LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:深度学习中的协同性和对称性、面向长尾识别的针对性监督对比学习、同质性是图神经网络的必要条件吗、从单目图像中学习基于几何和外观解缠的3D生成模型、基于全摘要上下文建模改进科学声明验证、在线幽默评分的性别和年龄差异分析、高效的非注意力视频漂移Transformer、基于结构化状态空间模型的扩散时间序列插补和预测、深度NLP模型的神经元级解释综述
1、[LG] Synergy and Symmetry in Deep Learning: Interactions between the Data, Model, and Inference Algorithm
L Xiao, J Pennington
[Google Research]
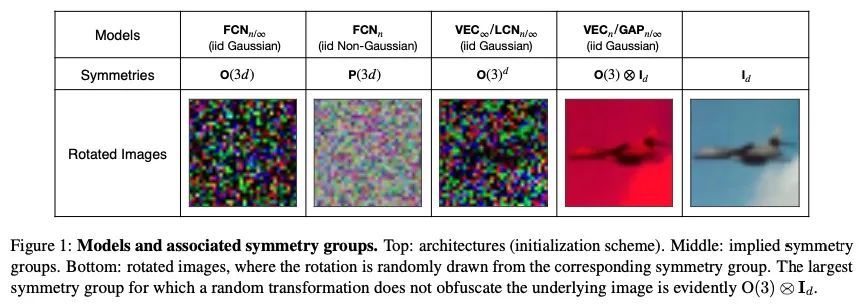
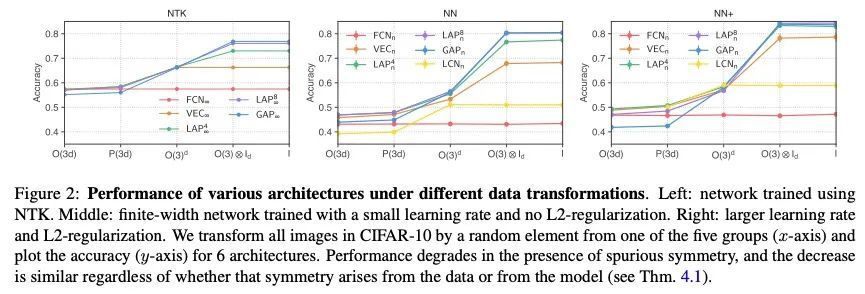
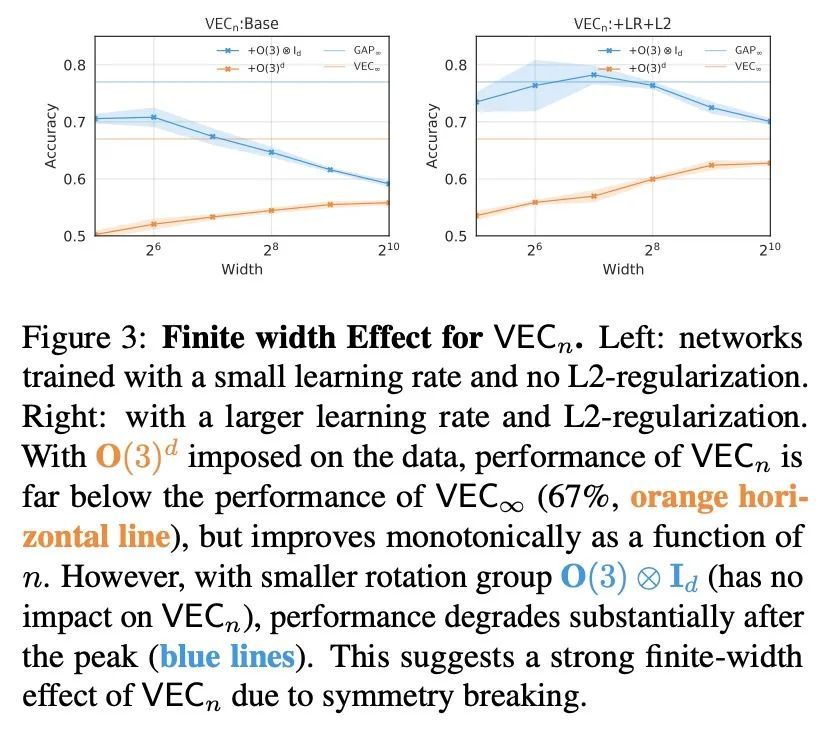
深度学习中的协同性和对称性:数据、模型和推理算法之间的相互作用。尽管人们普遍认为高维度的学习会受到维度诅咒的影响,但现代机器学习方法往往表现出惊人的力量,可以在不使用大量数据的情况下解决广泛的、具有挑战性的现实世界学习问题。这些方法究竟是如何打破这个诅咒的,仍然是深度学习理论中一个基本的开放性问题。之前的努力是将数据(D)、模型(M)和推理算法(I)作为独立的模块来研究该问题,本文将三元组(D, M, I)作为一个综合系统来分析,并找出有助于缓解维度诅咒的重要协同作用。首先研究了与各种学习算法(M, I)相关的基本对称性,重点是深度学习中的四个原型架构:全连接网络(FCN),局部连接网络(LCN),以及有池化和无池化的卷积网络(GAP/VEC)。结果发现,当这些对称性与数据分布的对称性兼容时,学习是最有效的,当(D, M, I)三要素中的任何成员不一致或次优时,性能会明显恶化。
Although learning in high dimensions is commonly believed to suffer from the curse of dimensionality, modern machine learning methods often exhibit an astonishing power to tackle a wide range of challenging real-world learning problems without using abundant amounts of data. How exactly these methods break this curse remains a fundamental open question in the theory of deep learning. While previous efforts have investigated this question by studying the data (D), model (M), and inference algorithm (I) as independent modules, in this paper, we analyze the triplet (D,M, I) as an integrated system and identify important synergies that help mitigate the curse of dimensionality. We first study the basic symmetries associated with various learning algorithms (M, I), focusing on four prototypical architectures in deep learning: fully-connected networks (FCN), locally-connected networks (LCN), and convolutional networks with and without pooling (GAP/VEC). We find that learning is most efficient when these symmetries are compatible with those of the data distribution and that performance significantly deteriorates when any member of the (D,M, I) triplet is inconsistent or suboptimal.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.04612

2、[CV] Targeted Supervised Contrastive Learning for Long-Tailed Recognition
T Li, P Cao, Y Yuan, L Fan, Y Yang, R Feris, P Indyk, D Katabi
[MIT CSAIL & MIT-IBM Watson AI Lab]
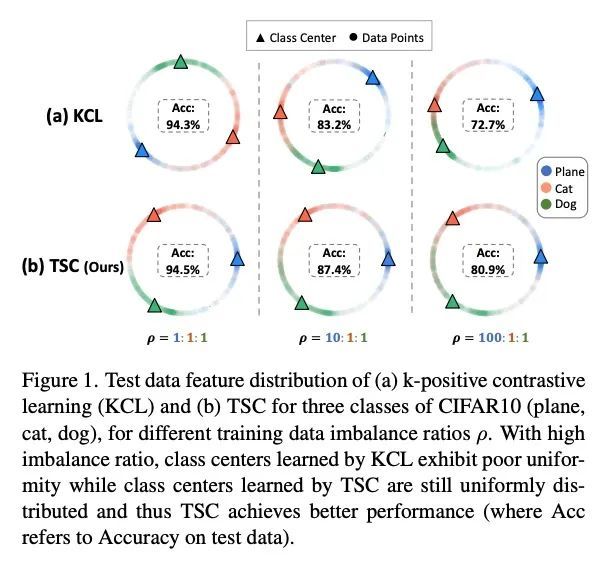
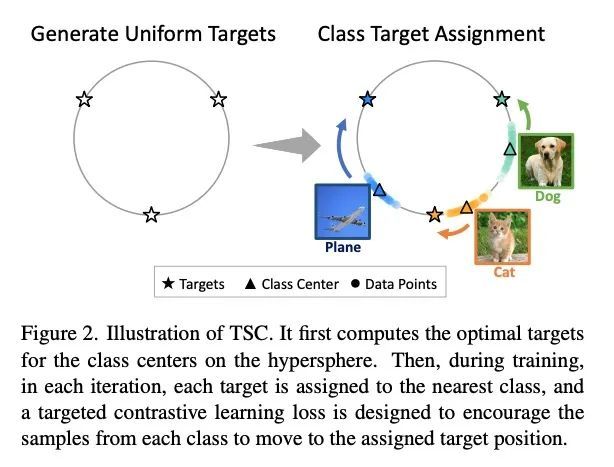
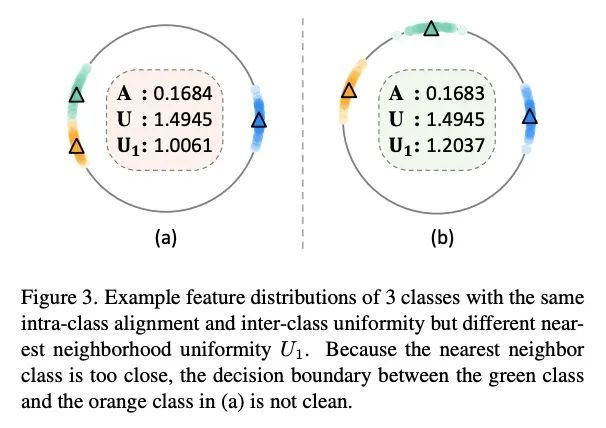
面向长尾识别的针对性监督对比学习。现实世界的数据经常表现出严重的类不平衡的长尾分布,其中多数类可以主导训练过程并改变少数类的决策边界。最近,研究人员调研了监督对比学习在长尾识别中的潜力,并证明它提供了一个强大的性能增益。本文表明,虽然监督对比学习有助于提高性能,但过去的基线受到不平衡的数据分布带来的不均匀性的影响。这种不均匀性表现在来自少数类的样本在特征空间中的可分离性很差。为解决该问题,本文提出了有针对性的监督对比学习(TSC),改善了超球上特征分布的均匀性。TSC首先生成一组均匀分布在超球上的目标,在训练过程中,使不同类别的特征收敛于这些不同的、均匀分布的目标。这迫使所有类,包括少数类,在特征空间中保持统一的分布,改善了类边界,即使在长尾数据存在的情况下也能提供更好的泛化。在多个数据集上的实验表明,TSC在长尾识别任务上实现了最先进的性能。
Real-world data often exhibits long tail distributions with heavy class imbalance, where the majority classes can dominate the training process and alter the decision boundaries of the minority classes. Recently, researchers have investigated the potential of supervised contrastive learning for long-tailed recognition, and demonstrated that it provides a strong performance gain. In this paper, we show that while supervised contrastive learning can help improve performance, past baselines suffer from poor uniformity brought in by imbalanced data distribution. This poor uniformity manifests in samples from the minority class having poor separability in the feature space. To address this problem, we propose targeted supervised contrastive learning (TSC), which improves the uniformity of the feature distribution on the hypersphere. TSC first generates a set of targets uniformly distributed on a hypersphere. It then makes the features of different classes converge to these distinct and uniformly distributed targets during training. This forces all classes, including minority classes, to maintain a uniform distribution in the feature space, improves class boundaries, and provides better generalization even in the presence of long-tail data. Experiments on multiple datasets show that TSC achieves state-of-the-art performance on long-tailed recognition tasks. Code is available here.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2111.13998

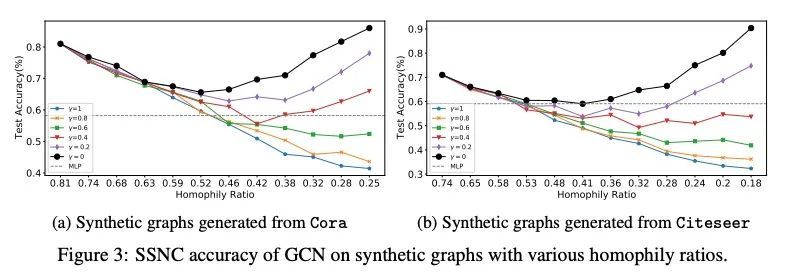
3、[LG] Is Homophily a Necessity for Graph Neural Networks?
Y Ma, X Liu, N Shah, J Tang
[New Jersey Institute of Technology & Michigan State University & Snap Inc]
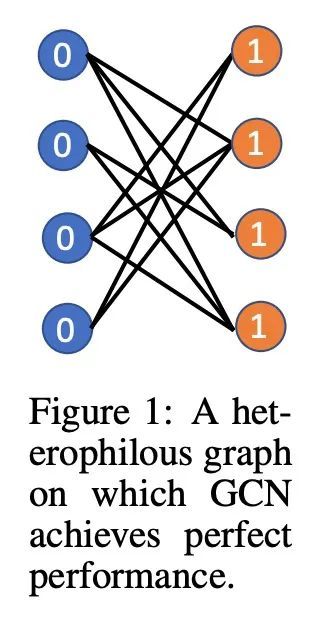
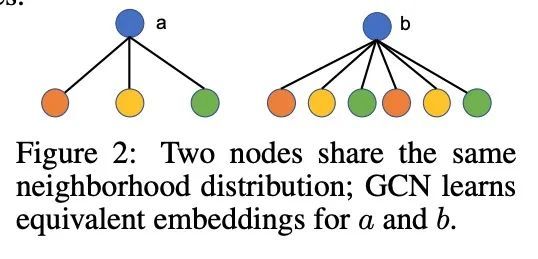
同质性是图神经网络的必要条件吗?图神经网络(GNN)在学习适合众多基于图的机器学习任务的表示方面显示出巨大的优势。当应用于半监督节点分类时,人们普遍认为,由于同质性假设("同类相吸"),GNN可以很好地工作,而不能推广到异质性的图,即不同的节点连接。最近的工作已经设计了新的架构来克服这种与异质性有关的限制。然而,本文根据经验发现,在一些常用的异质性图上,标准的图卷积网络(GCN)实际上可以取得比这种精心设计的方法更好的性能。这促使重新考虑同质性是否真的是GNN良好性能的必要条件。本文发现,这种说法并不完全正确,事实上,在某些条件下,GCN可以在异质性图上取得很好的性能。本文仔细描述了这些条件,并提供了支持性的理论理解和经验观察。最后,本文研究了现有的异质性图基准,并根据这一理解,调和了GCN在这些图上的(不足)表现。
Graph neural networks (GNNs) have shown great prowess in learning representations suitable for numerous graph-based machine learning tasks. When applied to semi-supervised node classification, GNNs are widely believed to work well due to the homophily assumption (“like attracts like”), and fail to generalize to heterophilous graphs where dissimilar nodes connect. Recent works have designed new architectures to overcome such heterophily-related limitations. However, we empirically find that standard graph convolutional networks (GCNs) can actually achieve better performance than such carefully designed methods on some commonly used heterophilous graphs. This motivates us to reconsider whether homophily is truly necessary for good GNN performance. We find that this claim is not quite true, and in fact, GCNs can achieve strong performance on heterophilous graphs under certain conditions. Our work carefully characterizes these conditions, and provides supporting theoretical understanding and empirical observations. Finally, we examine existing heterophilous graphs benchmarks and reconcile how the GCN (under)performs on them based on this understanding.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2106.06134

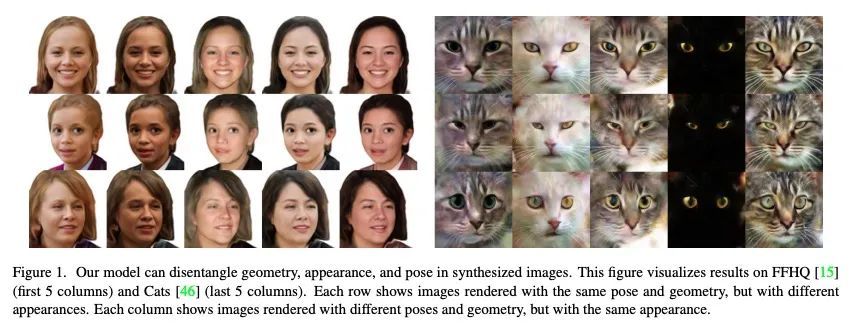
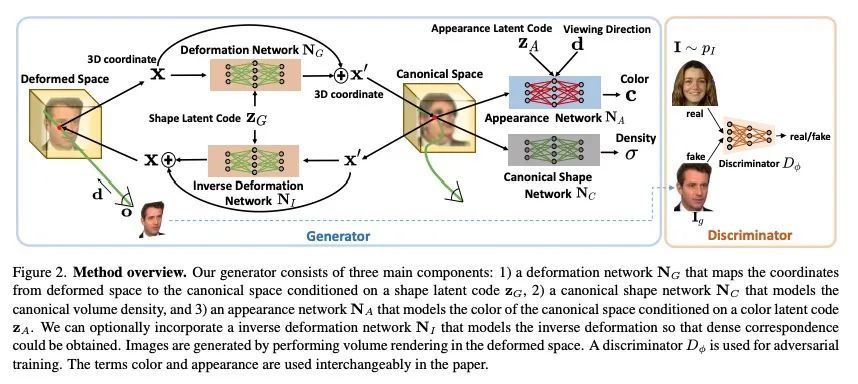
4、[CV] Disentangled3D: Learning a 3D Generative Model with Disentangled Geometry and Appearance from Monocular Images
A Tewari, M B R...
[Max Planck Insitute for Informatics & MIT & Stanford University]
Disentangled3D: 从单目图像中学习基于几何和外观解缠的3D生成模型。从单目图像数据集中学习3D生成模型,可实现自监督3D推理和可控合成。最先进的3D生成模型是GAN,用神经3D体表示法进行合成。图像是通过渲染给定相机的体来合成的。这些模型可以在任任意生成的图像中把3D场景与摄像机的视角分开。然而,大多数模型并不能解缠图像形成的其他因素,如几何和外观。本文设计了一种3D GAN,可以从单目观察中学习物体的解缠模型。该模型可以分解场景中的几何和外观变化,可以从生成模型的几何和外观空间独立采样。这是用一种新的非刚性可变形场景公式实现的。代表一个物体实例的3D体被计算为一个非刚性变形的典型3D体。所提出方法在训练过程中联合学习了典型体及其变形。这种提法有助于利用定义在3D变形场上的新姿态正则化损失来改善3D场景和摄像机视点之间的解缠。此外,本文进一步对反变形进行建模,使模型生成的图像之间的密集对应关系得到计算。最后,设计了一种方法,将真实图像嵌入到解缠生成模型的潜空间中,从而实现对真实图像的编辑。
Learning 3D generative models from a dataset of monocular images enables self-supervised 3D reasoning and controllable synthesis. State-of-the-art 3D generative models are GANs which use neural 3D volumetric representations for synthesis. Images are synthesized by rendering the volumes from a given camera. These models can disentangle the 3D scene from the camera viewpoint in any generated image. However, most models do not disentangle other factors of image formation, such as geometry and appearance. In this paper, we design a 3D GAN which can learn a disentangled model of objects, just from monocular observations. Our model can disentangle the geometry and appearance variations in the scene, i.e., we can independently sample from the geometry and appearance spaces of the generative model. This is achieved using a novel non-rigid deformable scene formulation. A 3D volume which represents an object instance is computed as a non-rigidly deformed canonical 3D volume. Our method learns the canonical volume, as well as its deformations, jointly during training. This formulation also helps us improve the disentanglement between the 3D scene and the camera viewpoints using a novel pose regularization loss defined on the 3D deformation field. In addition, we further model the inverse deformations, enabling the computation of dense correspondences between images generated by our model. Finally, we design an approach to embed real images into the latent space of our disentangled generative model, enabling editing of real images.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.15926


5、[CL] LongChecker: Improving scientific claim verification by modeling full-abstract context
D Wadden, K Lo, L L Wang, A Cohan...
[University of Washington & Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence]
LongChecker:基于全摘要上下文建模改进科学声明验证。本文提出了用于科学声明验证的LongChecker系统。给定一个科学声明和一个含有证据的研究摘要,LongChecker根据声明和摘要的共享编码,以多任务方式预测真实性标签并识别支持性理由。在SCIFACT数据集上进行了实验,发现LongChecker实现了最先进的性能。本文进行了分析,以了解这种改进的来源,并发现识别一个声明和报告科学发现的理由之间的关系往往需要了解理由出现的背景。通过基于所有可用的上下文做出标签决定,LongChecker在需要这种理解的情况下取得了更好的性能。此外,本文表明LongChecker能利用弱监督的域内数据来促进科学声明验证的少样本领域自适应。
We introduce the LONGCHECKER system for scientific claim verification. Given a scientific claim and an evidence-containing research abstract, LONGCHECKER predicts a veracity label and identifies supporting rationales in a multitask fashion based on a shared encoding of the claim and abstract. We perform experiments on the SCIFACT dataset, and find that LONGCHECKER achieves state-of-the-art performance. We conduct analysis to understand the source of this improvement, and find that identifying the relationship between a claim and a rationale reporting a scientific finding often requires understanding the context in which the rationale appears. By making labeling decisions based on all available context, LONGCHECKER achieves better performance on cases requiring this type of understanding. In addition, we show that LONGCHECKER is able to leverage weakly-supervised in-domain data to facilitate few-shot domain adaptation for scientific claim verification.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.01640



另外几篇值得关注的论文:
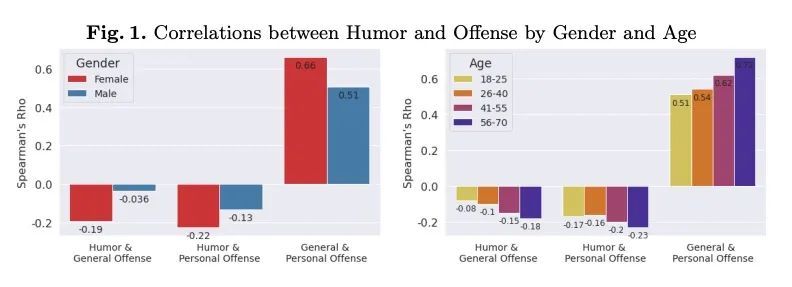
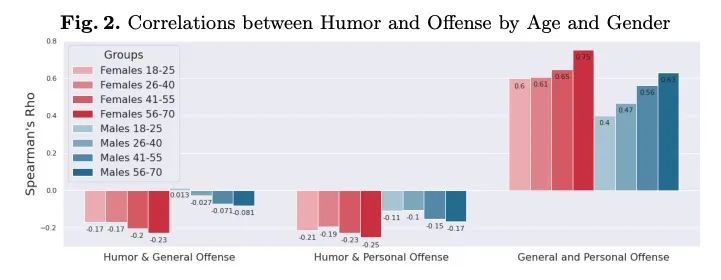
[CL] Don't Take it Personally: Analyzing Gender and Age Differences in Ratings of Online Humor
不要太主观:在线幽默评分的性别和年龄差异分析J. A. Meaney, S R. Wilson, L Chiruzzo, W Magdy
[University of Edinburgh & Universidad de la Republica]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.10898


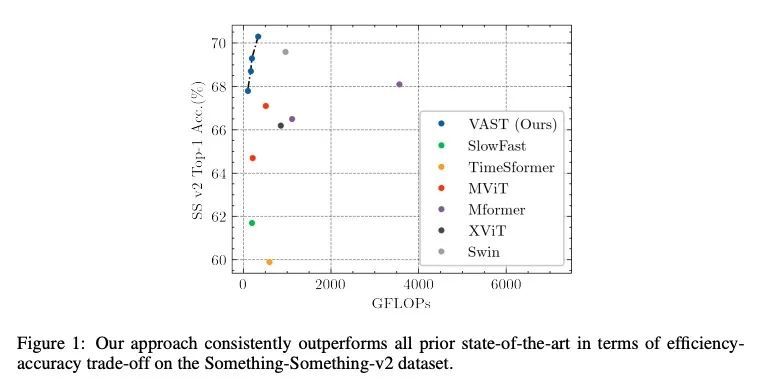
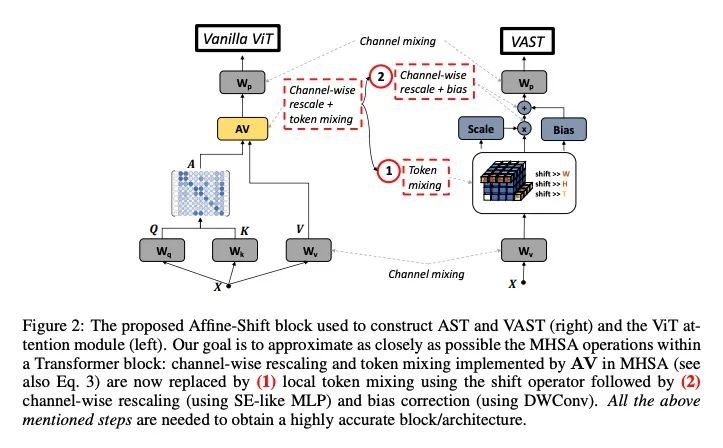
[CV] Efficient Attention-free Video Shift Transformers
高效的非注意力视频漂移Transformer
A Bulat, B Martinez, G Tzimiropoulos
[Samsung AI Center Cambridge]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.11108

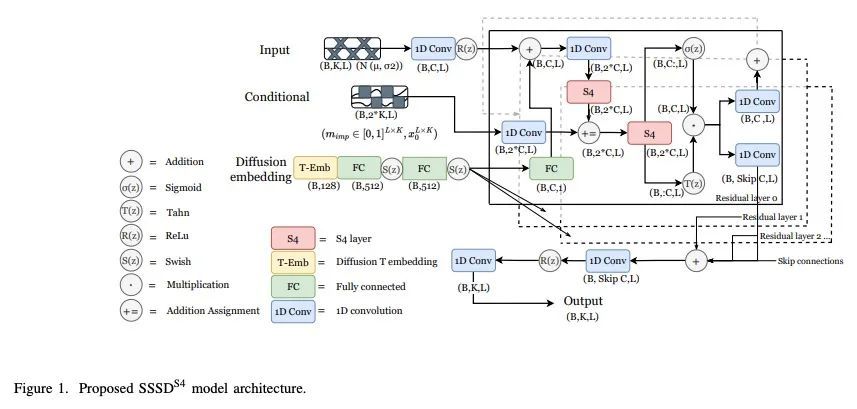
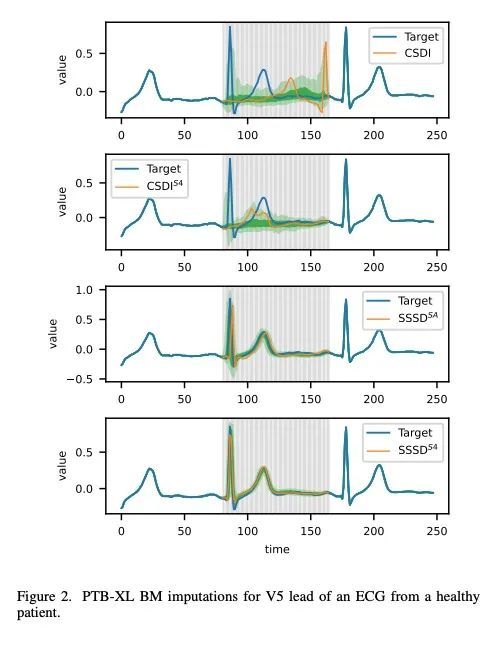
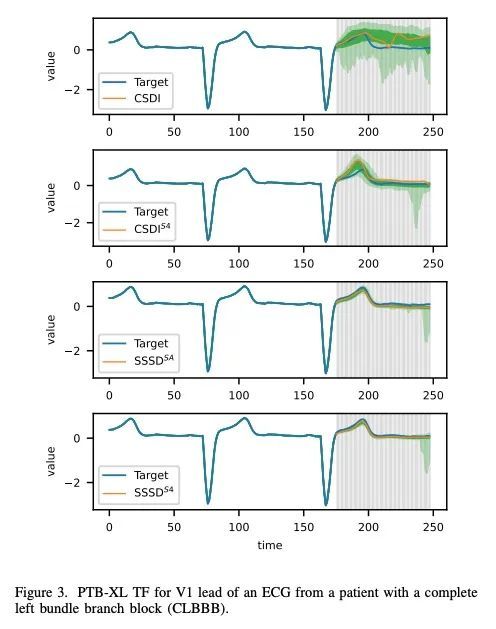
[LG] Diffusion-based Time Series Imputation and Forecasting with Structured State Space Models
基于结构化状态空间模型的扩散时间序列插补和预测
J M L Alcaraz, N Strodthoff
[University of Oldenburg]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.09399

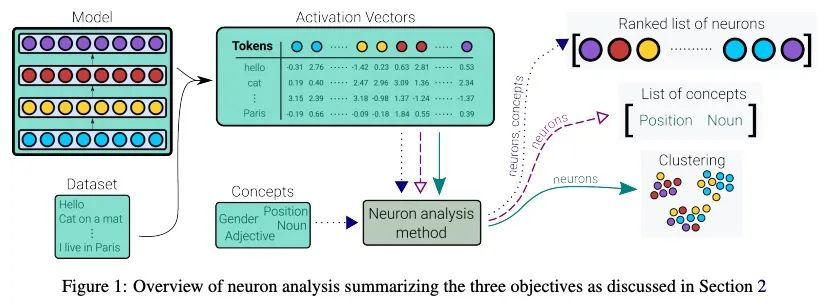
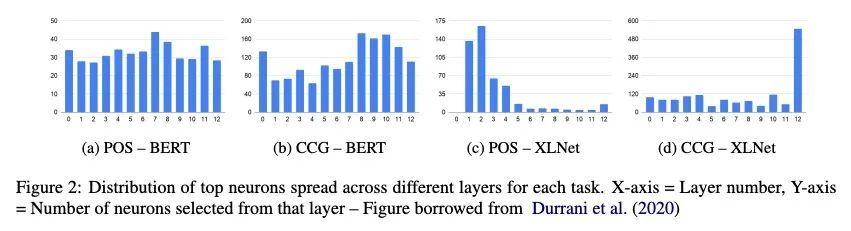
[CL] Neuron-level Interpretation of Deep NLP Models: A Survey
深度NLP模型的神经元级解释综述
H Sajjad, N Durrani, F Dalvi
[Dalhousie University & HBKU]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2108.13138


内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢