LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:基于神经网络检查点生成模型的学习方式学习、GPT-3时代的新闻摘要与评估、基于去噪的分子特性预测预训练、蕴含语义可从理想语言模型中提取、基于运动学习和局部导航端到端的高级技能、面向从像素进行数据高效控制的基于无监督模型的预训练、FPGA上的神经隐写和数字水印加速、上下文学习和归纳头、人工生命中的涌现
1、[LG] Learning to Learn with Generative Models of Neural Network Checkpoints
W Peebles, I Radosavovic, T Brooks, A A. Efros, J Malik
[UC Berkeley]
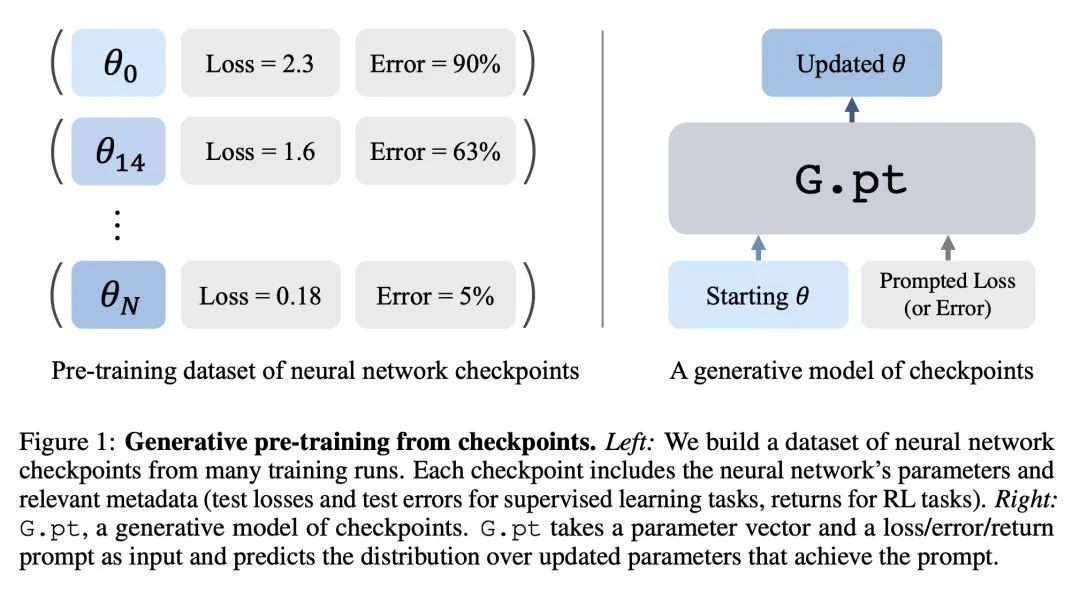
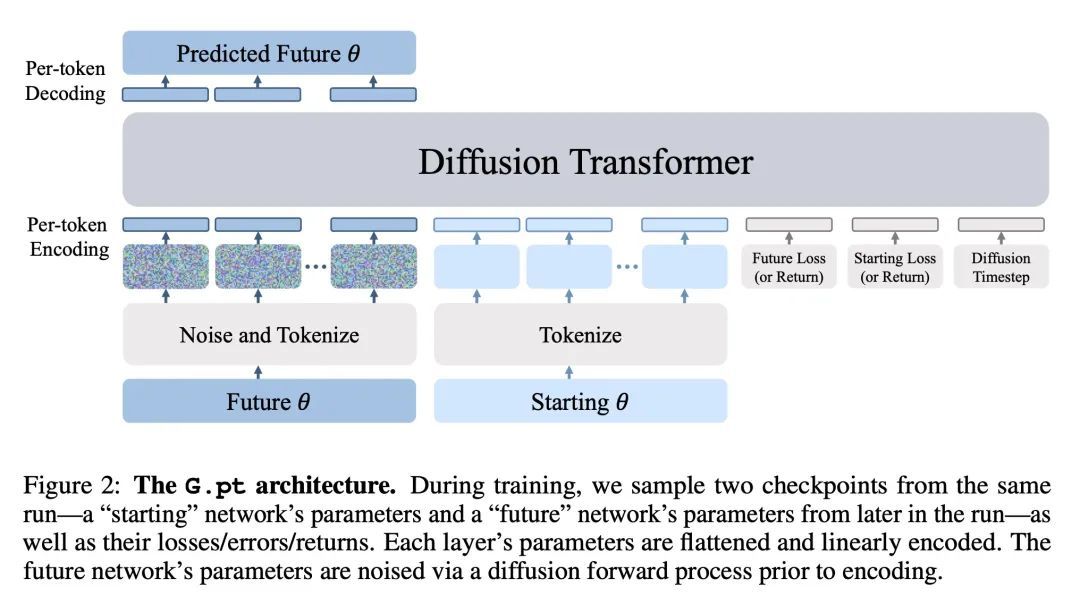
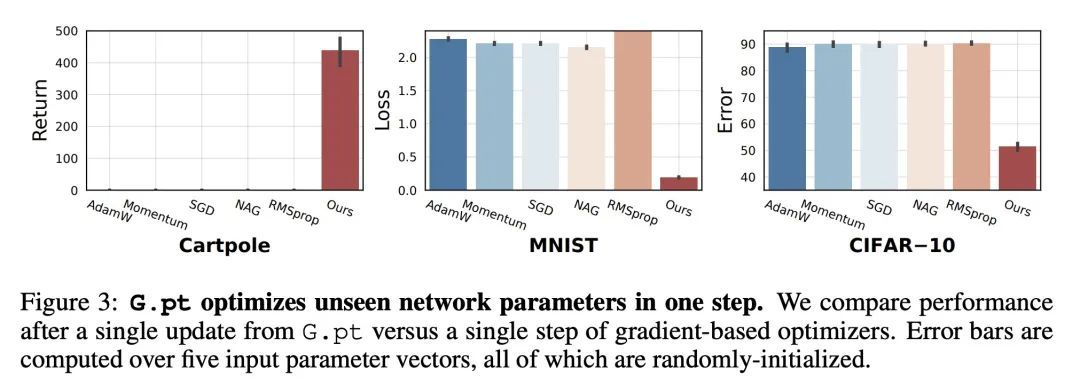
基于神经网络检查点生成模型的学习方式学习。本文探索了一种数据驱动的学习方法,以优化神经网络,构建一个神经网络检查点数据集,并对参数进行生成模型训练。特别是,所述模型是一种条件扩散Transformer,给定一个初始输入参数向量和一个提示的损失、错误或回报,预测实现预期指标的参数更新的分布。测试时,它可以在一次更新中用未见过的参数优化下游任务的神经网络。该方法成功生成了广泛的损失提示的参数。此外,其可以对多模态的参数解决方案进行采样,并具有有利的缩放特性。本文将所提出方法应用于不同的神经网络架构和监督与强化学习的任务。
We explore a data-driven approach for learning to optimize neural networks. We construct a dataset of neural network checkpoints and train a generative model on the parameters. In particular, our model is a conditional diffusion transformer that, given an initial input parameter vector and a prompted loss, error, or return, predicts the distribution over parameter updates that achieve the desired metric. At test time, it can optimize neural networks with unseen parameters for downstream tasks in just one update. We find that our approach successfully generates parameters for a wide range of loss prompts. Moreover, it can sample multimodal parameter solutions and has favorable scaling properties. We apply our method to different neural network architectures and tasks in supervised and reinforcement learning.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.12892

2、[CL] News Summarization and Evaluation in the Era of GPT-3
T Goyal, J J Li, G Durrett
[The University of Texas at Austin]
GPT-3时代的新闻摘要与评估。最近,GPT-3等模型在零样本和少样本提示方面的成功,带来了NLP研究的范式转变。本文研究了它对文本摘要的影响,重点是新闻摘要这一经典基准领域。首先,本文调研了GPT-3与在大型摘要数据集上训练的微调模型的比较情况。结果表明,不仅人类压倒性地喜欢GPT-3摘要,而且这些摘要也不存在常见的数据集的特定问题,如事实性差。接下来,本文研究这对评估意味着什么,特别是黄金标准测试集的作用。实验表明,基于参考的和无参考的自动指标,例如最近提出的基于QA或蕴含的事实性方法,都不能可靠地评估零样本的摘要。最后,本文讨论了通用摘要之外的未来研究挑战,特别是基于关键词和方面的摘要,展示了主流的微调方法与零样本提示的比较。为了支持进一步的研究,本文发布了:(a)一个由4个标准摘要基准的微调模型和零样本模型生成的1万条摘要的语料库;(b)1千条人类偏好判断和理由,比较不同的通用摘要和基于关键词的摘要系统。
The recent success of zeroand few-shot prompting with models like GPT-3 has led to a paradigm shift in NLP research. In this paper, we study its impact on text summarization, focusing on the classic benchmark domain of news summarization. First, we investigate how zero-shot GPT-3 compares against finetuned models trained on large summarization datasets. We show that not only do humans overwhelmingly prefer GPT-3 summaries, but these also do not suffer from common datasetspecific issues such as poor factuality. Next, we study what this means for evaluation, particularly the role of gold standard test sets. Our experiments show that both reference-based and reference-free automatic metrics, e.g. recently proposed QAor entailment-based factuality approaches, cannot reliably evaluate zero-shot summaries. Finally, we discuss future research challenges beyond generic summarization, specifically, keywordand aspectbased summarization, showing how dominant fine-tuning approaches compare to zero-shot prompting. To support further research, we release: (a) a corpus of 10K generated summaries from fine-tuned and zero-shot models across 4 standard summarization benchmarks, (b) 1K human preference judgments and rationales comparing different systems for genericand keyword-based summarization.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.12356



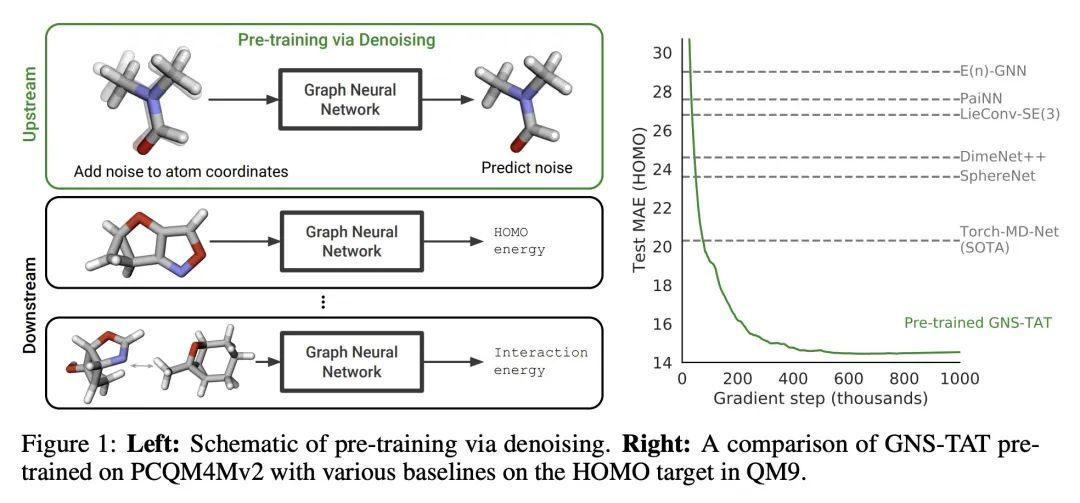
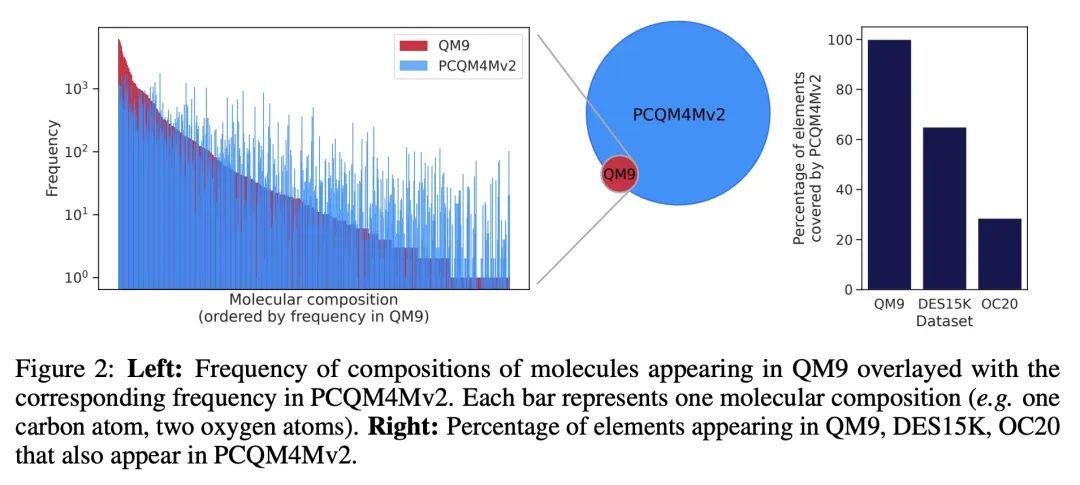
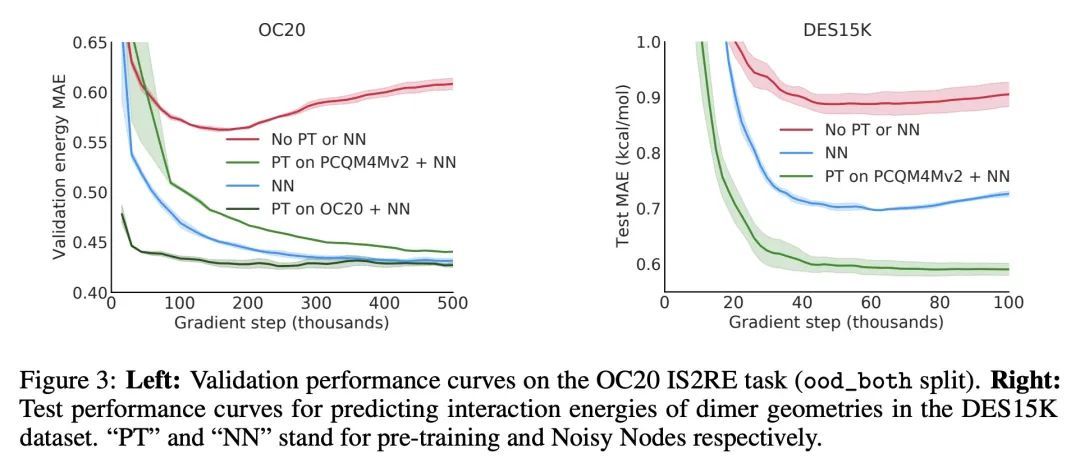
3、[LG] Pre-training via Denoising for Molecular Property Prediction
S Zaidi, M Schaarschmidt, J Martens, H Kim, Y W Teh, A Sanchez-Gonzalez, P Battaglia, R Pascanu, J Godwin
[University of Oxford & DeepMind]
基于去噪的分子特性预测预训练。许多涉及3D结构分子特性预测的重要问题的数据是有限的,这给神经网络的泛化带来了挑战。本文描述了一种预训练技术,利用平衡状态下的3D分子结构的大型数据集,为下游任务学习有意义的表示。受最近噪声正则化进展的启发,所提预训练目标是基于去噪。依靠去噪自编码器和分数匹配之间众所周知的联系,本文还表明,该目标对应于直接从平衡结构中学习分子力场——产生于用高斯混合近似物理状态分布。实验表明,用这个预训练目标可以大大改善多个基准的性能,在广泛使用的QM9数据集中的大多数目标上达到了新的最先进水平。然后,分析提供了关于不同因素——数据集大小、模型大小和结构、以及上游和下游数据集的选择——对预训练的影响的实用见解。
Many important problems involving molecular property prediction from 3D structures have limited data, posing a generalization challenge for neural networks. In this paper, we describe a pre-training technique that utilizes large datasets of 3D molecular structures at equilibrium to learn meaningful representations for downstream tasks. Inspired by recent advances in noise regularization, our pre-training objective is based on denoising. Relying on the well-known link between denoising autoencoders and score-matching, we also show that the objective corresponds to learning a molecular force field – arising from approximating the physical state distribution with a mixture of Gaussians – directly from equilibrium structures. Our experiments demonstrate that using this pre-training objective significantly improves performance on multiple benchmarks, achieving a new state-of-the-art on the majority of targets in the widely used QM9 dataset. Our analysis then provides practical insights into the effects of different factors – dataset sizes, model size and architecture, and the choice of upstream and downstream datasets – on pre-training.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.00133

4、[CL] Entailment Semantics Can Be Extracted from an Ideal Language Model
W Merrill, A Warstadt, T Linzen
[New York University & ETH Zürich]
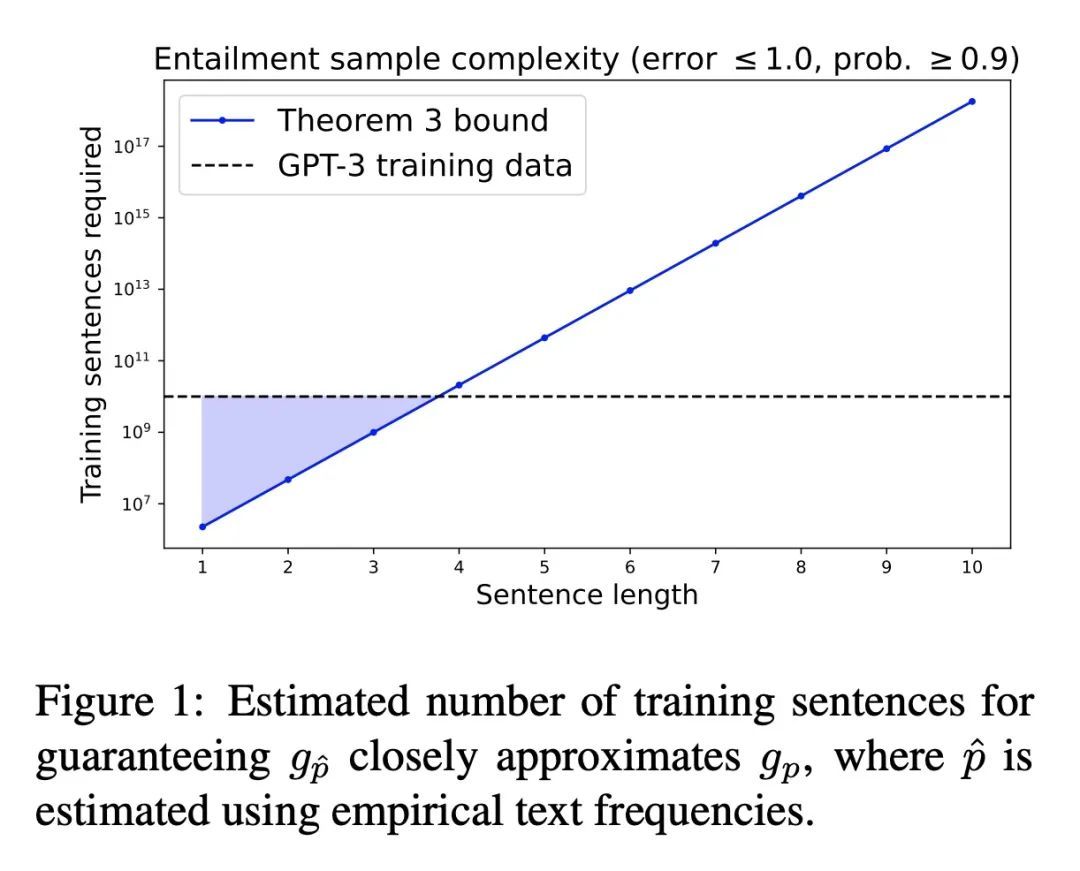
蕴含语义可从理想语言模型中提取。语言模型通常只在文本上进行训练,没有额外的基础。对于从这样的程序中能推断出多少自然语言的语义,人们有争议。本文证明了句子之间的连带判断可以从理想语言模型中提取出来,该模型已经完美地学习了其目标分布,假设训练句子是由Gricean智能体生成的,即遵循语用学语言理论中的基本交流原则的智能体。本文还表明,连带判断可以从在这种Gricean数据上训练的语言模型的预测中解读出来。所示结果揭示了理解无标签语言数据所编码的语义信息的途径以及从语言模型中提取语义的潜在框架。
Language models are often trained on text alone, without additional grounding. There is debate as to how much of natural language semantics can be inferred from such a procedure. We prove that entailment judgments between sentences can be extracted from an ideal language model that has perfectly learned its target distribution, assuming the training sentences are generated by Gricean agents, i.e., agents who follow fundamental principles of communication from the linguistic theory of pragmatics. We also show entailment judgments can be decoded from the predictions of a language model trained on such Gricean data. Our results reveal a pathway for understanding the semantic information encoded in unlabeled linguistic data and a potential framework for extracting semantics from language models.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.12407

5、[RO] Advanced Skills by Learning Locomotion and Local Navigation End-to-End
N Rudin, D Hoeller, M Bjelonic, M Hutter
[ETH Zurich]
基于运动学习和局部导航端到端的高级技能。四足机器人在具有挑战性的环境中进行局部导航的常见方法需要路径规划、路径跟踪和运动,这通常需要一个运动控制策略来准确跟踪指令速度。然而,通过将导航问题分解成这些子任务,限制了机器人的能力,因为各个任务并没有考虑完整的解空间。本文建议通过训练一个具有深度强化学习的端到端策略来解决整个问题。机器人需要在规定时间内到达目标位置,而不是持续跟踪预先计算的路径。任务的成功与否只在一轮结束时被评估,这意味着策略不需要尽可能快地到达目标。它可以自由选择其路径和运动步态。以这种方式训练一个策略,可以开辟出更大的可能解决方案,从而使机器人能够学习更复杂的行为。将所提方法与速度跟踪进行了比较,另外还表明,任务奖励的时间依赖性对于成功学习这些新行为至关重要。最后,本文展示了在一个真正的四足机器人上成功部署的政策。该机器人能够穿越具有挑战性的地形,这在之前是不可能的,同时使用更节能的步态并取得更高的成功率。
The common approach for local navigation on challenging environments with legged robots requires path planning, path following and locomotion, which usually requires a locomotion control policy that accurately tracks a commanded velocity. However, by breaking down the navigation problem into these sub-tasks, we limit the robot’s capabilities since the individual tasks do not consider the full solution space. In this work, we propose to solve the complete problem by training an end-to-end policy with deep reinforcement learning. Instead of continuously tracking a precomputed path, the robot needs to reach a target position within a provided time. The task’s success is only evaluated at the end of an episode, meaning that the policy does not need to reach the target as fast as possible. It is free to select its path and the locomotion gait. Training a policy in this way opens up a larger set of possible solutions, which allows the robot to learn more complex behaviors. We compare our approach to velocity tracking and additionally show that the time dependence of the task reward is critical to successfully learn these new behaviors. Finally, we demonstrate the successful deployment of policies on a real quadrupedal robot. The robot is able to cross challenging terrains, which were not possible previously, while using a more energy-efficient gait and achieving a higher success rate. Supplementary videos can be found on the project website: https://sites.google.com/ leggedrobotics.com/end-to-end-loco-navigation
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.12827

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
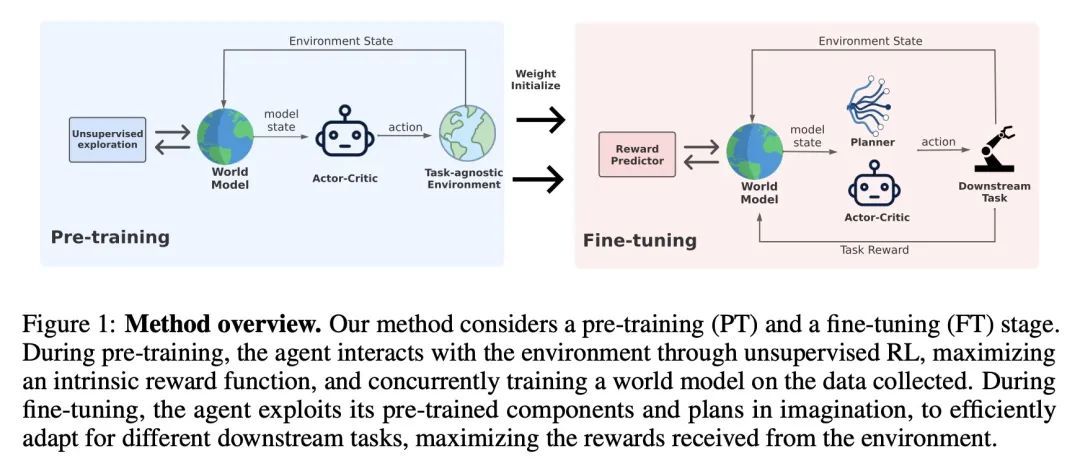
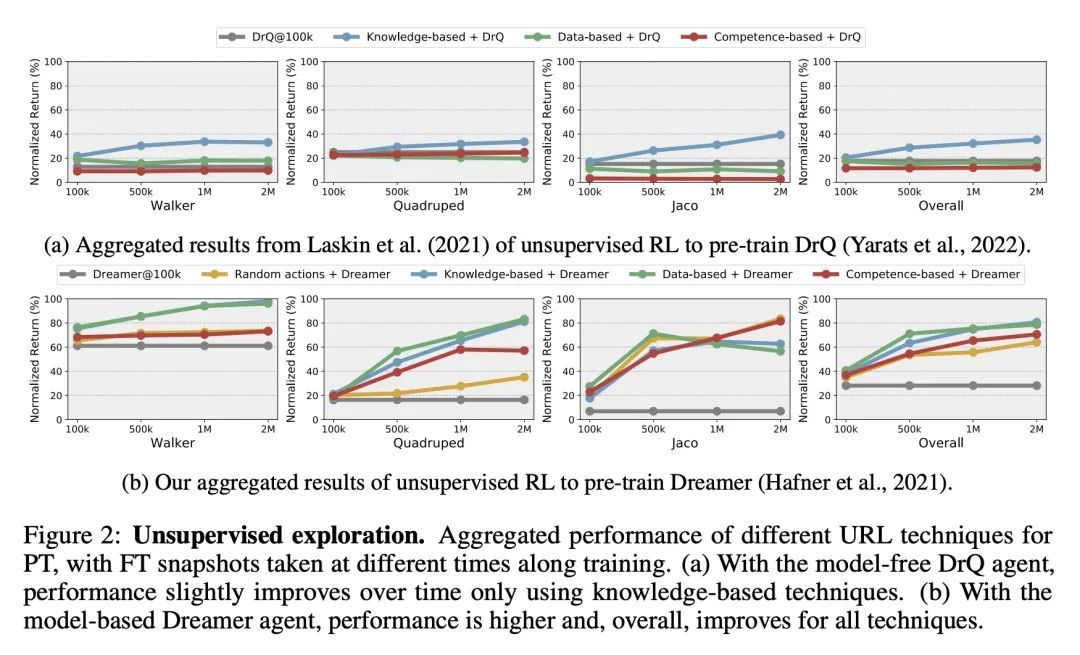
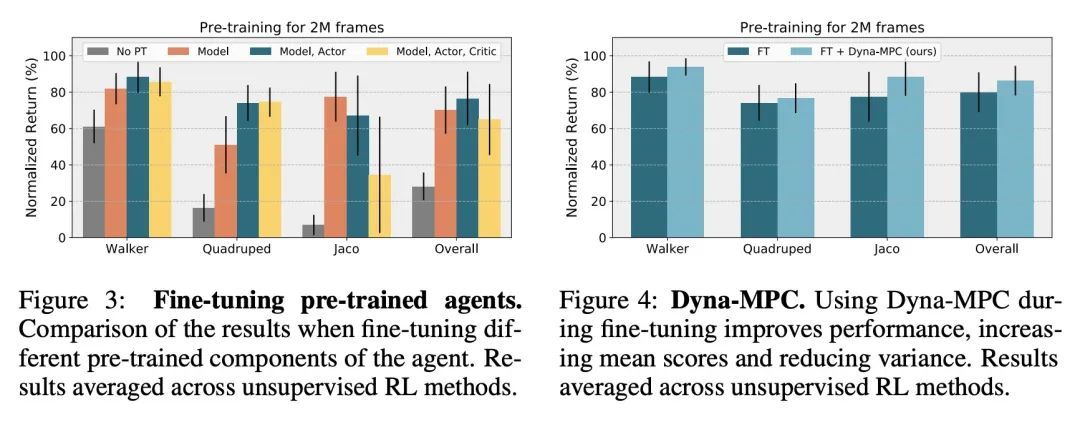
[LG] Unsupervised Model-based Pre-training for Data-efficient Control from Pixels
面向从像素进行数据高效控制的基于无监督模型的预训练
S Rajeswar, P Mazzaglia, T Verbelen, A Piché, B Dhoedt, A Courville, A Lacoste
[Mila & Ghent University & ServiceNow Research] https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.12016

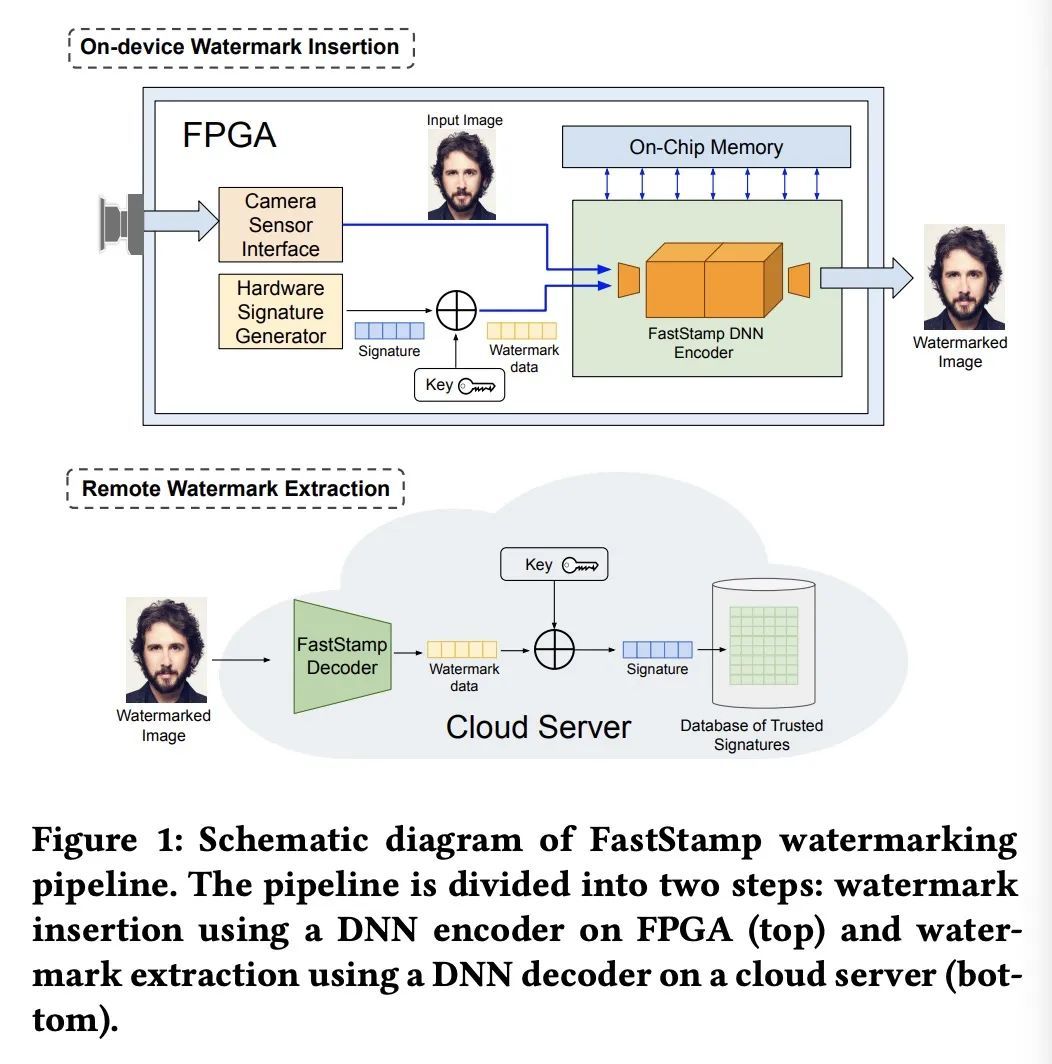
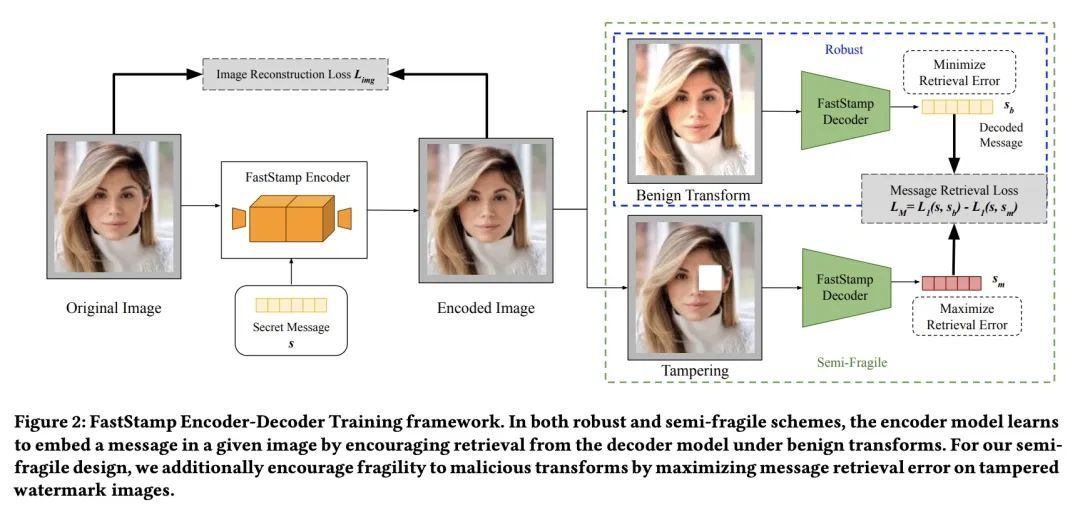
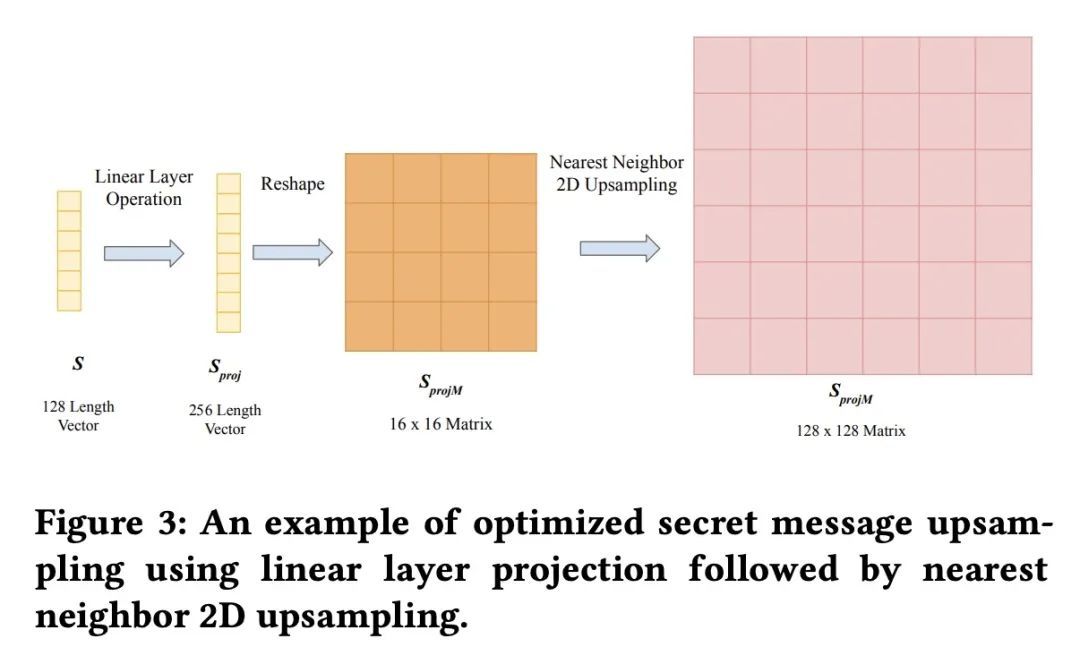
[CV] FastStamp: Accelerating Neural Steganography and Digital Watermarking of Images on FPGAs
FastStamp: FPGA上的神经隐写和数字水印加速
S Hussain, N Sheybani, P Neekhara, X Zhang, J Duarte, F Koushanfar
[UC San Diego]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.12391

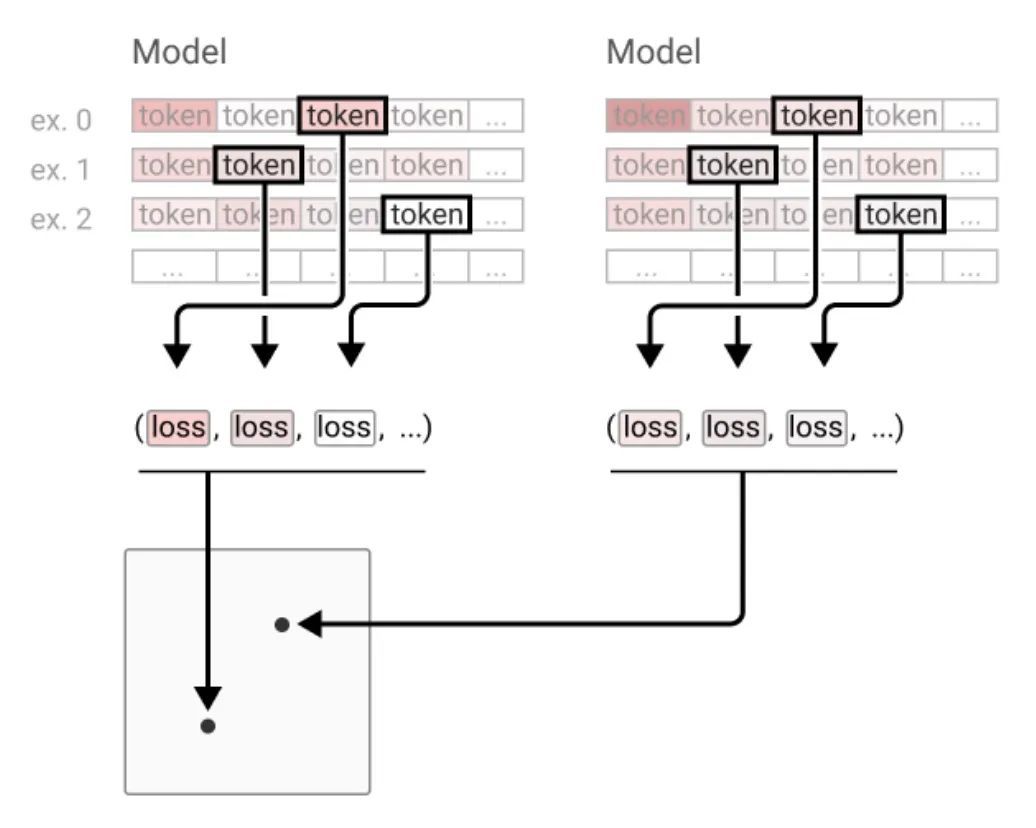
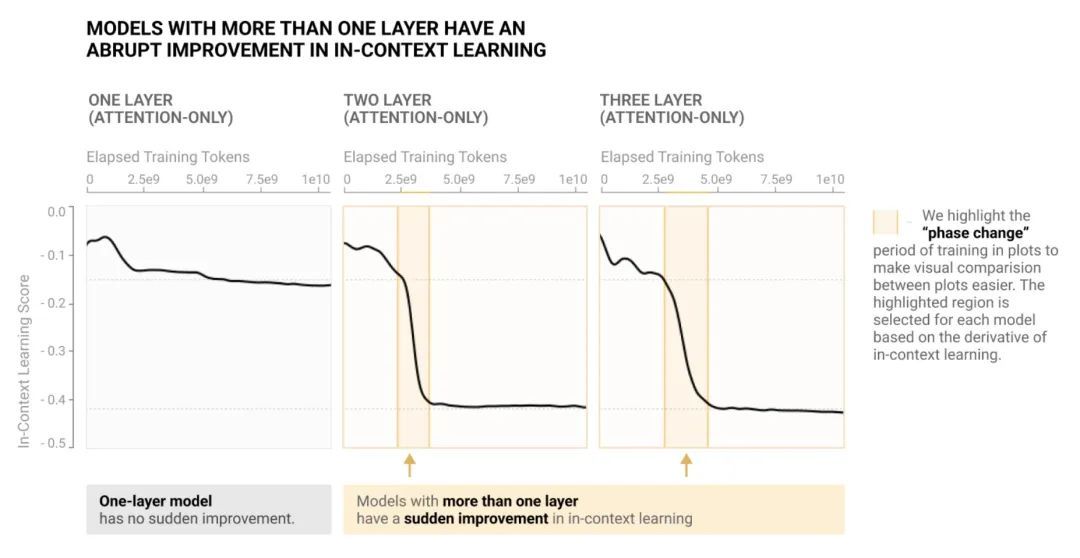
[LG] In-context Learning and Induction Heads
上下文学习和归纳头
C Olsson, N Elhage, N Nanda, N Joseph…
[Anthropic]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.11895


[LG] Emergence in artificial life
人工生命中的涌现
C Gershenson
[Universidad Nacional Autonoma de Mexico] https://arxiv.org/abs/2105.03216

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢