LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:用非形式证明指导形式化定理证明器、理解多模态对比表示学习中的模态差距、DALL-E 2未能可靠地捕捉常见句法过程、基于点轨迹的遮挡追踪、基于多跳注意力扩散的长序列高效Transformer、基于凸共轭摊销的最优传输、基于迭代共识构建预训练模型集成、基于CLIP引导像素级优化的实时文本到视频生成研究、基于共形覆盖保证的贝叶斯优化
1、[LG] Draft, Sketch, and Prove: Guiding Formal Theorem Provers with Informal Proofs
A Q. Jiang, S Welleck, J P Zhou, W Li...
[Meta AI & University of Washington & Google Research & University of Cambridge]
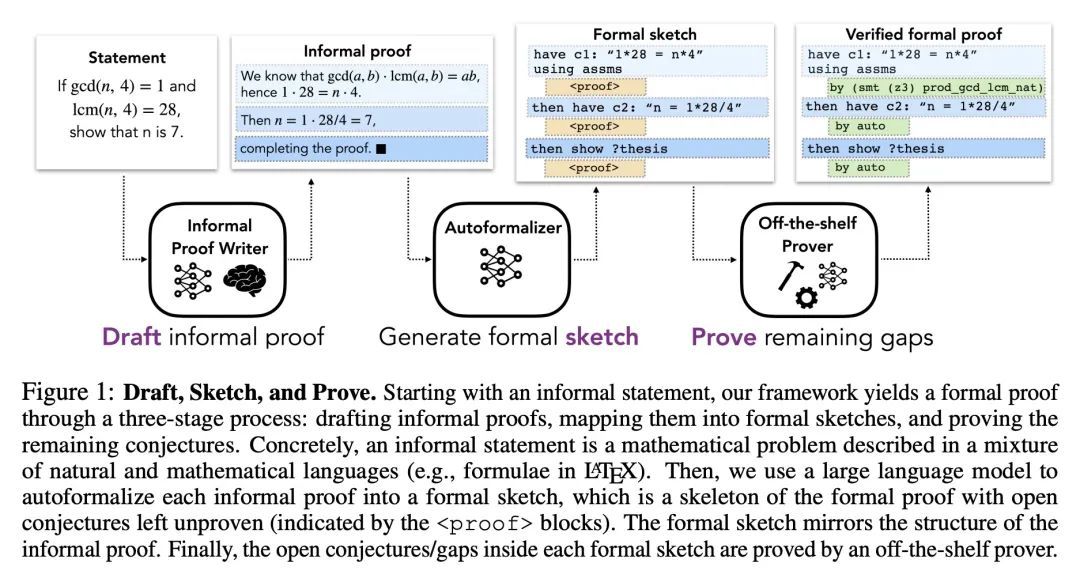
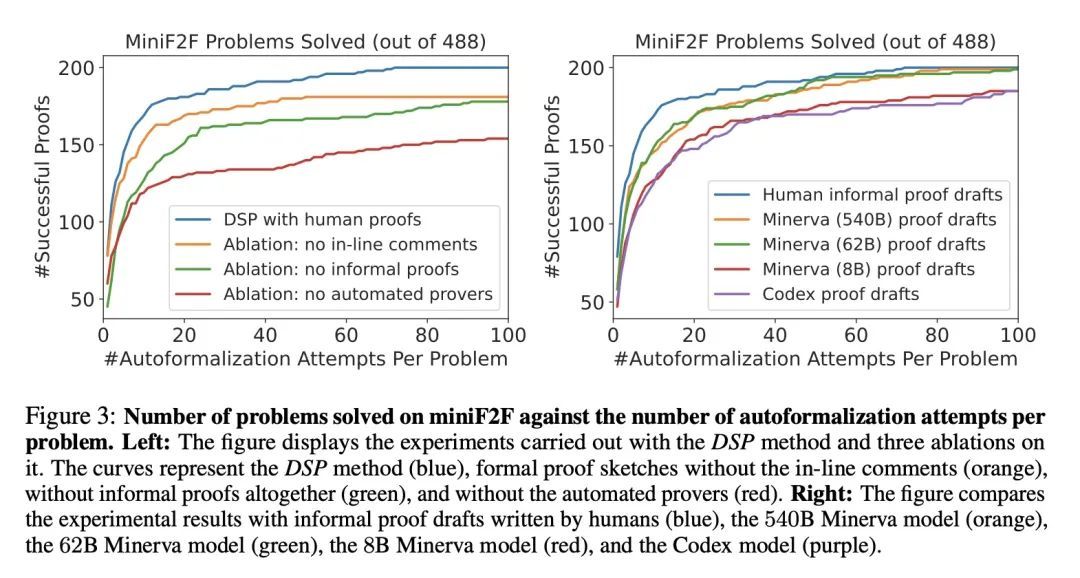
草稿、草图和证明:用非形式证明指导形式化定理证明器。现有数学证明的形式化是一个众所周知的困难过程。尽管几十年来对自动化证明器和证明助手进行了研究,但编写形式化证明仍然很艰巨,而且只有少数专家能做到。虽然之前对自动形式化的研究集中在强大的搜索算法上,但并没有尝试利用现有的非形式证明的优势。本文提出Draft, Sketch, and Prove (DSP),一种将非形式证明映射为形式证明草图的方法,并使用草图来指导自动验证器,将其搜索引向更容易的子问题。本文研究了两个相关的设置,其中非形式证明是由人写的或由语言模型生成的。实验和消融研究表明,大型语言模型能产生结构良好的形式化草图,这些草图遵循与非形式证明相同的推理步骤。用这些草图指导自动验证器,可以将其在一系列数学竞赛问题上的表现从20.9%提高到39.3%。
The formalization of existing mathematical proofs is a notoriously difficult process. Despite decades of research on automation and proof assistants, writing formal proofs remains arduous and only accessible to a few experts. While previous studies to automate formalization focused on powerful search algorithms, no attempts were made to take advantage of available informal proofs. In this work, we introduce Draft, Sketch, and Prove (DSP), a method that maps informal proofs to formal proof sketches, and uses the sketches to guide an automated prover by directing its search to easier sub-problems. We investigate two relevant setups where informal proofs are either written by humans or generated by a language model. Our experiments and ablation studies show that large language models are able to produce well-structured formal sketches that follow the same reasoning steps as the informal proofs. Guiding an automated prover with these sketches enhances its performance from 20.9% to 39.3% on a collection of mathematical competition problems.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.12283


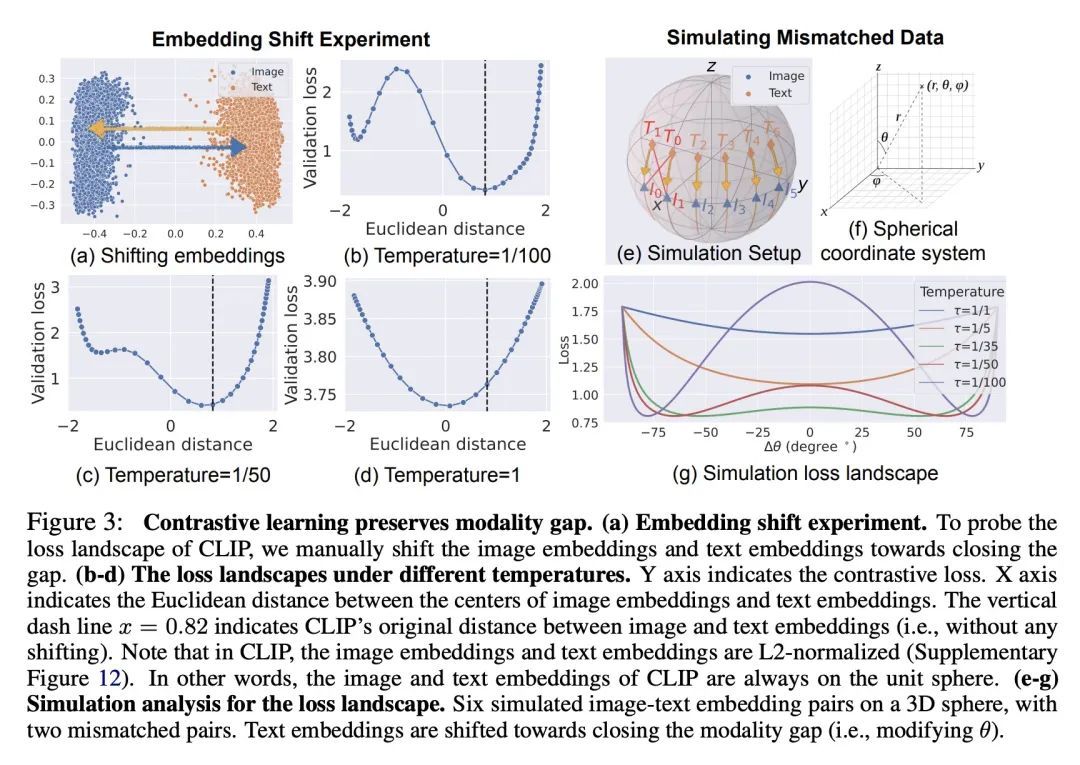
2、[CL] Mind the Gap: Understanding the Modality Gap in Multi-modal Contrastive Representation Learning
W Liang, Y Zhang, Y Kwon, S Yeung, J Zou
[Stanford University & Columbia University]
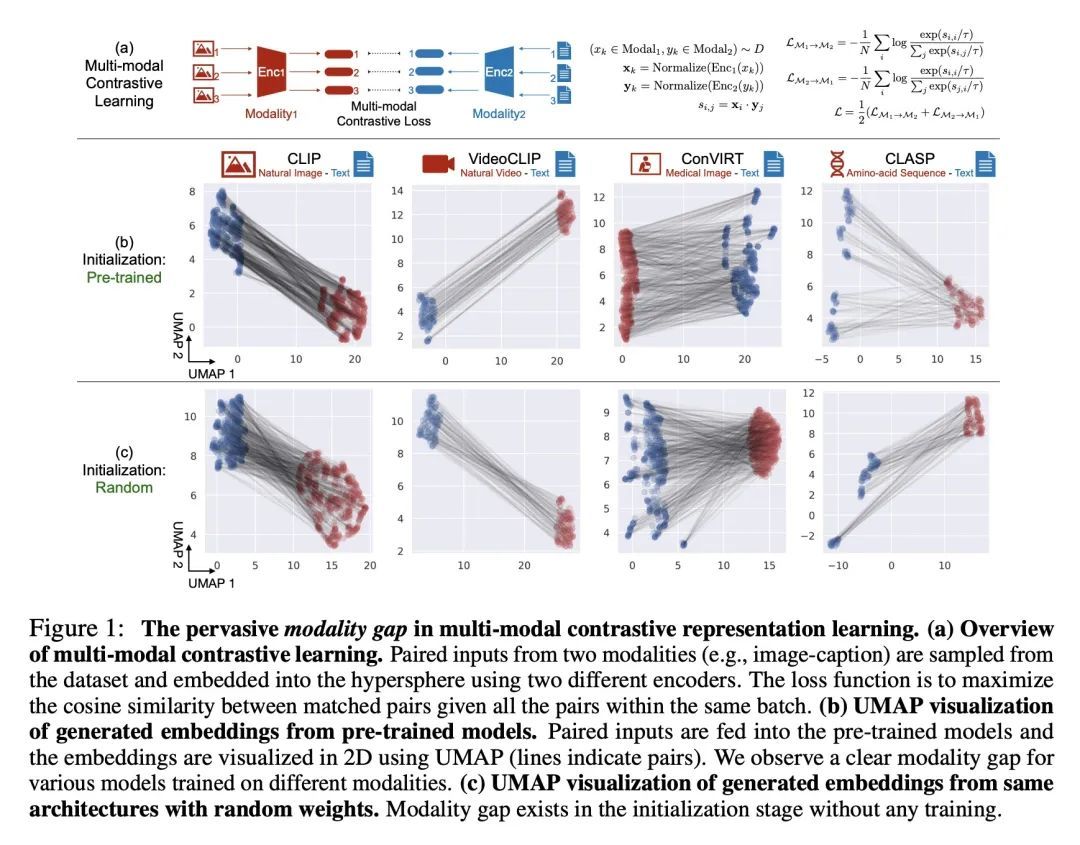
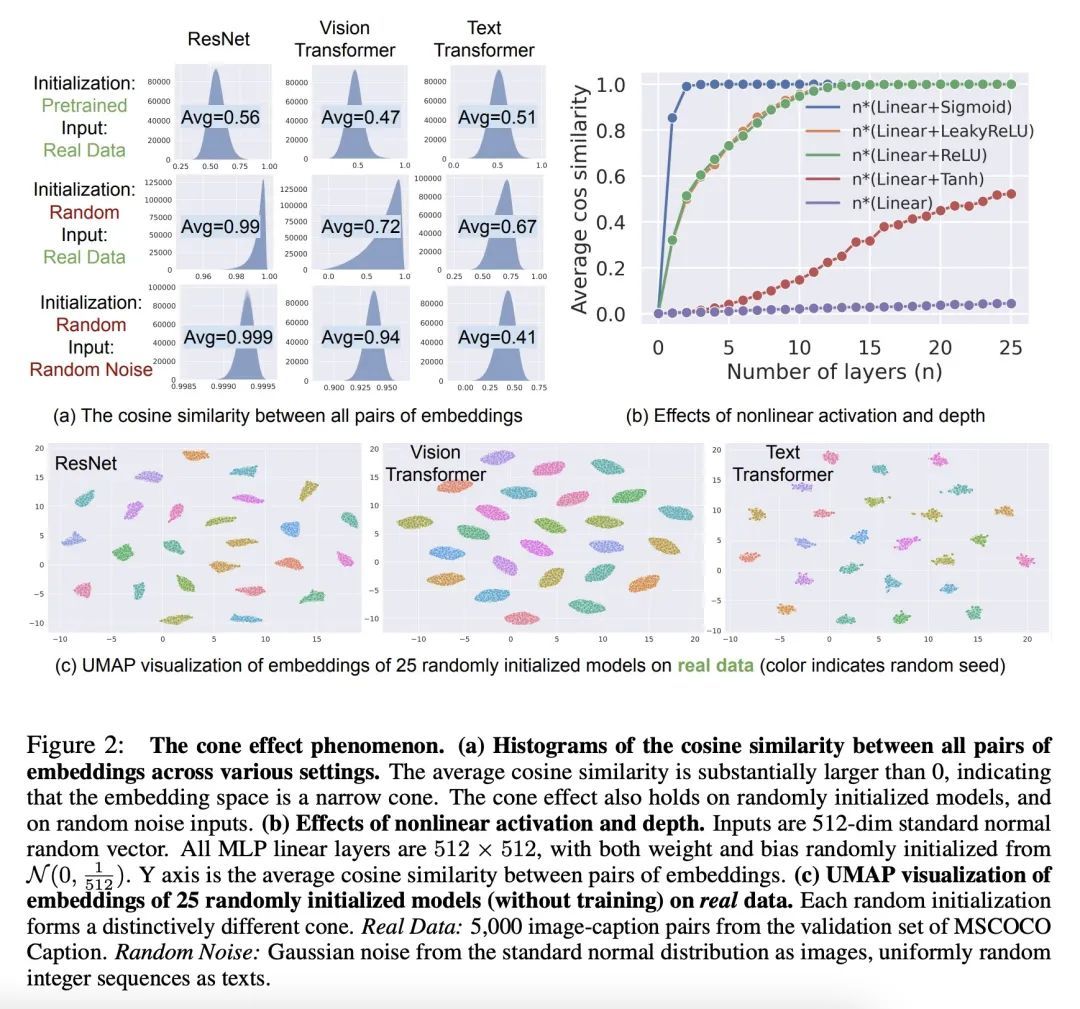
理解多模态对比表示学习中的模态差距。本文提出模态差距,这是多模态模型表示空间的一个有趣的几何现象。具体来说,不同的数据模态(如图像和文本)在多模态模型(如CLIP)的共享表示中是以一定距离嵌入的。系统分析表明,这种差距是由模型初始化和对比学习优化的组合造成的。在模型初始化中,本文从经验和理论上表明,一个普通的深度神经网络的表示被限制在一个狭窄的锥体中。因此,在一个有两个编码器的多模态模型中,当模型初始化时,两种模态的表示是明显分开的。在优化过程中,对比学习使不同的模态保持一定的距离,这个距离受损失函数中温度参数的影响。本文通过实验进一步证明,改变模态间隙距离对提高模型的下游零样本分类性能和公平性有很大影响。
We present modality gap, an intriguing geometric phenomenon of the representation space of multi-modal models. Specifically, we show that different data modalities (e.g. images and text) are embedded at arm's length in their shared representation in multi-modal models such as CLIP. Our systematic analysis demonstrates that this gap is caused by a combination of model initialization and contrastive learning optimization. In model initialization, we show empirically and theoretically that the representation of a common deep neural network is restricted to a narrow cone. As a consequence, in a multi-modal model with two encoders, the representations of the two modalities are clearly apart when the model is initialized. During optimization, contrastive learning keeps the different modalities separate by a certain distance, which is influenced by the temperature parameter in the loss function. Our experiments further demonstrate that varying the modality gap distance has a significant impact in improving the model's downstream zero-shot classification performance and fairness. Our code and data are available at this https URL
https://arxiv.org/abs/2203.02053

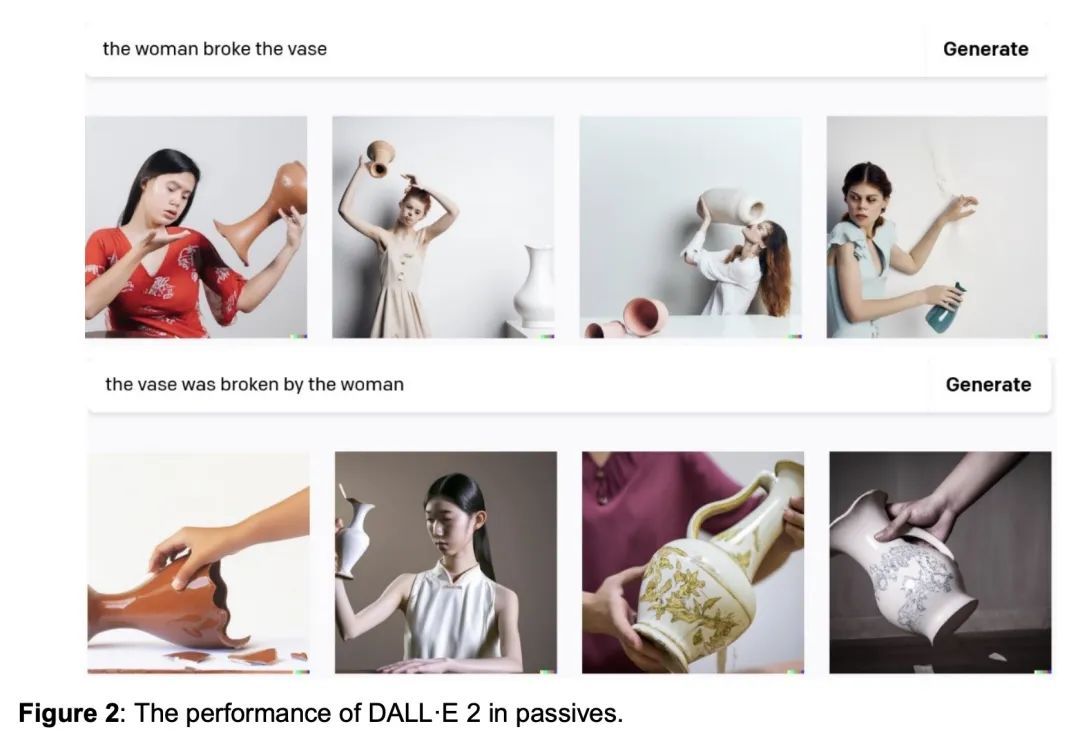
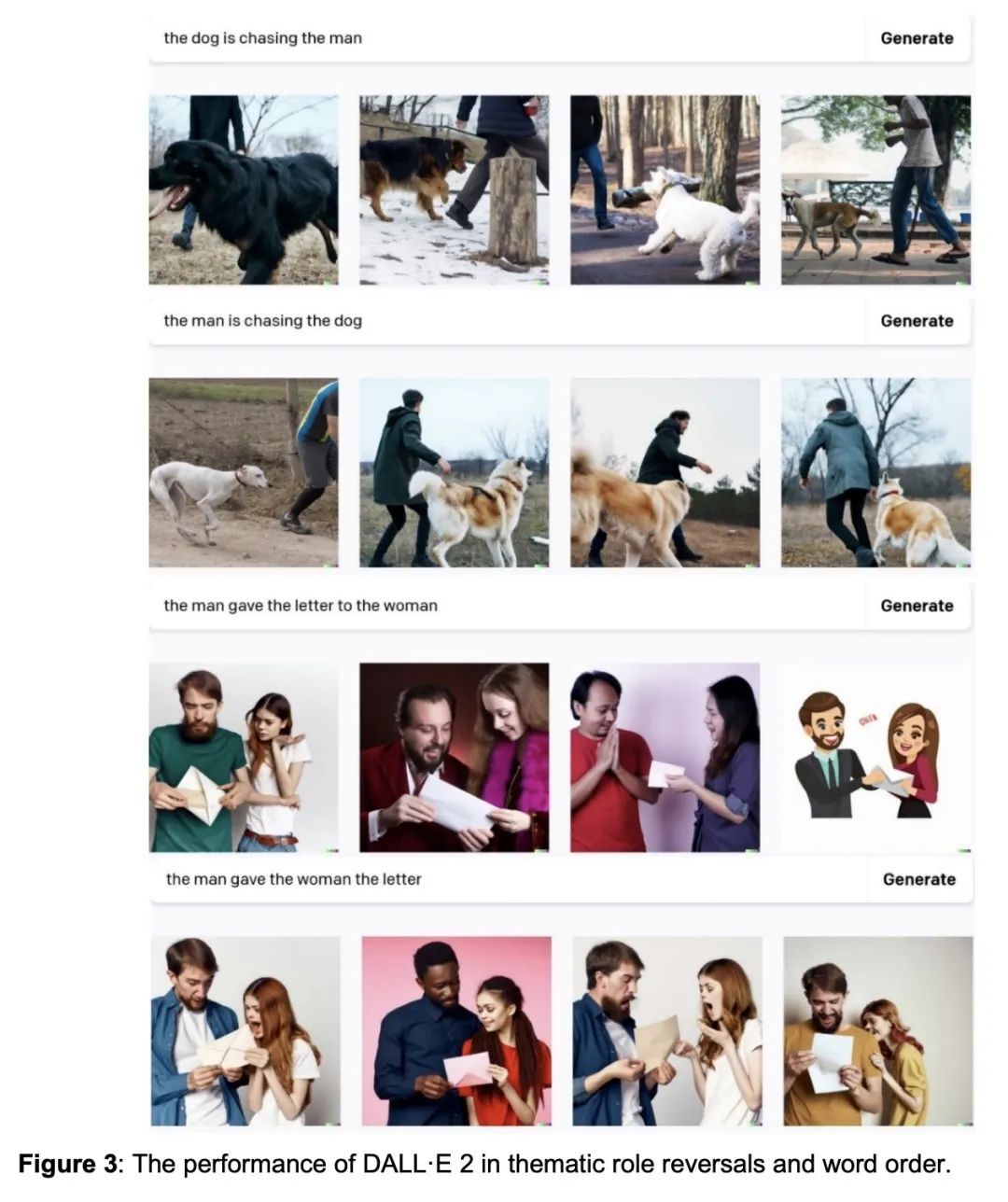
3、[CL] DALL-E 2 Fails to Reliably Capture Common Syntactic Processes
E Leivada, E Murphy, G Marcus
[Universitat Rovira i Virgili & University of Texas Health Science Center at Houston & New York University]
DALL-E 2未能可靠地捕捉常见句法过程。机器智能正越来越多地与关于智商、语言处理以及理解和转化自然语言的一系列刺激的能力的说法联系起来。本文系统分析了DALL-E 2捕捉8种与构成性有关的语法现象的能力,这些现象在语言学中被广泛讨论,并在人类语言中普遍存在:结合原则和核心推理、被动词、结构模糊性、否定词、词序、双宾语结构、句子协调、省略语和比较词。幼儿往往能掌握这些现象,学习语法和语义之间的系统映射,但DALL-E 2无法可靠地推断出与语法一致的含义。这些结果对最近关于此类系统理解人类语言的能力的说法提出了挑战。本文提供了全套的测试材料作为未来测试的基准。
Machine intelligence is increasingly being linked to claims about sentience, language processing, and an ability to comprehend and transform natural language into a range of stimuli. We systematically analyze the ability of DALL-E 2 to capture 8 grammatical phenomena pertaining to compositionality that are widely discussed in linguistics and pervasive in human language: binding principles and coreference, passives, structural ambiguity, negation, word order, double object constructions, sentence coordination, ellipsis, and comparatives. Whereas young children routinely master these phenomena, learning systematic mappings between syntax and semantics, DALL-E 2 is unable to reliably infer meanings that are consistent with the syntax. These results challenge recent claims concerning the capacity of such systems to understand of human language. We make available the full set of test materials as a benchmark for future testing.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.12889


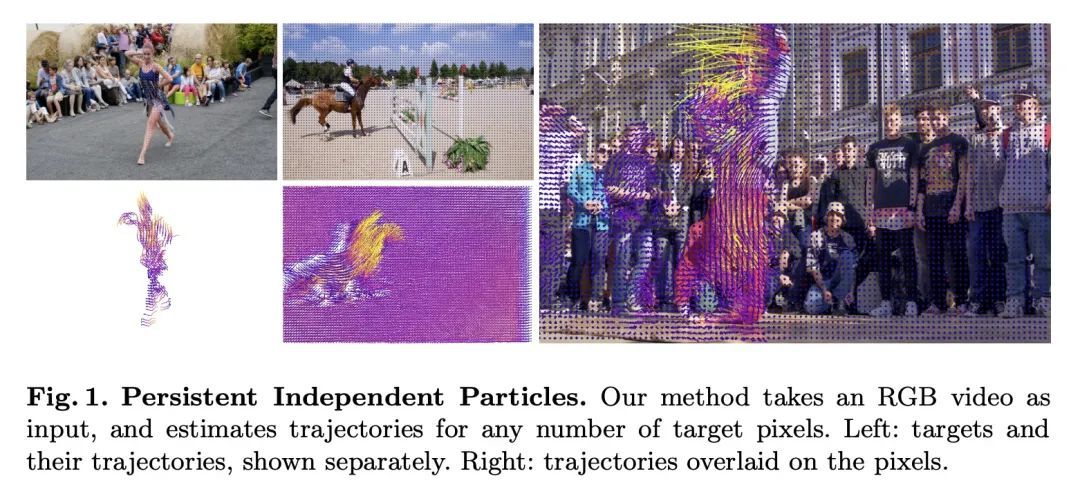
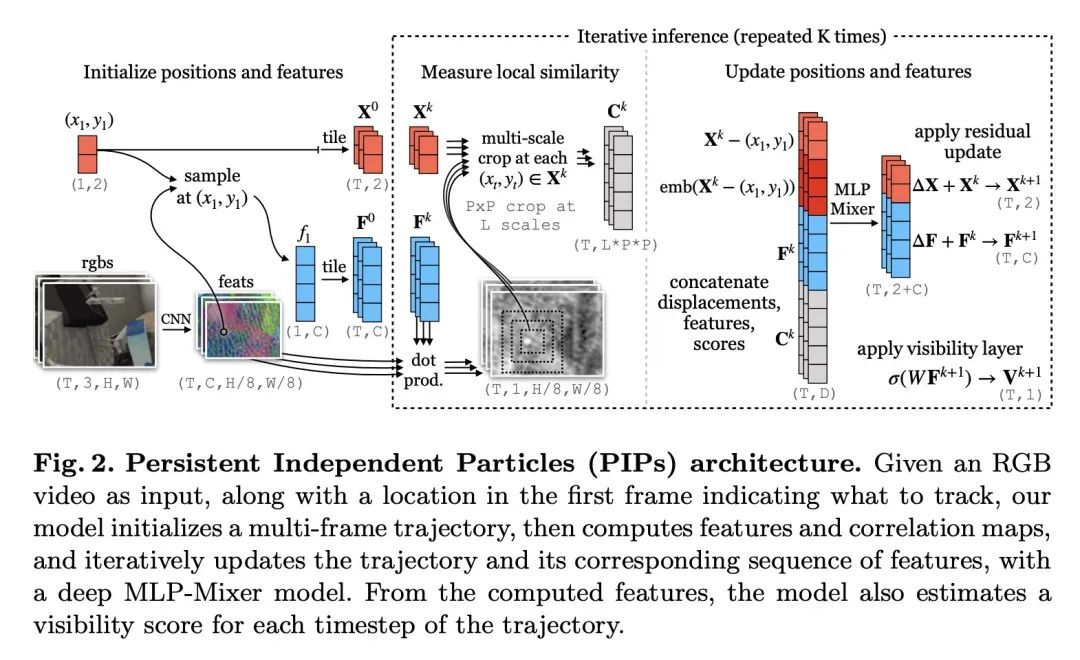
4、[CV] Particle Video Revisited: Tracking Through Occlusions Using Point Trajectories
A W. Harley, Z Fang, K Fragkiadaki
[CMU]
重新审视粒子视频:基于点轨迹的遮挡追踪。视频中的像素追踪通常作为一个光流估计问题进行研究,其中每个像素都被描述为一个位移矢量,用来定位它在下一帧的位置。尽管更广泛的时间上下文可以自由获得,但之前考虑到这一点的努力只产生了比2帧方法更小的收益。本文重新审视了"粒子视频"方法,并将像素追踪作为一个长程运动估计问题来研究,其中每个像素都被描述为一个轨迹,将其定位在未来多帧中。本文用推动当前最先进的流动和目标追踪的组件来重新构建这一经典方法,例如密集成本图、迭代优化和外观更新学习。用从现有的光流数据中挖掘出来的长程正交点轨迹来训练模型,用多帧的遮挡物来综合增强这些轨迹。在轨迹估计基准和关键点标签传播任务中测试了所提出方法,并与最先进的光流和特征跟踪方法进行了比较。
Tracking pixels in videos is typically studied as an optical flow estimation problem, where every pixel is described with a displacement vector that locates it in the next frame. Even though wider temporal context is freely available, prior efforts to take this into account have yielded only small gains over 2-frame methods. In this paper, we revisit Sand and Teller's "particle video" approach, and study pixel tracking as a long-range motion estimation problem, where every pixel is described with a trajectory that locates it in multiple future frames. We re-build this classic approach using components that drive the current state-of-the-art in flow and object tracking, such as dense cost maps, iterative optimization, and learned appearance updates. We train our models using long-range amodal point trajectories mined from existing optical flow data that we synthetically augment with multi-frame occlusions. We test our approach in trajectory estimation benchmarks and in keypoint label propagation tasks, and compare favorably against state-of-the-art optical flow and feature tracking methods.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.04153


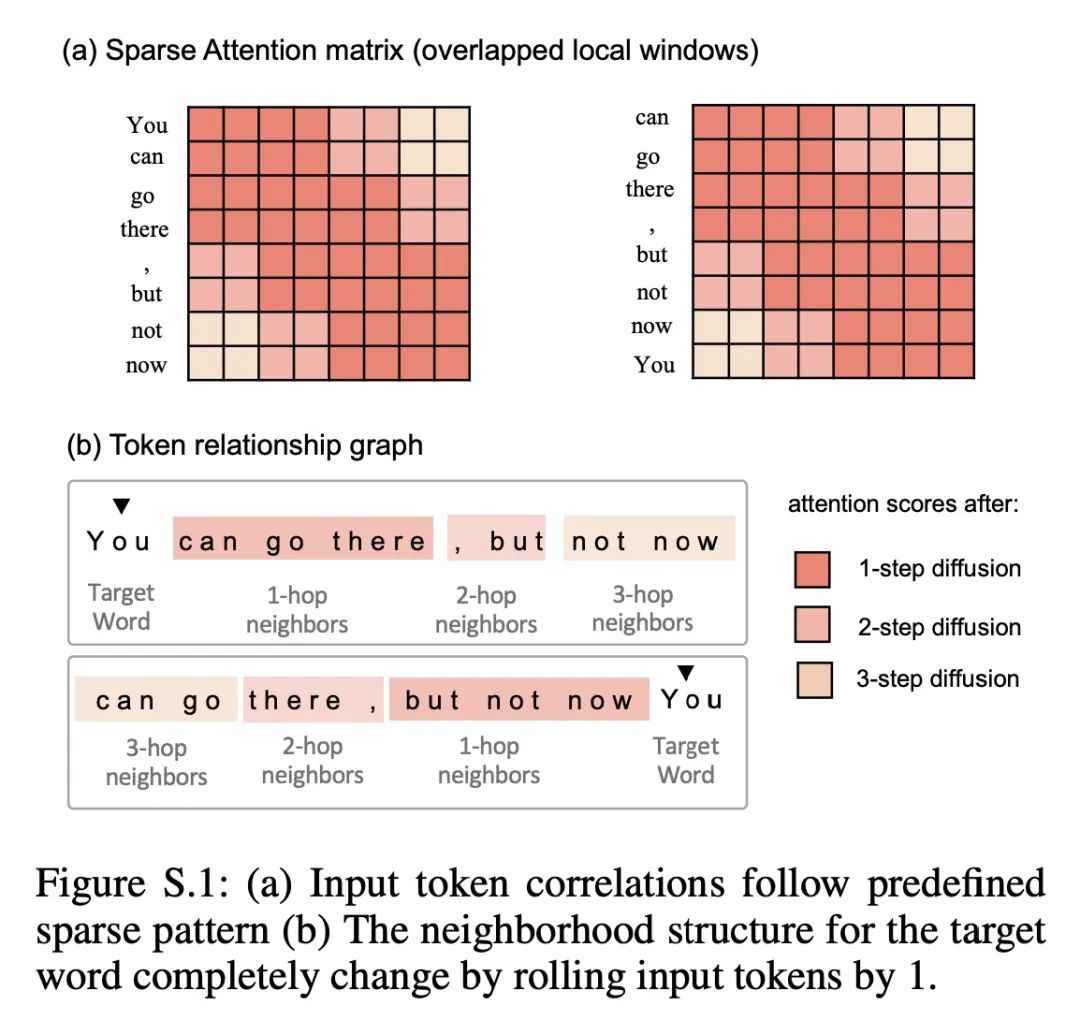
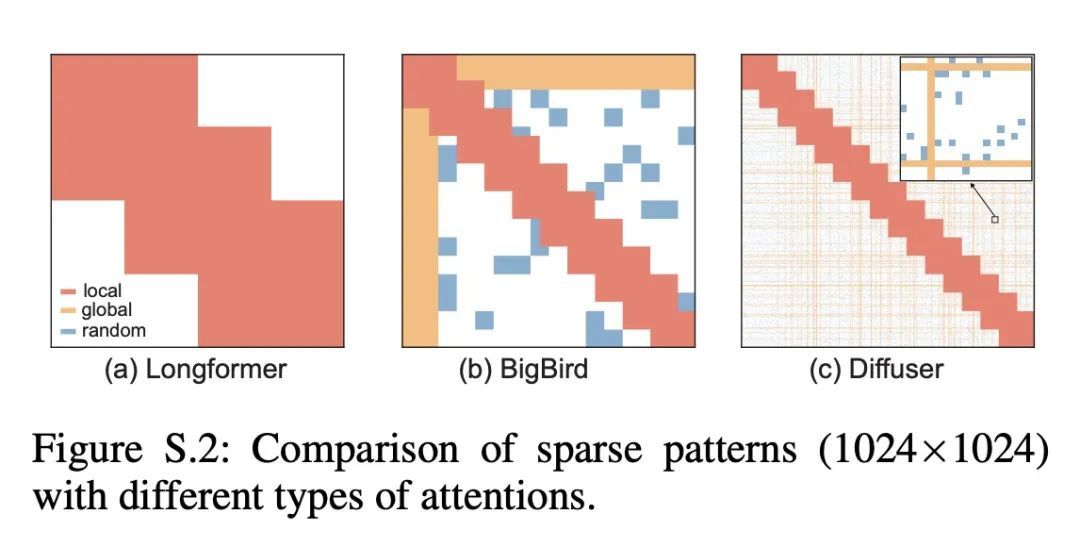
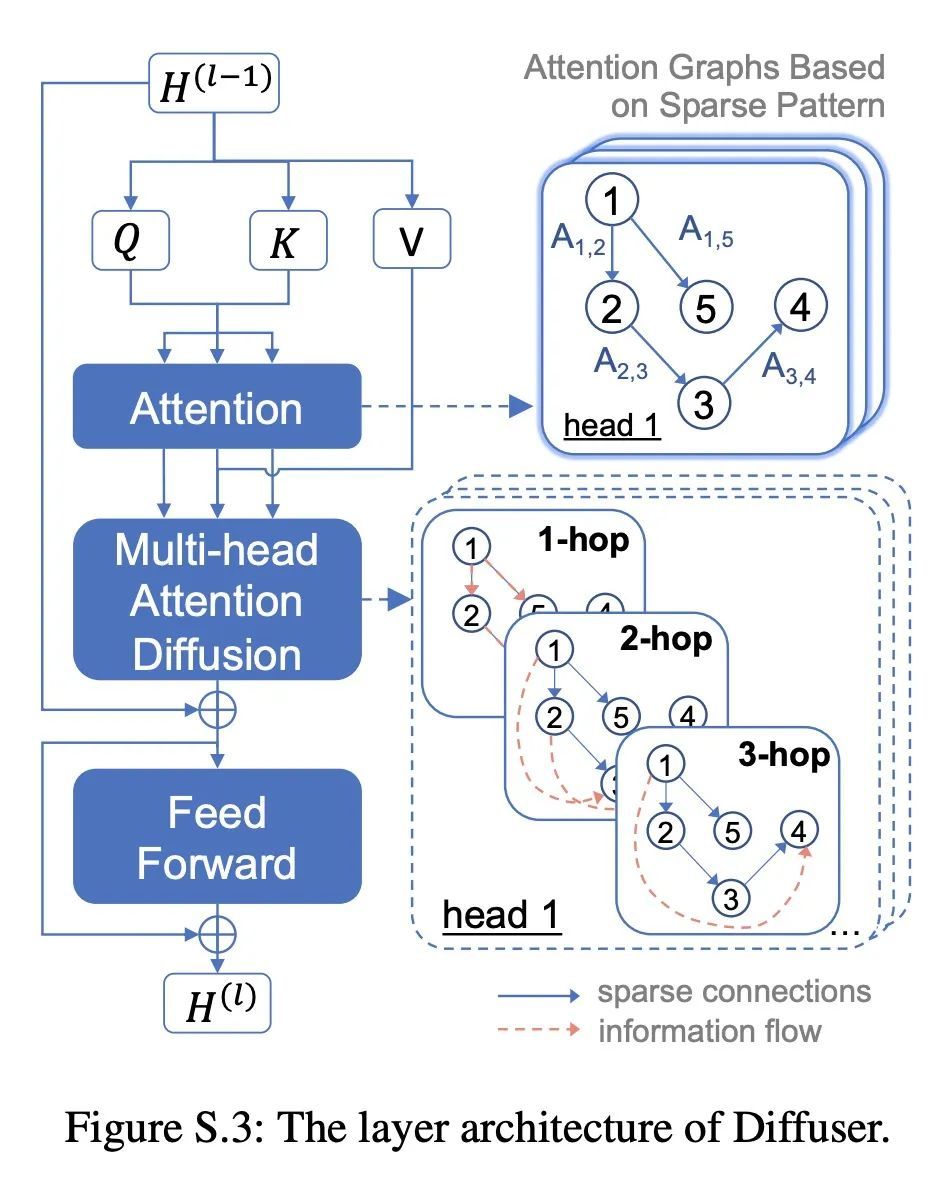
5、[CL] Diffuser: Efficient Transformers with Multi-hop Attention Diffusion for Long Sequences
A Feng, I Li, Y Jiang, R Ying
[Yale University]
Diffuser:基于多跳注意力扩散的长序列高效Transformer。由于高效Transformer的内存和时间复杂度低于二次方,因此已被开发用于长序列建模。稀疏Transformer是一种流行的方法,通过限制自注意力到预定义稀疏模式所指定的位置来提高Transformer的效率。然而,当重要的Token相关性在多跳之外时,利用稀疏性可能会牺牲全注意力的表现力。为了结合稀疏Transformer的效率和全注意力Transformer的表现力,本文提出Diffuser,一种新的最先进的高效Transformer。Diffuser在保持低计算和内存成本的同时,将所有token的交互纳入一个注意力层。其关键思想是利用注意力扩散来扩大稀疏注意力的感受野,除了相邻的token间的注意力外,它还根据相应的不相连的token之间的所有路径来计算多跳token的相关性。在理论上,本文展示了Diffuser作为序列对序列建模的通用序列近似器的表现力,并通过从频谱角度分析图扩张器的特性来研究其近似全注意力的能力。在实验上,本文通过广泛的评估来研究Diffuser的有效性,包括语言建模、图像建模和Long Range Arena(LRA)。评估结果显示,与最先进的基准相比,Diffuser在文本分类任务上平均提高了0.94%,在LRA上平均提高了2.30%,并节省了1.67倍的内存,这表明Diffuser在表达能力和效率方面都有优越性。
Efficient Transformers have been developed for long sequence modeling, due to their subquadratic memory and time complexity. Sparse Transformer is a popular approach to improving the efficiency of Transformers by restricting self-attention to locations specified by the predefined sparse patterns. However, leveraging sparsity may sacrifice expressiveness compared to full-attention, when important token correlations are multiple hops away. To combine advantages of both the efficiency of sparse transformer and the expressiveness of full-attention Transformer, we propose Diffuser, a new state-of-the-art efficient Transformer. Diffuser incorporates all token interactions within one attention layer while maintaining low computation and memory costs. The key idea is to expand the receptive field of sparse attention using Attention Diffusion, which computes multi-hop token correlations based on all paths between corresponding disconnected tokens, besides attention among neighboring tokens. Theoretically, we show the expressiveness of Diffuser as a universal sequence approximator for sequence-to-sequence modeling, and investigate its ability to approximate full-attention by analyzing the graph expander property from the spectral perspective. Experimentally, we investigate the effectiveness of Diffuser with extensive evaluations, including language modeling, image modeling, and Long Range Arena (LRA). Evaluation results show that Diffuser achieves improvements by an average of 0.94% on text classification tasks and 2.30% on LRA, with 1.67× memory savings compared to state-of-the-art benchmarks, which demonstrates superior performance of Diffuser in both expressiveness and efficiency aspects.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.11794

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
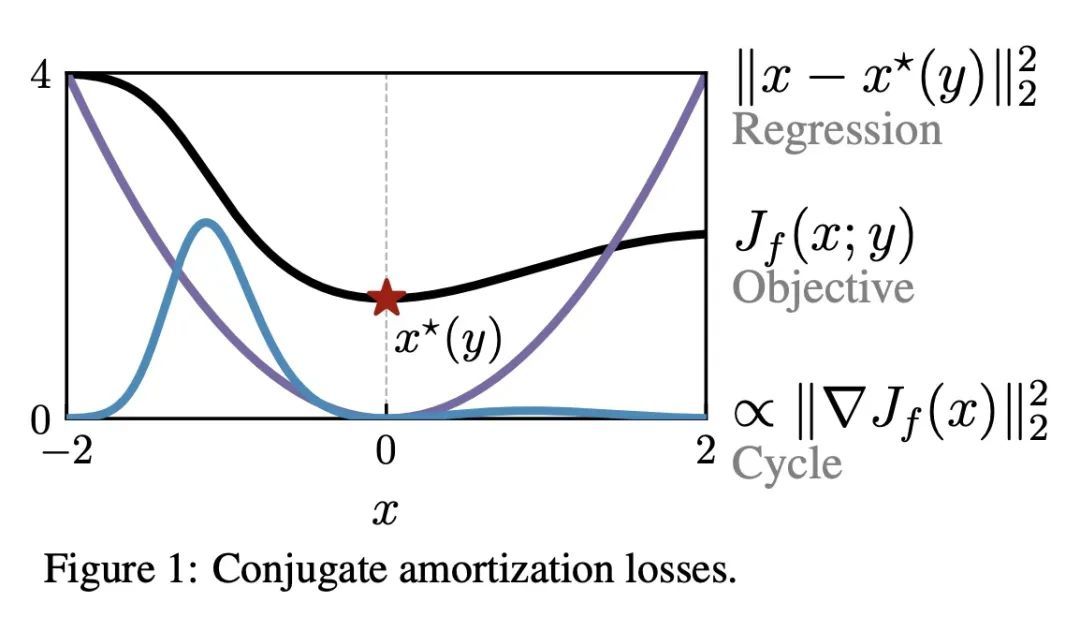
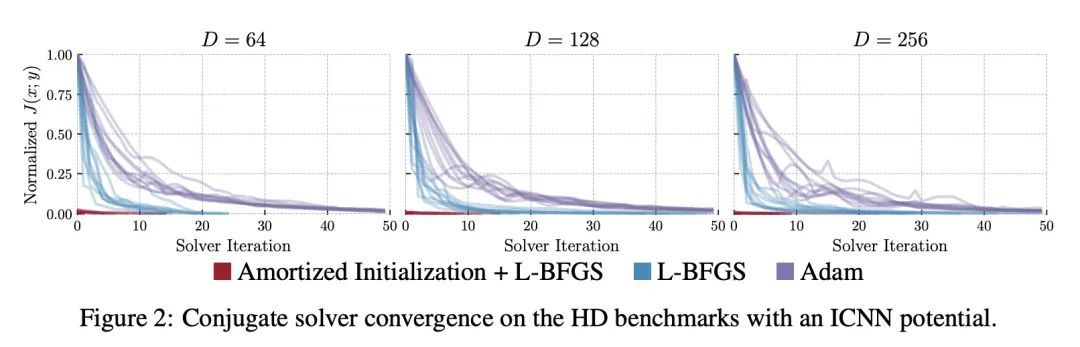
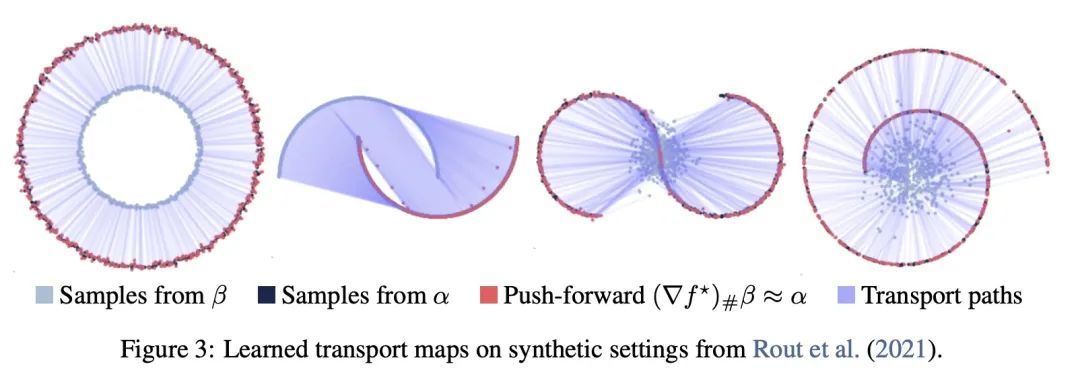
[LG] On amortizing convex conjugates for optimal transport
基于凸共轭摊销的最优传输
B Amos
[Meta AI]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.12153

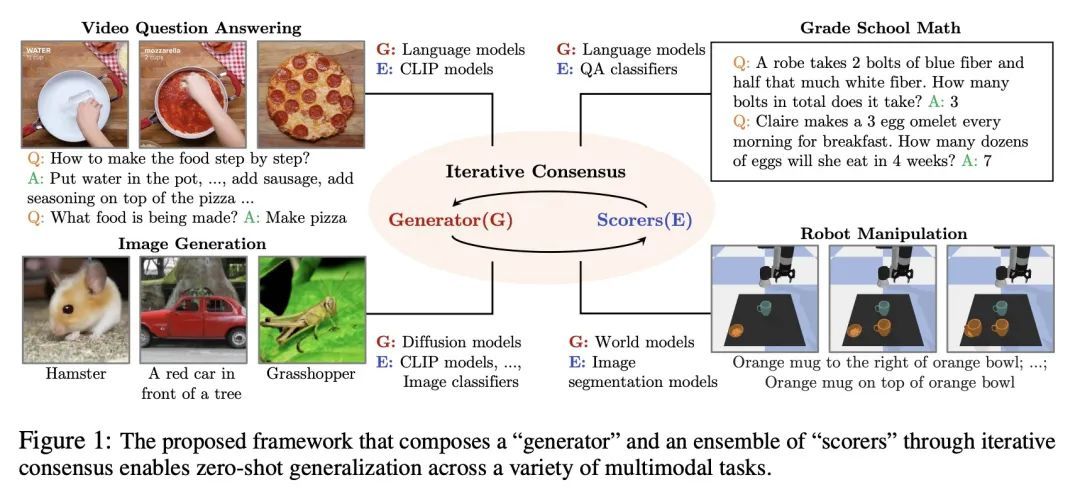
[CV] Composing Ensembles of Pre-trained Models via Iterative Consensus
基于迭代共识构建预训练模型集成
S Li, Y Du, J B. Tenenbaum, A Torralba, I Mordatch
[MIT CSAIL & Google Brain]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.11522

[CV] Towards Real-Time Text2Video via CLIP-Guided, Pixel-Level Optimization
基于CLIP引导像素级优化的实时文本到视频生成研究
P Schaldenbrand, Z Liu, J Oh
[CMU]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.12826




[LG] Bayesian Optimization with Conformal Coverage Guarantees
基于共形覆盖保证的贝叶斯优化
S Stanton, W Maddox, A G Wilson
[Genentech & New York University]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.12496

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢