LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:采用基于分数扩散的全频段通用音频合成、从合并树中学习星系属性、通过观看无标签在线视频进行顺序行动决策学习、有百万GPU算力该训练什么语言模型、基于梯度下降的正弦波频率估计、稳态时间序列预测的动态误差界、基于知识增强去噪专家混合的改进文本到图像扩散模型、大型语言模型理解能力之争、用上下文化语义轴发现人的表达差异
1、[AS] Full-band General Audio Synthesis with Score-based Diffusion
S Pascual, G Bhattacharya, C Yeh, J Pons, J Serrà
[Dolby Laboratories]
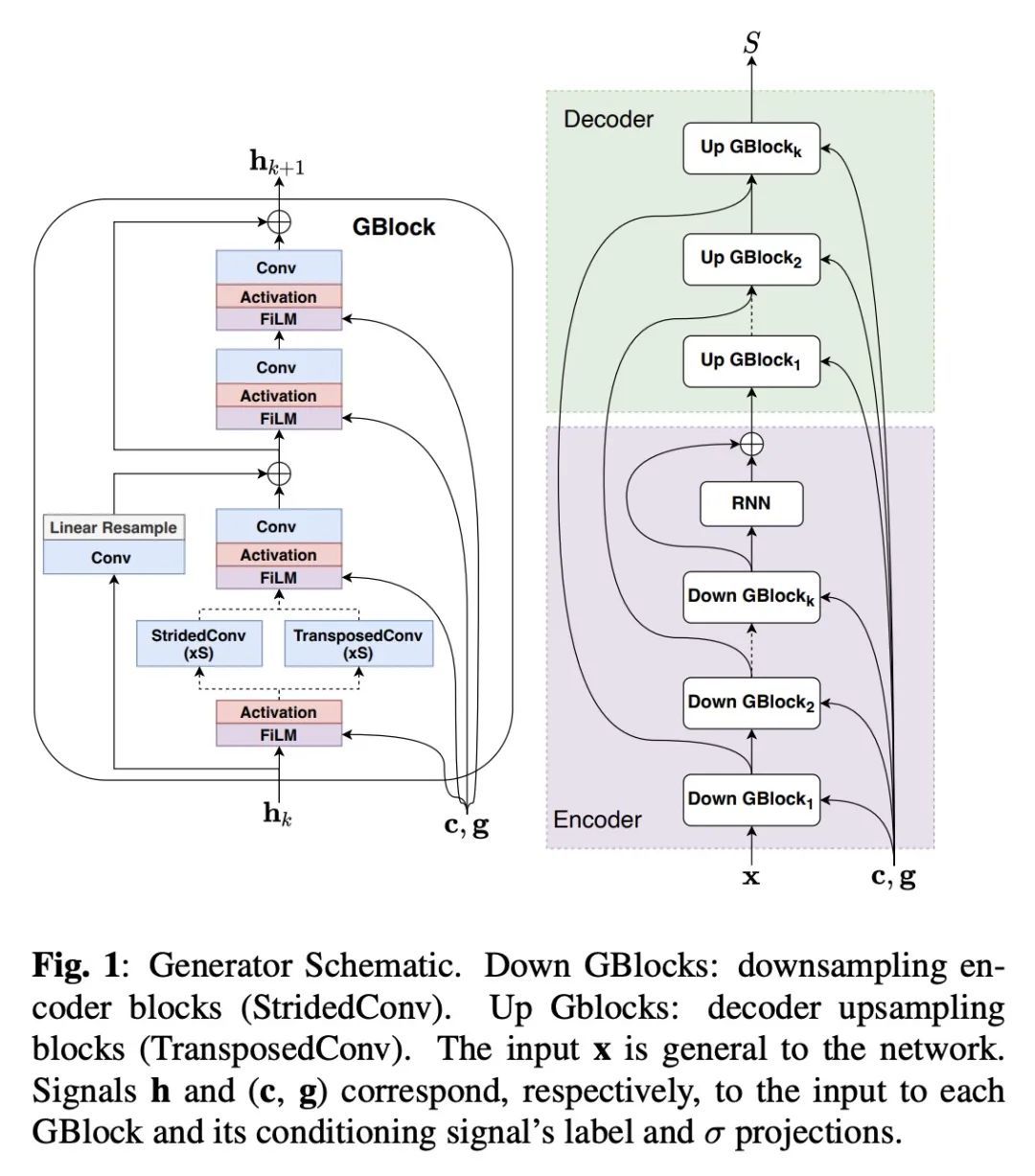
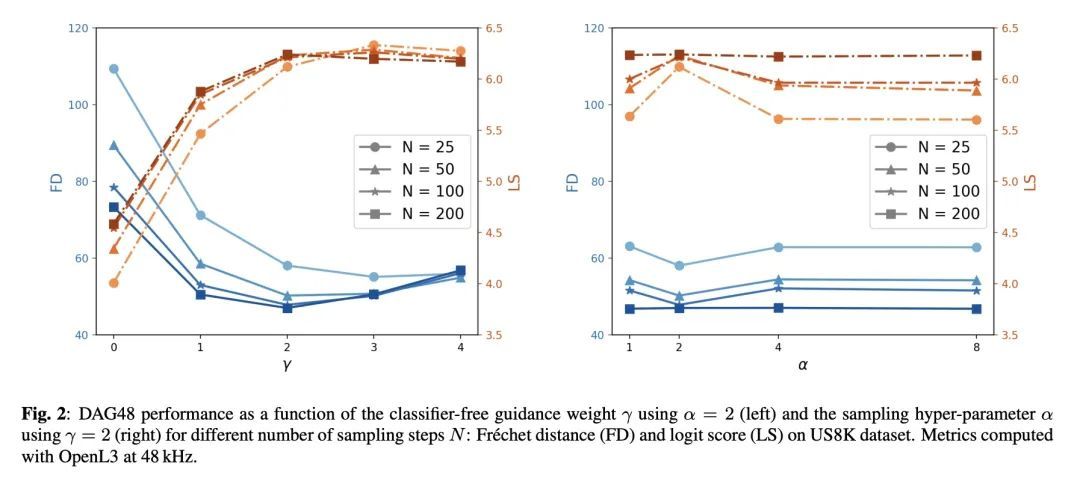
采用基于分数扩散的全频段通用音频合成。最近的工作表明,深度生成模型有能力处理来自单个标签的一般音频合成,产生各种脉冲的、音调的和环境的声音。这类模型在频带有限的信号上运行,由于采用了自回归方法,通常由预训练好的潜编码器和/或几个级联模块组成。本文提出一种用于一般音频合成的基于扩散的生成模型DAG,一种采用基于分数扩散的全频段通用音频合成模型,在波形域端到端处理全带信号。结果表明,DAG在质量和多样性方面都优于现有的标签条件生成器。与现有技术水平相比,DAG的限带和全带版本的相对改进分别达到了40%和65%。
Recent works have shown the capability of deep generative models to tackle general audio synthesis from a single label, producing a variety of impulsive, tonal, and environmental sounds. Such models operate on band-limited signals and, as a result of an autoregressive approach, they are typically conformed by pre-trained latent encoders and/or several cascaded modules. In this work, we propose a diffusion-based generative model for general audio synthesis, named DAG, which deals with full-band signals end-to-end in the waveform domain. Results show the superiority of DAG over existing label-conditioned generators in terms of both quality and diversity. More specifically, when compared to the state of the art, the band-limited and full-band versions of DAG achieve relative improvements that go up to 40 and 65%, respectively. We believe DAG is flexible enough to accommodate different conditioning schemas while providing good quality synthesis.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.14661

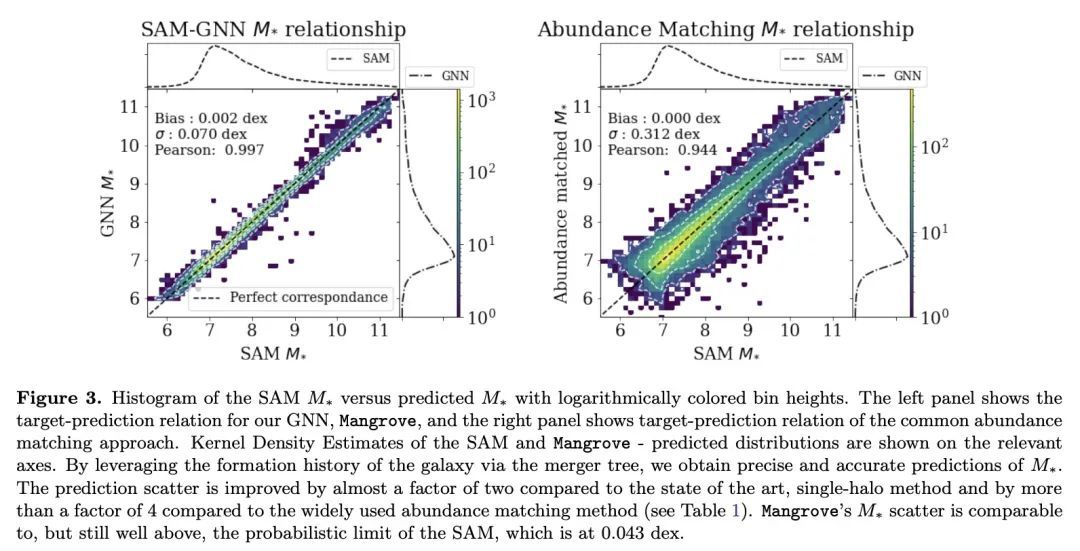
2、[LG] Mangrove: Learning Galaxy Properties from Merger Trees
C K Jespersen, M Cranmer, P Melchior, S Ho...
[Princeton University & Flatiron Institute & Catholic University of America]
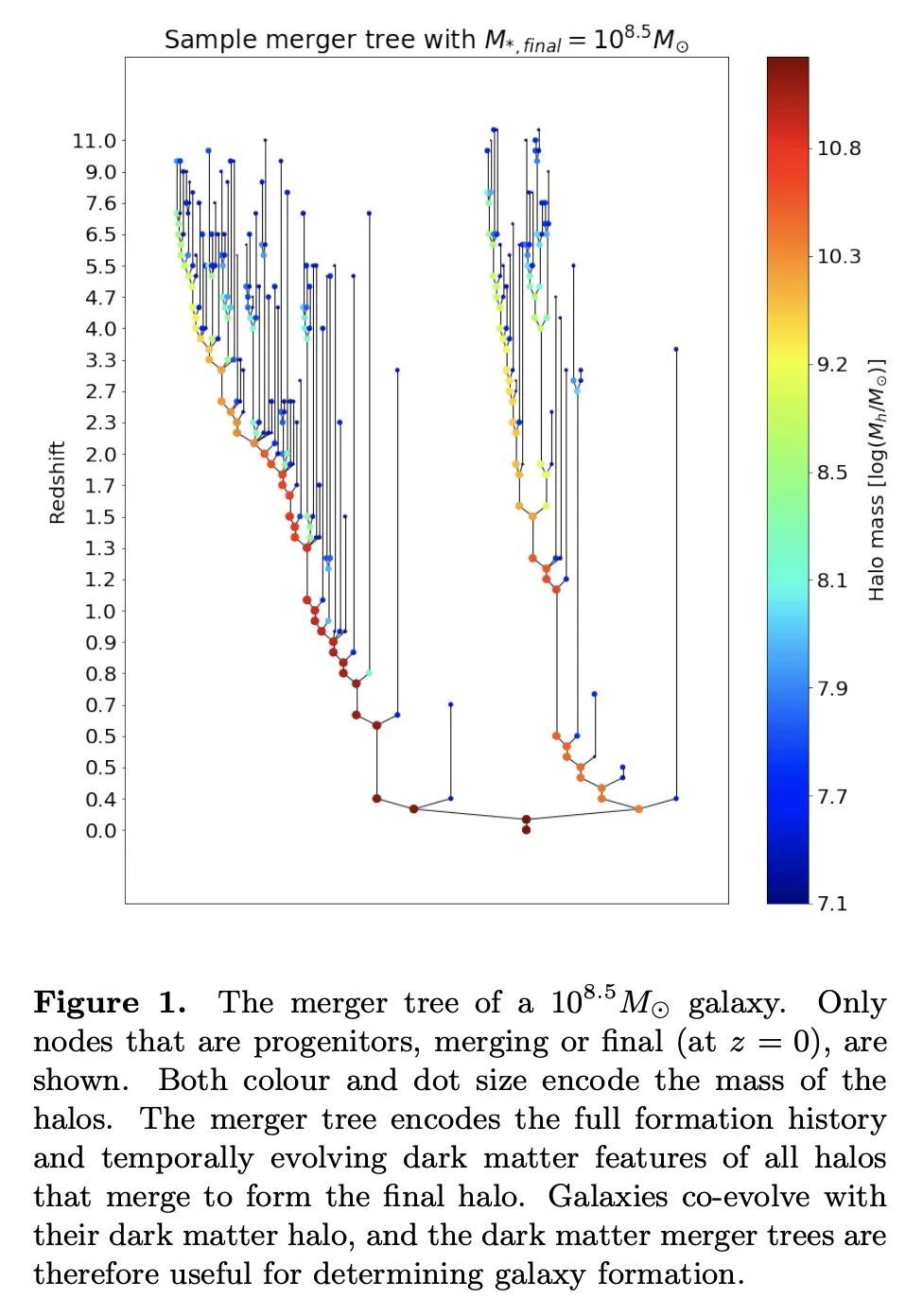
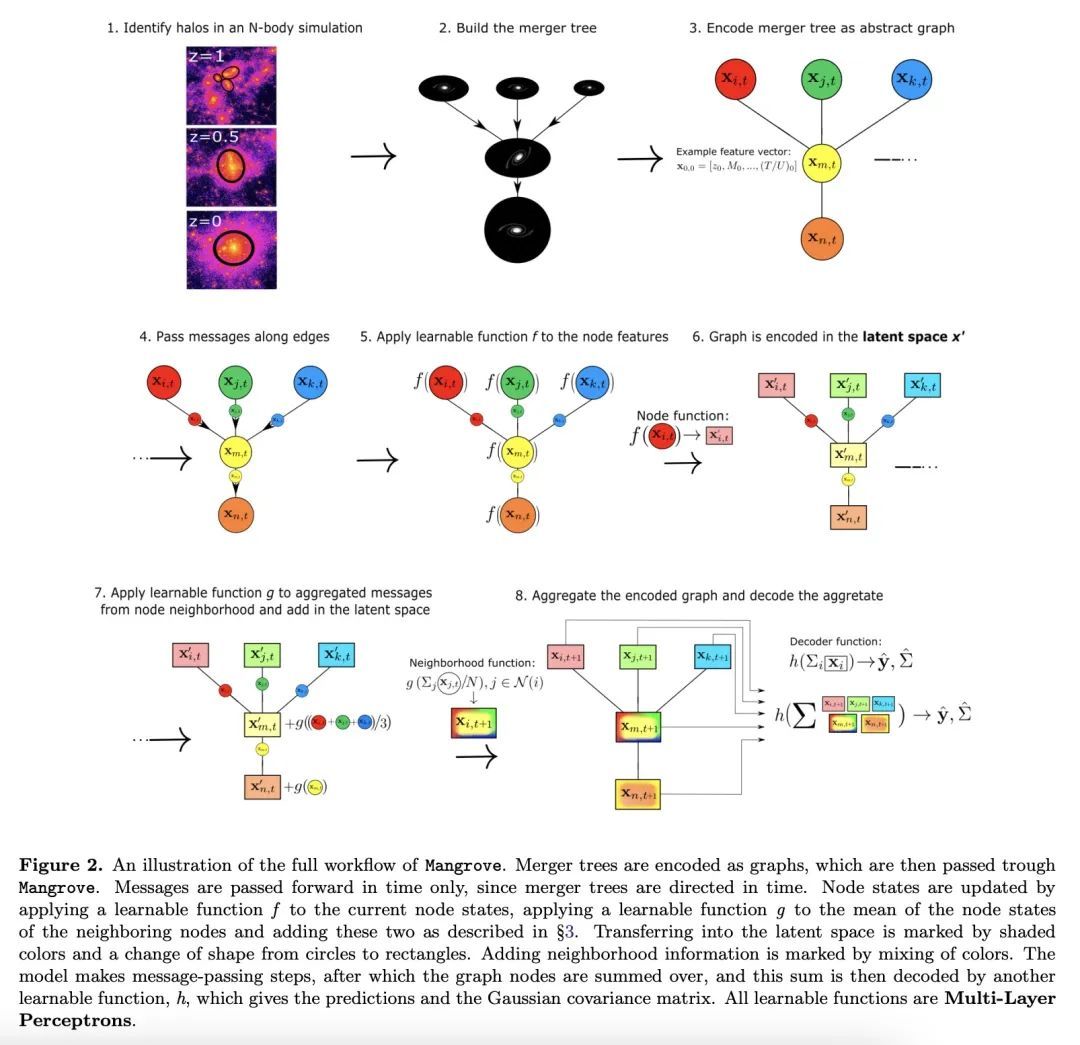
Mangrove:从合并树中学习星系属性。有效地将重子属性映射到暗物质是天体物理学的一个主要挑战。虽然半分析模型(SAM)和流体力学模拟在再现星系观测数据方面取得了令人印象深刻的进展,但这些方法仍然需要大量的计算时间,对许多应用来说是一个障碍。图神经网络(GNN)最近被证明是学习物理关系的自然选择。在天体物理学中发现的最内在的类似图的结构是暗物质合并树,它编码了暗物质光环的演变。本文提出一种新的、基于图的仿真框架𝙼𝚊𝚗𝚛𝚘𝚟𝚎,可以仿真银河系恒星质量、冷气体质量和金属度、瞬时和时间平均恒星形成率,以及黑洞质量——正如用SAM预测的那样——在一个(75Mpc/h)³的模拟盒中,平均根误差比其他方法低2倍,只需40秒,比SAM快4个数量级。𝙼𝚊𝚗𝚐𝚛𝚘𝚟𝚎可以量化星系特性对合并历史的依赖。将以上结果与该领域的现有技术水平进行了比较,并显示出所有目标属性的明显改进。
Efficiently mapping baryonic properties onto dark matter is a major challenge in astrophysics. Although semi-analytic models (SAMs) and hydrodynamical simulations have made impressive advances in reproducing galaxy observables across cosmologically significant volumes, these methods still require significant computation times, representing a barrier to many applications. Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) have recently proven to be the natural choice for learning physical relations. Among the most inherently graph-like structures found in astrophysics are the dark matter merger trees that encode the evolution of dark matter halos. In this paper we introduce a new, graph-based emulator framework, 𝙼𝚊𝚗𝚐𝚛𝚘𝚟𝚎, and show that it emulates the galactic stellar mass, cold gas mass and metallicity, instantaneous and time-averaged star formation rate, and black hole mass -- as predicted by a SAM -- with root mean squared error up to two times lower than other methods across a (75Mpc/h)3 simulation box in 40 seconds, 4 orders of magnitude faster than the SAM. We show that 𝙼𝚊𝚗𝚐𝚛𝚘𝚟𝚎 allows for quantification of the dependence of galaxy properties on merger history. We compare our results to the current state of the art in the field and show significant improvements for all target properties. 𝙼𝚊𝚗𝚐𝚛𝚘𝚟𝚎 is publicly available.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.13473

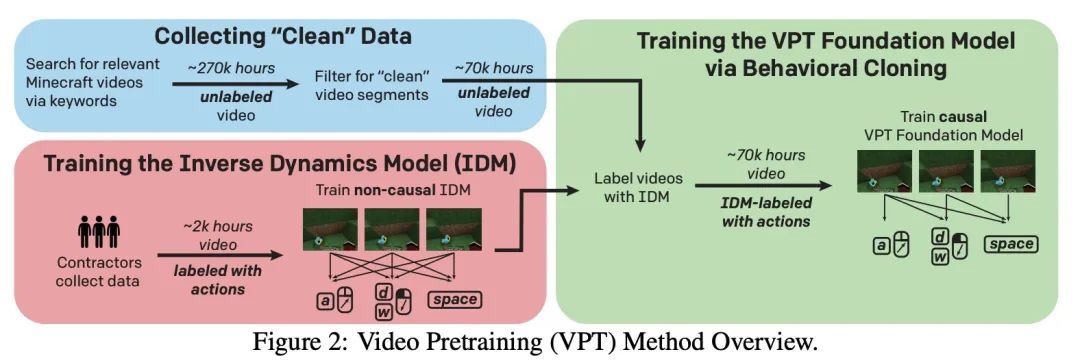
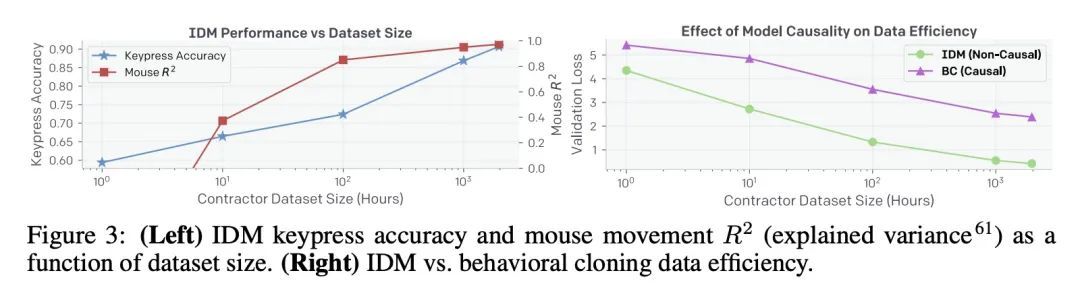
3、[LG] Video PreTraining (VPT): Learning to Act by Watching Unlabeled Online Videos
B Baker, I Akkaya, P Zhokhov, J Huizinga, J Tang, A Ecoffet, B Houghton, R Sampedro, J Clune
[OpenAI]
视频预训练(VPT):通过观看无标签在线视频进行顺序行动决策学习。在嘈杂的互联网规模数据集上进行预训练,作为一种训练模型的技术,对文本、图像和其他模态具有广泛而普遍的能力,已经被大量研究。然而,对于许多顺序决策领域,如机器人、视频游戏和计算机使用,公开可用的数据并不包含以同样方式训练行为先验的标签。本文通过半监督模仿学习将互联网规模的预训练范式扩展到顺序决策领域,智能体通过观看在线无标签视频来学习如何行动。通过少量的标记数据,可以训练出一个足够准确的逆动力学模型来标记巨大的未标记在线数据源——本文采用人们玩Minecraft的在线视频——然后可以从中训练出一般的行为先验。尽管使用的是原生的人工界面(鼠标和键盘,频率为20Hz),本文表明该行为先验具有非平凡的零样本能力,可以通过模仿学习和强化学习进行微调,以完成不可能通过强化学习从头学习的硬探索任务。对于许多任务,所提出的模型表现出人类水平的性能,本文首次报告了计算机智能体可以制作钻石工具,这可能需要熟练的人类在游戏中花费20分钟以上(24000个环境动作)才能完成。
Pretraining on noisy, internet-scale datasets has been heavily studied as a technique for training models with broad, general capabilities for text, images, and other modalities. However, for many sequential decision domains such as robotics, video games, and computer use, publicly available data does not contain the labels required to train behavioral priors in the same way. We extend the internet-scale pretraining paradigm to sequential decision domains through semi-supervised imitation learning wherein agents learn to act by watching online unlabeled videos. Specifically, we show that with a small amount of labeled data we can train an inverse dynamics model accurate enough to label a huge unlabeled source of online data -- here, online videos of people playing Minecraft -- from which we can then train a general behavioral prior. Despite using the native human interface (mouse and keyboard at 20Hz), we show that this behavioral prior has nontrivial zero-shot capabilities and that it can be fine-tuned, with both imitation learning and reinforcement learning, to hard-exploration tasks that are impossible to learn from scratch via reinforcement learning. For many tasks our models exhibit human-level performance, and we are the first to report computer agents that can craft diamond tools, which can take proficient humans upwards of 20 minutes (24,000 environment actions) of gameplay to accomplish.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.11795


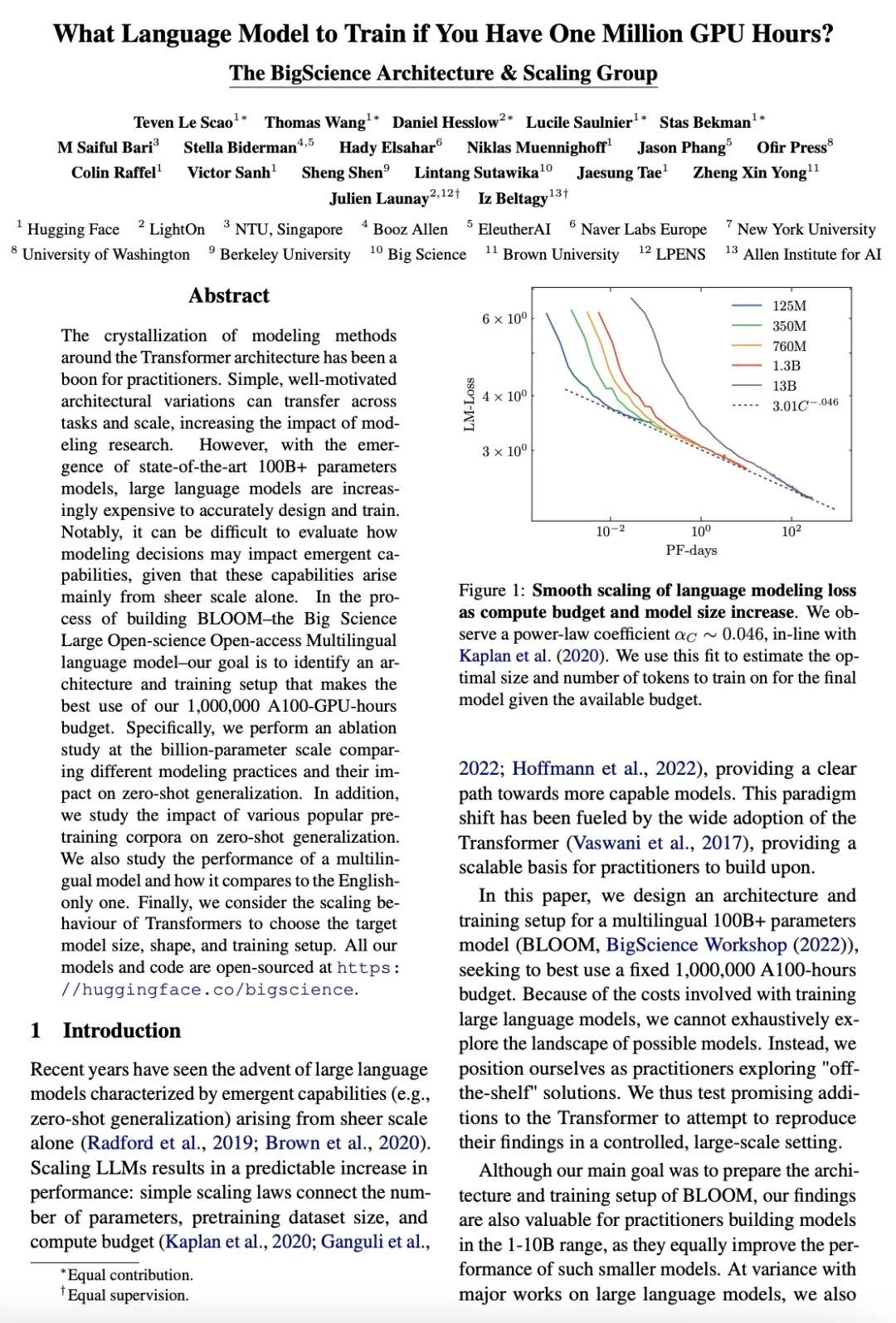
4、[CL] What Language Model to Train if You Have One Million GPU Hours?
T L Scao, T Wang, D Hesslow, L Saulnier, S Bekman...
[Hugging Face & LightOn & NTU & Booz Allen & Naver Labs Europe & Berkeley University]
有百万GPU算力该训练什么语言模型?围绕Transformer架构的建模方法的结晶,对从业者来说是一个福音。简单的、动机良好的架构变化可以跨任务和规模迁移,增加建模研究的影响。然而,随着最先进的100B+参数模型的出现,大型语言模型的精确设计及训练成本越来越高。值得注意的是,鉴于这些能力主要是由纯粹的规模产生的,因此很难评估建模决策如何影响新兴的能力。在建立BLOOM——大科学大型开放科学多语言模型的过程中,目标是确定一个架构和训练设置,使得1,000,000个A100-GPU-算力小时的预算得到最佳利用。具体来说,在十亿级参数规模上进行了一项消融研究,比较不同的建模方法及其对零样本泛化的影响。此外,还研究了各种流行的预训练语料对零样本泛化的影响。还研究了一个多语言模型的性能,以及它与纯英语模型的比较。最后,考虑了Transformer的缩放行为来选择目标模型的大小、形状和训练设置。
The crystallization of modeling methods around the Transformer architecture has been a boon for practitioners. Simple, well-motivated architectural variations can transfer across tasks and scale, increasing the impact of modeling research. However, with the emergence of state-of-the-art 100B+ parameters models, large language models are increasingly expensive to accurately design and train. Notably, it can be difficult to evaluate how modeling decisions may impact emergent capabilities, given that these capabilities arise mainly from sheer scale alone. In the process of building BLOOM--the Big Science Large Open-science Open-access Multilingual language model--our goal is to identify an architecture and training setup that makes the best use of our 1,000,000 A100-GPU-hours budget. Specifically, we perform an ablation study at the billion-parameter scale comparing different modeling practices and their impact on zero-shot generalization. In addition, we study the impact of various popular pre-training corpora on zero-shot generalization. We also study the performance of a multilingual model and how it compares to the English-only one. Finally, we consider the scaling behaviour of Transformers to choose the target model size, shape, and training setup. All our models and code are open-sourced at this https URL .
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.15424

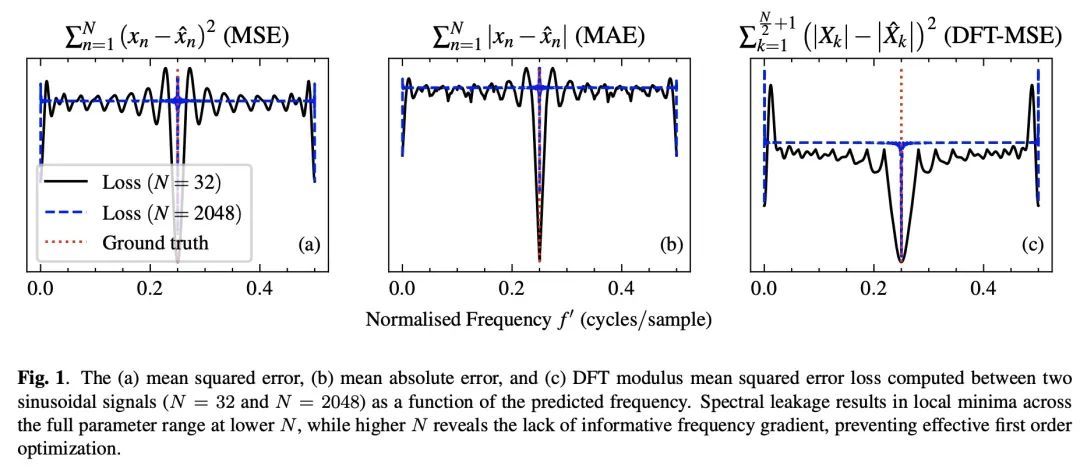
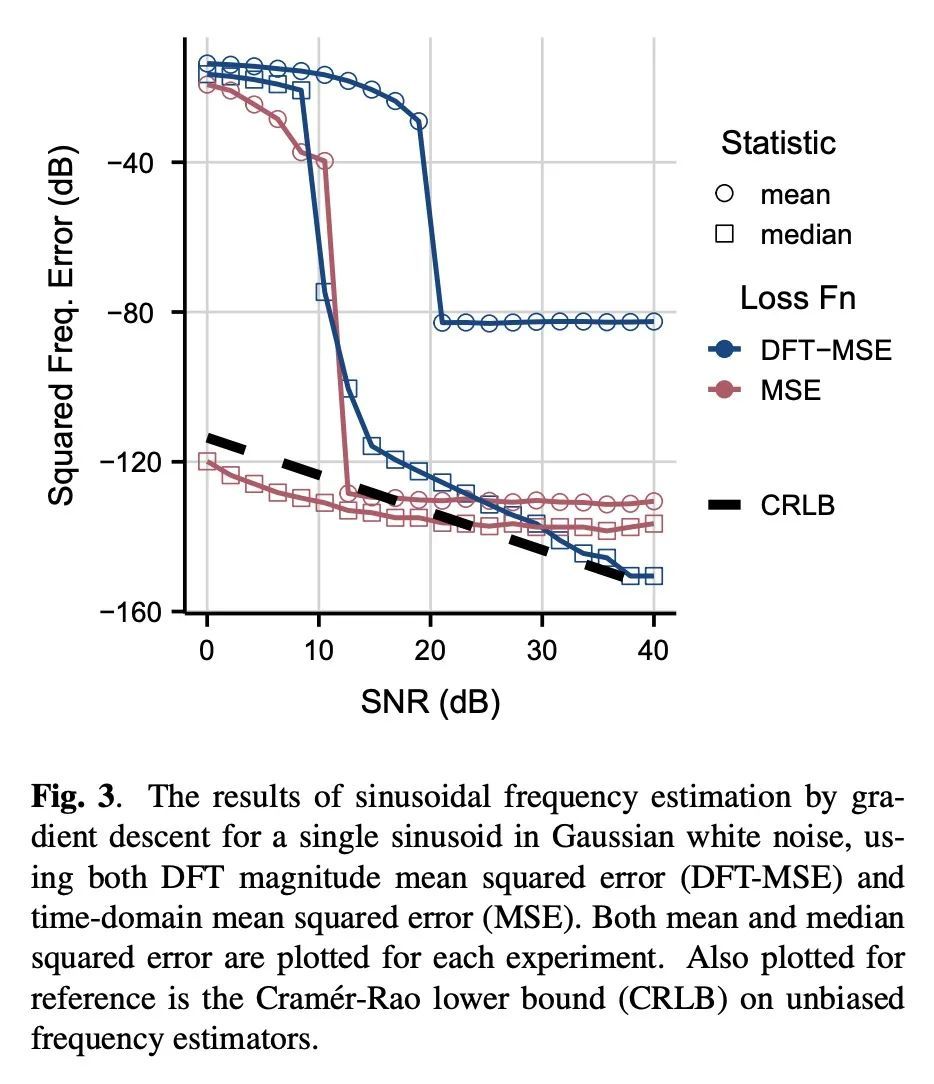
5、[AS] Sinusoidal Frequency Estimation by Gradient Descent
B Hayes, C Saitis, G Fazekas
[Queen Mary University of London]
基于梯度下降的正弦波频率估计。正弦波参数估计是光谱分析和时间序列预测等应用中的一项基本任务。然而,通过梯度下降法估计正弦频率参数往往是不可能的,因为误差函数是非凸的,而且密布着局部极值。因此,越来越多的可微信号处理方法族一直无法调整振荡成分的频率,使其无法在广泛的应用中使用。本文提出一种用复杂指数代数的Wirtinger导数和任意基于一阶梯度的优化器进行正弦频率和振幅联合估计的技术,使无约束的正弦模型的神经网络控制器的端到端训练成为可能。
Sinusoidal parameter estimation is a fundamental task in applications from spectral analysis to time-series forecasting. Estimating the sinusoidal frequency parameter by gradient descent is, however, often impossible as the error function is non-convex and densely populated with local minima. The growing family of differentiable signal processing methods has therefore been unable to tune the frequency of oscillatory components, preventing their use in a broad range of applications. This work presents a technique for joint sinusoidal frequency and amplitude estimation using the Wirtinger derivatives of a complex exponential surrogate and any first order gradient-based optimizer, enabling end to-end training of neural network controllers for unconstrained sinusoidal models.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.14476

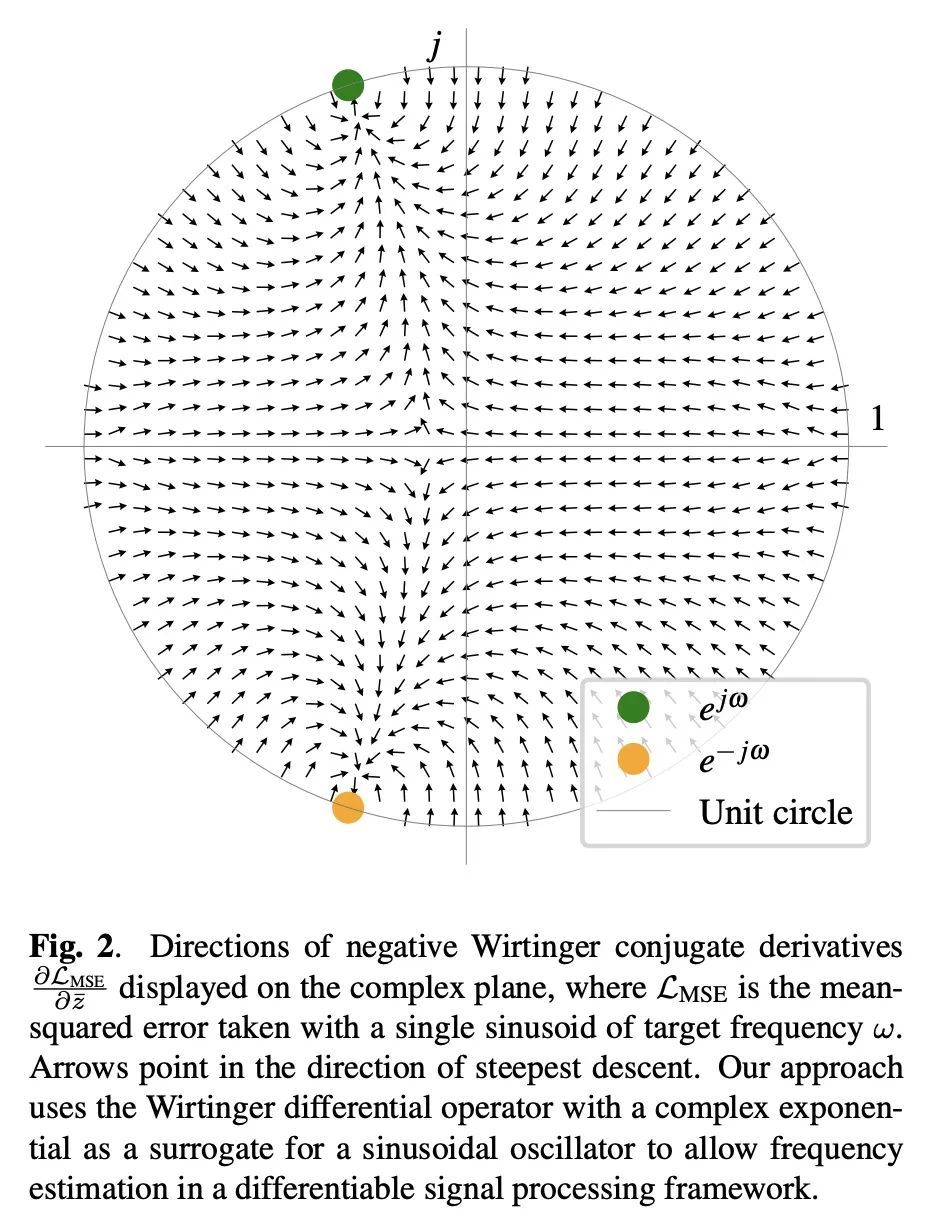
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
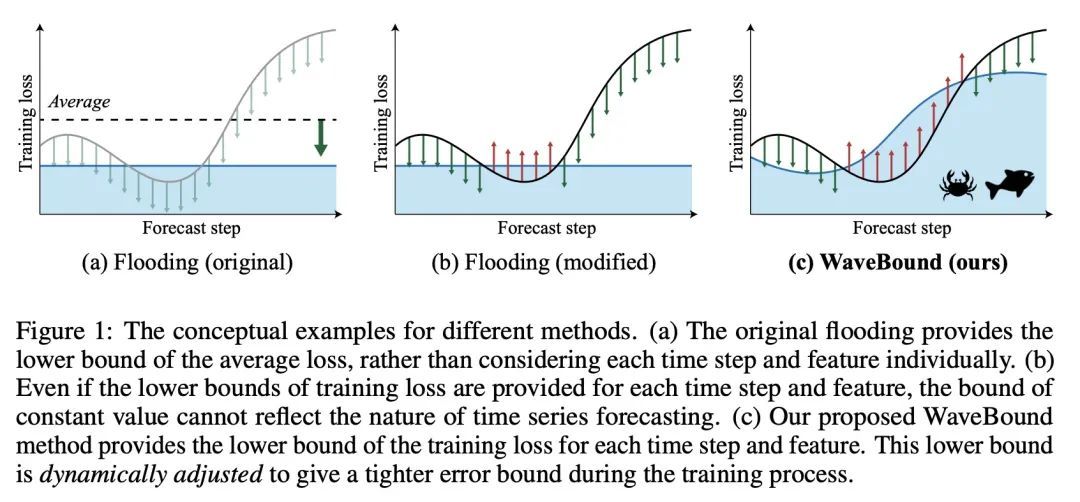
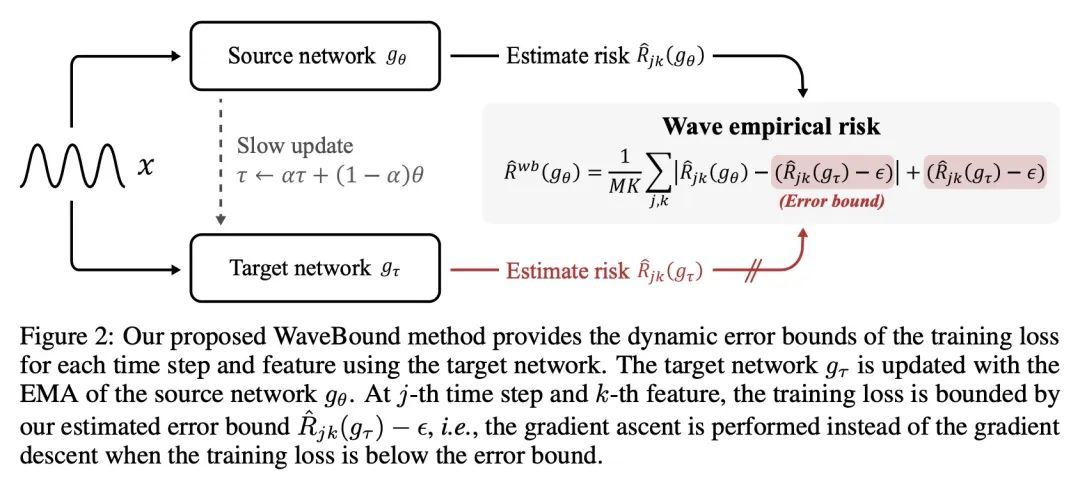
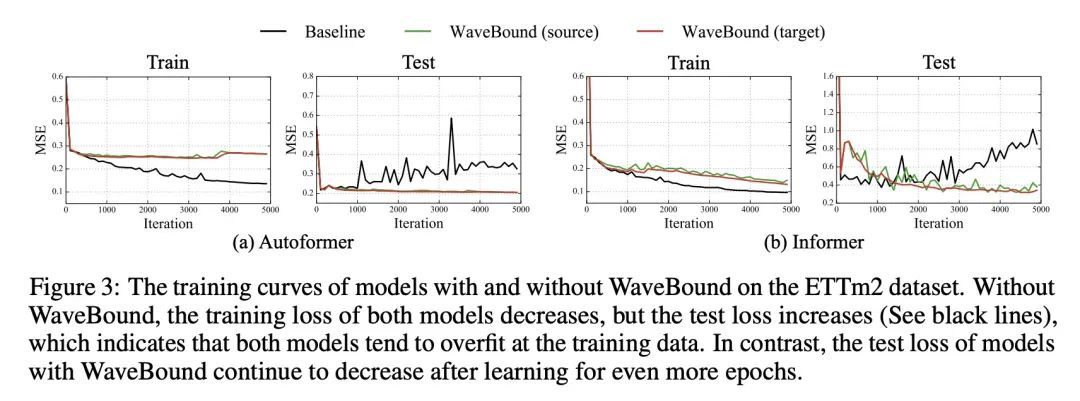
[LG] WaveBound: Dynamic Error Bounds for Stable Time Series Forecasting
WaveBound:稳态时间序列预测的动态误差界
Y Cho, D Kim, D Kim, M A Khan, J Choo
[KAIST AI]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.14303

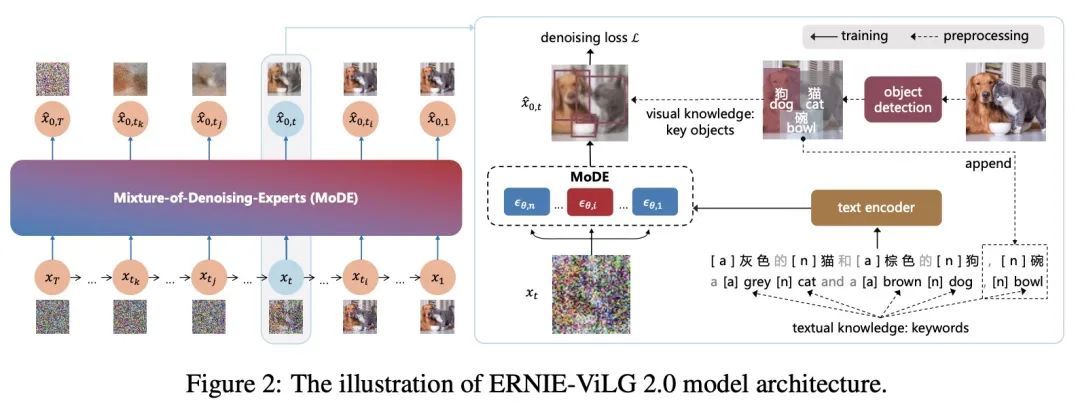
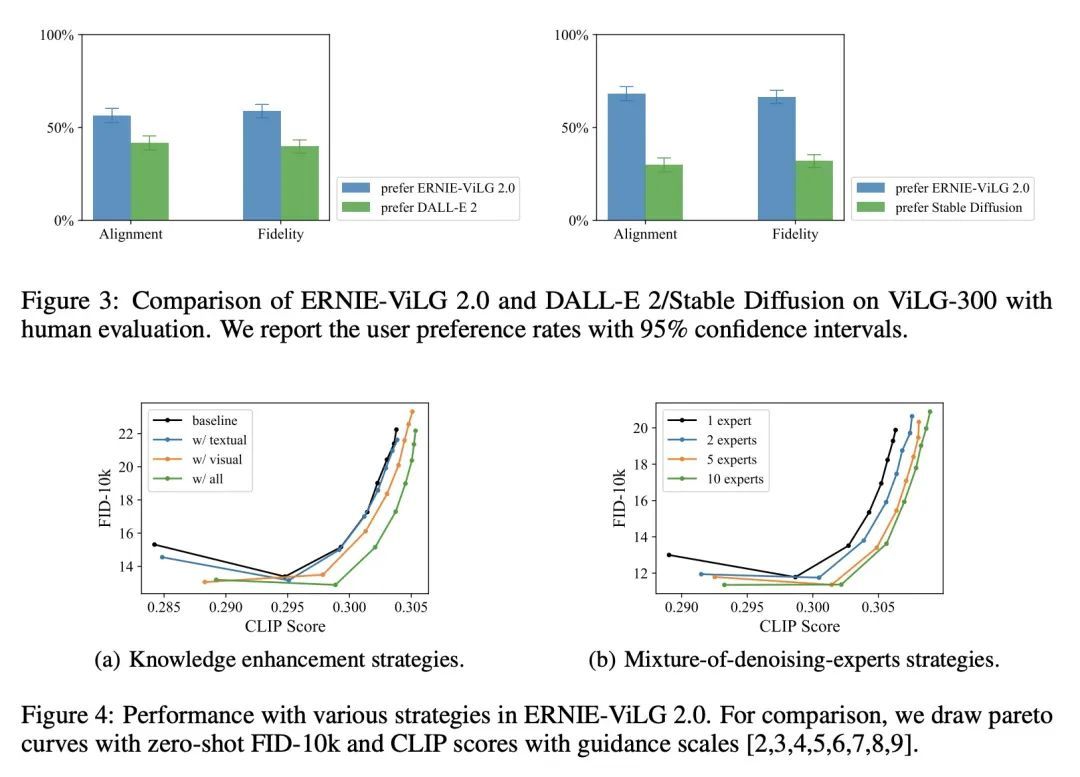
[CV] ERNIE-ViLG 2.0: Improving Text-to-Image Diffusion Model with Knowledge-Enhanced Mixture-of-Denoising-Experts
ERNIE-ViLG 2.0:基于知识增强去噪专家混合的改进文本到图像扩散模型
Z Feng, Z Zhang, X Yu, Y Fang, L Li...
[Baidu Inc]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.15257


[LG] The Debate Over Understanding in AI's Large Language Models
大型语言模型理解能力之争
M Mitchell, D C. Krakauer
[Santa Fe Institute]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.13966

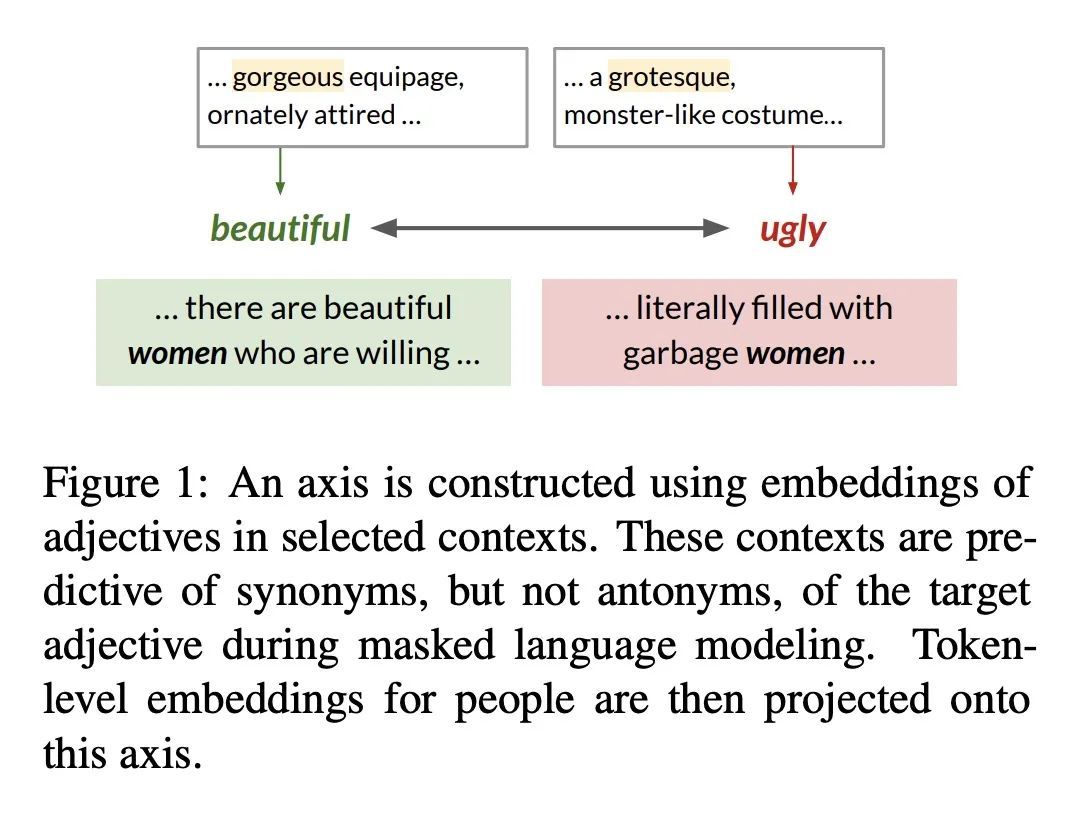
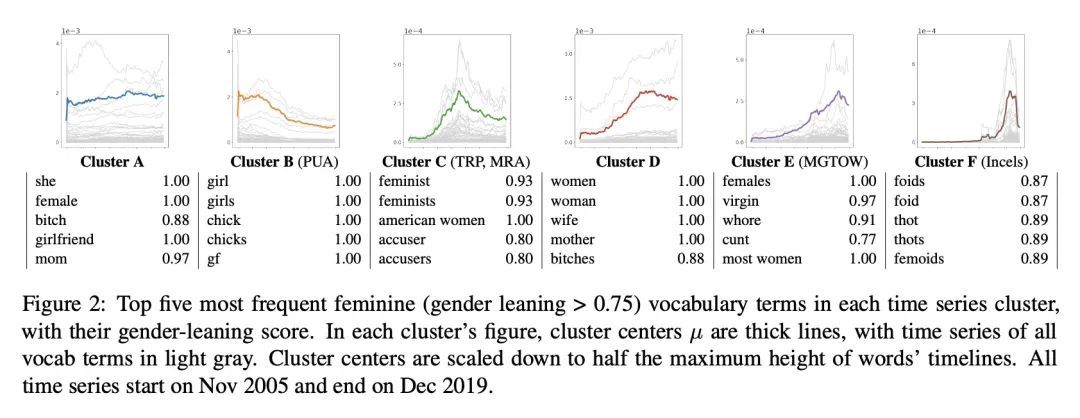
[CL] Discovering Differences in the Representation of People using Contextualized Semantic Axes
用上下文化语义轴发现人的表达差异
L Lucy, D Tadimeti, D Bamman
[UC Berkeley]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.12170

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢