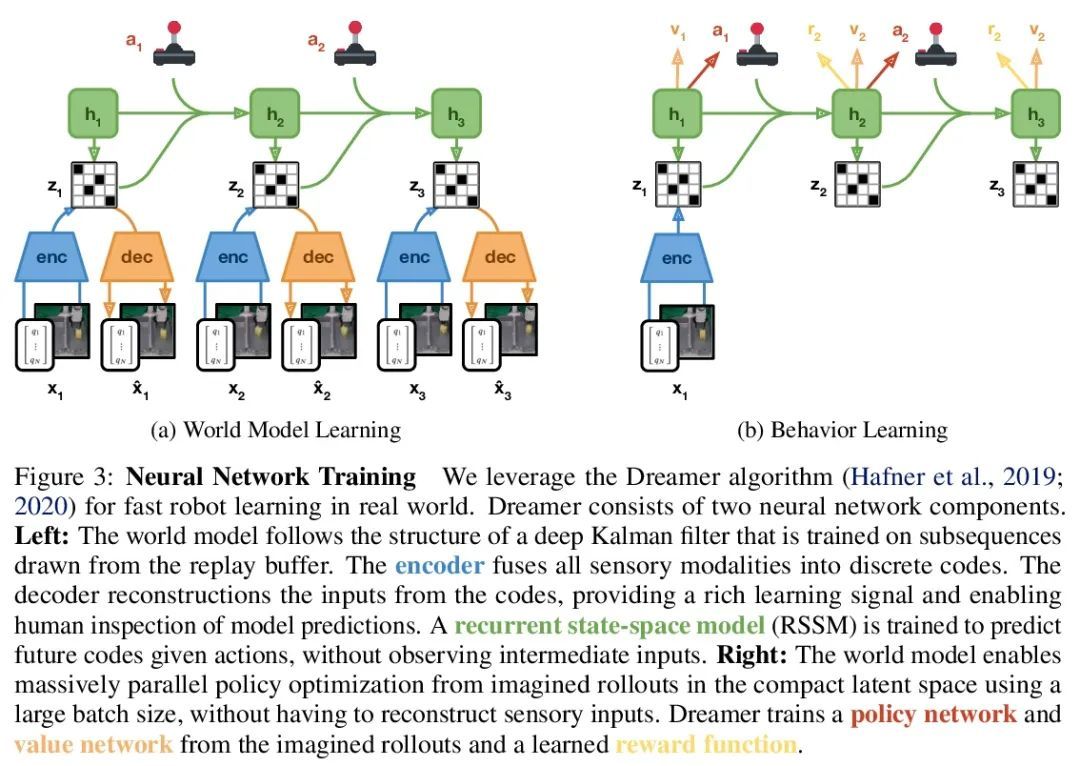
2、[RO] DayDreamer: World Models for Physical Robot Learning
P Wu, A Escontrela, D Hafner, K Goldberg, P Abbeel
[UC Berkeley]
DayDreamer: 物理机器人学习的世界模型。为解决复杂环境中的任务,机器人需要从经验中学习。深度强化学习是一种常见的机器人学习方法,但需要从大量的试错中学习,限制了其在物理世界的部署。因此,机器人学习方面的许多进展都依赖于模拟器。另一方面,在模拟器内的学习不能捕捉到真实世界的复杂性,容易出现模拟器不准确的情况,而且所产生的行为不能适应世界的变化。最近,Dreamer算法通过在学习的世界模型内进行规划,显示出从少量互动中学习的巨大前景,在视频游戏中的表现优于纯粹的强化学习。通过学习世界模型来预测潜在行动的结果,可以在想象中进行规划,减少在真实环境中所需要的试错的数量。然而,Dreamer是否能促进物理机器人的快速学习还不得而知。本文将Dreamer应用于4个机器人,在没有任何模拟器的情况下,直接在现实世界中在线学习。Dreamer只用了1个小时就训练了一个四足机器人从头开始翻滚、站立和行走,而且没有复位。推动机器人,发现Dreamer在10分钟内就能适应,以承受扰动或快速翻身和站起来。在两个不同的机器人手臂上,Dreamer学会了直接从摄像头图像和稀疏的奖励中挑选和放置多个物体,接近人类的表现。在一个有轮子的机器人上,Dreamer学会了纯粹从摄像机图像中导航到目标位置,自动解决了关于机器人方向的模糊性。在所有实验中使用相同的超参数,发现Dreamer能在现实世界中进行在线学习,这就建立了一个强大的基线。
To solve tasks in complex environments, robots need to learn from experience. Deep reinforcement learning is a common approach to robot learning but requires a large amount of trial and error to learn, limiting its deployment in the physical world. As a consequence, many advances in robot learning rely on simulators. On the other hand, learning inside of simulators fails to capture the complexity of the real world, is prone to simulator inaccuracies, and the resulting behaviors do not adapt to changes in the world. The Dreamer algorithm has recently shown great promise for learning from small amounts of interaction by planning within a learned world model, outperforming pure reinforcement learning in video games. Learning a world model to predict the outcomes of potential actions enables planning in imagination, reducing the amount of trial and error needed in the real environment. However, it is unknown whether Dreamer can facilitate faster learning on physical robots. In this paper, we apply Dreamer to 4 robots to learn online and directly in the real world, without any simulators. Dreamer trains a quadruped robot to roll off its back, stand up, and walk from scratch and without resets in only 1 hour. We then push the robot and find that Dreamer adapts within 10 minutes to withstand perturbations or quickly roll over and stand back up. On two different robotic arms, Dreamer learns to pick and place multiple objects directly from camera images and sparse rewards, approaching human performance. On a wheeled robot, Dreamer learns to navigate to a goal position purely from camera images, automatically resolving ambiguity about the robot orientation. Using the same hyperparameters across all experiments, we find that Dreamer is capable of online learning in the real world, which establishes a strong baseline. We release our infrastructure for future applications of world models to robot learning. Videos are available on the project website: https://danijar.com/daydreamer
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.14176



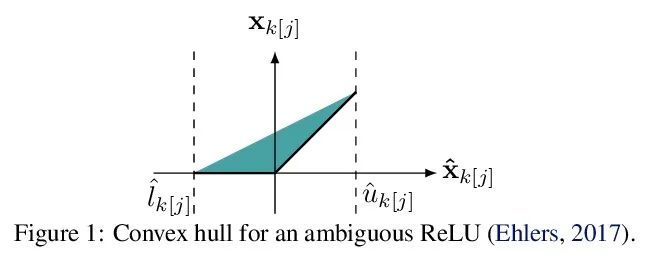
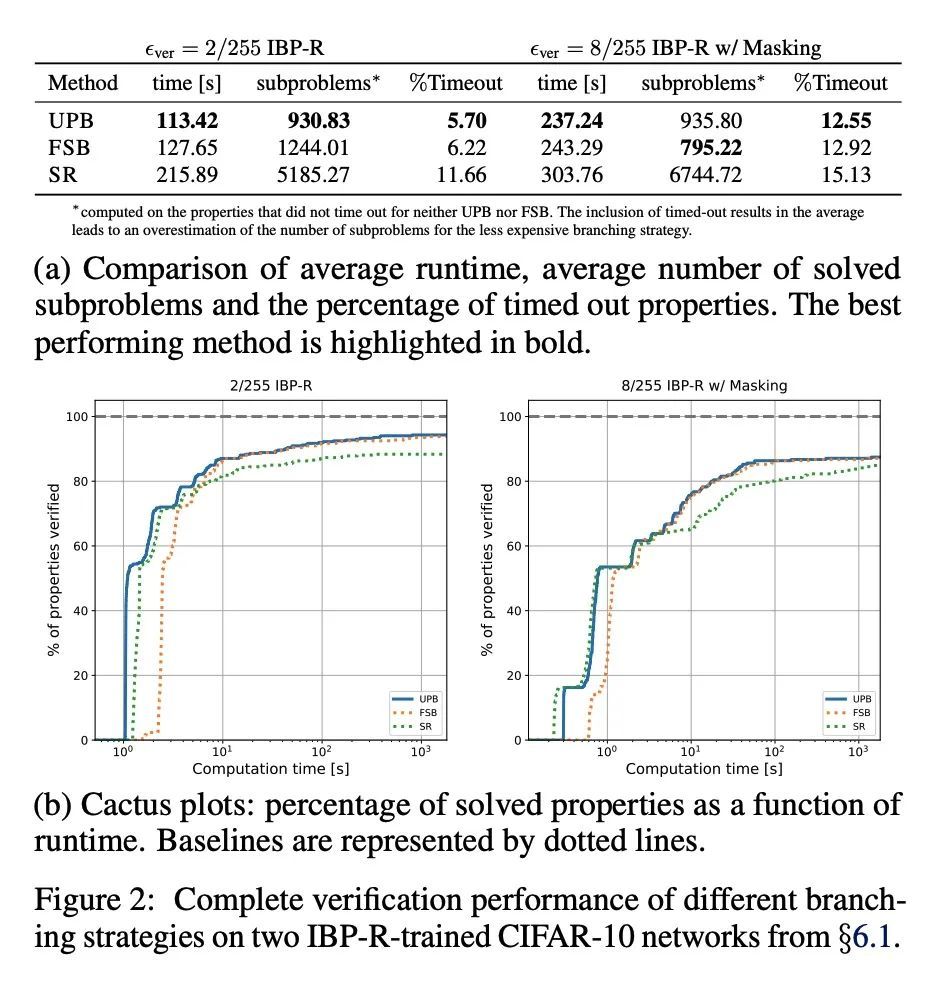
3、[LG] IBP Regularization for Verified Adversarial Robustness via Branch-and-Bound
A D Palma, R Bunel, K Dvijotham, M. P Kumar, R Stanforth
[University of Oxford & DeepMind & Google Brain]
通过分支定界验证对抗鲁棒性的IBP正则化。最近的工作试图通过在比原始扰动更大的域上运行攻击并向目标添加各种正则化项来提高对抗性训练网络的可验证性。然而,这些算法要么表现不佳,要么需要复杂而昂贵的阶段性训练程序,阻碍了它们的实际应用性。本文提出了IBP-R,一种既简单又有效的新型验证训练算法。IBP-R通过将对扩大域的对抗性攻击与基于廉价的区间边界传播的正则化项结合起来,使非凸验证问题与其近似值之间的差距最小化,从而带来网络可验证性。通过利用最近的分支定界框架,本文表明IBP-R在CIFAR-10的小扰动下获得了最先进的验证鲁棒性-准确性权衡,同时训练速度明显快于之前的相关工作。此外,本文提出UPB,一种新的分支策略,依靠基于β-CROWN的简单启发式方法,降低了最先进的分支算法的成本,同时产生了质量相当的分支。
Recent works have tried to increase the verifiability of adversarially trained networks by running the attacks over domains larger than the original perturbations and adding various regularization terms to the objective. However, these algorithms either underperform or require complex and expensive stage-wise training procedures, hindering their practical applicability. We present IBP-R, a novel verified training algorithm that is both simple and effective. IBP-R induces network verifiability by coupling adversarial attacks on enlarged domains with a regularization term, based on inexpensive interval bound propagation, that minimizes the gap between the non-convex verification problem and its approximations. By leveraging recent branch-and-bound frameworks, we show that IBP-R obtains state-of-the-art verified robustness-accuracy trade-offs for small perturbations on CIFAR-10 while training significantly faster than relevant previous work. Additionally, we present UPB, a novel branching strategy that, relying on a simple heuristic based on β-CROWN, reduces the cost of state-of-the-art branching algorithms while yielding splits of comparable quality.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.14772

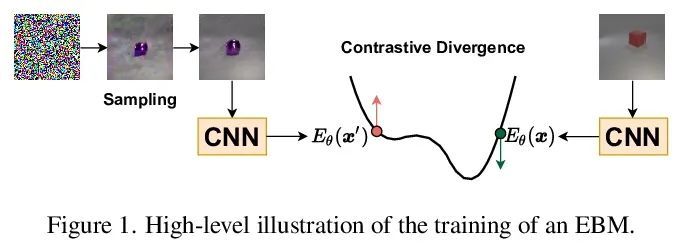
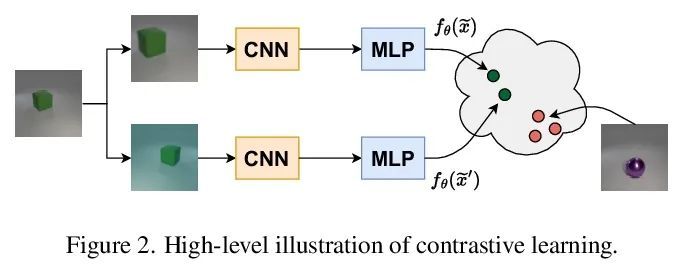
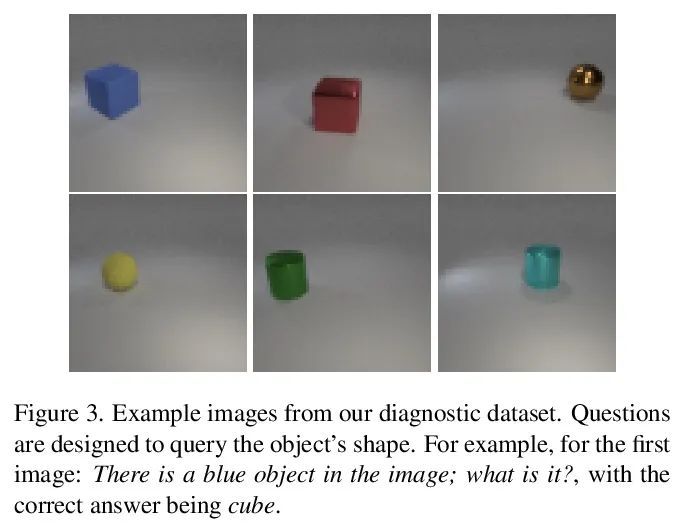
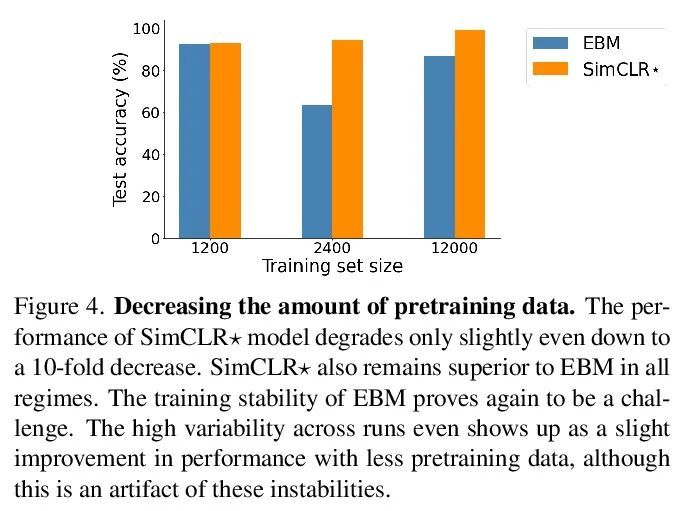
4、[CV] EBMs vs. CL: Exploring Self-Supervised Visual Pretraining for Visual Question Answering
V Shevchenko, E Abbasnejad, A Dick, A v d Hengel, D Teney
[University of Adelaide]
EBMs vs. CL:视觉问答自监督视觉预训练探索。干净和多样标记数据的可用性,是训练复杂任务模型的主要障碍,如视觉问答(VQA)。在大型视觉和语言模型方面的大量工作表明,自监督学习对于预训练多模态交互是有效的。本文专注于视觉表示,回顾并评估了自监督方法,以利用未标记图像预训练一个模型,在一个自定义的VQA任务上对其进行微调,该任务允许可控的评估和诊断。本文比较了基于能量的模型(EBM)和对比学习(CL)。虽然EBM越来越受欢迎,但它们缺乏对下游任务的评估。研究结果表明,EBM和CL都可以从未标记图像中学习表示,从而在很少的标注数据上训练一个VQA模型。在一个类似于CLEVR的简单设置中,CL表示也改善了系统泛化,甚至与来自一个更大的、有监督的、经过ImageNet训练的模型的表示的性能相匹配。然而,EBM由于其结果的不稳定性和高变异性而难以训练。因此,本文调研了EBM的其他声称的好处。它们被证明对OOD检测很有用,但其他基于能量的监督训练和不确定性校准的结果基本上是负面的。本文提出了一个令人鼓舞的观点,即自监督视觉预训练允许将对训练数据的一些要求从主/监督阶段转移到预训练/无监督阶段。CL目前似乎是比EBM更好的选择。令我们惊讶的是,EBM无法实现文献中所宣称的好处,即使是在简单环境中。
Recent works have tried to increase the verifiability of adversarially trained networks by running the attacks over domains larger than the original perturbations and adding various regularization terms to the objective. However, these algorithms either underperform or require complex and expensive stage-wise training procedures, hindering their practical applicability. We present IBP-R, a novel verified training algorithm that is both simple and effective. IBP-R induces network verifiability by coupling adversarial attacks on enlarged domains with a regularization term, based on inexpensive interval bound propagation, that minimizes the gap between the non-convex verification problem and its approximations. By leveraging recent branch-and-bound frameworks, we show that IBP-R obtains state-of-the-art verified robustness-accuracy trade-offs for small perturbations on CIFAR-10 while training significantly faster than relevant previous work. Additionally, we present UPB, a novel branching strategy that, relying on a simple heuristic based on β-CROWN, reduces the cost of state-of-the-art branching algorithms while yielding splits of comparable quality.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.14355

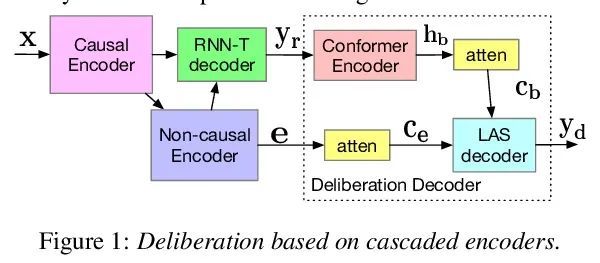
5、[CL] Improving Deliberation by Text-Only and Semi-Supervised Training
K Hu, T N. Sainath, Y He, R Prabhavalkar, T Strohman, S Mavandadi, W Wang
[Google]
通过纯文本和半监督训练提高推敲能力。由于未标记的文本和语音数据的广泛存在,基于纯文本和半监督的训练最近得到了普及。本文建议将纯文本和半监督训练纳入基于注意力的推敲模型。通过在训练推敲文本编码器的双向编码器表示法(BERT)中加入纯文本数据,以及用声学文本联合解码器(JATD)和半监督训练的大规模文本转语音和纯音频语料,与基线审议相比,在各种任务中实现了4%-12%的误码率降低。与最先进的语言模型(LM)重评分方法相比,推敲模型使Google语音搜索的误码率相对降低了11%。与最先进的LM重评分方法相比,推敲模型也取得了积极的人工侧面评价,并具有合理的终端延迟。
Text-only and semi-supervised training based on audio-only data has gained popularity recently due to the wide availability of unlabeled text and speech data. In this work, we propose incorporating text-only and semi-supervised training into an attention-based deliberation model. By incorporating textonly data in training a bidirectional encoder representation from transformer (BERT) for the deliberation text encoder, and large-scale text-to-speech and audio-only utterances using joint acoustic and text decoder (JATD) and semi-supervised training, we achieved 4%-12% WER reduction for various tasks compared to the baseline deliberation. Compared to a state-of-theart language model (LM) rescoring method, the deliberation model reduces the Google Voice Search WER by 11% relative. We show that the deliberation model also achieves a positive human side-by-side evaluation compared to the state-of-the-art LM rescorer with reasonable endpointer latencies.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.14716

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
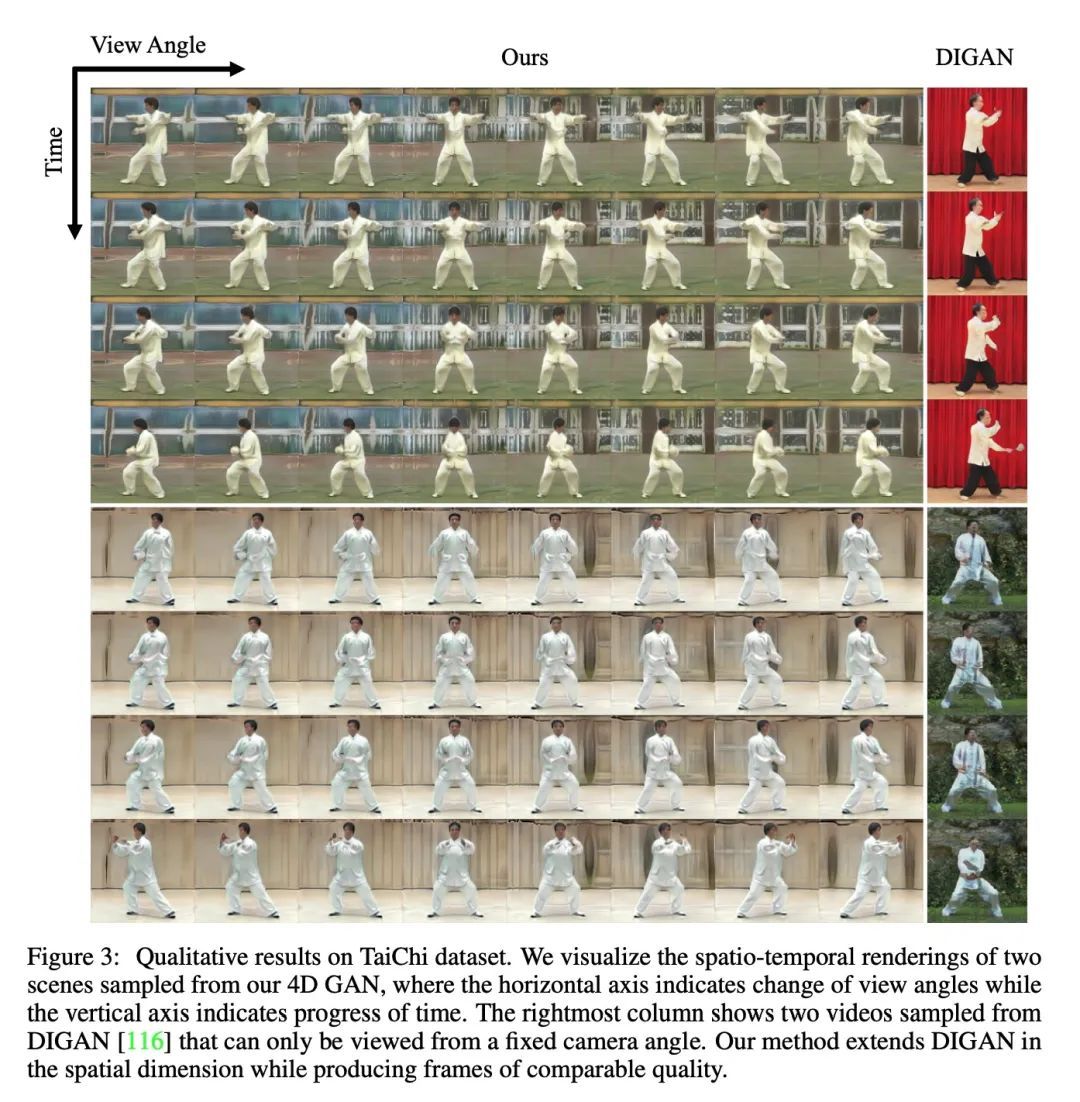
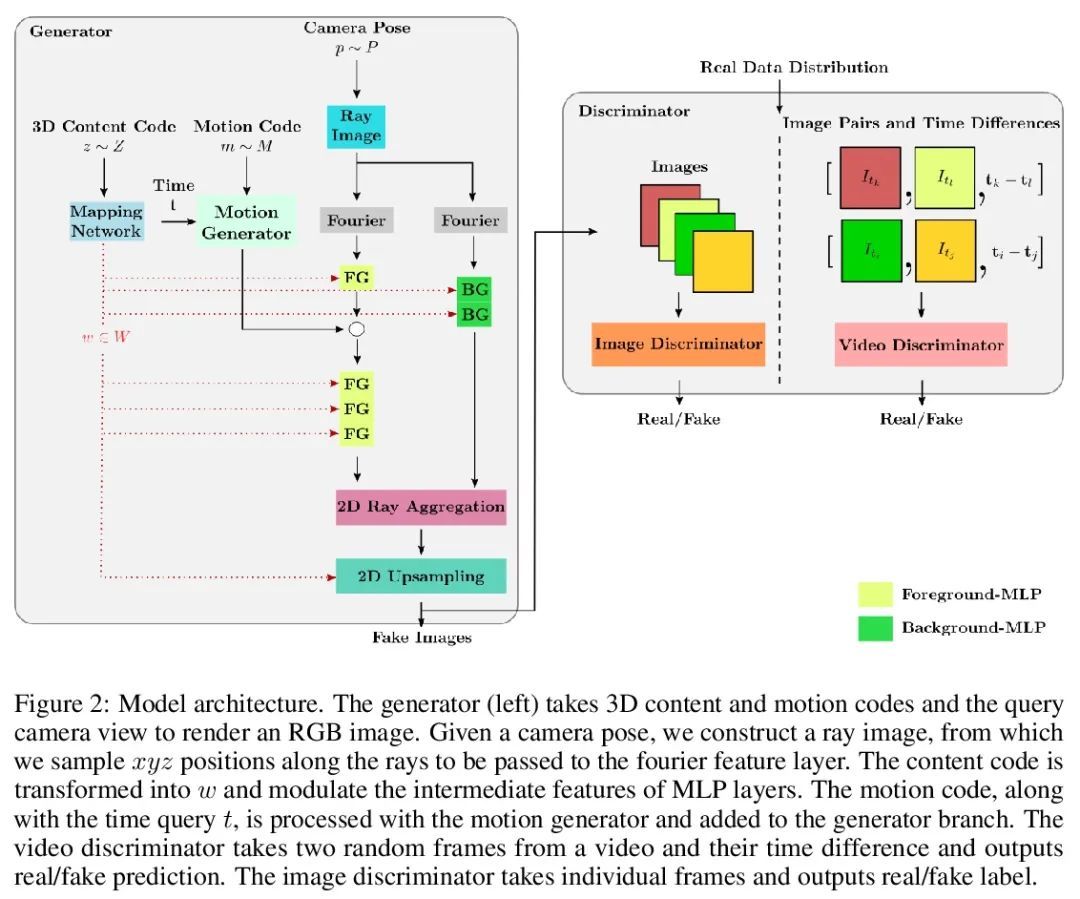
[CV] 3D-Aware Video Generation
3D感知视频生成
S Bahmani, J J Park, D Paschalidou, H Tang, G Wetzstein, L Guibas, L V Gool, R Timofte
[ETH Zürich & Stanford University]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.14797



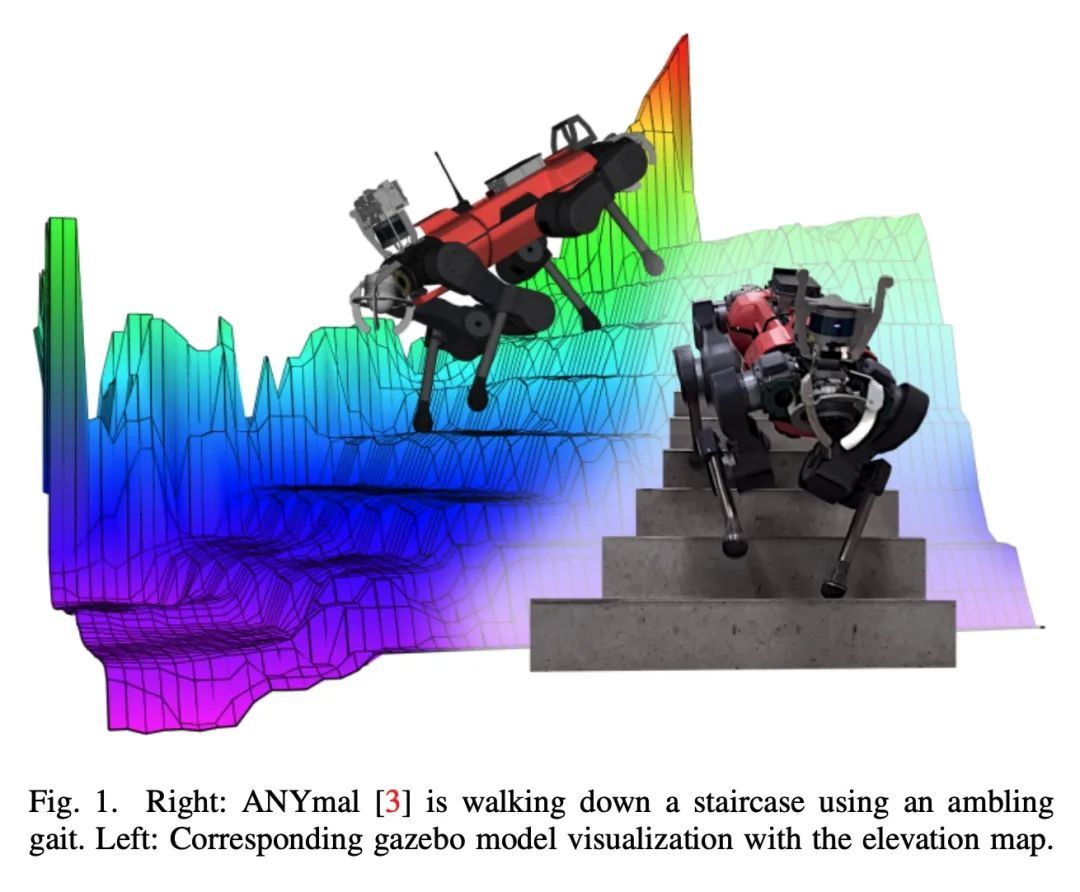
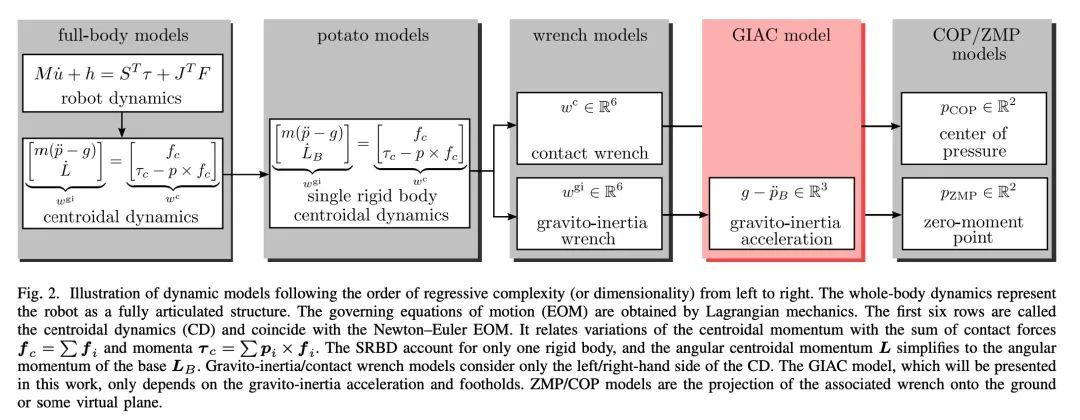
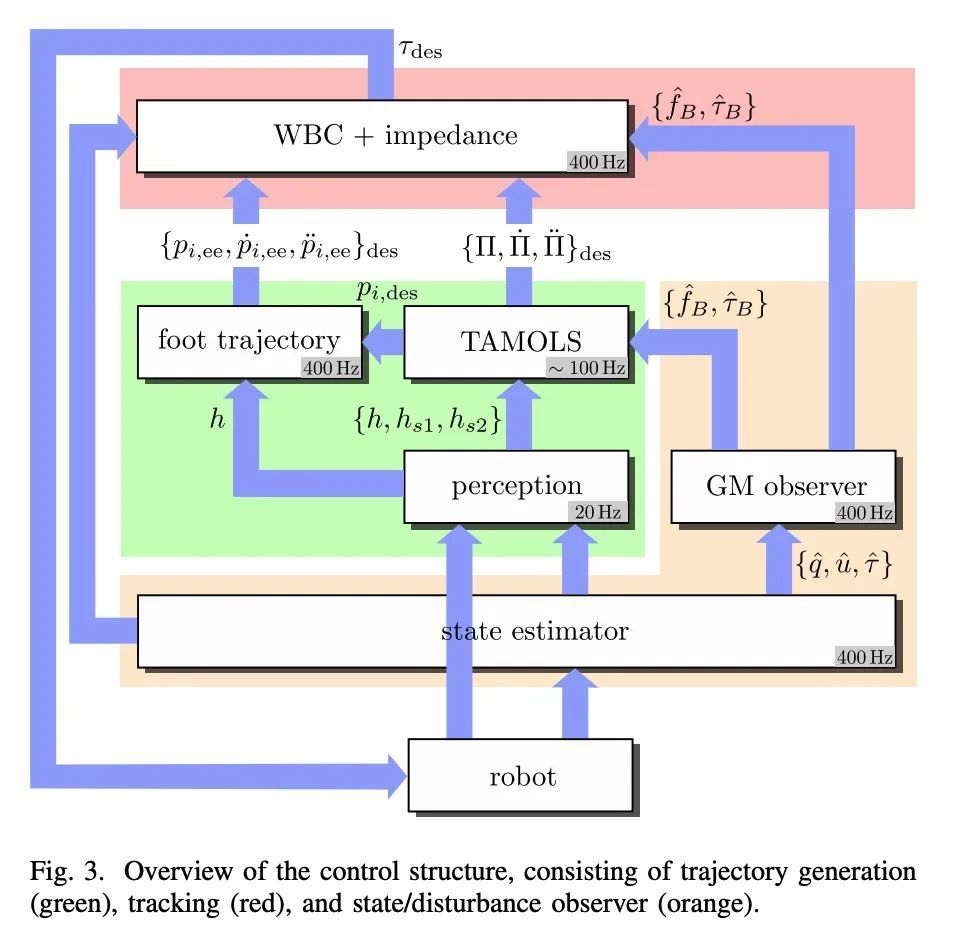
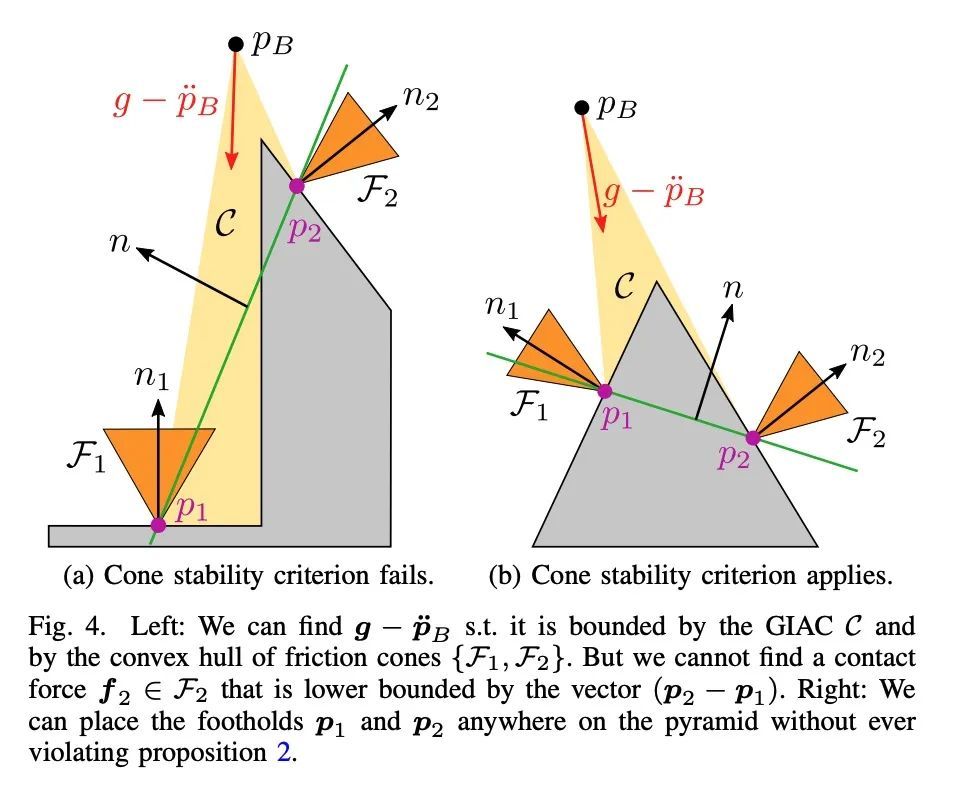
[RO] TAMOLS: Terrain-Aware Motion Optimization for Legged Systems
TAMOLS:步行系统地形感知运动优化
F Jenelten, R Grandia, F Farshidian, M Hutter
[ETH Zurich]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.14049

[LG] Evaluating Understanding on Conceptual Abstraction Benchmarks
概念抽象基准理解评估
V V Odouard, M Mitchell
[Santa Fe Institute]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.14187

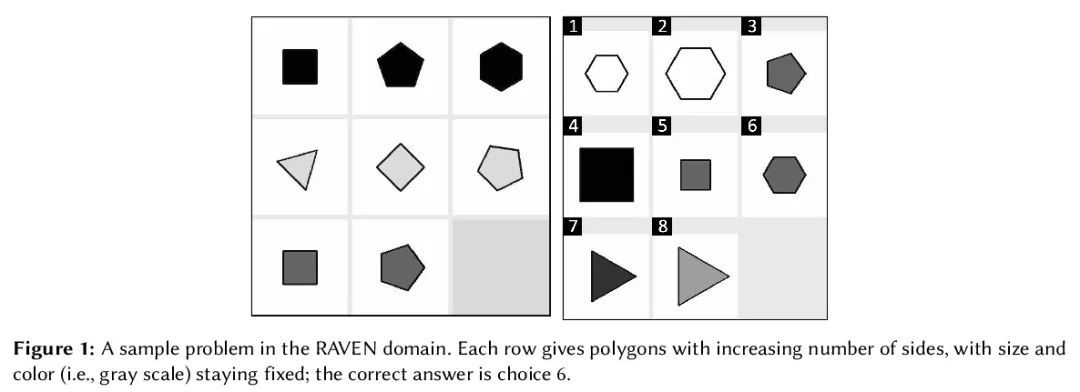
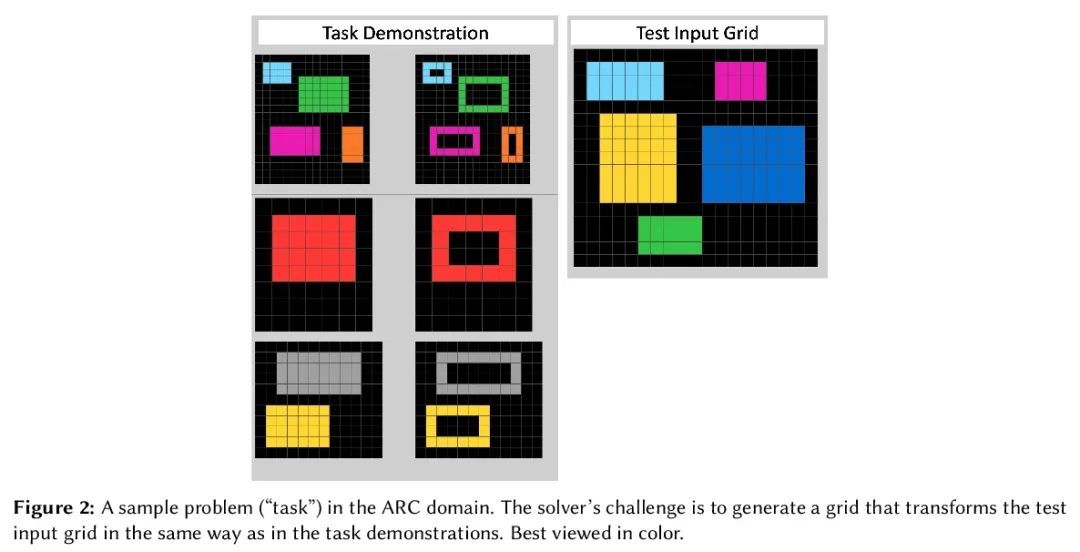
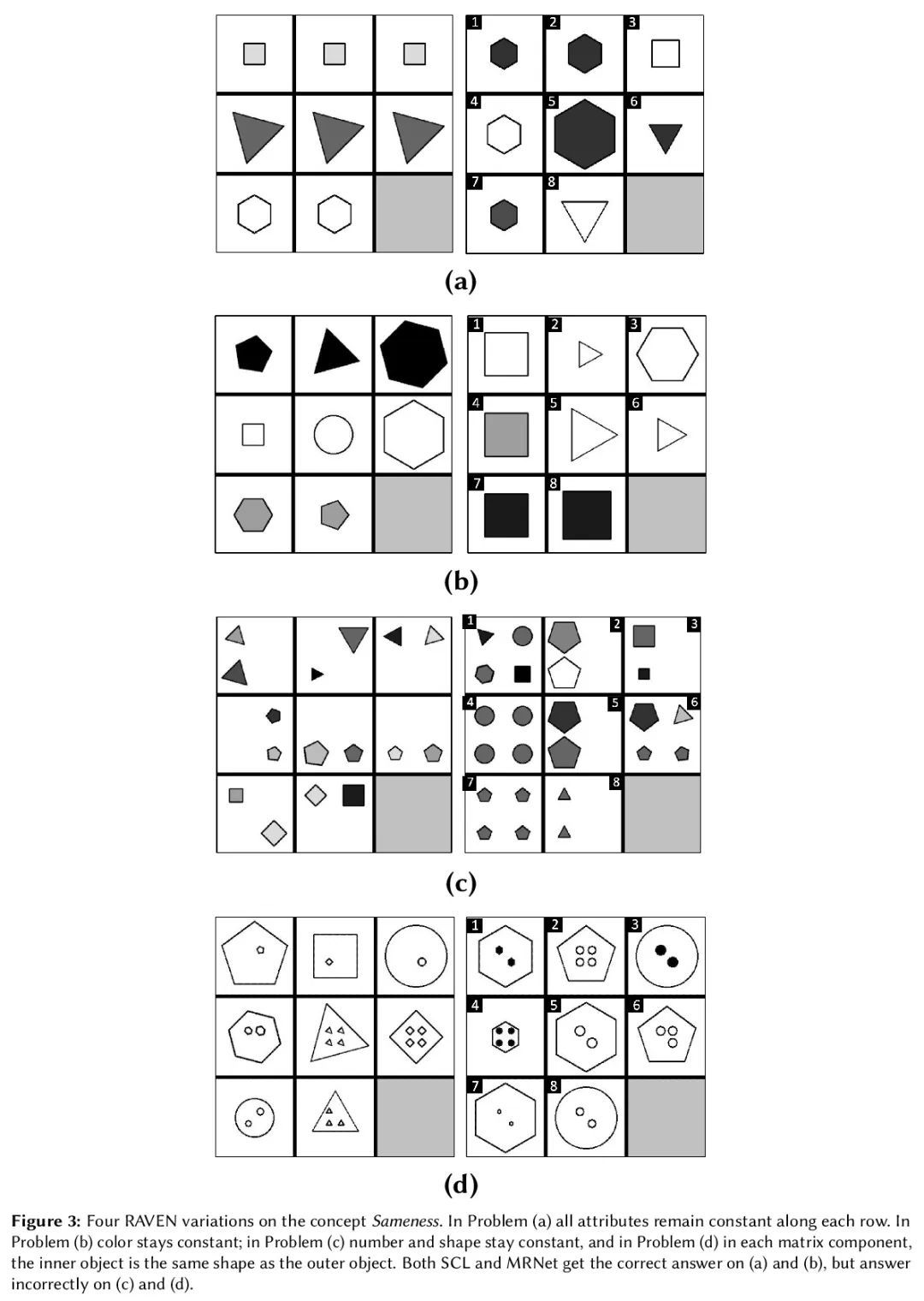
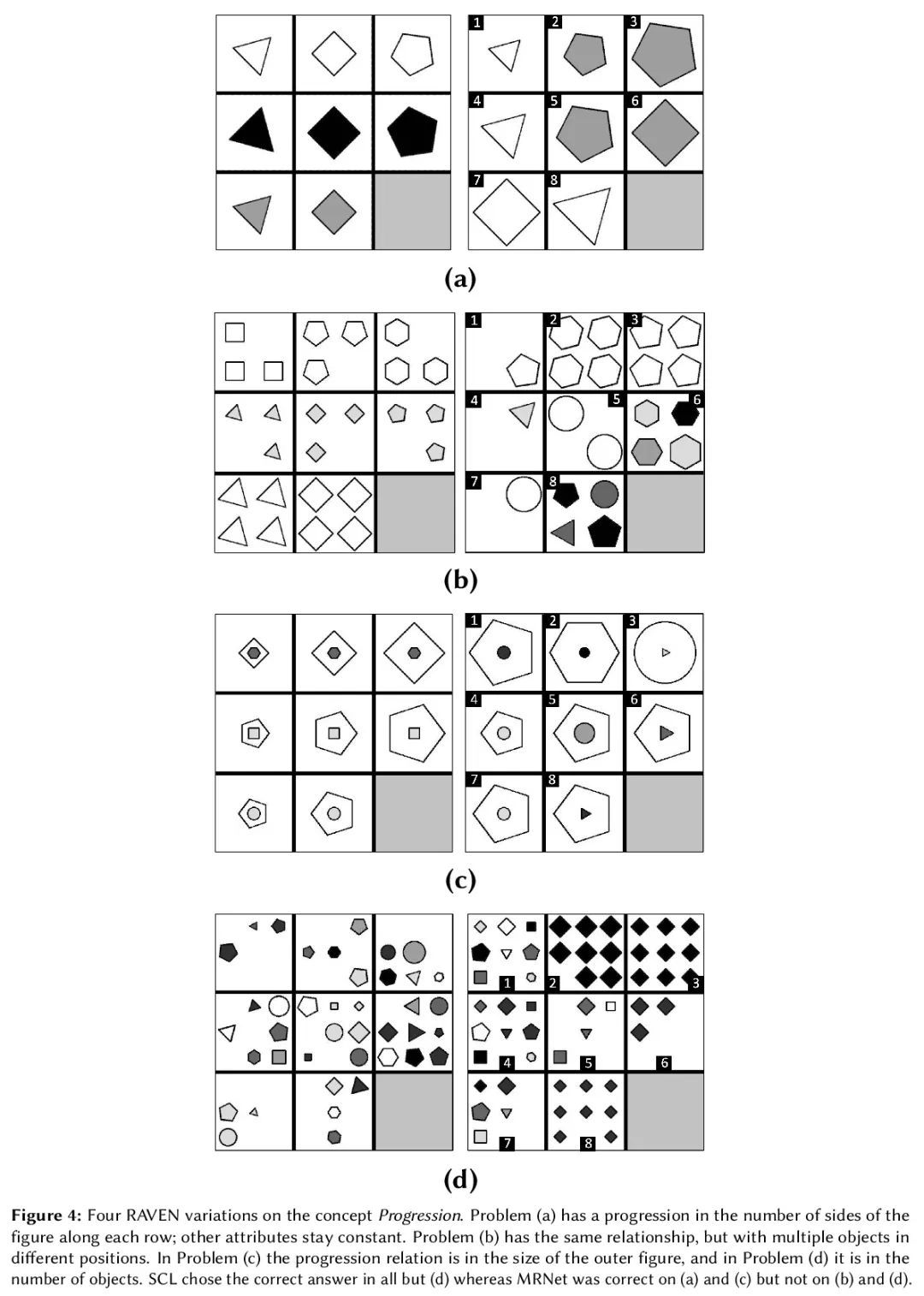
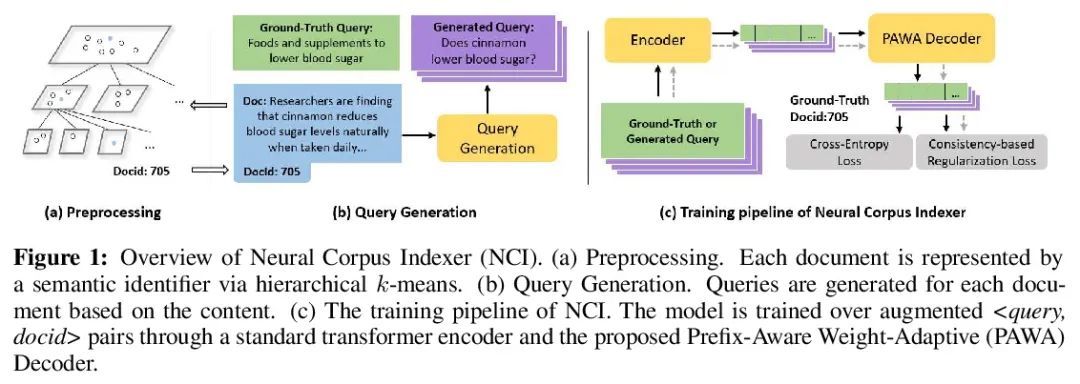
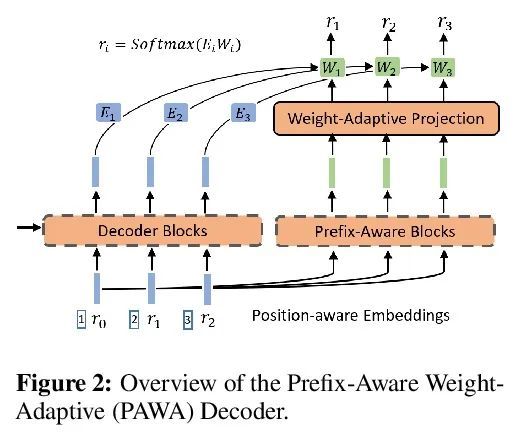
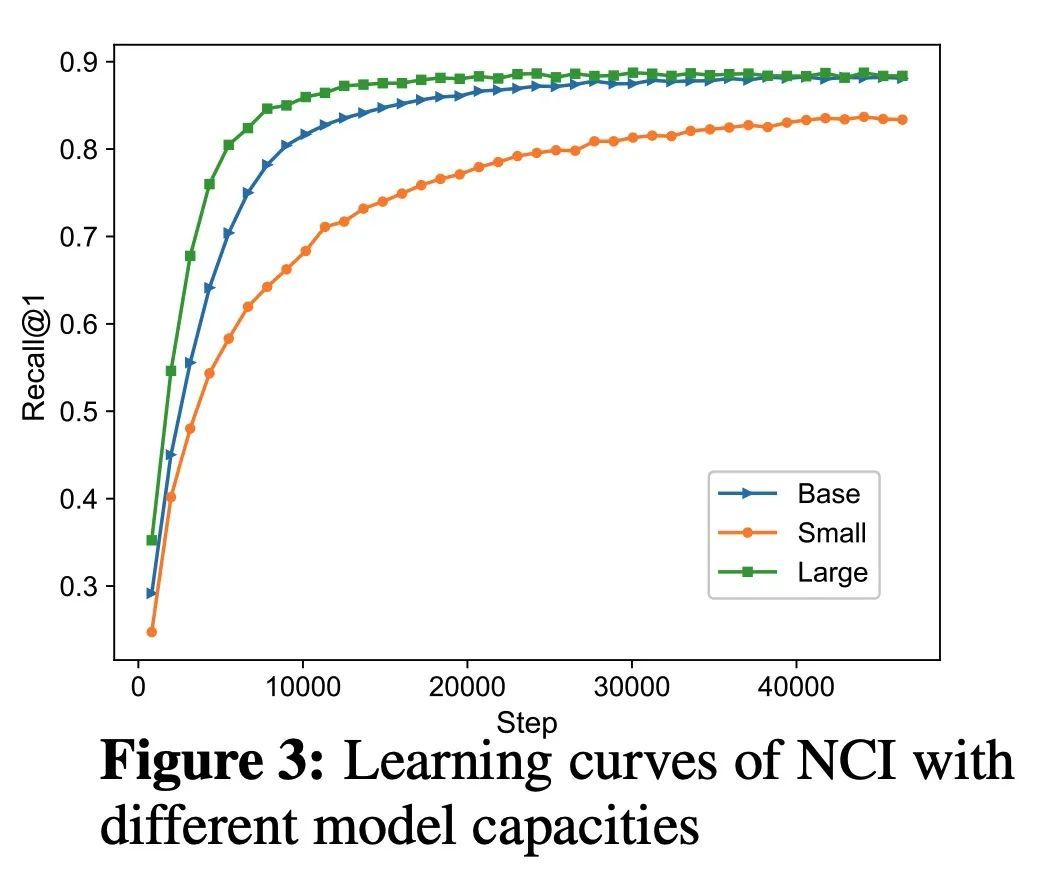
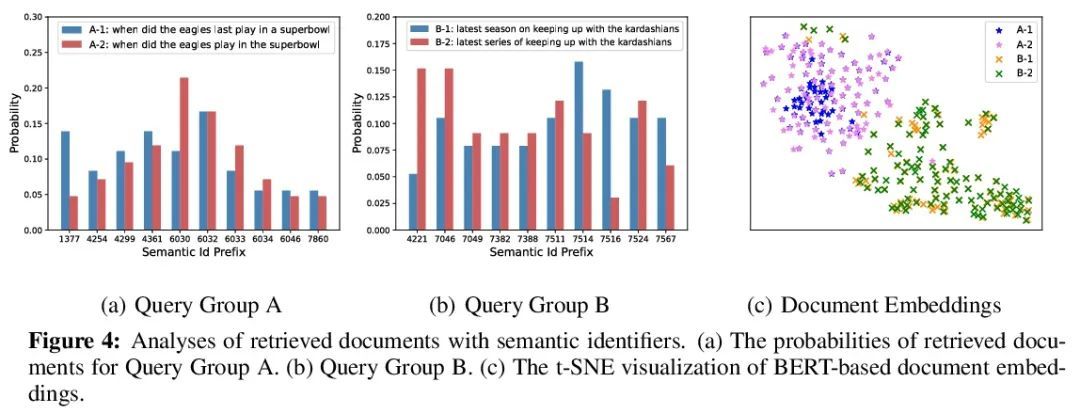
[IR] A Neural Corpus Indexer for Document Retrieval
面向文档检索的神经语料库索引器
Y Wang, Y Hou, H Wang, Z Miao, S Wu, H Sun, Q Chen, Y Xia, C Chi, G Zhao, Z Liu, X Xie, H A Sun, W Deng, Q Zhang, M Yang
[Microsoft]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.02743

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢