LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:无需文本-视频数据的文本-视频生成、面向图生成的离散去噪扩散、通过生成式建模获得无限高质量MIR数据、基于大型语言模型的组合语义解析、面向无人驾驶的实时雷达障碍物和自由空间检测、基于稀疏单目捕捉数据的实际动态场景完整视图合成、基于SGD的神经网络低维表示高效学习、面向上下文词获取的语言模型探测、基于多级训练的极小极大最优核算子学习
1、[CV] Make-A-Video: Text-to-Video Generation without Text-Video Data
U Singer, A Polyak, T Hayes, X Yin, J An, S Zhang, Q Hu, H Yang, O Ashual, O Gafni, D Parikh, S Gupta, Y Taigman
[Meta AI & University of Rochester]
Make-A-Video:无需文本-视频数据的文本-视频生成。本文提出Make-A-Video——一种直接将最近在文本-图像(T2I)生成中取得的巨大进展转化到文本-视频(T2V)的方法。其直觉很简单:从成对的文本-图像数据中学习世界的样子和描述方式,并从无监督的视频片段中学习世界的运动方式。Make-A-Video有三个优点:(1)它加速了T2V模型的训练(不需要从头开始学习视觉和多模态表示),(2)不需要成对的文本-视频数据,以及(3)生成的视频继承了当今图像生成模型的宏大性(审美多样性、幻想描述等)。本文设计了一种简单而有效的方法,在T2I模型的基础上建立新的有效的空间-时间模块。首先,分解了完整的时间性U-Net和注意力张量,并在空间和时间上对它们进行了近似。其次,设计了一个空间时间管线,通过视频解码器、插值模型和两个超分辨率模型生成高分辨率和帧率的视频,可实现除T2V之外的各种应用。在所有方面,空间和时间分辨率、对文本的忠实度和质量,Make-A-Video设定了文本到视频生成的新的最先进水平,定性和定量皆是如此。
We propose Make-A-Video – an approach for directly translating the tremendous recent progress in Text-to-Image (T2I) generation to Text-to-Video (T2V). Our intuition is simple: learn what the world looks like and how it is described from paired text-image data, and learn how the world moves from unsupervised video footage. Make-A-Video has three advantages: (1) it accelerates training of the T2V model (it does not need to learn visual and multimodal representations from scratch), (2) it does not require paired text-video data, and (3) the generated videos inherit the vastness (diversity in aesthetic, fantastical depictions, etc.) of today’s image generation models. We design a simple yet effective way to build on T2I models with novel and effective spatial-temporal modules. First, we decompose the full temporal U-Net and attention tensors and approximate them in space and time. Second, we design a spatial temporal pipeline to generate high resolution and frame rate videos with a video decoder, interpolation model and two super resolution models that can enable various applications besides T2V. In all aspects, spatial and temporal resolution, faithfulness to text, and quality, Make-A-Video sets the new state-of-the-art in text-to-video generation, as determined by both qualitative and quantitative measures.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.14792




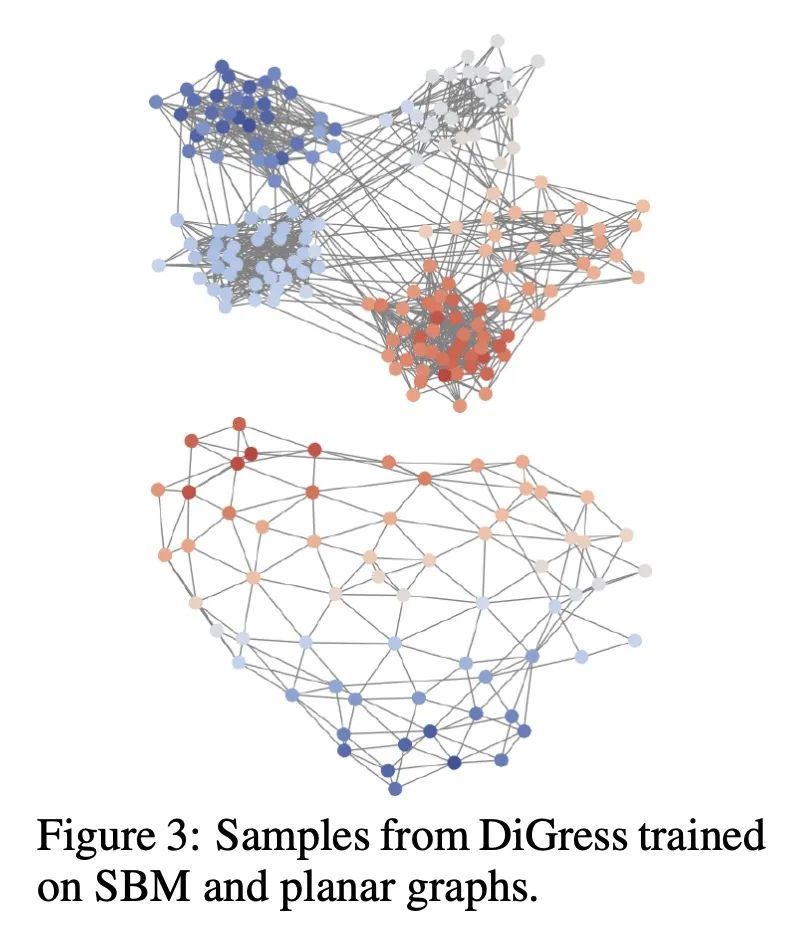
2、[LG] DiGress: Discrete Denoising diffusion for graph generation
C Vignac, I Krawczuk, A Siraudin, B Wang, V Cevher, P Frossard
[EPFL]
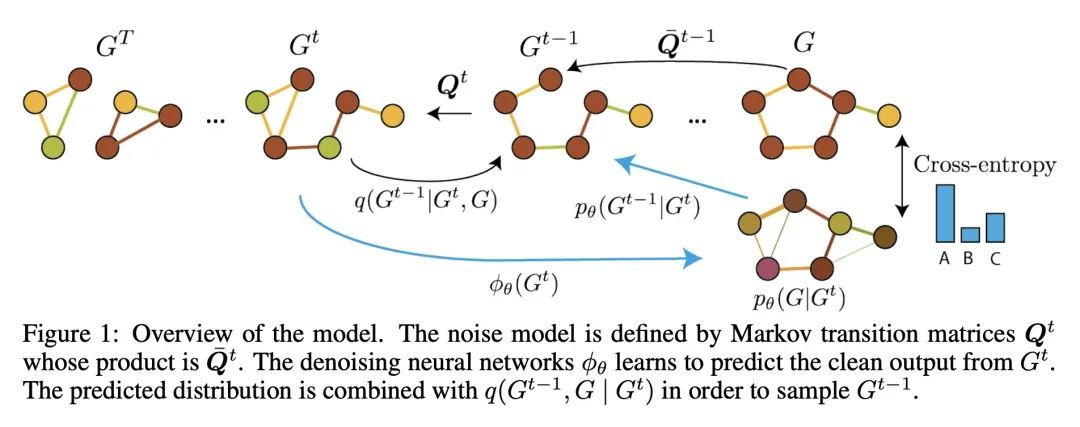
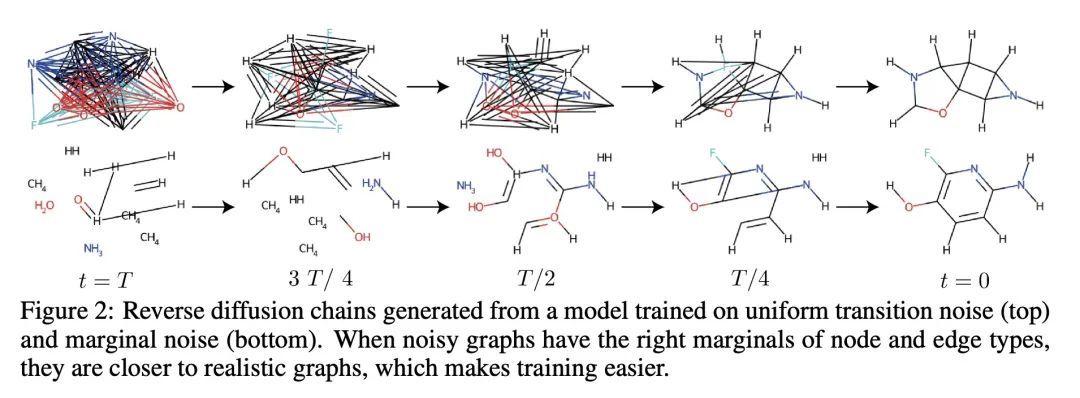
DIGRESS: 面向图生成的离散去噪扩散。本文介绍DiGress,一种用于生成具有分类节点和边缘属性的图的离散去噪扩散模型。该模型定义了一个逐步编辑带有噪声的图的扩散过程(添加或删除边缘,改变类别),以及一个学习恢复这一过程的图变换器网络。有了这两个成分,将图上的分布学习减少到一个简单的分类任务序列。通过提出一种新的马尔科夫噪声模型,在扩散过程中保留节点和边缘类型的边际分布,并在每个扩散步骤中添加从噪声图中得到的辅助图论特征,进一步提高样本质量。最后,提出一个指导程序,用于调节图层面特征的生成。总的来说,DiGress在分子和非分子数据集上都达到了最先进的性能,在平面图的数据集上有高达3倍的有效性改进。特别是,它是第一个可以扩展到包含130万种药物类分子的大型GuacaMol数据集的模型,而没有使用SMILES或片段等分子特定的表示方法。
This work introduces DiGress, a discrete denoising diffusion model for generating graphs with categorical node and edge attributes. Our model defines a diffusion process that progressively edits a graph with noise (adding or removing edges, changing the categories), and a graph transformer network that learns to revert this process. With these two ingredients in place, we reduce distribution learning over graphs to a simple sequence of classification tasks. We further improve sample quality by proposing a new Markovian noise model that preserves the marginal distribution of node and edge types during diffusion, and by adding auxiliary graph-theoretic features derived from the noisy graph at each diffusion step. Finally, we propose a guidance procedure for conditioning the generation on graph-level features. Overall, DiGress achieves state-of-the-art performance on both molecular and non-molecular datasets, with up to 3x validity improvement on a dataset of planar graphs. In particular, it is the first model that scales to the large GuacaMol dataset containing 1.3M drug-like molecules without using a molecule-specific representation such as SMILES or fragments.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.14734


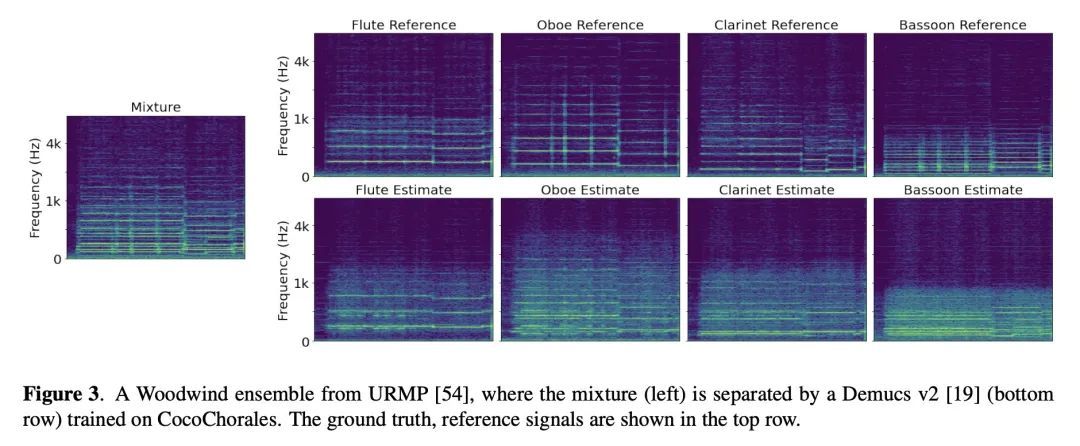
3、[AS] The Chamber Ensemble Generator: Limitless High-Quality MIR Data via Generative Modeling
Y Wu, J Gardner, E Manilow, I Simon, C Hawthorne, J Engel
[Université de Montréal & University of Washington & Google Research]
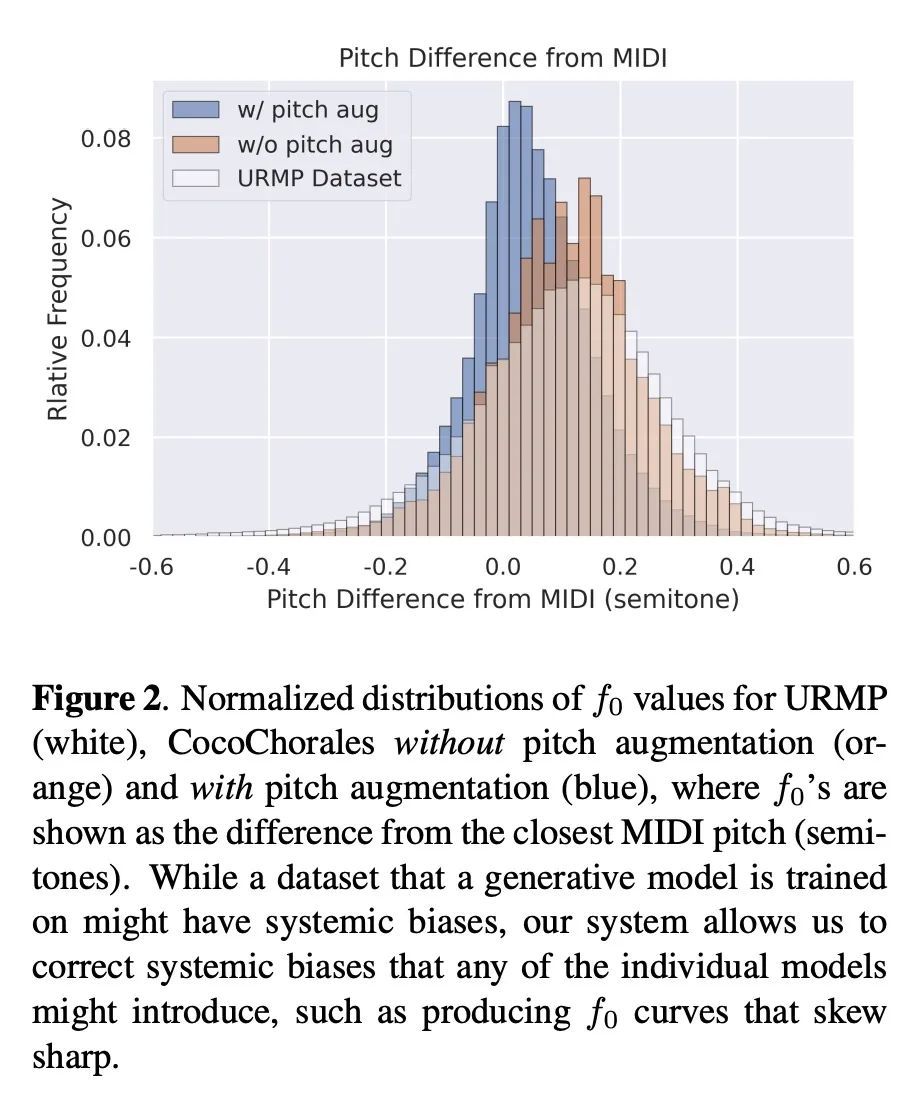
室内乐合奏发生器:通过生成式建模获得无限高质量MIR数据。数据是现代机器学习系统的命脉,包括那些音乐信息检索(MIR)系统。然而,长期以来,MIR一直被小数据集和不可靠的标签所困扰。本文建议用生成式建模来打破这一瓶颈。通过将音符的生成模型在巴赫众赞歌数据集上训练的Coconet)与室内乐团的结构化合成模型(在URMP上训练的MIDI-DDSP)进行管道连接,展示了一个能产生无限量的具有丰富标注的真实合唱团音乐的系统,包括混音、音源、MIDI、音符级的表演属性(顿挫、颤音等),甚至是细粒度的合成参数(音高、振幅等)。将该系统称为室内乐团生成器(CEG),并用它来生成四个不同的室内乐团(CocoChorales)的大型合唱数据集。实验证明了用该方法生成的数据改善了音乐转录和音源分离的先进模型。
Data is the lifeblood of modern machine learning systems, including for those in Music Information Retrieval (MIR). However, MIR has long been mired by small datasets and unreliable labels. In this work, we propose to break this bottleneck using generative modeling. By pipelining a generative model of notes (Coconet trained on Bach Chorales) with a structured synthesis model of chamber ensembles (MIDI-DDSP trained on URMP), we demonstrate a system capable of producing unlimited amounts of realistic chorale music with rich annotations including mixes, stems, MIDI, note-level performance attributes (staccato, vibrato, etc.), and even fine-grained synthesis parameters (pitch, amplitude, etc.). We call this system the Chamber Ensemble Generator (CEG), and use it to generate a large dataset of chorales from four different chamber ensembles (CocoChorales). We demonstrate that data generated using our approach improves state-of-theart models for music transcription and source separation, and we release both the system and the dataset as an opensource foundation for future work in the MIR community.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.14458


4、[CL] Compositional Semantic Parsing with Large Language Models
A Drozdov, N Schärli, E Akyuürek, N Scales, X Song, X Chen, O Bousquet, D Zhou
[Google Research]
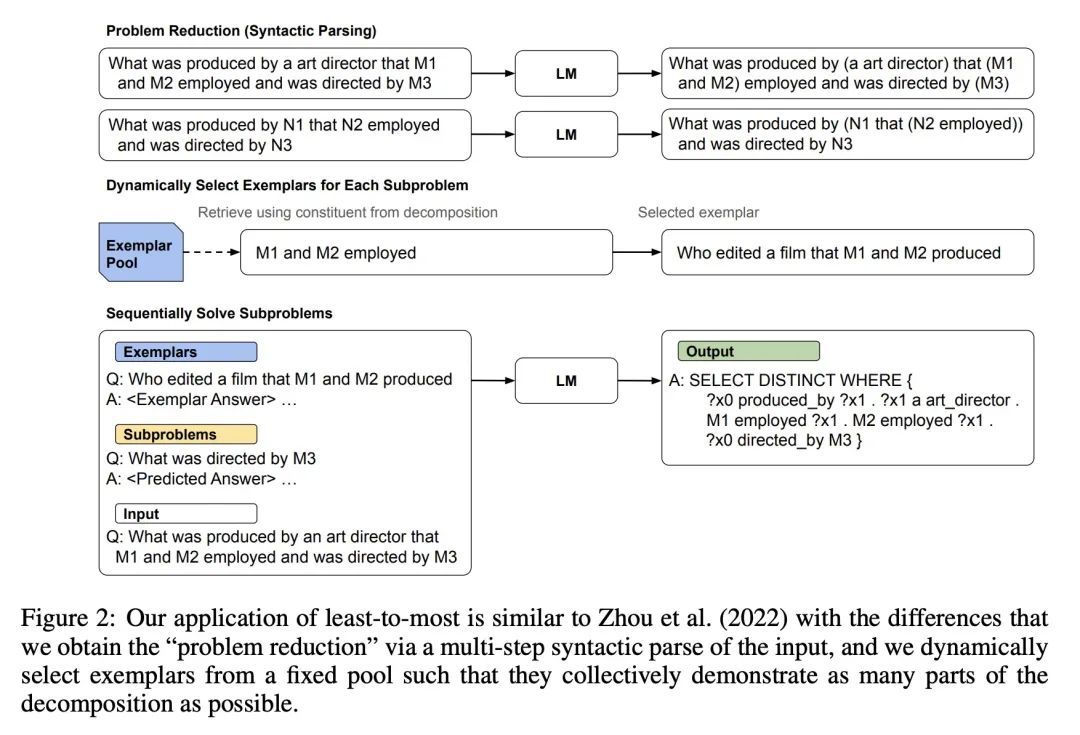
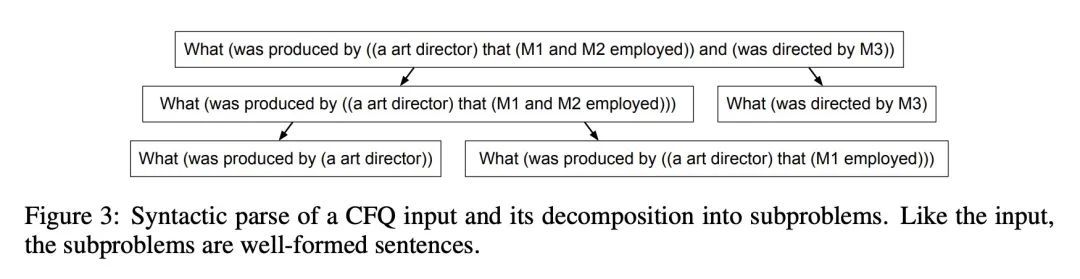
基于大型语言模型的组合语义解析。人类在面对新任务时可以进行组合推理。之前的研究表明,适当的提示技术使大型语言模型(LLM)能解决诸如SCAN这样的人工合成泛化任务。本文确定了在具有更大词汇量的更现实的语义解析任务中的额外挑战,并完善了这些提示技术以解决这些问题。最好的方法是基于最小到最大的提示:用基于提示的句法解析对问题进行分解,然后用这种分解来选择适当的示例,并依次生成语义解析。这种方法使得能为CFQ达到一个新的技术水平,同时只需要传统方法所用的1%的训练数据。由于该方法的通用性,预计类似的努力将在其他任务和领域中带来新的结果,特别是对于知识密集型应用。
Humans can reason compositionally when presented with new tasks. Previous research shows that appropriate prompting techniques enable large language models (LLMs) to solve artificial compositional generalization tasks such as SCAN. In this work, we identify additional challenges in more realistic semantic parsing tasks with larger vocabulary and refine these prompting techniques to address them. Our best method is based on least-to-most prompting: it decomposes the problem using prompting-based syntactic parsing, then uses this decomposition to select appropriate exemplars and to sequentially generate the semantic parse. This method allows us to set a new state of the art for CFQ while requiring only 1% of the training data used by traditional approaches. Due to the general nature of our approach, we expect similar efforts will lead to new results in other tasks and domains, especially for knowledge-intensive applications.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.15003


5、[CV] NVRadarNet: Real-Time Radar Obstacle and Free Space Detection for Autonomous Driving
A Popov, P Gebhardt, K Chen, R Oldja, H Lee, S Murray, R Bhargava, N Smolyanskiy
[NVIDIA]
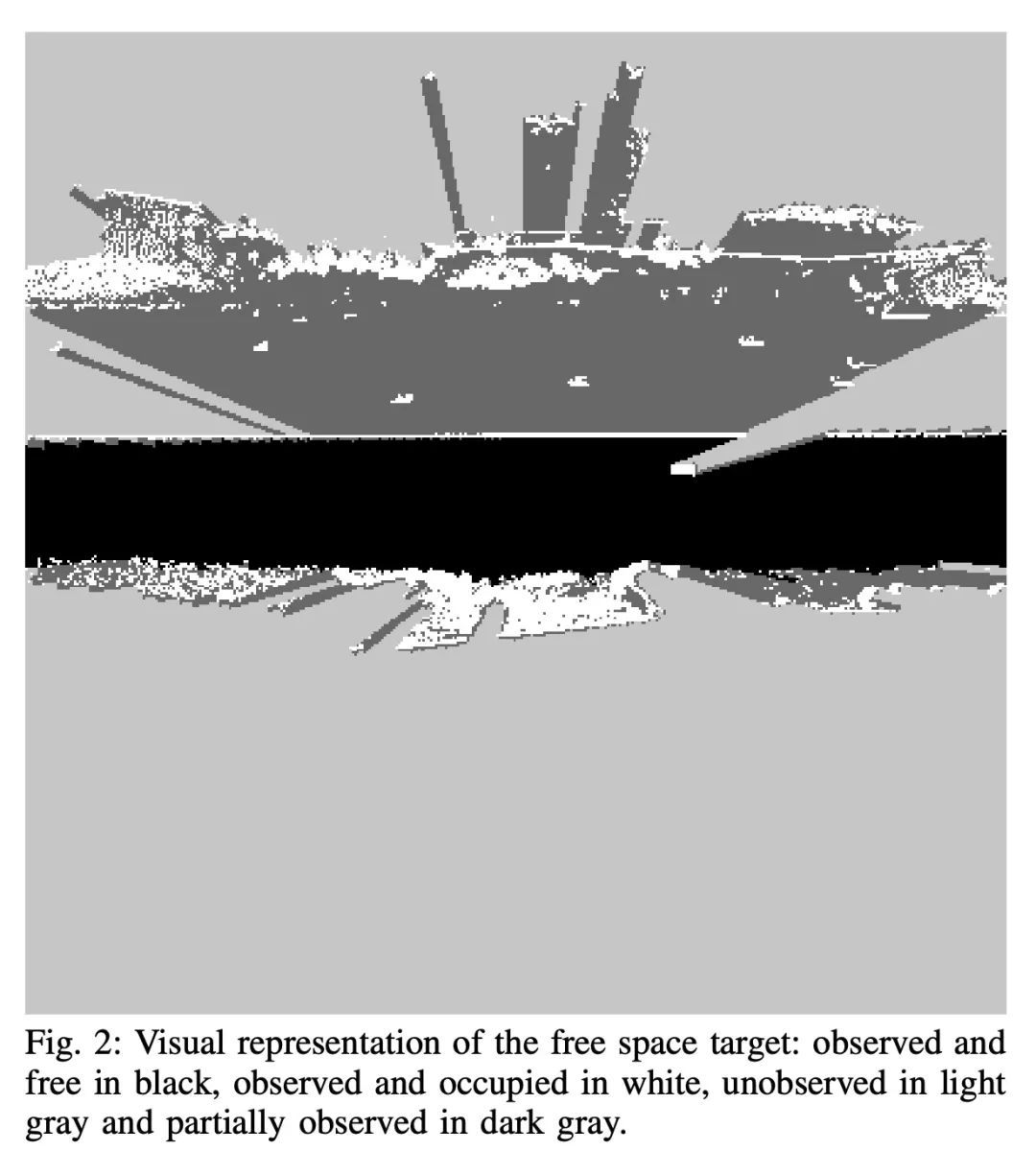
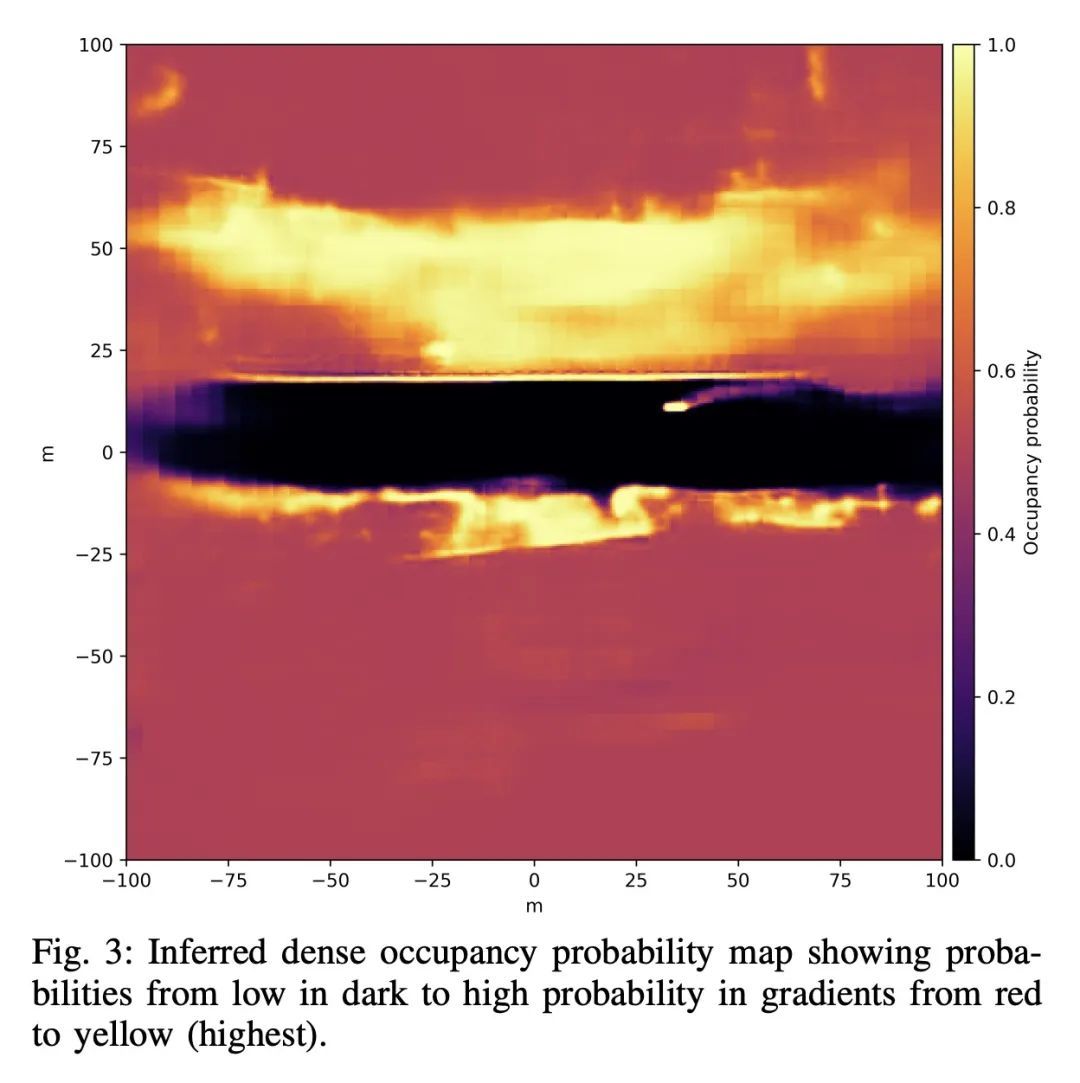
NVRadarNet: 面向无人驾驶的实时雷达障碍物和自由空间检测。检测障碍物对于安全和高效的无人驾驶至关重要。为此,本文提出NVRadarNet,一种深度神经网络(DNN),利用汽车雷达传感器检测动态障碍物和可驾驶自由空间。该网络利用来自多个雷达传感器的时间累积数据来检测动态障碍物,并在自上而下的鸟瞰图(BEV)中计算其方向。该网络还对可驾驶自由空间进行回归,以检测未分类的障碍物。该DNN是第一个利用稀疏RADAR信号,以便从RADAR数据中实时进行障碍物和自由空间检测。该网络已被成功地用于自主车辆在实际自驾场景中的感知。该网络在嵌入式GPU上的运行速度比实时快,并且在不同的地理区域显示出良好的泛化性。
Detecting obstacles is crucial for safe and efficient autonomous driving. To this end, we present NVRadarNet, a deep neural network (DNN) that detects dynamic obstacles and drivable free space using automotive RADAR sensors. The network utilizes temporally accumulated data from multiple RADAR sensors to detect dynamic obstacles and compute their orientation in a top-down bird’s-eye view (BEV). The network also regresses drivable free space to detect unclassified obstacles. Our DNN is the first of its kind to utilize sparse RADAR signals in order to perform obstacle and free space detection in real time from RADAR data only. The network has been successfully used for perception on our autonomous vehicles in real self-driving scenarios. The network runs faster than real time on an embedded GPU and shows good generalization across geographic regions.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.14499


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
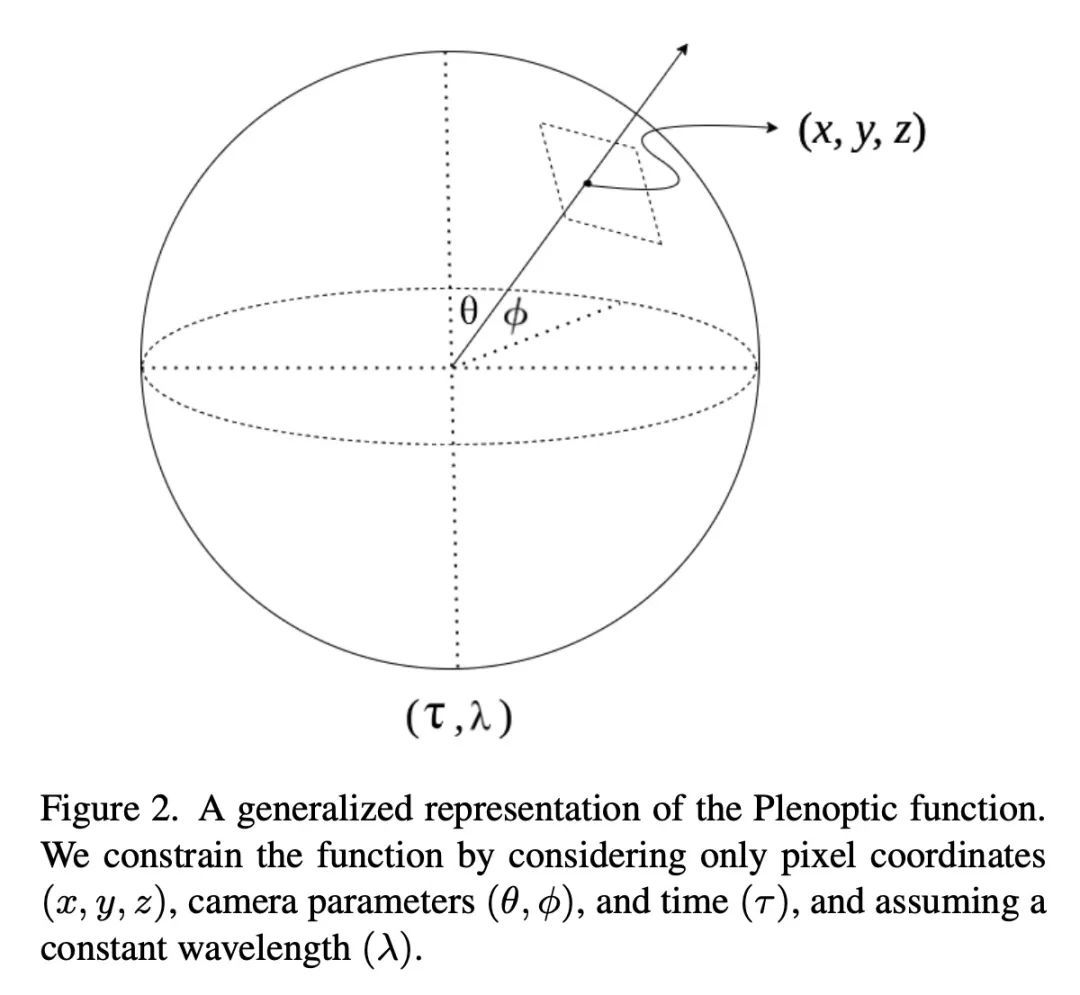
[CV] wildNeRF: Complete view synthesis of in-the-wild dynamic scenes captured using sparse monocular data
wildNeRF:基于稀疏单目捕捉数据的实际动态场景完整视图合成
S Khalid, F Rudzicz
[University of Toronto]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.10399


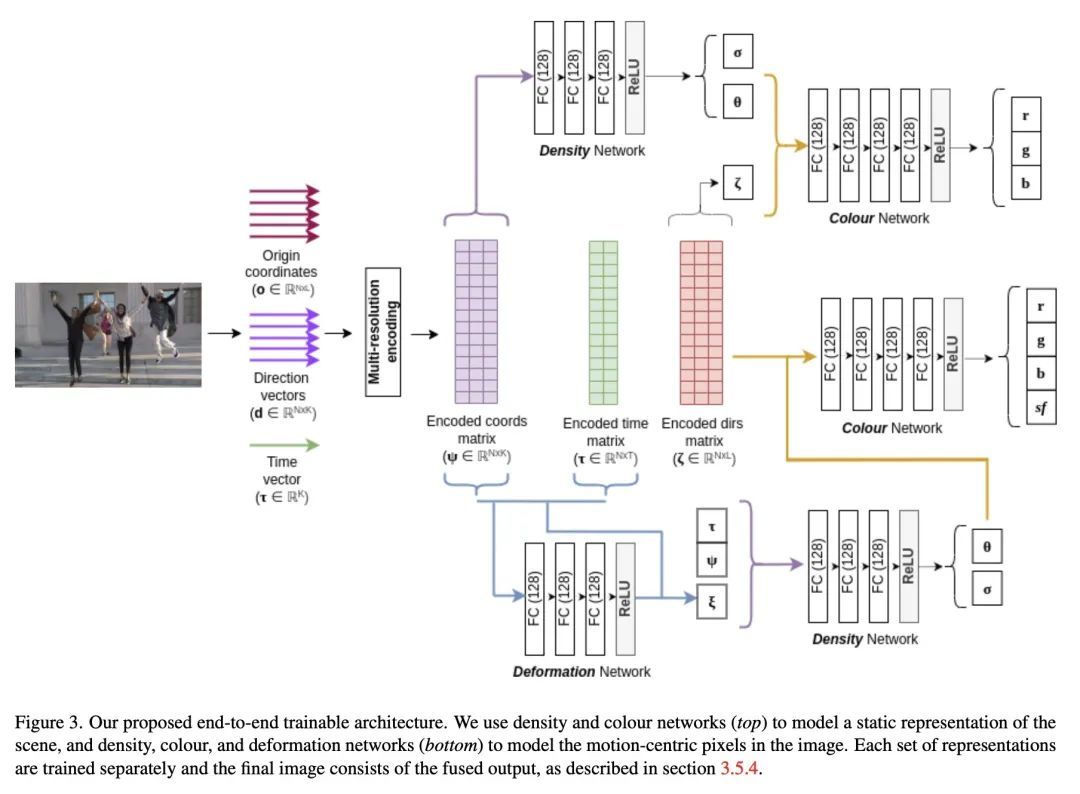
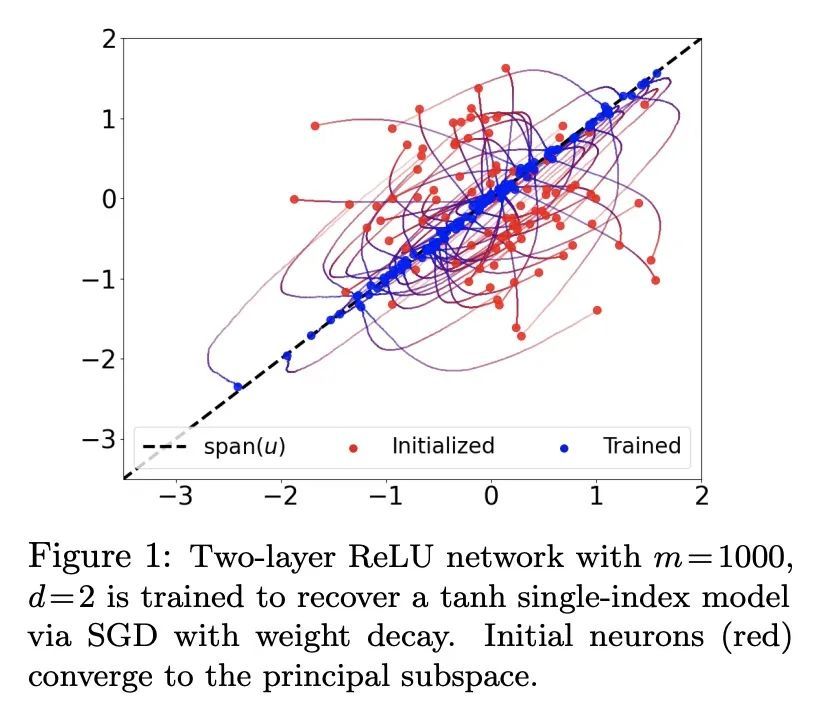
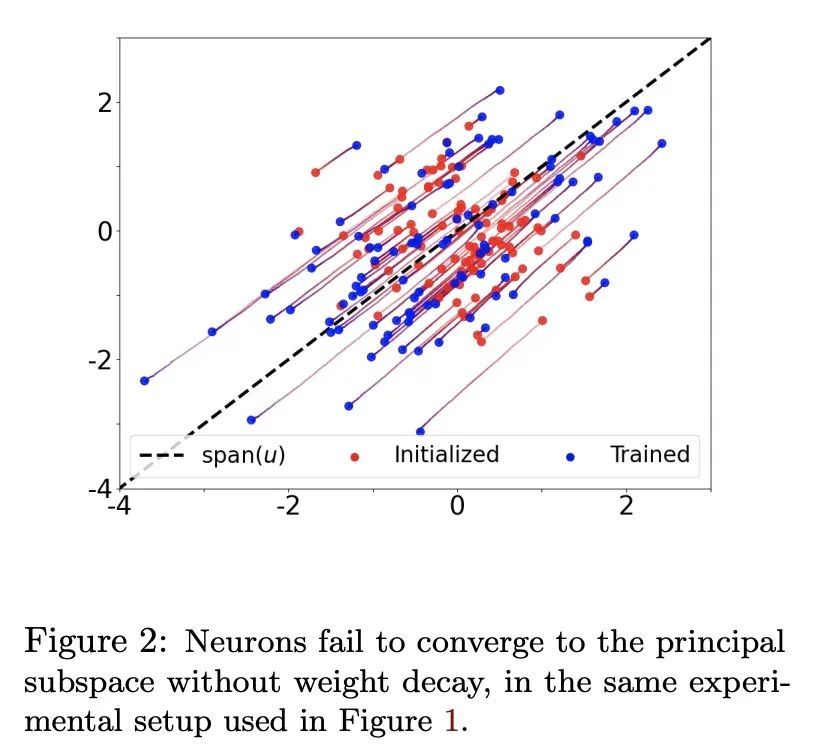
[LG] Neural Networks Efficiently Learn Low-Dimensional Representations with SGD
基于SGD的神经网络低维表示高效学习
A Mousavi-Hosseini, S Park, M Girotti...
[University of Toronto & Korea University & Saint Mary’s University & Universite de Montreal]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.14863

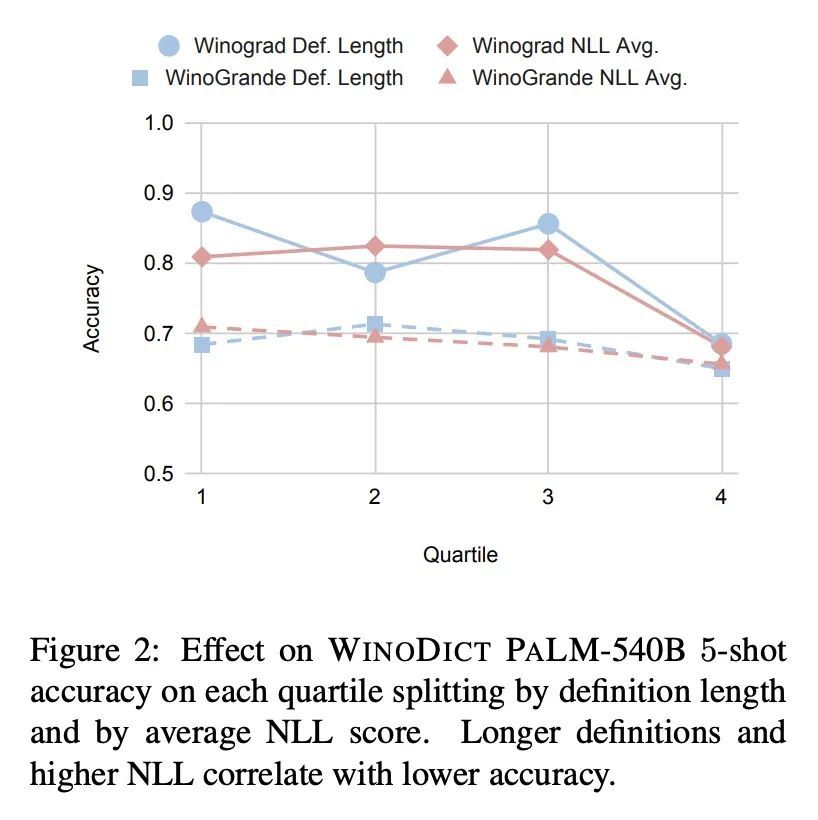
[CL] WinoDict: Probing language models for in-context word acquisition
WinoDict:面向上下文词获取的语言模型探测
J M Eisenschlos, J R. Cole, F Liu, W W. Cohen
[Google Research & University of Cambridge]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.12153


[LG] Minimax Optimal Kernel Operator Learning via Multilevel Training
基于多级训练的极小极大最优核算子学习
J Jin, Y Lu, J Blanchet, L Ying
[Peking University & Stanford University]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.14430


内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢