最近 MICCAI 2022 的论文集开放下载了,地址:https://link.springer.com/book/10.1007/978-3-031-16443-9 ,每个部分的内容如下所示:
Part I: Brain development and atlases; DWI and tractography; functional brain networks; neuroimaging; heart and lung imaging; dermatology;
Part II: Computational (integrative) pathology; computational anatomy and physiology; ophthalmology; fetal imaging;
Part III: Breast imaging; colonoscopy; computer aided diagnosis;
Part IV: Microscopic image analysis; positron emission tomography; ultrasound imaging; video data analysis; image segmentation I;
Part V: Image segmentation II; integration of imaging with non-imaging biomarkers;
Part VI: Image registration; image reconstruction;
Part VII: Image-Guided interventions and surgery; outcome and disease prediction; surgical data science; surgical planning and simulation; machine learning – domain adaptation and generalization;
Part VIII: Machine learning – weakly-supervised learning; machine learning – model interpretation; machine learning – uncertainty; machine learning theory and methodologies.
其中关于分割有两个部分,Image segmentation I 在 Part IV, 而 Image segmentation II 在 Part V。计划对其中开放源代码和典型的方法注意解读,这次要分享的论文是其中的 UNeXt: MLP-based Rapid Medical Image Segmentation Network,arXiv 链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.04967 。
随着医学图像的解决方案变得越来越适用,我们更需要关注使深度网络轻量级、快速且高效的方法。具有高推理速度的轻量级网络可以被部署在手机等设备上,例如 POCUS(point-of-care ultrasound)被用于检测和诊断皮肤状况。这就是 UNeXt 的动机。
方法概述
之前我们解读过基于 Transformer 的 U-Net 变体,近年来一直是领先的医学图像分割方法,但是参数量往往不乐观,计算复杂,推理缓慢。这篇文章提出了基于卷积多层感知器(MLP)改进 U 型架构的方法,可以用于图像分割。设计了一个 tokenized MLP 块有效地标记和投影卷积特征,使用 MLPs 来建模表示。这个结构被应用到 U 型架构的下两层中(这里我们假设纵向一共五层)。文章中提到,为了进一步提高性能,建议在输入到 MLP 的过程中改变输入的通道,以便专注于学习局部依赖关系特征。还有额外的设计就是跳跃连接了,并不是我们主要关注的地方。最终,UNeXt 将参数数量减少了 72 倍,计算复杂度降低了 68 倍,推理速度提高了 10 倍,同时还获得了更好的分割性能,如下图所示。
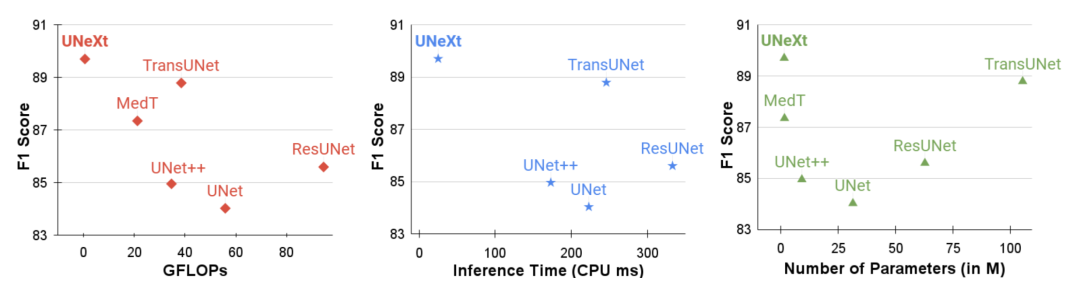
UNeXt 架构
UNeXt 的设计如下图所示。纵向来看,一共有两个阶段,普通的卷积和 Tokenized MLP 阶段。其中,编码器和解码器分别设计两个 Tokenized MLP 块。每个编码器将分辨率降低两倍,解码器工作相反,还有跳跃连接结构。每个块的通道数(C1-C5)被设计成超参数为了找到不掉点情况下最小参数量的网络,对于使用 UNeXt 架构的实验,遵循 C1 = 32、C2 = 64、C3 = 128、C4 = 160 和 C5 = 256。
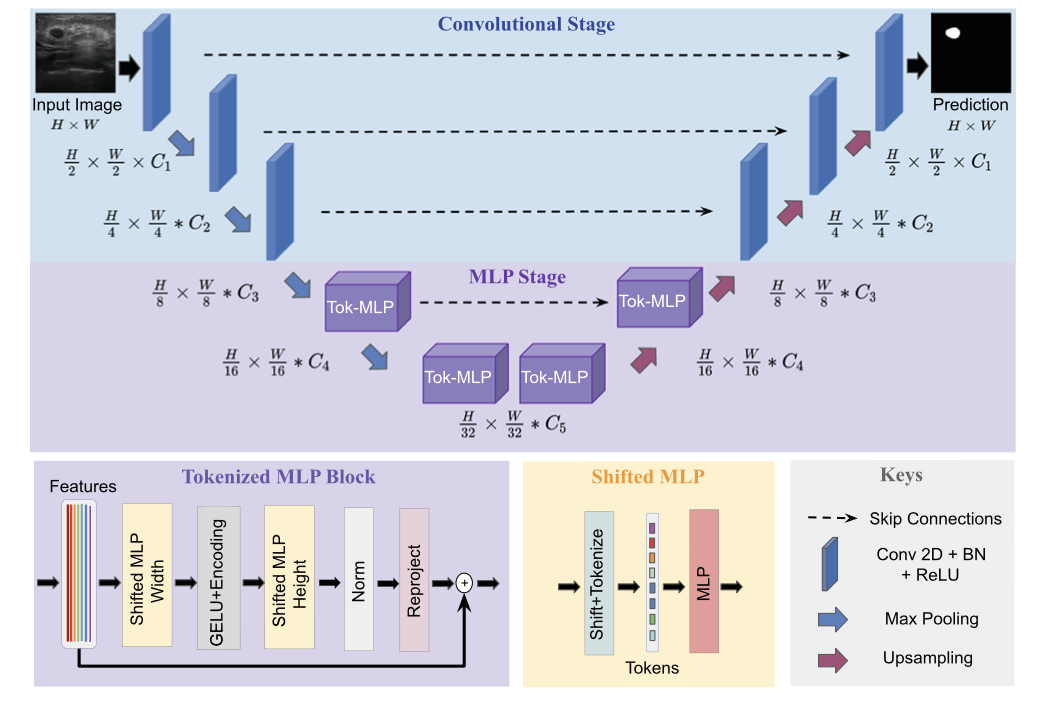
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢