LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:从非侵入性脑记录中解码语言、李群及其同质空间上的平稳核和高斯过程的紧凑案例、细粒度分布相关学习曲线、面向MRI膝关节异常分类的基于切片的自监督Transformer、利用最优传输和流行学习发现守恒定律、高效稀疏激活Transformer、风格无关强化学习、面向镜头和相机校准的深度感知测量、群体估计的熵正则化
1、[AS] Decoding speech from non-invasive brain recordings
A Défossez, C Caucheteux, J Rapin, O Kabeli, J King
[Meta AI]
从非侵入性脑记录中解码语言。从大脑活动中解码语言,是医疗保健和神经科学中一个期待已久的目标。由于颅内设备的出现,最近已经达到了重要的里程碑:针对特定对象的管道,通过对基本语言任务的侵入性大脑反应进行训练,现在开始有效地解码可解释的特征(如字母、单词、频谱图)。然而,将这种方法扩展到自然语音和非侵入性的大脑记录仍然是一个重大挑战。本文提出一种单一的端到端架构,用对比学习的方式在大量的个体群中进行训练,以预测自然语音的自监督表示。本文在四个公共数据集上评估了提出的模型,包括169名志愿者在听自然语音时用磁电脑图(M/EEG)记录的数据。结果显示,提出的模型可以从3秒的脑电信号中识别出相应的语音片段,在1,594个不同的片段中,top-10准确率高达72.5%(top-1准确率高达44%),在2,604个EEG记录中,准确率高达19.1%,因此可以对训练集中没有的短语进行解码。模型比较和消融分析表明,这些表现直接受益于最初的设计选择,即使用(i)对比性目标,(ii)预训练语音表示和(iii)在几个参与者中同时训练的共同卷积架构。这些结果共同划定了一条有希望的道路,从非侵入性的脑活动记录中实时解码自然语言处理。
Decoding language from brain activity is a long-awaited goal in both healthcare and neuroscience. Major milestones have recently been reached thanks to intracranial devices: subject-specific pipelines trained on invasive brain responses to basic language tasks now start to efficiently decode interpretable features (e.g. letters, words, spectrograms). However, scaling this approach to natural speech and non-invasive brain recordings remains a major challenge. Here, we propose a single end-to-end architecture trained with contrastive learning across a large cohort of individuals to predict self-supervised representations of natural speech. We evaluate our model on four public datasets, encompassing 169 volunteers recorded with magnetoor electro-encephalography (M/EEG), while they listened to natural speech. The results show that our model can identify, from 3 s of MEG signals, the corresponding speech segment with up to 72.5% top-10 accuracy out of 1,594 distinct segments (and 44% top-1 accuracy), and up to 19.1% out of 2,604 segments for EEG recordings – hence allowing the decoding of phrases absent from the training set. Model comparison and ablation analyses show that these performances directly benefit from our original design choices, namely the use of (i) a contrastive objective, (ii) pretrained representations of speech and (iii) a common convolutional architecture simultaneously trained across several participants. Together, these results delineate a promising path to decode natural language processing in real time from non-invasive recordings of brain activity.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.12266

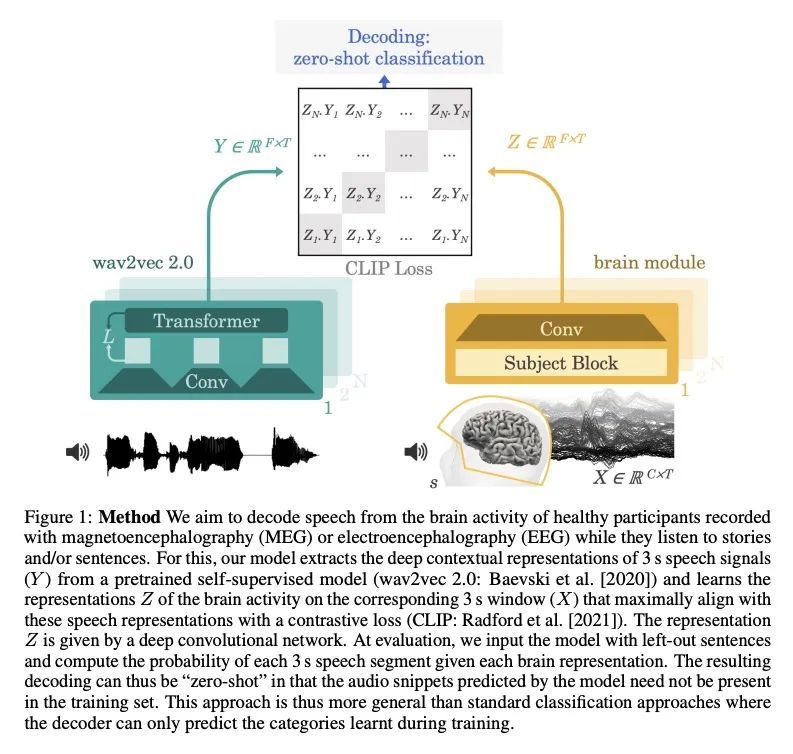
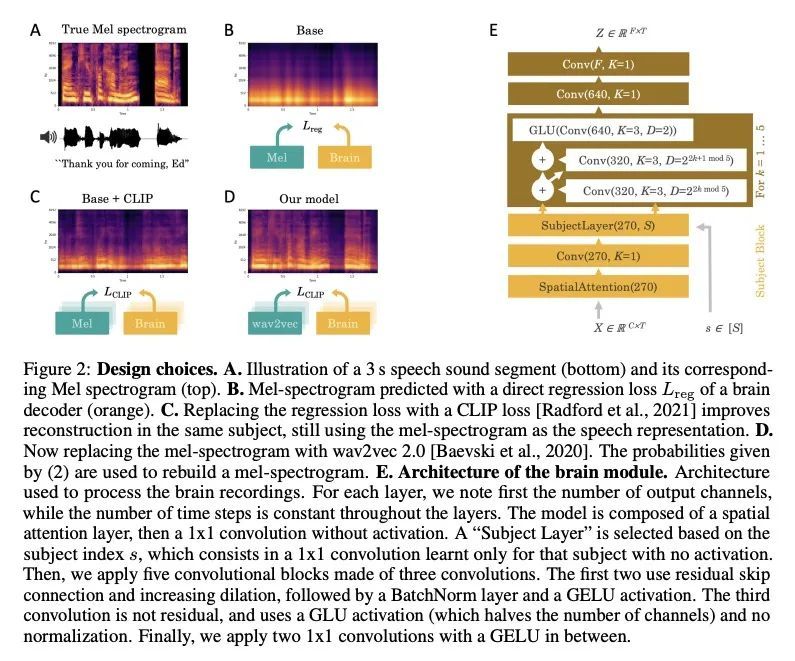
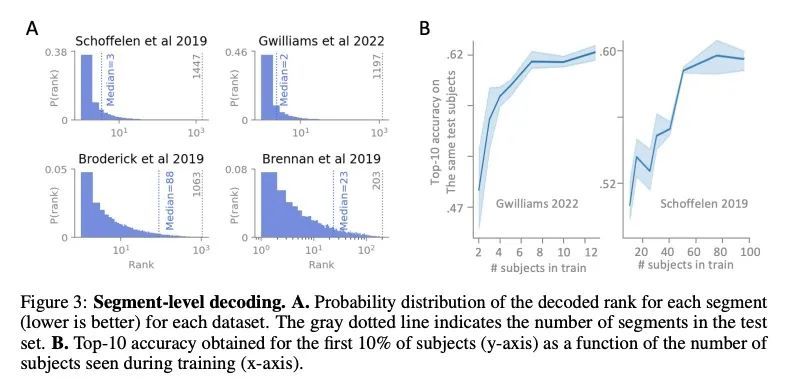
2、[LG] Stationary Kernels and Gaussian Processes on Lie Groups and their Homogeneous Spaces I: the Compact Case
I Azangulov, A Smolensky, A Terenin...
[Petersburg State University & University of Cambridge & ETH Zürich]
李群及其同质空间上的平稳核和高斯过程的紧凑案例。高斯过程可以说是空间统计中最重要的模型类别。它们编码了关于建模函数的先验信息,可用于精确或近似的贝叶斯推断。在许多应用中,特别是在物理科学和工程领域,也包括地理统计和神经科学等领域,对对称性的不变性是可以考虑的最基本的先验信息形式之一。高斯过程的协方差对此类对称性的不变性导致平稳性概念对此类空间的最自然概括。本文开发了建设性的实用技术,用于在对称性背景下产生的一大类非欧几里得空间上建立平稳的高斯过程。该技术使得 (i)计算协方差核 和 (ii)从定义在这类空间上的先验和后验高斯过程中取样成为可能,而且都是以一种实用的方式。这项工作分为两部分,分别涉及不同的技术考虑:第一部分研究紧凑空间,第二部分研究具有一定结构的非紧凑空间。我们的贡献使我们研究的非欧几里得高斯过程模型与标准高斯过程软件包中的公认的计算技术兼容,从而使从业者能够使用这些模型。
Gaussian processes are arguably the most important model class in spatial statistics. They encode prior information about the modeled function and can be used for exact or approximate Bayesian inference. In many applications, particularly in physical sciences and engineering, but also in areas such as geostatistics and neuroscience, invariance to symmetries is one of the most fundamental forms of prior information one can consider. The invariance of a Gaussian process’ covariance to such symmetries gives rise to the most natural generalization of the concept of stationarity to such spaces. In this work, we develop constructive and practical techniques for building stationary Gaussian processes on a very large class of non-Euclidean spaces arising in the context of symmetries. Our techniques make it possible to (i) calculate covariance kernels and (ii) sample from prior and posterior Gaussian processes defined on such spaces, both in a practical manner. This work is split into two parts, each involving different technical considerations: part I studies compact spaces, while part II studies non-compact spaces possessing certain structure. Our contributions make the non-Euclidean Gaussian process models we study compatible with well-understood computational techniques available in standard Gaussian process software packages, thereby making them accessible to practitioners.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.14960

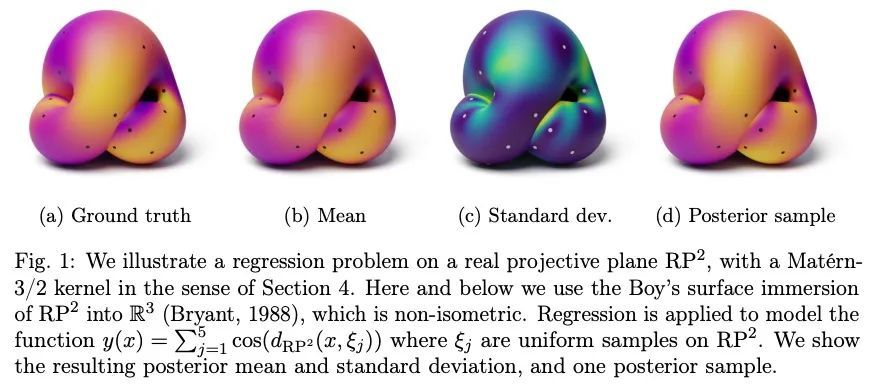
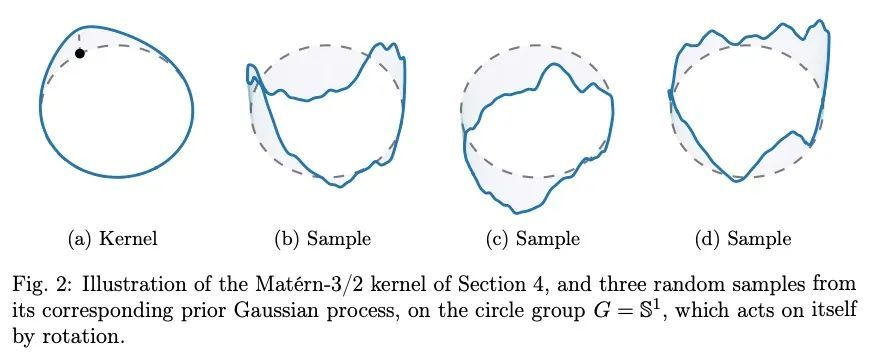
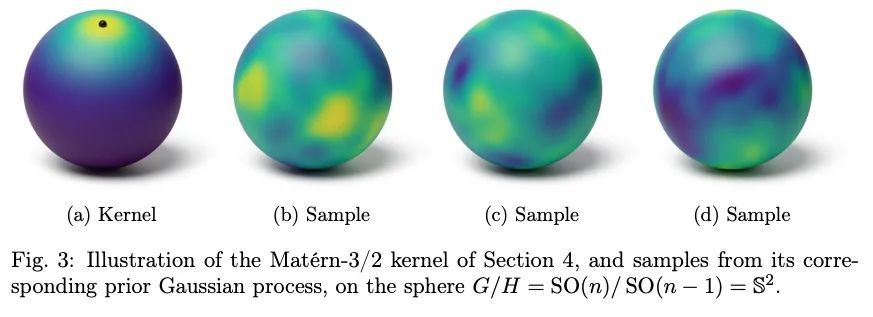
3、[LG] Fine-Grained Distribution-Dependent Learning Curves
O Bousquet, S Hanneke, S Moran, J Shafer, I Tolstikhin
[Google & Purdue University & Technion – Israel Institute of Technology & UC Berkeley]
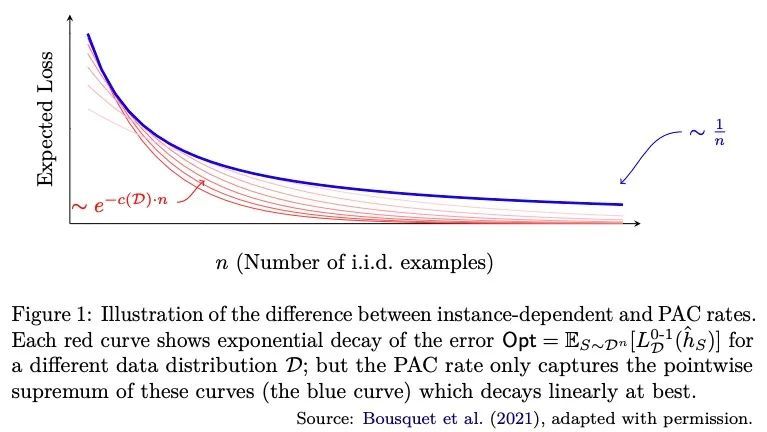
细粒度分布相关学习曲线。学习曲线描绘了一个学习算法的预期误差与标记输入样本数量的函数。它们被机器学习从业者广泛用于衡量算法的性能,但经典的PAC学习理论无法解释其行为。本文提出一种新的组合表征,称为VCL维度,它改进并完善了Bousquet等人的最新成果。表征通过提供细粒度的界对学习曲线的结构进行了新的揭示,并表明对于具有有限VCL的类,衰减率可以分解为只取决于假设类的线性部分和也取决于目标分布的指数部分。特别是,VCL维度的细微差别意味着下界在数量上强于Bousquet等人的下界,在质量上强于经典的"没有免费午餐"下界。VCL表征解决了Antos和Lugosi研究的一个开放性问题,他们询问在什么情况下存在这种下界。作为一个推论,本文用R恢复了半空间的下界,而且是以一种原则性的方式做到的,应该也适用于其他情况。最后,为了提供关于本文工作的另一个观点以及它与传统的PAC学习界的比较,本文还提出了所得结果在更接近PAC设置的语言中的另一种表述。
Learning curves plot the expected error of a learning algorithm as a function of the number of labeled input samples. They are widely used by machine learning practitioners as a measure of an algorithm’s performance, but classic PAC learning theory cannot explain their behavior. In this paper we introduce a new combinatorial characterization called the VCL dimension that improves and refines the recent results of Bousquet et al. (2021). Our characterization sheds new light on the structure of learning curves by providing fine-grained bounds, and showing that for classes with finite VCL, the rate of decay can be decomposed into a linear component that depends only on the hypothesis class and an exponential component that depends also on the target distribution. In particular, the finer nuance of the VCL dimension implies lower bounds that are quantitatively stronger than the bounds of Bousquet et al. (2021) and qualitatively stronger than classic ‘no free lunch’ lower bounds. The VCL characterization solves an open problem studied by Antos and Lugosi (1998), who asked in what cases such lower bounds exist. As a corollary, we recover their lower bound for half-spaces in R, and we do so in a principled way that should be applicable to other cases as well. Finally, to provide another viewpoint on our work and how it compares to traditional PAC learning bounds, we also present an alternative formulation of our results in a language that is closer to the PAC setting.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.14615


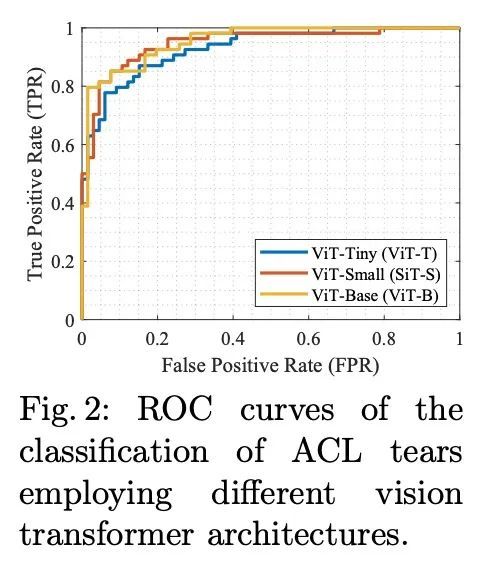
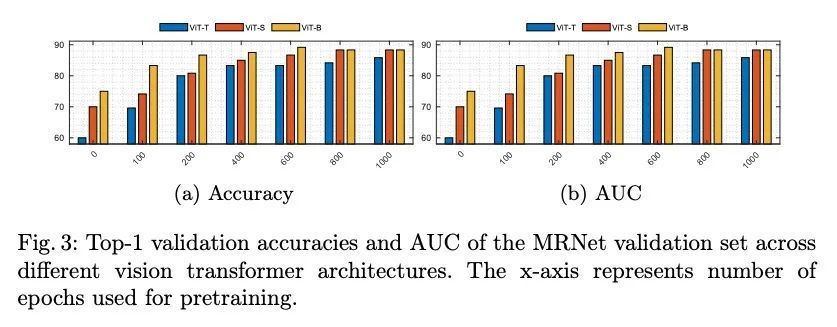
4、[CV] SB-SSL: Slice-Based Self-Supervised Transformers for Knee Abnormality Classification from MRI
S Atito, S M Anwar, M Awais, J Kitler
[University of Surrey & Children’s National Hospital]
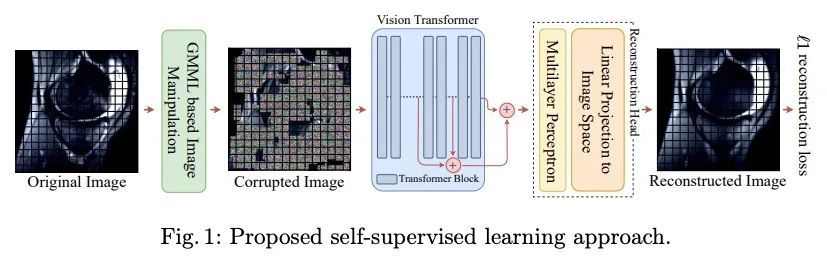
SB-SSL:面向MRI膝关节异常分类的基于切片的自监督Transformer。在为医疗领域开发有监督机器学习解决方案时,具有高质量的真实标签的大规模数据的可用性是一个挑战。虽然,临床工作流程中的数字数据量在不断增加,但这些数据大多分布在临床现场,并受到保护以确保病人的隐私。放射性读数和处理大规模临床数据给现有资源带来了巨大的负担,而这正是机器学习和人工智能发挥关键作用的地方。用于肌肉骨骼(MSK)诊断的磁共振成像(MRI)就是个例子,扫描有大量的信息,但需要大量的时间来阅读和标记。自监督学习(SSL)可以作为处理缺乏真实标签的解决方案,但通常在预训练阶段需要大量的训练数据。本文提出一种基于切片的自监督深度学习框架(SB-SSL),一种基于切片的新范式,用于对膝关节MRI扫描的异常情况进行分类。对于有限的案例(<1000),所提出的框架能够识别前交叉韧带撕裂,准确率为89.17%,AUC为0.954,在预训练期间不使用外部数据的情况下,表现优于最先进的技术。这表明所提出的框架适合在有限的数据设置下实现SSL。
The availability of large scale data with high quality ground truth labels is a challenge when developing supervised machine learning solutions for healthcare domain. Although, the amount of digital data in clinical workflows is increasing, most of this data is distributed on clinical sites and protected to ensure patient privacy. Radiological readings and dealing with large-scale clinical data puts a significant burden on the available resources, and this is where machine learning and artificial intelligence play a pivotal role. Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) for musculoskeletal (MSK) diagnosis is one example where the scans have a wealth of information, but require a significant amount of time for reading and labeling. Self-supervised learning (SSL) can be a solution for handling the lack of availability of ground truth labels, but generally requires a large amount of training data during the pretraining stage. Herein, we propose a slice-based self-supervised deep learning framework (SB-SSL), a novel slice-based paradigm for classifying abnormality using knee MRI scans. We show that for a limited number of cases (<1000), our proposed framework is capable to identify anterior cruciate ligament tear with an accuracy of 89.17% and an AUC of 0.954, outperforming state-of-the-art without usage of external data during pretraining. This demonstrates that our proposed framework is suited for SSL in the limited data regime.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.13923

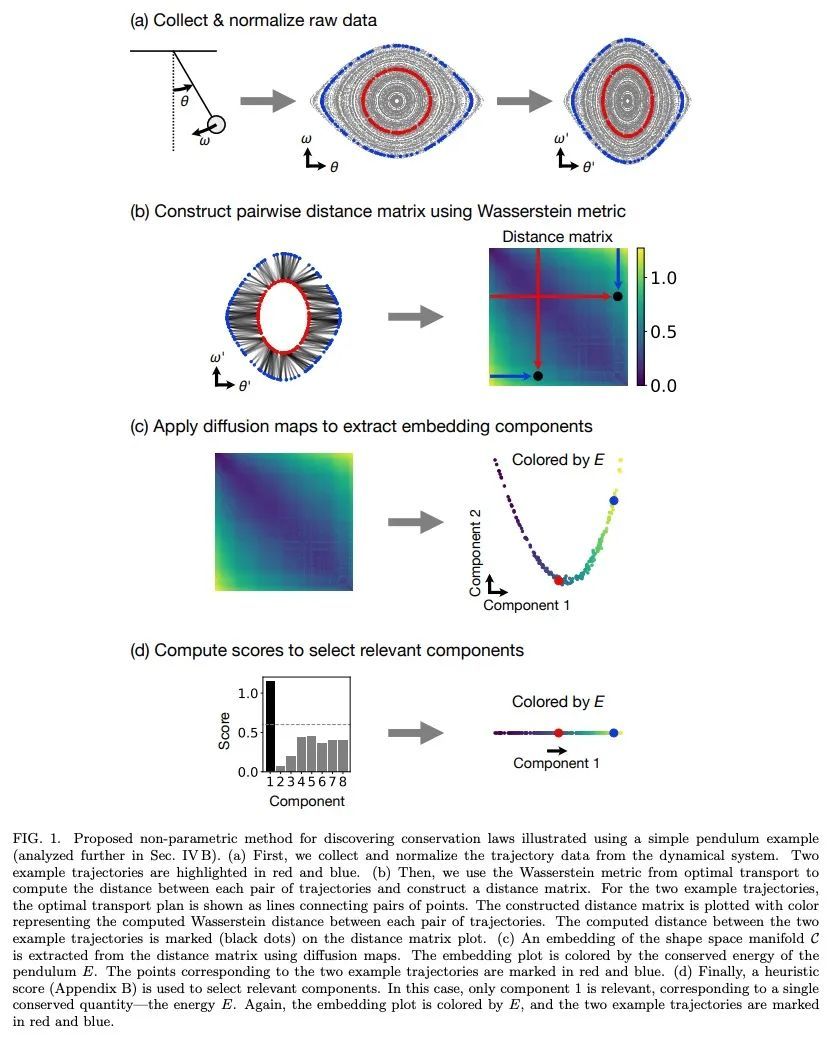
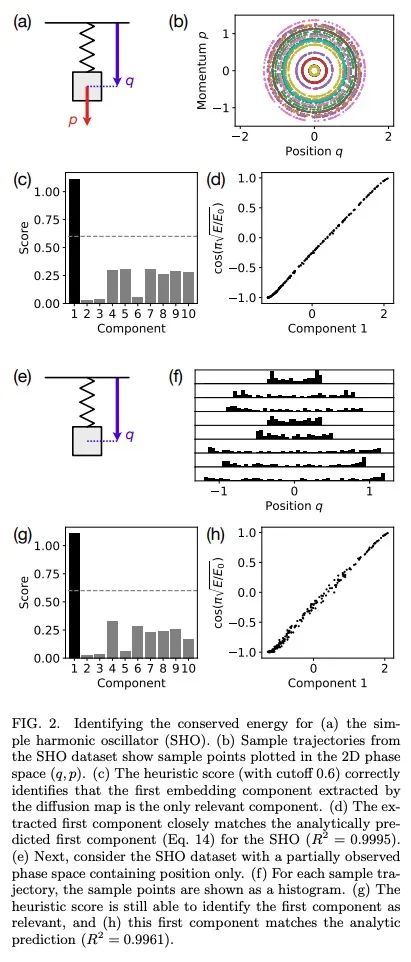
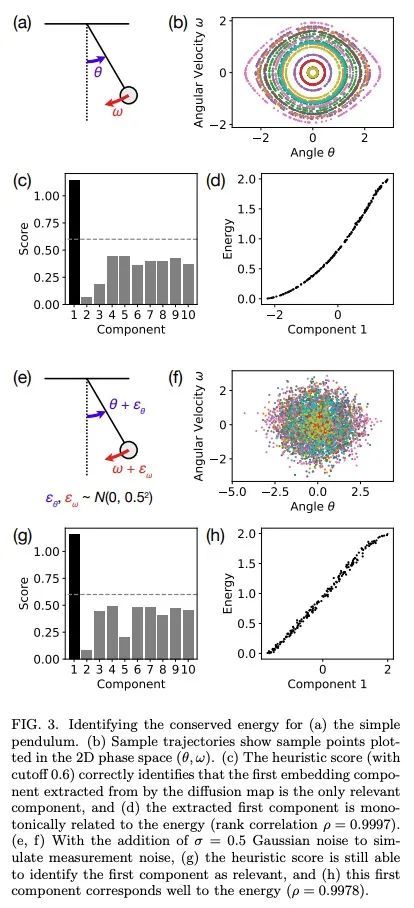
5、[LG] Discovering Conservation Laws using Optimal Transport and Manifold Learning
P Y. Lu, R Dangovski, M Soljačić
[University of Chicago & MIT]
利用最优传输和流行学习发现守恒定律。守恒定律是理解、描述和模拟非线性动态系统的关键理论和实践工具。然而,对于许多复杂的动力系统来说,相应的守恒量是很难识别的,因此很难分析它们的动力学并建立高效、稳定的预测模型。目前发现守恒定律的方法往往依赖于详细的动力学信息,如运动方程或细粒度的时间测量,最近的许多建议也依赖于黑箱参数化的深度学习方法。本文将这一任务重新表述为流形学习问题,并提出了一种非参数化的方法,将最优运输中的Wasserstein度量与扩散图相结合,以发现从动态系统中采样的不同轨迹的守恒量。本文在各种物理系统(包括保守的哈密尔顿系统、耗散系统和时空系统)上测试了这种新方法,证明该流形学习方法能识别守恒量的数量并提取它们的值。利用最优传输理论和流形学习的工具,本文提出的方法提供了一种直接的几何方法来识别守恒定律,这种方法既鲁棒又可解释,不需要系统的明确模型,也不需要准确的时间信息。
Conservation laws are key theoretical and practical tools for understanding, characterizing, and modeling nonlinear dynamical systems. However, for many complex dynamical systems, the corresponding conserved quantities are difficult to identify, making it hard to analyze their dynamics and build efficient, stable predictive models. Current approaches for discovering conservation laws often depend on detailed dynamical information, such as the equation of motion or fine-grained time measurements, with many recent proposals also relying on black box parametric deep learning methods. We instead reformulate this task as a manifold learning problem and propose a non-parametric approach, combining the Wasserstein metric from optimal transport with diffusion maps, to discover conserved quantities that vary across trajectories sampled from a dynamical system. We test this new approach on a variety of physical systems—including conservative Hamiltonian systems, dissipative systems, and spatiotemporal systems—and demonstrate that our manifold learning method is able to both identify the number of conserved quantities and extract their values. Using tools from optimal transport theory and manifold learning, our proposed method provides a direct geometric approach to identifying conservation laws that is both robust and interpretable without requiring an explicit model of the system nor accurate time information.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.14995

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
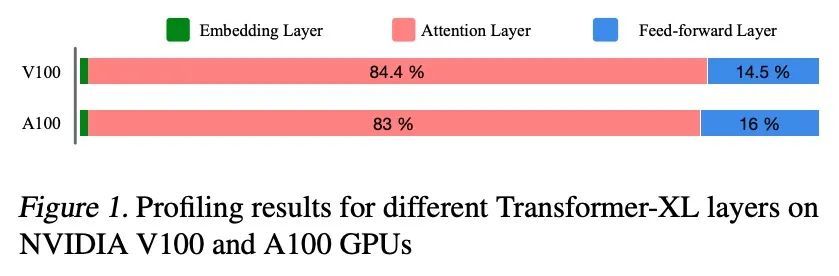
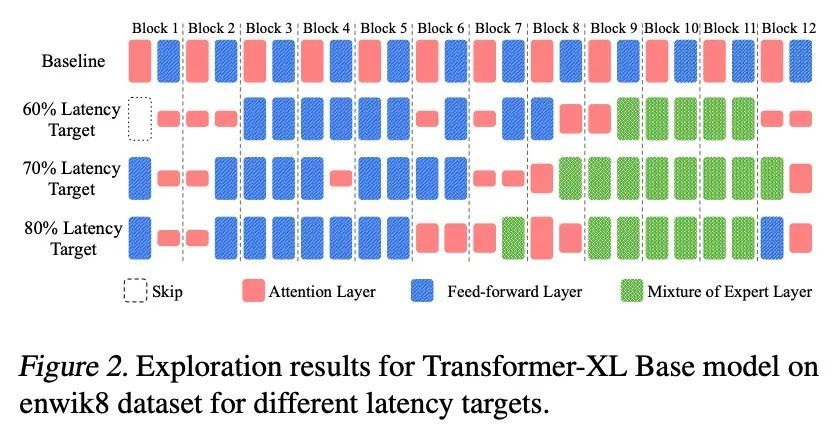
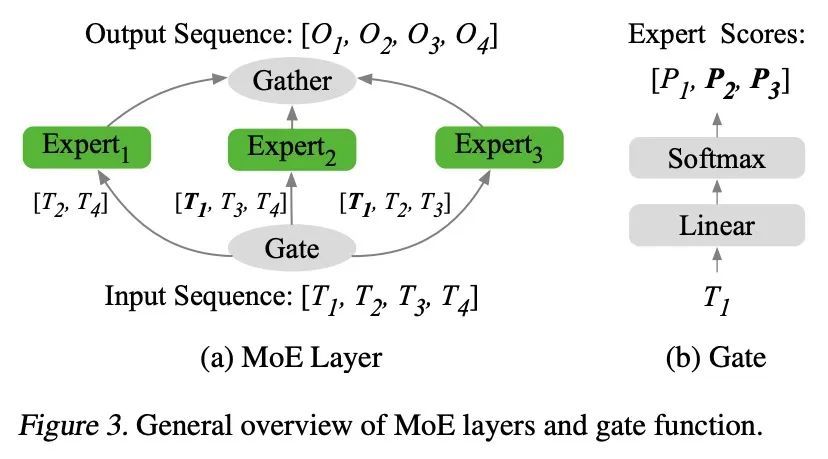
[LG] Efficient Sparsely Activated Transformers
高效稀疏激活Transformer
S Latifi, S Muralidharan, M Garland
[University of Michigan & NVIDIA]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.14580

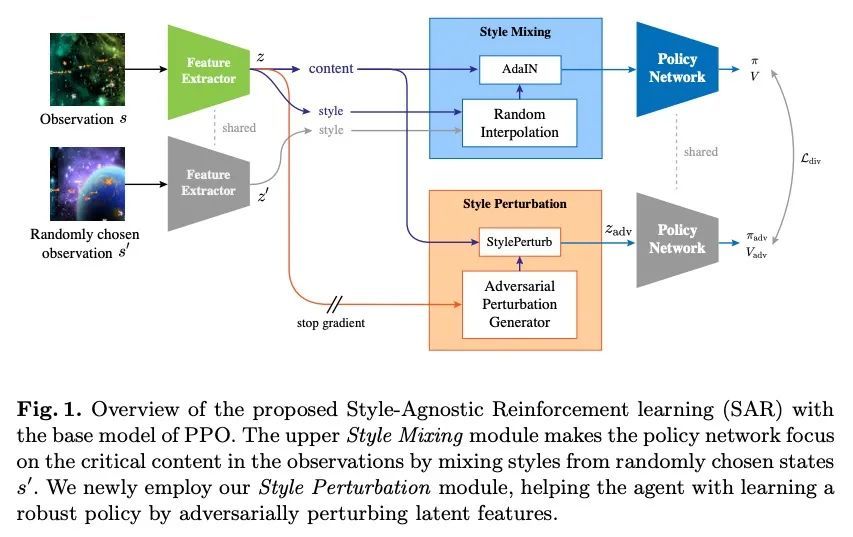
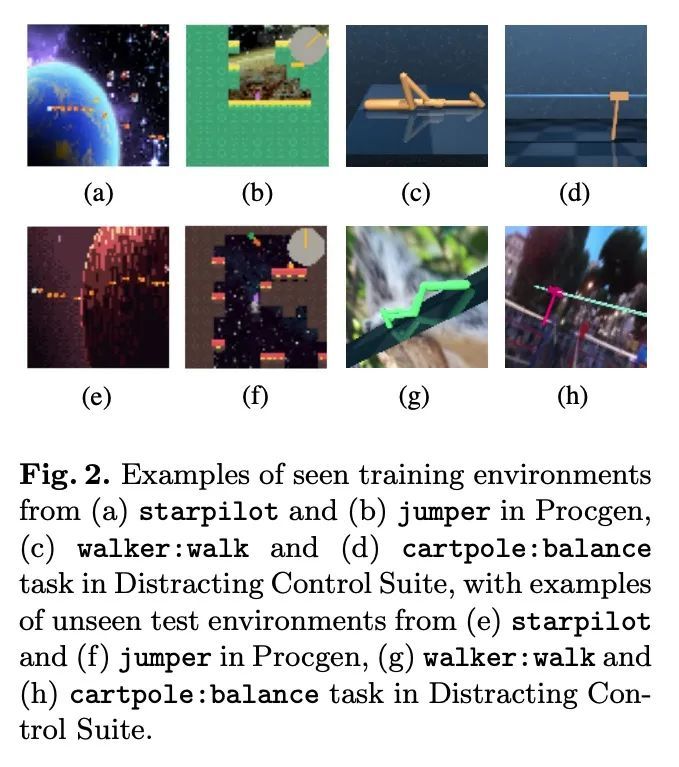
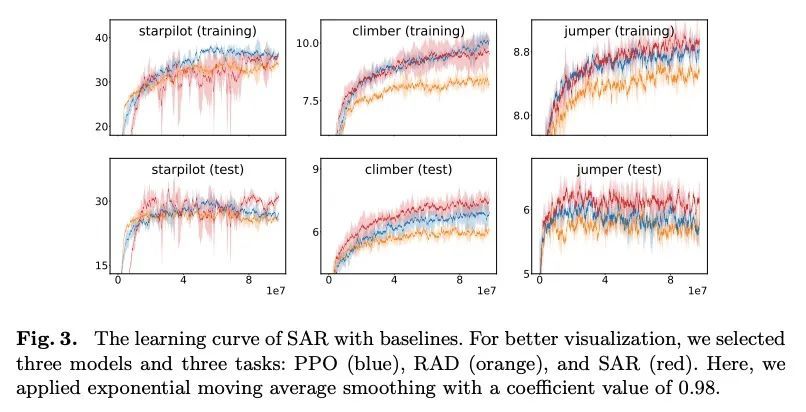
[CV] Style-Agnostic Reinforcement Learning
风格无关强化学习
J Lee, S Ahn, J Park
[Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH)]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.14863

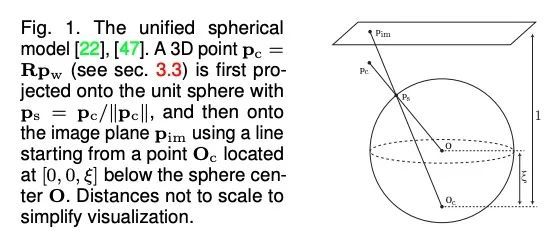
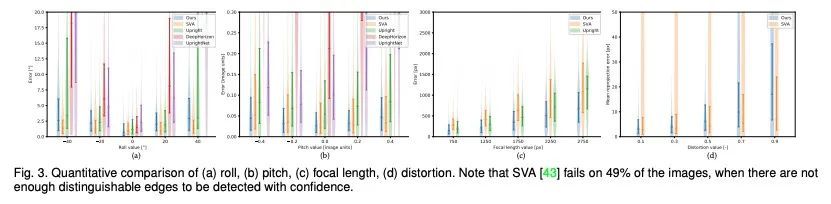
[CV] A Deep Perceptual Measure for Lens and Camera Calibration
面向镜头和相机校准的深度感知测量
Y Hold-Geoffroy, D Piché-Meunier, K Sunkavalli, J Bazin, F Rameau, J Lalonde
[Adobe Research & KAIST & Universite Laval]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.12300


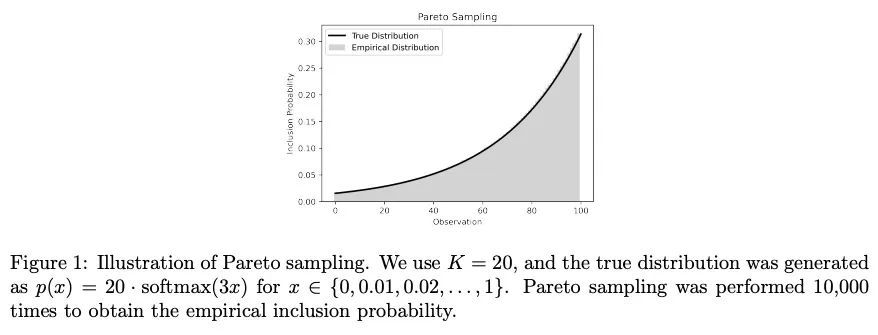
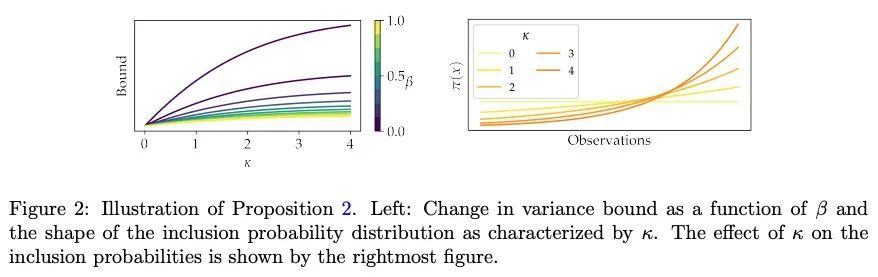
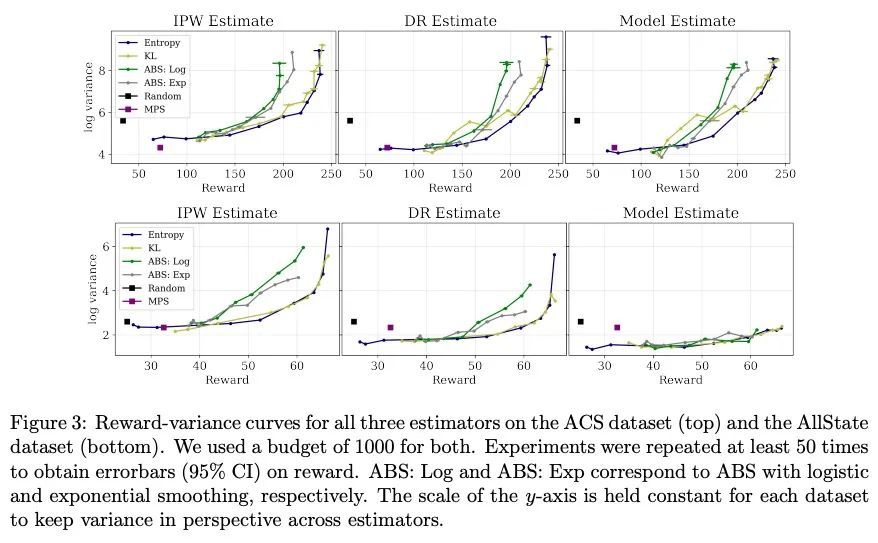
[LG] Entropy Regularization for Population Estimation
群体估计的熵正则化
B Chugg, P Henderson, J Goldin, D E. Ho
[CMU & Stanford University & University of Chicago]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.11747

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢