LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:大规模半监督视觉Transformer、通过权重插值修补开放词表模型、基于Hessian迹随机估计器的深度神经网络正则化、大规模场景下异常检测器的改进和评估、周期性漂移分布下的多分支网络联邦学习、提高多语言翻译零样本性能的超简单方法、数据集设计与CLIP鲁棒性之间相互作用研究、通过回收参数高效提示减少重训练、词-曲生成新范式
1、[CV] Semi-supervised Vision Transformers at Scale
Z Cai, A Ravichandran, P Favaro, M Wang, D Modolo, R Bhotika, Z Tu, S Soatto
[AWS AI Labs]
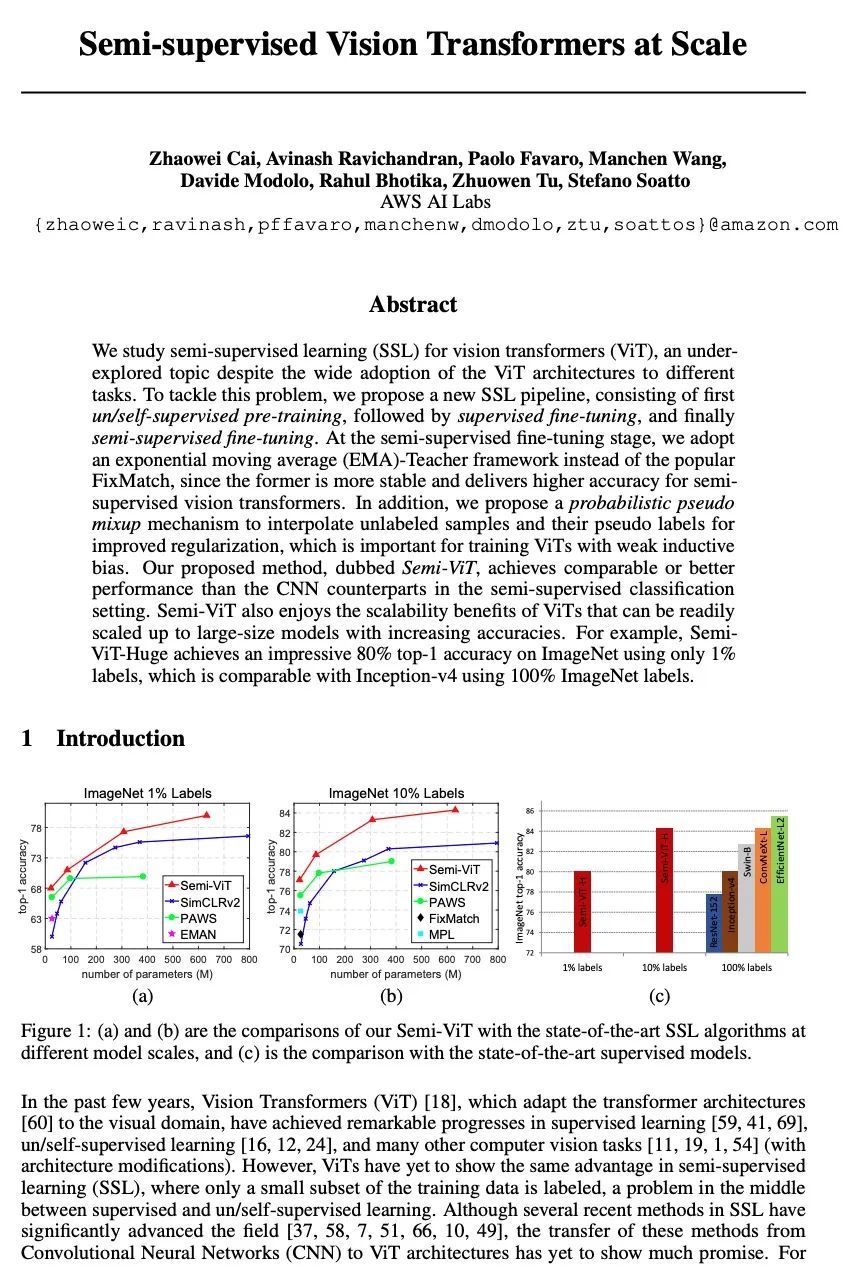
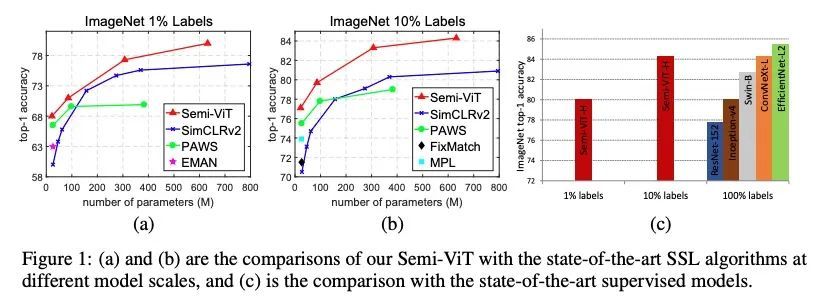
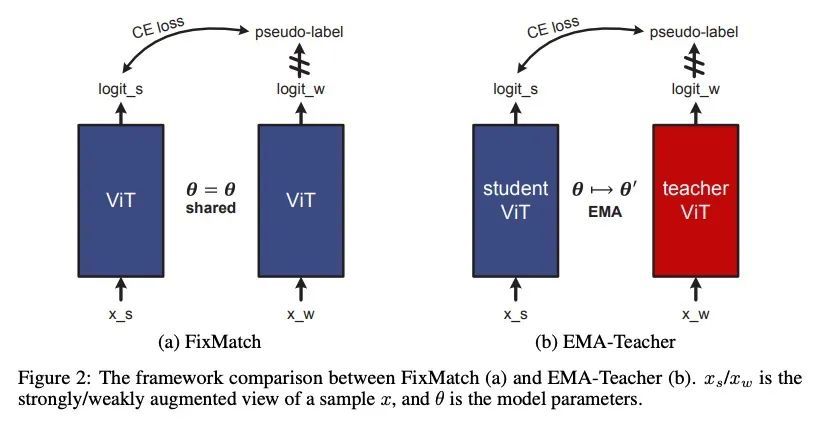
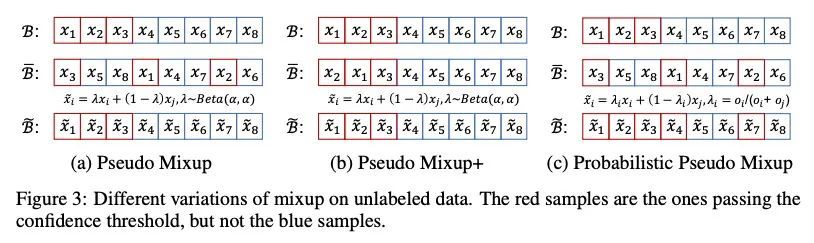
大规模半监督视觉Transformer。本文研究视觉Transformer(ViT)半监督学习(SSL),尽管ViT架构被广泛用于不同的任务,但这是一个未被探索的话题。为了解决该问题,本文提出一种新的SSL管道,首先是无监督/自监督预训练,然后是监督微调,最后是半监督微调。在半监督微调阶段,采用指数移动平均(EMA)教师框架,而不是流行的FixMatch,因为前者更稳定,为半监督视觉Transformer提供更高的精度。此外,本文提出一种概率性的伪混杂机制来插值未标记样本及其伪标签,以改善正则化,这对于训练具有弱归纳偏差的ViT非常重要。所提出的方法称为Semi-ViT,在半监督分类环境中取得了与CNN对应的相当或更好的性能。Semi-ViT还享有ViT的可扩展性优势,可以很容易地扩展到大尺寸的模型,并提高准确率。例如,SemiViT-Huge仅用1%的标签就在ImageNet上取得了令人印象深刻的80%的Top 1精度,这与Inception-v4用100%的ImageNet标签相媲美。
We study semi-supervised learning (SSL) for vision transformers (ViT), an underexplored topic despite the wide adoption of the ViT architectures to different tasks. To tackle this problem, we propose a new SSL pipeline, consisting of first un/self-supervised pre-training, followed by supervised fine-tuning, and finally semi-supervised fine-tuning. At the semi-supervised fine-tuning stage, we adopt an exponential moving average (EMA)-Teacher framework instead of the popular FixMatch, since the former is more stable and delivers higher accuracy for semisupervised vision transformers. In addition, we propose a probabilistic pseudo mixup mechanism to interpolate unlabeled samples and their pseudo labels for improved regularization, which is important for training ViTs with weak inductive bias. Our proposed method, dubbed Semi-ViT, achieves comparable or better performance than the CNN counterparts in the semi-supervised classification setting. Semi-ViT also enjoys the scalability benefits of ViTs that can be readily scaled up to large-size models with increasing accuracies. For example, SemiViT-Huge achieves an impressive 80% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet using only 1% labels, which is comparable with Inception-v4 using 100% ImageNet labels.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.05688
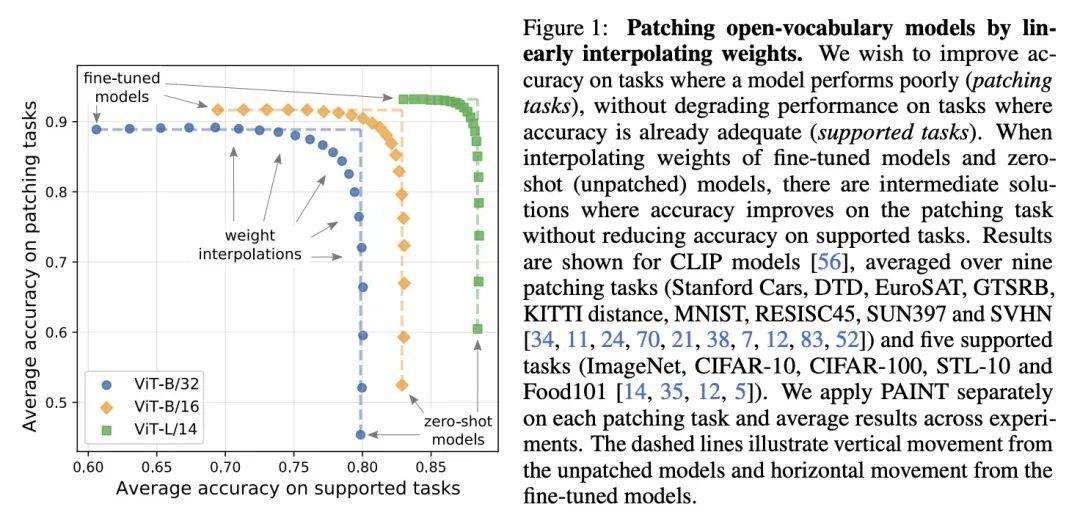
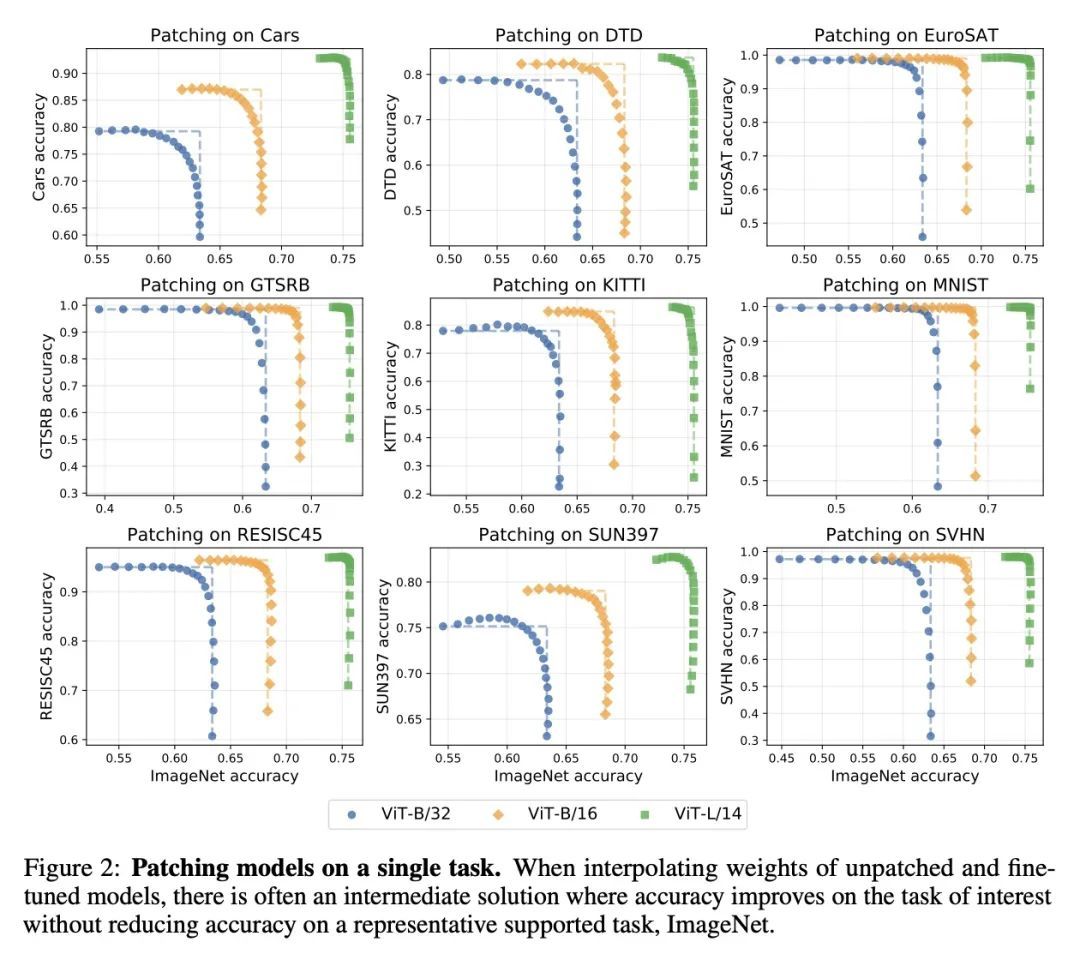
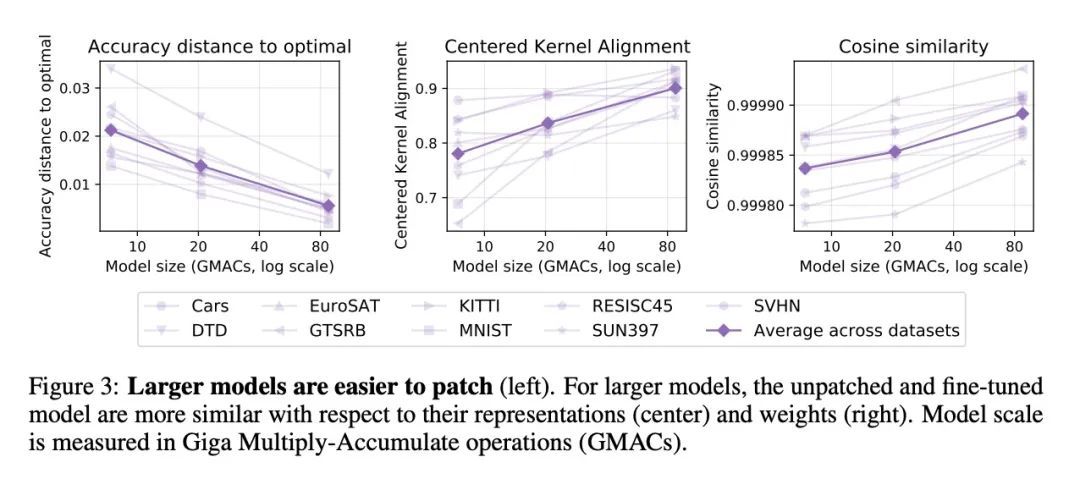
2、[CV] Patching open-vocabulary models by interpolating weights
G Ilharco, M Wortsman, S Y Gadre, S Song, H Hajishirzi, S Kornblith, A Farhadi, L Schmidt
[University of Washington & Columbia University & Google Research]
通过权重插值修补开放词表模型。像CLIP这样的开放词表模型在许多图像分类任务中取得了高精度。然而,有一些情况下,其零样本性能远非最佳。本文研究了模型的修补,目标是提高特定任务的精度,而不降低性能已经足够的任务的精度。为实现这一目标,本文引入PAINT,一种修补方法,用微调前的模型权重和在任务上微调后的权重之间的插值来进行修补。在zeroshot CLIP表现不佳的九个任务上,PAINT将精度提高了15到60个百分点,同时将ImageNet的精度保持在零样本模型的一个百分点之内。PAINT还允许一个单一模型在多个任务上进行修补,并随着模型规模的扩大而改善。此外,本文还发现了一些广泛的迁移案例,在一个任务上打补丁可以提高其他任务的精度,即使这些任务的类别不相干。最后,调查了普通基准以外的应用,如计算或减少对CLIP的字体攻击的影响。结果表明,有可能扩大开放词表模型达到高准确性的任务集,而不需要从头开始重新进行训练。
Open-vocabulary models like CLIP achieve high accuracy across many image classification tasks. However, there are still settings where their zero-shot performance is far from optimal. We study model patching, where the goal is to improve accuracy on specific tasks without degrading accuracy on tasks where performance is already adequate. Towards this goal, we introduce PAINT, a patching method that uses interpolations between the weights of a model before fine-tuning and the weights after fine-tuning on a task to be patched. On nine tasks where zeroshot CLIP performs poorly, PAINT increases accuracy by 15 to 60 percentage points while preserving accuracy on ImageNet within one percentage point of the zero-shot model. PAINT also allows a single model to be patched on multiple tasks and improves with model scale. Furthermore, we identify cases of broad transfer, where patching on one task increases accuracy on other tasks even when the tasks have disjoint classes. Finally, we investigate applications beyond common benchmarks such as counting or reducing the impact of typographic attacks on CLIP. Our findings demonstrate that it is possible to expand the set of tasks on which open-vocabulary models achieve high accuracy without re-training them from scratch.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.05592

3、[LG] Regularizing Deep Neural Networks with Stochastic Estimators of Hessian Trace
Y Liu, S Yu, T Lin
[University of Chicago & University of Texas Austin & Peking University]
基于Hessian迹随机估计器的深度神经网络正则化。本文通过惩罚Hessian迹,为深度神经网络开发了一种新的正则化方法。这种正则化方法是由最近的泛化误差的保证约束所激发的。Hutchinson方法是一个经典的无偏估计矩阵迹的方法,但它在深度学习模型上非常耗时。因此,本文提出一种dropout方案来有效地实现Hutchinson方法。然后,讨论了与非线性动态系统的线性稳定性和平坦/尖锐的最小值的联系。实验证明,所提出方法优于现有的正则化器和数据增强方法,如Jacobian、置信度惩罚、标签平滑、cutout和mixup。
In this paper we develop a novel regularization method for deep neural networks by penalizing the trace of Hessian. This regularizer is motivated by a recent guarantee bound of the generalization error. Hutchinson method is a classical unbiased estimator for the trace of a matrix, but it is very time-consuming on deep learning models. Hence a dropout scheme is proposed to efficiently implements the Hutchinson method. Then we discuss a connection to linear stability of a nonlinear dynamical system and flat/sharp minima. Experiments demonstrate that our method outperforms existing regularizers and data augmentation methods, such as Jacobian, confidence penalty, and label smoothing, cutout and mixup.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.05924

4、[LG] Improving and Assessing Anomaly Detectors for Large-Scale Settings
D Hendrycks, S Basart, M Mazeika, A Zou, J Kwon…
[UC Berkeley & University of Chicago]
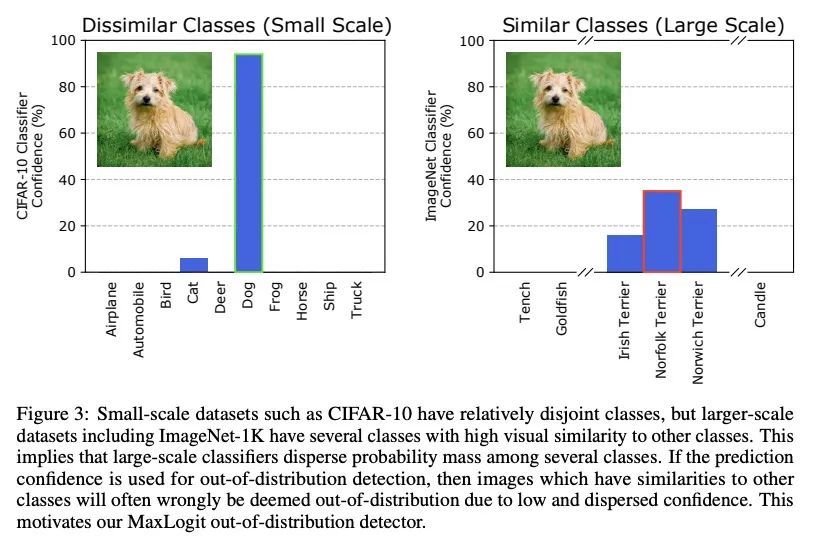
大规模场景下异常检测器的改进和评估。检测分布外样本对于安全关键的机器学习应用非常重要,如检测新的生物现象和自动驾驶汽车。然而,现有的研究主要集中在简单的小规模场景。为了给更现实的分布外检测创造条件,本文从小规模场景出发,探索具有高分辨率图像和数千个类的大规模多类和多标签场景。为了使未来在真实世界环境中的工作成为可能,本文为三种大规模环境创建了新的基准。为了测试ImageNet多类异常检测器,本文引入一种新的异常物种数据集。利用ImageNet-21K来评估PASCAL VOC和COCO多标签异常检测器。第三,通过引入一个带有道路异常的分割基准,为异常分割引入了一个新基准。在这些更现实的环境中对分布外检测进行了广泛的实验,发现一个基于最大对数的简单检测器在所有大规模的多类、多标签和分割任务中都优于之前的方法,为未来的工作建立了一个简单的新基线。
Detecting out-of-distribution examples is important for safety-critical machine learning applications such as detecting novel biological phenomena and self-driving cars. However, existing research mainly focuses on simple small-scale settings. To set the stage for more realistic out-of-distribution detection, we depart from small-scale settings and explore large-scale multiclass and multi-label settings with high-resolution images and thousands of classes. To make future work in real-world settings possible, we create new benchmarks for three large-scale settings. To test ImageNet multiclass anomaly detectors, we introduce a new dataset of anomalous species. We leverage ImageNet-21K to evaluate PASCAL VOC and COCO multilabel anomaly detectors. Third, we introduce a new benchmark for anomaly segmentation by introducing a segmentation benchmark with road anomalies. We conduct extensive experiments in these more realistic settings for out-of-distribution detection and find that a surprisingly simple detector based on the maximum logit outperforms prior methods in all the large-scale multi-class, multi-label, and segmentation tasks, establishing a simple new baseline for future work.
https://openreview.net/forum?id=vruwp11pWnO



5、[LG] Diurnal or Nocturnal? Federated Learning of Multi-branch Networks from Periodically Shifting Distributions
C Zhu, Z Xu, M Chen, J Konečný, A Hard, T Goldstein
[University of Maryland & Google]
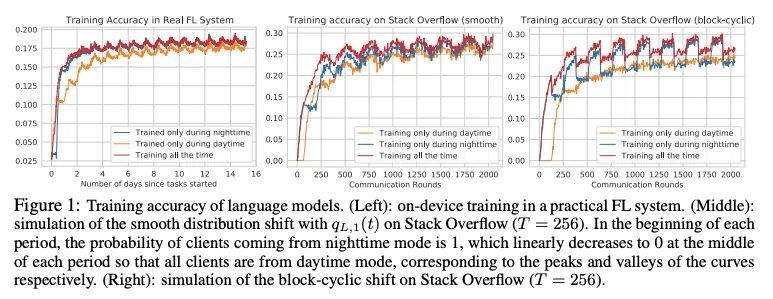
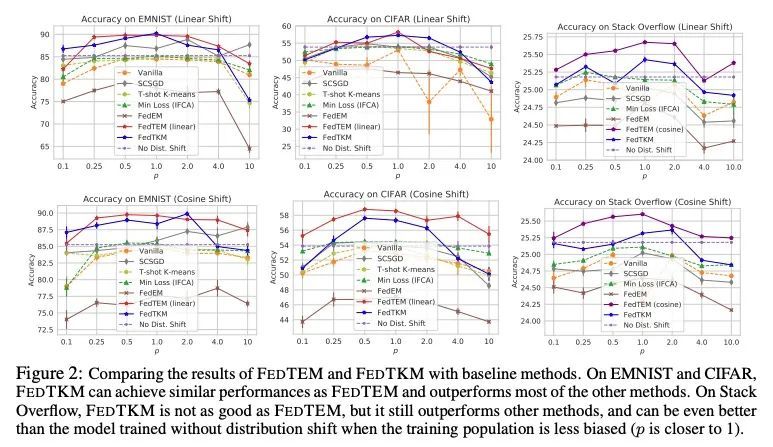
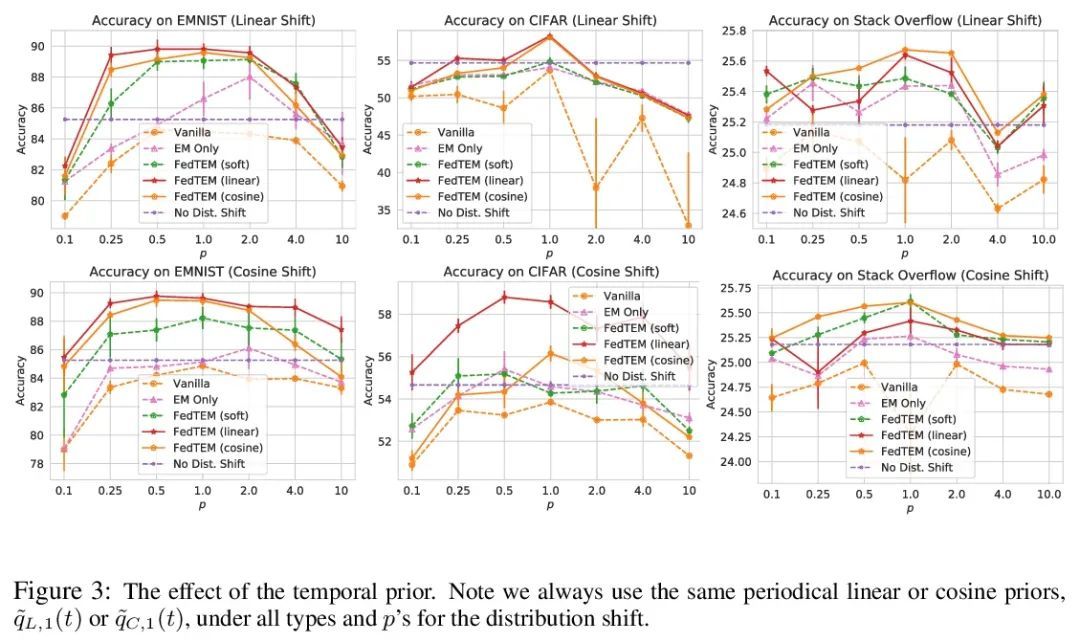
周期性漂移分布下的多分支网络联邦学习。在实践中,联邦学习已被部署为从移动设备上分散的客户数据中训练机器学习模型。据观察,可用于训练的客户端具有随时间变化而变化的周期性分布,这可能导致训练的不稳定性并降低模型性能。本文没有像之前的工作那样用块循环模式来模拟分布变化,而是用混合分布来模拟,在白天和夜间模式之间逐渐转变,并发现这种直观模型更符合实际联邦学习系统中的观察。此外,本文建议联合训练一个聚类模型和一个多分支网络,为来自不同模式的客户分配轻量的专门分支。一个时间性先验被用来大幅提高训练性能。在EMNIST和CIFAR数据集上进行的图像分类以及在Stack Overflow数据集上进行的下一单词预测的实验表明,所提出的算法可以对抗分布漂移的影响,并显著提高最终模型的性能。
Federated learning has been deployed to train machine learning models from decentralized client data on mobile devices in practice. The clients available for training are observed to have periodically shifting distributions changing with the time of day, which can cause instability in training and degrade the model performance. In this paper, instead of modeling the distribution shift with a block-cyclic pattern as previous works, we model it with a mixture of distributions that gradually shifts between daytime and nighttime modes, and find this intuitive model to better match the observations in practical federated learning systems. Furthermore, we propose to jointly train a clustering model and a multi-branch network to allocate lightweight specialized branches to clients from different modes. A temporal prior is used to significantly boost the training performance. Experiments for image classification on EMNIST and CIFAR datasets, and next word prediction on the Stack Overflow dataset show that the proposed algorithm can counter the effects of the distribution shift and significantly improve the final model performance.
https://openreview.net/forum?id=E4EE_ohFGz

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[CL] Language Tokens: A Frustratingly Simple Approach Improves Zero-Shot Performance of Multilingual Translation
语言Token:提高多语言翻译零样本性能的超简单方法
M ElNokrashy, A Hendy, M Maher, M Afify, H H Awadalla
[Microsoft]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.05852

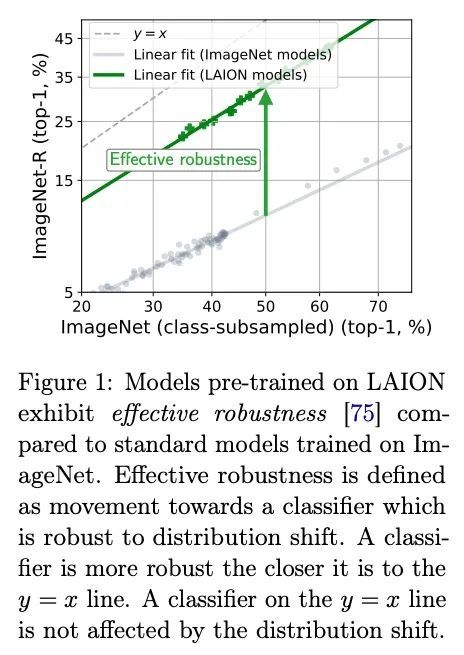
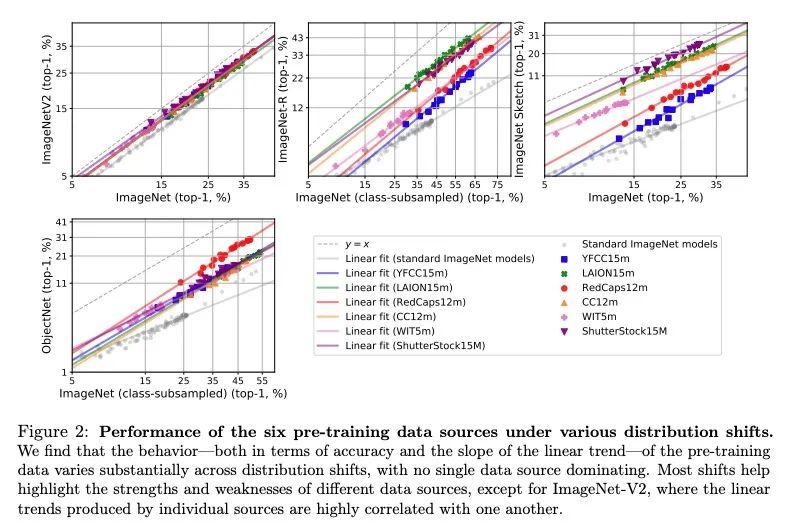
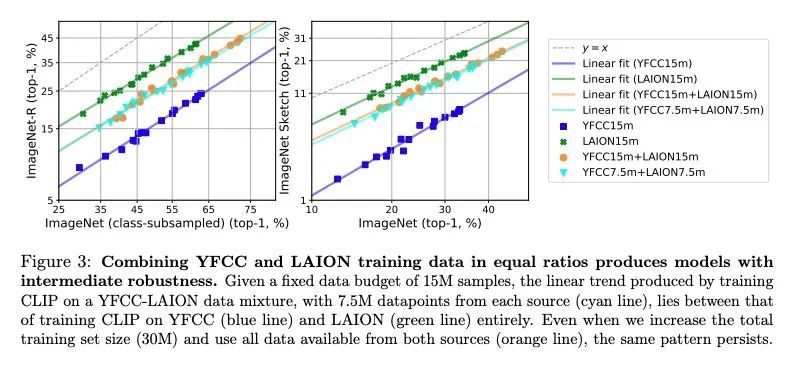
[LG] Quality Not Quantity: On the Interaction between Dataset Design and Robustness of CLIP
质量非数量:数据集设计与CLIP鲁棒性之间相互作用研究
T Nguyen, G Ilharco, M Wortsman, S Oh, L Schmidt
[University of Washington]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.05516

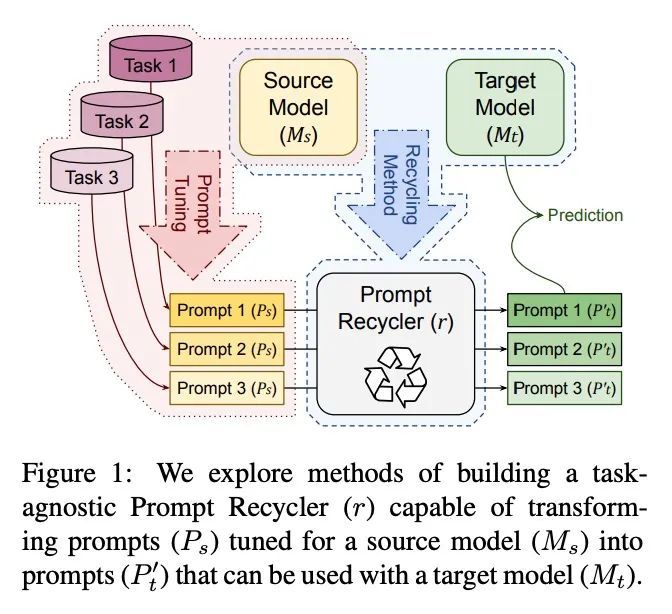
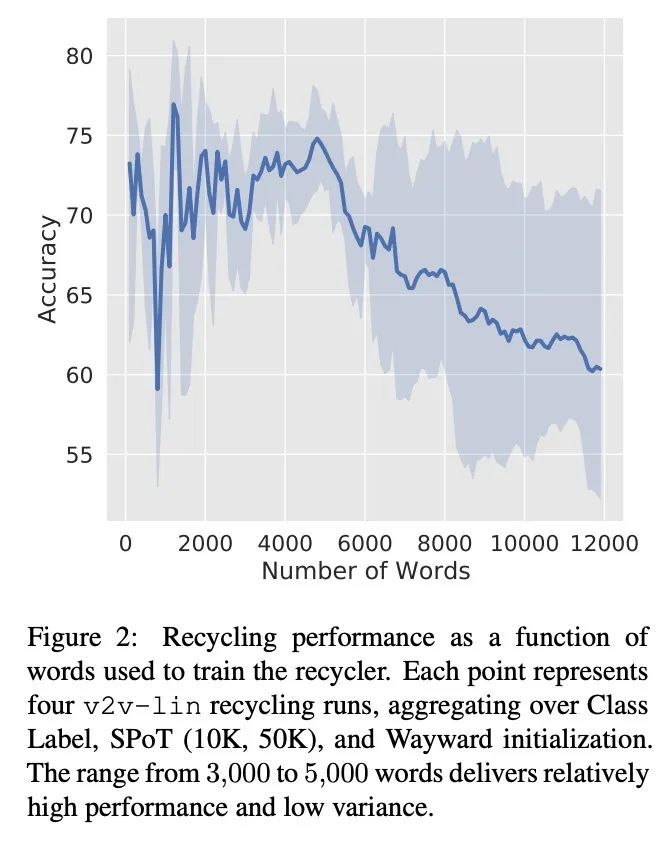
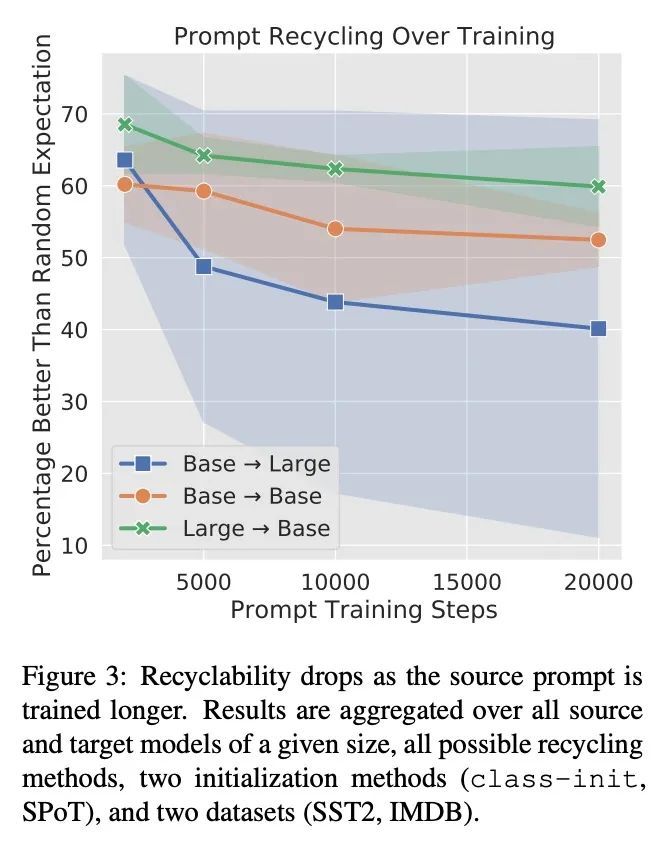
[CL] Reducing Retraining by Recycling Parameter-Efficient Prompts
通过回收参数高效提示减少重训练
B Lester, J Yurtsever, S Shakeri, N Constant
[Google Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.05577
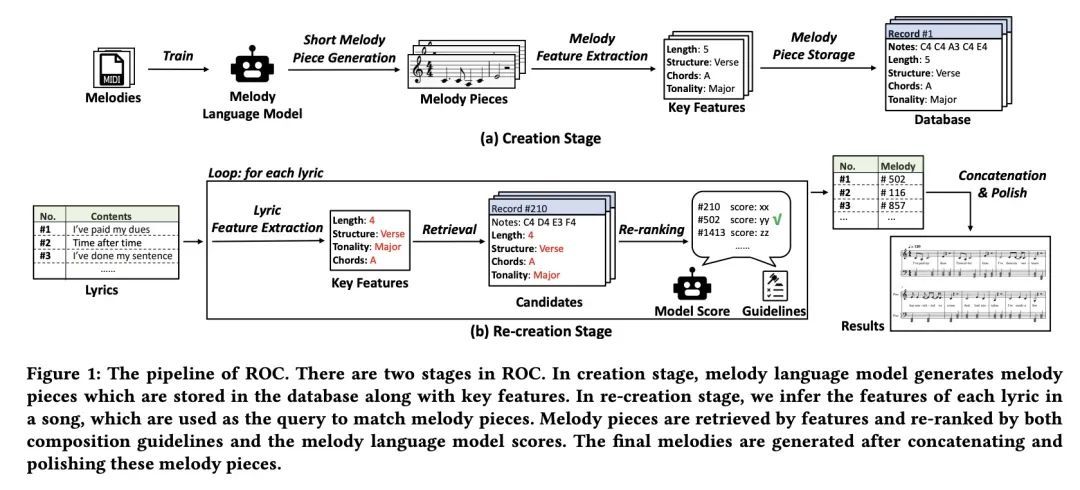
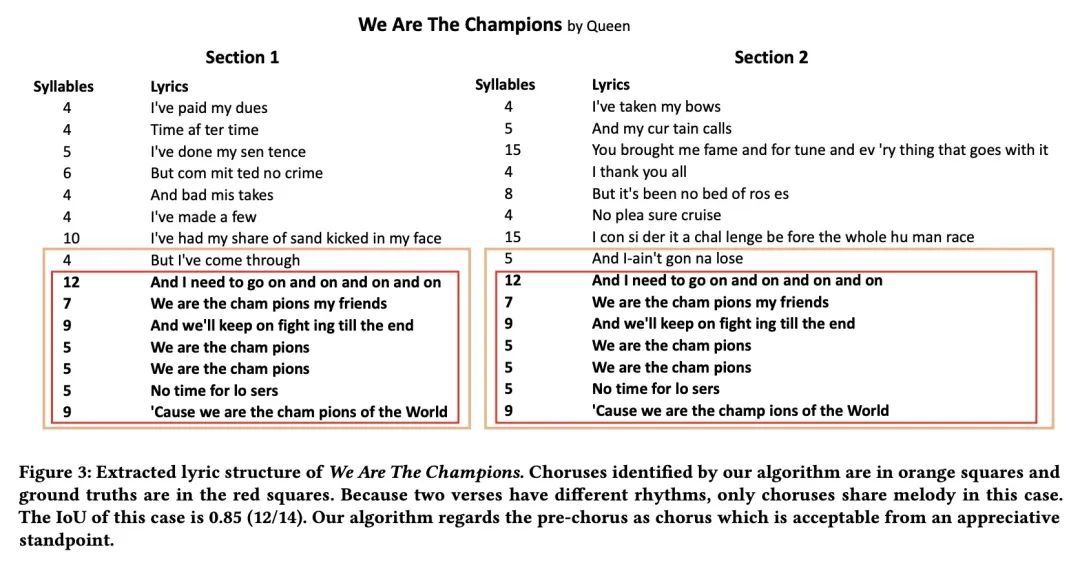
[AS] ROC: A New Paradigm for Lyric-to-Melody Generation
ROC:词-曲生成新范式
A Lv, X Tan, T Qin, T Liu, R Yan
[Renmin University of China & Microsoft Research Asia]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.05697


内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢