LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:一种基于模型特定信息自适应权重衰减的Adam式优化器、用外科式微调提高对分布漂移的自适应性、基于等变扩散模型的基于结构药物设计、任意量子过程预测学习、将SAM看做贝叶斯最优松弛、文本到图像生成模型大规模提示库数据集、多域端到端语音识别基准、检索增强常识推理统一方法、高精度机器学习
1、[LG] Amos: An Adam-style Optimizer with Adaptive Weight Decay towards Model-Oriented Scale
R Tian, A P. Parikh
[Google Research]
Amos: 一种基于模型特定信息自适应权重衰减的Adam式优化器。本文提出Amos,一种基于随机梯度的优化器,用于训练深度神经网络,可看作是一个具有理论支持的、自适应学习率衰减和权重衰减的Adam优化器。Amos背后的一个关键见解是,利用特定的模型信息来确定初始学习率和衰减时间表。当用于预训练BERT变体和T5时,Amos始终比AdamW的最先进设置收敛得更快,在<=70%的训练步骤和时间内实现了更好的验证损失,同时需要<=51%的内存用于槽变量。
We present Amos, a stochastic gradient-based optimizer designed for training deep neural networks. It can be viewed as an Adam optimizer with theoretically supported, adaptive learning-rate decay and weight decay. A key insight behind Amos is that it leverages model-specific information to determine the initial learning-rate and decaying schedules. When used for pre-training BERT variants and T5, Amos consistently converges faster than the state-of-the-art settings of AdamW, achieving better validation loss within <=70% training steps and time, while requiring <=51% memory for slot variables. Our code is open-sourced at: this https URL
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.11693

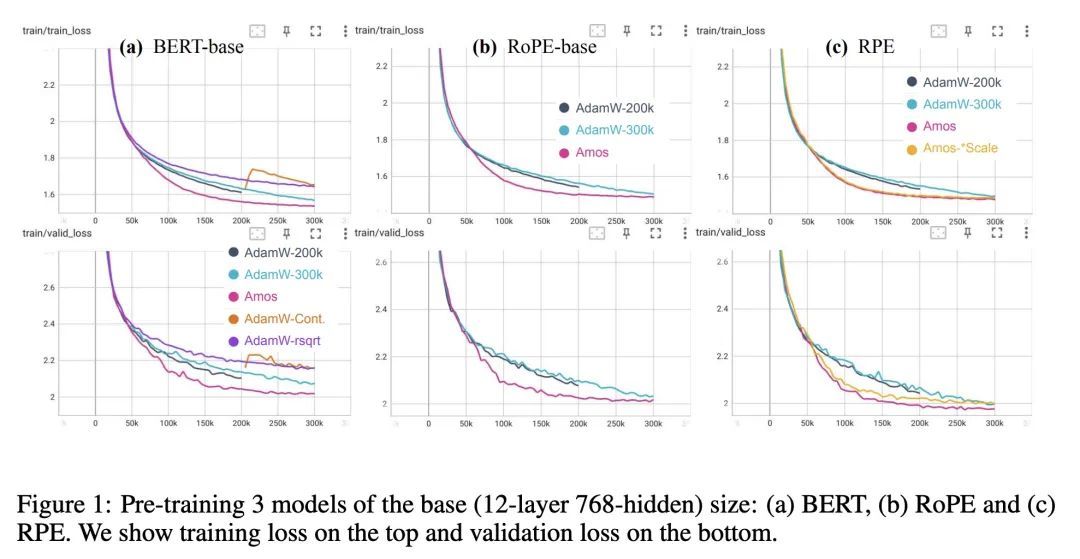
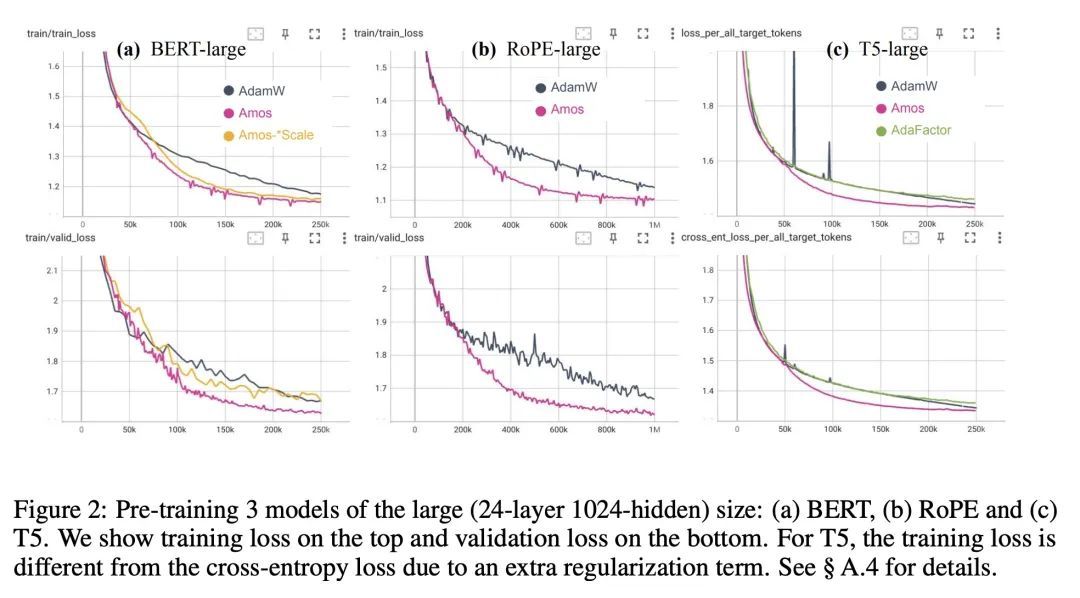

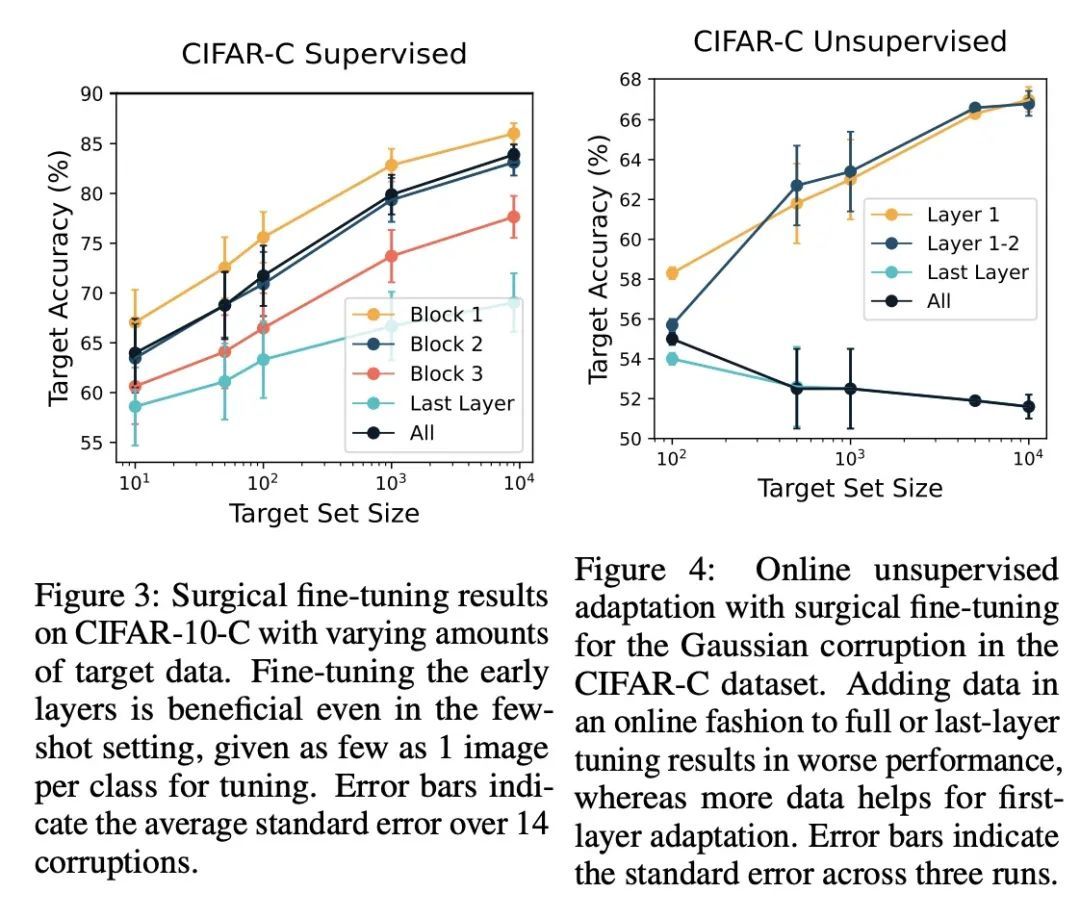
2、[LG] Surgical Fine-Tuning Improves Adaptation to Distribution Shifts
Y Lee, A S. Chen, F Tajwar, A Kumar, H Yao, P Liang, C Finn
[Stanford University]
用外科手术式微调提高对分布漂移的自适应性。在分布漂移下进行迁移学习的一种常见方法是对预训练模型的最后几层进行微调,在保留所学特征的同时适应新的任务。本文表明,在这种情况下,有选择地微调一个层的子集(称为外科式微调)与常用的微调方法相匹配或优于后者。此外,分布漂移的类型影响着哪一个子集更有效地进行调整:例如,对于图像损坏,只对前几层进行微调效果最好。本文在七个真实世界数据任务中系统地验证了以上发现,这些任务横跨三种类型的分布漂移。理论上,本文证明了在一个理想化的环境中,对于两层神经网络,第一层的调整可以胜过所有层的微调。直观地说,在一个小的目标数据集上微调更多的参数会导致在预训练期间学到的信息被遗忘,而相关信息取决于漂移的类型。
A common approach to transfer learning under distribution shift is to fine-tune the last few layers of a pre-trained model, preserving learned features while also adapting to the new task. This paper shows that in such settings, selectively fine-tuning a subset of layers (which we term surgical fine-tuning) matches or outperforms commonly used fine-tuning approaches. Moreover, the type of distribution shift influences which subset is more effective to tune: for example, for image corruptions, fine-tuning only the first few layers works best. We validate our findings systematically across seven real-world data tasks spanning three types of distribution shifts. Theoretically, we prove that for two-layer neural networks in an idealized setting, first-layer tuning can outperform fine-tuning all layers. Intuitively, fine-tuning more parameters on a small target dataset can cause information learned during pre-training to be forgotten, and the relevant information depends on the type of shift.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.11466

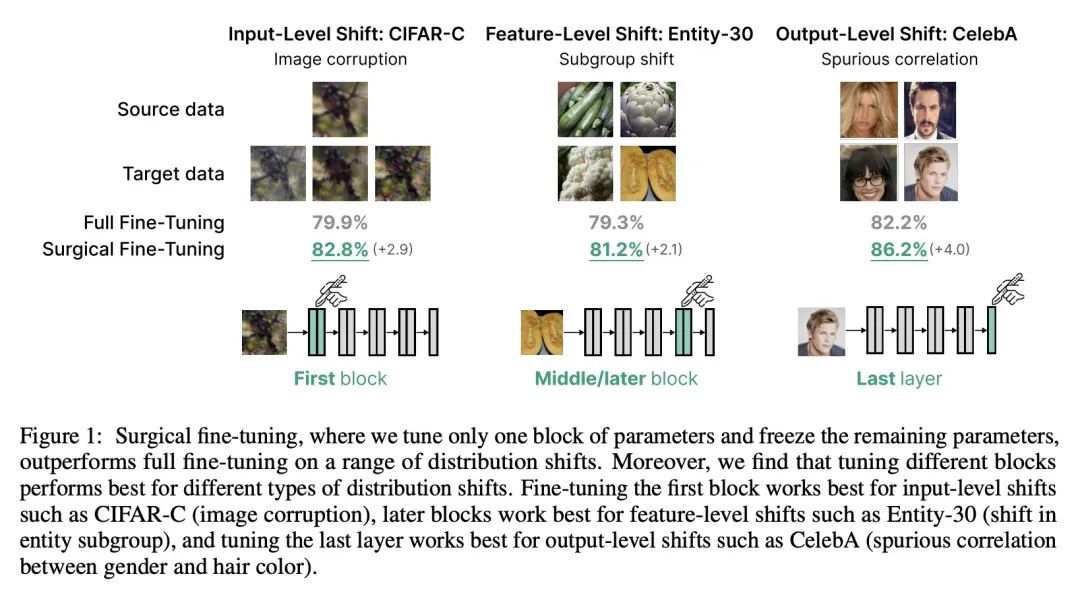
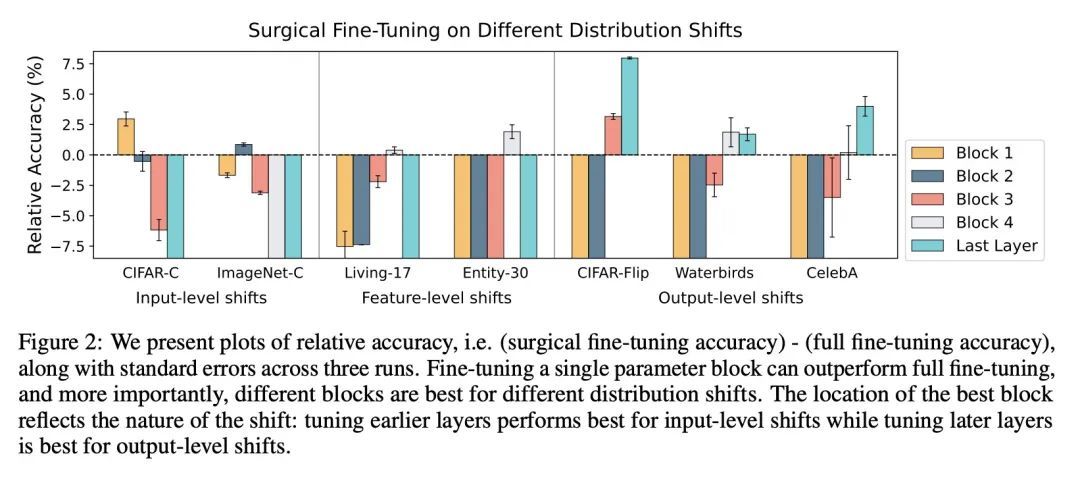
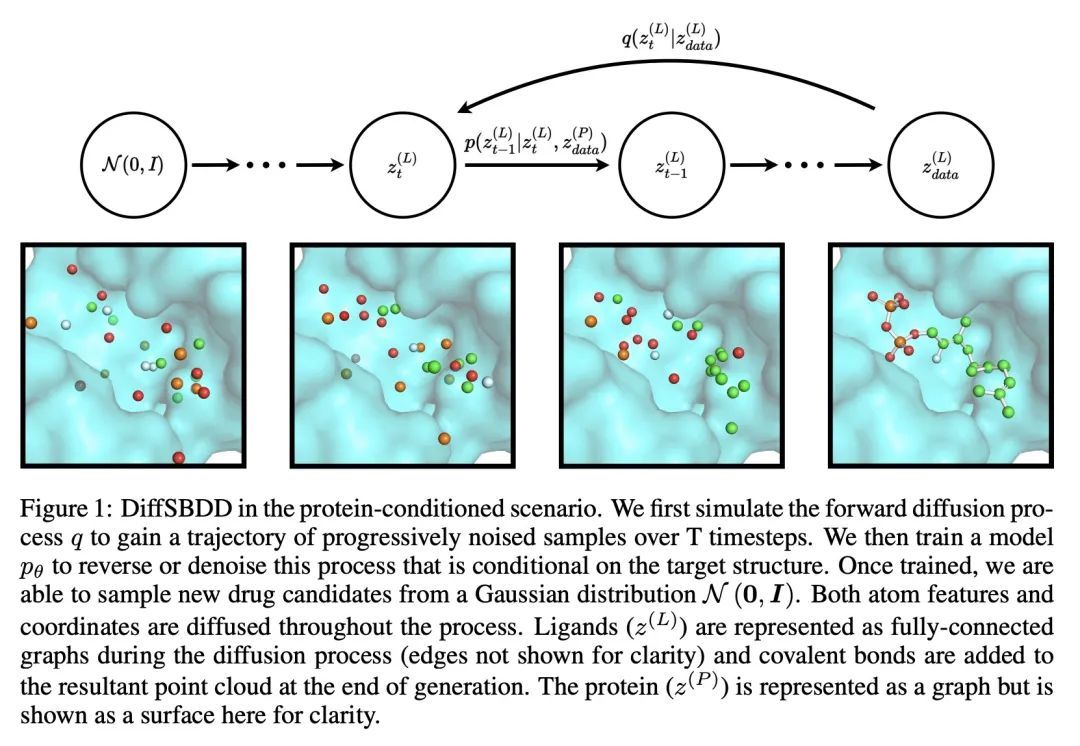
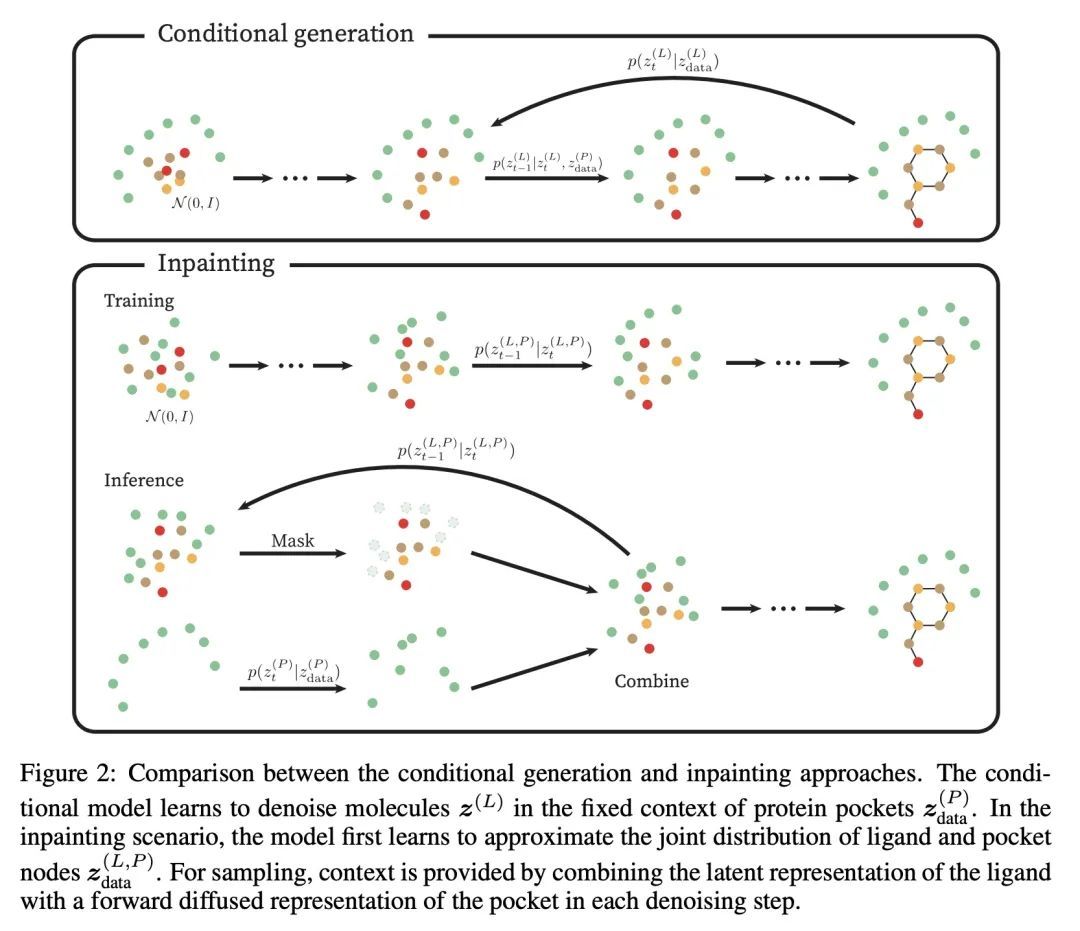
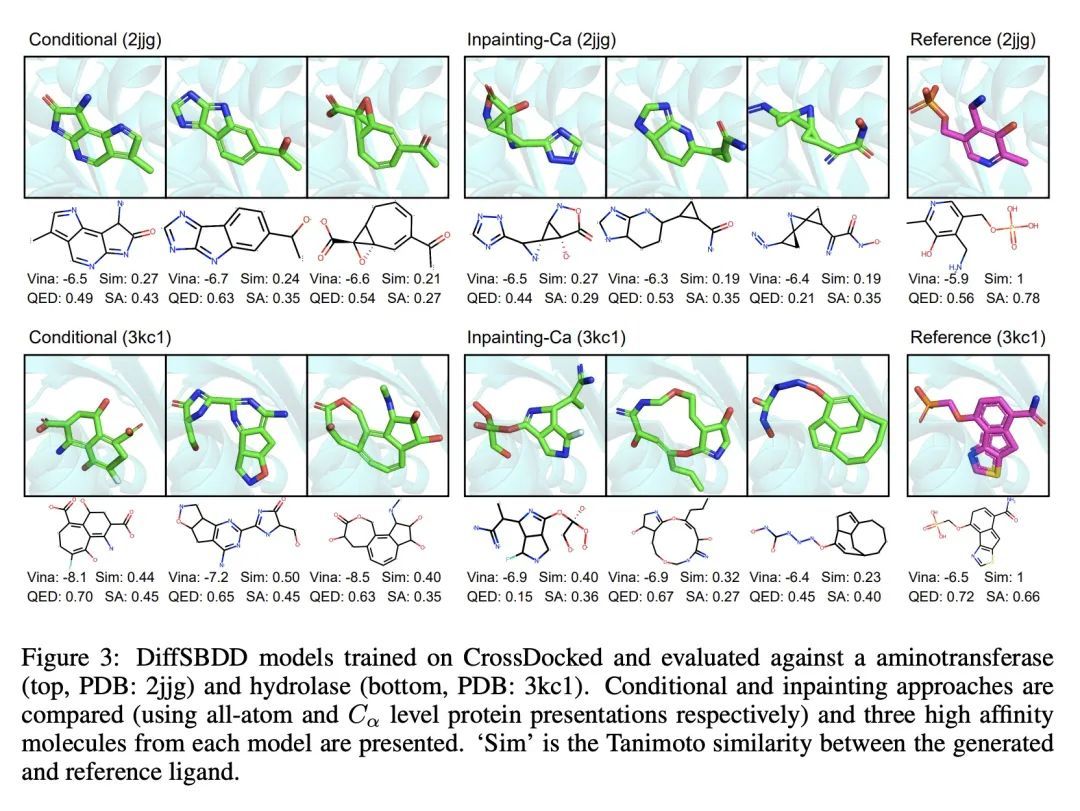
3、[LG] Structure-based Drug Design with Equivariant Diffusion Models
A Schneuing, Y Du...
[Ecole Polytechnique Federale de Lausanne & Cornell University & University of Cambridge & USTC & Microsoft Research AI4Science & ...]
基于等变扩散模型的基于结构药物设计。基于结构的药物设计(SBDD)旨在设计具有高亲和力和特异性的小分子配体,与预先确定的蛋白质目标结合。传统的SBDD管道从公共数据库的大规模对接化合物库开始,将化学空间的探索限制在现有的先前研究区域。最近的机器学习方法采用逐个原子生成的方法来处理该问题,在计算上很昂贵。本文将SBDD表述为一个3D条件生成问题,提出DiffSBDD,一种E(3)等变3D条件扩散模型,该模型根据蛋白质袋的条件生成新的配体。从Binding MOAD策划了一个新的实验确定的结合复合物数据集,以提供一个现实的结合场景,补充合成的CrossDocked数据集。全面的硅学实验证明了DiffSBDD在生成新的和多样化的类似药物的配体方面的效率,这些配体以硅学对接预测的高结合能量参与蛋白质袋。
Structure-based drug design (SBDD) aims to design small-molecule ligands that bind with high affinity and specificity to pre-determined protein targets. Traditional SBDD pipelines start with large-scale docking of compound libraries from public databases, thus limiting the exploration of chemical space to existent previously studied regions. Recent machine learning methods approached this problem using an atom-by-atom generation approach, which is computationally expensive. In this paper, we formulate SBDD as a 3D-conditional generation problem and present DiffSBDD, an E(3)-equivariant 3D-conditional diffusion model that generates novel ligands conditioned on protein pockets. Furthermore, we curate a new dataset of experimentally determined binding complex data from Binding MOAD to provide a realistic binding scenario that complements the synthetic CrossDocked dataset. Comprehensive in silico experiments demonstrate the efficiency of DiffSBDD in generating novel and diverse drug-like ligands that engage protein pockets with high binding energies as predicted by in silico docking.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.13695

4、[LG] Learning to predict arbitrary quantum processes
H Huang, S Chen, J Preskill
[Caltech & UC Berkeley]
任意量子过程预测学习。本文提出一种高效的机器学习(ML)算法,用于预测n量子比特上的任意未知量子过程ε。对于任意n量子比特状态上的广泛分布D,本文表明这种机器学习算法可以学习预测未知过程D的输出的任意局部属性,并且对从ε中抽取的输入状态具有小的平均误差。所提出算法结合了学习未知状态的属性和学习未知观测点的低度近似的有效程序。分析的关键在于证明新的模不等式,包括经典的Bohnenblust-Hille不等式的量子类似物,通过给出优化局部哈密尔顿的改进算法来推导。总的来说,本文结果突出了机器学习模型预测复杂量子动力学输出的潜力,比运行过程本身所需的时间快得多。
We present an efficient machine learning (ML) algorithm for predicting any unknown quantum process ε over n qubits. For a wide range of distributions D on arbitrary n-qubit states, we show that this ML algorithm can learn to predict any local property of the output from the unknown process D, with a small average error over input states drawn from ε. The ML algorithm is computationally efficient even when the unknown process is a quantum circuit with exponentially many gates. Our algorithm combines efficient procedures for learning properties of an unknown state and for learning a low-degree approximation to an unknown observable. The analysis hinges on proving new norm inequalities, including a quantum analogue of the classical Bohnenblust-Hille inequality, which we derive by giving an improved algorithm for optimizing local Hamiltonians. Overall, our results highlight the potential for ML models to predict the output of complex quantum dynamics much faster than the time needed to run the process itself.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.14894

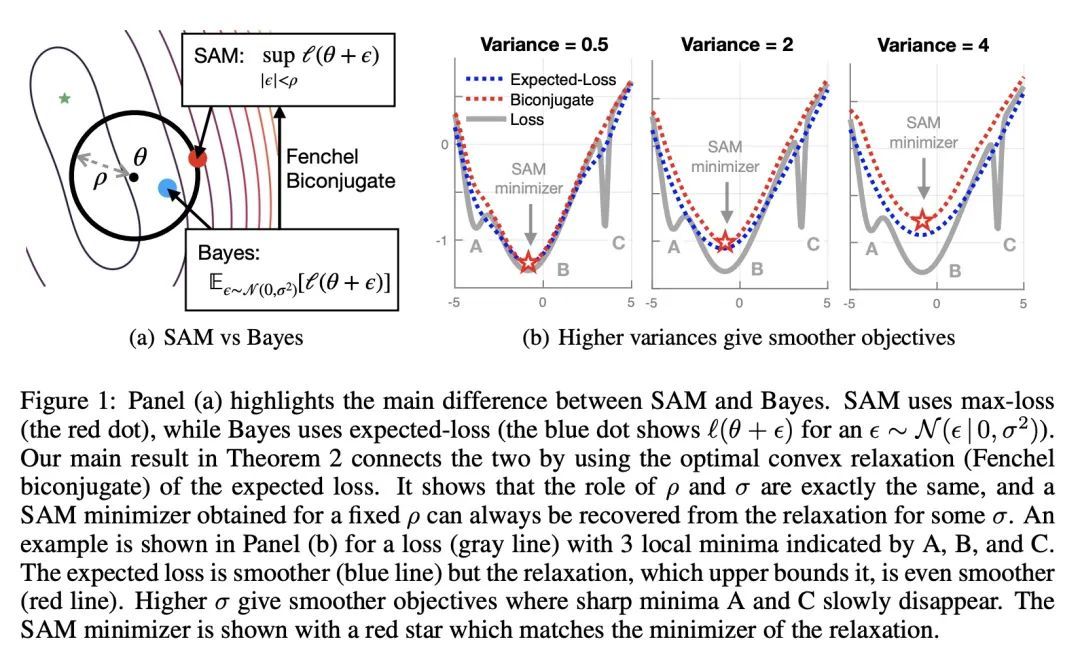
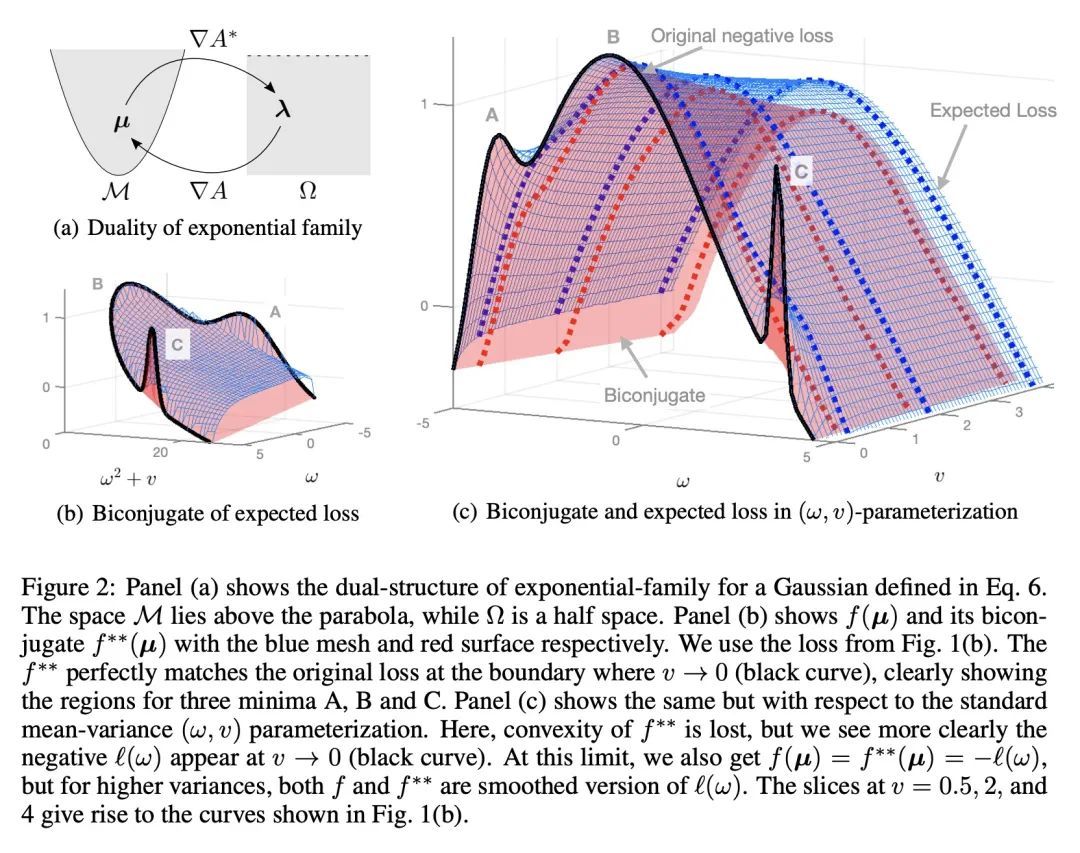
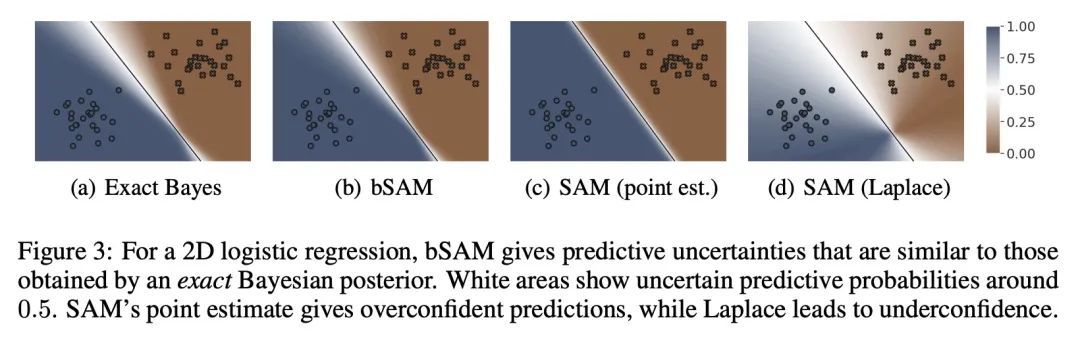
5、[LG] SAM as an Optimal Relaxation of Bayes
T Möllenhoff, M E Khan
[RIKEN Center for Advanced Intelligence Project]
将SAM看做贝叶斯最优松弛。锐度感知最小化(SAM)和相关对抗性深度学习方法可以极大地提高泛化能力,但其基本机制还没有被完全理解。本文将SAM确立为贝叶斯目标的松弛,其中预期的负损失被最佳凸下界所取代,该下界是通过使用所谓的Fenchel双共轭得到的。这种联系使得SAM的一个新的类似Adam的扩展能自动获得合理的不确定性估计,同时有时还能提高其准确性。通过连接对抗性和贝叶斯方法,本文工作开辟了一条通往鲁棒性的新道路。
Sharpness-aware minimization (SAM) and related adversarial deep-learning methods can drastically improve generalization, but their underlying mechanisms are not yet fully understood. Here, we establish SAM as a relaxation of the Bayes objective where the expected negative-loss is replaced by the optimal convex lower bound, obtained by using the so-called Fenchel biconjugate. The connection enables a new Adam-like extension of SAM to automatically obtain reasonable uncertainty estimates, while sometimes also improving its accuracy. By connecting adversarial and Bayesian methods, our work opens a new path to robustness.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.01620

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
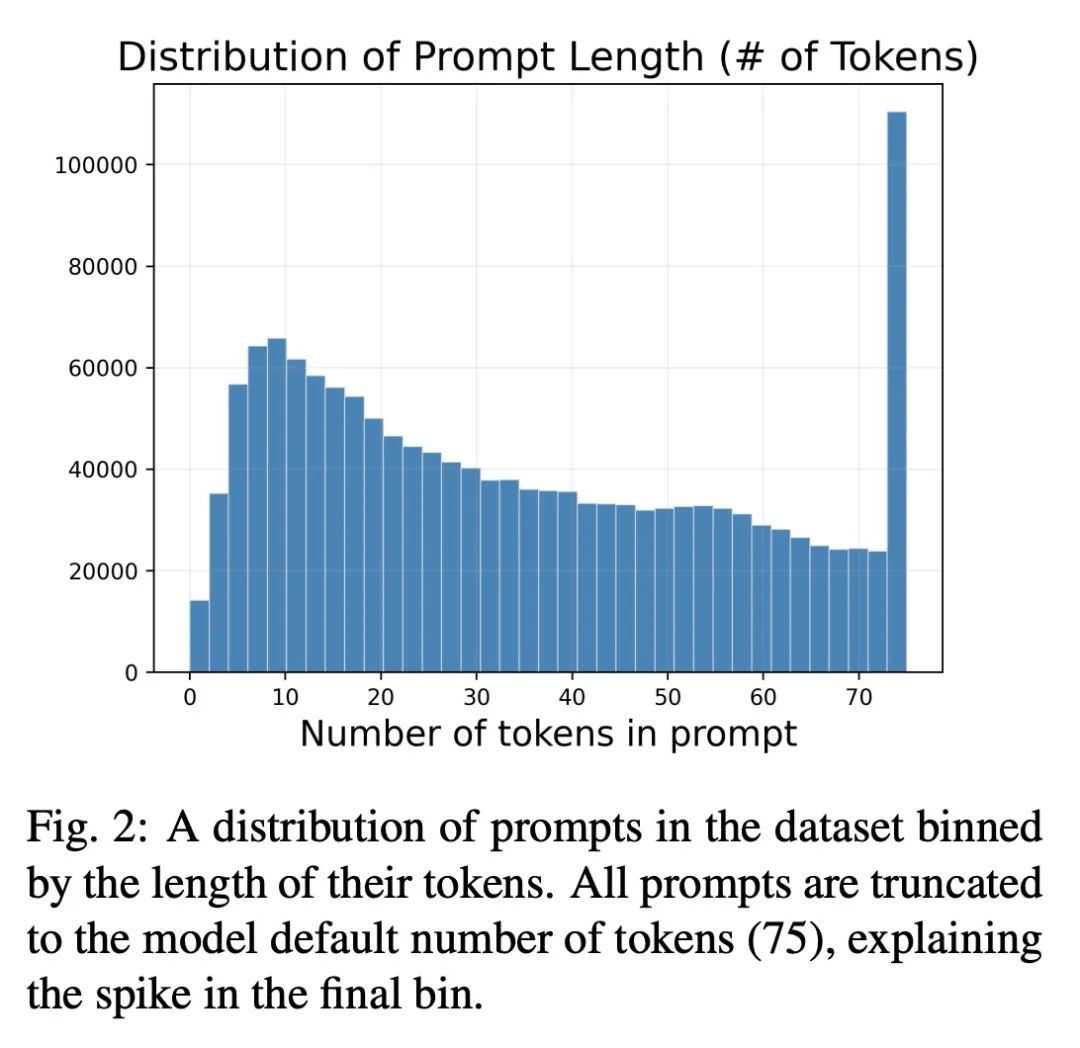
[CV] DiffusionDB: A Large-scale Prompt Gallery Dataset for Text-to-Image Generative Models
DiffusionDB:文本到图像生成模型大规模提示库数据集
Z J. Wang, E Montoya, D Munechika, H Yang, B Hoover, D H Chau
[Georgia Tech]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.14896



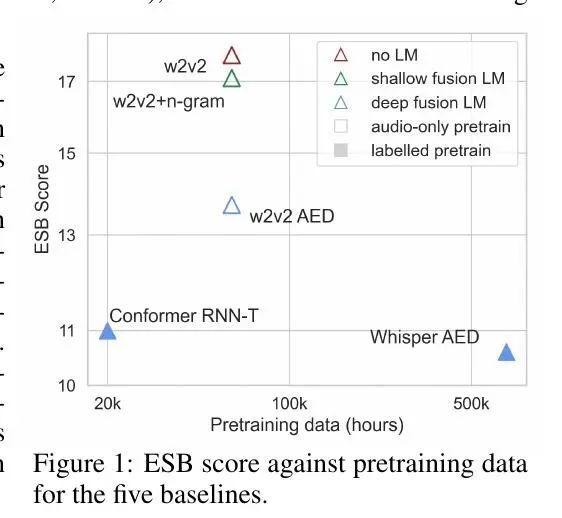
[CL] ESB: A Benchmark For Multi-Domain End-to-End Speech Recognition
ESB:多域端到端语音识别基准
S Gandhi, P v Platen, A M. Rush
[Hugging Face]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.13352

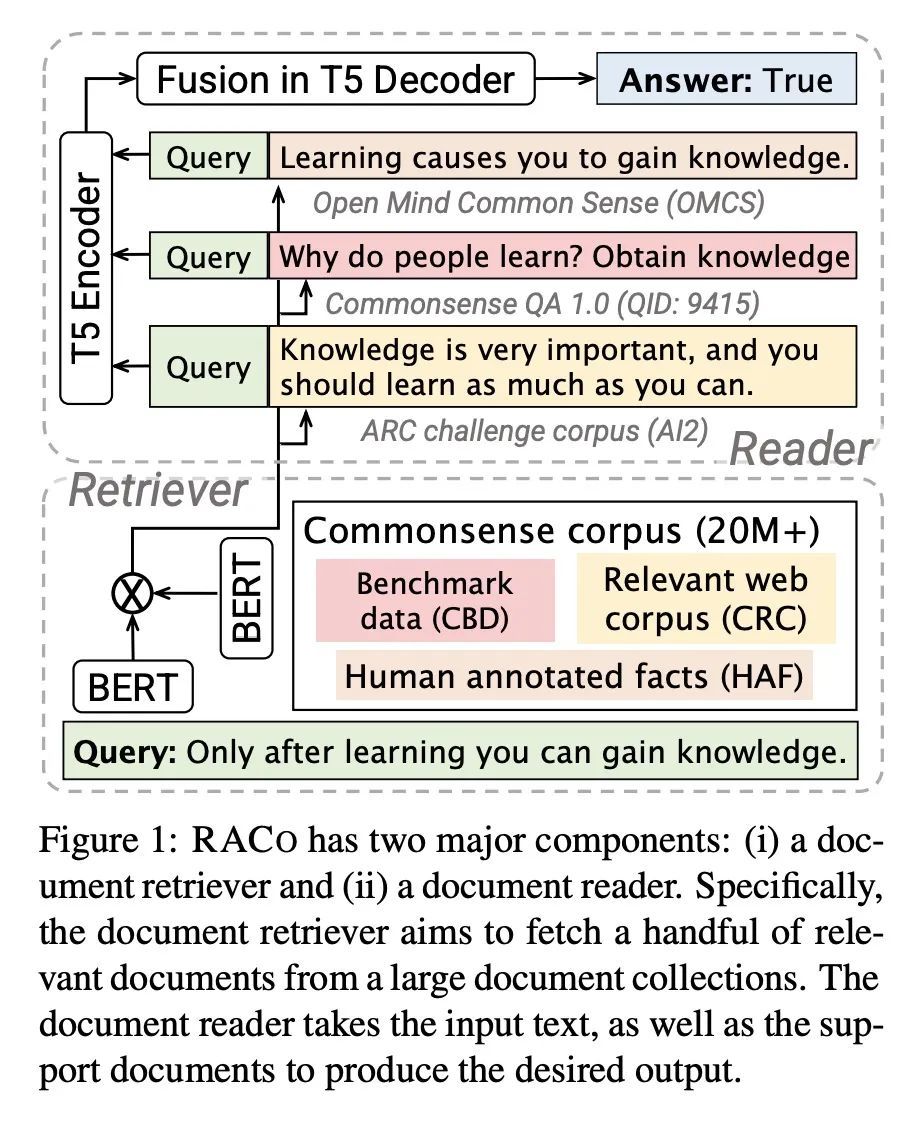
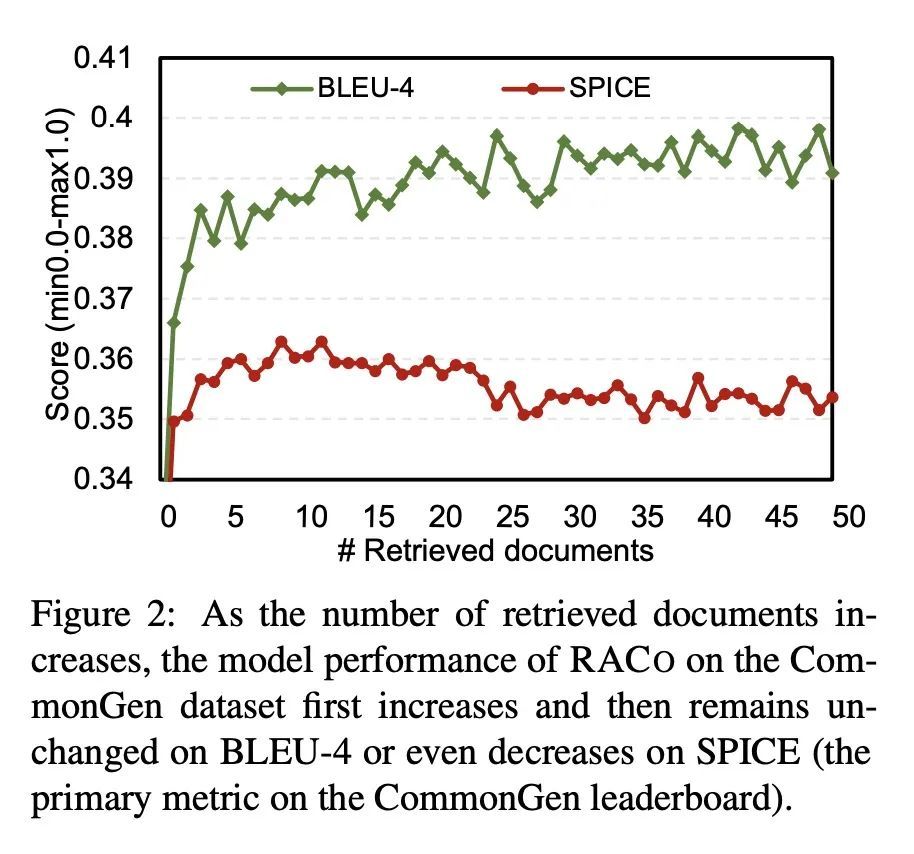
[CL] Retrieval Augmentation for Commonsense Reasoning: A Unified Approach
检索增强常识推理:一种统一方法
W Yu, C Zhu, Z Zhang, S Wang...
[University of Notre Dame & Microsoft Cognitive Services Research & Shanghai Jiaotong University]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.12887

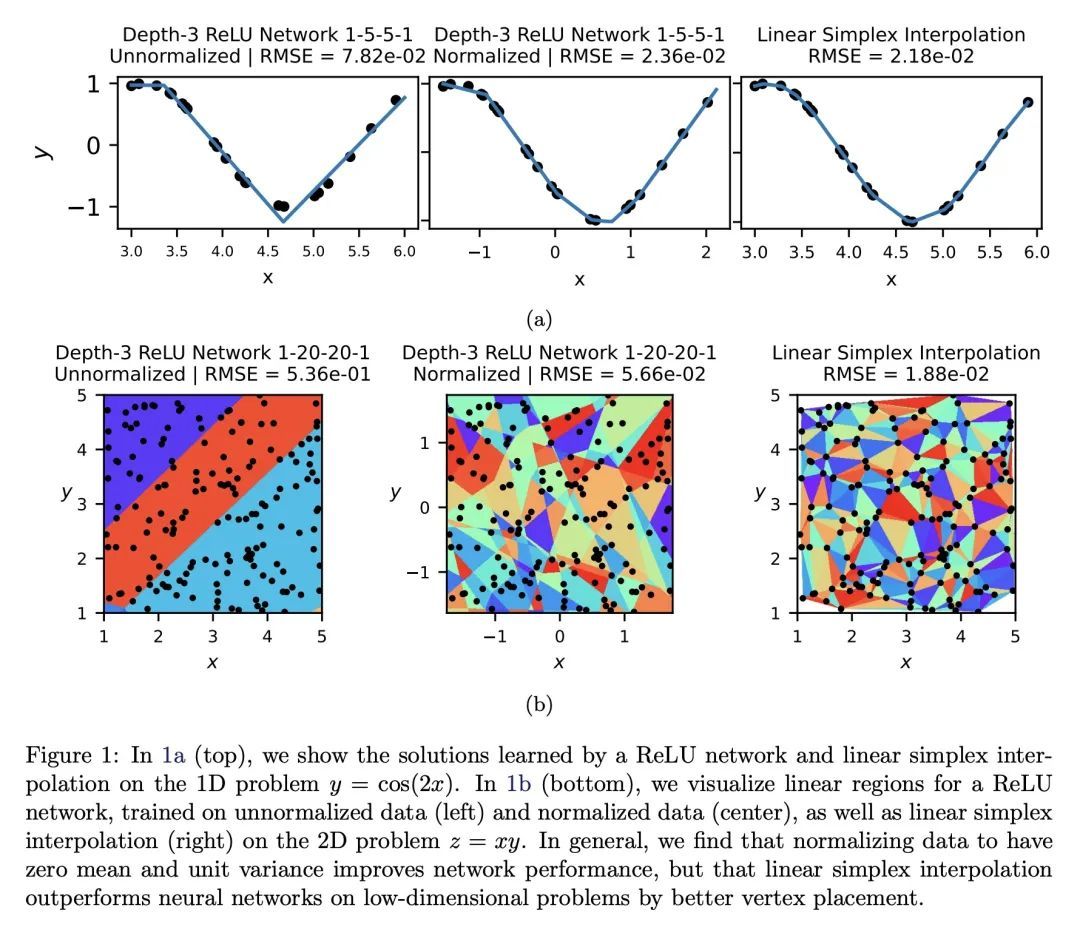
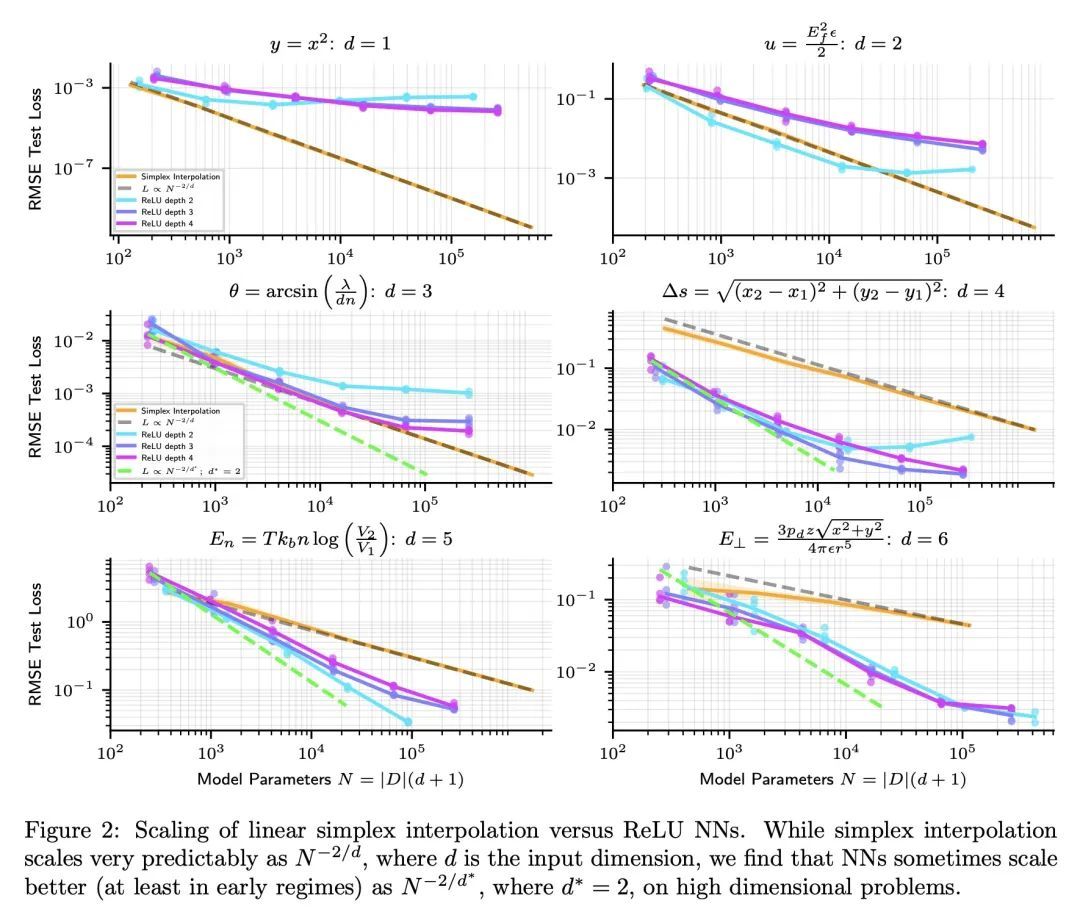
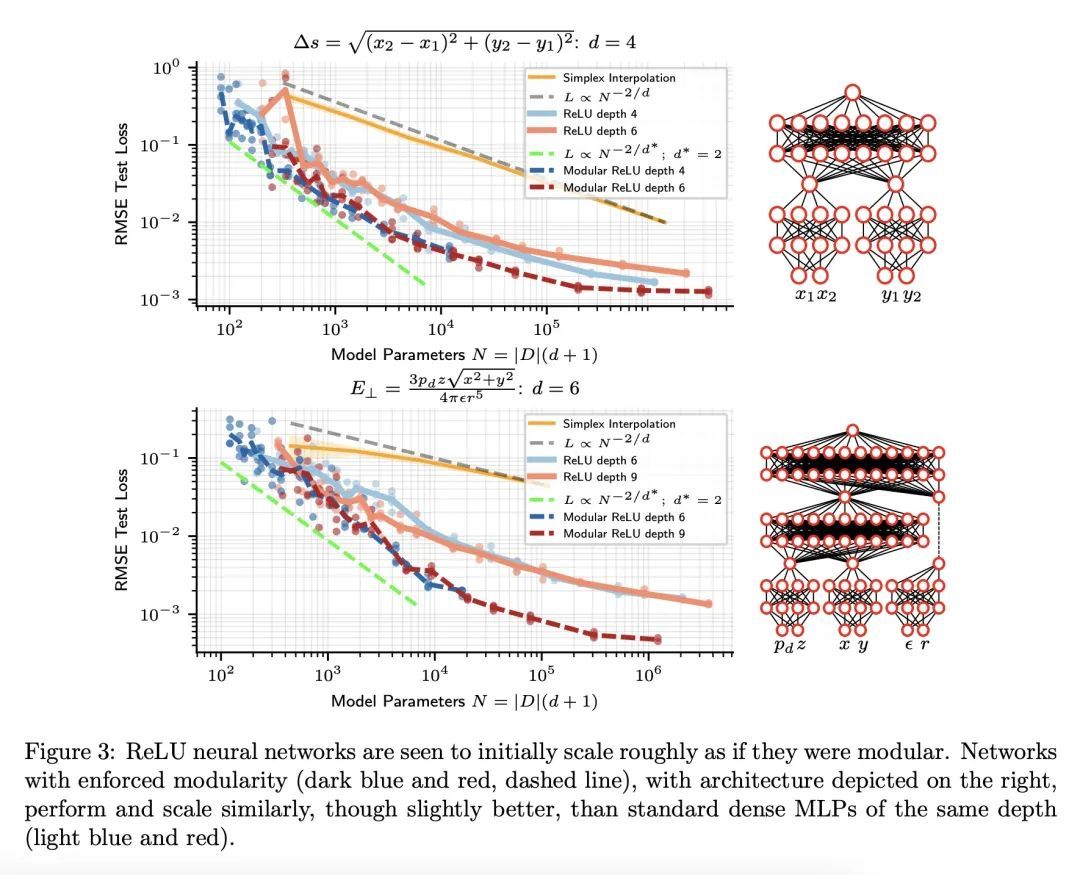
[LG] Precision Machine Learning
高精度机器学习
E J. Michaud, Z Liu, M Tegmark
[MIT]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.13447

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢