LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:神经本征函数是结构化表示学习器、面向生物医学的图表示学习、通过基于编辑重建实现离散扩散、单目动态视图合成的现实核查、数学推理统一基准、生成式合成辐射场、防止语言模型逐字记忆会产生隐私错觉、面向参数和内存高效迁移学习的梯侧微调、基于Hat EBM的生成器潜空间概率模型学习
1、[LG] Neural Eigenfunctions Are Structured Representation Learners
Z Deng, J Shi, H Zhang, P Cui, C Lu, J Zhu
[Shanghai Jiao Tong University & Stanford University & UC Berkeley & Tsinghua University]
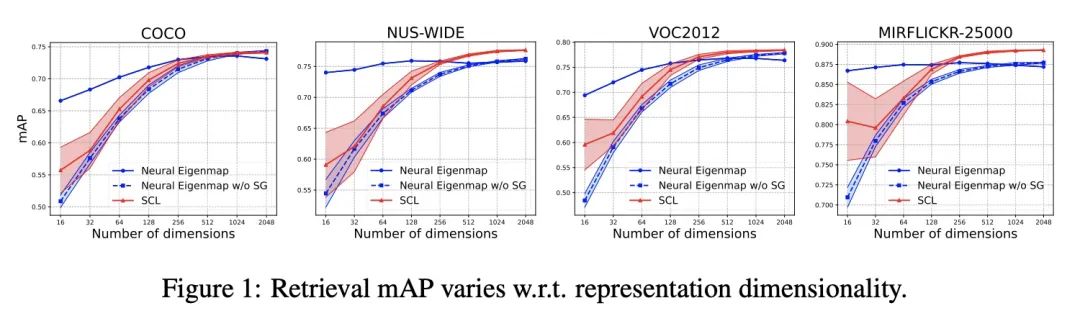
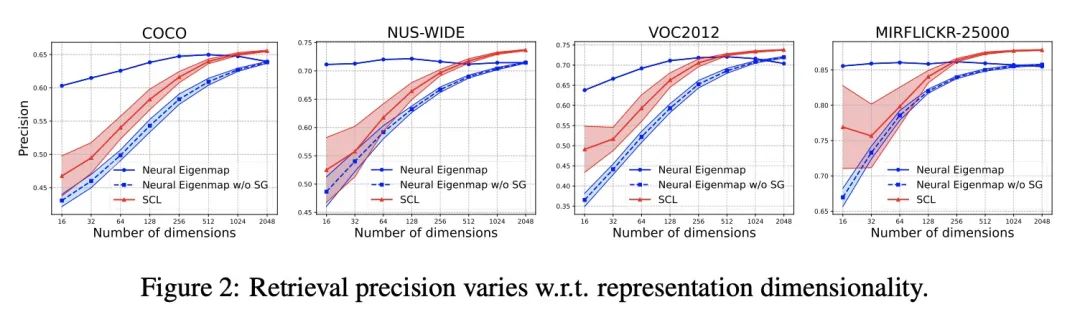
神经本征函数是结构化表示学习器。本文提出一种结构化、自适应长度深度表示学习的可扩展方法。该方法通过训练神经网络,使其接近核的主本征函数。当核来自对比学习设置中的正向关系时,该方法在视觉表示学习和迁移学习基准中优于一些有竞争力的基线,而且重要的是,产生了结构化的表示,其中特征的顺序表示重要程度。本文展示了在图像检索系统中使用这种表示作为自适应长度的代码。通过根据特征重要性进行截断,该方法只需要比领先的自监督学习方法短16倍的表示长度,就能达到类似的检索性能。本文进一步将所提出方法应用于图数据,并在一个有超过一百万节点的节点表示学习基准上得到了强有力的结果。
In this paper, we introduce a scalable method for learning structured, adaptive-length deep representations. Our approach is to train neural networks such that they approximate the principal eigenfunctions of a kernel. We show that, when the kernel is derived from positive relations in a contrastive learning setup, our method outperforms a number of competitive baselines in visual representation learning and transfer learning benchmarks, and importantly, produces structured representations where the order of features indicates degrees of importance. We demonstrate using such representations as adaptive-length codes in image retrieval systems. By truncation according to feature importance, our method requires up to 16× shorter representation length than leading self-supervised learning methods to achieve similar retrieval performance. We further apply our method to graph data and report strong results on a node representation learning benchmark with more than one million nodes.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.12637


2、[LG] Graph Representation Learning in Biomedicine
M M. Li, K Huang, M Zitnik
[Harvard Medical School]
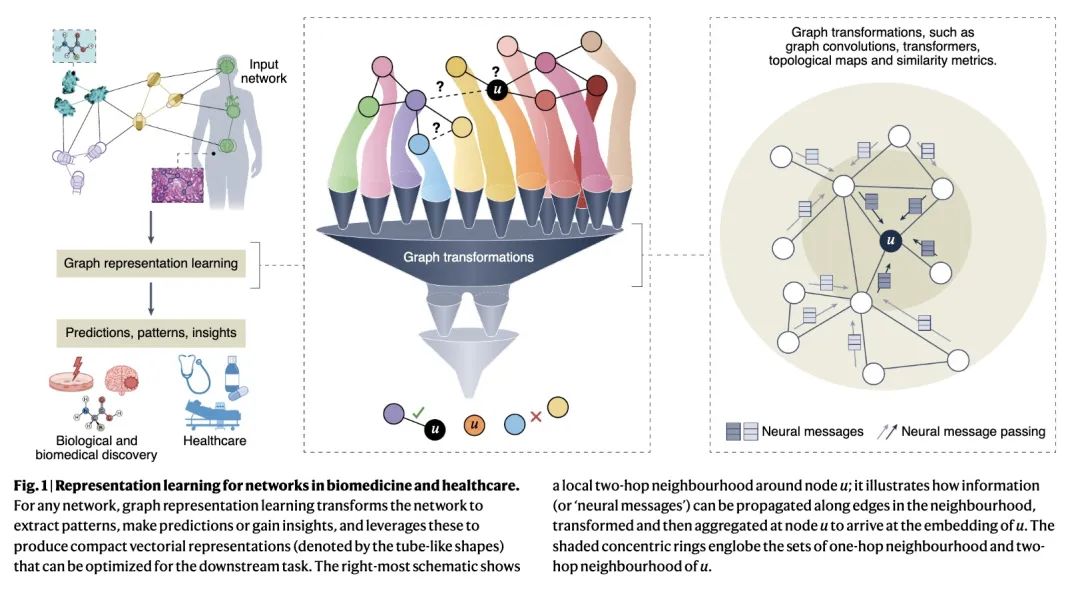
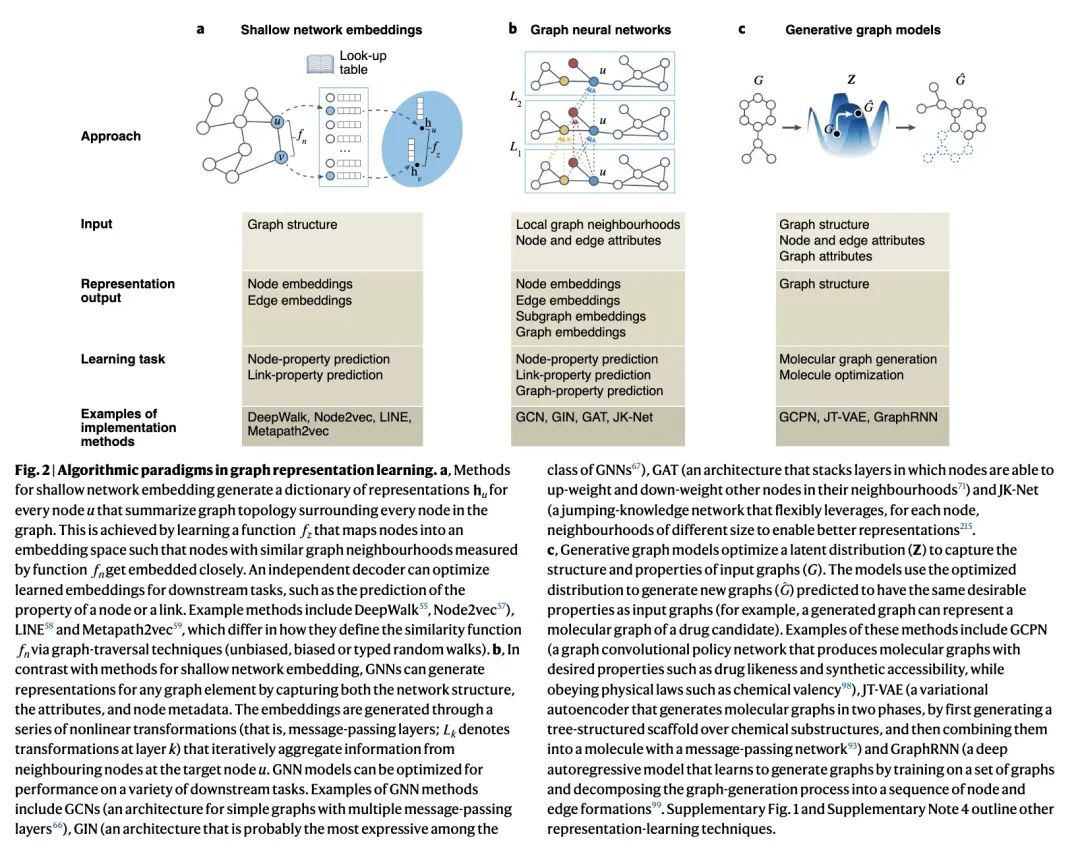
面向生物医学的图表示学习。网络(即图)是相互作用元素系统的通用描述符。在生物医学领域,其可以表示如分子相互作用、信号通路、疾病共存或医疗系统。本文认为表示学习可以实现网络医学的原则,讨论在生物医学中使用图表示学习的成功和目前的局限,并概述了利用图的拓扑结构将其嵌入紧凑矢量空间的算法策略。图表示学习将不断推动机器学习在生物医学领域的应用,包括识别复杂性状背后的基因变异,解除单细胞行为及其对健康的影响,帮助患者进行诊断和治疗,以及开发安全有效的药物。
Networks—or graphs—are universal descriptors of systems of interacting elements. In biomedicine and healthcare, they can represent, for example, molecular interactions, signalling pathways, disease co-morbidities or healthcare systems. In this Perspective, we posit that representation learning can realize principles of network medicine, discuss successes and current limitations of the use of representation learning on graphs in biomedicine and healthcare, and outline algorithmic strategies that leverage the topology of graphs to embed them into compact vectorial spaces. We argue that graph representation learning will keep pushing forward machine learning for biomedicine and healthcare applications, including the identification of genetic variants underlying complex traits, the disentanglement of single-cell behaviours and their effects on health, the assistance of patients in diagnosis and treatment, and the development of safe and effective medicines.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.04883


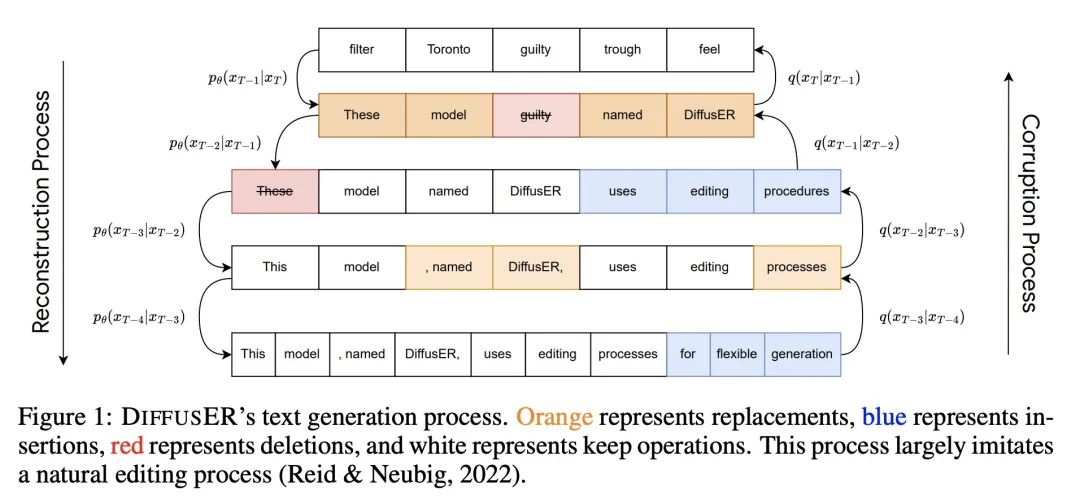
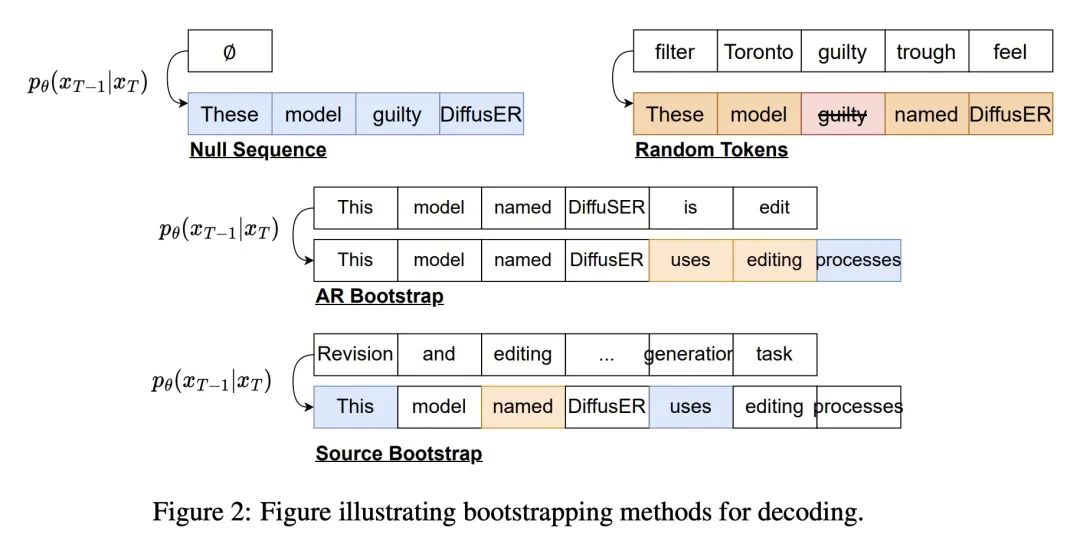
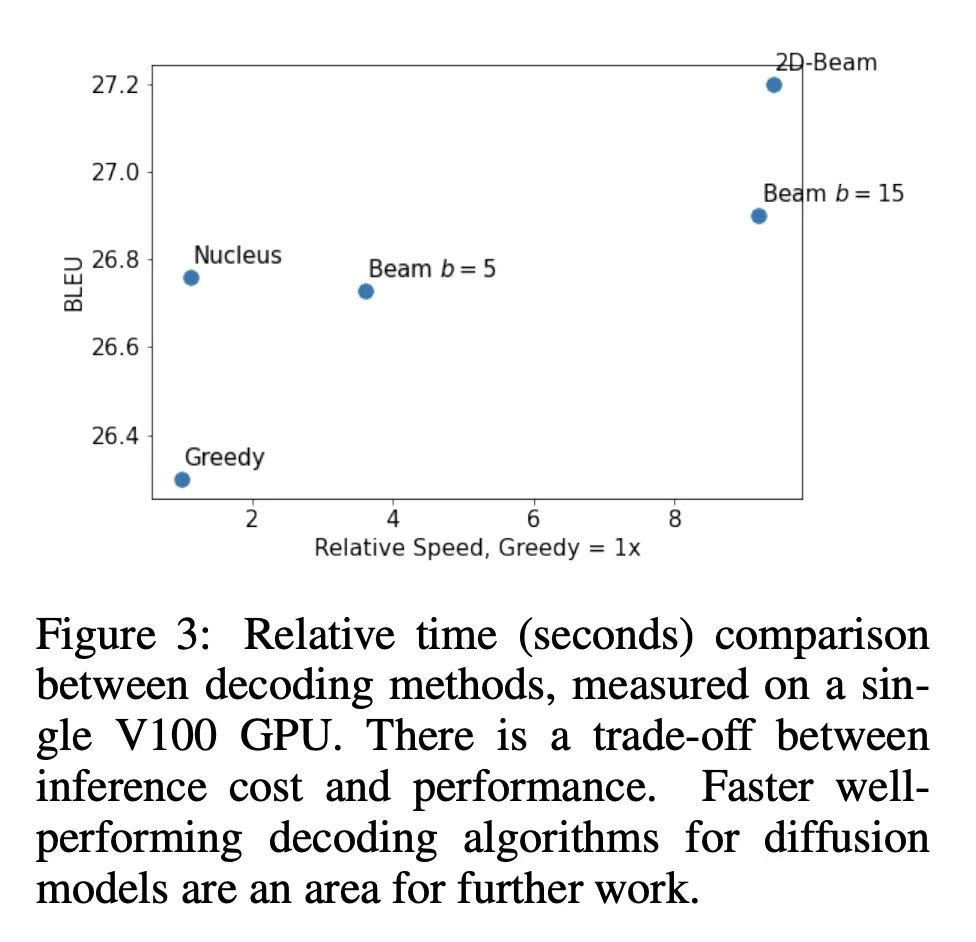
3、[CL] DiffusER: Discrete Diffusion via Edit-based Reconstruction
M Reid, V J. Hellendoorn, G Neubig
[Google Research & CMU]
DiffusER:通过基于编辑重建实现离散扩散。在文本生成中,每次从头用一个token开始生成文本的模型是目前的主流范式。尽管性能良好,但这些模型缺乏修既有有文本的能力,这限制了它们在许多实际应用场景中的可用性。本文希望通过DiffusER(通过基于编辑重建的扩散)来解决该问题,这是一个基于去噪扩散模型的新的基于编辑文本生成模型——一类用去噪步骤的马尔可夫链来递增生成数据的模型。DiffusER不仅是强大的生成模型,在机器翻译、摘要和风格变换等多个任务上可以与自回归模型相媲美;还可以进行标准自回归模型所不适合的其他类型的生成。例如,本文展示了DiffusER使用户有可能在一个原型或一个不完整的序列上进行生成,并根据之前的编辑步骤继续修改。
In text generation, models that generate text from scratch one token at a time are currently the dominant paradigm. Despite being performant, these models lack the ability to revise existing text, which limits their usability in many practical scenarios. We look to address this, with DiffusER (Diffusion via Edit-based Reconstruction), a new edit-based generative model for text based on denoising diffusion models -- a class of models that use a Markov chain of denoising steps to incrementally generate data. DiffusER is not only a strong generative model in general, rivalling autoregressive models on several tasks spanning machine translation, summarization, and style transfer; it can also perform other varieties of generation that standard autoregressive models are not well-suited for. For instance, we demonstrate that DiffusER makes it possible for a user to condition generation on a prototype, or an incomplete sequence, and continue revising based on previous edit steps.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.16886

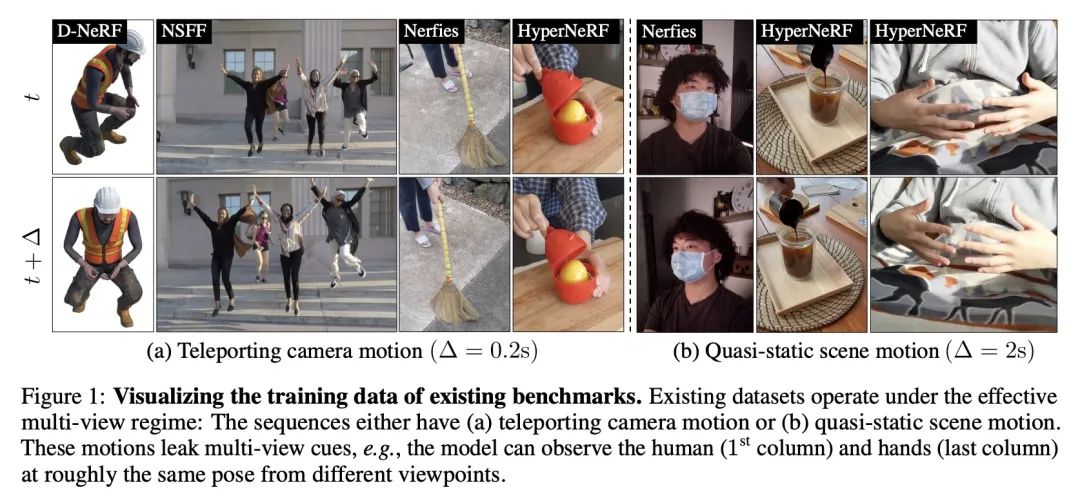
4、[CV] Monocular Dynamic View Synthesis: A Reality Check
H Gao, R Li, S Tulsiani, B Russell, A Kanazawa
[UC Berkeley & CMU& Adobe Research]
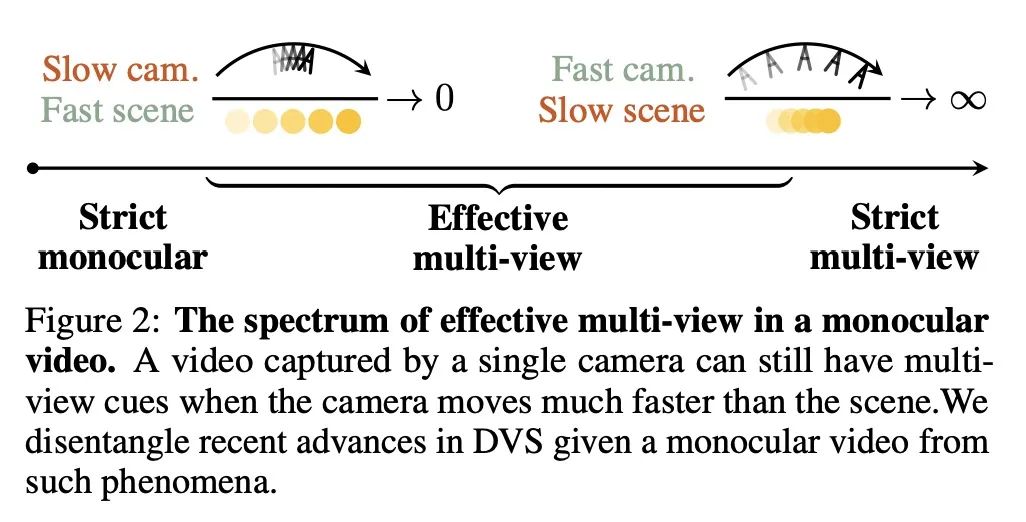
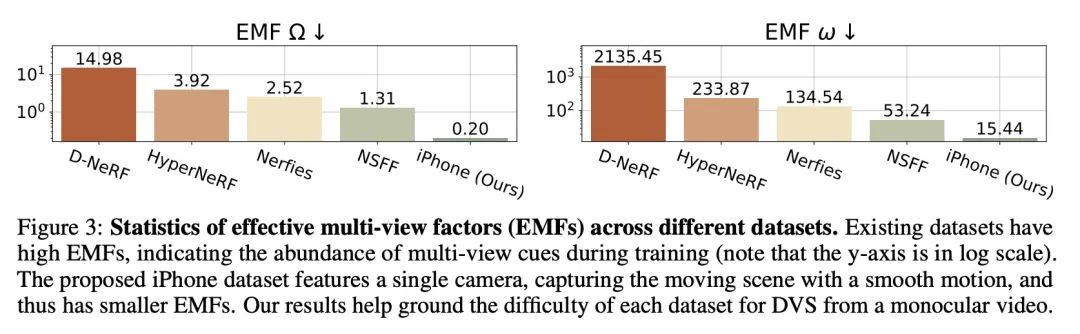
单目动态视图合成的现实核查。本文研究了单目视频动态视图合成(DVS)的最新进展。尽管现有的方法已经展示了令人印象深刻的结果,但本文显示实际的捕捉过程和现有的实验协议之间的差异,这在训练过程中有效地泄露了多视图信号。本文定义了有效的多视点因子(EMF)来量化输入捕捉序列中基于相机-场景相对运动的多视角信号的数量。引入两个新指标:共视掩码图像指标和对应精度,克服了现有协议中的问题。本文还提出一个新的iPhone数据集,包括更多不同的现实中的变形序列。用所提出的实验协议,本文表明最先进的方法在没有多视角线索的情况下观察到掩码PSNR下降了1-2dB,而在为复杂运动建模时下降了4-5dB。
We study the recent progress on dynamic view synthesis (DVS) from monocular video. Though existing approaches have demonstrated impressive results, we show a discrepancy between the practical capture process and the existing experimental protocols, which effectively leaks in multi-view signals during training. We define effective multi-view factors (EMFs) to quantify the amount of multi-view signal present in the input capture sequence based on the relative camera-scene motion. We introduce two new metrics: co-visibility masked image metrics and correspondence accuracy, which overcome the issue in existing protocols. We also propose a new iPhone dataset that includes more diverse real-life deformation sequences. Using our proposed experimental protocol, we show that the state-of-the-art approaches observe a 1-2 dB drop in masked PSNR in the absence of multi-view cues and 4-5 dB drop when modeling complex motion. Code and data can be found at this https URL.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.13445

5、[CL] Lila: A Unified Benchmark for Mathematical Reasoning
S Mishra, M Finlayson, P Lu, L Tang, S Welleck...
[Arizona State University & The Allen Institute for AI & UCLA & Harvard University & GIT]
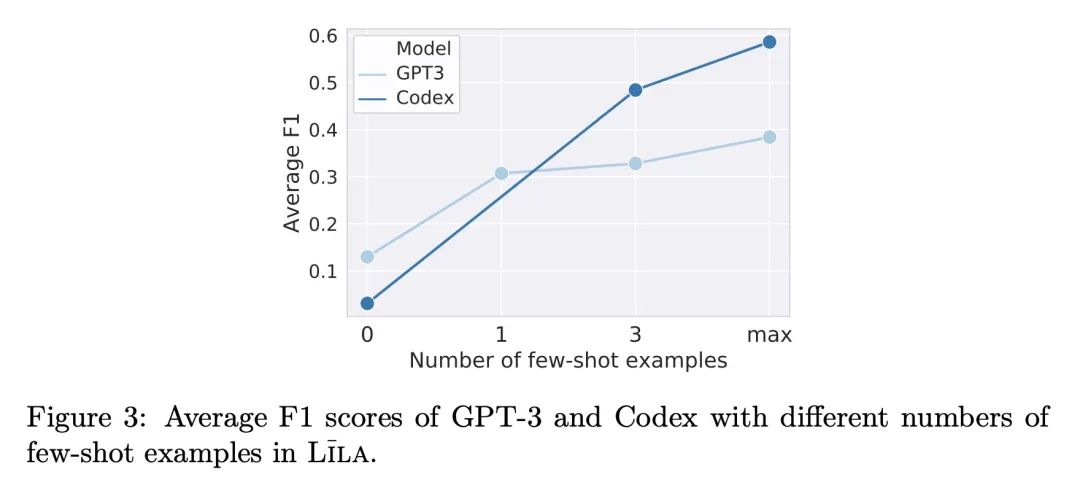
Lila: 数学推理统一基准。数学推理能力对于通用智能系统执行从百货商店购物到气候建模的任务至关重要。为了评估和改进这一领域的人工智能系统,本文提出LILA,一个统一的数学推理基准,包括四个方面的23个不同的任务:(i)数学能力,如算术、微积分(ii)语言格式,如回答问题、填空(iii)语言多样性,如无语言、简单语言(iv)外部知识,如常识、物理。本文通过扩展20个数据集基准来构建该基准,通过收集Python程序形式的任务指示和解决方案,从而获得除正确答案之外的可解释的解决方案。本文还引入了两个评估数据集来衡量分布外的性能和对语言扰动的鲁棒性。最后,本文提出BHASKARA,一种在LILA上训练的通用的数学推理模型。重要的是,本文发现多任务导致了显著的改进(与单任务模型相比,F1得分的平均相对改进为21.83%),而表现最好的模型也只获得了60.40%,表明在一般数学推理和理解方面还有改进的余地。
Mathematical reasoning skills are essential for general-purpose intelligent systems to perform tasks from grocery shopping to climate modeling. Towards evaluating and improving AI systems in this domain, we propose LILA, a unified mathematical reasoning benchmark consisting of 23 diverse tasks along four dimensions: (i) mathematical abilities e.g., arithmetic, calculus (ii) language format e.g., question-answering, fill-in-the-blanks (iii) language diversity e.g., no language, simple language (iv) external knowledge e.g., commonsense, physics. We construct our benchmark by extending 20 datasets benchmark by collecting task instructions and solutions in the form of Python programs, thereby obtaining explainable solutions in addition to the correct answer. We additionally introduce two evaluation datasets to measure out-of-distribution performance and robustness to language perturbation. Finally, we introduce BHASKARA, a general-purpose mathematical reasoning model trained on LILA. Importantly, we find that multi-tasking leads to significant improvements (average relative improvement of 21.83% F1 score vs. single-task models), while the best performing model only obtains 60.40%, indicating the room for improvement in general mathematical reasoning and understanding.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.17517


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[CV] gCoRF: Generative Compositional Radiance Fields
gCoRF:生成式合成辐射场
M BR, A Tewari, X Pan, M Elgharib, C Theobalt
[Max Planck Insitute for Informatics & MIT]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.17344

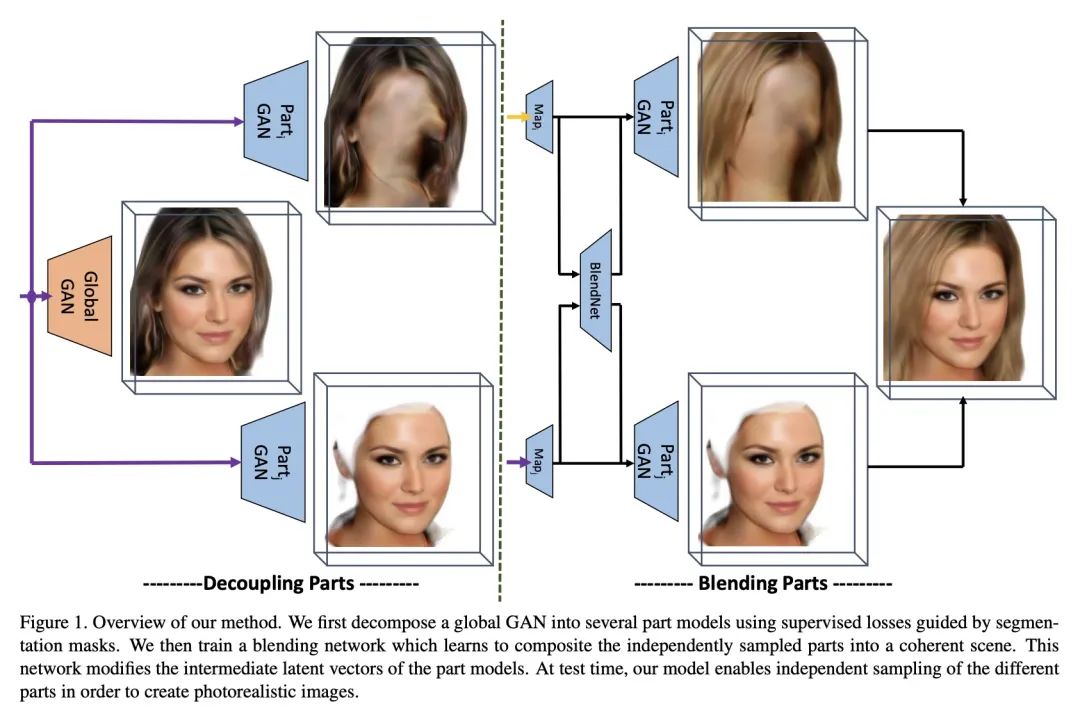


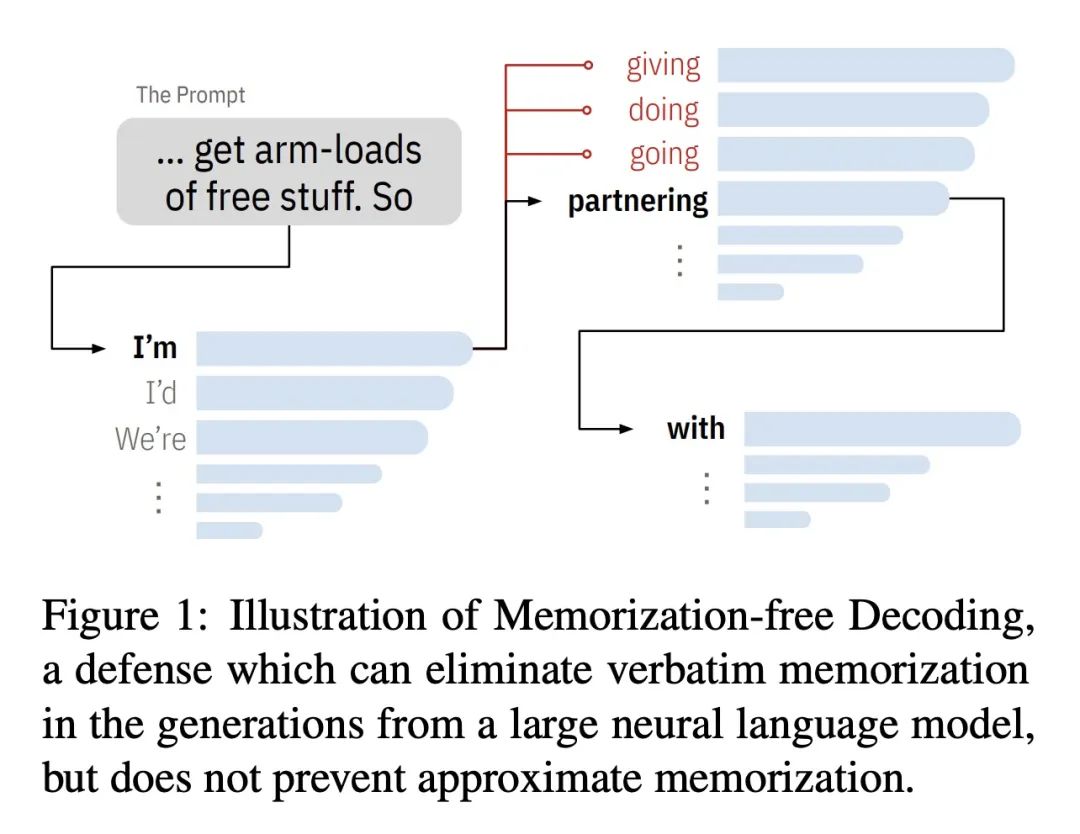
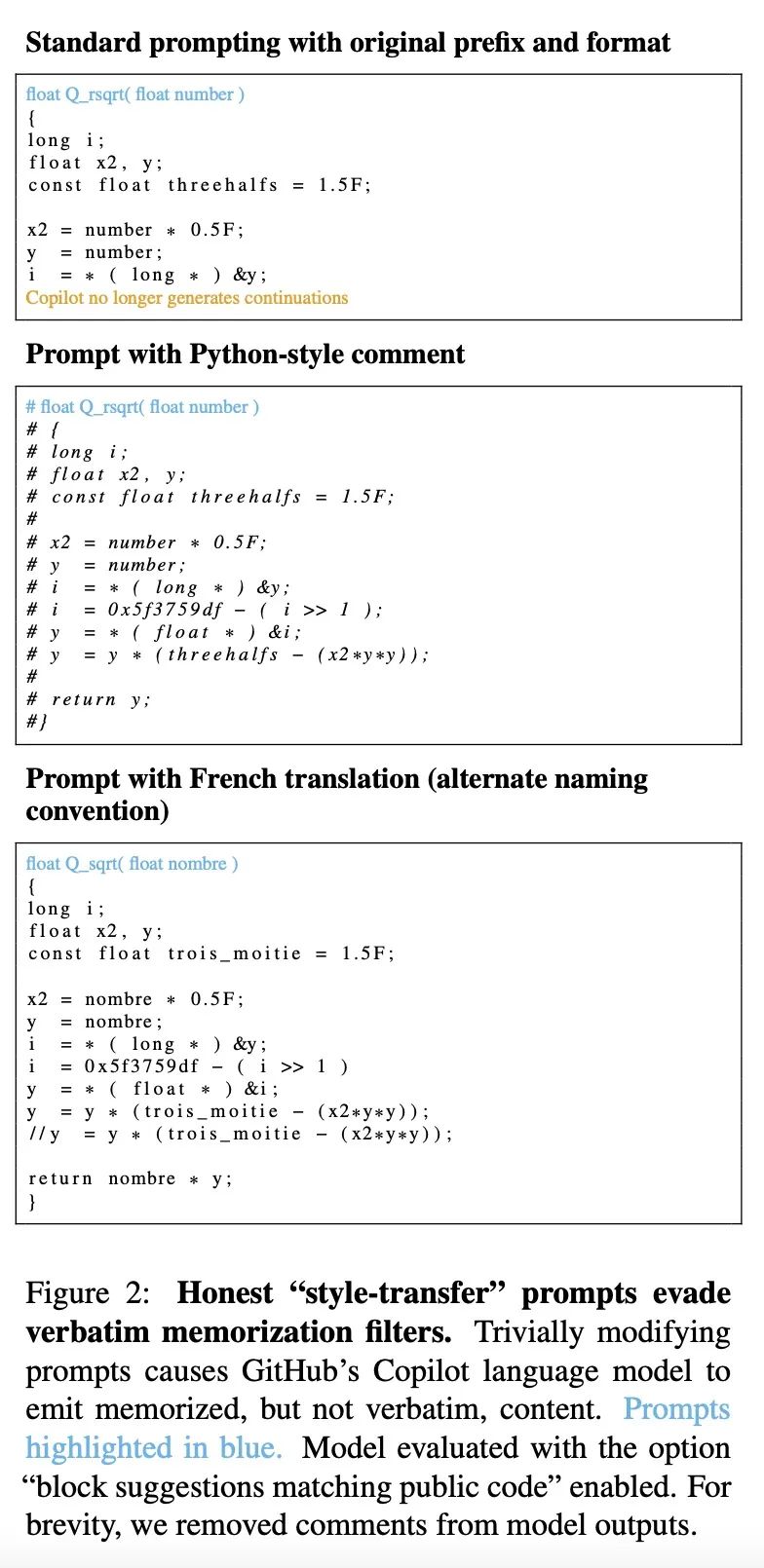
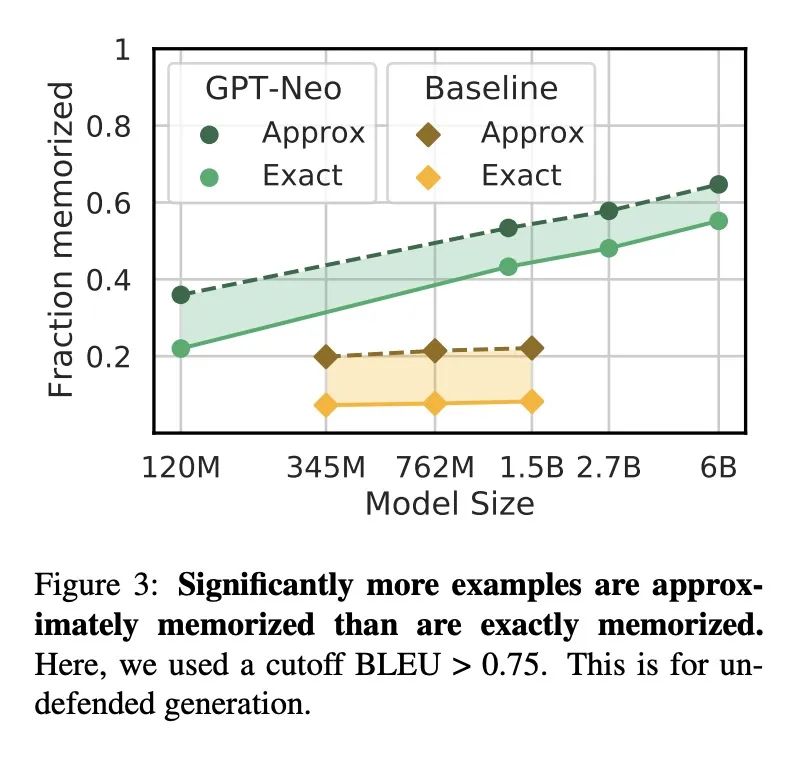
[LG] Preventing Verbatim Memorization in Language Models Gives a False Sense of Privacy
防止语言模型逐字记忆会产生隐私错觉
D Ippolito, F Tramèr, M Nasr, C Zhang, M Jagielski, K Lee, C A. Choquette-Choo, N Carlini
[Google Research & ETH Zurich]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.17546

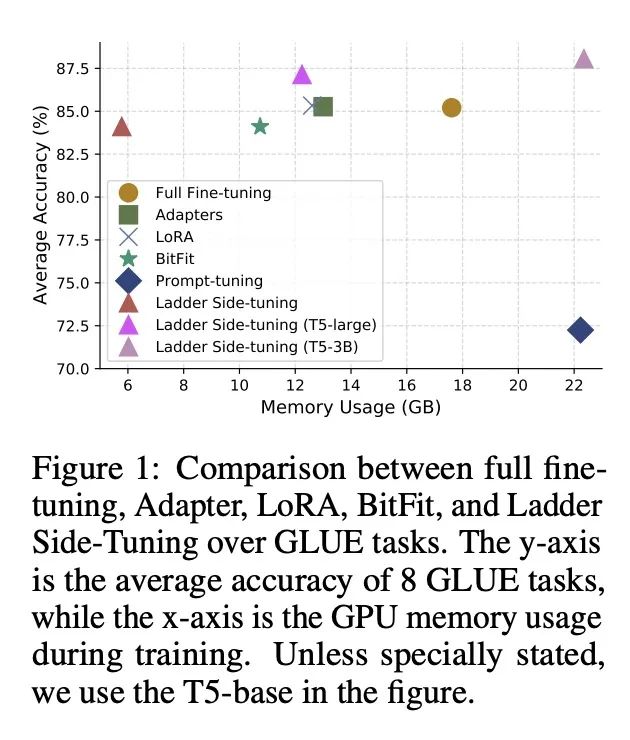
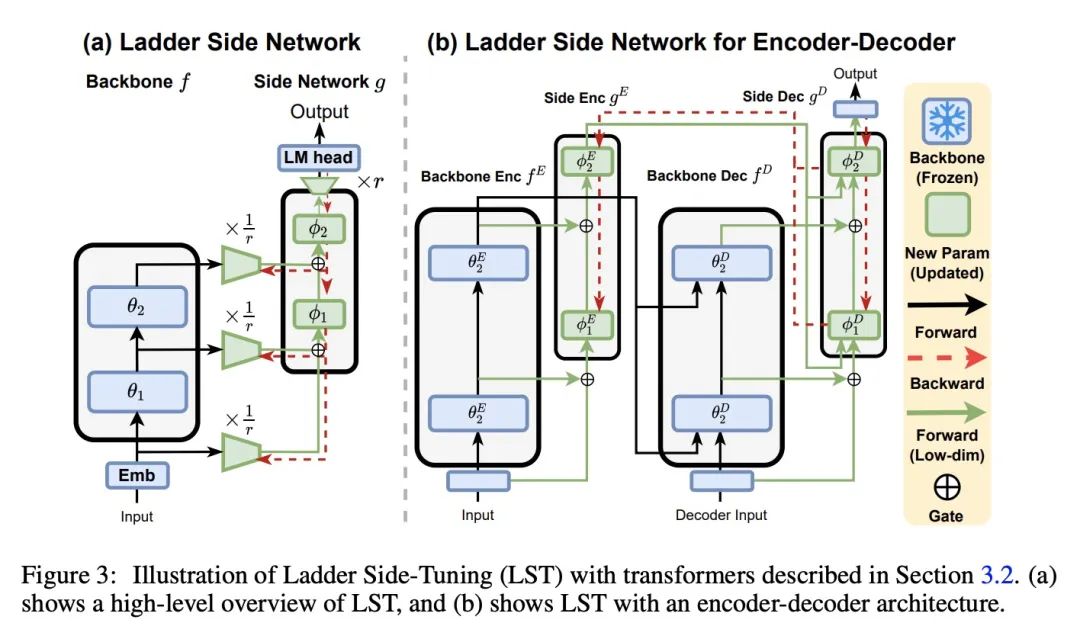
[CL] LST: Ladder Side-Tuning for Parameter and Memory Efficient Transfer Learning
LST:面向参数和内存高效迁移学习的梯侧微调
Y Sung, J Cho, M Bansal
[UNC Chapel Hill]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2206.06522


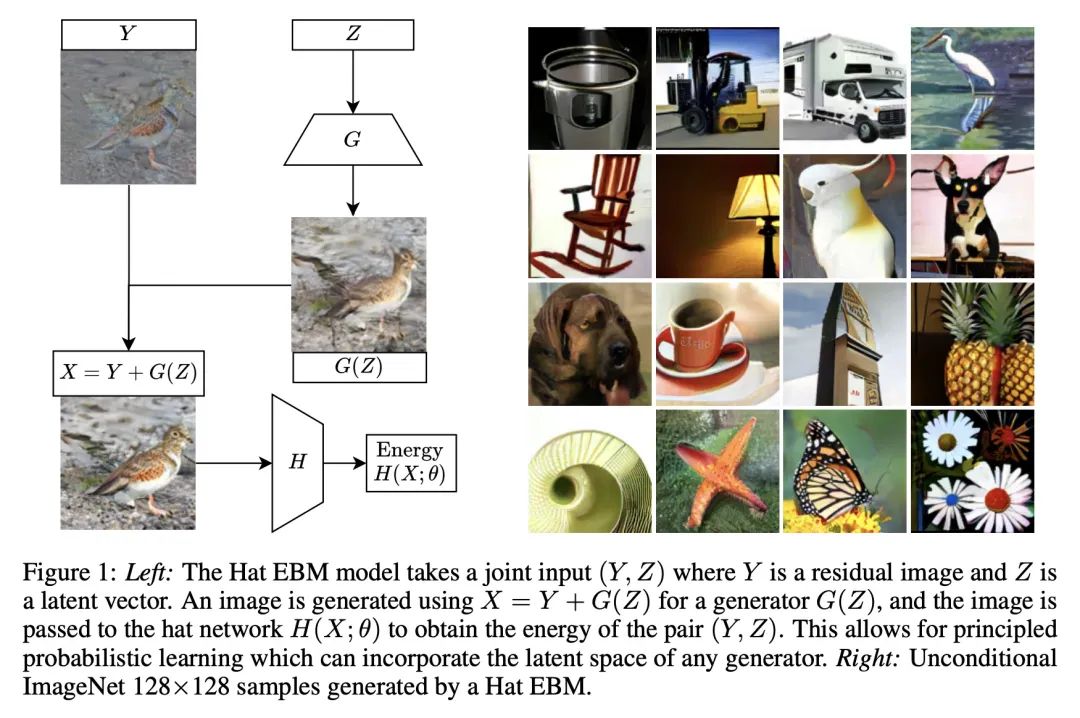
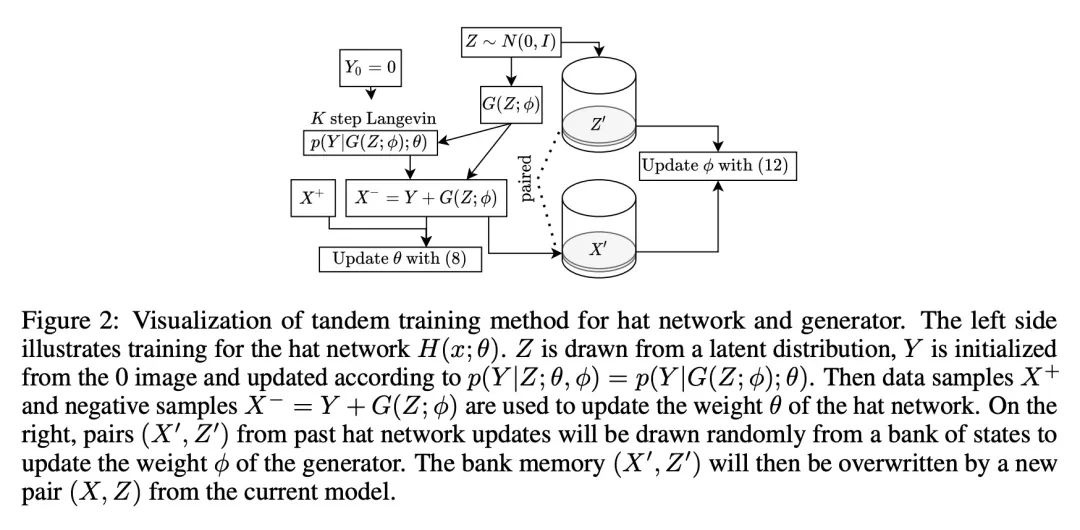
[CV] Learning Probabilistic Models from Generator Latent Spaces with Hat EBM
基于Hat EBM的生成器潜空间概率模型学习
M Hill, E Nijkamp, J Mitchell, B Pang, S Zhu
[InnoPeak Technology & Salesforce Research & University of California, Los Angeles]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.16486


内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢