LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:在GPT中定位和编辑事实性关联、独立自纠正学习器序列生成、基于代码生成语言模型的自编程AI、通向自主机器智能之路、基于随机微分方程的超逼真歌声生成、面向视觉识别稀疏卷积模型的深入研究、无监督学习算法对人类实时学习和终身学习的建模基准、基于变异因子标注的模型错误理解、神经网络表示的人类对齐
1、[CL] Locating and Editing Factual Associations in GPT
K Meng, D Bau, A Andonian, Y Belinkov
[MIT CSAIL & Northeastern University & Technion – IIT]
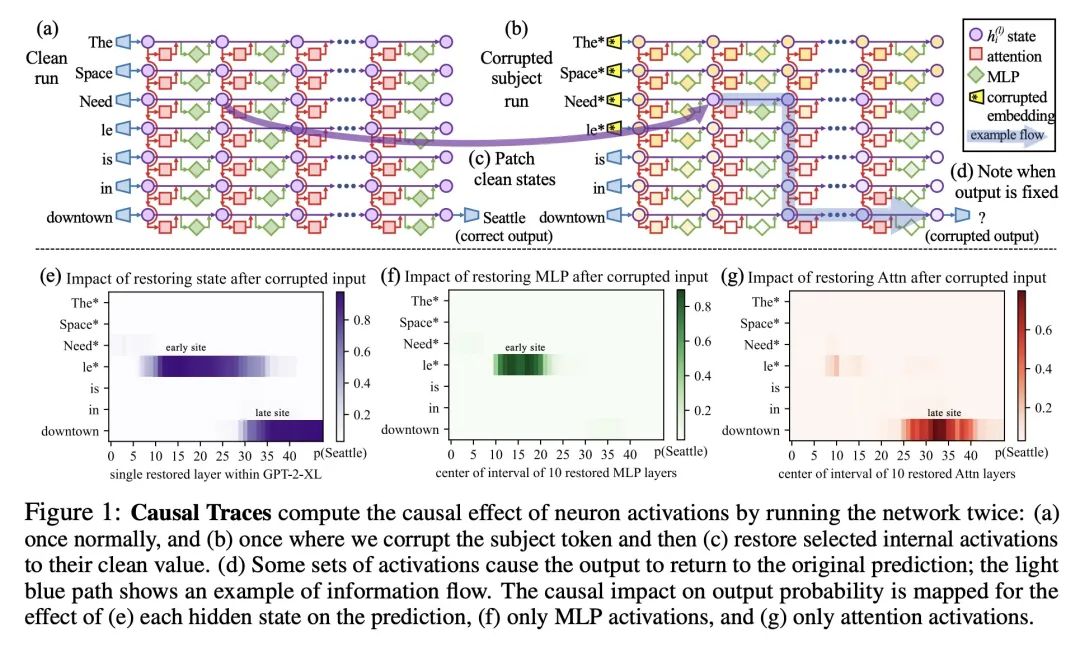
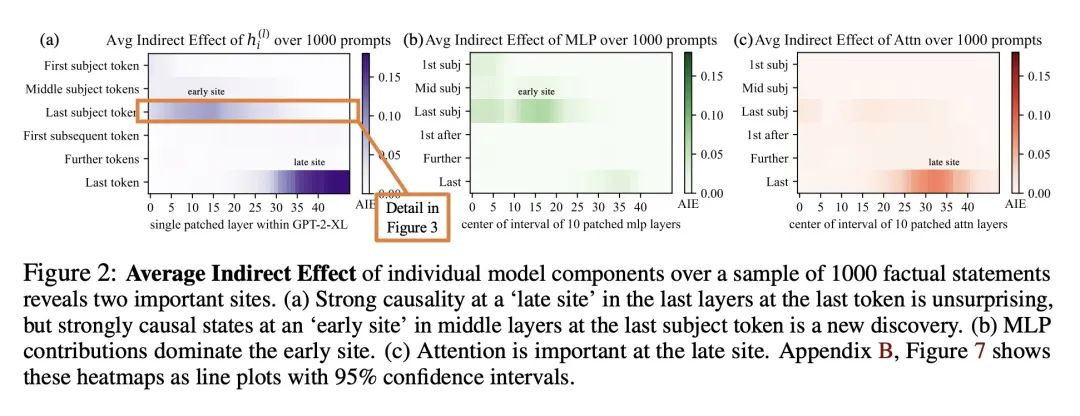
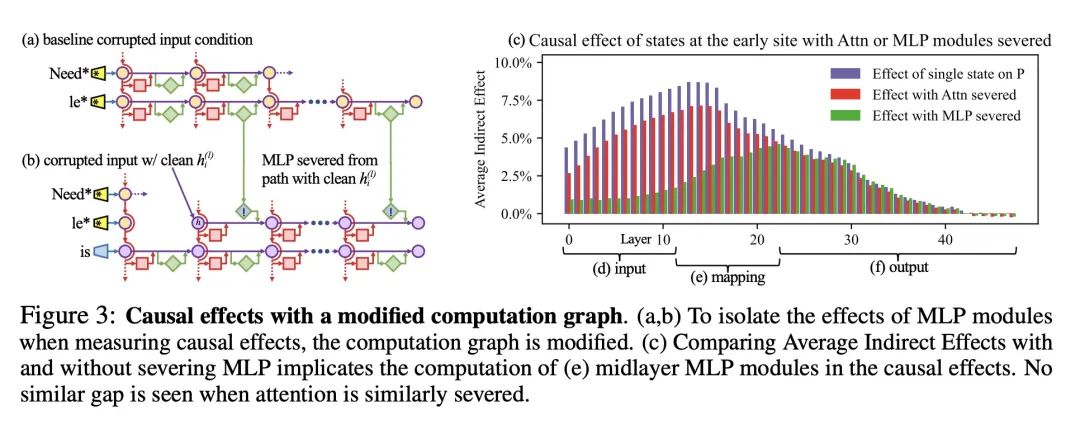
在GPT中定位和编辑事实性关联。本文分析了自回归transformer语言模型中事实联想的存储和回忆,发现有证据表明这些联想对应于局部化的、可直接编辑的计算。本文首先开发了一种因果干预方法,用于识别对模型的事实预测起决定性作用的神经元激活。这揭示了中间层前馈模块的一组独特的步骤,这些步骤在处理主题标记时调解了事实预测。为了测试所述假设,即这些计算对应于事实联想的回忆,本文修改了前馈权重,以使用Rank-One Model Editing(ROME)更新特定的事实联想。结果发现,ROME在标准的零样本元关系提取(zsRE)模型编辑任务上是有效的,与现有的方法相当。为了进行更敏感的评估,在一个新的反事实断言数据集上评估了ROME,在该数据集上,同时保持了特异性和泛化性,而其他方法则牺牲了其中之一。所得结果证实了中层前馈模块在存储事实关联方面的重要作用,并表明直接操纵计算机制可能是一种可行的模型编辑方法。
We analyze the storage and recall of factual associations in autoregressive transformer language models, finding evidence that these associations correspond to localized, directly-editable computations. We first develop a causal intervention for identifying neuron activations that are decisive in a model's factual predictions. This reveals a distinct set of steps in middle-layer feed-forward modules that mediate factual predictions while processing subject tokens. To test our hypothesis that these computations correspond to factual association recall, we modify feed-forward weights to update specific factual associations using Rank-One Model Editing (ROME). We find that ROME is effective on a standard zero-shot relation extraction (zsRE) model-editing task, comparable to existing methods. To perform a more sensitive evaluation, we also evaluate ROME on a new dataset of counterfactual assertions, on which it simultaneously maintains both specificity and generalization, whereas other methods sacrifice one or another. Our results confirm an important role for mid-layer feed-forward modules in storing factual associations and suggest that direct manipulation of computational mechanisms may be a feasible approach for model editing. The code, dataset, visualizations, and an interactive demo notebook are available at this https URL
https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.05262

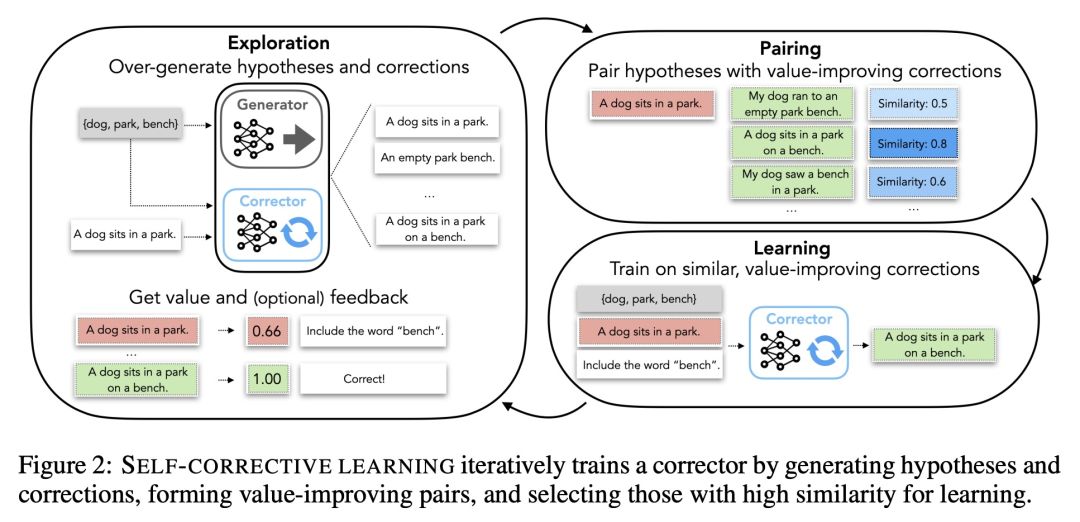
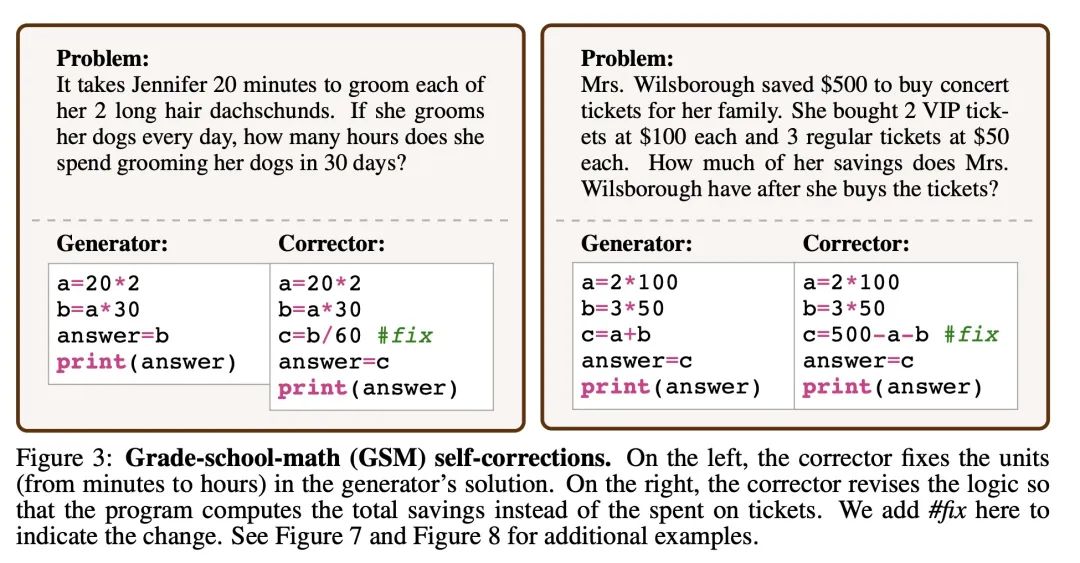
2、[CL] Generating Sequences by Learning to Self-Correct
S Welleck, X Lu, P West, F Brahman, T Shen...
[Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence & Johns Hopkins University & University of Washington]
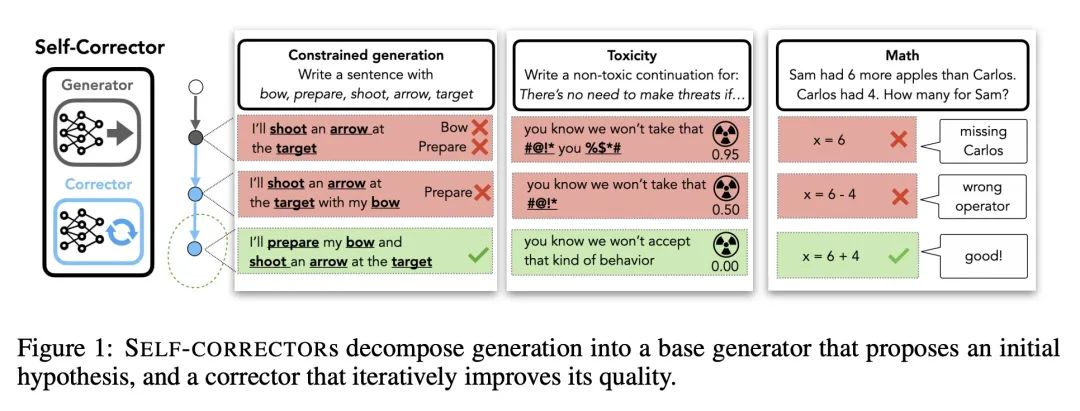
独立自纠正学习器序列生成。序列生成应用需要满足语义约束,如确保程序的正确性,使用某些关键词,或避免不受欢迎的内容。语言模型,无论是微调的还是用少样本演示来提示的,都经常违反这些约束条件,而且缺乏一种机制来反复修改其输出。此外,一些强大的语言模型规模极大或无法访问,使得更新其参数以适应特定任务的效率低下,甚至不可行。本文提出自纠正(Self-Correction),一种将不完美的基础生成器(现成的语言模型或有监督的序列到序列模型)与单独的修正器解耦的方法,该修正器可以学习迭代修正不完美的生成。为了训练纠正器器,本文提出一种在线训练程序,可以用标量或自然语言对中间不完善的代次进行反馈。本文表明,在三种不同的生成任务——数学程序合成、词汇约束生成和毒性控制——中,自纠正器比基本生成器要小得多。
Sequence generation applications require satisfying semantic constraints, such as ensuring that programs are correct, using certain keywords, or avoiding undesirable content. Language models, whether fine-tuned or prompted with few-shot demonstrations, frequently violate these constraints, and lack a mechanism to iteratively revise their outputs. Moreover, some powerful language models are of extreme scale or inaccessible, making it inefficient, if not infeasible, to update their parameters for task-specific adaptation. We present Self-Correction, an approach that decouples an imperfect base generator (an off-the-shelf language model or supervised sequence-to-sequence model) from a separate corrector that learns to iteratively correct imperfect generations. To train the corrector, we propose an online training procedure that can use either scalar or natural language feedback on intermediate imperfect generations. We show that Self-Correction improves upon the base generator in three diverse generation tasks - mathematical program synthesis, lexically-constrained generation, and toxicity control - even when the corrector is much smaller than the base generator.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.00053

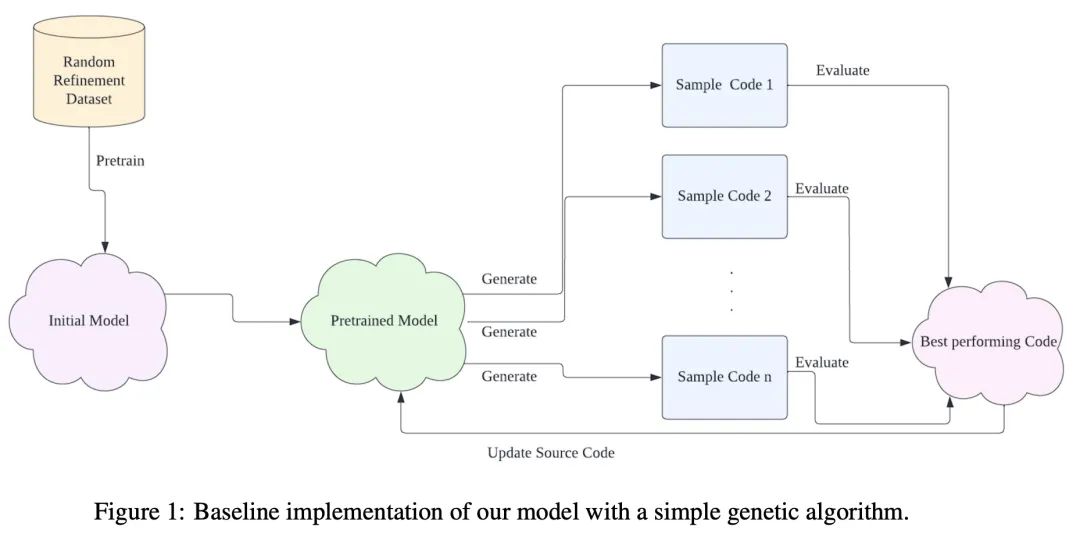
3、[LG] Self-Programming Artificial Intelligence Using Code-Generating Language Models
基于代码生成语言模型的自编程AI。大规模语言模型的最新进展使得以前难以解决的计算机编程任务有了突破性进展。之前在元学习和神经结构搜索方面的工作导致了各任务领域的巨大成功,催生了无数的深度学习模型的设计和学习动态算法优化方法。在这些研究领域的交叉点上,本文实现了一种具有修改自身源码能力的代码生成的语言模型。自编程AI算法自AI本身诞生以来就一直备受关注。尽管已经提出了各种广义的自编程AI的理论范式,但迄今为止,在现实世界的计算限制下,还没有这样的系统能成功实施。将基于AI的代码生成应用于AI本身,本文开发并实验验证了第一个实用的自编程AI系统的实现。通过经验表明,用代码生成模型实现的自编程AI可以成功地修改自己的源码以提高性能,并对子模型进行编程以执行辅助任务。该模型可以自我修改各种属性,包括模型结构、计算能力和学习动态。
Recent progress in large-scale language models has enabled breakthroughs in previously intractable computer programming tasks. Prior work in meta-learning and neural architecture search has led to substantial successes across various task domains, spawning myriad approaches for algorithmically optimizing the design and learning dynamics of deep learning models. At the intersection of these research areas, we implement a code-generating language model with the ability to modify its own source code. Self-programming AI algorithms have been of interest since the dawn of AI itself. Although various theoretical formulations of generalized self-programming AI have been posed, no such system has been successfully implemented to date under real-world computational constraints. Applying AI-based code generation to AI itself, we develop and experimentally validate the first practical implementation of a self-programming AI system. We empirically show that a self-programming AI implemented using a code generation model can successfully modify its own source code to improve performance and program sub-models to perform auxiliary tasks. Our model can self-modify various properties including model architecture, computational capacity, and learning dynamics.
https://openreview.net/forum?id=SKat5ZX5RET

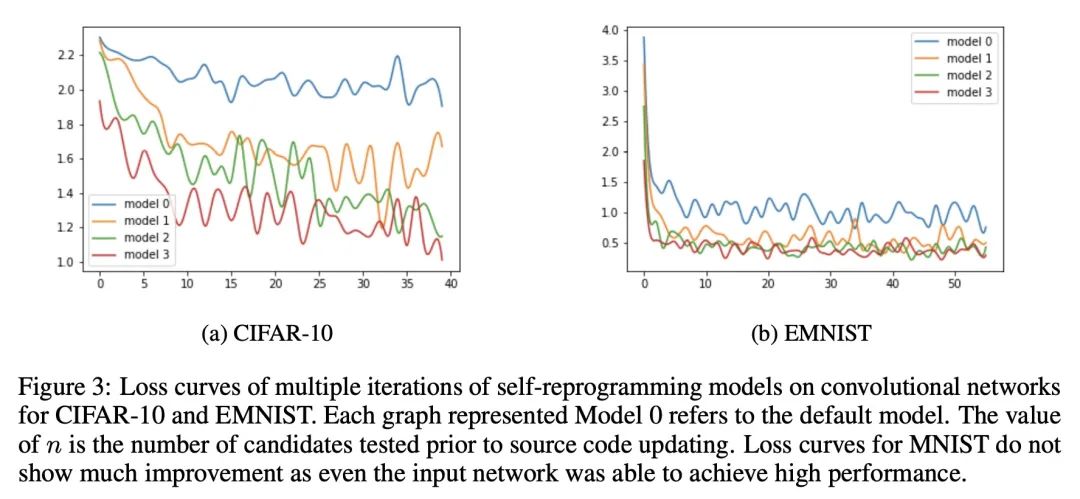
4、[LG] A Path Towards Autonomous Machine Intelligence
Yann LeCun
[New York University]
通向自主机器智能之路。机器如何能像人和动物一样高效地学习? 机器如何能学会推理和规划? 机器如何能在多个抽象层次上学习感知和行动规划的表示,使它们能在多个时间范围内进行推理、预测和规划? 本文提出了一个架构和训练范式,用以构建自主智能智能体,结合了一些概念,如可配置的预测世界模型,通过内在动机驱动的行为,以及用自监督学习训练的分层联合嵌入架构。
How could machines learn as efficiently as humans and animals? How could machines learn to reason and plan? How could machines learn representations of percepts and action plans at multiple levels of abstraction, enabling them to reason, predict, and plan at multiple time horizons? This position paper proposes an architecture and training paradigms with which to construct autonomous intelligent agents. It combines concepts such as configurable predictive world model, behavior driven through intrinsic motivation, and hierarchical joint embedding architectures trained with self-supervised learning.
https://openreview.net/forum?id=BZ5a1r-kVsf

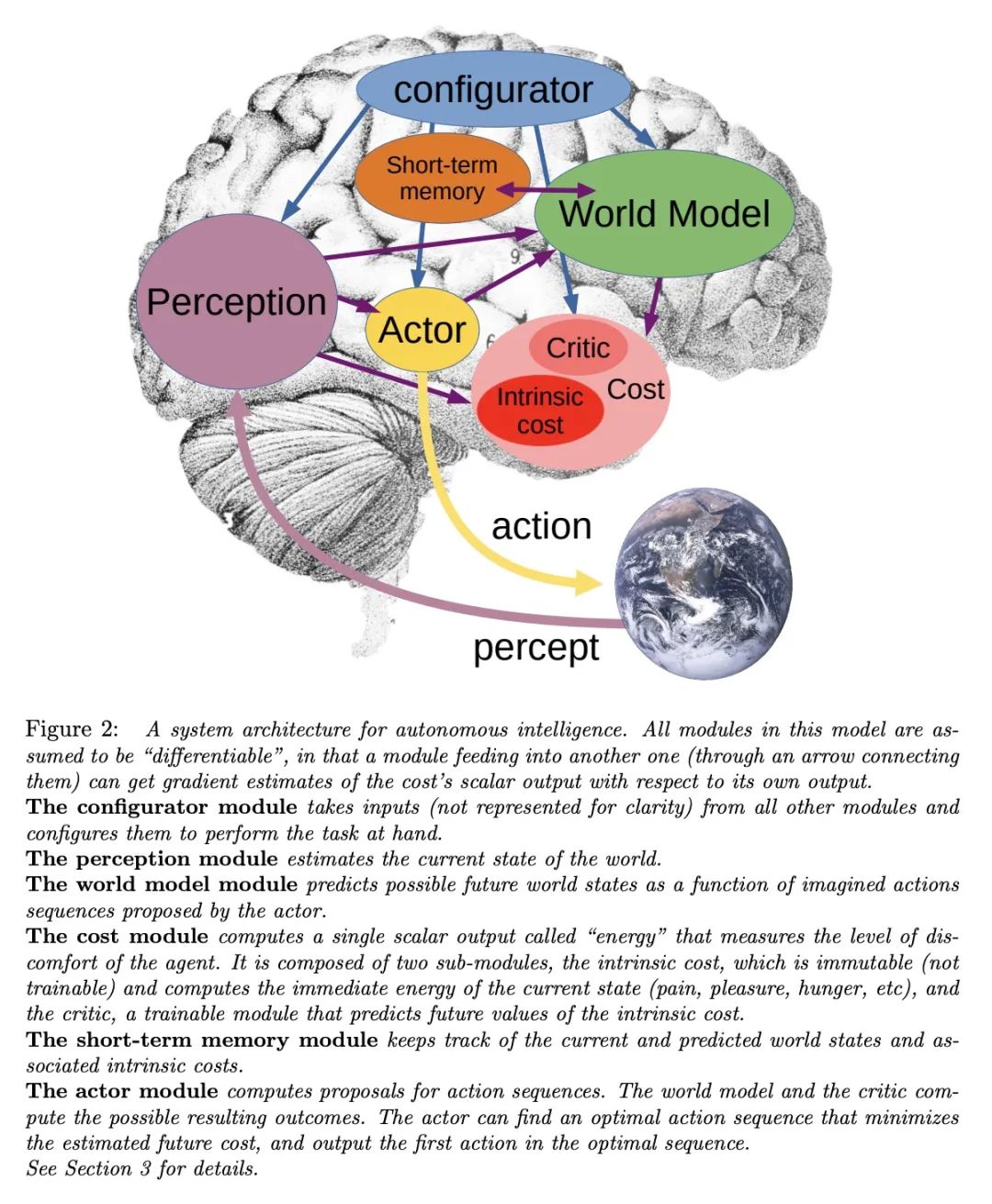
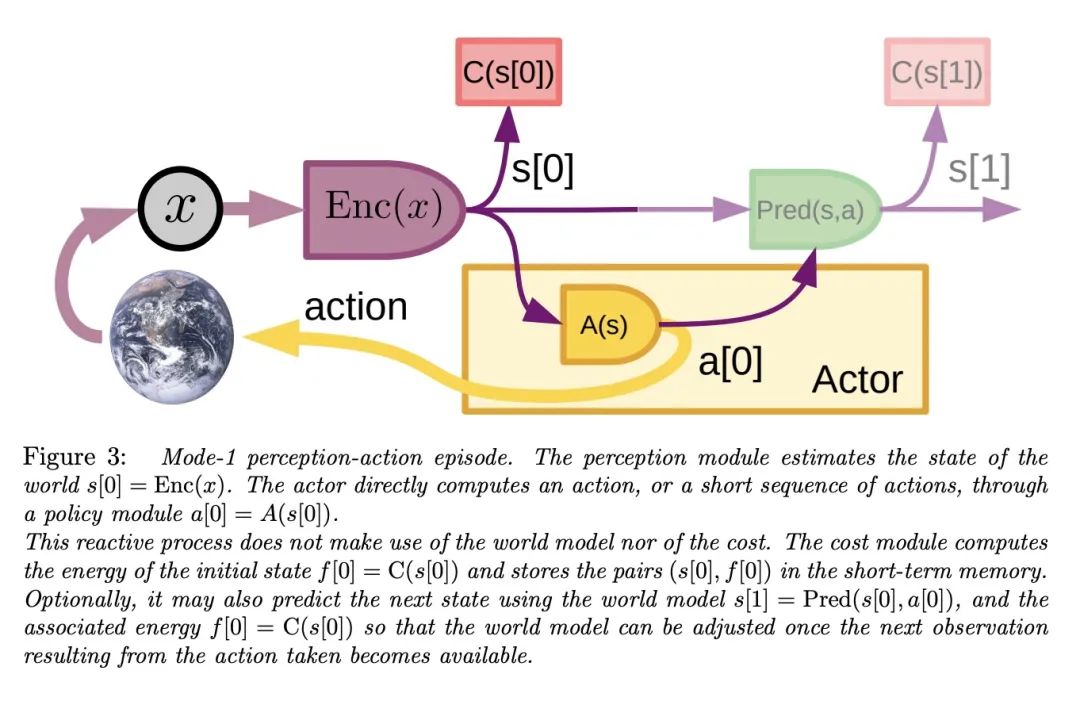
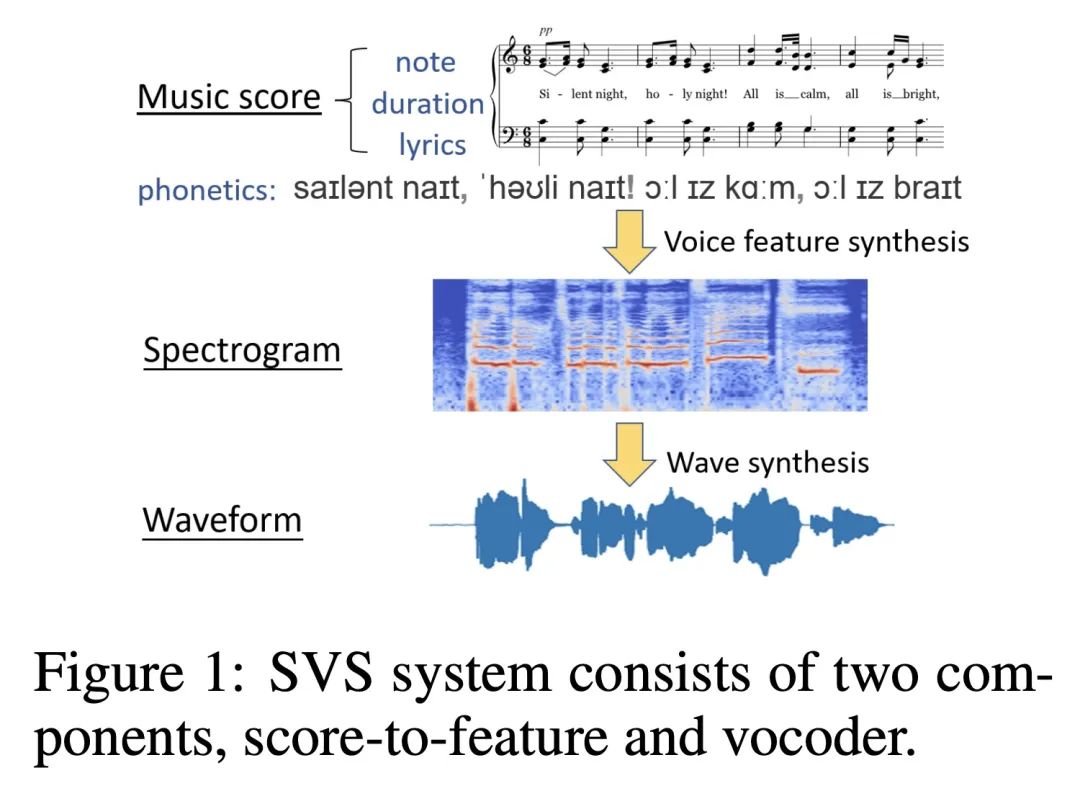
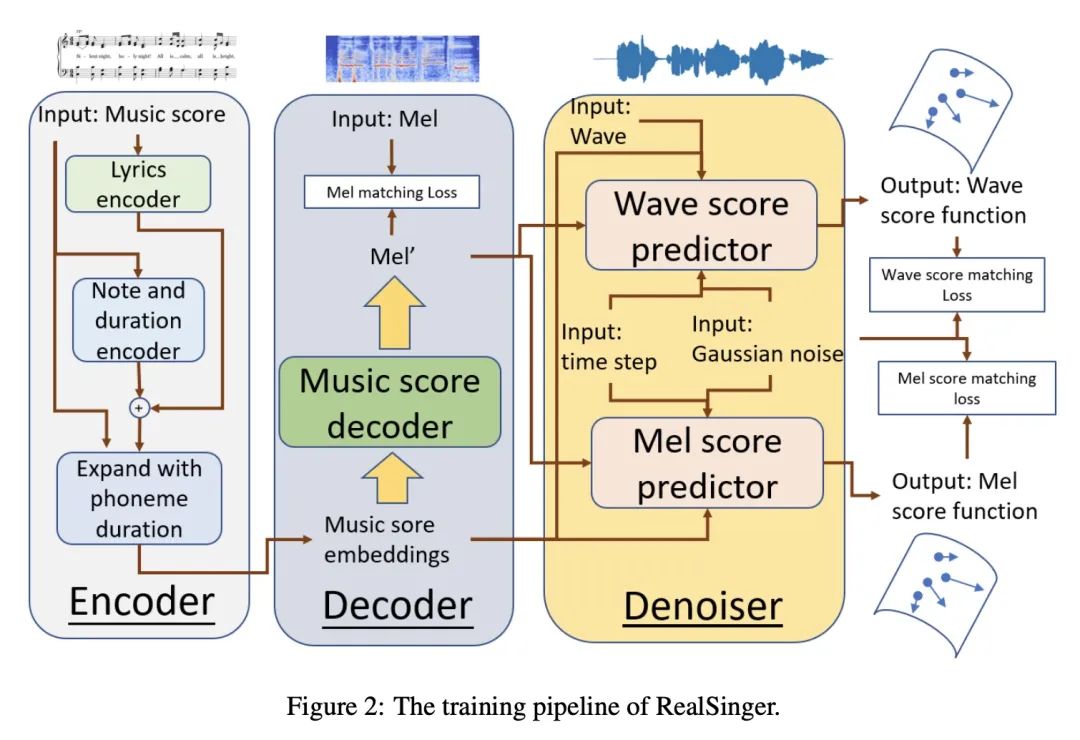
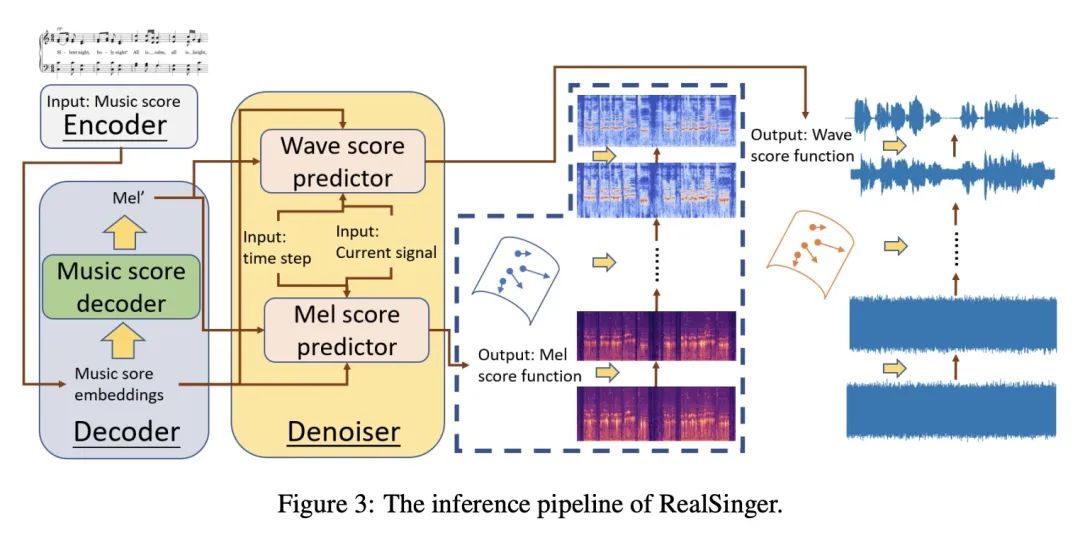
5、[AS] RealSinger: Ultra-Realistic Singing Voice Generation via Stochastic Differential Equations
RealSinger: 基于随机微分方程的超逼真歌声生成。从乐谱合成高质量歌唱是音乐生成中一个具有挑战性的问题,并有许多实际应用。现有的歌唱合成(SVS)系统产生的样本可以大致反映给定乐谱中的歌词、音高和时长,但它们未能包含必要的细节。本文基于随机微分方程(SDE)提出RealSinger,以乐谱为条件生成22.05kHz的超逼真的歌唱。RealSinger学会了在乐谱约束下找到从白噪声源到目标歌唱流形的随机过程路径,允许在保持目标歌手的局部声音细节的同时唱出乐谱。在训练过程中,该模型学会准确预测环境欧几里得空间在低维歌唱声音流形上的运动方向。RealSinger的框架是非常灵活的,既可以生成歌唱的中间特征表示,如mel-spectrogram,也可以直接生成最终的波形,如端到端风格,纠正两阶段连接的歌唱合成系统所带来的缺陷和累积错误。在基准数据集上进行的广泛的主观和客观测试表明,RealSinger在感知质量上有明显的提高。用RealSinger获得的平均意见分数(MOS)比使用任何先进方法获得的分数更接近人类歌手的原始高保真歌声。
Synthesizing high-quality singing voice from music score is a challenging problem in music generation and has many practical applications. Samples generated by existing singing voice synthesis (SVS) systems can roughly reflect the lyrics, pitch and duration in a given score, but they fail to contain necessary details. In this paper, based on stochastic differential equations (SDE) we propose RealSinger to generate 22.05kHz ultra-realistic singing voice conditioned on a music score. Our RealSinger learns to find the stochastic process path from a source of white noise to the target singing voice manifold under the conditional music score, allowing to sing the music score while maintaining the local voice details of the target singer. During training, our model learns to accurately predict the direction of movement in the ambient Euclidean space onto the low-dimensional singing voice manifold. RealSinger's framework is very flexible. It can either generate intermediate feature representations of the singing voice, such as mel-spectrogram, or directly generate the final waveform, as in the end-to-end style which rectify defects and accumulation errors introduced by two-stage connected singing synthesis systems. An extensive subjective and objective test on benchmark datasets shows significant gains in perceptual quality using RealSinger. The mean opinion scores (MOS) obtained with RealSinger are closer to those of the human singer's original high-fidelity singing voice than to those obtained with any state-of-the-art method. Audio samples are available at https://realsinger.github.io/.
https://openreview.net/forum?id=ctnmrjv6lU5

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
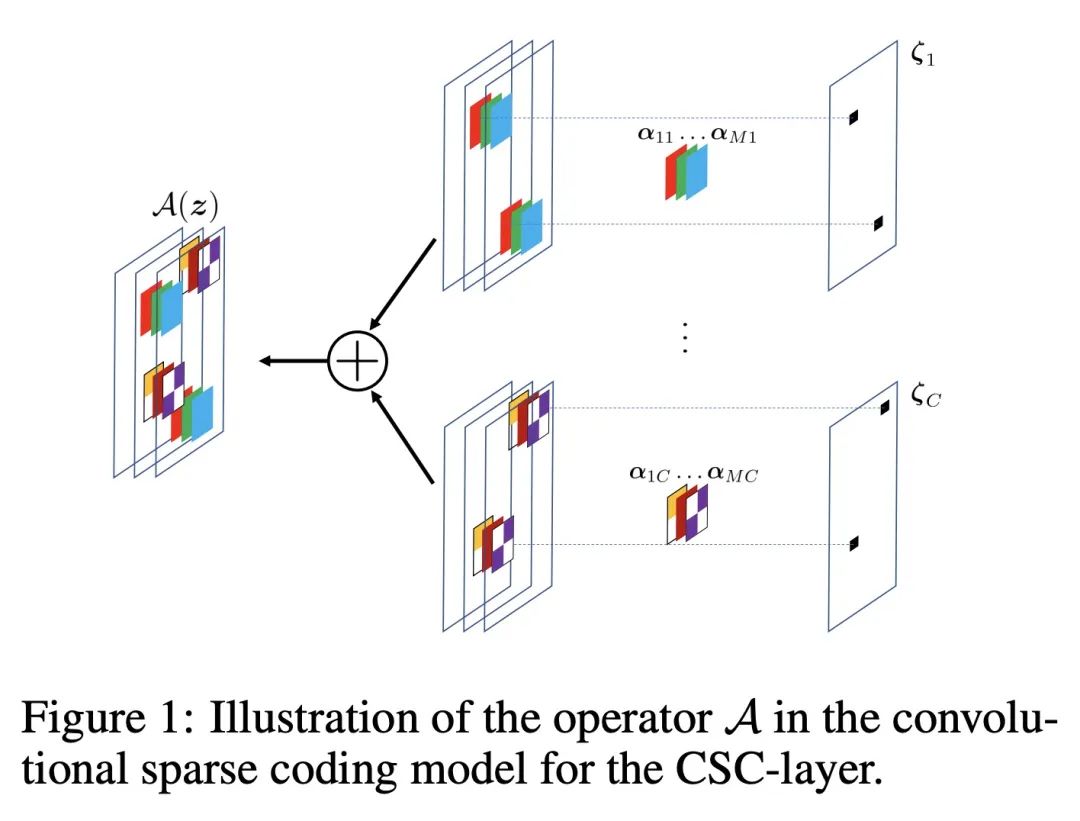
[CV] Revisiting Sparse Convolutional Model for Visual Recognition
面向视觉识别稀疏卷积模型的深入研究
X Dai, M Li...
[The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology & Tsinghua University & Harvard University & UC Berkeley & Ohio State University]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.12945

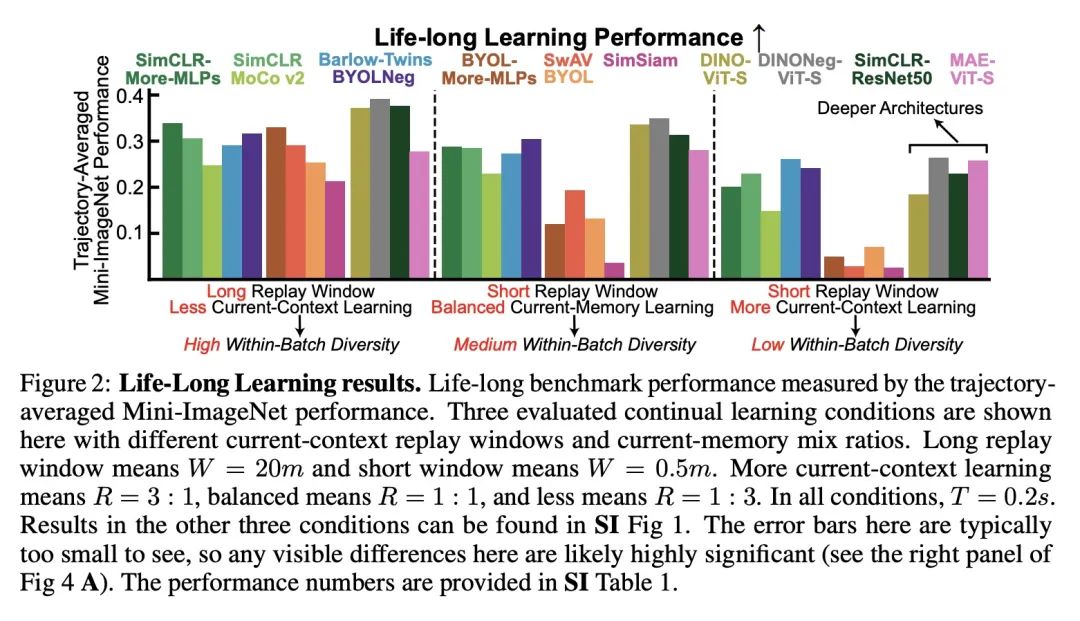
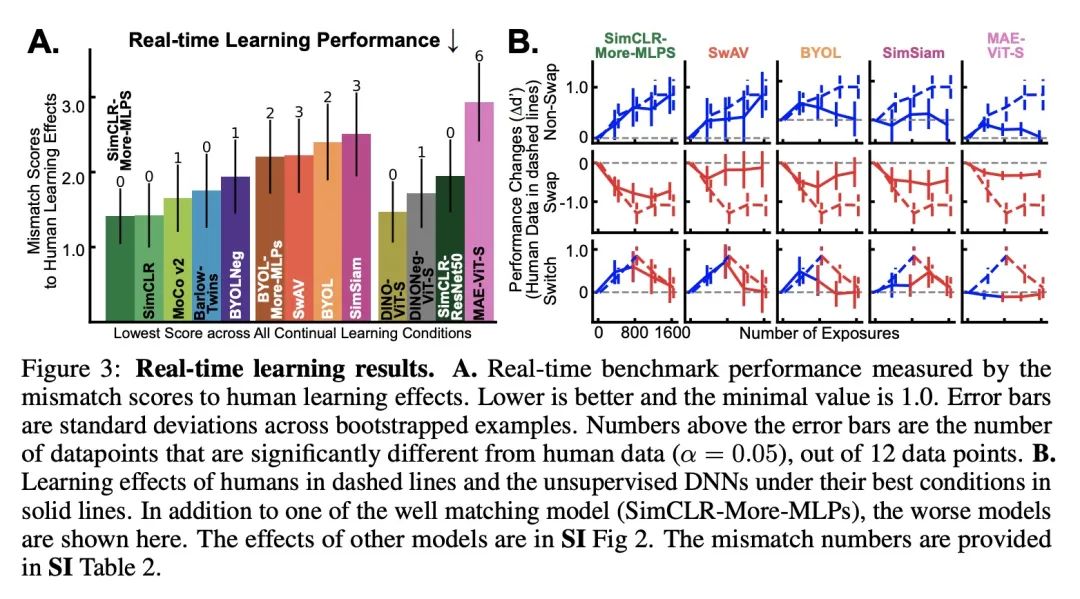
[LG] How Well Do Unsupervised Learning Algorithms Model Human Real-time and Life-long Learning?
无监督学习算法对人类实时学习和终身学习的建模基准
C Zhuang, V Xiang, Y Bai, X Jia...
[Stanford University & MIT & Tsinghua University & Yale University & Princeton University]
https://openreview.net/forum?id=c0l2YolqD2T…


[CV] ImageNet-X: Understanding Model Mistakes with Factor of Variation Annotations
ImageNet-X:基于变异因子标注的模型错误理解
B Y Idrissi, D Bouchacourt, R Balestriero, I Evtimov, C Hazirbas, N Ballas, P Vincent, M Drozdzal, D Lopez-Paz, M Ibrahim
[Meta AI]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.01866


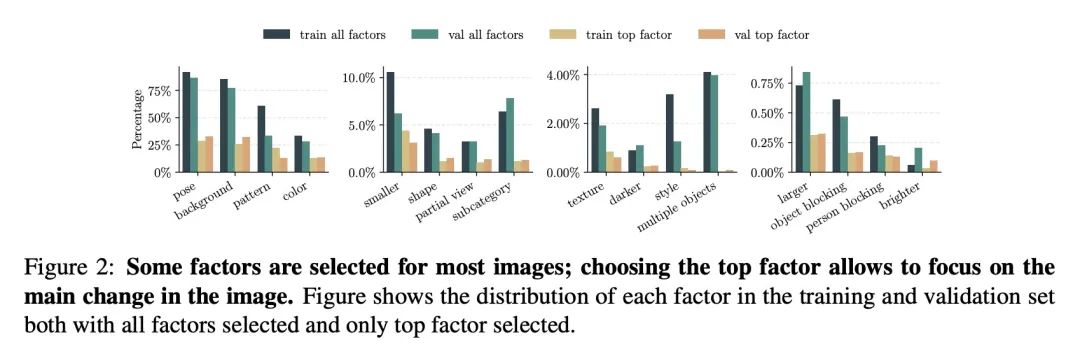
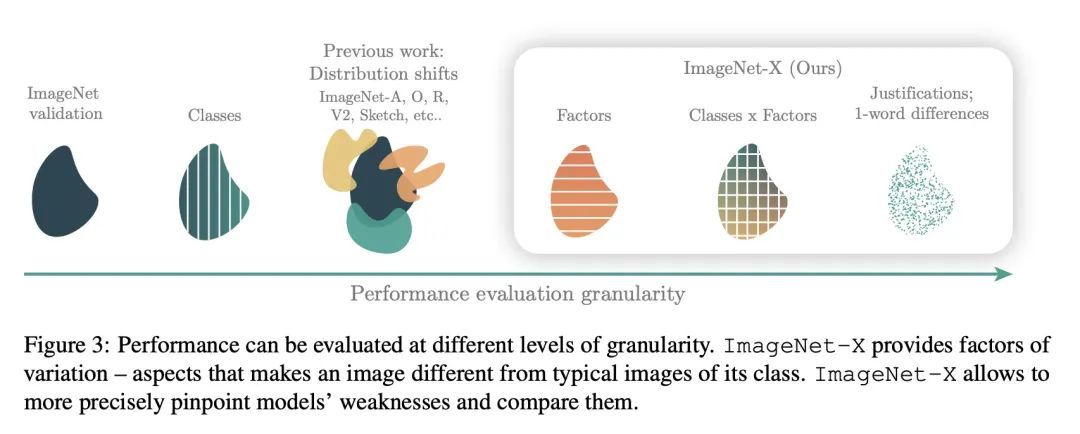
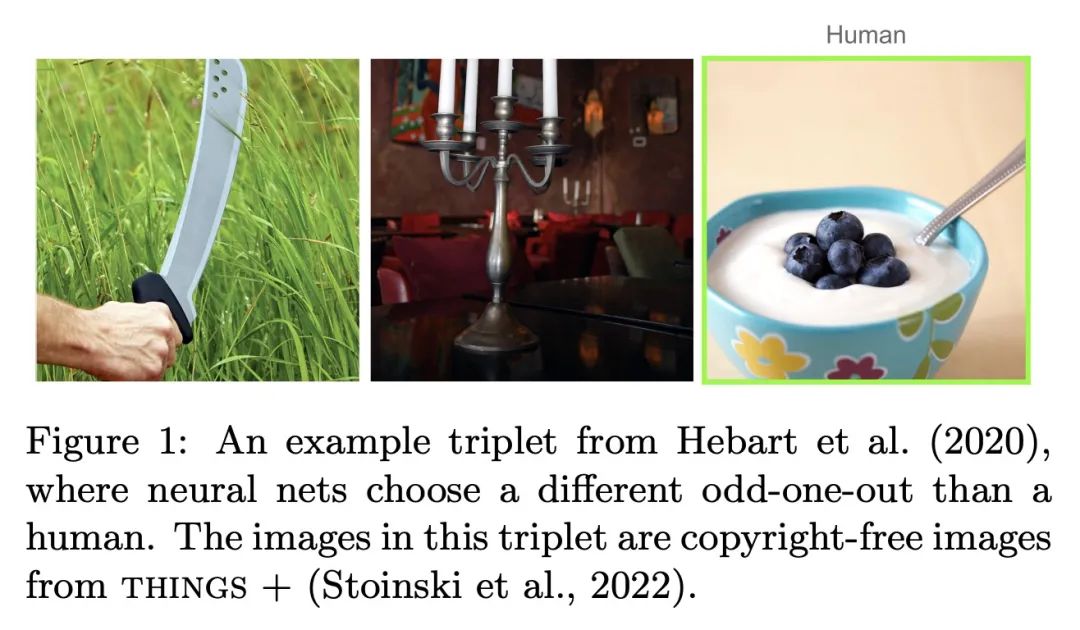
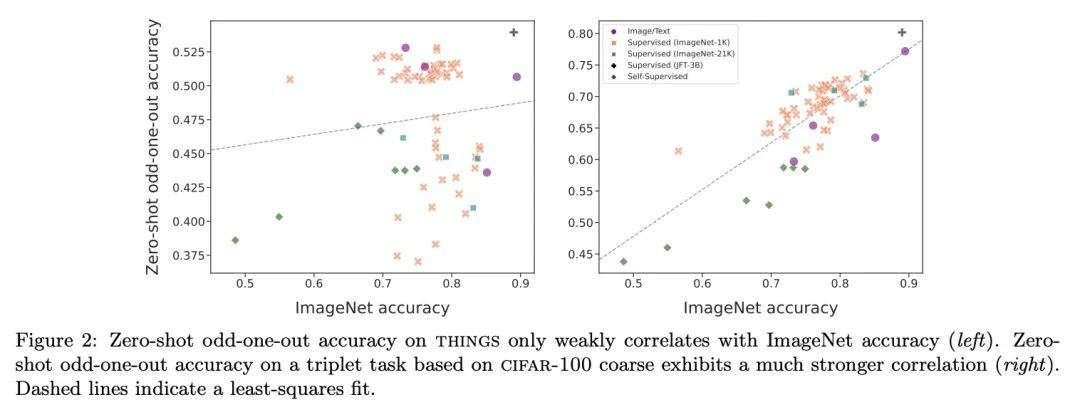
[CV] Human alignment of neural network representations
神经网络表示的人类对齐
L Muttenthaler, J Dippel, L Linhardt, R A. Vandermeulen, S Kornblith
[Technische Universitat Berlin & Google Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.01201

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢