LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:快200倍达到人类玩Atari水平、重参数化模型梯度下降的隐性偏差、基于概率重参数化的离散和混合空间贝叶斯优化、数据分布属性驱动Transformer的新兴语境学习、基于神经试验台的联合预测评估、语义图像分割无监督域自适应综述、AI辅助药物发现深度非平衡学习基准、思维推理中文本和模式的共生关系、减少危害的红队语言模型
1、[LG] Human-level Atari 200x faster
S Kapturowski, V Campos, R Jiang, N Rakićević, H v Hasselt, C Blundell, A P Badia
[DeepMind]
快200倍达到人类玩Atari水平。构建在各种任务中表现良好的通用智能体的任务,从一开始就是强化学习的一个重要目标。该问题已经成为大量工作的研究对象,其性能经常通过观察Atari 57基准中包含的各种环境的分数来衡量。Agent57是第一个在所有57个游戏中超过人类基准的智能体,但这是以数据效率低下为代价的,需要近800亿帧的经验才能实现。以Agent57为起点,本文采用一系列不同的策略,以实现超越人类基准,只需要200分之一的经验。本文研究了在减少数据系统时遇到的一系列不稳定因素和瓶颈,并提出了有效的解决方案,以建立一个更强大和高效的智能体。本文还展示了与Muesli和MuZero等高性能方法的竞争性能。所提出方法的四个关键部分是:(1)一种近似的信任区域方法,它能从在线网络中稳定地引导;(2)一种损失和优先权的归一化方案,它能在学习一组具有广泛规模的价值函数时提高鲁棒性;(3)一种改进架构,采用了NFNets的技术,以利用更深的网络,而不需要归一化层;(4)一种策略提炼方法,用于平滑瞬时贪婪策略的超时。
The task of building general agents that perform well over a wide range of tasks has been an importantgoal in reinforcement learning since its inception. The problem has been subject of research of alarge body of work, with performance frequently measured by observing scores over the wide rangeof environments contained in the Atari 57 benchmark. Agent57 was the first agent to surpass thehuman benchmark on all 57 games, but this came at the cost of poor data-efficiency, requiring nearly 80billion frames of experience to achieve. Taking Agent57 as a starting point, we employ a diverse set ofstrategies to achieve a 200-fold reduction of experience needed to outperform the human baseline. Weinvestigate a range of instabilities and bottlenecks we encountered while reducing the data regime, andpropose effective solutions to build a more robust and efficient agent. We also demonstrate competitiveperformance with high-performing methods such as Muesli and MuZero. The four key components toour approach are (1) an approximate trust region method which enables stable bootstrapping from theonline network, (2) a normalisation scheme for the loss and priorities which improves robustness whenlearning a set of value functions with a wide range of scales, (3) an improved architecture employingtechniques from NFNets in order to leverage deeper networks without the need for normalization layers,and (4) a policy distillation method which serves to smooth out the instantaneous greedy policy overtime.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.07550

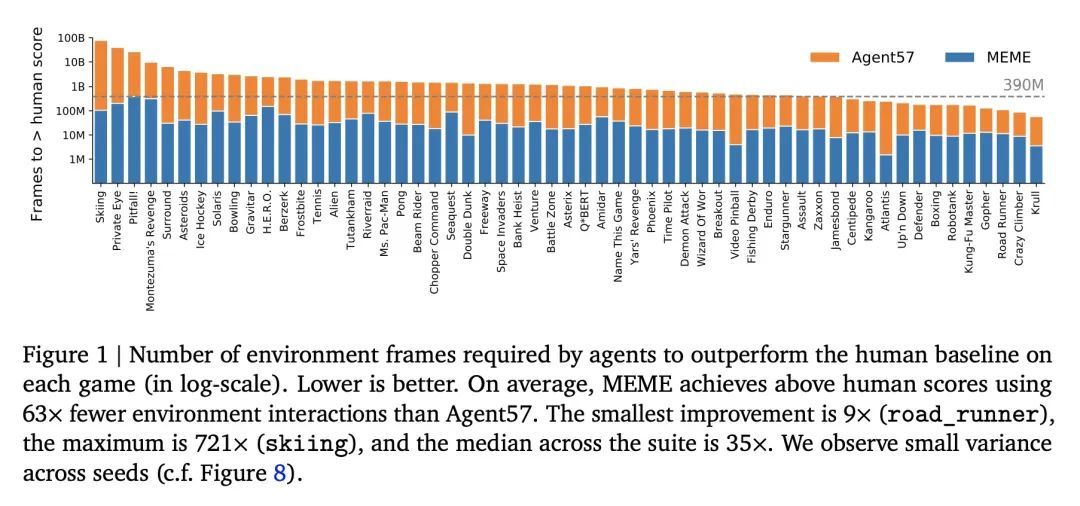


2、[LG] Implicit Bias of Gradient Descent on Reparametrized Models: On Equivalence to Mirror Descent
Z Li, T Wang, JasonD. Lee, S Arora
[Princeton University & Yale University]
重参数化模型梯度下降的隐性偏差:镜像下降的等效性。作为理解过参数化模型中梯度下降的隐性偏差的努力的一部分,一些结果表明过参数化模型上的训练轨迹可以理解为不同目标上的镜像下降。这里的主要结果是在一个被称为换元参数化的概念下对这一现象的描述,它包含了这一背景下的所有之前的结果。结果表明,任何换元参数化的梯度流都等同于具有相关Legendre函数的连续镜像下降。反过来说,具有任何Legendre函数的连续镜像下降可以被视为具有相关换元参数的梯度流。后者的结果依赖于Nash的嵌入定理。
As part of the effort to understand implicit bias of gradient descent in overparametrized models, several results have shown how the training trajectory on the overparametrized model can be understood as mirror descent on a different objective. The main result here is a characterization of this phenomenon under a notion termed commuting parametrization, which encompasses all the previous results in this setting. It is shown that gradient flow with any commuting parametrization is equivalent to continuous mirror descent with a related Legendre function. Conversely, continuous mirror descent with any Legendre function can be viewed as gradient flow with a related commuting parametrization. The latter result relies upon Nash’s embedding theorem.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.04036


3、[LG] Bayesian Optimization over Discrete and Mixed Spaces via Probabilistic Reparameterization
S Daulton, X Wan, D Eriksson…
[University of Oxford & Meta]
基于概率重参数化的离散和混合空间贝叶斯优化。优化离散(且潜在连续)设计参数的昂贵的评估黑箱函数,是科学和工程应用中的一个普遍问题。贝叶斯优化(BO)是一种流行的样本高效方法,通过优化基于概率代理模型的某个域的获取函数(AF)来选择有希望的设计进行评估。然而,在混合或高基数离散搜索空间上最大化AF是个挑战,因为不能使用标准的基于梯度的方法或在搜索空间的每个点上评估AF。为解决这个问题,本文建议用概率重参数化(PR)。不直接优化包含离散参数的搜索空间的自动增益,而是最大化连续参数定义的概率分布的自动增益的期望值。本文证明,在合适的重参数化下,使概率目标最大化的BO策略与使自动增益最大化的策略相同,因此,PR享有与基础自动增益相同的遗憾界。此外,所提出方法可以证明在梯度上升法下收敛到概率目标的静止点,使用的是概率目标及其梯度的可扩展无偏估计,因此,随着起点和梯度步数的增加,所提出方法将恢复到自动增益的最大化(这是常用的BO遗憾界经常被忽略的必要条件)。本文通过经验验证了所提出方法,并在许多真实世界的应用中展示了最先进的优化性能。PR是对最近工作的补充(并使之受益),并自然地推广到具有多目标和黑箱约束的环境中。
Optimizing expensive-to-evaluate black-box functions of discrete (and potentially continuous) design parameters is a ubiquitous problem in scientific and engineering applications. Bayesian optimization (BO) is a popular sample-efficient method that selects promising designs to evaluate by optimizing an acquisition function (AF) over some domain based on a probabilistic surrogate model. However, maximizing the AF over mixed or high-cardinality discrete search spaces is challenging as we cannot use standard gradient-based methods or evaluate the AF at every point in the search space. To address this issue, we propose using probabilistic reparameterization (PR). Instead of directly optimizing the AF over the search space containing discrete parameters, we instead maximize the expectation of the AF over a probability distribution defined by continuous parameters. We prove that under suitable reparameterizations, the BO policy that maximizes the probabilistic objective is the same as that which maximizes the AF, and therefore, PR enjoys the same regret bounds as the underlying AF. Moreover, our approach admits provably converges to a stationary point of the probabilistic objective under gradient ascent using scalable, unbiased estimators of both the probabilistic objective and its gradient, and therefore, as the numbers of starting points and gradient steps increase our approach will recover of a maximizer of the AF (an often neglected requisite for commonly-used BO regret bounds). We validate our approach empirically and demonstrate state-of-the-art optimization performance on many real-world applications. PR is complementary to (and benefits) recent work and naturally generalizes to settings with multiple objectives and black-box constraints.
https://realworldml.github.io/files/cr/paper22.pdf

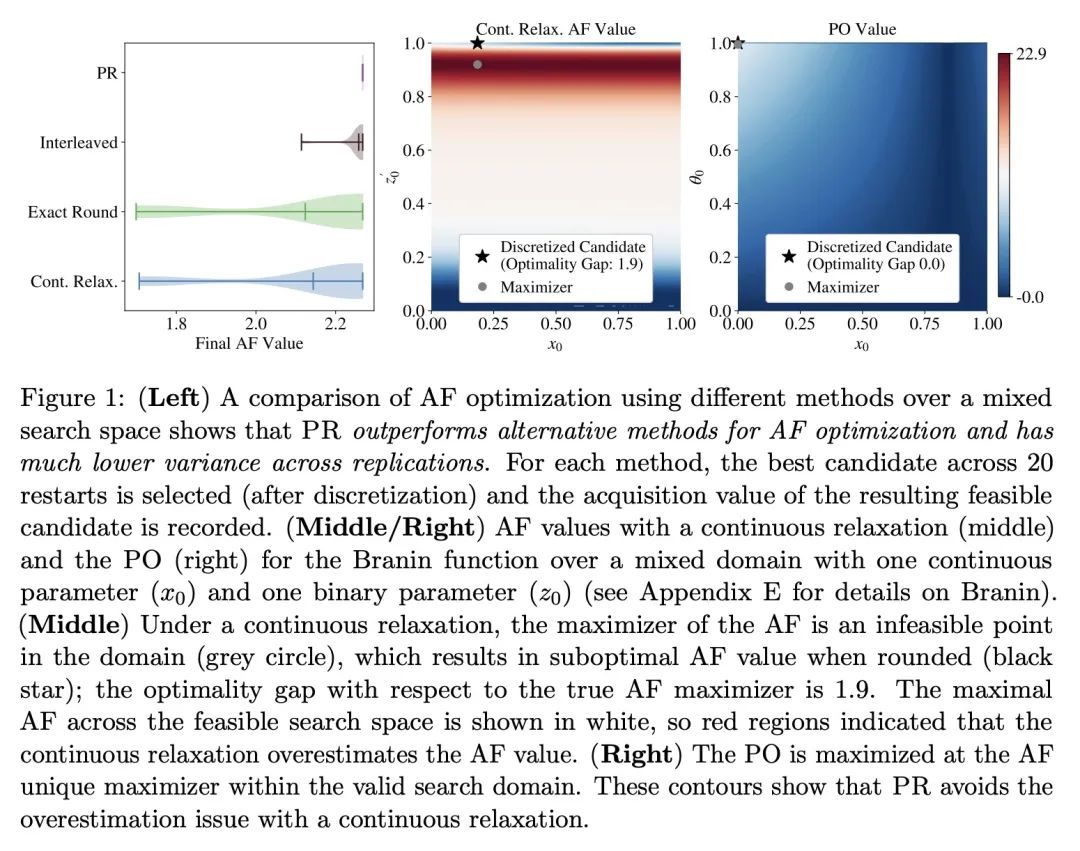
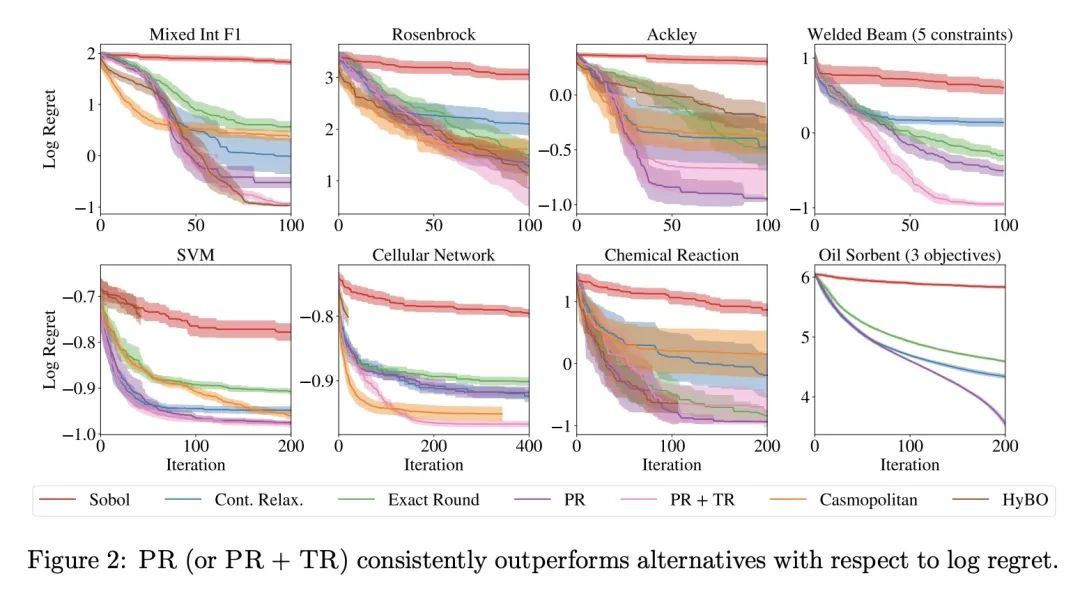
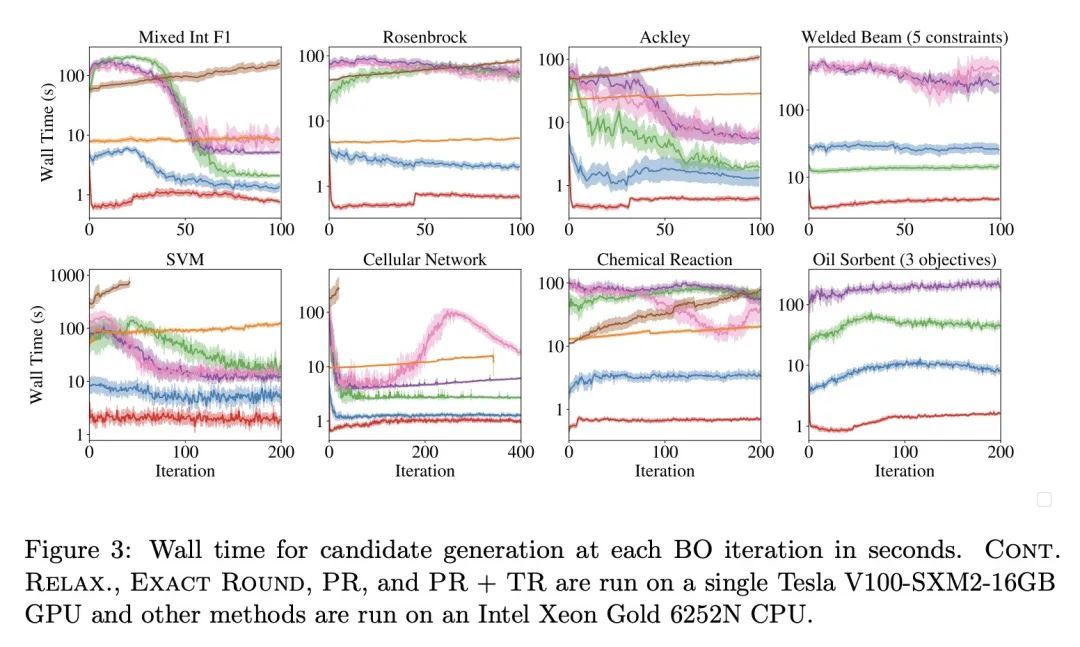
4、[LG] Data Distributional Properties Drive Emergent In-Context Learning in Transformers
S C.Y. Chan, A Santoro, A K. Lampinen, J X. Wang, A Singh, P H. Richemond, J McClelland, F Hill
[DeepMind & University College London]
数据分布属性驱动Transformer的新兴语境学习。基于Transformer的大型模型能进行上下文少样本学习,而不需要进行显式的训练。这一观察提出了一个问题:训练方案的哪些方面导致了这种新兴行为?本文表明,这种行为是由训练数据本身的分布驱动的。当训练数据表现出特殊的分布属性,如突发性(item在集群中出现,而不是在一段时间内均匀分布)和有大量很少出现的类时,就会出现上下文学习。当项目的含义或解释是动态的而不是固定的,上下文学习也会更强烈地出现。这些属性以自然语言为例,但也是其他广泛领域的自然数据所固有的。它们也大大偏离了通常用于标准监督学习的统一的、i.i.d.训练分布。在最初的实验中,本文发现上下文学习与更传统的基于权重的学习进行了权衡,模型无法同时实现两者。然而,我后来的实验中发现,当模型按照倾斜的Zipfian分布训练时,这两种学习模式可以在一个模型中共存——这是包括语言在内的自然数据的另一个共同属性。在进一步的实验中,本文发现自然数据分布只能在Transformer中引起语境学习,而不能在循环模型中引起。总而言之,本文发现表明了Transformer架构是如何与训练数据的特定属性共同作用,驱动大型语言模型耐人寻味的上下文学习行为的,以及未来的工作如何鼓励在语言以外的领域进行上下文学习和权重学习。
Large transformer-based models are able to perform in-context few-shot learning, without being explicitly trained for it. This observation raises the question: what aspects of the training regime lead to this emergent behavior? Here, we show that this behavior is driven by the distributions of the training data itself. In-context learning emerges when the training data exhibits particular distributional properties such as burstiness (items appear in clusters rather than being uniformly distributed over time) and having large numbers of rarely occurring classes. In-context learning also emerges more strongly when item meanings or interpretations are dynamic rather than fixed. These properties are exemplified by natural language, but are also inherent to naturalistic data in a wide range of other domains. They also depart significantly from the uniform, i.i.d. training distributions typically used for standard supervised learning. In our initial experiments, we found that in-context learning traded off against more conventional weight-based learning, and models were unable to achieve both simultaneously. However, our later experiments uncovered that the two modes of learning could co-exist in a single model when it was trained on data following a skewed Zipfian distribution – another common property of naturalistic data, including language. In further experiments, we found that naturalistic data distributions were only able to elicit in-context learning in transformers, and not in recurrent models. In sum, our findings indicate how the transformer architecture works together with particular properties of the training data to drive the intriguing emergent in-context learning behaviour of large language models, and how future work might encourage both in-context and in-weights learning in domains beyond language.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.05055




5、[LG] The Neural Testbed: Evaluating Joint Predictions
I Osband, Z Wen, S M Asghari, V Dwaracherla, B Hao, M Ibrahimi, D Lawson, X Lu, B O'Donoghue, B V Roy
[DeepMind]
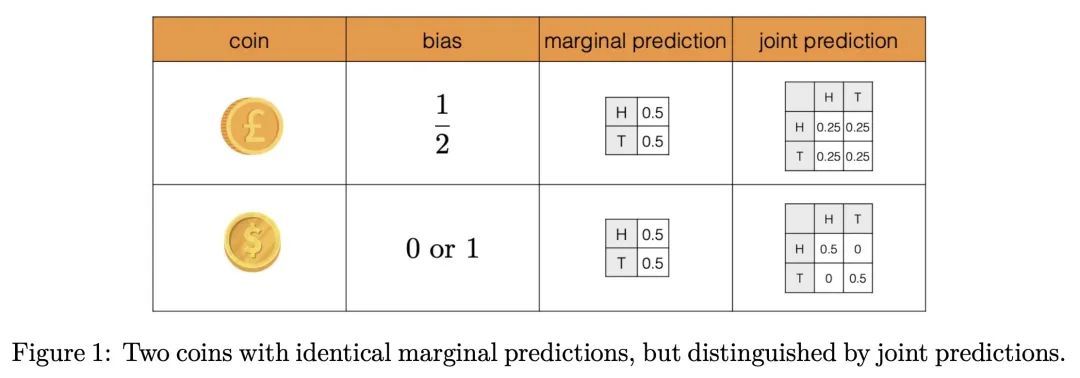
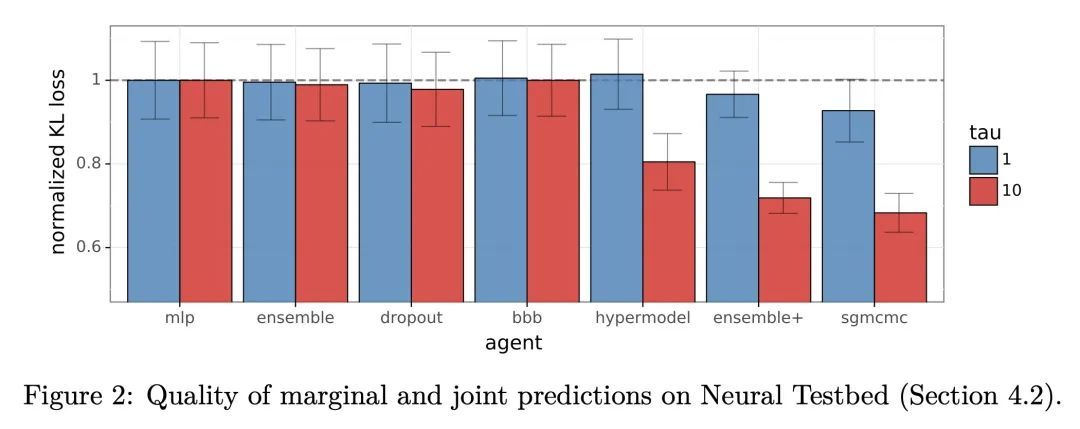
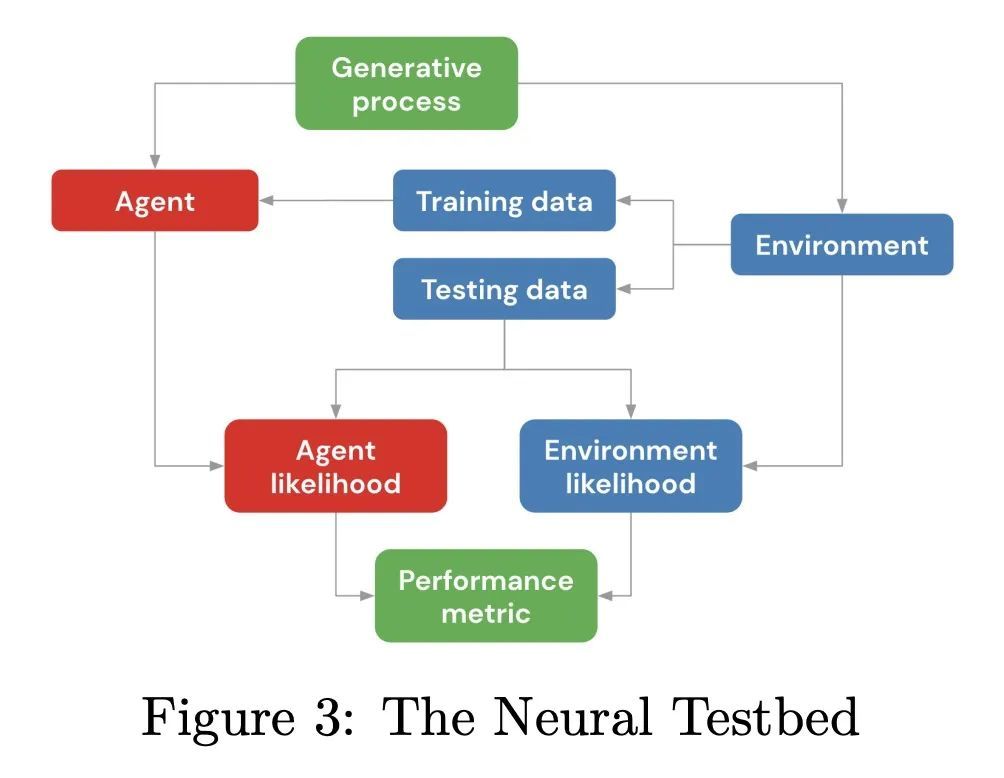
神经试验台:联合预测评估。预测性分布量化了被点估计忽略的不确定性。本文提出神经试验台(Neural Testbed):一个开源基准,用于对产生这种预测的智能体进行控制和原则性的评估。最重要的是,该测试平台不仅评估智能体对每个输入的边际预测的质量,而且还评估它们对许多输入的联合预测。用一个简单的神经网络数据生成过程来评估一系列的智能体。结果表明,一些流行的贝叶斯深度学习智能体在联合预测方面表现不佳,即使它们能够产生准确的边际预测。本文还表明,联合预测的质量推动了下游决策任务的表现。这些结果在选择广泛的生成模型时是鲁棒的,并强调联合预测对社区的实际重要性。
Predictive distributions quantify uncertainties ignored by point estimates. This paper introduces The Neural Testbed: an open-source benchmark for controlled and principled evaluation of agents that generate such predictions. Crucially, the testbed assesses agents not only on the quality of their marginal predictions per input, but also on their joint predictions across many inputs. We evaluate a range of agents using a simple neural network data generating process. Our results indicate that some popular Bayesian deep learning agents do not fare well with joint predictions, even when they can produce accurate marginal predictions. We also show that the quality of joint predictions drives performance in downstream decision tasks. We find these results are robust across choice a wide range of generative models, and highlight the practical importance of joint predictions to the community.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2110.04629v3

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[CV] Unsupervised Domain Adaptation for Semantic Image Segmentation: a Comprehensive Survey
语义图像分割无监督域自适应综述
G Csurka, R Volpi, B Chidlovskii
[Naver Labs Europe]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2112.03241



[LG] ImDrug: A Benchmark for Deep Imbalanced Learning in AI-aided Drug Discovery
ImDrug:AI辅助药物发现深度非平衡学习基准
L Li, L Zeng, Z Gao, S Yuan...
[Tencent AI Lab & The Chinese University of Hong Kong & Hong Kong University of Science and Technology & ...]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.07921


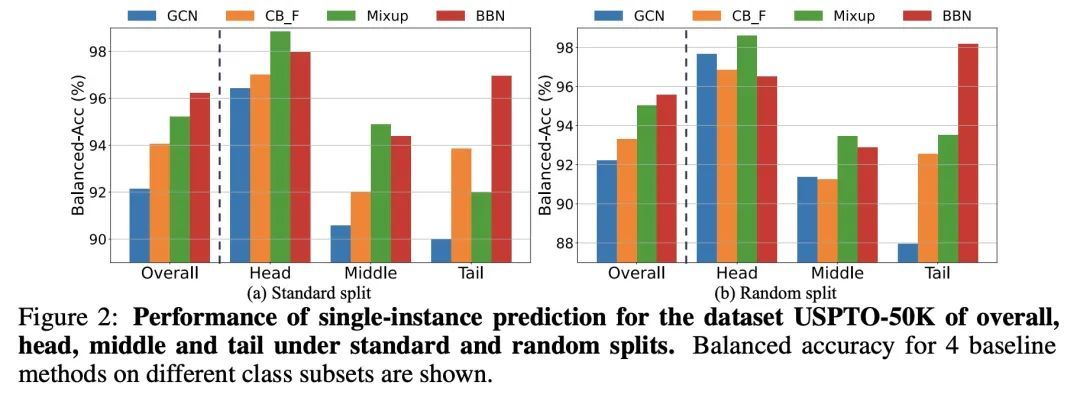

[CL] Text and Patterns: For Effective Chain of Thought, It Takes Two to Tango
思维推理中文本和模式的共生关系
A Madaan, A Yazdanbakhsh
[CMU & Google Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.07686



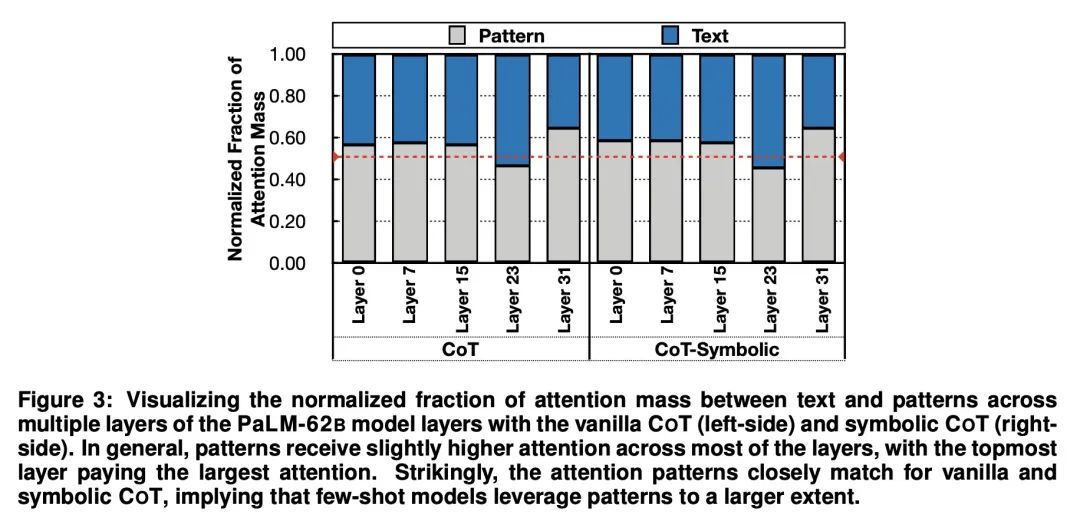
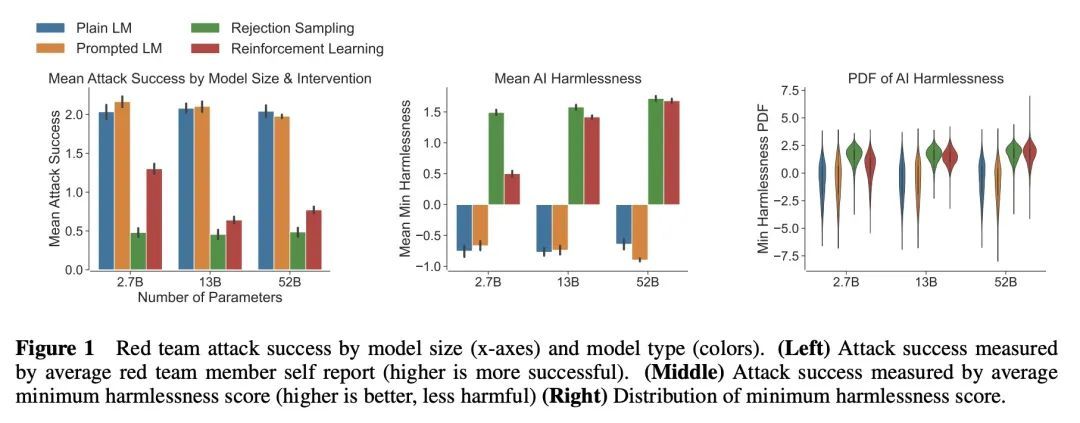
[CL] Red Teaming Language Models to Reduce Harms: Methods, Scaling Behaviors, and Lessons Learned
减少危害的红队语言模型:方法、扩展行为和经验教训
D Ganguli, L Lovitt, J Kernion...
[Anthropic]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.07858



内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢