LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:指令微调语言模型扩展、目标发现与检测学习、用0.1%的额外计算量超越扩展律、高斯-伯努利RBM的训练方法改进、能用一秒解决小型表格分类问题的Transformer、了解奖励工程对样本复杂性的好处、基于MovieCLIP的电影视觉场景识别、神经注意力回路、面向长序列建模的结构化全局卷积
1、[LG] Scaling Instruction-Finetuned Language Models
H W Chung, L Hou, S Longpre, B Zoph, Y Tay, W Fedus, E Li, X Wang, M Dehghani, S Brahma, A Webson...
[Google]
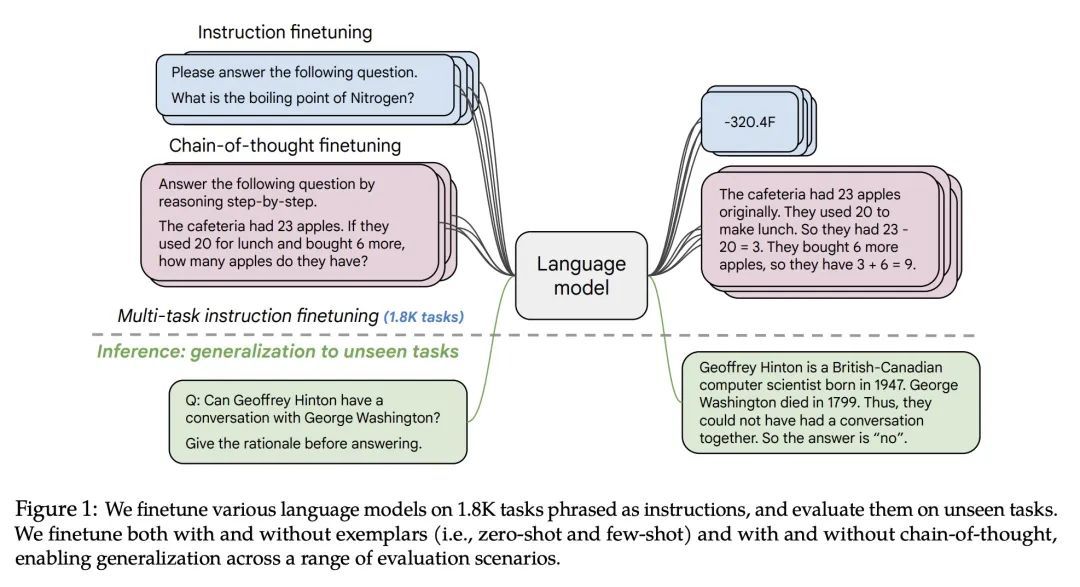
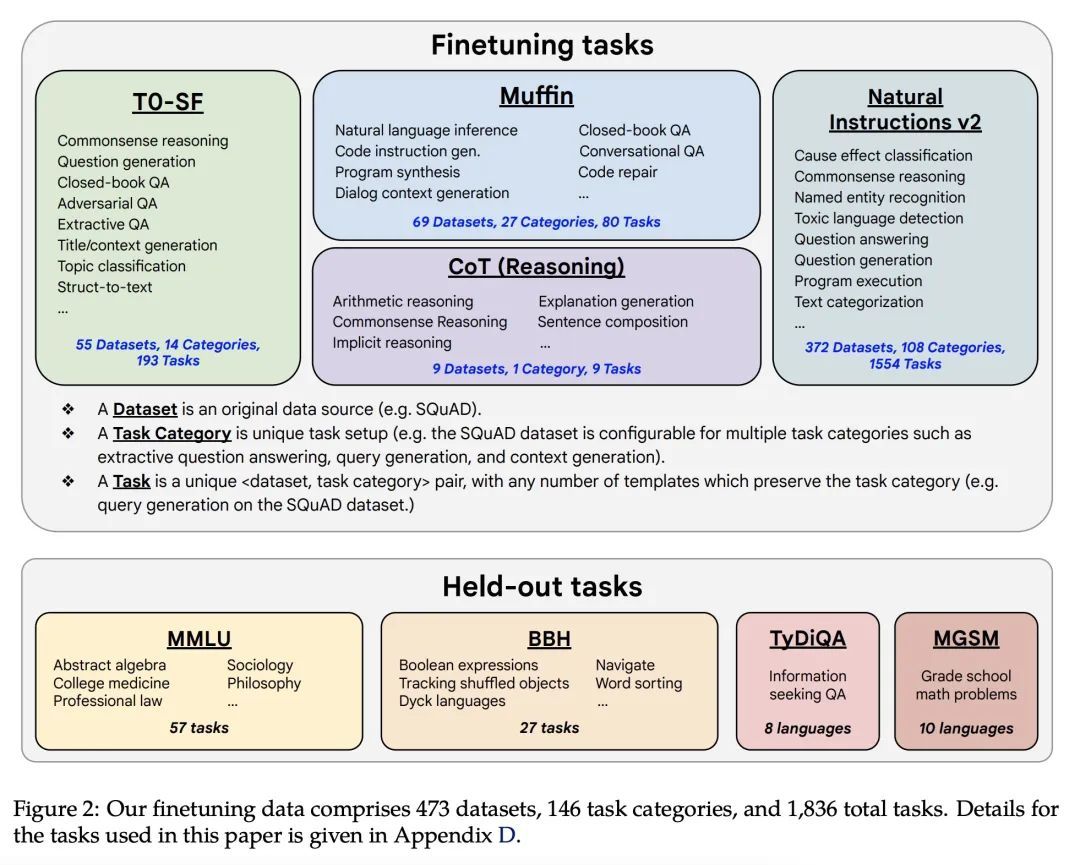
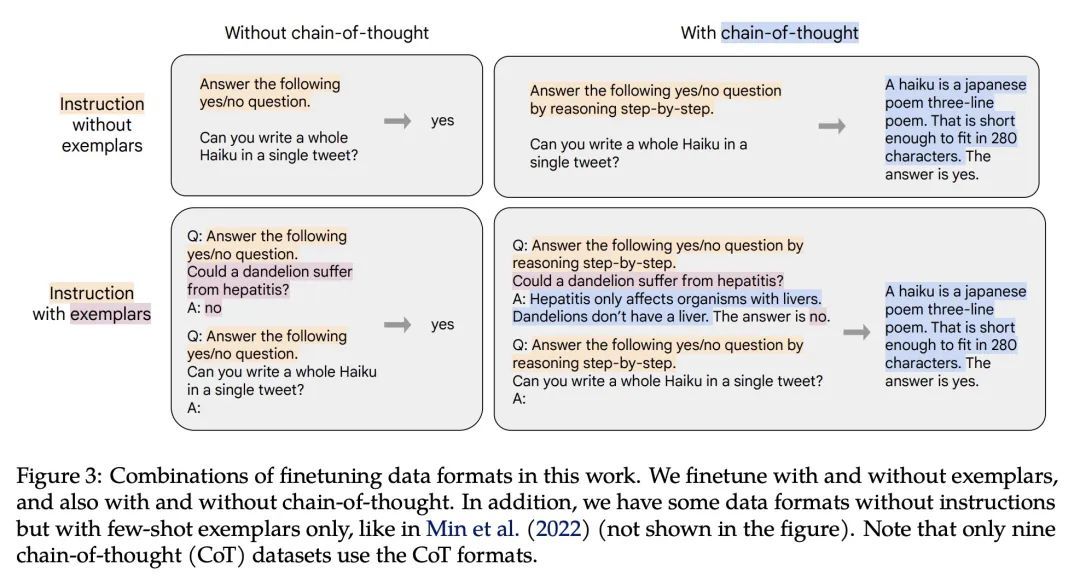
指令微调语言模型扩展。在以指令为措辞的数据集上对语言模型进行微调,已被证明可以提高模型的性能和对未见任务的泛化性。本文探讨了指令的微调,特别关注 (1) 任务数量的扩展,(2) 模型规模的扩展,以及 (3)思维链数据的微调。本文发现,上述方面的指令微调极大地提高了各种模型类别(PaLM、T5、U-PaLM)、提示设置(零样本、少样本、CoT)和评估基准(MMLU、BBH、TyDiQA、MGSM、开放式生成)的性能。例如,Flan-PaLM 540B在1.8K任务上的指令微调比PALM 540B要好很多(平均+9.4%)。Flan-PaLM 540B在一些基准测试上达到了最先进的性能,例如在五样本的MMLU上达到了75.2%。本文还公开发布了Flan-T5检查点,即使与PaLM 62B等大得多的模型相比,也取得了强大的少样本性能。总的来说,指令微调是一种提高预训练语言模型性能和可用性的通用方法。
Finetuning language models on a collection of datasets phrased as instructions has been shown to improve model performance and generalization to unseen tasks. In this paper we explore instruction finetuning with a particular focus on (1) scaling the number of tasks, (2) scaling the model size, and (3) finetuning on chain-of-thought data. We find that instruction finetuning with the above aspects dramatically improves performance on a variety of model classes (PaLM, T5, U-PaLM), prompting setups (zero-shot, few-shot, CoT), and evaluation benchmarks (MMLU, BBH, TyDiQA, MGSM, open-ended generation). For instance, Flan-PaLM 540B instruction-finetuned on 1.8K tasks outperforms PALM 540B by a large margin (+9.4% on average). Flan-PaLM 540B achieves state-of-the-art performance on several benchmarks, such as 75.2% on five-shot MMLU. We also publicly release Flan-T5 checkpoints, which achieve strong few-shot performance even compared to much larger models, such as PaLM 62B. Overall, instruction finetuning is a general method for improving the performance and usability of pretrained language models.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.11416

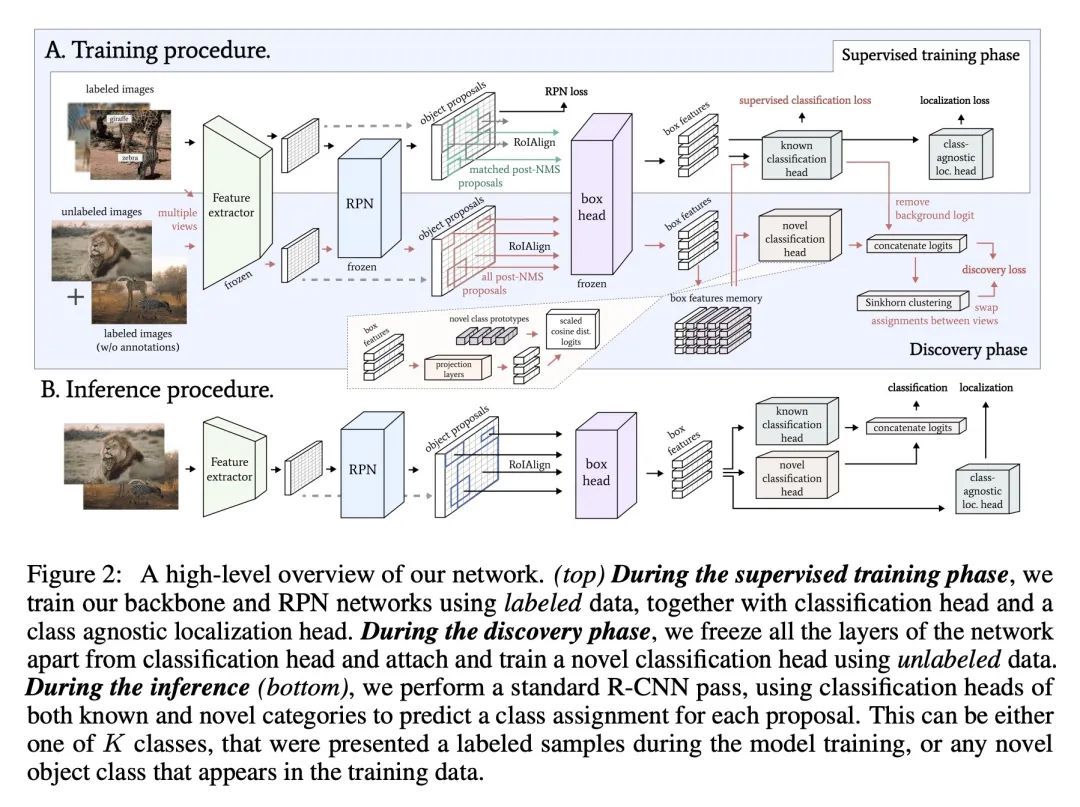
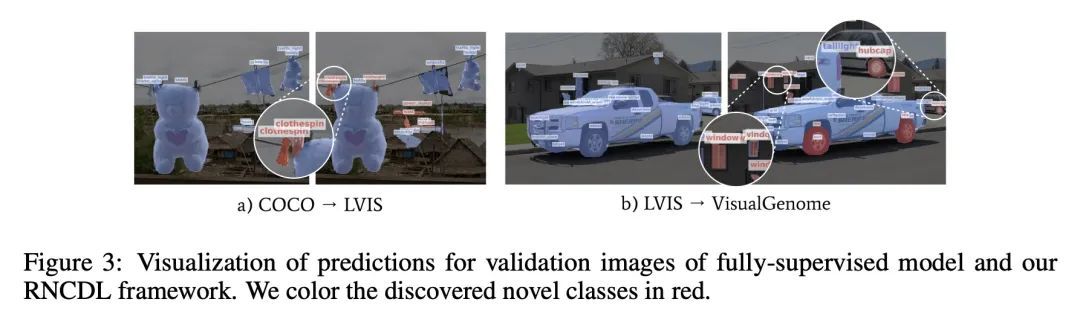
2、[CV] Learning to Discover and Detect Objects
V Fomenko, I Elezi, D Ramanan, L Leal-Taixé, A Ošep
[Microsoft Azure AI & Technical University of Munich & CMU]
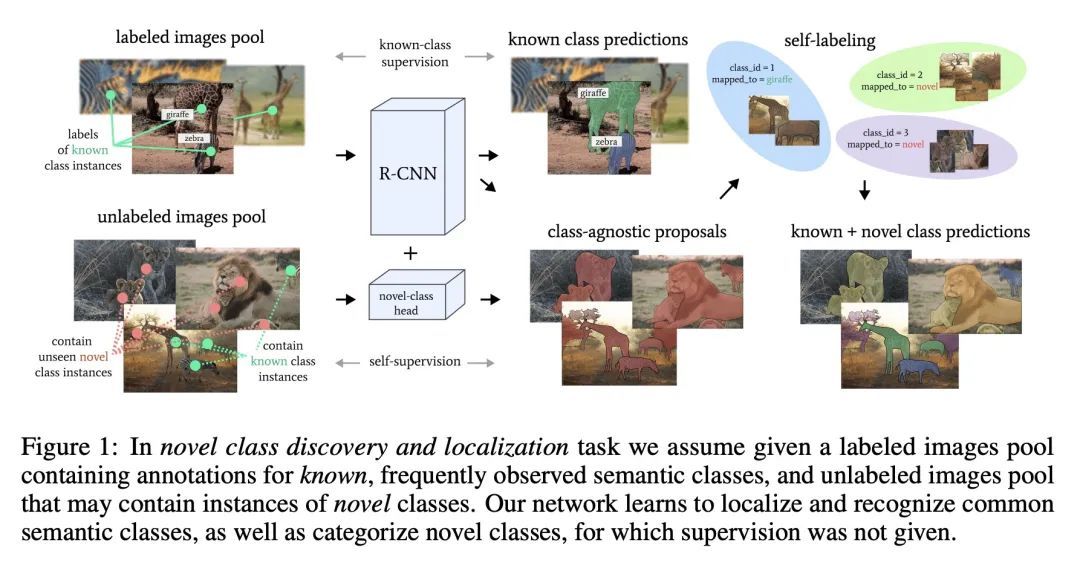
目标发现与检测学习。本文解决的是新类发现、检测和定位(NCDL)的问题。在这种情况下,假设有一个源数据集,其中有通常观察到的类的对象的标签。其他类别的实例需要根据视觉相似性自动发现、分类和定位,而无需人工监督。为此,本文提出一种两阶段的目标检测网络——基于区域的NCDL(RNCDL),用一个区域建议网络来定位候选目标,并训练为将每个候选目标分类,要么是源数据集中的已知类之一,要么是扩展的新类之一,对类的分配有一个长尾分布约束,反映了现实世界中类的自然频率。通过以端到端方式训练该检测网络,它学会了对所有区域的建议进行分类,包括那些不属于标记的对象类别词汇的大量类别。用COCO和LVIS数据集进行的实验显示,与依靠传统聚类算法或用预提取物的多阶段管道相比,所提出的方法明显更有效。此外,本文通过将该方法应用于大规模的视觉基因组数据集来证明其通用性,网络成功地学会了在没有明确监督的情况下检测各种语义类别。
We tackle the problem of novel class discovery, detection, and localization (NCDL). In this setting, we assume a source dataset with labels for objects of commonly observed classes. Instances of other classes need to be discovered, classified, and localized automatically based on visual similarity, without human supervision. To this end, we propose a two-stage object detection network Region-based NCDL (RNCDL), that uses a region proposal network to localize object candidates and is trained to classify each candidate, either as one of the known classes, seen in the source dataset, or one of the extended set of novel classes, with a long-tail distribution constraint on the class assignments, reflecting the natural frequency of classes in the real world. By training our detection network with this objective in an end-to-end manner, it learns to classify all region proposals for a large variety of classes, including those that are not part of the labeled object class vocabulary. Our experiments conducted using COCO and LVIS datasets reveal that our method is significantly more effective compared to multi-stage pipelines that rely on traditional clustering algorithms or use pre-extracted crops. Furthermore, we demonstrate the generality of our approach by applying our method to a large-scale Visual Genome dataset, where our network successfully learns to detect various semantic classes without explicit supervision.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.10774

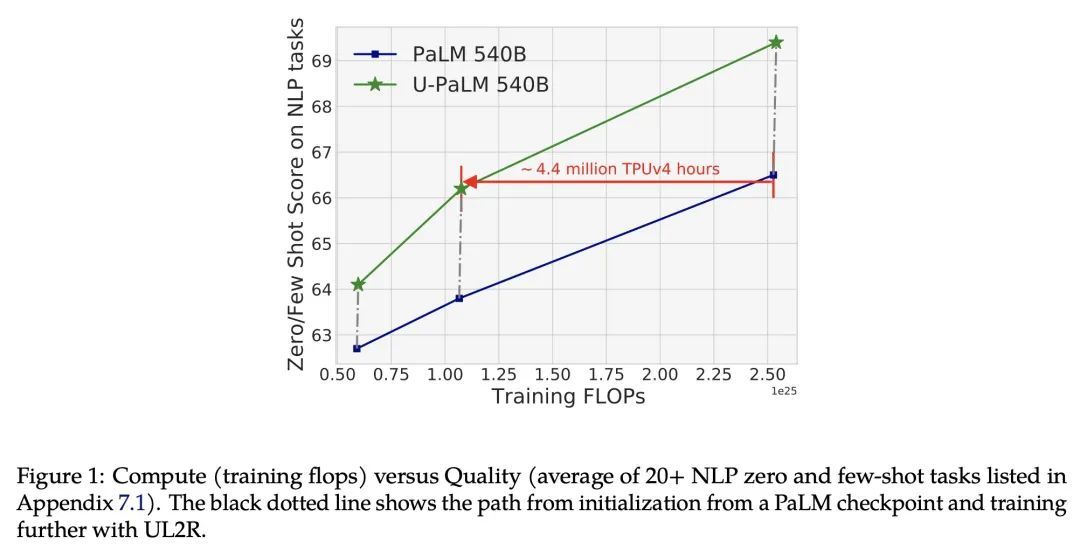
3、[CL] Transcending Scaling Laws with 0.1% Extra Compute
Y Tay, J Wei, H W Chung, V Q. Tran, D R. So, S Shakeri...
[Google]
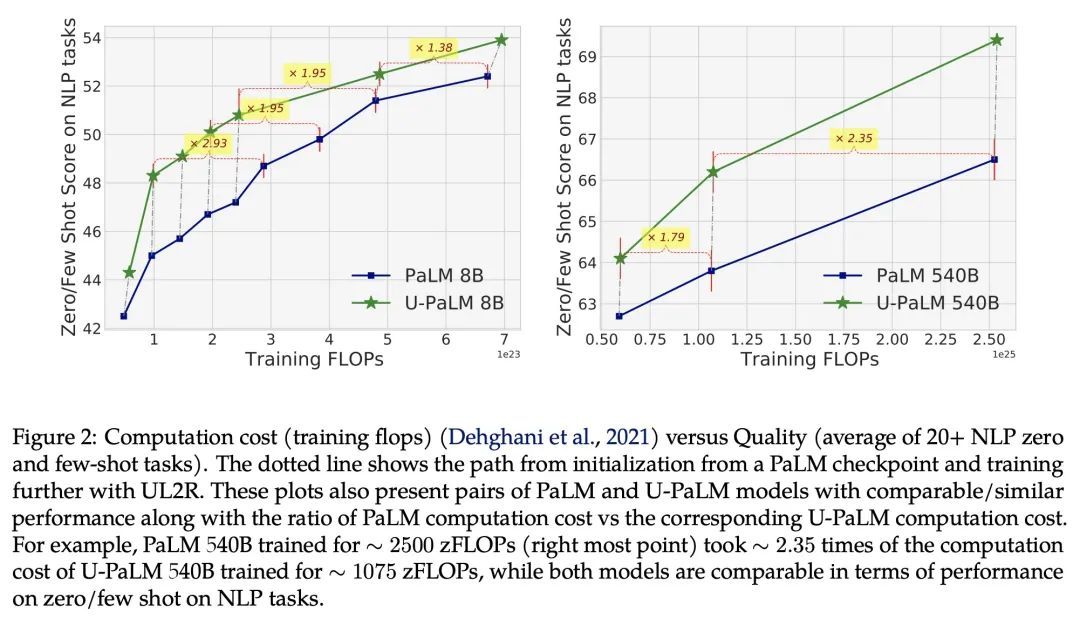
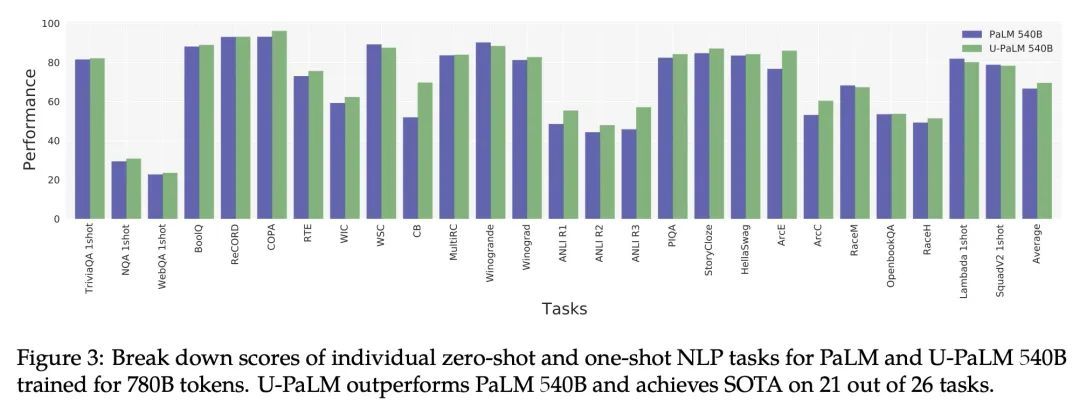
用0.1%的额外计算量超越扩展律。扩展语言模型规模可以提高性能,但会带来巨大的计算成本。本文提出UL2R,一种能大幅提高现有语言模型及其缩放曲线的方法,只需相对少量的额外计算。关键的想法是继续训练一个最先进的大型语言模型(如PaLM),采用UL2的去噪器混合目标增加的几个步骤。在几乎可以忽略不计的额外计算成本和没有新数据来源的情况下,能大幅提高大型语言模型在下游指标上的扩展特性。本文中,继续用UL2R训练PaLM,在8B、62B和540B的规模上引入一组新的模型,称为U-PaLM。令人印象深刻的是,在540B的规模下,显示了大约2倍的计算节省率,U-PaLM以大约一半的计算预算实现了与最终PaLM 540B模型相同的性能(即节省了440万TPUv4小时)。这种改进的扩展曲线在具有挑战性的BIG-Bench任务上带来了"涌现能力"——例如,U-PaLM在某些任务上比PaLM做得更好,或者在更小的规模(62B而非540B)上显示出更好的质量。总的来说,本文展示了U-PaLM在许多少见的设置上优于PaLM,即英语NLP任务(如常识推理、问答)、带有思维链的推理任务(如GSM8K)、多语言任务(MGSM、TydiQA)、MMLU和具有挑战性的BIG-Bench任务。最后,提供了定性的例子,展示了U-PaLM在单跨和多跨填空方面的新能力。
Scaling language models improves performance but comes with significant computational costs. This paper proposes UL2R, a method that substantially improves existing language models and their scaling curves with a relatively tiny amount of extra compute. The key idea is to continue training a state-of-the-art large language model (e.g., PaLM) on a few more steps with UL2's mixture-of-denoiser objective. We show that, with almost negligible extra computational costs and no new sources of data, we are able to substantially improve the scaling properties of large language models on downstream metrics. In this paper, we continue training PaLM with UL2R, introducing a new set of models at 8B, 62B, and 540B scale which we call U-PaLM. Impressively, at 540B scale, we show an approximately 2x computational savings rate where U-PaLM achieves the same performance as the final PaLM 540B model at around half its computational budget (i.e., saving ∼4.4 million TPUv4 hours). We further show that this improved scaling curve leads to 'emergent abilities' on challenging BIG-Bench tasks -- for instance, U-PaLM does much better than PaLM on some tasks or demonstrates better quality at much smaller scale (62B as opposed to 540B). Overall, we show that U-PaLM outperforms PaLM on many few-shot setups, i.e., English NLP tasks (e.g., commonsense reasoning, question answering), reasoning tasks with chain-of-thought (e.g., GSM8K), multilingual tasks (MGSM, TydiQA), MMLU and challenging BIG-Bench tasks. Finally, we provide qualitative examples showing the new capabilities of U-PaLM for single and multi-span infilling.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.11399
4、[LG] Gaussian-Bernoulli RBMs Without Tears
R Liao, S Kornblith, M Ren, D J. Fleet, G Hinton
[University of British Columbia & Google Research & New York University]
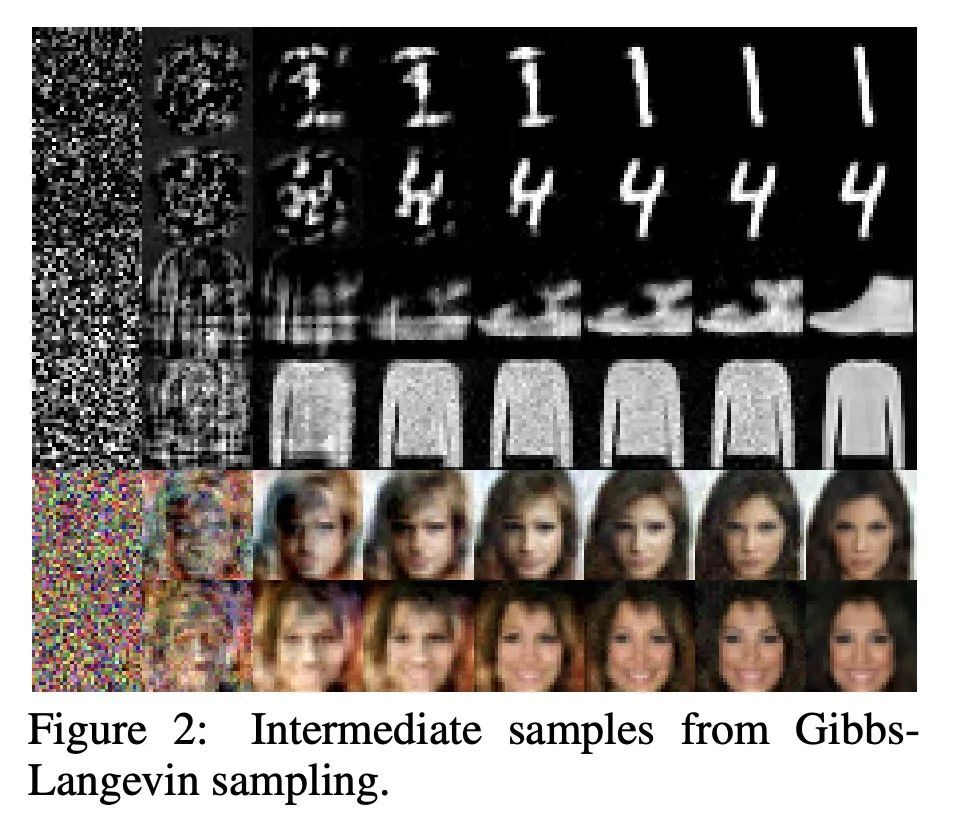
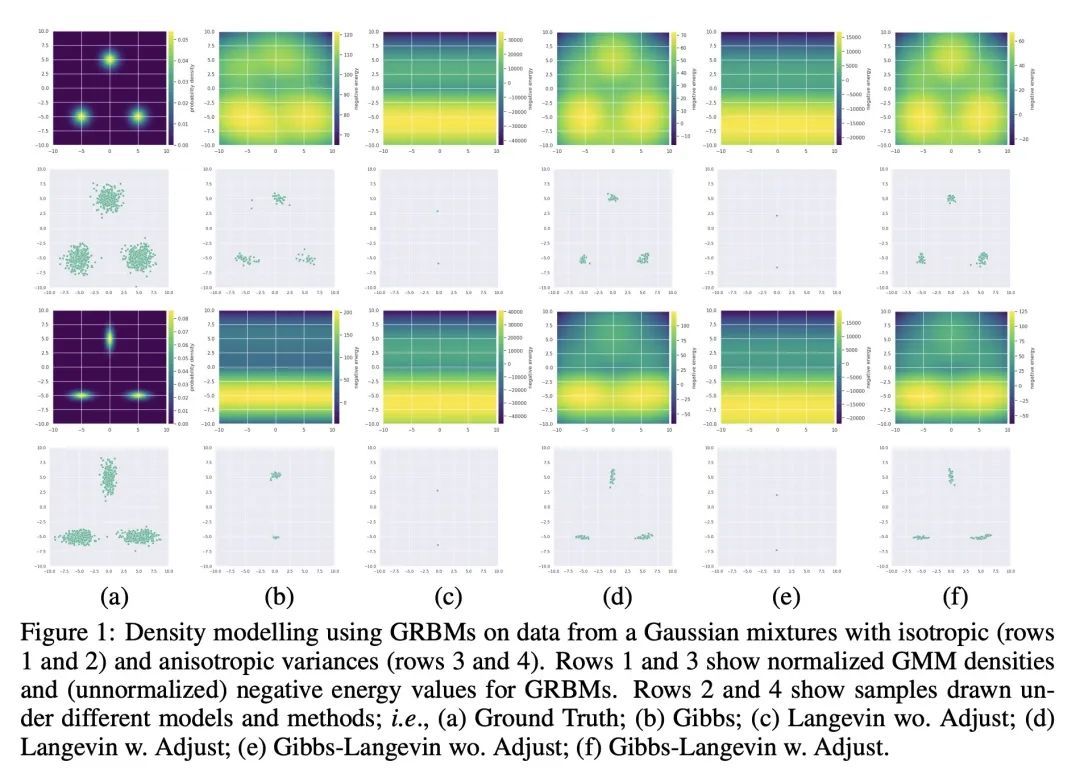
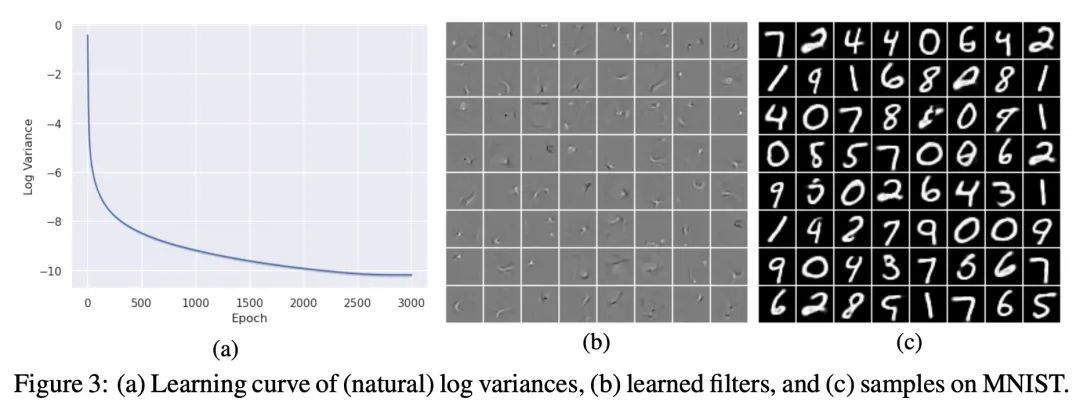
高斯-伯努利RBM的训练方法改进。本文重新审视了训练高斯-伯努利限制性波尔兹曼机(GRBM)的挑战性问题,并引入了两项创新。提出了一种新的吉布斯-朗格文采样算法,其性能优于现有的吉布斯采样等方法。提出了一种改进的对比发散(CD)算法,以便从噪声开始用GRBM生成图像。这使得GRBM与深度生成模型的直接比较成为可能,改善了RBM文献中的评估协议。此外,本文表明修正的CD和梯度剪裁足以鲁棒地训练具有大学习率的GRBM,从而消除了文献中各种技巧的必要性。在高斯混合、MNIST、FashionMNIST和CelebA上的实验表明,尽管GRBM是单层隐藏的结构,但它可以产生良好的样本。
We revisit the challenging problem of training Gaussian-Bernoulli restricted Boltzmann machines (GRBMs), introducing two innovations. We propose a novel Gibbs-Langevin sampling algorithm that outperforms existing methods like Gibbs sampling. We propose a modified contrastive divergence (CD) algorithm so that one can generate images with GRBMs starting from noise. This enables direct comparison of GRBMs with deep generative models, improving evaluation protocols in the RBM literature. Moreover, we show that modified CD and gradient clipping are enough to robustly train GRBMs with large learning rates, thus removing the necessity of various tricks in the literature. Experiments on Gaussian Mixtures, MNIST, FashionMNIST, and CelebA show GRBMs can generate good samples, despite their single-hidden-layer architecture. Our code is released at: this https URL.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.10318


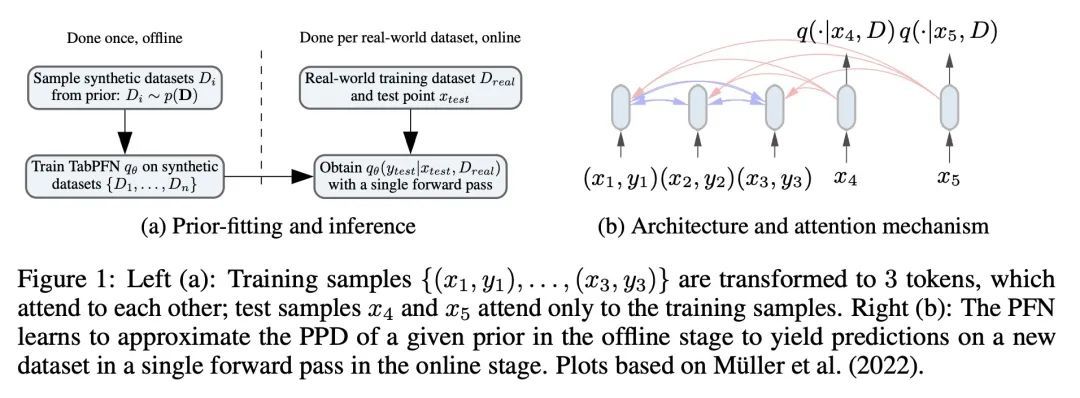
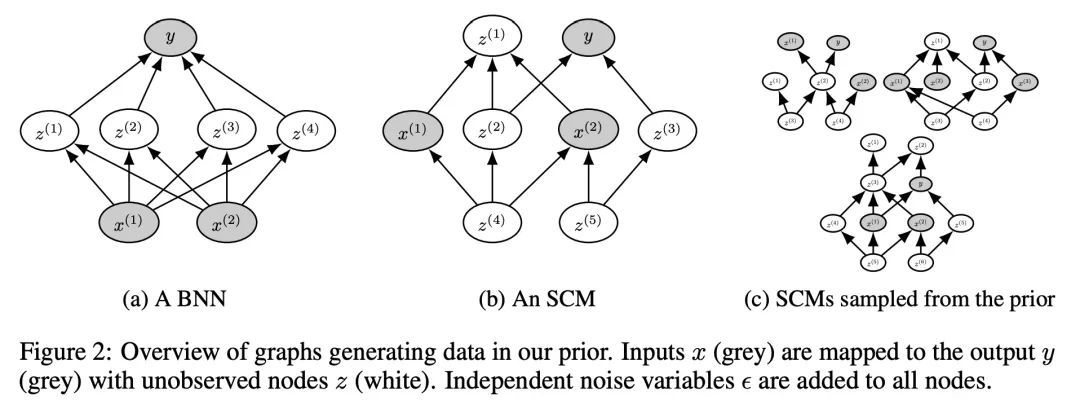
5、[LG] TabPFN: A Transformer That Solves Small Tabular Classification Problems in a Second
N Hollmann, S Müller, K Eggensperger, F Hutter
[University of Freiburg]
TabPFN:能用一秒解决小型表格分类问题的Transformer。本文提出TabPFN,一个经过训练的Transformer,可以在一秒钟内完成小型表格数据集的有监督分类,不需要调整超参数,并且与最先进的分类方法相比具有竞争力。TabPFN完全包含在网络的权重中,接受训练和测试样本作为一个集合值的输入,并在一次前向传递中产生对整个测试集的预测。TabPFN是一个先验数据拟合网络(PFN),并被离线训练一次,以近似于从先验中提取的合成数据集上的贝叶斯推理。这个先验包含了因果推理的思想。它包含了一个大的结构性因果模型空间,偏向于简单的结构。在OpenML-CC18套件的30个数据集上,所提出方法明显优于提升树,并且与复杂的最先进的AutoML系统的性能相当,速度提高70倍。在有GPU的情况下,速度会提高到3200倍。
We present TabPFN, a trained Transformer that can do supervised classification for small tabular datasets in less than a second, needs no hyperparameter tuning and is competitive with state-of-the-art classification methods. TabPFN is fully entailed in the weights of our network, which accepts training and test samples as a set-valued input and yields predictions for the entire test set in a single forward pass. TabPFN is a Prior-Data Fitted Network (PFN) and is trained offline once, to approximate Bayesian inference on synthetic datasets drawn from our prior. This prior incorporates ideas from causal reasoning: It entails a large space of structural causal models with a preference for simple structures. On 30 datasets from the OpenML-CC18 suite, we show that our method clearly outperforms boosted trees and performs on par with complex state-of-the-art AutoML systems with up to 70× speedup. This increases to a 3200× speedup when a GPU is available. We provide all our code, the trained TabPFN, an interactive browser demo and a Colab notebook at this https URL.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.01848


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
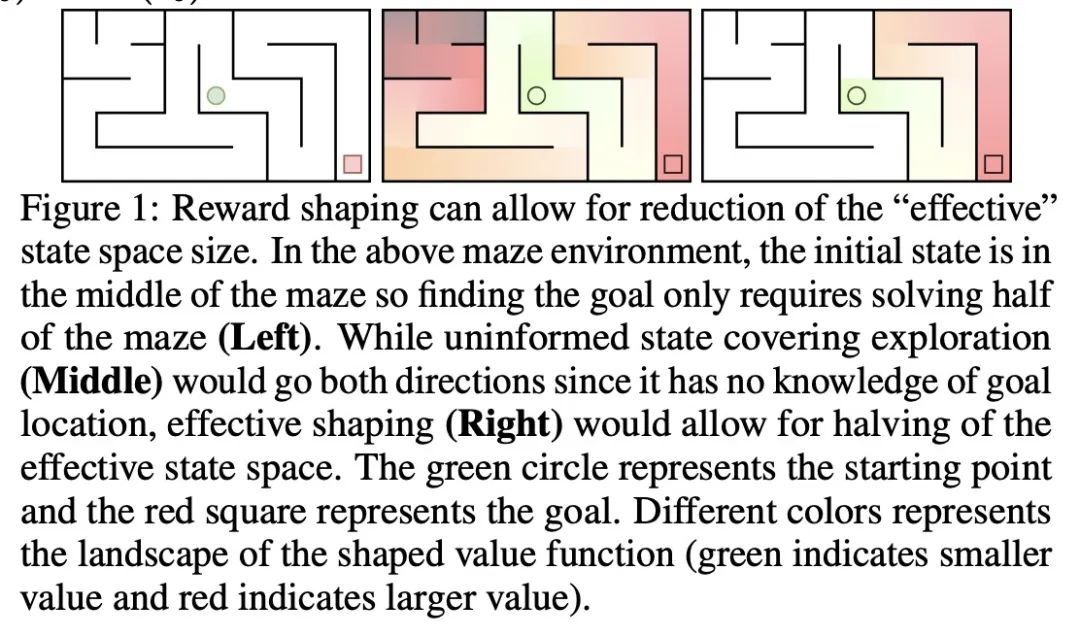
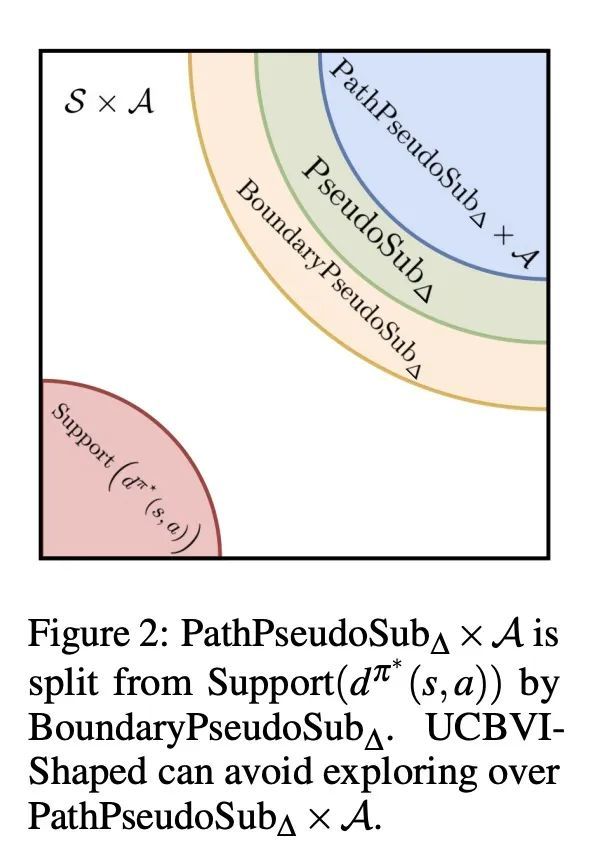
[LG] Unpacking Reward Shaping: Understanding the Benefits of Reward Engineering on Sample Complexity
奖励塑造拆解:了解奖励工程对样本复杂性的好处
A Gupta, A Pacchiano, Y Zhai...
[University of Washington & Microsoft Research & UC Berkeley & Harvard University]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.09579

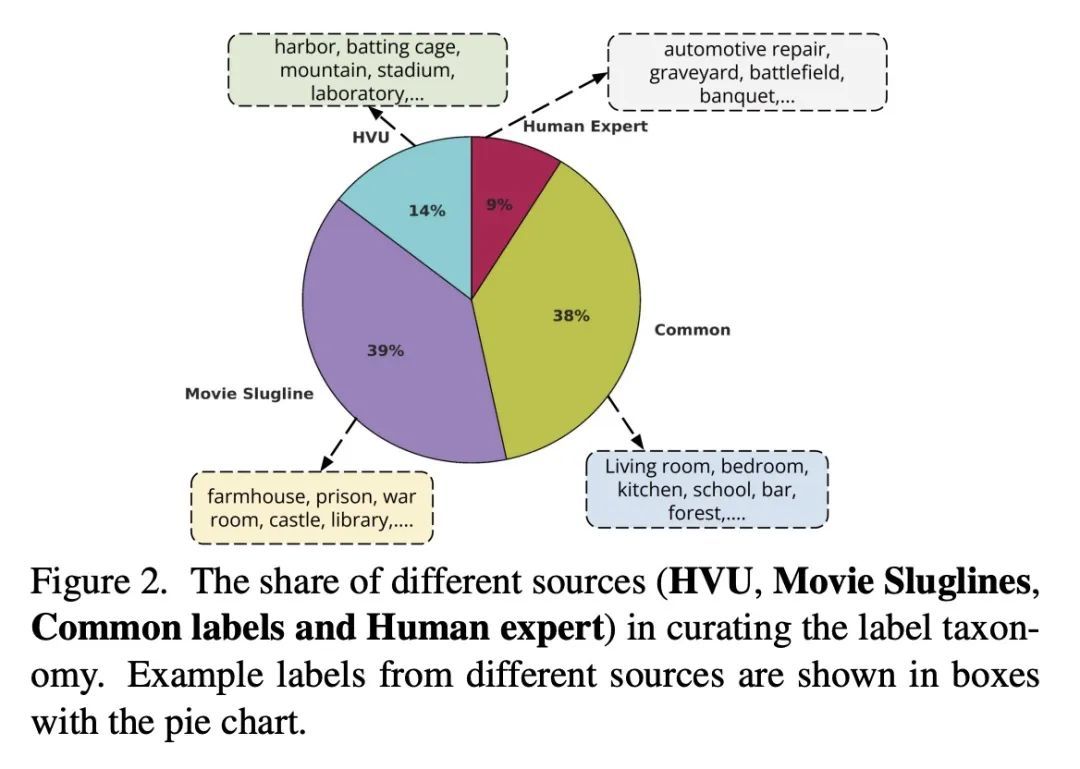
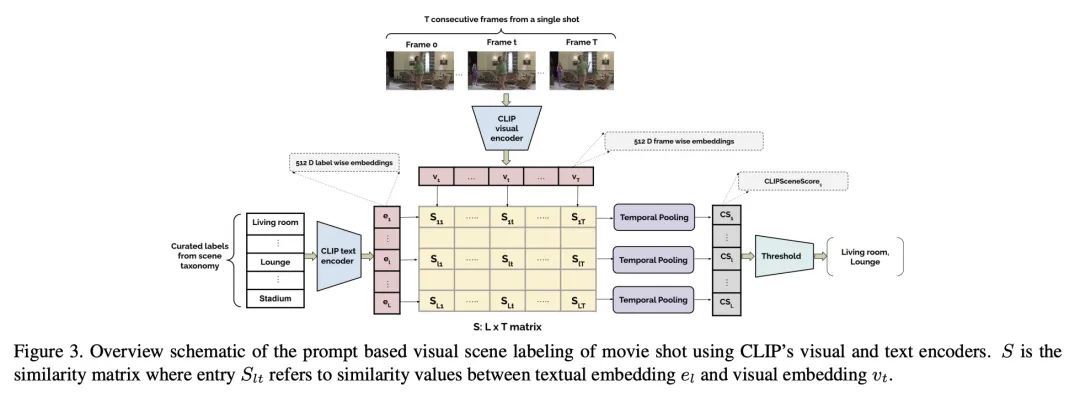
[CV] MovieCLIP: Visual Scene Recognition in Movies
MovieCLIP:电影视觉场景识别
D Bose, R Hebbar, K Somandepalli, H Zhang, Y Cui, K Cole-McLaughlin, H Wang, S Narayanan
[University of Southern California & Google Research & Google] https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.11065


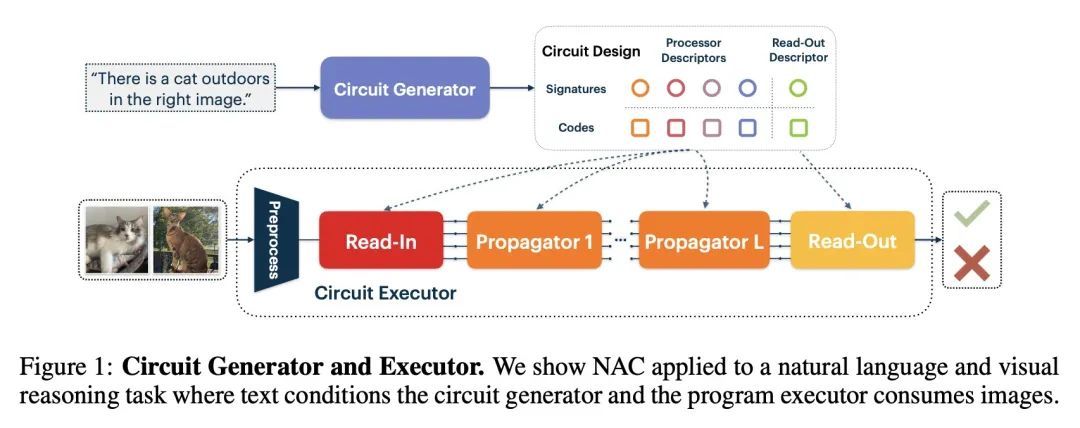
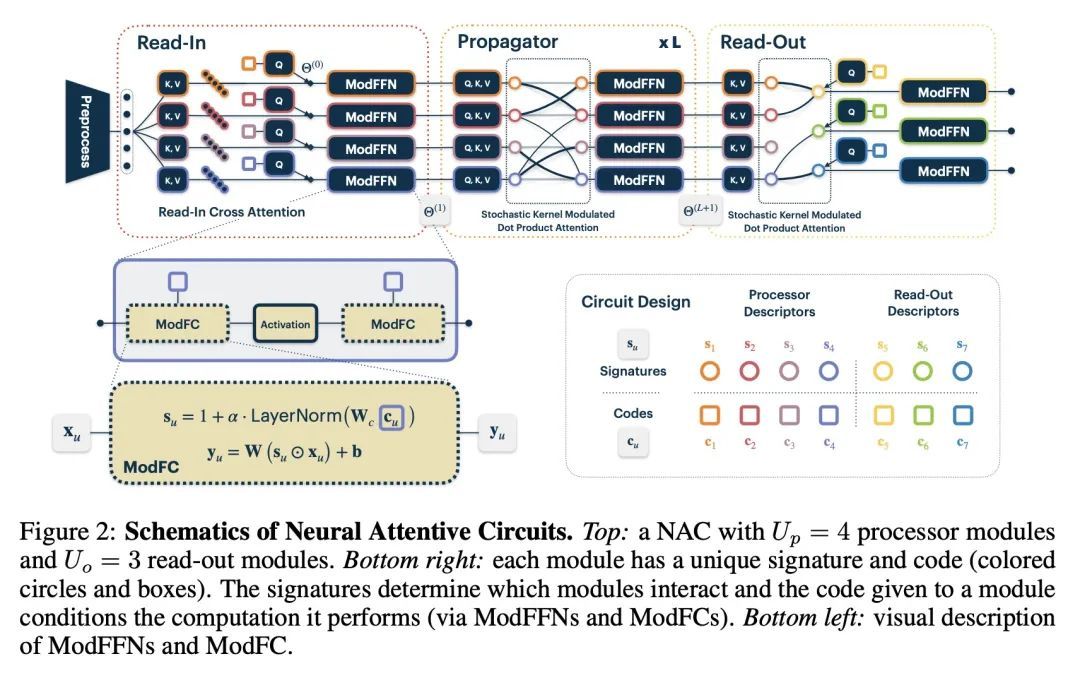
[LG] Neural Attentive Circuits
神经注意力回路
N Rahaman, M Weiss, F Locatello, C Pal, Y Bengio, B Schölkopf, L E Li, N Ballas
[Mila, Quebec AI Institute & AWS AI & Max Planck Institute for Intelligent Systems & Meta AI]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.08031

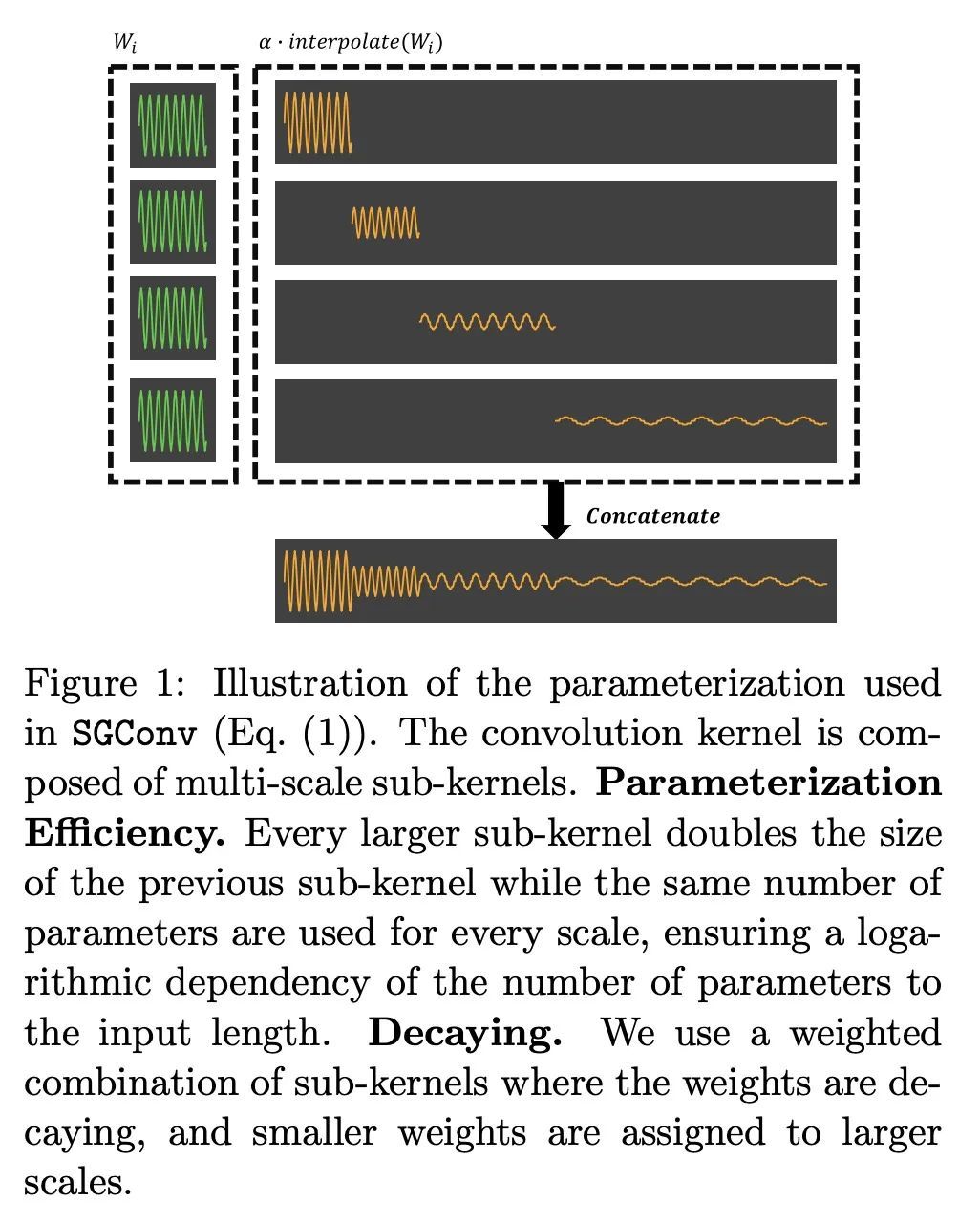
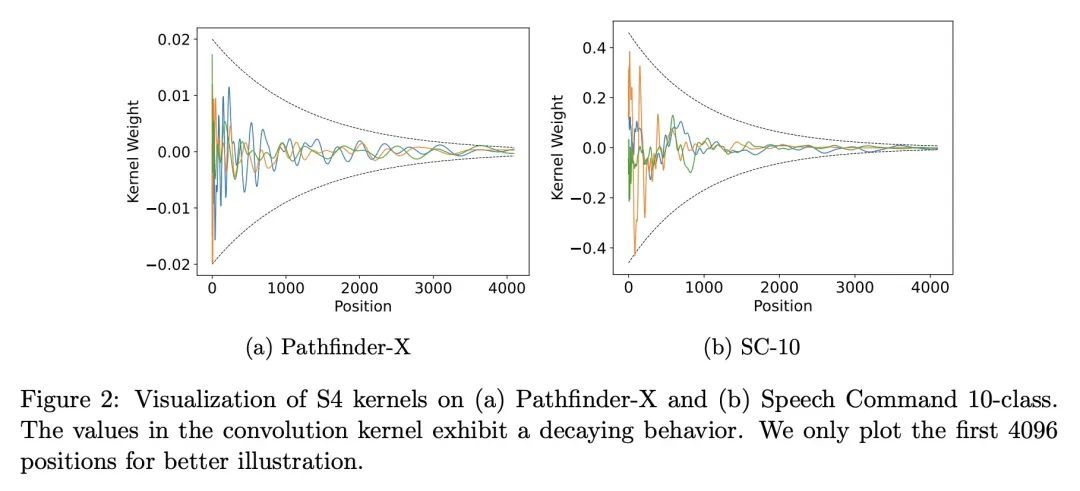
[LG] What Makes Convolutional Models Great on Long Sequence Modeling?
面向长序列建模的结构化全局卷积
Y Li, T Cai, Y Zhang, D Chen, D Dey
[University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign & Princeton University & Microsoft Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.09298

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢