LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:视觉扩散模型综述、面向故事接龙调整预训练文本-图像Transformer、 四足机器人通用运动控制器、模糊化扩散模型、工业规模广告推荐模型机器学习工程、基于联合语言识别的流端到端多语言语音识别、非平稳环境下的元梯度、深度学习的Mori-Zwanzig范式、揭示多元时间序列的高阶组织
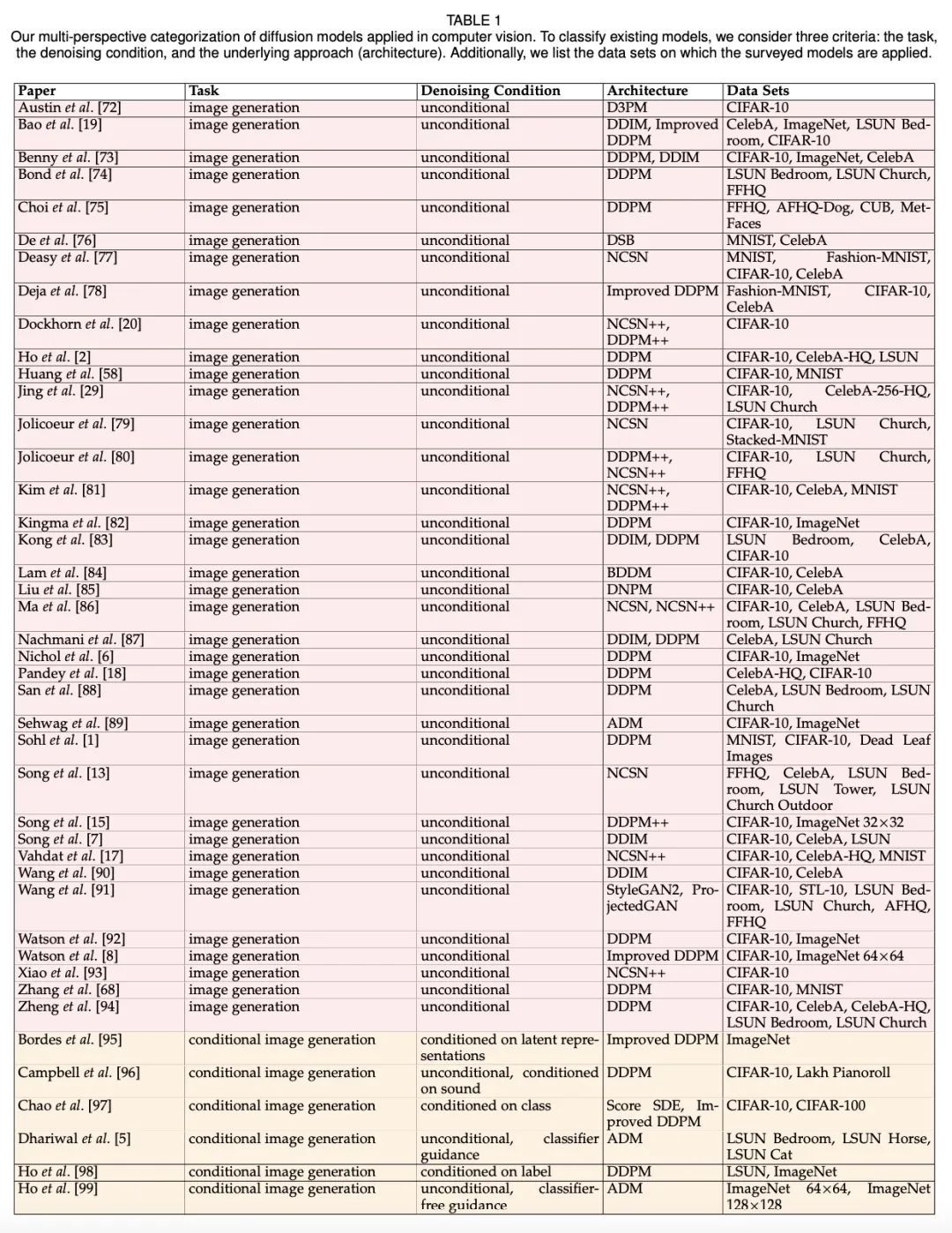
1、[CV] Diffusion Models in Vision: A Survey
F Croitoru, V Hondru, R T Ionescu, M Shah
[University of Bucharest & University of Central Florida]
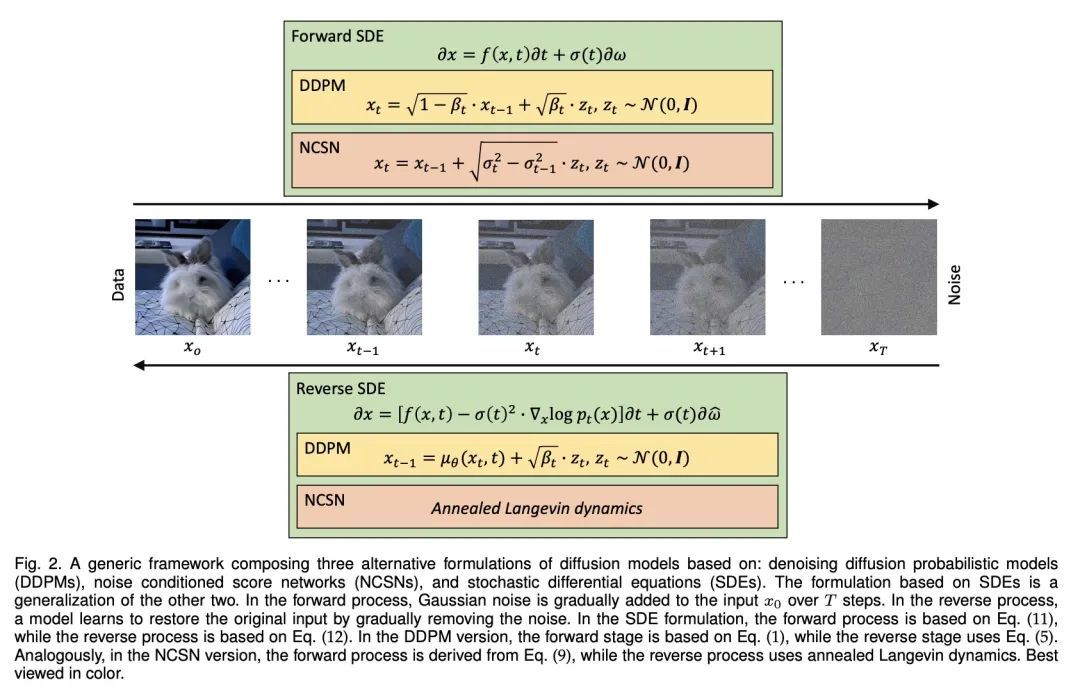
视觉扩散模型综述。去噪扩散模型代表了计算机视觉领域的一个新兴课题,在生成模型领域展示了显著的成果。扩散模型是一种深度生成模型,它基于两个阶段,正向扩散阶段和反向扩散阶段。在正向扩散阶段,输入数据通过添加高斯噪声,在几个步骤中逐渐被扰乱。在反向阶段,模型的任务是通过学习逐步逆向扩散过程来恢复原始输入数据。扩散模型因其生成样本的质量和多样性而受到广泛赞赏,尽管它们有已知的计算负担,即由于采样过程中涉及的步骤较多而速度较低。本综述对应用于视觉的去噪扩散模型的文章进行了全面的调研,包括该领域的理论和实践贡献。首先,确定并介绍了三种通用的扩散模型框架,它们是基于去噪扩散概率模型、噪声条件下的得分网络和随机微分方程。本文进一步讨论了扩散模型和其他深度生成模型之间的关系,包括变分自编码器、生成对抗网络、基于能量的模型、自回归模型和归一化流。然后,本文介绍了计算机视觉中应用的扩散模型的多角度分类。最后,说明了目前扩散模型的局限性,并设想了一些有趣的未来研究方向。
Denoising diffusion models represent a recent emerging topic in computer vision, demonstrating remarkable results in the area of generative modeling. A diffusion model is a deep generative model that is based on two stages, a forward diffusion stage and a reverse diffusion stage. In the forward diffusion stage, the input data is gradually perturbed over several steps by adding Gaussian noise. In the reverse stage, a model is tasked at recovering the original input data by learning to gradually reverse the diffusion process, step by step. Diffusion models are widely appreciated for the quality and diversity of the generated samples, despite their known computational burdens, i.e. low speeds due to the high number of steps involved during sampling. In this survey, we provide a comprehensive review of articles on denoising diffusion models applied in vision, comprising both theoretical and practical contributions in the field. First, we identify and present three generic diffusion modeling frameworks, which are based on denoising diffusion probabilistic models, noise conditioned score networks, and stochastic differential equations. We further discuss the relations between diffusion models and other deep generative models, including variational auto-encoders, generative adversarial networks, energy-based models, autoregressive models and normalizing flows. Then, we introduce a multi-perspective categorization of diffusion models applied in computer vision. Finally, we illustrate the current limitations of diffusion models and envision some interesting directions for future research.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.0474

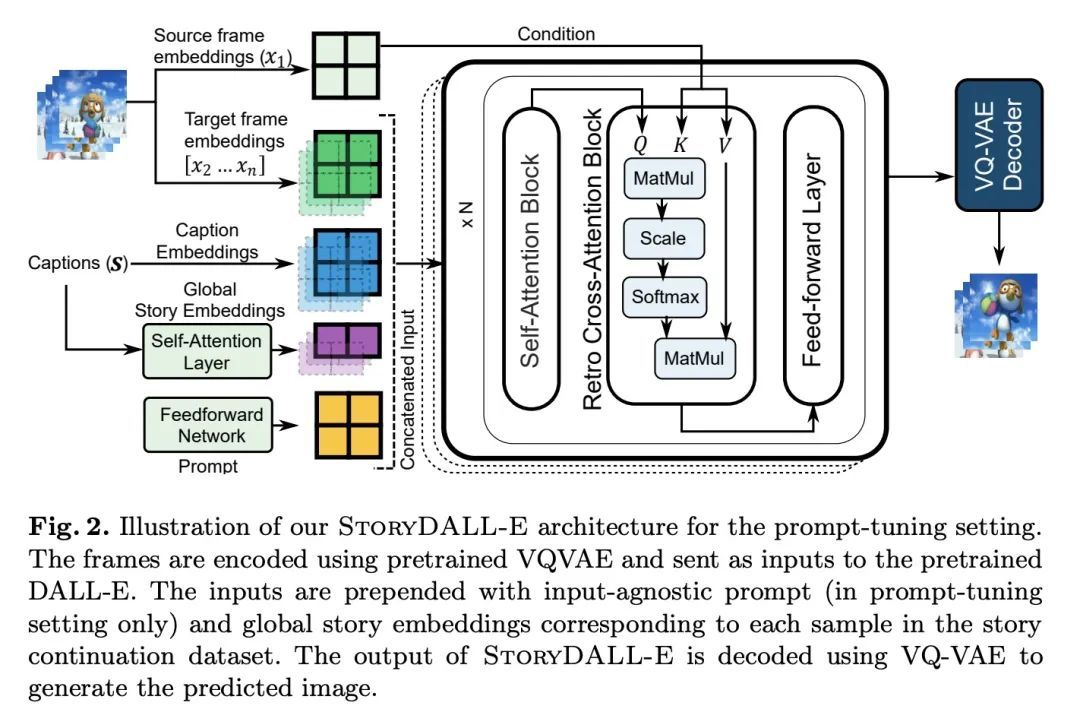
2、[CV] StoryDALL-E: Adapting Pretrained Text-to-Image Transformers for Story Continuation
A Maharana, D Hannan, M Bansal
[UNC Chapel Hill]
StoryDALL-E:面向故事接龙调整预训练文本-图像Transformer。最近在文本到图像合成方面的进展带来了大型预训练Transformer,其具有从给定文本生成可视化的卓越能力。然而,这些模型并不适合像故事可视化这样的专门任务,其要求智能体产生一连串的图像,并给出相应的标题序列,形成叙述。此外,故事可视化任务不能适应对新的叙述中未见过的情节和人物的泛化。本文首先提出了故事延续任务,即生成的视觉故事以源图像为条件,允许更好地泛化到有新人物的叙述中。由于故事中的图像需要有连续性和明确的叙述,因此很难收集大规模的数据集来从头训练这个任务的大型模型。本文建议利用文本-图像合成模型的预训练知识来克服低资源的状况,并改善故事延续性的生成。为此,本文加强或 "改装"预训练的文本-图像合成模型,使其具有特定的任务模块,用于 (a) 连续的图像生成和 (b) 从初始帧复制相关元素。然后,本文探索对预训练模型的全模型微调,以及基于提示的参数有效自适应的调整。在两个现有的数据集PororoSV和FlintstonesSV上评估了所提出的方法StoryDALL-E,并介绍了一个新的数据集DiDeMoSV,该数据集收集自一个视频描述数据集。还开发了一个基于生成对抗网络(GAN)的故事延续模型StoryGANc,并将其与StoryDALL-E模型进行比较,以证明所提出方法的优势。逆向拟合方法在故事延续方面优于基于GAN的模型,并且有利于复制源图像中的视觉元素,从而提高了生成的视觉故事的连续性。分析表明,预训练的Transformer在理解包含多个角色的叙事并将其转化为适当的图像时很困难。总的来说,预训练的文本-图像合成模型可以适应复杂的、低资源的任务,如故事的延续性。
Recent advances in text-to-image synthesis have led to large pretrained transformers with excellent capabilities to generate visualizations from a given text. However, these models are ill-suited for specialized tasks like story visualization, which requires an agent to produce a sequence of images given a corresponding sequence of captions, forming a narrative. Moreover, we find that the story visualization task fails to accommodate generalization to unseen plots and characters in new narratives. Hence, we first propose the task of story continuation, where the generated visual story is conditioned on a source image, allowing for better generalization to narratives with new characters. It is difficult to collect large-scale datasets to train large models for this task from scratch due to the need for continuity and an explicit narrative among the images in a story. Therefore, we propose to leverage the pretrained knowledge of text-to-image synthesis models to overcome the low-resource scenario and improve generation for story continuation. To that end, we enhance or ‘retro-fit’ the pretrained text-to-image synthesis models with taskspecific modules for (a) sequential image generation and (b) copying relevant elements from an initial frame. Then, we explore full-model finetuning, as well as prompt-based tuning for parameter-efficient adaptation, of the pre-trained model. We evaluate our approach StoryDALL-E on two existing datasets, PororoSV and FlintstonesSV, and introduce a new dataset DiDeMoSV collected from a video-captioning dataset. We also develop a model StoryGANc based on Generative Adversarial Networks (GAN) for story continuation, and compare it with the StoryDALL-E model to demonstrate the advantages of our approach. We show that our retro-fitting approach outperforms GAN-based models for story continuation and facilitates copying of visual elements from the source image, thereby improving continuity in the generated visual story. Finally, our analysis suggests that pretrained transformers struggle to comprehend narratives containing several characters and translating them into appropriate imagery. Overall, our work demonstrates that pretrained text-to-image synthesis models can be adapted for complex and low-resource tasks like story continuation. Our results encourage future research into story continuation as well as exploration of the latest, larger models for the task. Code, data, demo and model card available at https://github.com/adymaharana/storydalle.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.06192


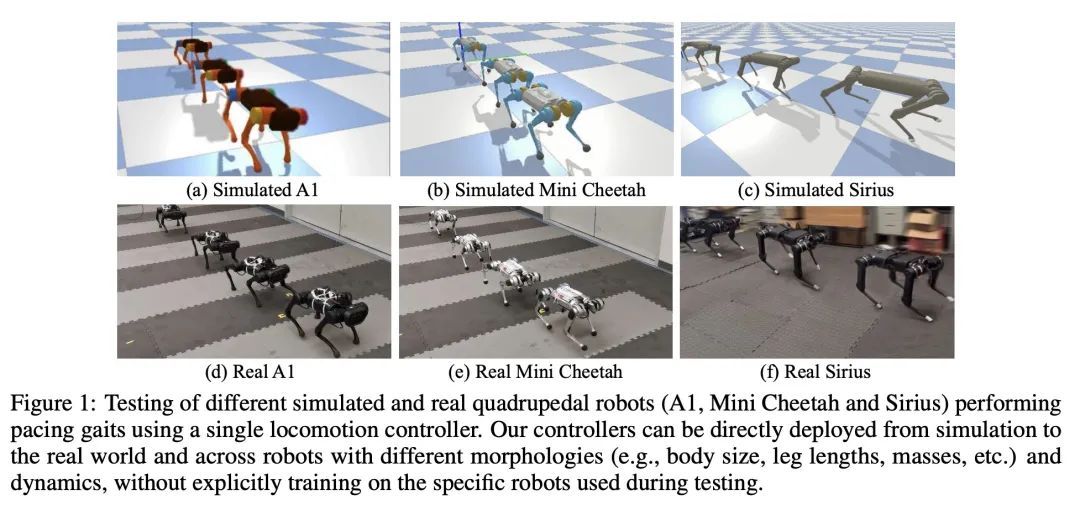
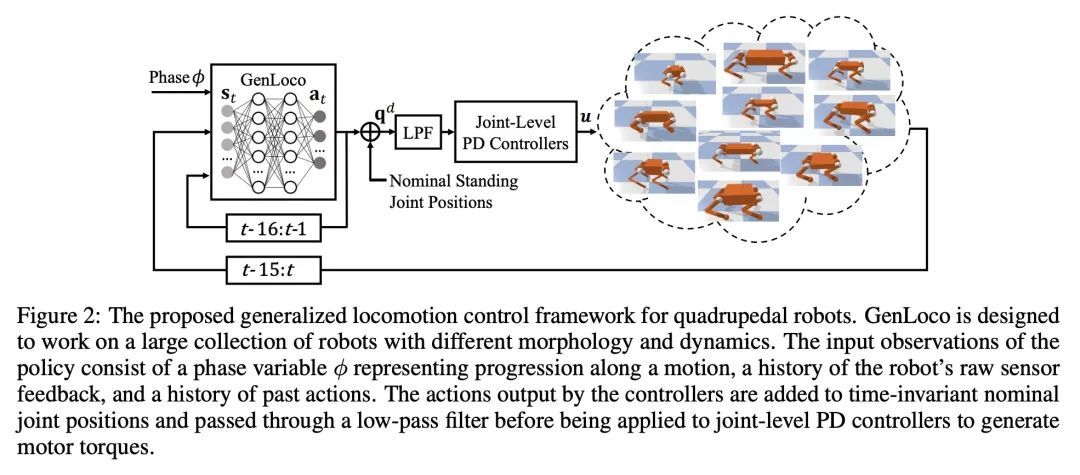
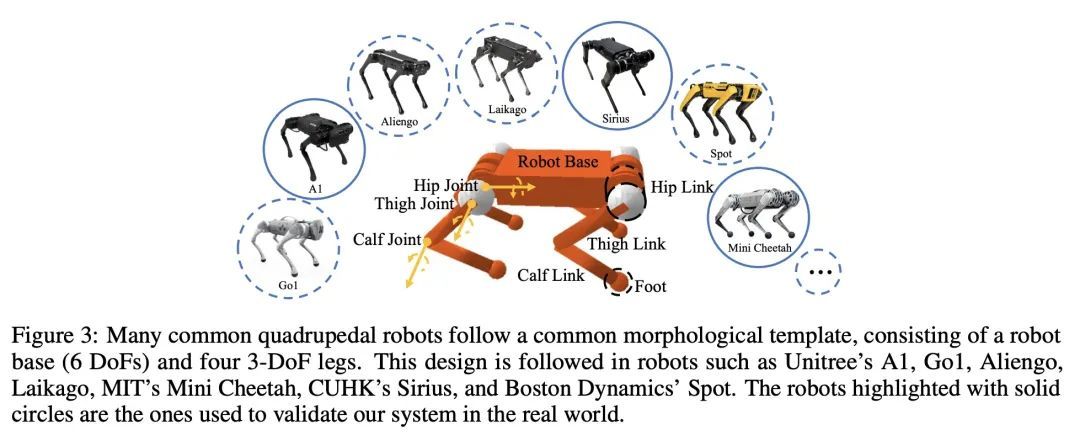
3、[RO] GenLoco: Generalized Locomotion Controllers for Quadrupedal Robots
G Feng, H Zhang, Z Li, X B Peng, B Basireddy...
[UC Berkeley & The Chinese University of Hong Kong]
GenLoco: 四足机器人通用运动控制器。近年来,市场上可获得的、价格低廉的四足机器人数量激增,其中许多平台被积极用于研究和工业。随着有足机器人可用性的增加,对能够使这些机器人发挥有用技能的控制器的需求也随之增加。然而,大多数基于学习的控制器开发框架都集中在训练机器人特定的控制器上,这个过程需要为每一个新的机器人重复进行。本文提出一种用于训练四足机器人的通用运动(GenLoco)控制器的框架,该框架合成了通用的运动控制器,可部署在具有类似形态的各种四足机器人上。本文提出一种简单而有效的形态随机化方法,该方法按程序生成了一组不同的仿真机器人用于训练。实验表明,通过在这一大组仿真机器人上训练控制器,所提模型获得了更多的通用控制策略,可以直接迁移到具有不同形态的新型仿真机器人和真实世界的机器人上,而这些机器人在训练过程中是没见过的。
Recent years have seen a surge in commercially-available and affordable quadrupedal robots, with many of these platforms being actively used in research and industry. As the availability of legged robots grows, so does the need for controllers that enable these robots to perform useful skills. However, most learning-based frameworks for controller development focus on training robot-specific controllers, a process that needs to be repeated for every new robot. In this work, we introduce a framework for training generalized locomotion (GenLoco) controllers for quadrupedal robots. Our framework synthesizes general-purpose locomotion controllers that can be deployed on a large variety of quadrupedal robots with similar morphologies. We present a simple but effective morphology randomization method that procedurally generates a diverse set of simulated robots for training. We show that by training a controller on this large set of simulated robots, our models acquire more general control strategies that can be directly transferred to novel simulated and real-world robots with diverse morphologies, which were not observed during training. https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.05309

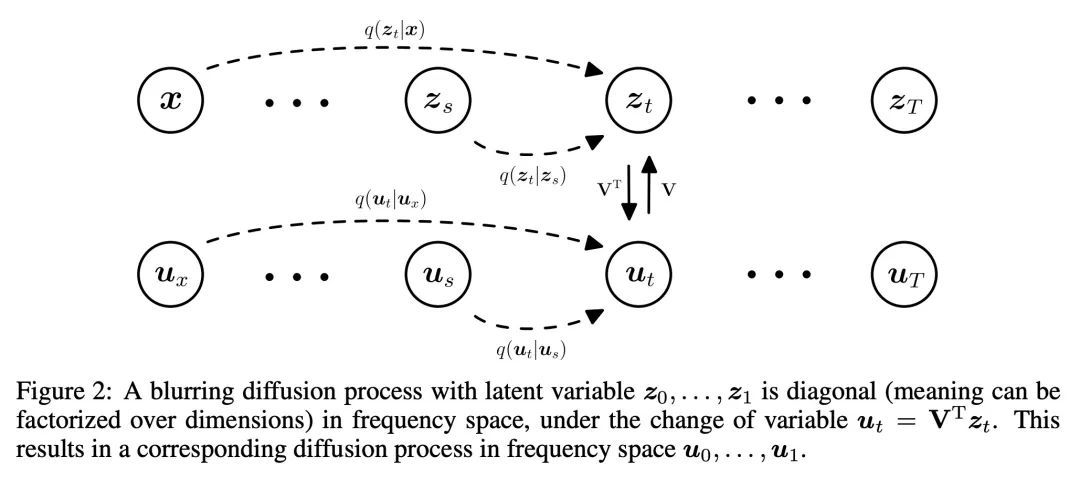
4、[LG] Blurring Diffusion Models
E Hoogeboom, T Salimans
[Google Research]
模糊化扩散模型。最近提出了一种新的扩散过程,用于基于热耗散的生成性建模,即模糊化,作为各向同性高斯扩散的替代。本文表明模糊化可以通过具有非各向异性噪声的高斯扩散过程等效地定义。在建立这种联系的过程中,弥合了逆热耗散和去噪扩散之间的差距,并阐明了这种建模选择所带来的归纳偏差。最后,本文提出一类广义的扩散模型,提供了标准高斯去噪扩散和逆热耗散的优点,称为模糊化扩散模型。
Recently, (Rissanen et al., 2022) have presented a new type of diffusion process for generative modeling based on heat dissipation, or blurring, as an alternative to isotropic Gaussian diffusion. Here, we show that blurring can equivalently be defined through a Gaussian diffusion process with non-isotropic noise. In making this connection, we bridge the gap between inverse heat dissipation and denoising diffusion, and we shed light on the inductive bias that results from this modeling choice. Finally, we propose a generalized class of diffusion models that offers the best of both standard Gaussian denoising diffusion and inverse heat dissipation, which we call Blurring Diffusion Models.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.05557



5、[IR] On the Factory Floor: ML Engineering for Industrial-Scale Ads Recommendation Models
R Anil, S Gadanho, D Huang, N Jacob, Z Li, D Lin, T Phillips, C Pop, K Regan, G I. Shamir, R Shivanna, Q Yan
[Google]
回到工厂车间:工业规模广告推荐模型机器学习工程。对于工业规模的广告系统来说,广告点击率(CTR)预测是个核心问题。广告点击率构成了用户参与的一个重要类别,并经常被用作衡量广告对用户有用性的主要信号。此外,在按点击率收费的广告系统中,广告商按点击率收费,点击率预期直接反馈到价值评估中。因此,对于大多数互联网广告公司来说,点击率模型的开发是一项重大投资。针对此类问题的工程需要许多适合在线学习的机器学习(ML)技术,这些技术远远超出了传统的准确性改进,特别是关于效率、可复现性、校准、信用归属。本文提供了一个部署在谷歌搜索广告CTR模型中的实用技术的案例研究,强调了当前机器学习研究的重要领域,并说明了如何在大规模工业环境中评估有影响力的新机器学习方法并使其发挥作用。
For industrial-scale advertising systems, prediction of ad click-through rate (CTR) is a central problem. Ad clicks constitute a significant class of user engagements and are often used as the primary signal for the usefulness of ads to users. Additionally, in cost-per-click advertising systems where advertisers are charged per click, click rate expectations feed directly into value estimation. Accordingly, CTR model development is a significant investment for most Internet advertising companies. Engineering for such problems requires many machine learning (ML) techniques suited to online learning that go well beyond traditional accuracy improvements, especially concerning efficiency, reproducibility, calibration, credit attribution. We present a case study of practical techniques deployed in Google's search ads CTR model. This paper provides an industry case study highlighting important areas of current ML research and illustrating how impactful new ML methods are evaluated and made useful in a large-scale industrial setting.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.05310

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[AS] Streaming End-to-End Multilingual Speech Recognition with Joint Language Identification基于联合语言识别的流端到端多语言语音识别
C Zhang, B Li, T Sainath, T Strohman, S Mavandadi, S Chang, P Haghani
[Google]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.06058

[LG] Meta-Gradients in Non-Stationary Environments
非平稳环境下的元梯度
J Luketina, S Flennerhag, Y Schroecker, D Abel, T Zahavy, S Singh
[University of Oxford & DeepMind]https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.06159

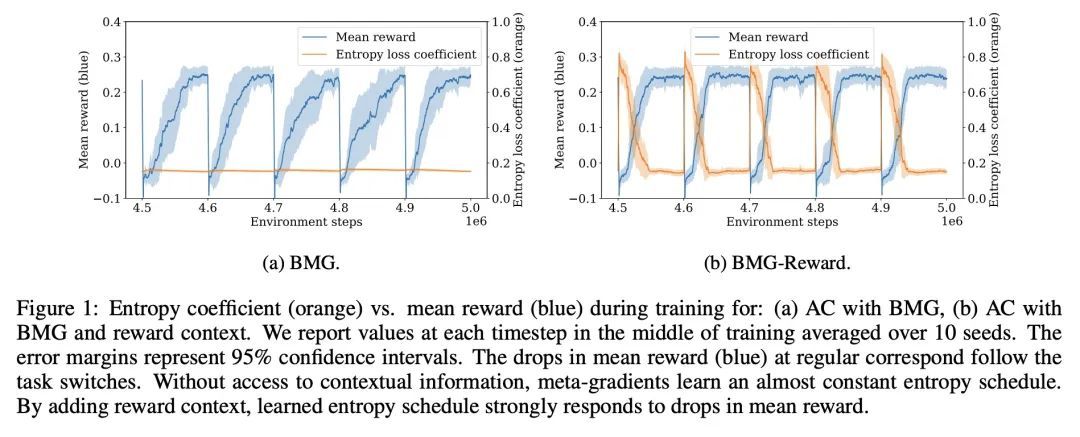
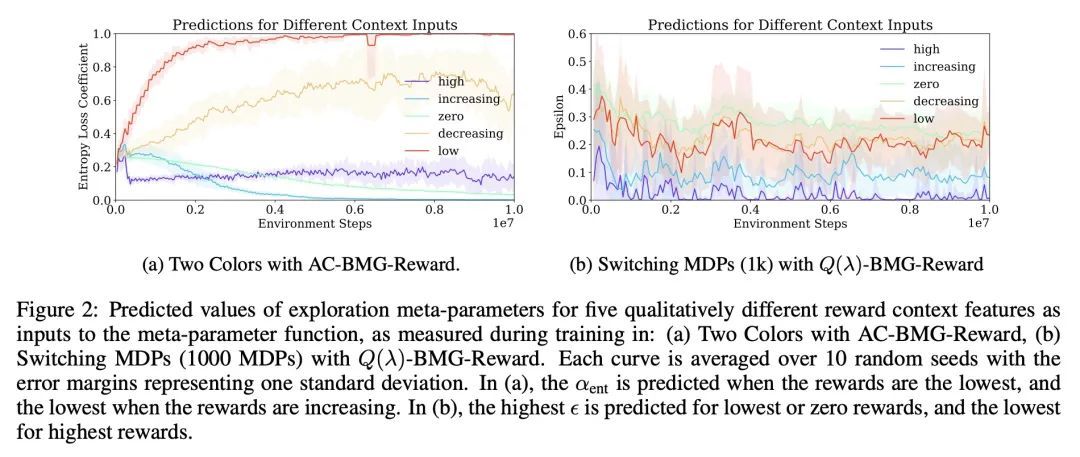
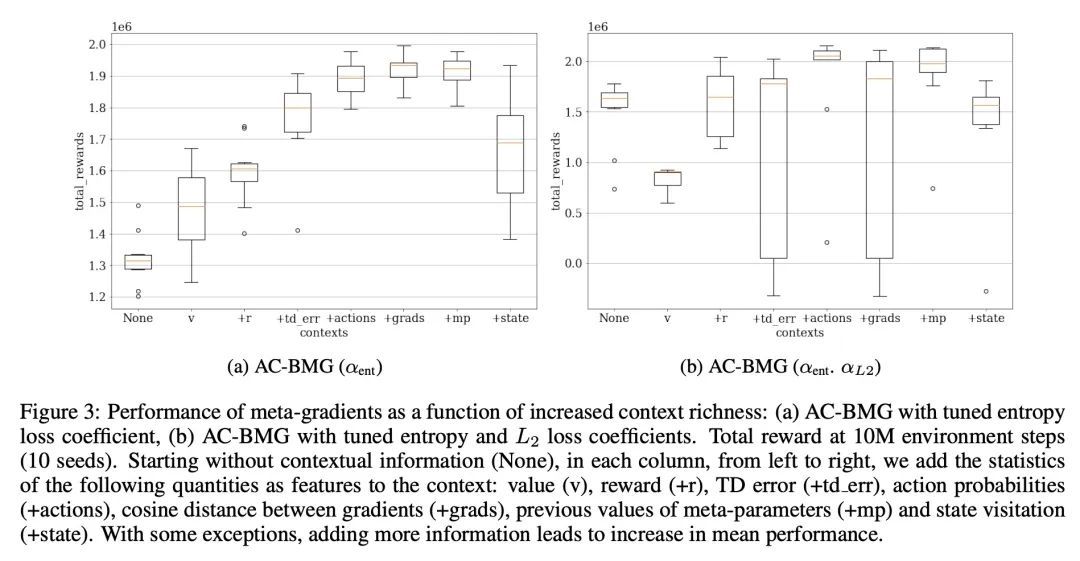
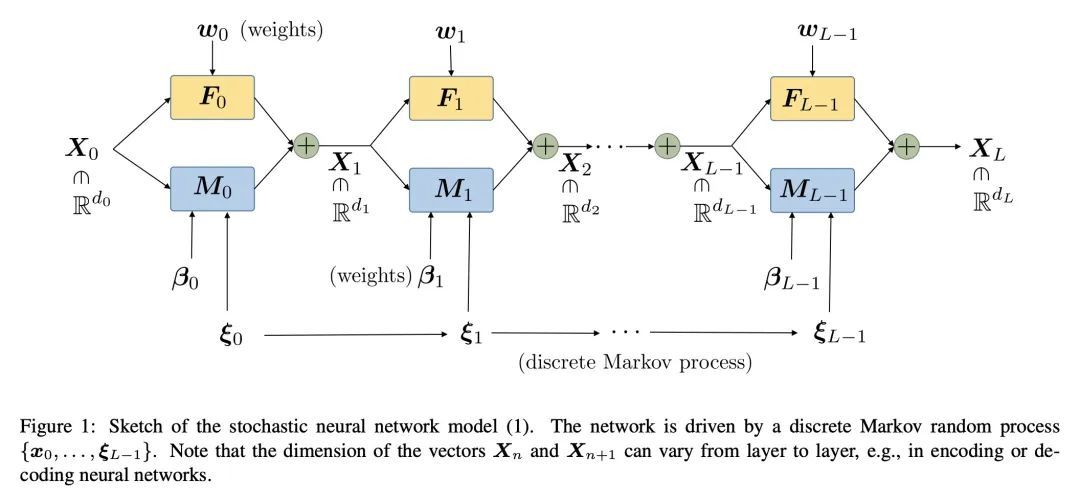
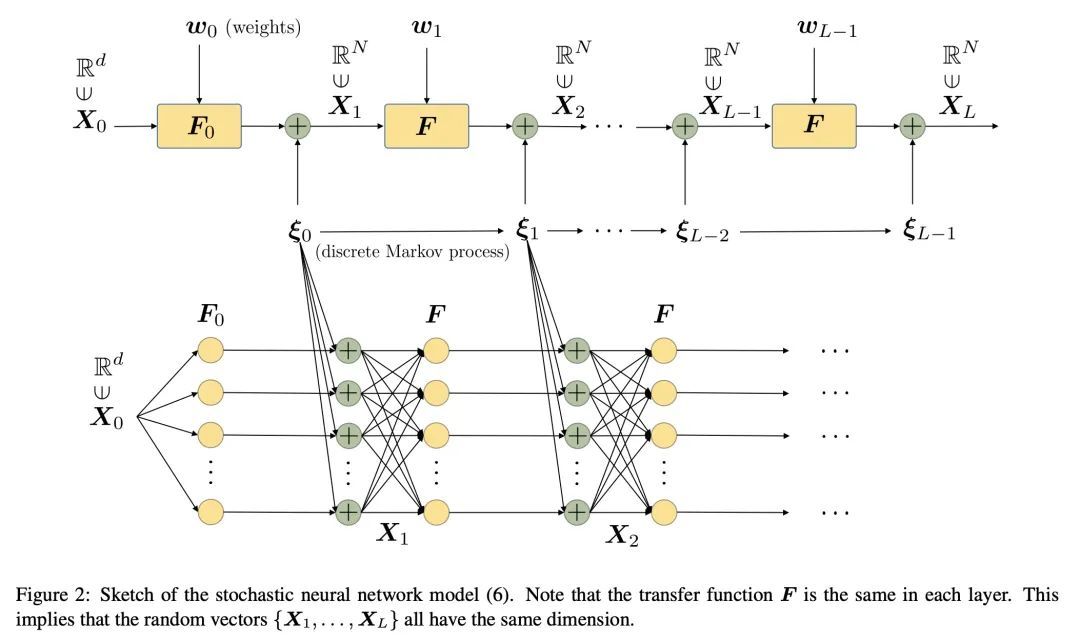
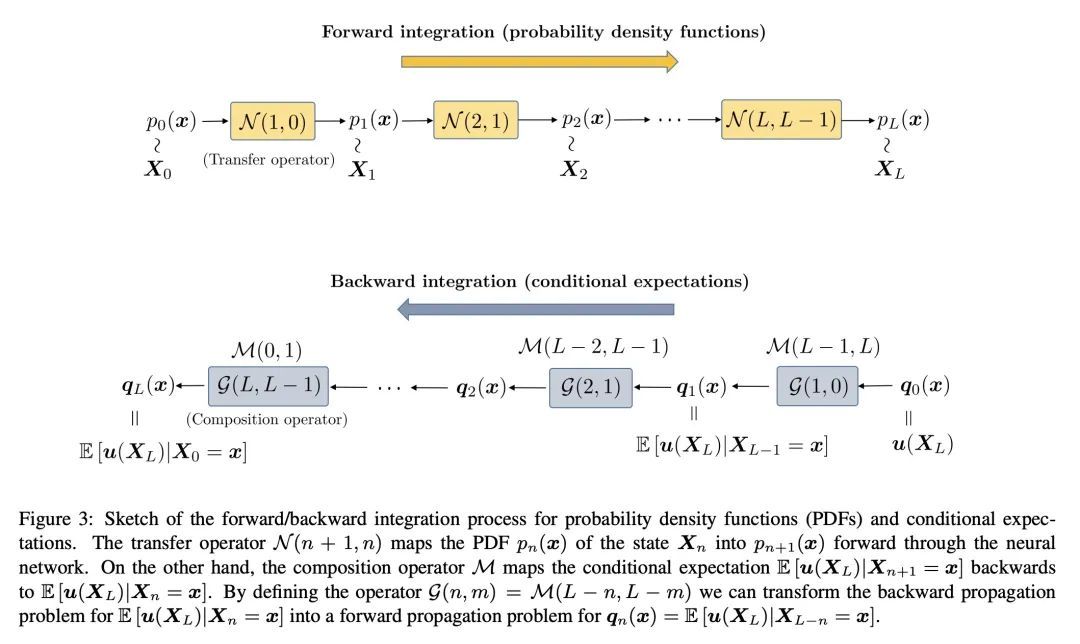
[LG] The Mori-Zwanzig formulation of deep learning
深度学习的Mori-Zwanzig范式
D Venturi, X Li
[UC Santa Cruz & Pennsylvania State University] https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.05544

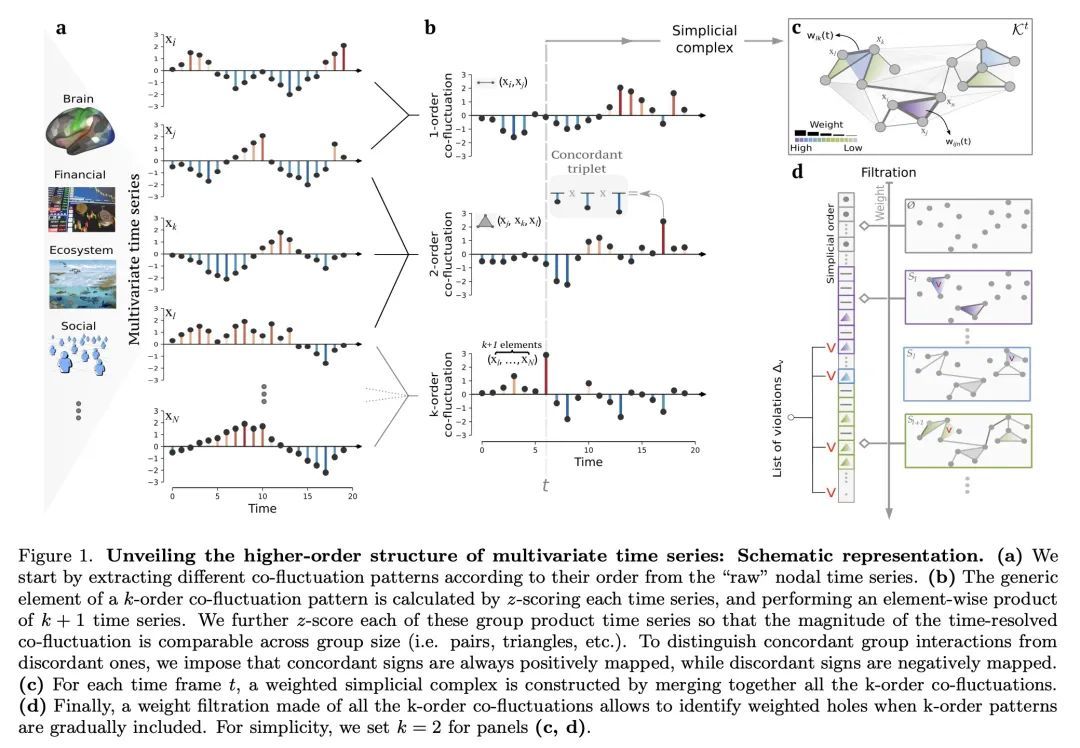
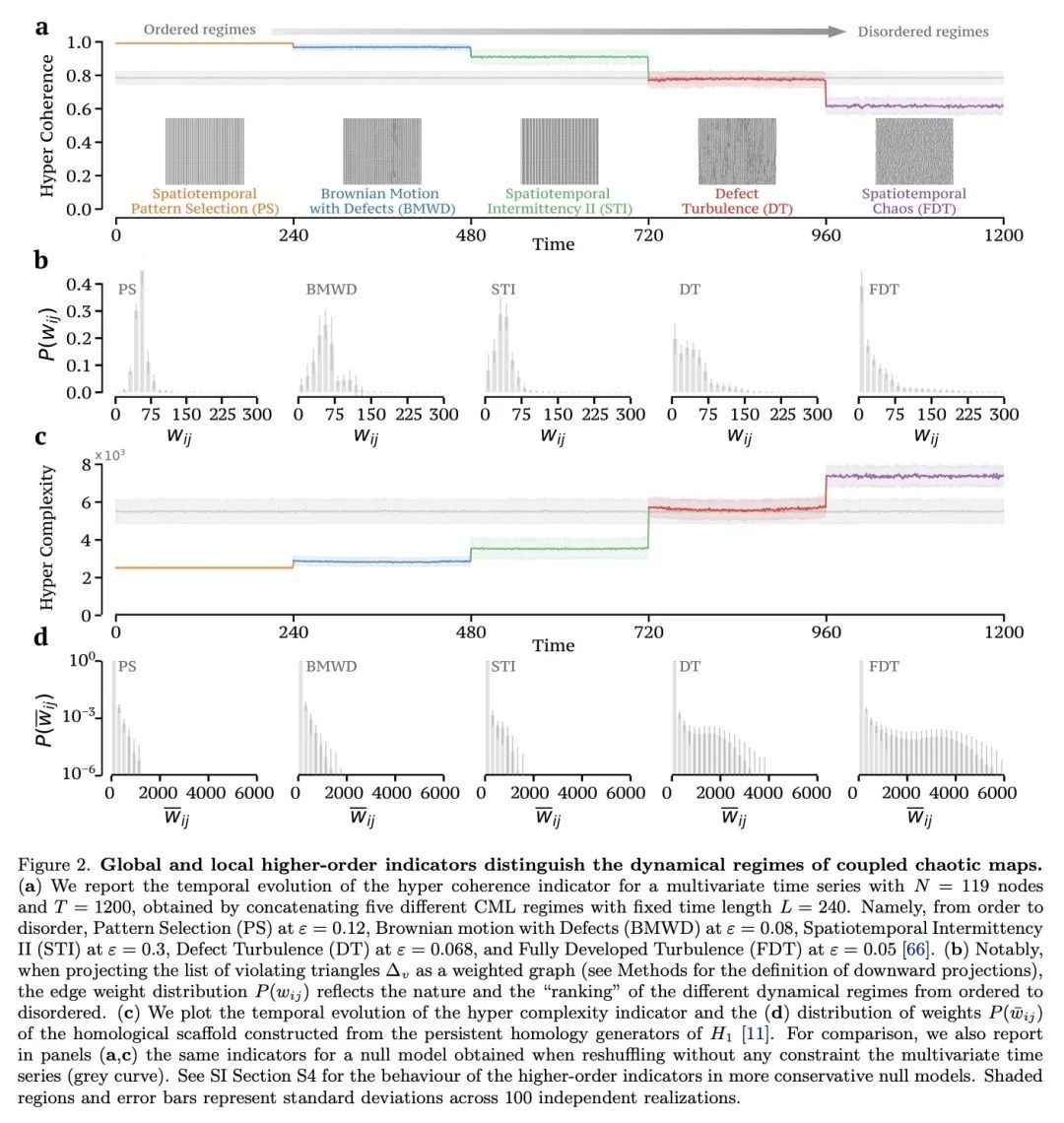
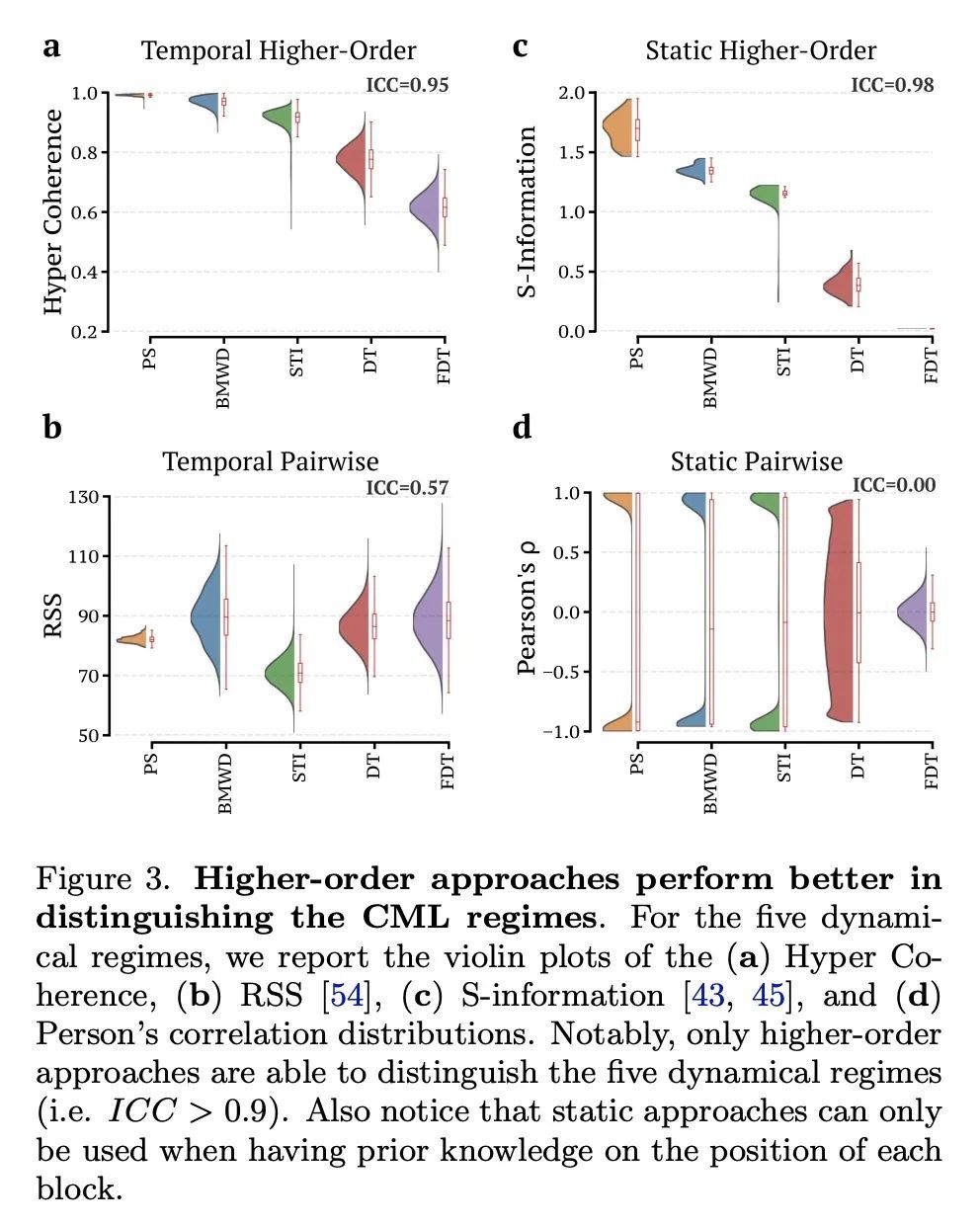
[LG] Unveiling the higher-order organization of multivariate time series
揭示多元时间序列的高阶组织
A Santoro, F Battiston, G Petri, E Amico
[Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne & Central European University & CENTAI]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.10702

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢