转自爱可可爱生活
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
摘要:人类被试者单体神经元在线内在语音解码、Transformer推理高效扩展、基于Shapley的特征归因的分析和改进、基于分割引导对比学习的多层神经纤维网图谱、176B参数的开放多语种语言模型、人类通过权衡效用和计算成本来分解任务、用AI写作助手进行创造性写作、视频任意点追踪基准、面向新对象语义重排的以对象为中心的扩散
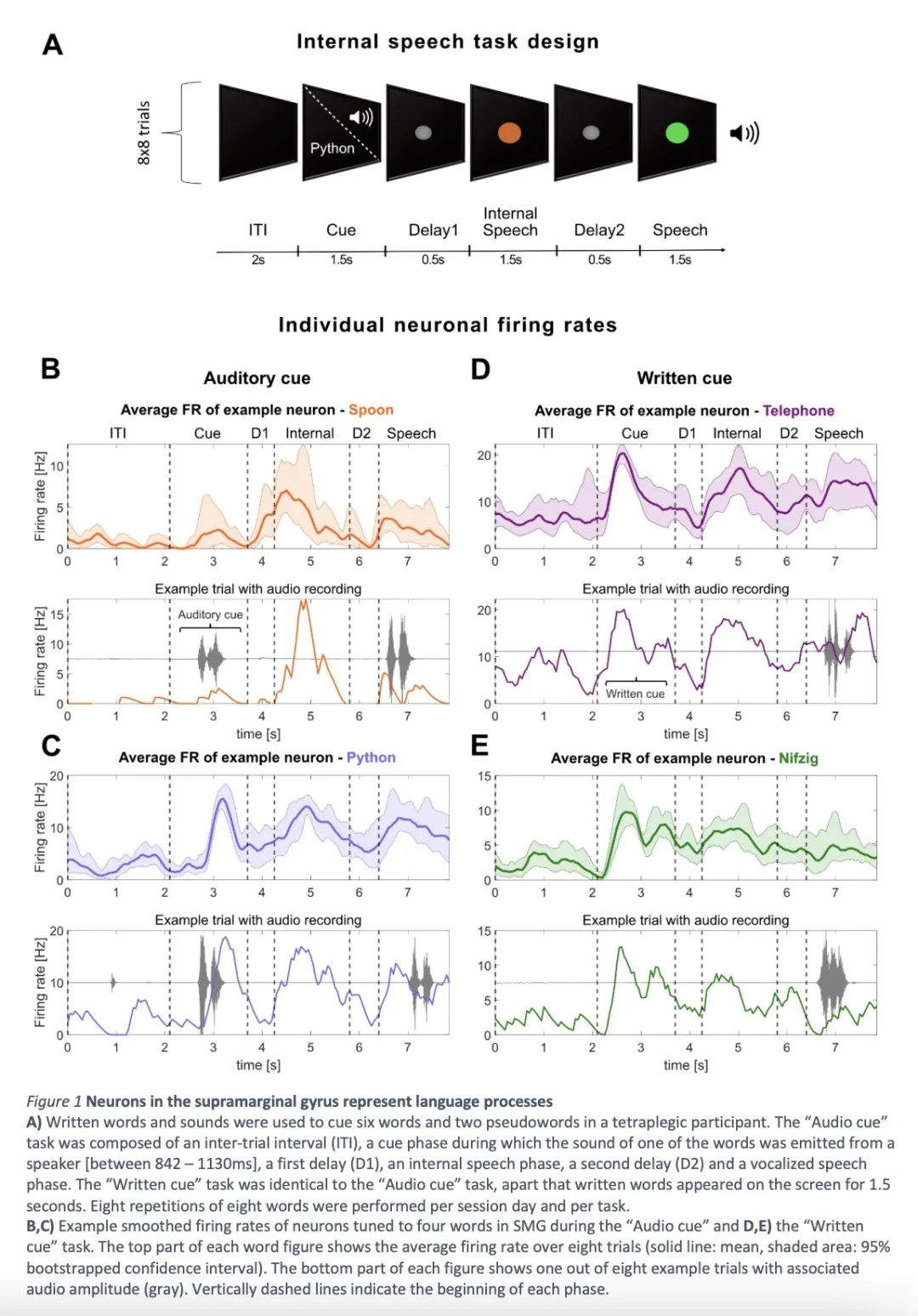
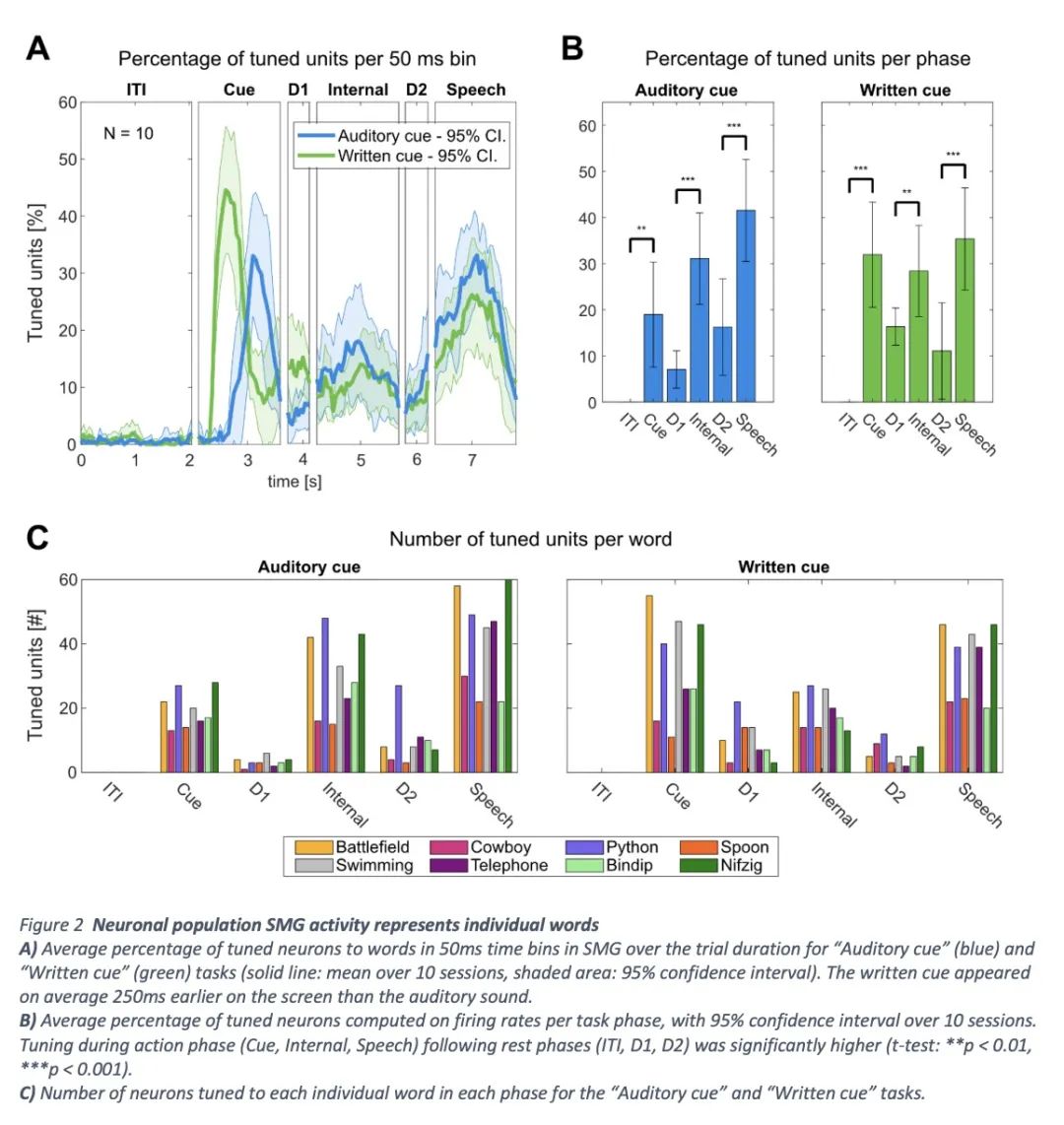
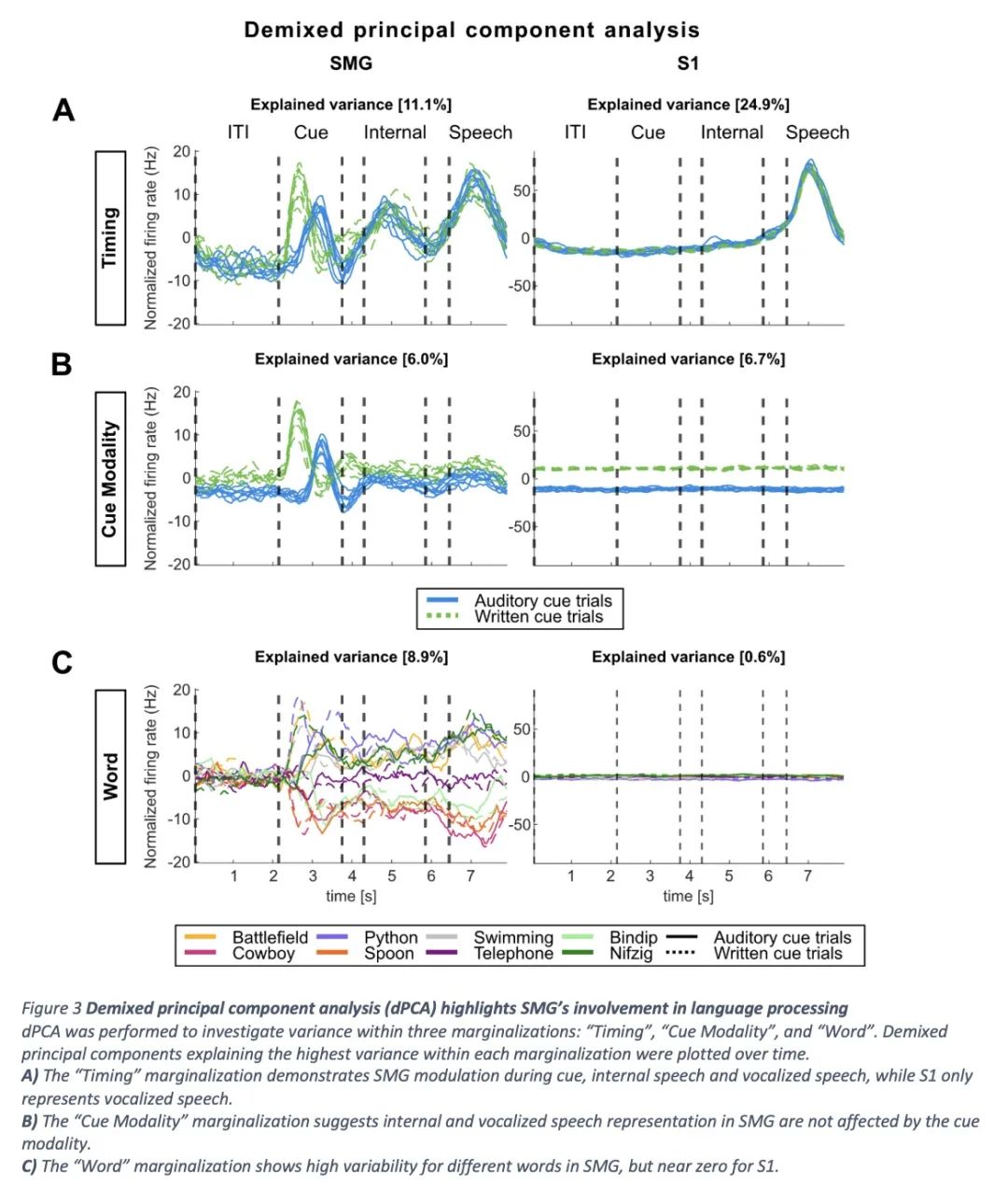
1、[LG] Online internal speech decoding from single neurons in a human participant
S K. Wandelt, D A. Bjånes, K Pejsa, B Lee, C Liu, R A. Andersen
[California Institute of Technology]
人类被试者单体神经元在线内在语音解码。语音脑机接口(BMI)将大脑信号转化为文字或音频输出,使因疾病或受伤而失去语言能力的人能够进行交流。虽然在发声、尝试和模拟语音解码方面已经取得了重要进展,但内在语音解码的结果却很少。语音解码方面取得了重要进展,但内部语音解码的结果却很少,而且还没有实现高功能性。值得注意的是,目前还不清楚从哪些大脑区域可以对内在语音进行解码。本文中,一位四肢瘫痪的参与者被植入了位于边上回(SMG)和初级体感皮层(S1)的微电极阵,进行了六个单词和两个假词的内在和发声讲话。结果发现,从SMG单神经的内在语音解码,在一个在线任务中实现了高达91%的分类准确性。在线任务(偶然水平为12.5%)。有证据表明内在语音、单词阅读和发声语音过程之间有共同的神经表征。SMG代表了不同语言(英语/西班牙语)中的单词。 语言(英语/西班牙语)以及假词,提供了语音编码的证据。此外,该解码器通过多种内部语音策略(听觉想象/视觉想象)实现了高分类。S1的活动受到发声的调节,但没有受到内在语音的调节。 这表明,在内在语音产生过程中,没有发生声道的发音器运动。本文工作代表了第一个高性能内在语音BMI的概念证明。
Speech brain-machine interfaces (BMI’s) translate brain signals into words or audio outputs, enabling communication for people having lost their speech abilities due to diseases or injury. While important advances in vocalized, attempted, and mimed speech decoding have been achieved, results for internal speech decoding are sparse, and have yet to achieve high functionality. Notably, it is still unclear from which brain areas internal speech can be decoded. In this work, a tetraplegic participant with implanted microelectrode arrays located in the supramarginal gyrus (SMG) and primary somatosensory cortex (S1) performed internal and vocalized speech of six words and two pseudowords. We found robust internal speech decoding from SMG single neuron activity, achieving up to 91% classification accuracy during an online task (chance level 12.5%). Evidence of shared neural representations between internal speech, word reading, and vocalized speech processes were found. SMG represented words in differentlanguages (English/ Spanish) as well as pseudowords, providing evidence for phonetic encoding. Furthermore, our decoder achieved high classification with multiple internal speech strategies (auditoryimagination/ visual imagination). Activity in S1 was modulated by vocalized but not internal speech,suggesting no articulator movements of the vocal tract occurred during internal speech production. This works represents the first proof-of-concept for a high-performance internal speech BMI.
https://medrxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.11.02.22281775v1

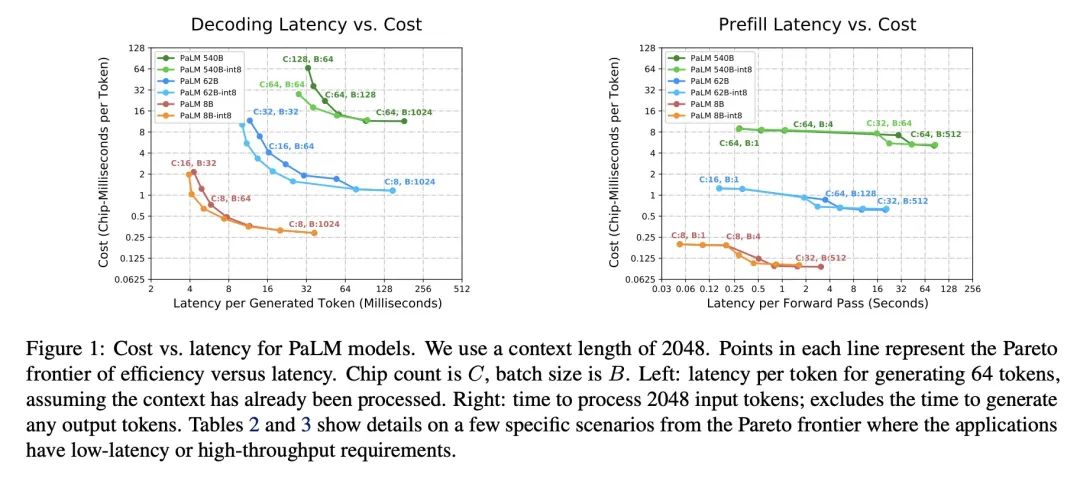
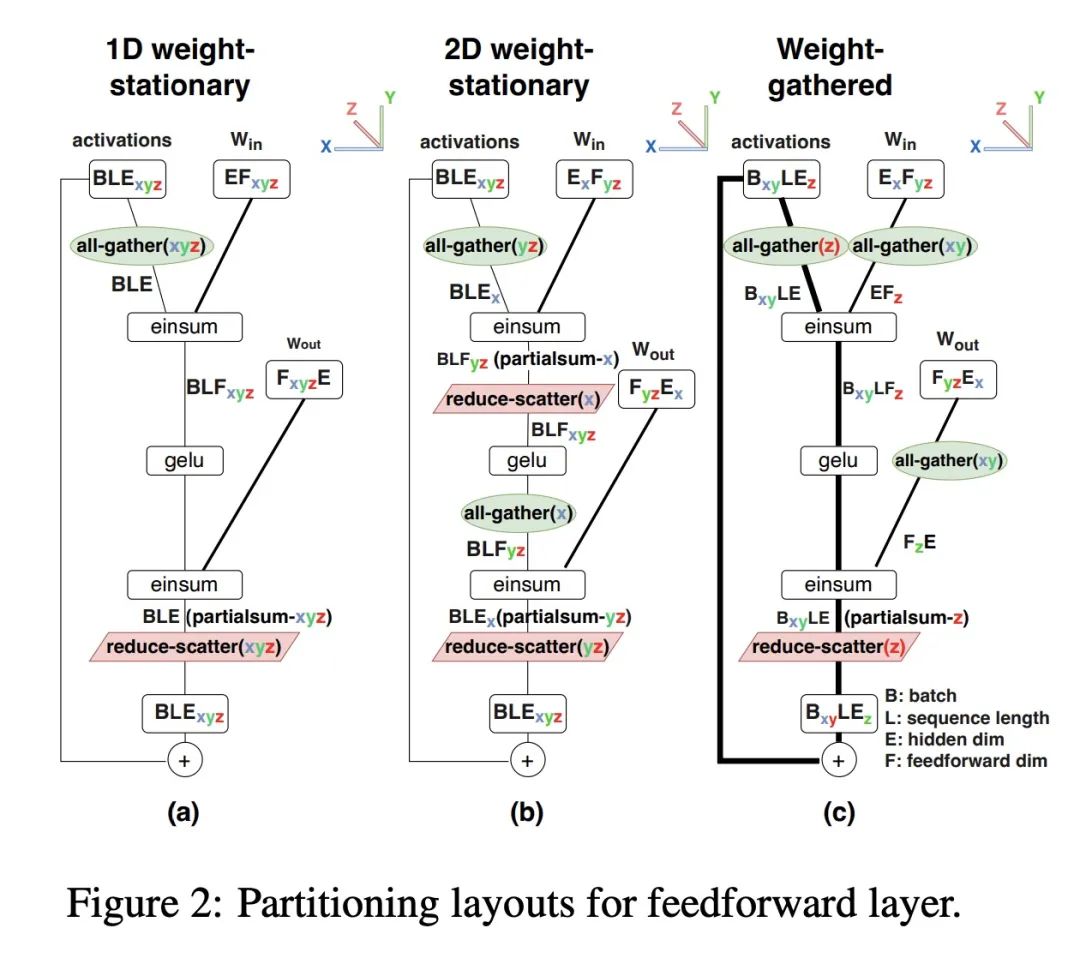
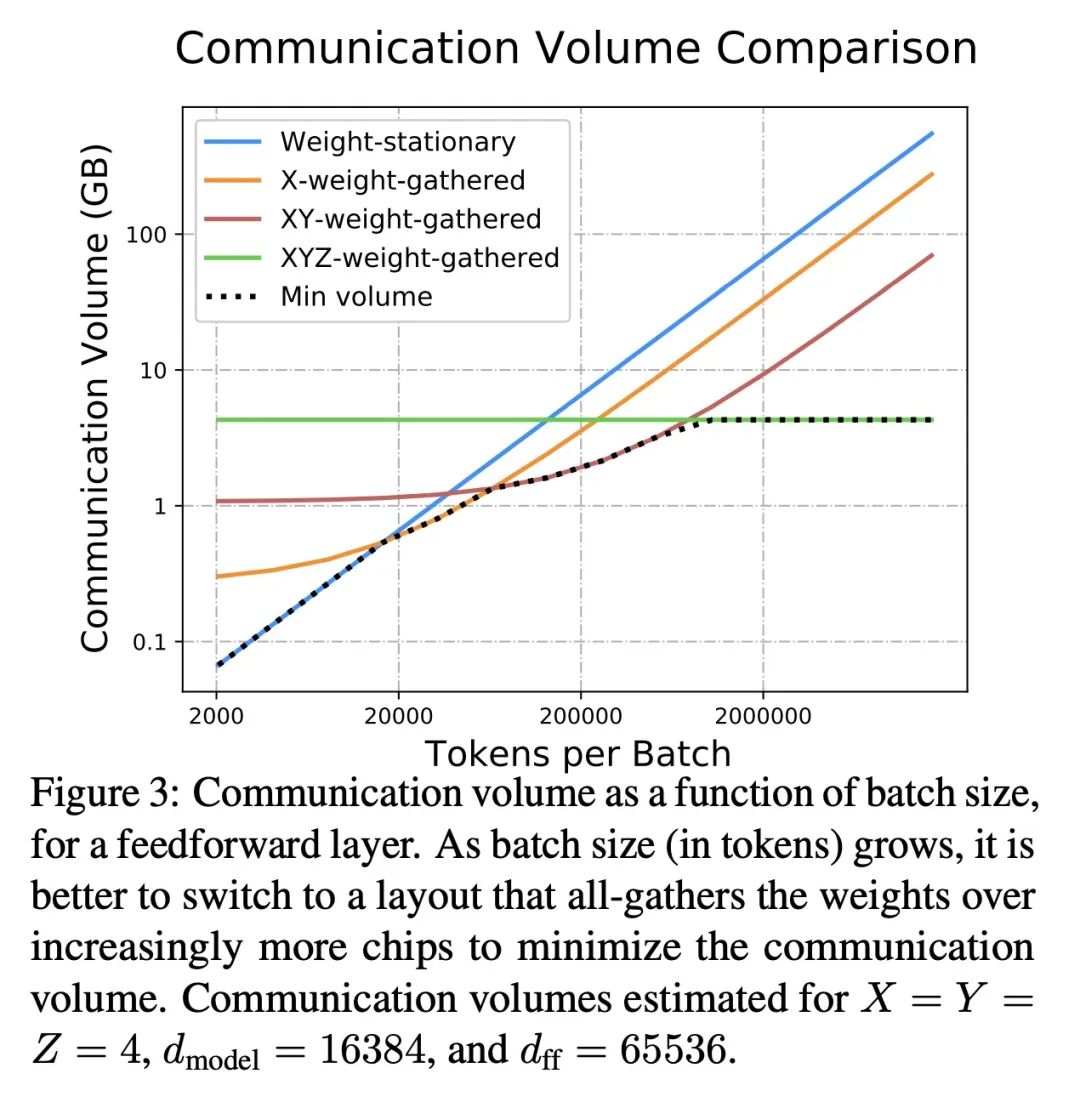
2、[LG] Efficiently Scaling Transformer Inference
R Pope, S Douglas, A Chowdhery, J Devlin, J Bradbury, A Levskaya, J Heek, K Xiao, S Agrawal, J Dean
[Google]
Transformer推理高效扩展。本文研究了Transformer模型的高效生成式推理问题,在其最具挑战性的设置中:大型深度模型,具有严格的延迟目标和长序列长度。更好地理解基于Transformer的大型模型推理的工程权衡是非常重要的,因为这些模型的用例在整个应用领域都在快速增长。本文开发了一个简单的推理效率分析模型,根据应用要求选择为TPU v4切片优化的最佳多维分割技术。将其与一套低级别的优化结合起来,在500B以上参数模型的延迟和模型FLOPS利用率(MFU)的权衡上实现了新的帕累托前沿,超过了FasterTransformer系列基准测试。本文进一步表明,通过适当的分区,多查询注意力(即多个查询头共享单个键/值头)的较低内存要求使得扩展到32倍的上下文长度。最后,本文在生成过程中实现了每个token 29ms的低批量大小的延迟(使用int8权重量化),在大批量处理输入token的过程中实现了76%的MFU,同时支持PaLM 540B参数模型上的2048个token的长上下文。
We study the problem of efficient generative inference for Transformer models, in one of its most challenging settings: large deep models, with tight latency targets and long sequence lengths. Better understanding of the engineering tradeoffs for inference for large Transformer-based models is important as use cases of these models are growing rapidly throughout application areas. We develop a simple analytical model for inference efficiency to select the best multi-dimensional partitioning techniques optimized for TPU v4 slices based on the application requirements. We combine these with a suite of low-level optimizations to achieve a new Pareto frontier on the latency and model FLOPS utilization (MFU) tradeoffs on 500B+ parameter models that outperforms the FasterTransformer suite of benchmarks. We further show that with appropriate partitioning, the lower memory requirements of multiquery attention (i.e. multiple query heads share single key/value head) enables scaling up to 32x larger context lengths. Finally, we achieve a low-batch-size latency of 29ms per token during generation (using int8 weight quantization) and a 76% MFU during large-batch-size processing of input tokens, while supporting a long 2048-token context length on the PaLM 540B parameter model.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05102

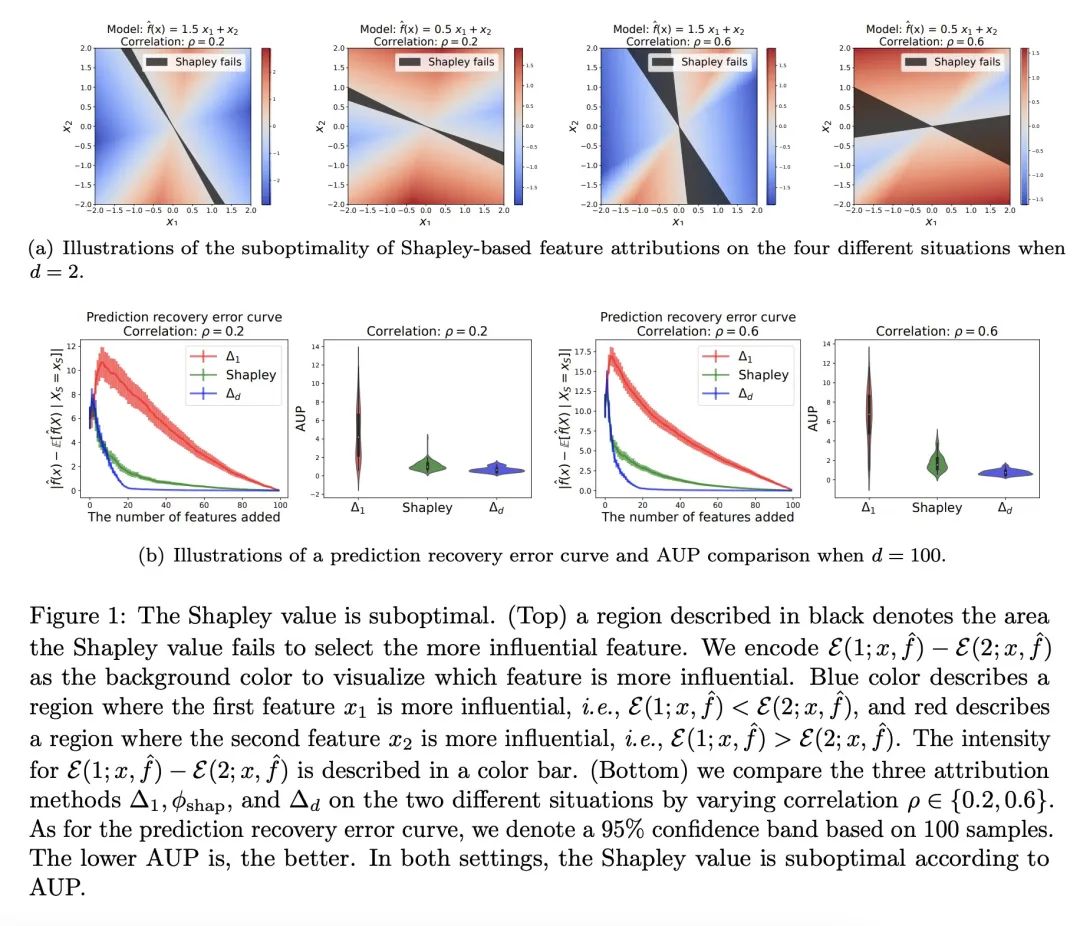
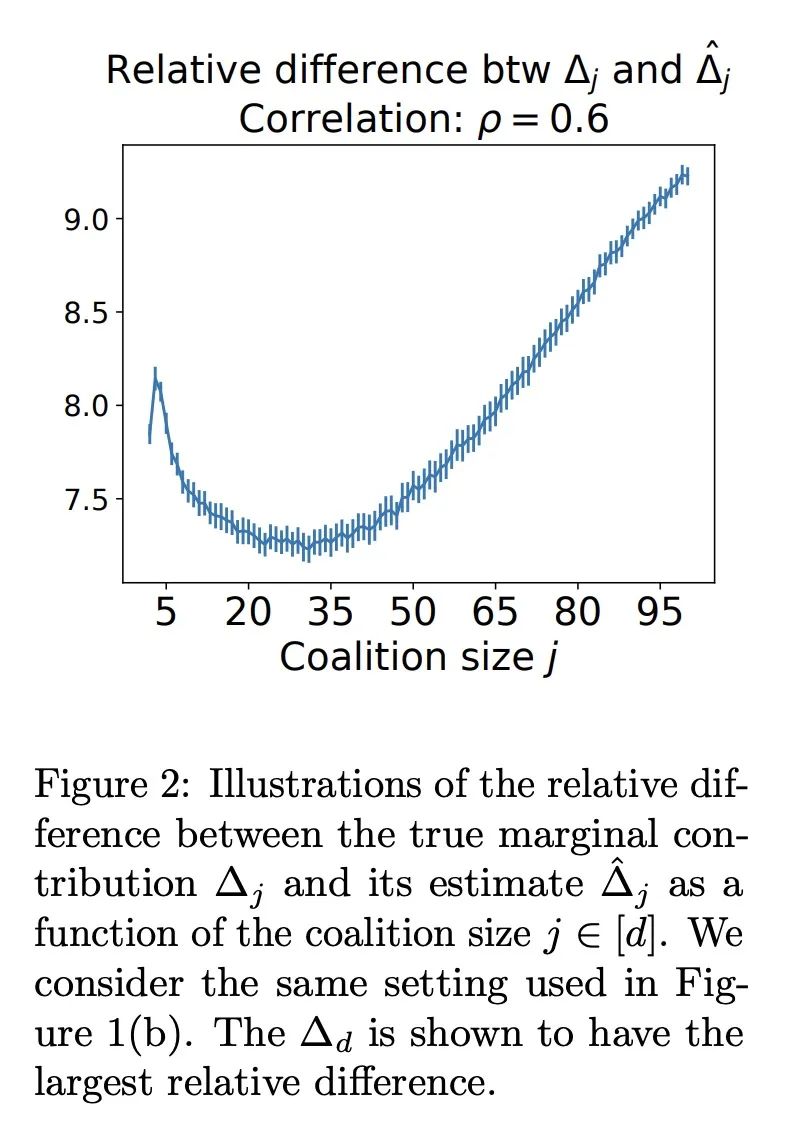
3、[LG] WeightedSHAP: analyzing and improving Shapley based feature attributions
Y Kwon, J Zou
[Columbia University & Stanford University]
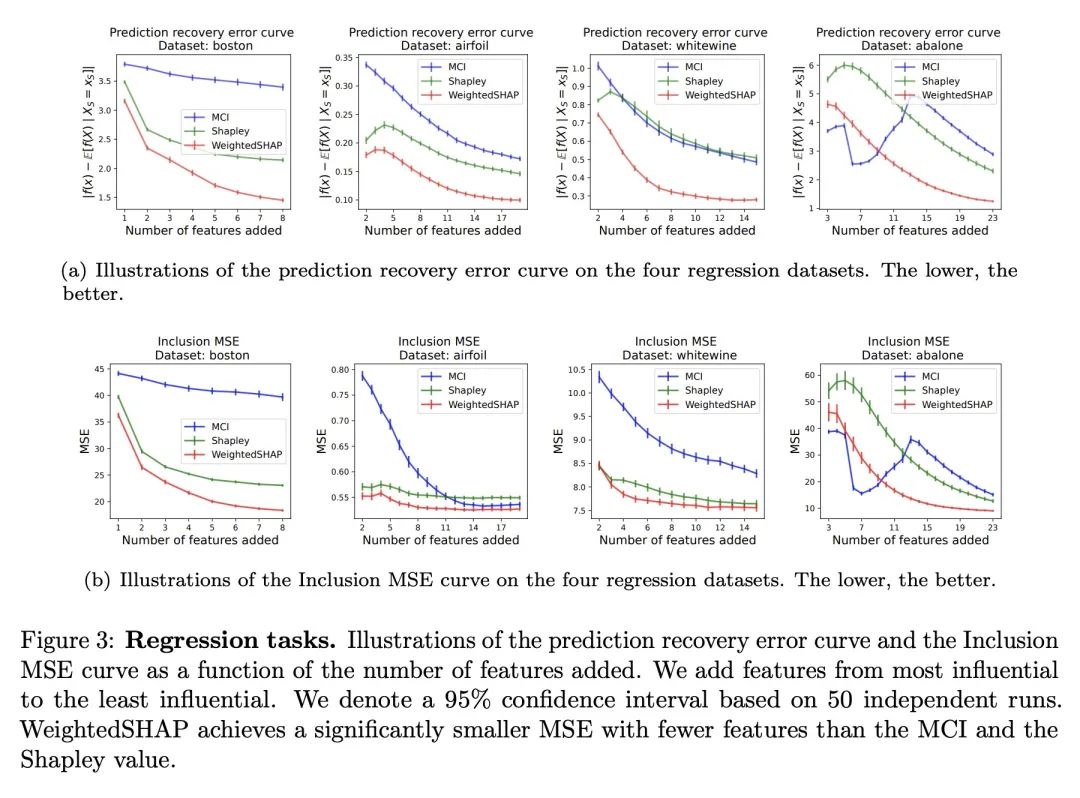
WeightedSHAP:基于Shapley的特征归因的分析和改进。Shapley值是一种测量单个特征影响的流行方法。虽然Shapley特征归因是建立在博弈论的期望值上,但在某些机器学习环境中,它的一些约束可能不太自然,导致不直观的模型解释。特别是,Shapley值对所有的边际贡献使用相同的权重——也就是说,当给出大量的其他特征与给出少量的其他特征时,它的重要性相同。如果较大的特征集比较小的特征集的信息量更大或更小,那么这个属性就会有问题。本文对Shapley特征归属的潜在限制进行了严格的分析,确定了简单的设置,其中Shapley值在数学上是次优的,因为它为影响较小的特征分配了较大的归因。在这一观察的激励下,本文提出WeightedSHAP,它推广了Shapley值,并直接从数据中学习哪些边际贡献需要关注。在几个真实世界的数据集上,本文证明了由WeightedSHAP确定的有影响力的特征与由Shapley值确定的特征相比,能更好地再现模型的预测。
Shapley value is a popular approach for measuring the influence of individual features. While Shapley feature attribution is built upon desiderata from game theory, some of its constraints may be less natural in certain machine learning settings, leading to unintuitive model interpretation. In particular, the Shapley value uses the same weight for all marginal contributions -- i.e. it gives the same importance when a large number of other features are given versus when a small number of other features are given. This property can be problematic if larger feature sets are more or less informative than smaller feature sets. Our work performs a rigorous analysis of the potential limitations of Shapley feature attribution. We identify simple settings where the Shapley value is mathematically suboptimal by assigning larger attributions for less influential features. Motivated by this observation, we propose WeightedSHAP, which generalizes the Shapley value and learns which marginal contributions to focus directly from data. On several real-world datasets, we demonstrate that the influential features identified by WeightedSHAP are better able to recapitulate the model's predictions compared to the features identified by the Shapley value.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2209.13429

4、[LG] Multi-Layered Maps of Neuropil with Segmentation-Guided Contrastive Learning
S Dorkenwald, P H. Li, M Januszewski...
[Google Research]
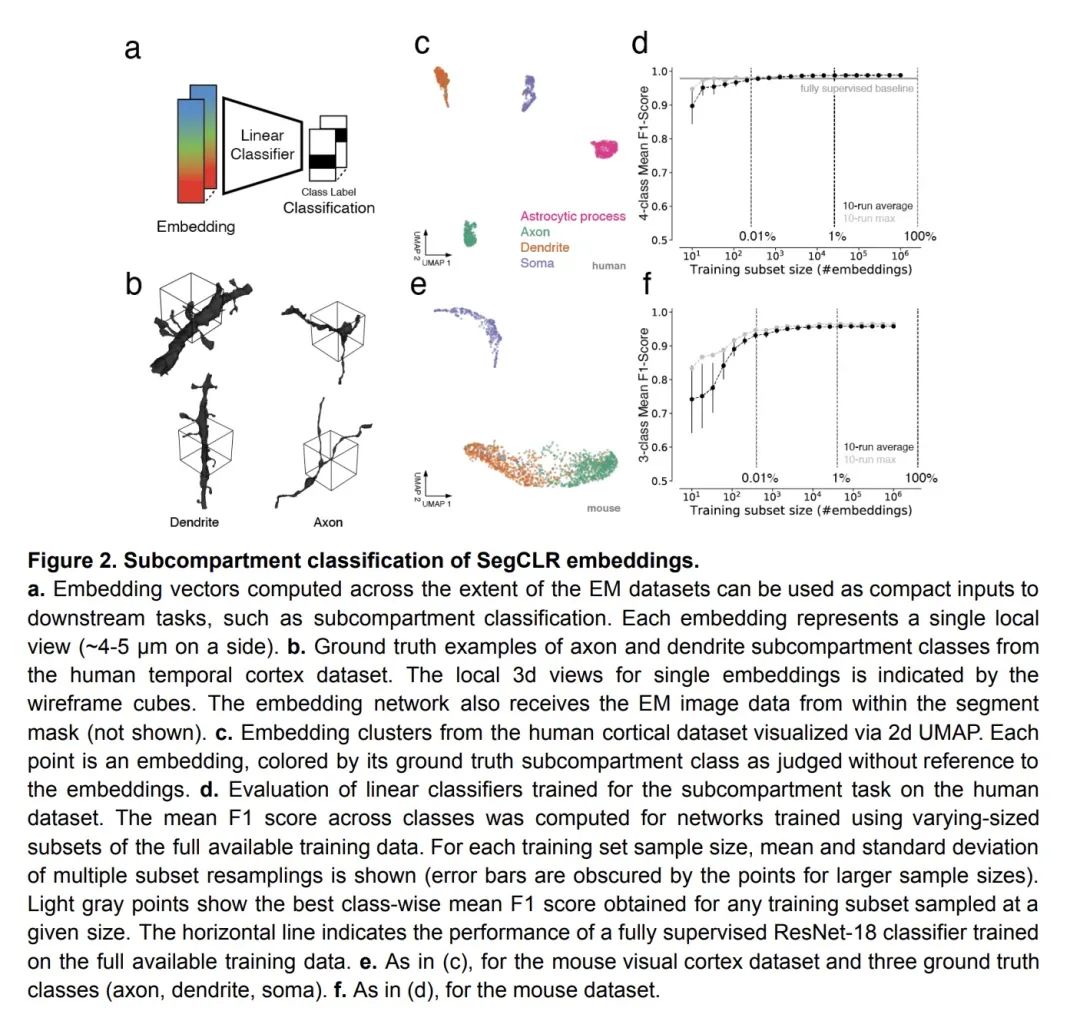
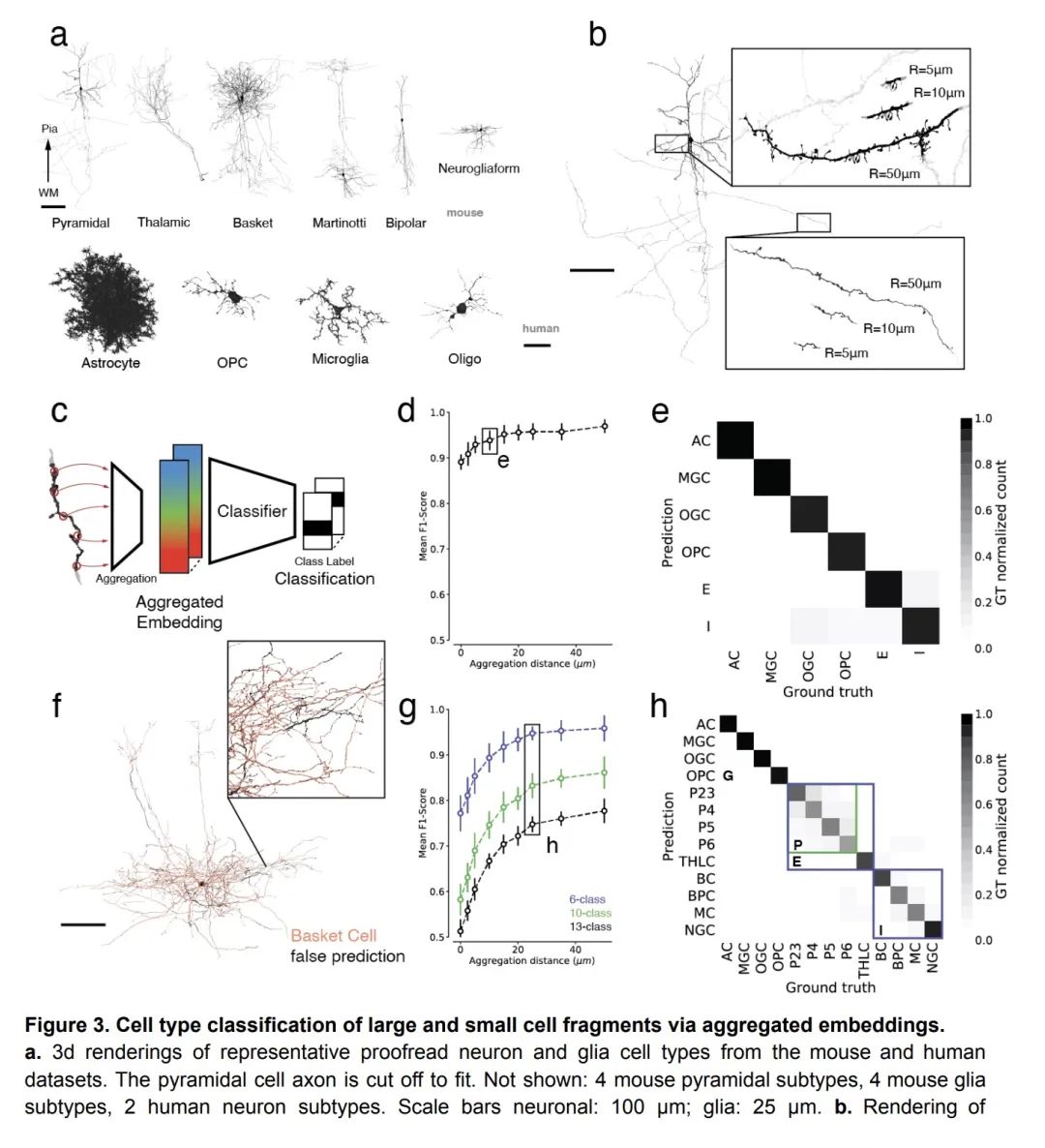
基于分割引导对比学习的多层神经纤维网图谱。识别单个细胞及其类型、亚细胞成分和连接性的神经系统图有可能揭示神经回路的基本组织原则。脑组织的体纳米分辨率成像提供了建立这种地图所需的原始数据,但推断所有相关的细胞和亚细胞标注层是一个挑战。本文提出"分割引导表示对比学习"(SegCLR),一种自监督机器学习技术,可直接从3D电子显微镜图像和分割中产生高度信息化的细胞表征。当应用于人类和小鼠的大脑皮层时,SegCLR使细胞亚区(轴突、树突、体细胞、星形细胞过程)的分类与全监督方法相比少了4000倍的标记数据。令人惊讶的是,SegCLR还能从长度为10微米的片段中推断出细胞类型(神经元、胶质细胞和每种细胞的亚型),这是一项人类难以完成的任务,其可行性大大增强了对大脑中许多神经元片段终止于体边界的部分的成像效用。这些预测通过高斯过程的不确定性估计得到了进一步的增强,使分析限于数据的高置信度子集。最后,SegCLR实现了对第5层锥体细胞亚型的详细探索和对小鼠视觉皮层上下游突触伴的自动大规模统计分析。
Maps of the nervous system that identify individual cells along with their type, subcellular components, and connectivity have the potential to reveal fundamental organizational principles of neural circuits. Volumetric nanometer-resolution imaging of brain tissue provides the raw data needed to build such maps, but inferring all the relevant cellular and subcellular annotation layers is challenging. Here, we present Segmentation-Guided Contrastive Learning of Representations (“SegCLR”), a self-supervised machine learning technique that produces highly informative representations of cells directly from 3d electron microscope imagery and segmentations. When applied to volumes of human and mouse cerebral cortex, SegCLR enabled the classification of cellular subcompartments (axon, dendrite, soma, astrocytic process) with 4,000-fold less labeled data compared to fully supervised approaches. Surprisingly, SegCLR also enabled inference of cell types (neurons, glia, and subtypes of each) from fragments with lengths as small as 10 micrometers, a task that can be difficult for humans to perform and whose feasibility greatly enhances the utility of imaging portions of brains in which many neuron fragments terminate at a volume boundary. These predictions were further augmented via Gaussian process uncertainty estimation to enable analyses restricted to high confidence subsets of the data. Finally, SegCLR enabled detailed exploration of layer-5 pyramidal cell subtypes and automated large-scale statistical analysis of upstream and downstream synaptic partners in mouse visual cortex.
https://biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.03.29.486320v2


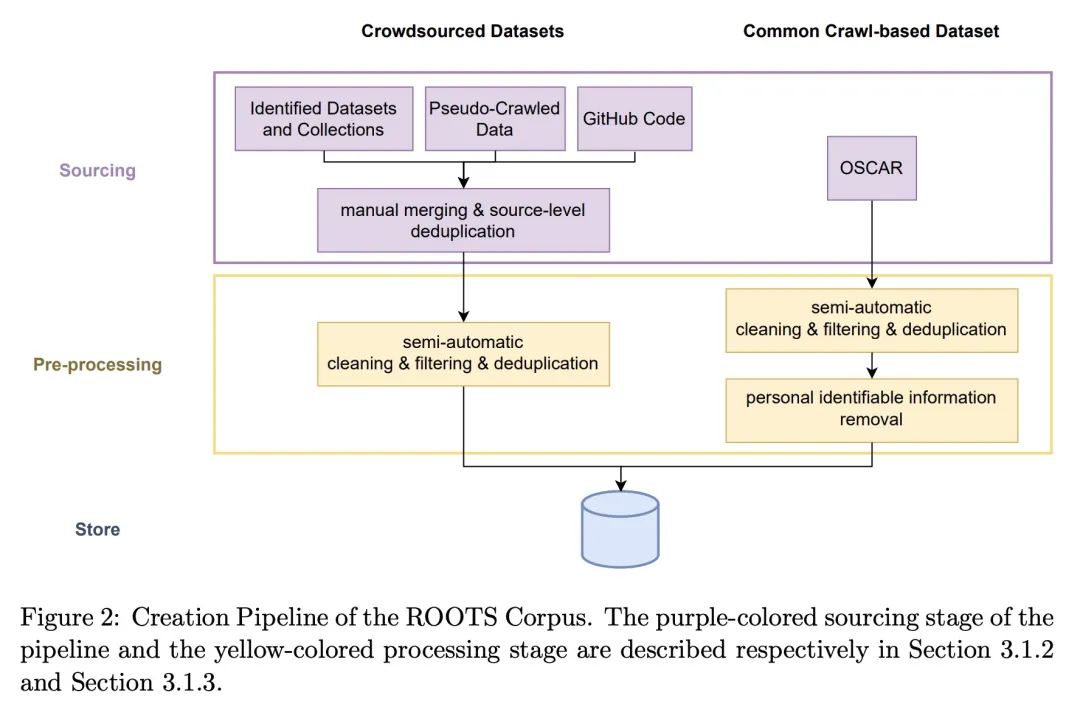
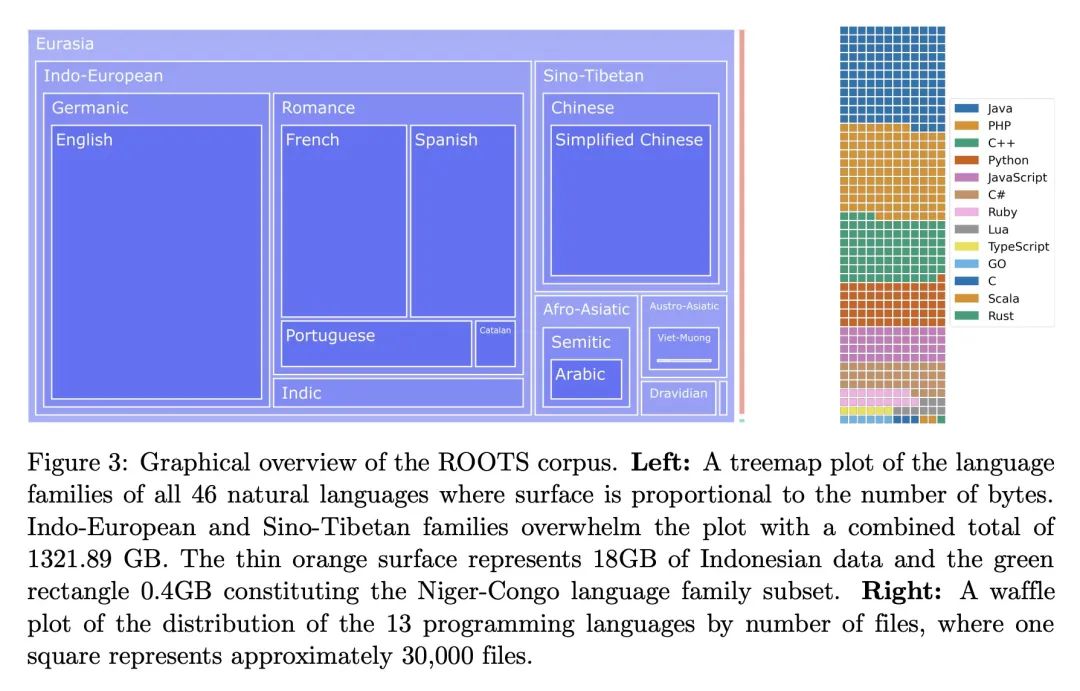
5、[CL] BLOOM: A 176B-Parameter Open-Access Multilingual Language Model
T L Scao, A Fan, C Akiki, E Pavlick, S Ilić, D Hesslow, R Castagné...
BLOOM:176B参数的开放多语种语言模型。大型语言模型(LLM)已被证明能够根据一些演示或自然语言指令执行新任务。虽然这些能力已经得到了广泛的采用,但大多数LLM是由资源丰富的组织开发的,而且经常不对公众开放。作为使这一强大技术大众化的一步,本文提出BLOOM,一个176B参数的开放语言模型,其设计和建立要感谢数百名研究人员的合作。BLOOM是一个仅有解码器的Transformer语言模型,在ROOTS语料库上训练出来,该数据集包括46种自然语言和13种编程语言(共59种)的数百个来源。本文发现,BLOOM在各种基准上取得了有竞争力的性能,在经历了多任务提示的微调后,其结果更加强大。
Large language models (LLMs) have been shown to be able to perform new tasks based on a few demonstrations or natural language instructions. While these capabilities have led to widespread adoption, most LLMs are developed by resource-rich organizations and are frequently kept from the public. As a step towards democratizing this powerful technology, we present BLOOM, a 176B-parameter open-access language model designed and built thanks to a collaboration of hundreds of researchers. BLOOM is a decoder-only Transformer language model that was trained on the ROOTS corpus, a dataset comprising hundreds of sources in 46 natural and 13 programming languages (59 in total). We find that BLOOM achieves competitive performance on a wide variety of benchmarks, with stronger results after undergoing multitask prompted finetuning. To facilitate future research and applications using LLMs, we publicly release our models and code under the Responsible AI License.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05100

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
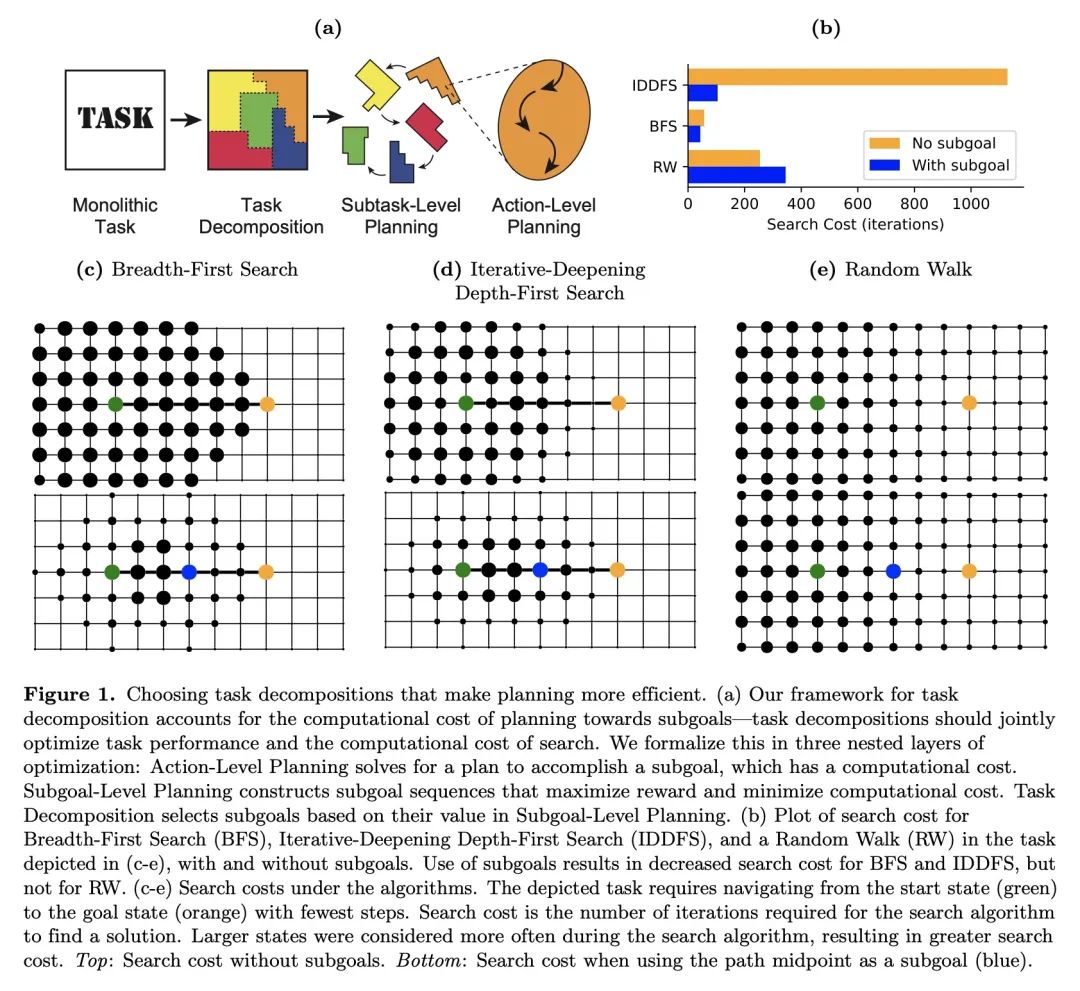
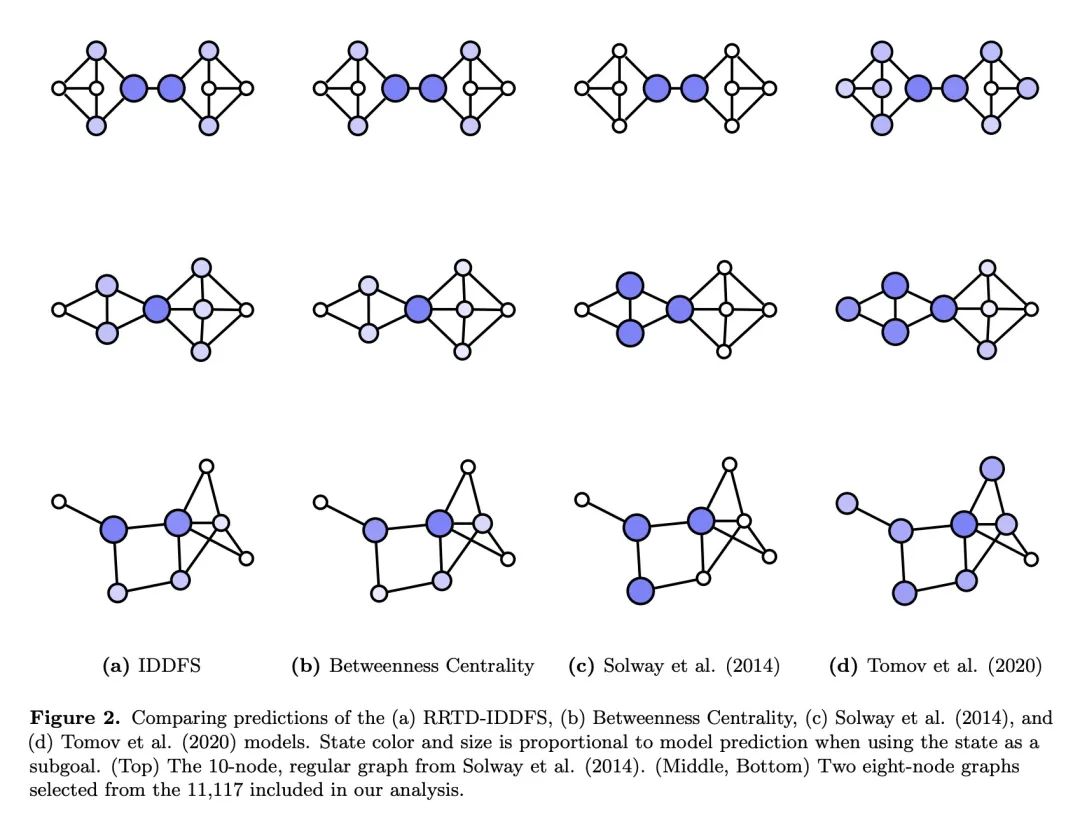
[AI] Humans decompose tasks by trading off utility and computational cost
人类通过权衡效用和计算成本来分解任务
C G. Correa, M K. Ho, F Callaway, N D. Daw, T L. Griffiths
[Princeton University]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.03890

[CL] Creative Writing with an AI-Powered Writing Assistant: Perspectives from Professional Writers
用AI写作助手进行创造性写作:专业作家观点
D Ippolito, A Yuan, A Coenen, S Burnam
[Google Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05030

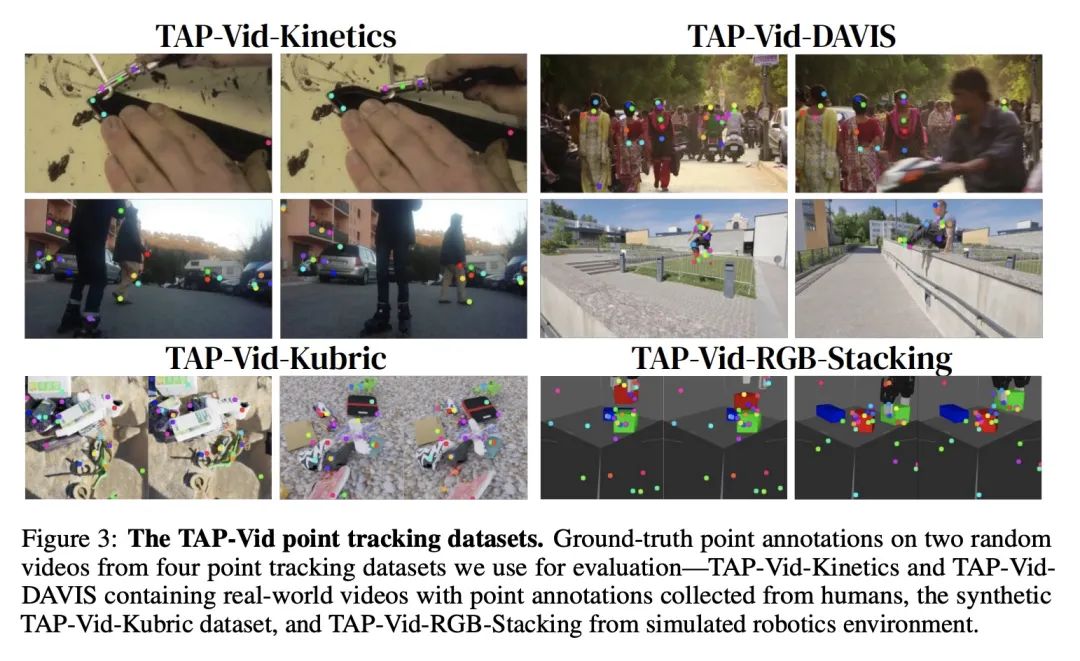
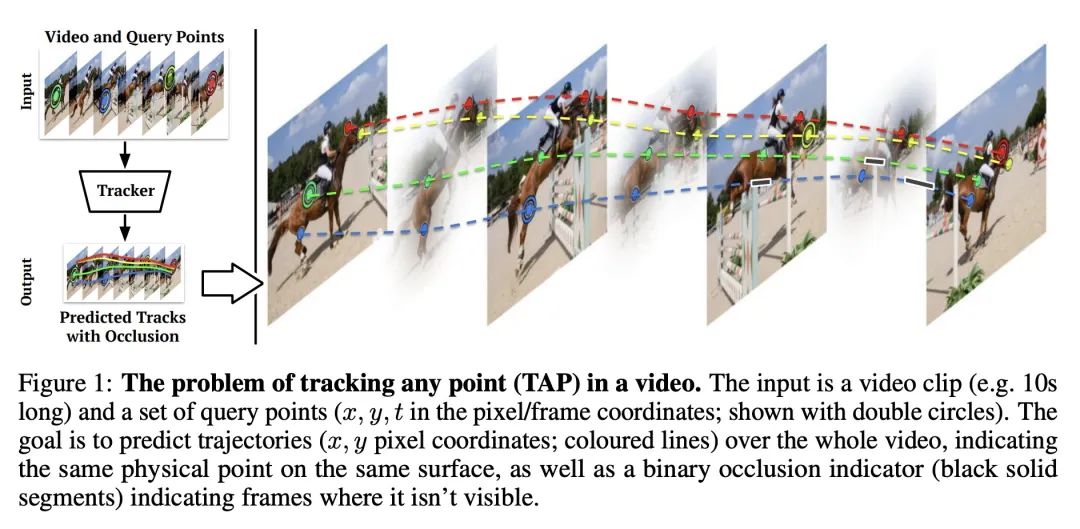
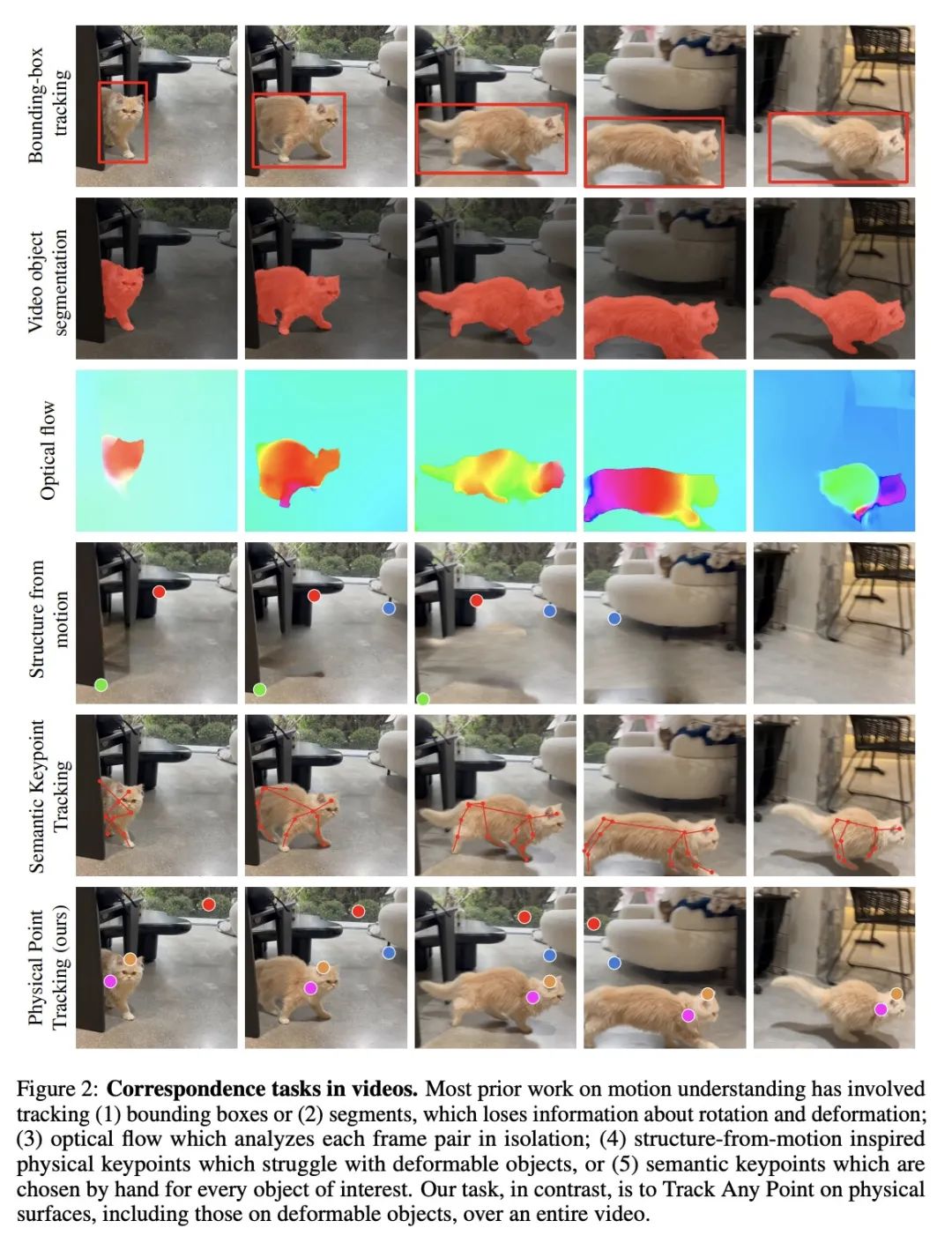
[CV] TAP-Vid: A Benchmark for Tracking Any Point in a Video
TAP-Vid:视频任意点追踪基准
C Doersch, A Gupta, L Markeeva, A Recasens, L Smaira, Y Aytar, J Carreira, A Zisserman, Y Yang
[DeepMind]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.03726


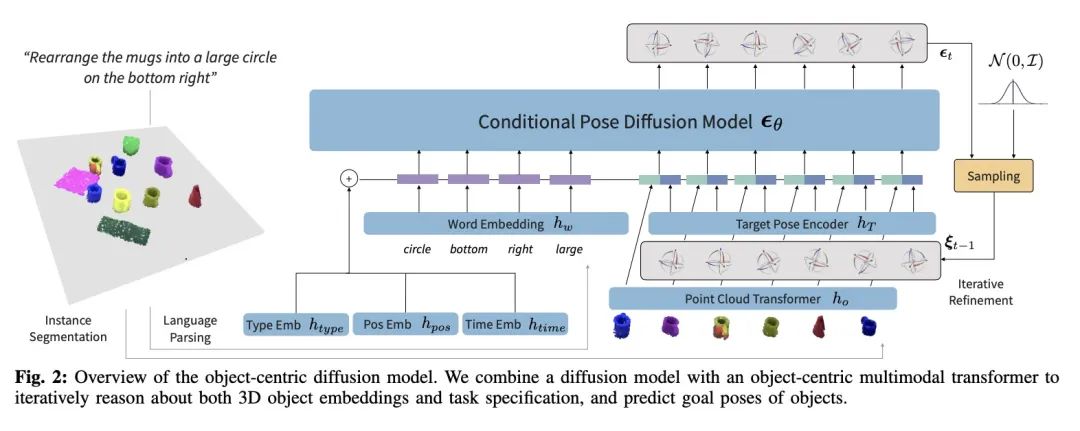
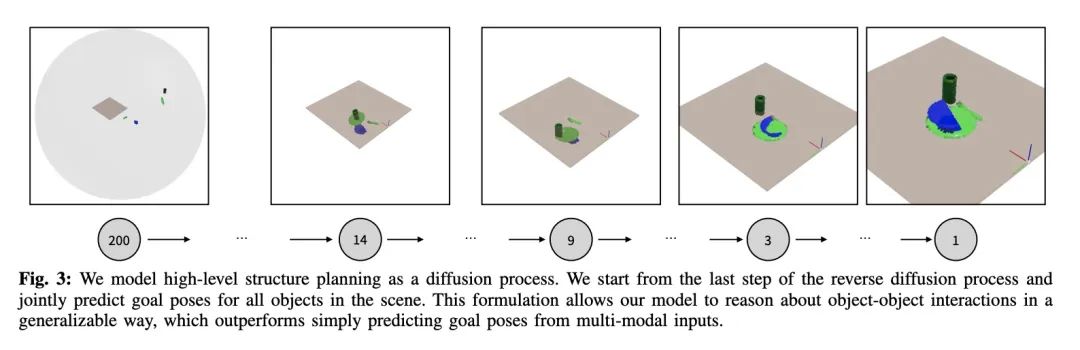
[RO] StructDiffusion: Object-Centric Diffusion for Semantic Rearrangement of Novel Objects
StructDiffusion:面向新对象语义重排的以对象为中心的扩散
W Liu, T Hermans, S Chernova, C Paxton
[Georgia Tech & University of Utah & Meta AI]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.04604


内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢