LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:基于结合亲和力和自然度预测的抗体优化、快速无限波形音乐生成、面向细粒度3D分割的多视稠密对应学习、基于标准化流的流形隐性表示、八点算法作为ViT相对姿态预测的归纳偏差、基于隐视觉引导和超网络的文本到图像生成、推荐模型缩放率解析、神经网络的提升Bregman训练、面向任意分布漂移在线预测的保形推理
1、[LG] Antibody optimization enabled by artificial intelligence predictions of binding affinity and naturalness
S Bachas, G Rakocevic, D Spencer...
[Absci Corporation]
基于结合亲和力和自然度预测的抗体优化。传统的抗体优化方法涉及筛选可用序列空间的某个小子集,往往导致候选药物具有次优的结合亲和力、可开发性或免疫原性。基于两种不同的抗体,本文证明了根据高通量亲和力数据训练的深度上下文语言模型可以定量预测未见过的抗体序列变体的结合。这些变体在一个大的突变空间中跨越了三个数量级的KD范围。所提出的模型揭示了强烈的表观效应,突出了对智能筛选方法的需求。此外,本文还提出了"自然度"建模,这是一种对抗体变体与天然免疫球蛋白的相似度进行评分的指标。自然度与药物可开发性和免疫原性的衡量标准有关,而且它可以与结合亲和力一起用遗传算法进行优化。这种方法有望加速和改善抗体工程,并可能提高开发新抗体和相关候选药物的成功率。
Traditional antibody optimization approaches involve screening a small subset of the available sequence space, often resulting in drug candidates with suboptimal binding affinity, developability or immunogenicity. Based on two distinct antibodies, we demonstrate that deep contextual language models trained on high-throughput affinity data can quantitatively predict binding of unseen antibody sequence variants. These variants span a KD range of three orders of magnitude over a large mutational space. Our models reveal strong epistatic effects, which highlight the need for intelligent screening approaches. In addition, we introduce the modeling of “naturalness”, a metric that scores antibody variants for similarity to natural immunoglobulins. We show that naturalness is associated with measures of drug developability and immunogenicity, and that it can be optimized alongside binding affinity using a genetic algorithm. This approach promises to accelerate and improve antibody engineering, and may increase the success rate in developing novel antibody and related drug candidates.
https://www.biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.08.16.504181v1




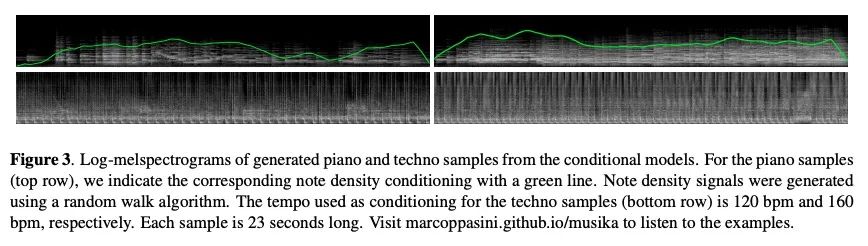
2、[AS] Musika! Fast Infinite Waveform Music Generation
M Pasini, J Schlüter
[Johannes Kepler University Linz]
MUSIKA! 快速无限波形音乐生成。采用快速和用户可控的音乐生成,可以实现新的音乐创作或表演方式。然而,最先进的音乐生成系统需要大量的数据和计算资源进行训练,而且推理速度很慢。这使得它们对于实时交互使用来说不切实际。本文提出Musika,一个非自回归音乐生成系统,可以用单个消费级GPU对数百小时的音乐进行训练,并允许在消费级CPU上比实时还快很多的速度生成任意长度的音乐。首先用对抗自编码器学习谱图大小和相位的紧凑可逆表示,然后针对特定音乐域在该表示上训练生成对抗网络(GAN)来实现这一目标。一个潜在的坐标系统可平行生成任意长的节选序列,而一个全局背景向量可以使音乐在时间上保持风格的一致性。本文进行了定量评估,以评估生成样本的质量,并展示了在钢琴和电子音乐生成中用户控制的选项。
Fast and user-controllable music generation could enable novel ways of composing or performing music. However, state-of-the-art music generation systems require large amounts of data and computational resources for training, and are slow at inference. This makes them impractical for real-time interactive use. In this work, we introduce Musika, a music generation system that can be trained on hundreds of hours of music using a single consumer GPU, and that allows for much faster than real-time generation of music of arbitrary length on a consumer CPU. We achieve this by first learning a compact invertible representation of spectrogram magnitudes and phases with adversarial autoencoders, then training a Generative Adversarial Network (GAN) on this representation for a particular music domain. A latent coordinate system enables generating arbitrarily long sequences of excerpts in parallel, while a global context vector allows the music to remain stylistically coherent through time. We perform quantitative evaluations to assess the quality of the generated samples and showcase options for user control in piano and techno music generation. We release the source code and pretrained autoencoder weights at github.com/marcoppasini/musika, such that a GAN can be trained on a new music domain with a single GPU in a matter of hours.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.08706



3、[CV] MvDeCor: Multi-view Dense Correspondence Learning for Fine-grained 3D Segmentation
G Sharma, K Yin, S Maji, E Kalogerakis, O Litany, S Fidler
[University of Massachusetts & NVIDIA] (2022)
MvDeCor: 面向细粒度3D分割的多视稠密对应学习。本文提出将2D域自监督技术用于精细的3D形状分割任务,受到基于视图的表面表示比基于点云或体素占位的3D对应方法更有效模拟高分辨率表面细节和纹理这一观察的启发。给定一个3D形状,从多个视角进行渲染,并在对比学习框架内设置一个稠密的对应学习任务。结果,学到的2D表示是视图不变的,且在几何上是一致的,与单独利用2D或3D的自监督方法相比,在有限数量的标记形状上训练时,能实现更好的泛化。在有纹理(RenderPeople)和无纹理(PartNet)3D数据集上的实验表明,所提出方法在细粒度的组件分割方面优于最先进的方法。当只有稀疏的视图集可用于训练或形状为纹理时,对基线的改进更大,表明MvDeCor同时受益于2D处理和3D几何推理。
We propose to utilize self-supervised techniques in the 2D domain for fine-grained 3D shape segmentation tasks. This is inspired by the observation that view-based surface representations are more effective at modeling high-resolution surface details and texture than their 3D counterparts based on point clouds or voxel occupancy. Specifically, given a 3D shape, we render it from multiple views, and set up a dense correspondence learning task within the contrastive learning framework. As a result, the learned 2D representations are view-invariant and geometrically consistent, leading to better generalization when trained on a limited number of labeled shapes compared to alternatives that utilize self-supervision in 2D or 3D alone. Experiments on textured (RenderPeople) and untextured (PartNet) 3D datasets show that our method outperforms state-of-the-art alternatives in fine-grained part segmentation. The improvements over baselines are greater when only a sparse set of views is available for training or when shapes are textured, indicating that MvDeCor benefits from both 2D processing and 3D geometric reasoning. Project page: https://nv-tlabs.github.io/MvDeCor/
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.08580




4、[CV] ManiFlow: Implicitly Representing Manifolds with Normalizing Flows
J Postels, M Danelljan, L V Gool, F Tombari
[ETH Zurich & Google]
ManiFlow:基于标准化流的流形隐性表示。标准化流(NF)是灵活的显式生成模型,已被证明可以准确地模拟复杂的现实世界数据分布。然而,其可逆性约束对位于嵌入高维空间的低维流形上的数据分布施加了限制。实际上,该缺点往往是通过向数据中添加噪声来绕过的,这影响了生成样本的质量。与之前的工作不同,本文通过从原始数据分布中生成样本来解决该问题,因为对扰动分布和噪声模型有充分的了解。在扰动数据上训练的NF隐性地表示了最大似然区域的流形。本文提出一种优化目标,即从扰动分布的样本中恢复流形上最可能的点。本文专注于3D点云,对于这些点云,利用NF的明确性质,即从对数似然梯度和对数似然本身提取的表面法线,应用泊松表面重建来细化生成的点集。
Normalizing Flows (NFs) are flexible explicit generative models that have been shown to accurately model complex real-world data distributions. However, their invertibility constraint imposes limitations on data distributions that reside on lower dimensional manifolds embedded in higher dimensional space. Practically, this shortcoming is often bypassed by adding noise to the data which impacts the quality of the generated samples. In contrast to prior work, we approach this problem by generating samples from the original data distribution given full knowledge about the perturbed distribution and the noise model. To this end, we establish that NFs trained on perturbed data implicitly represent the manifold in regions of maximum likelihood. Then, we propose an optimization objective that recovers the most likely point on the manifold given a sample from the perturbed distribution. Finally, we focus on 3D point clouds for which we utilize the explicit nature of NFs, i.e. surface normals extracted from the gradient of the log-likelihood and the log-likelihood itself, to apply Poisson surface reconstruction to refine generated point sets.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.08932



5、[CV] The 8-Point Algorithm as an Inductive Bias for Relative Pose Prediction by ViTs
C Rockwell, J Johnson, D F. Fouhey
[University of Michigan]
八点算法作为ViT相对姿态预测的归纳偏差。本文提出一种简单基线来直接估计两幅图像间的相对姿态(旋转和平移,包括比例)。深度方法最近显示出强劲的进展,但往往需要复杂或多阶段的架构。本文表明,可以对视觉Transformer(ViT)进行小幅修改,使其计算接近于八点算法。这种归纳偏差使一个简单的方法在多种环境下具有竞争力,往往比最先进的技术水平有大幅度的提高,在有限数据场景下有很强的性能提升。
We present a simple baseline for directly estimating the relative pose (rotation and translation, including scale) between two images. Deep methods have recently shown strong progress but often require complex or multi-stage architectures. We show that a handful of modifications can be applied to a Vision Transformer (ViT) to bring its computations close to the Eight-Point Algorithm. This inductive bias enables a simple method to be competitive in multiple settings, often substantially improving over the state of the art with strong performance gains in limited data regimes.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.08988




另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[CV] Text-to-Image Generation via Implicit Visual Guidance and Hypernetwork
基于隐视觉引导和超网络的文本到图像生成
X Yuan, Z Lin, J Kuen, J Zhang, J Collomosse
[University of Chicago & Adobe Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.08493




[IR] Understanding Scaling Laws for Recommendation Models
推荐模型缩放率解析
N Ardalani, C Wu, Z Chen, B Bhushanam, A Aziz
[Meta]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.08489




[LG] Lifted Bregman Training of Neural Networks
神经网络的提升Bregman训练
X Wang, M Benning
[Queen Mary University of London]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.08772




[LG] Conformal Inference for Online Prediction with Arbitrary Distribution Shifts
面向任意分布漂移在线预测的保形推理
I Gibbs, E Candès
[Stanford University]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.08401




内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢