LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:统一视角理解扩散模型、用实验室规模的资源训练T5模型、目标检测中的未知目标检测、无监督段落检索学习、提供者公平感知新闻推荐、校准选择性分类、用语言模型构建知识库、因果熵优化、深度结构化因果形状模型
1、[LG] Understanding Diffusion Models: A Unified Perspective
C Luo
[Google Research]
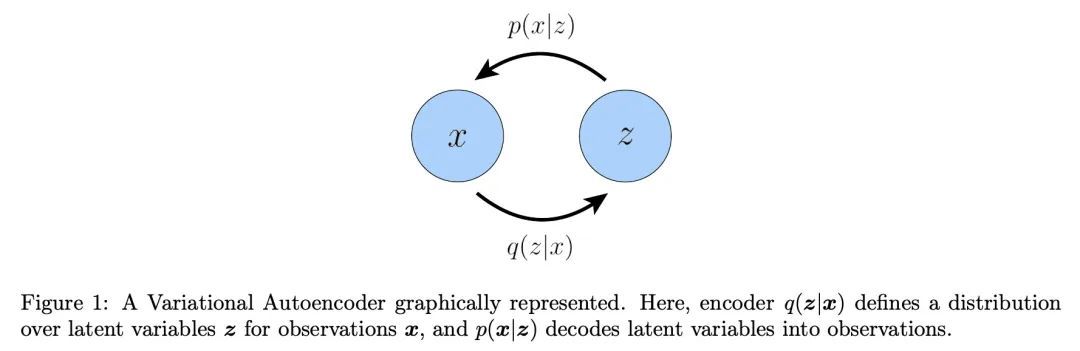
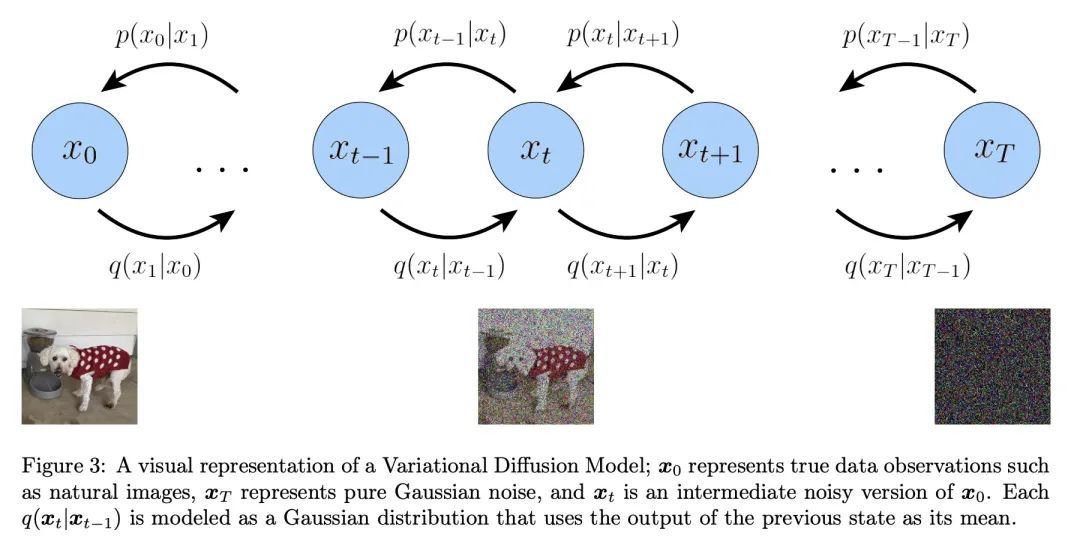
理解扩散模型:统一视角。扩散模型作为生成模型,显示了令人难以置信的能力;事实上,它们为目前最先进的文本条件图像生成模型提供了动力,如Imagen和DALL-E 2。本文从变分和基于得分的角度回顾、解密并统一了对扩散模型的理解。首先推导出变分扩散模型(VDM),作为马尔科夫分级变分自编码器的一个特例,其中三个关键假设使ELBO的计算和优化具有可操作性。本文证明,优化VDM可以归结为学习一个神经网络来预测三个潜在目标之一:从任意噪声化的原始源输入,从任意噪声化的输入的原始源噪声,或任意噪声水平的噪声化输入的得分函数。本文深入探讨了得分函数学习的意义,并通过Tweedie公式将扩散模型的变分观点与基于得分的生成模型观点明确地联系起来。最后,本文介绍了如何通过引导使用扩散模型学习条件分布。
Diffusion models have shown incredible capabilities as generative models; indeed, they power the current state-of-the-art models on text-conditioned image generation such as Imagen and DALL-E 2. In this work we review, demystify, and unify the understanding of diffusion models across both variational and score-based perspectives. We first derive Variational Diffusion Models (VDM) as a special case of a Markovian Hierarchical Variational Autoencoder, where three key assumptions enable tractable computation and scalable optimization of the ELBO. We then prove that optimizing a VDM boils down to learning a neural network to predict one of three potential objectives: the original source input from any arbitrary noisification of it, the original source noise from any arbitrarily noisified input, or the score function of a noisified input at any arbitrary noise level. We then dive deeper into what it means to learn the score function, and connect the variational perspective of a diffusion model explicitly with the Score-based Generative Modeling perspective through Tweedie's Formula. Lastly, we cover how to learn a conditional distribution using diffusion models via guidance.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.11970


2、[CL] Training a T5 Using Lab-sized Resources
M R. Ciosici, L Derczynski
[USC Information Sciences Institute & ITU Copenhagen]
用实验室规模的资源训练T5模型。在大型数据集上训练大型神经语言模型,是资源密集和时间密集的。这些要求造成了一个进入壁垒,即那些资源较少的人无法建立有竞争力的模型。本文介绍了各种技术,使之有可能:(a)利用普通研究实验室可能拥有的资源,训练一个大规模语言模型,以及 (b)在合理的时间内完成训练。本文为从业者提供了参数值、软件和硬件配置策略,以及加强使用现有数据的技术,并以一个案例来说明:丹麦语的T5模型,也是该语言的第一个模型。
Training large neural language models on large datasets is resourceand time-intensive. These requirements create a barrier to entry, where those with fewer resources cannot build competitive models. This paper presents various techniques for making it possible to (a) train a large language model using resources that a modest research lab might have, and (b) train it in a reasonable amount of time. We provide concrete recommendations for practitioners, which we illustrate with a case study: a T5 model for Danish, the first for this language.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.12097


3、[CV] Detecting the unknown in Object Detection
D Fontanel, M Tarantino, F Cermelli, B Caputo
[Politecnico di Torino]
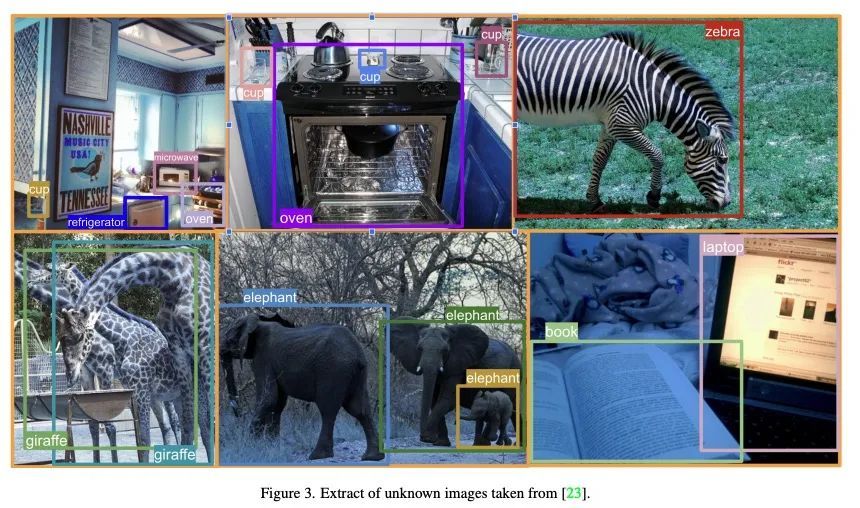
目标检测中的未知目标检测。由于新的神经网络结构设计和大规模数据集的可用性,目标检测方法在过去几年里有了令人印象深刻的改进。然而,目前的方法有一个显著的局限性:它们只能检测在训练期间观察到的类别,而这些类别只是检测器在现实世界中可能遇到的所有类别的一个子集。此外,在训练时往往不考虑未知类别的存在,导致方法甚至不能检测到图像中存在未知目标。本文解决了检测未知目标的问题,即所谓的开放集目标检测。本文提出一种新的训练策略UNKAD,能在不需要任何标注的情况下预测未知目标,利用已经存在于训练图像背景中的非标注目标。特别是,利用Faster R-CNN的四步训练策略,UNKAD首先识别和伪标记未知目标,然后用伪标记来训练一个额外的未知类别。虽然UNKAD可以直接检测未知目标,但进一步将其与之前的未知目标检测技术相结合,显示出它在不付出任何代价的情况下提高了它们的性能。
Object detection methods have witnessed impressive improvements in the last years thanks to the design of novel neural network architectures and the availability of large scale datasets. However, current methods have a significant limitation: they are able to detect only the classes observed during training time, that are only a subset of all the classes that a detector may encounter in the real world. Furthermore, the presence of unknown classes is often not considered at training time, resulting in methods not even able to detect that an unknown object is present in the image. In this work, we address the problem of detecting unknown objects, known as open-set object detection. We propose a novel training strategy, called UNKAD, able to predict unknown objects without requiring any annotation of them, exploiting non annotated objects that are already present in the background of training images. In particular, exploiting the four-steps training strategy of Faster R-CNN, UNKAD first identifies and pseudo-labels unknown objects and then uses the psuedo-annotation to train an additional unknown class. While UNKAD can directly detect unknown objects, we further combine it with previous unknown detection techniques, showing that it improves their performance at no costs.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.11641




4、[CL] Learning to Retrieve Passages without Supervision
O Ram, G Shachaf, O Levy, J Berant, A Globerson
[Tel Aviv University]
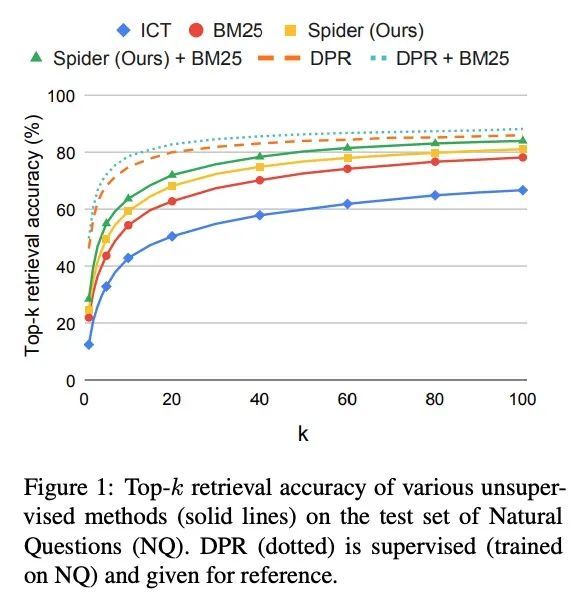
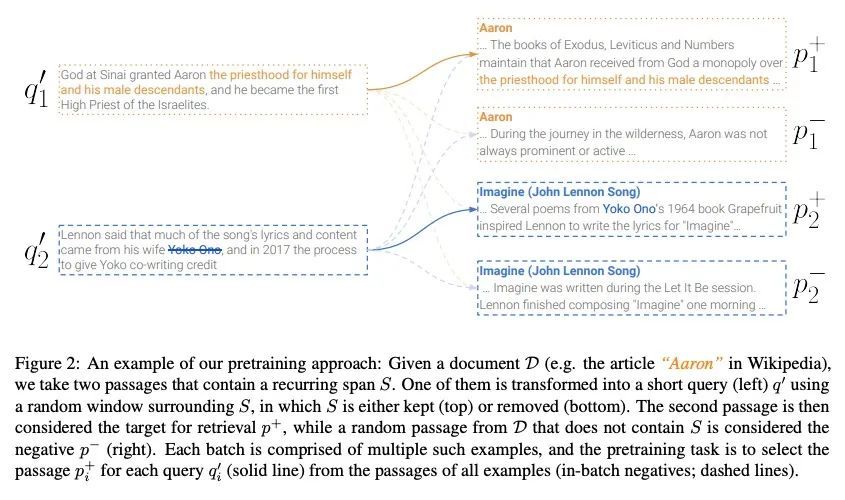
无监督段落检索学习。用于开放域问答(ODQA)的稠密检索器通过对问题-段落对的大型数据集进行训练,已被证明能取得令人印象深刻的性能。本文研究是否可通过针对ODQA的无监督预训练,来减少这种对标记数据的依赖。通过一个为检索设计的新的预训练方案,证明这实际上是可能的。所提出的"循环跨度检索"方法用文档中的重复跨度来创建对比学习的伪样本。所提出的预训练方案直接控制了伪查询和相关段落之间的术语重叠,因此可以对它们之间的词汇和语义关系进行建模。由此产生的模型即Spider,在广泛的ODQA数据集上,不需要任何标记的训练样本就能表现出令人惊讶的性能。具体来说,它在领样本设置中的表现明显优于所有其他预训练基线,并与BM25(一个强大的稀疏基线)相竞争。此外,在Spider和BM25上的混合检索器比两者都要好,并且通常与DPR模型竞争,后者是在数万个样本上训练的。最后,当使用Spider作为监督训练的初始化时,可以观察到明显的收益。
Dense retrievers for open-domain question answering (ODQA) have been shown to achieve impressive performance by training on large datasets of question-passage pairs. In this work we ask whether this dependence on labeled data can be reduced via unsupervised pretraining that is geared towards ODQA. We show this is in fact possible, via a novel pretraining scheme designed for retrieval. Our “recurring span retrieval” approach uses recurring spans across passages in a document to create pseudo examples for contrastive learning. Our pretraining scheme directly controls for term overlap across pseudo queries and relevant passages, thus allowing to model both lexical and semantic relations between them. The resulting model, named Spider, performs surprisingly well without any labeled training examples on a wide range of ODQA datasets. Specifically, it significantly outperforms all other pretrained baselines in a zero-shot setting, and is competitive with BM25, a strong sparse baseline. Moreover, a hybrid retriever over Spider and BM25 improves over both, and is often competitive with DPR models, which are trained on tens of thousands of examples. Last, notable gains are observed when using Spider as an initialization for supervised training.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.07708

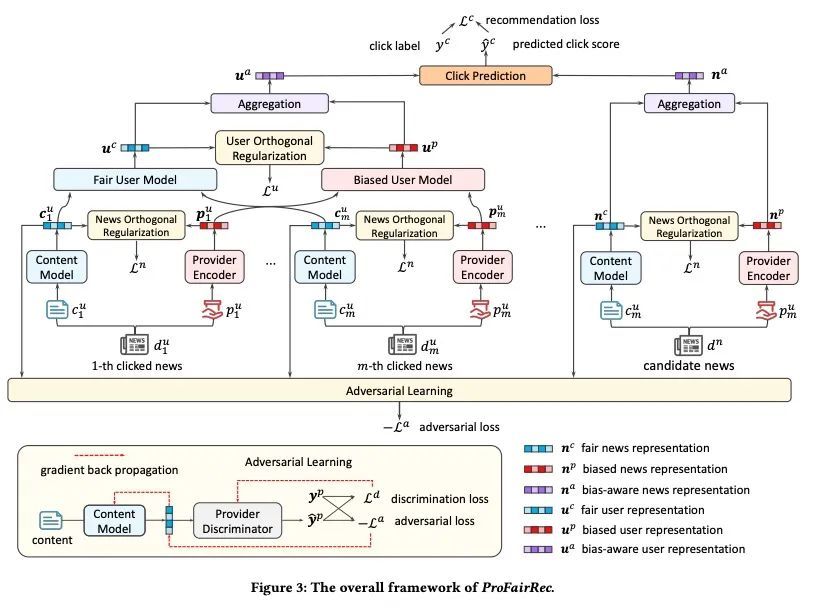
5、[IR] ProFairRec: Provider Fairness-aware News Recommendation
T Qi, F Wu, C Wu, P Sun, L Wu, X Wang, Y Huang, X Xie
[Tsinghua University & Microsoft Research Asia & Hefei University of Technology]
ProFairRec: 提供者公平感知新闻推荐。新闻推荐的目的,是帮助在线新闻平台用户找到他们喜欢的新闻文章。现有的新闻推荐方法通常从用户的历史新闻行为中学习模型。然而,这些行为通常对新闻提供者有偏差。在有偏差的用户数据上训练出来的模型,可能会捕捉甚至放大对新闻提供者的偏差,对一些少数的新闻提供者是不公平的。本文提出一种提供者公平感知的新闻推荐框架ProFairRec,可以从有偏差的用户数据中学习对不同新闻提供者公平的新闻推荐模型。ProFairRec的核心思想是学习提供者公平的新闻表示和提供者公平的用户表示以实现提供者公平。为了从有偏差的数据中学习提供者公平的表示,本文采用有偏差的提供者表示来继承数据中的提供者偏差。提供者公平和有偏差的新闻表示分别从新闻内容和提供者ID中学习,这些表示被进一步汇总以建立基于用户点击历史的公平和有偏差的用户表示。所有这些表示都被用于模型训练,而只有公平表示被用于用户-新闻匹配,以实现公平的新闻推荐。此外,本文提出一种关于新闻提供者歧视的对抗学习任务,以防止提供者的公平新闻表示被编码为提供者的偏差。本文还提出了一种关于提供者-公平和有偏差的表示的正交正则化,以更好地减少提供者-公平表示中的提供者偏差。此外,ProFairRec是一个通用框架,可以应用于不同的新闻推荐方法。在一个公共数据集上进行的大量实验证明,所提出的ProFairRec方法可以有效地改善许多现有方法的提供者公平性,同时保持它们的推荐准确性。
News recommendation aims to help online news platform users find their preferred news articles. Existing news recommendation methods usually learn models from historical user behaviors on news. However, these behaviors are usually biased on news providers. Models trained on biased user data may capture and even amplify the biases on news providers, and are unfair for some minority news providers. In this paper, we propose a provider fairness-aware news recommendation framework (named ProFairRec), which can learn news recommendation models fair for different news providers from biased user data. The core idea of ProFairRec is to learn provider-fair news representations and provider-fair user representations to achieve provider fairness. To learn provider-fair representations from biased data, we employ provider-biased representations to inherit provider bias from data. Provider-fair and -biased news representations are learned from news content and provider IDs respectively, which are further aggregated to build fair and biased user representations based on user click history. All of these representations are used in model training while only fair representations are used for user-news matching to achieve fair news recommendation. Besides, we propose an adversarial learning task on news provider discrimination to prevent provider-fair news representation from encoding provider bias. We also propose an orthogonal regularization on provider-fair and -biased representations to better reduce provider bias in provider-fair representations. Moreover, ProFairRec is a general framework and can be applied to different news recommendation methods. Extensive experiments on a public dataset verify that our ProFairRec approach can effectively improve the provider fairness of many existing methods and meanwhile maintain their recommendation accuracy.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.04724


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
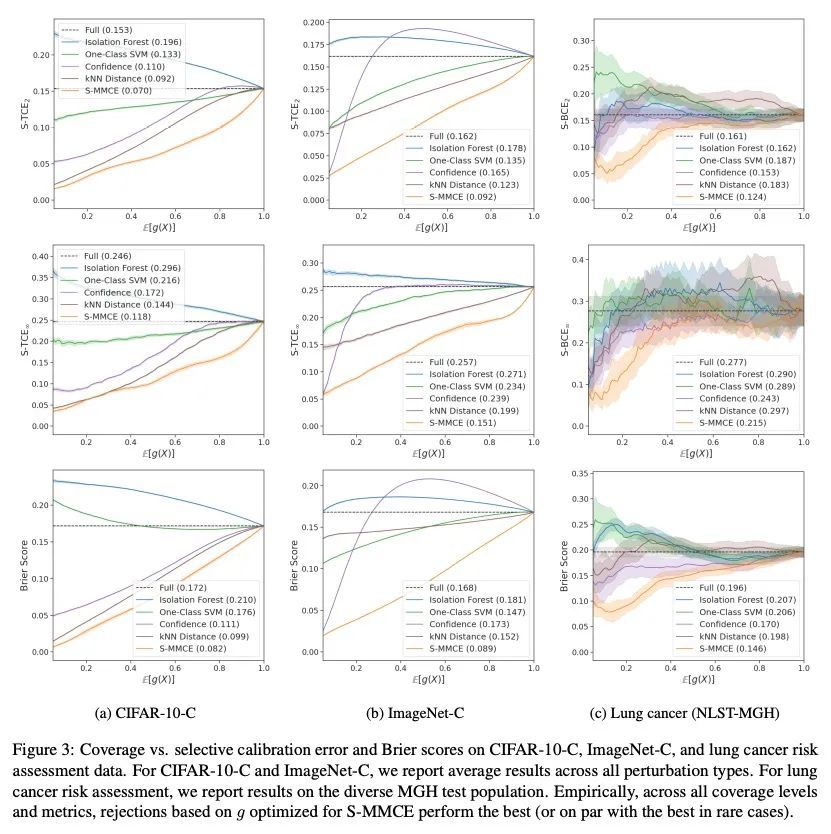
[LG] Calibrated Selective Classification
校准选择性分类
A Fisch, T Jaakkola, R Barzilay
[MIT]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.12084



[CL] Prompting as Probing: Using Language Models for Knowledge Base Construction
提示即探测:用语言模型构建知识库
D Alivanistos, S B Santamaría, M Cochez, J Kalo, E v Krieken, T Thanapalasingam
[Vrije Universiteit Amsterdam]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.11057


[LG] Causal Entropy Optimization
因果熵优化
N Branchini, V Aglietti, N Dhir, T Damoulas
[University of Edinburgh & University of Warwick & The Alan Turing Institute]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.10981


[CV] Deep Structural Causal Shape Models
深度结构化因果形状模型
R Rasal, D C. Castro, N Pawlowski, B Glocker
[Imperial College London & Microsoft Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.10950


内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢