LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:面向多文档摘要的基于金字塔的掩码句子预训练、准计量的学习和可学习性研究、表格文档信息提取中序列建模之外的结构编码、统一的基于查询的点云理解范式、面向图表示学习的结构感知Transformer、高动态范围辐射场自校准、点卷积深度网络架构模块、将一般反射率表示为未校准光度立体神经本征场、机器学习中使用的log-cosh损失函数的统计特性
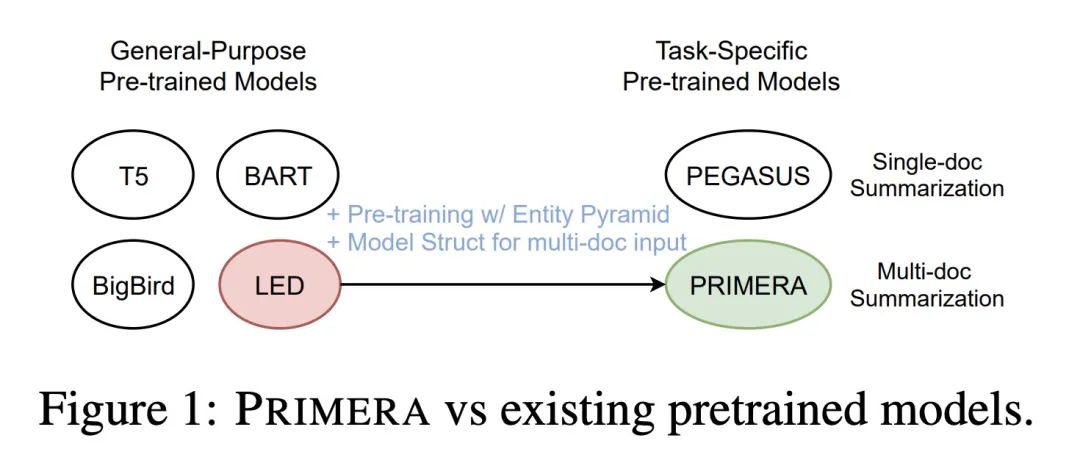
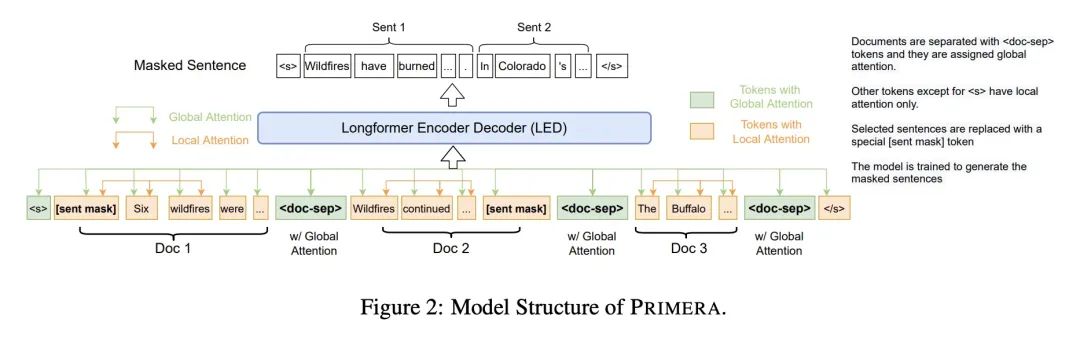
1、[CL] PRIMERA: Pyramid-based Masked Sentence Pre-training for Multi-document Summarization
W Xiao, I Beltagy, G Carenini, A Cohan
[Allen Institute for AI & University of British Columbia]
PRIMERA:面向多文档摘要的基于金字塔的掩码句子预训练。本文提出PRIMERA,一个用于多文档表示的预训练模型,重点是摘要,减少了对数据集特定架构和大量微调标记数据的需求。PRIMERA使用了新提出的预训练目标,旨在教导模型连接和聚合整个文档的信息。它还使用了高效的编-解码器Transformer来简化对级联输入文档的处理。通过在3个不同领域的6个多文档摘要数据集上进行广泛的实验,PRIMERA在零样本、少样本和全监督的设置下,在大多数这些设置上以较大的优势胜过目前最先进的特定数据集和预训练模型。
We introduce PRIMERA, a pre-trained model for multi-document representation with a focus on summarization that reduces the need for dataset-specific architectures and large amounts of fine-tuning labeled data. PRIMERA uses our newly proposed pre-training objective designed to teach the model to connect and aggregate information across documents. It also uses efficient encoder-decoder transformers to simplify the processing of concatenated input documents. With extensive experiments on 6 multi-document summarization datasets from 3 different domains on zero-shot, few-shot and full-supervised settings, PRIMERA outperforms current state-of-the-art dataset-specific and pre-trained models on most of these settings with large margins.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.08499


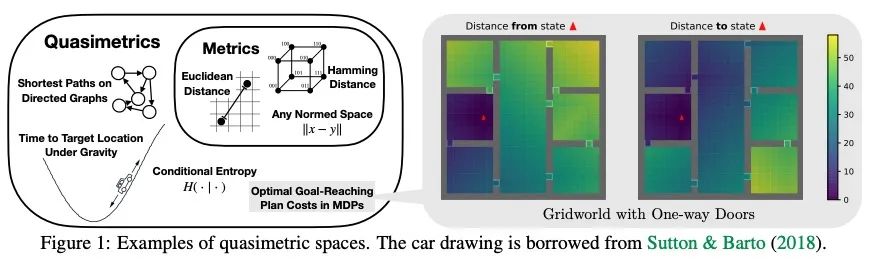
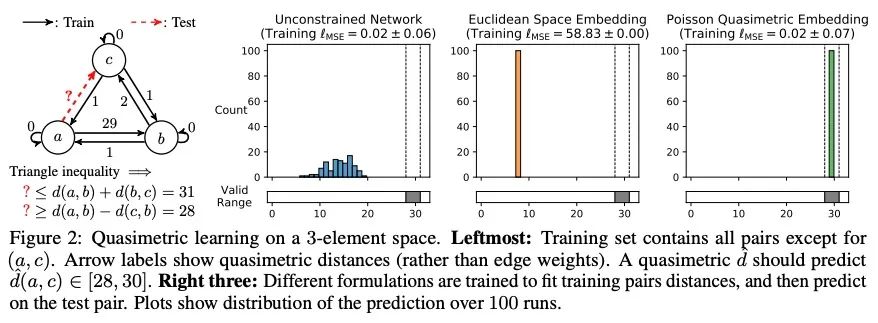
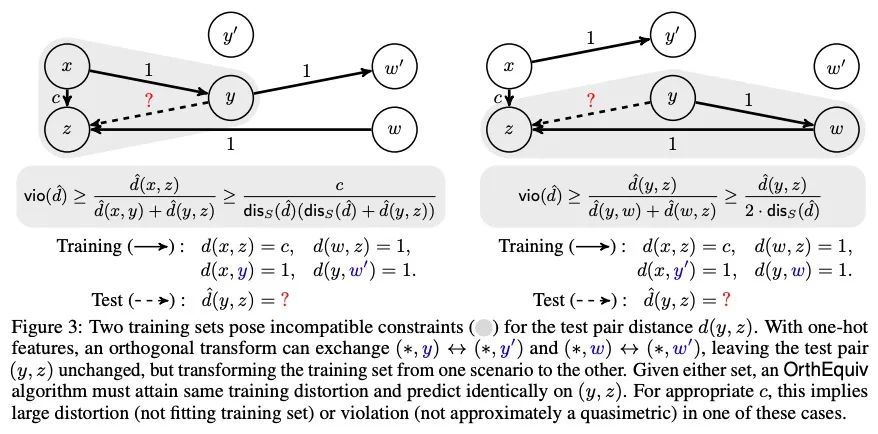
2、[LG] On the Learning and Learnablity of Quasimetrics
T Wang, P Isola
[MIT CSAIL]
准计量的学习和可学习性研究。世界充满不对称性。重力和风可以使去一个地方比回来更容易。社会化的家谱图和引文图等,本质上是有方向的。在强化学习和控制中,最佳目标到达策略很少是可逆的(对称的)。在这些不对称的结构上支持的距离函数被称为准计量。尽管它们经常出现,但对准度量学习的研究却很少。理论分析显示,一类常见的学习算法,包括无约束的多层感知器(MLP),被证明无法学习到与训练数据一致的准计量。相比之下,本文提出的Poisson Quasimetric Embedding(PQE)是第一个既可以用基于梯度的优化学习,又享有强大性能保证的准计量学习框架。在随机图、社会化图和离线Q-learning上的实验证明了它比许多普通基线更有效。
Our world is full of asymmetries. Gravity and wind can make reaching a place easier than coming back. Social artifacts such as genealogy charts and citation graphs are inherently directed. In reinforcement learning and control, optimal goal-reaching strategies are rarely reversible (symmetrical). Distance functions supported on these asymmetrical structures are called quasimetrics. Despite their common appearance, little research has been done on the learning of quasimetrics. Our theoretical analysis reveals that a common class of learning algorithms, including unconstrained multilayer perceptrons (MLPs), provably fails to learn a quasimetric consistent with training data. In contrast, our proposed Poisson Quasimetric Embedding (PQE) is the first quasimetric learning formulation that both is learnable with gradient-based optimization and enjoys strong performance guarantees. Experiments on random graphs, social graphs, and offline Q-learning demonstrate its effectiveness over many common baselines.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.15478

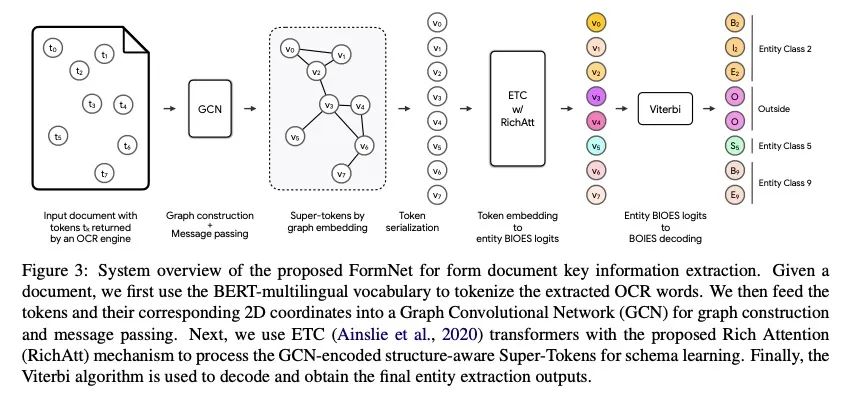
3、[CL] FormNet: Structural Encoding beyond Sequential Modeling in Form Document Information Extraction
C Lee, C Li, T Dozat, V Perot, G Su, N Hua...
[Google Cloud AI Research & Google Research]
FormNet: 表格文档信息提取中序列建模之外的结构编码。序列建模在自然语言和文档理解任务上表现出最先进的性能。然而,在实践中,由于表单类文档的布局模式多种多样,要正确对其Token序列化是很有挑战性的。本文提出FormNet,一种结构化感知的序列模型,以减轻表单的次优序列化。本文设计了富注意力(Rich Attention),利用表格中Token间的空间关系来进行更精确的注意力分数计算。其次,为每个词构建了超级Token,通过图的卷积嵌入其相邻Token的表示。因此,FormNet显式地恢复了在序列化过程中可能丢失的局部句法信息。在实验中,FormNet以更紧凑的模型规模和更少的预训练数据超越了现有方法,在CORD、FUNSD和Payment基准上达到了新的最先进性能。
Sequence modeling has demonstrated state-ofthe-art performance on natural language and document understanding tasks. However, it is challenging to correctly serialize tokens in form-like documents in practice due to their variety of layout patterns. We propose FormNet, a structure-aware sequence model to mitigate the suboptimal serialization of forms. First, we design Rich Attention that leverages the spatial relationship between tokens in a form for more precise attention score calculation. Second, we construct Super-Tokens for each word by embedding representations from their neighboring tokens through graph convolutions. FormNet therefore explicitly recovers local syntactic information that may have been lost during serialization. In experiments, FormNet outperforms existing methods with a more compact model size and less pretraining data, establishing new state-of-the-art performance on CORD, FUNSD and Payment benchmarks.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.08411


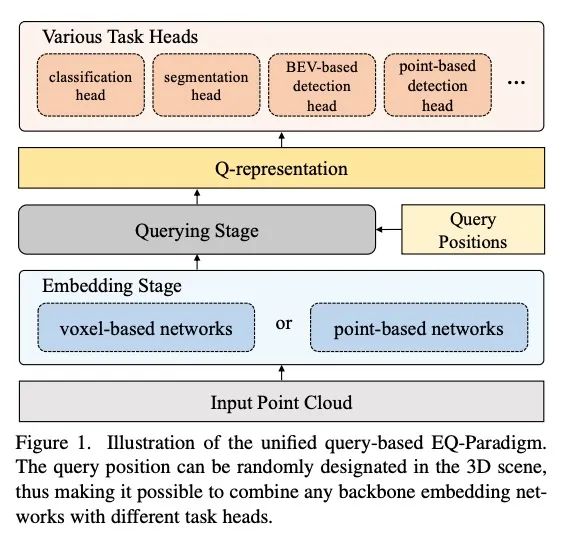
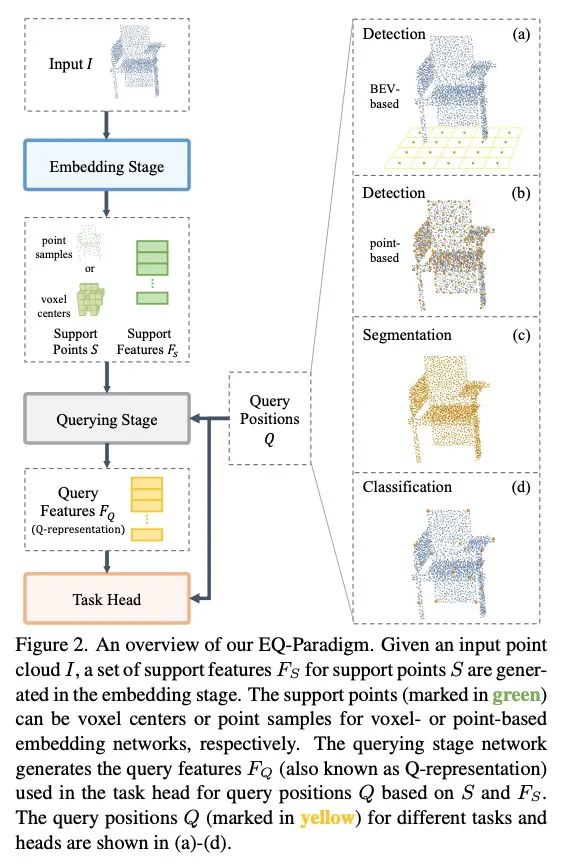
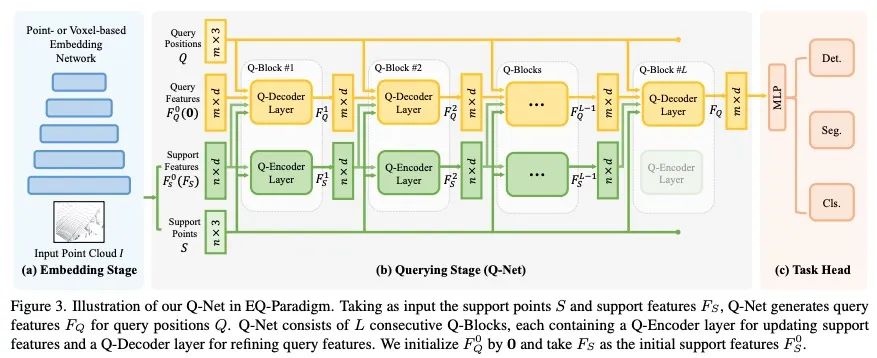
4、[CV] A Unified Query-based Paradigm for Point Cloud Understanding
Z Yang, L Jiang, Y Sun, B Schiele, J Jia
[CUHK & MPI Informatics & HKUST]
统一的基于查询的点云理解范式。3D点云理解是无人驾驶和机器人技术的一个重要组成部分。本文提出了一个新的嵌入查询范式(EQParadigm),用于3D理解任务,包括检测、分割和分类。EQ-Paradigm是一个统一的范式,能将任何现有的3D骨干架构与不同的任务头结合起来。在EQ-Paradigm下,输入首先在嵌入阶段用一个任意的特征提取架构进行编码,该架构与任务和头无关。然后,查询阶段使编码后的特征能适用于不同的任务头。这是通过在查询阶段引入一个中间表示,即Q-representation,作为嵌入阶段和任务头之间的桥梁来实现的。本文设计了一种新的QNet作为查询阶段的网络。在各种3D任务上的大量实验结果表明,EQ-Paradigm与Q-Net串联是一个通用的、有效的管道,它能使骨干和头灵活协作,并进一步提高了先进方法的性能。
3D point cloud understanding is an important component in autonomous driving and robotics. In this paper, we present a novel Embedding-Querying paradigm (EQParadigm) for 3D understanding tasks including detection, segmentation and classification. EQ-Paradigm is a unified paradigm that enables the combination of any existing 3D backbone architectures with different task heads. Under the EQ-Paradigm, the input is firstly encoded in the embedding stage with an arbitrary feature extraction architecture, which is independent of tasks and heads. Then, the querying stage enables the encoded features to be applicable for diverse task heads. This is achieved by introducing an intermediate representation, i.e., Q-representation, in the querying stage to serve as a bridge between the embedding stage and task heads. We design a novel QNet as the querying stage network. Extensive experimental results on various 3D tasks show that EQ-Paradigm in tandem with Q-Net is a general and effective pipeline, which enables a flexible collaboration of backbones and heads, and further boosts the performance of the stateof-the-art methods. Codes and models are available at https://github.com/dvlab-research/DeepVision3D.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.01252

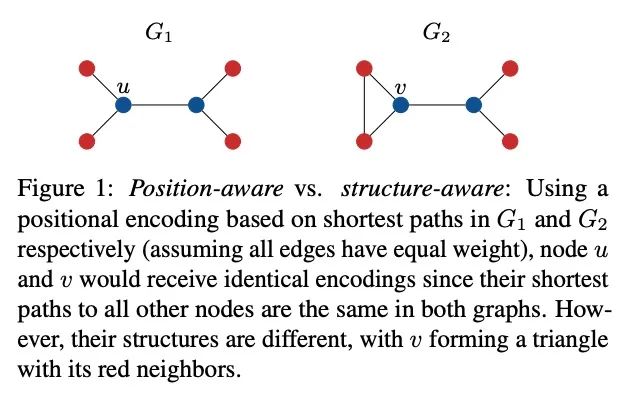
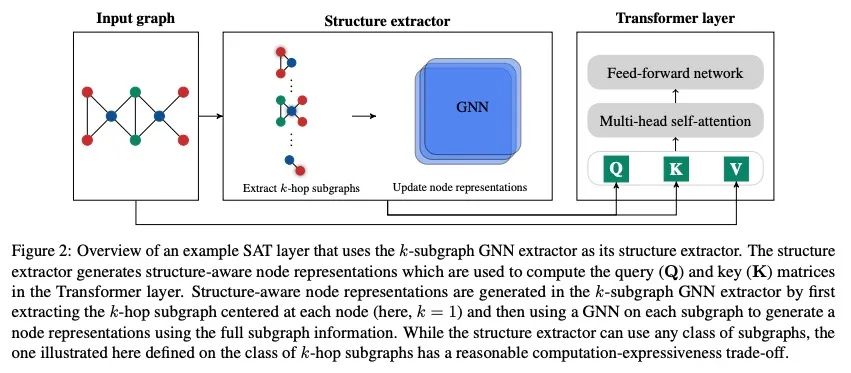
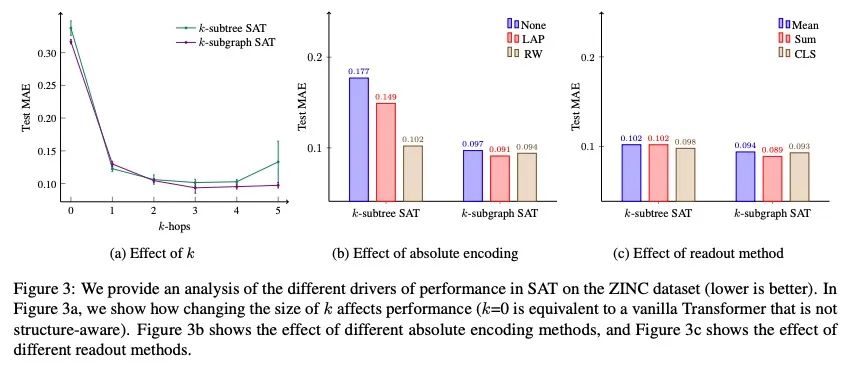
5、[LG] Structure-Aware Transformer for Graph Representation Learning
D Chen, L O'Bray, K Borgwardt
[ETH Zurich]
面向图表示学习的结构感知Transformer。最近,Transformer架构在图表示学习中获得了越来越多的关注,因为它自然地克服了图神经网络(GNN)的一些局限性,避免了其严格的结构归纳偏差,而只是通过位置编码对图结构进行编码。本文表明,由Transformer生成的具有位置编码的节点表示不一定能捕捉到它们之间的结构相似性。为了解决这个问题,本文提出了结构感知Transformer,一类建立在新的自注意力机制上的简单灵活的图Transformer。这种新的自注意力机制通过在计算注意力前提取根植于每个节点的子图表示,将结构信息纳入原始自注意力。本文提出几种自动生成子图表示的方法,并在理论上表明,所产生的表示至少与子图表示一样具有表达力。从经验上看,所提出方法在五个图预测基准上取得了最先进的性能。所提出的结构感知框架可以利用任何现有的GNN来提取子图表示,相对于基本的GNN模型,它系统地提高了性能,成功地结合了GNN和Transformers的优势。
The Transformer architecture has gained growing attention in graph representation learning recently, as it naturally overcomes several limitations of graph neural networks (GNNs) by avoiding their strict structural inductive biases and instead only encoding the graph structure via positional encoding. Here, we show that the node representations generated by the Transformer with positional encoding do not necessarily capture structural similarity between them. To address this issue, we propose the Structure-Aware Transformer, a class of simple and flexible graph Transformers built upon a new self-attention mechanism. This new self-attention incorporates structural information into the original self-attention by extracting a subgraph representation rooted at each node before computing the attention. We propose several methods for automatically generating the subgraph representation and show theoretically that the resulting representations are at least as expressive as the subgraph representations. Empirically, our method achieves state-of-the-art performance on five graph prediction benchmarks. Our structure-aware framework can leverage any existing GNN to extract the subgraph representation, and we show that it systematically improves performance relative to the base GNN model, successfully combining the advantages of GNNs and Transformers. Our code is available at https: //github.com/BorgwardtLab/SAT.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.03036

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
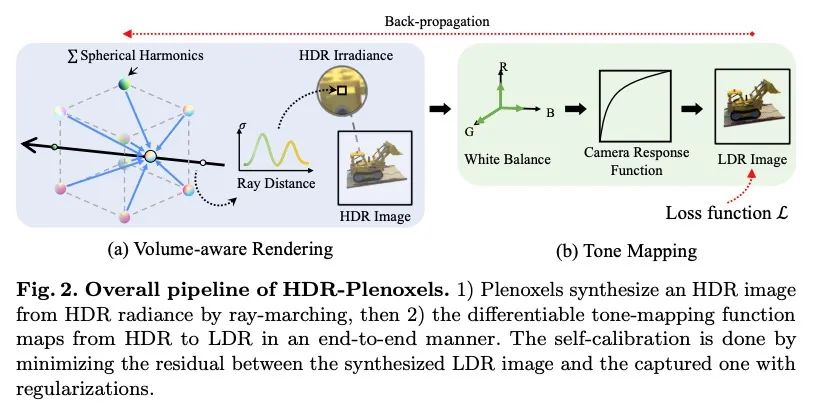
[CV] HDR-Plenoxels: Self-Calibrating High Dynamic Range Radiance Fields
HDR-Plenoxels:高动态范围辐射场自校准
K Jun-Seong, K Yu-Ji, M Ye-Bin, T Oh
[POSTECH]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.06787


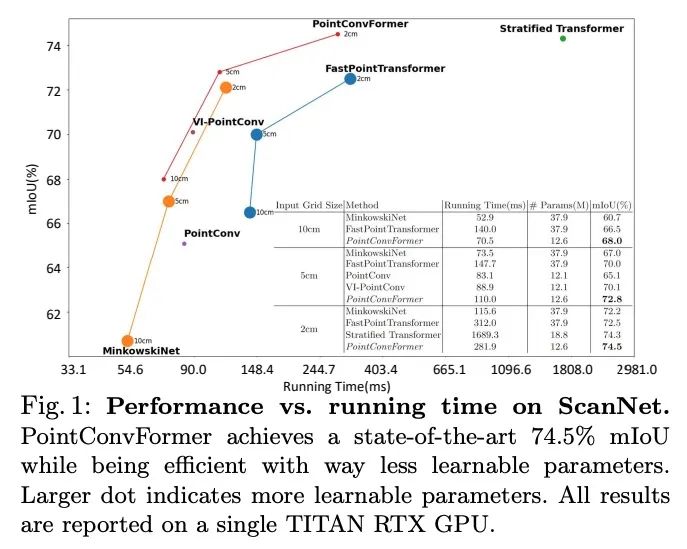
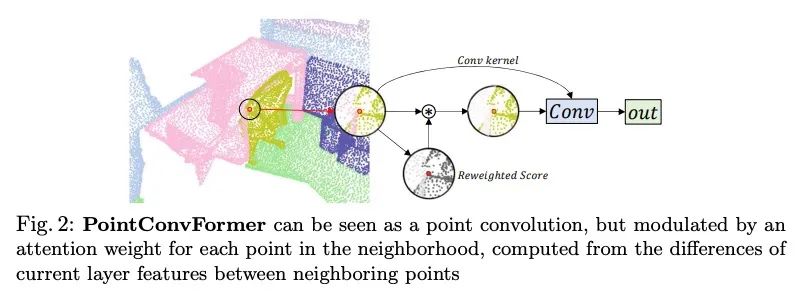
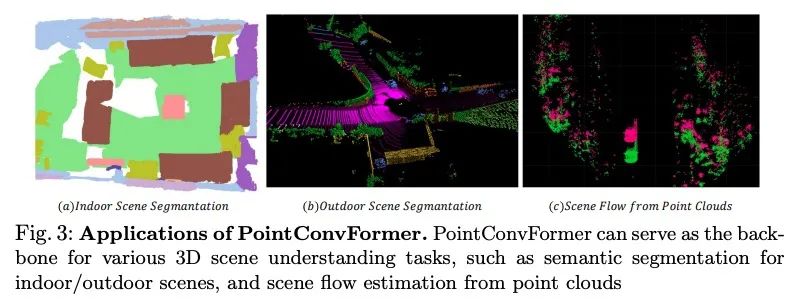
[CV] PointConvFormer: Revenge of the Point-based Convolution
PointConvFormer:点卷积深度网络架构模块
W Wu, Q Shan, L Fuxin
[Oregon State University & Apple Inc]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.02879

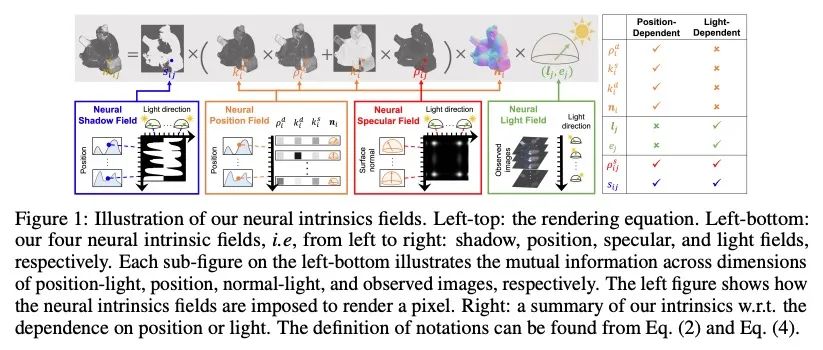
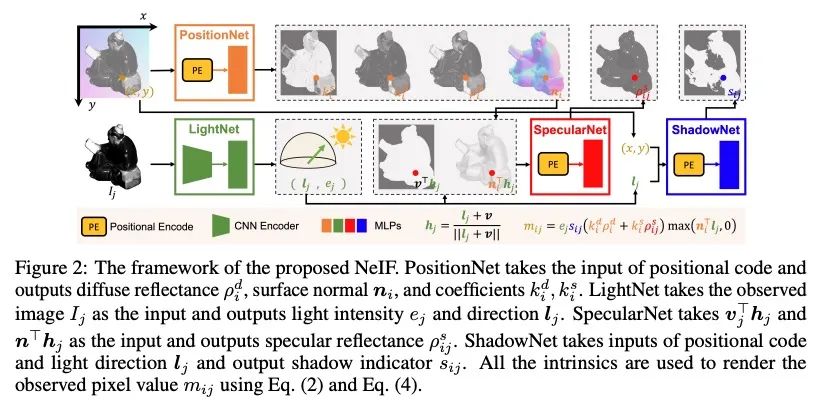
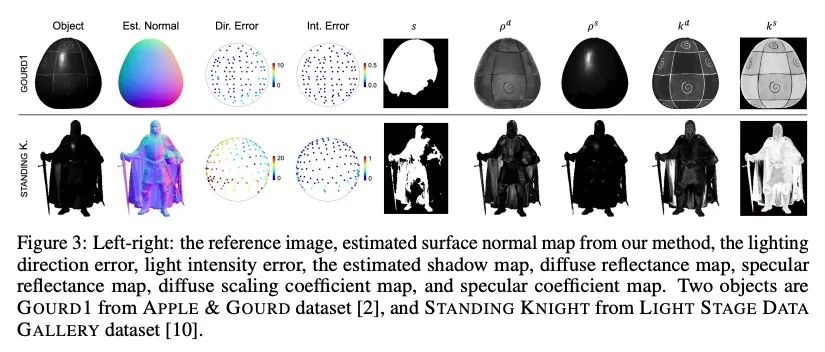
[CV] NeIF: Representing General Reflectance as Neural Intrinsics Fields for Uncalibrated Photometric Stereo
NeIF:将一般反射率表示为未校准光度立体神经本征场
Z Li, Q Zheng, F Wang...
[Nanyang Technological University & Zhejiang University & Peking University]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.08897

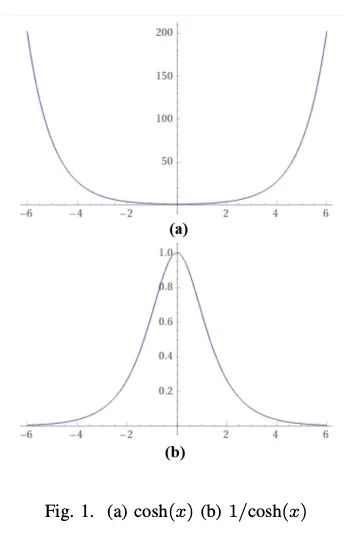
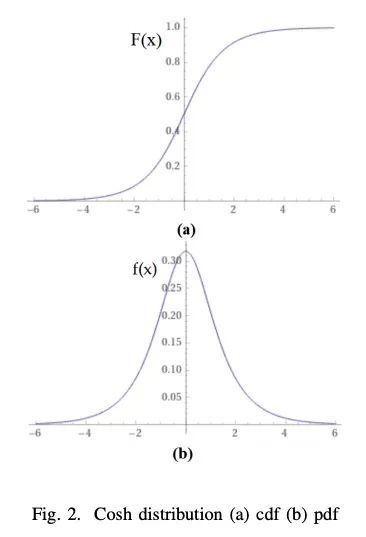
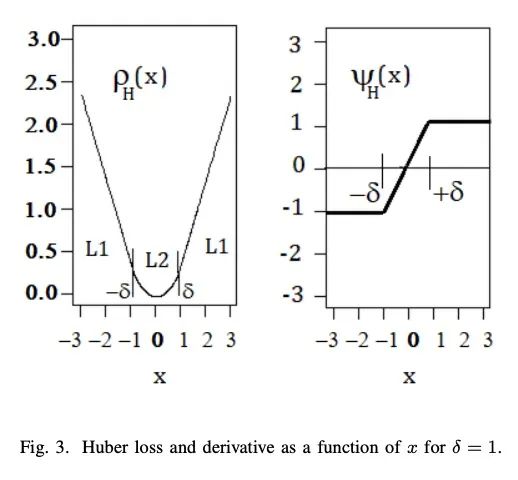
[LG] Statistical Properties of the log-cosh Loss Function Used in Machine Learning
机器学习中使用的log-cosh损失函数的统计特性
R A. Saleh, A.K.Md, E Saleh
[University of British Columbia & Carleton University]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2208.04564

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢