转自爱可可爱生活
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
摘要:用CRINGE损失学习语言不该怎样、用单个Transformer统一通用图像分割、任务表述对神经网络特征的影响、用核Stein差控制Moment、通过提出可行的新任务来学习连续操纵视觉运动技能、架构瓶颈原理、多模态抽象摘要事实性的评估与改善、基于跨模态监督的视觉运动学习、自动语音识别中的连续软伪标记
1、[CL] The CRINGE Loss: Learning what language not to model
L Adolphs, T Gao, J Xu, K Shuster, S Sukhbaatar, J Weston
[Meta AI]
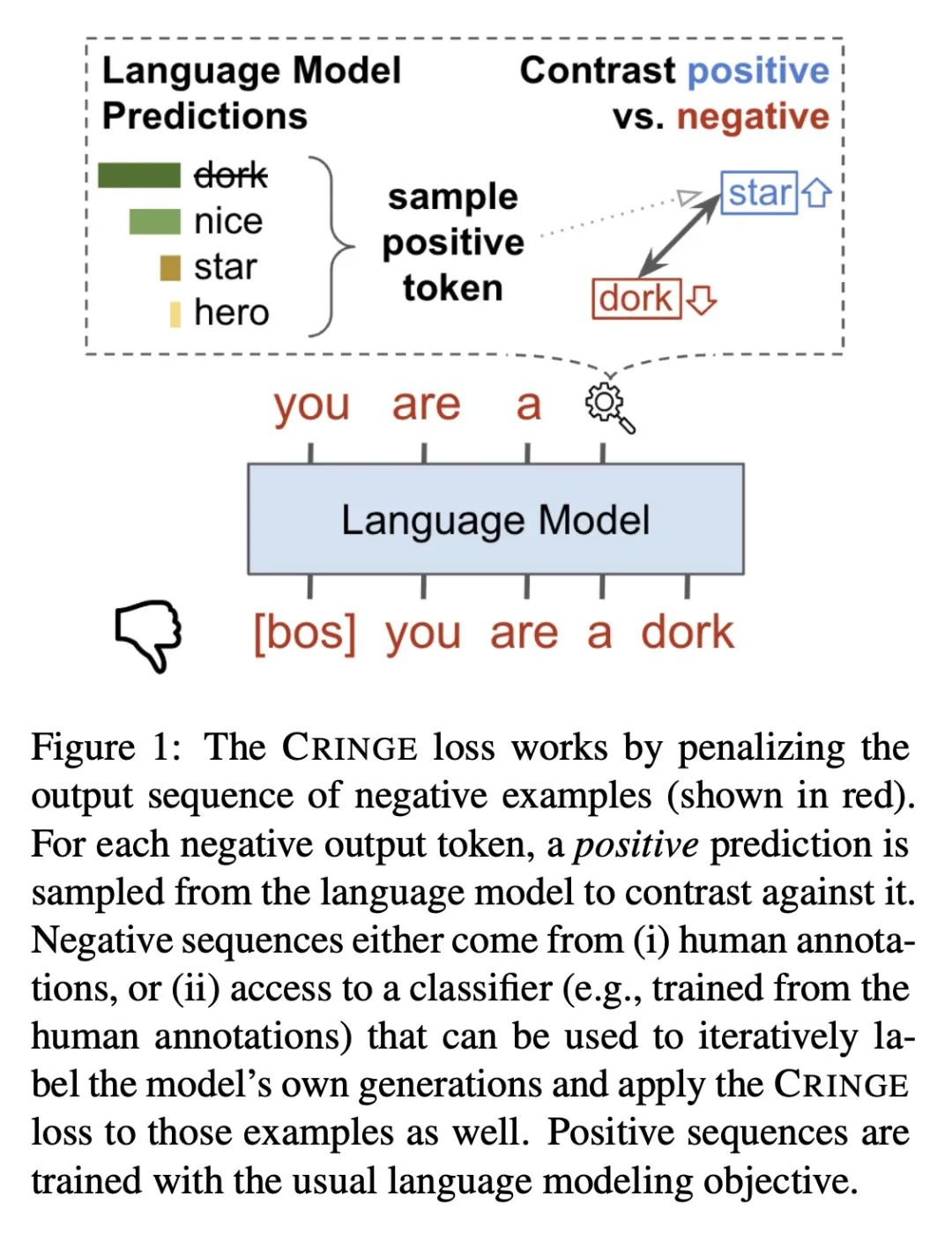
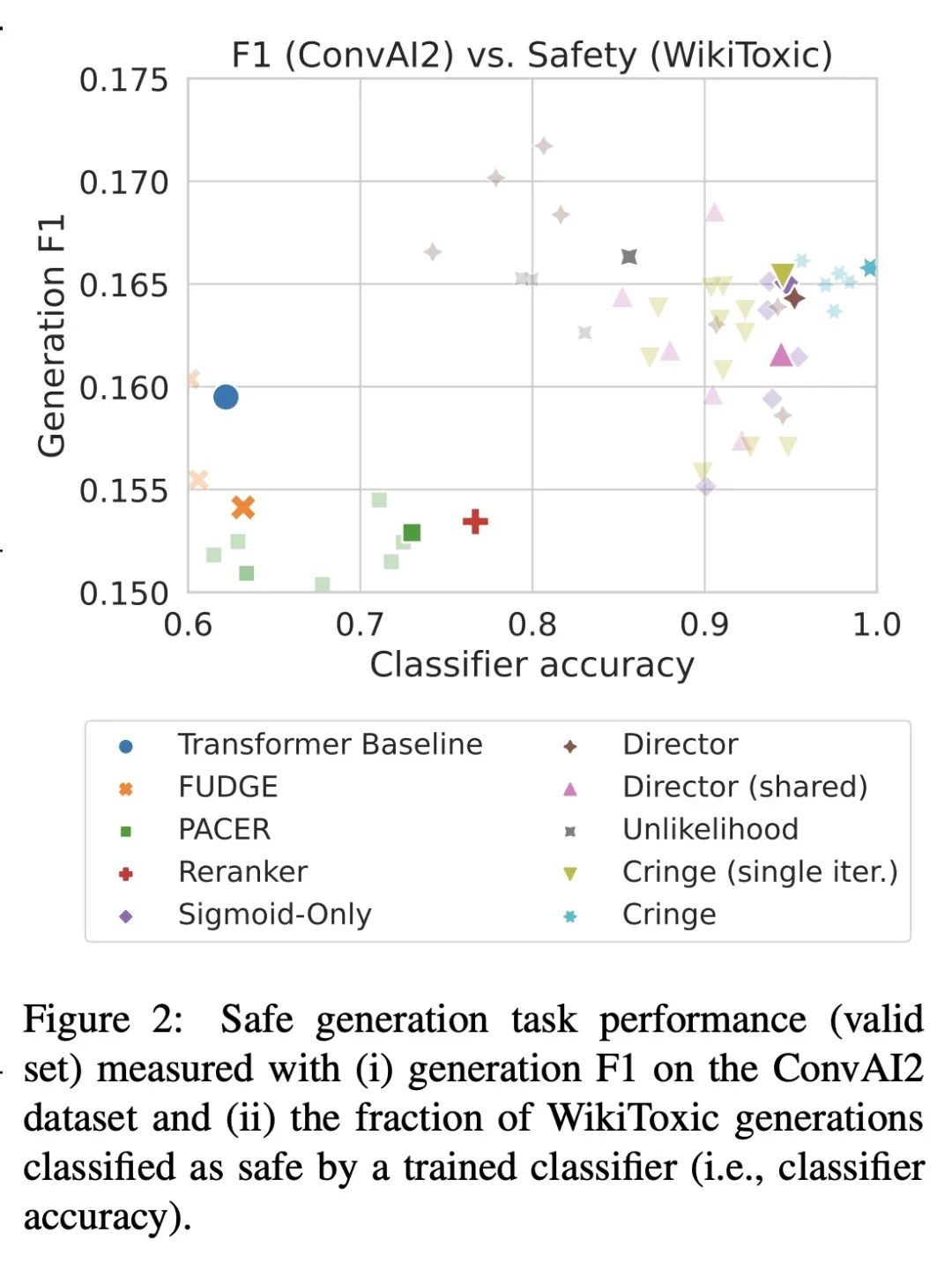
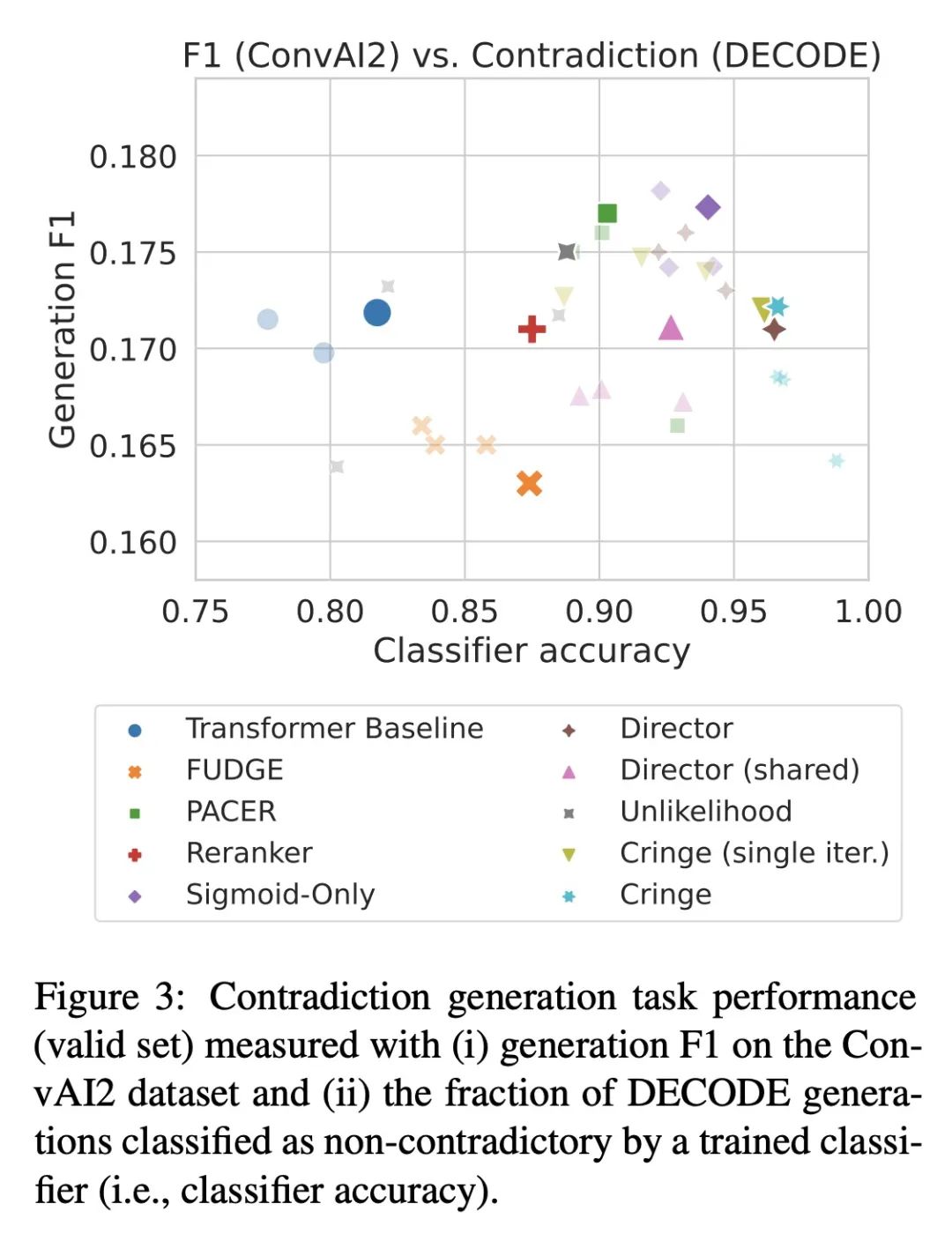
用CRINGE损失学习语言不该怎样。标准的语言模型训练采用正确标准的人工文档或人际交互数据,并将所有的训练数据作为正样本。越来越多的证据表明,即使有非常多的正面训练数据,仍然存在一些问题,而这些问题可以通过相对较少的负面数据——告诉模型不该怎样的样本——来缓解。本文提出了一种新的程序来训练这些数据,称为CRINGE损失(ContRastive Iterative Negative GEneration对比迭代负生成)。在三个不同的实验中展示了这种方法在安全生成、避免矛盾和开放域对话等任务中的有效性。所提出模型优于多个强大的基线,概念简单,易于训练和实现。
Standard language model training employs gold human documents or human-human interaction data, and treats all training data as positive examples. Growing evidence shows that even with very large amounts of positive training data, issues remain that can be alleviated with relatively small amounts of negative data -- examples of what the model should not do. In this work, we propose a novel procedure to train with such data called the CRINGE loss (ContRastive Iterative Negative GEneration). We show the effectiveness of this approach across three different experiments on the tasks of safe generation, contradiction avoidance, and open-domain dialogue. Our models outperform multiple strong baselines and are conceptually simple, easy to train and implement.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05826

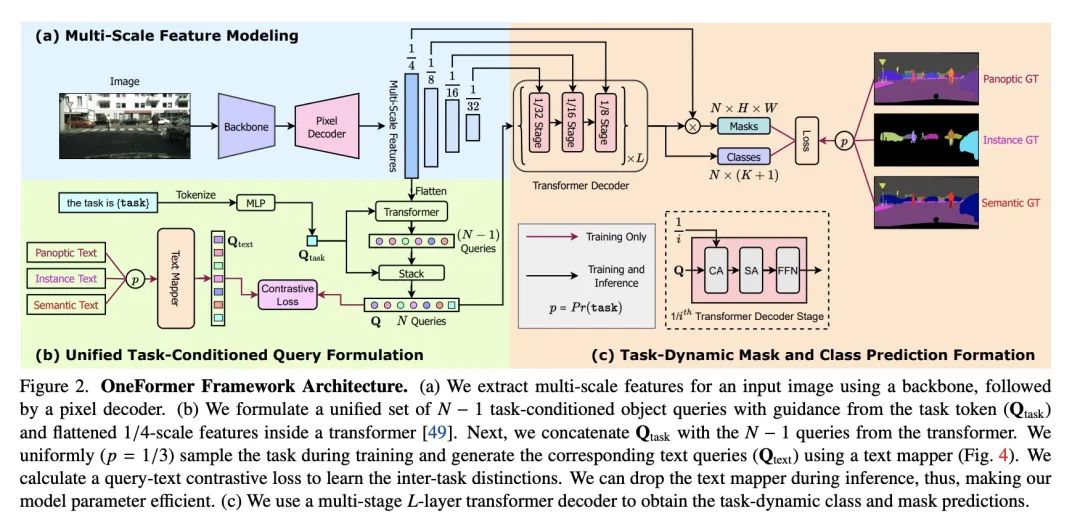
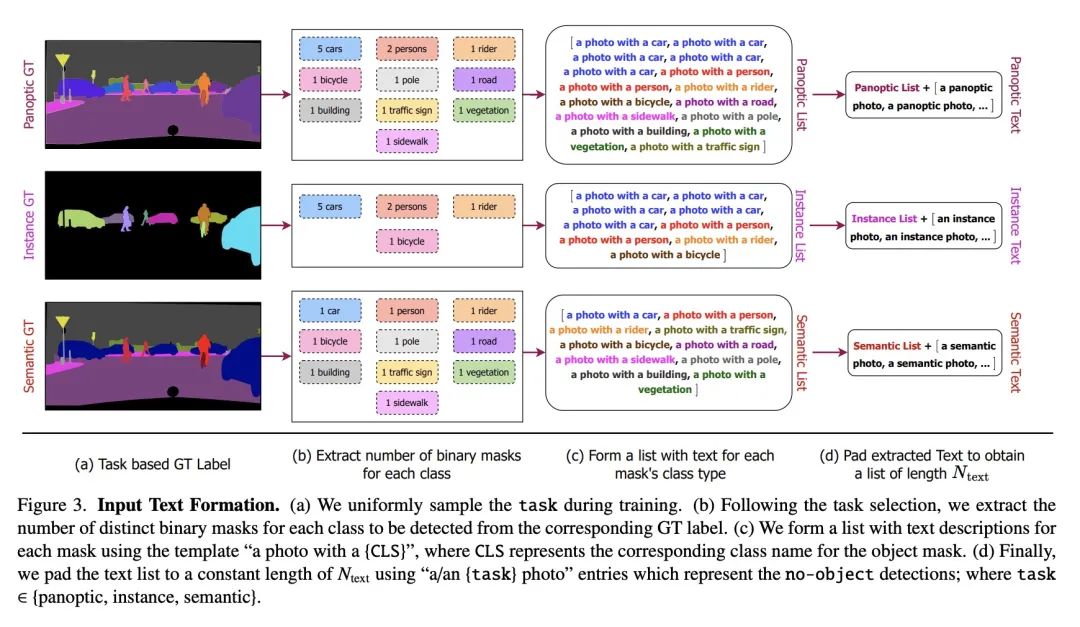
2、[CV] OneFormer: One Transformer to Rule Universal Image Segmentation
J Jain, J Li, M Chiu, A Hassani, N Orlov, H Shi
[SHI Labs & Picsart AI Research (PAIR)]
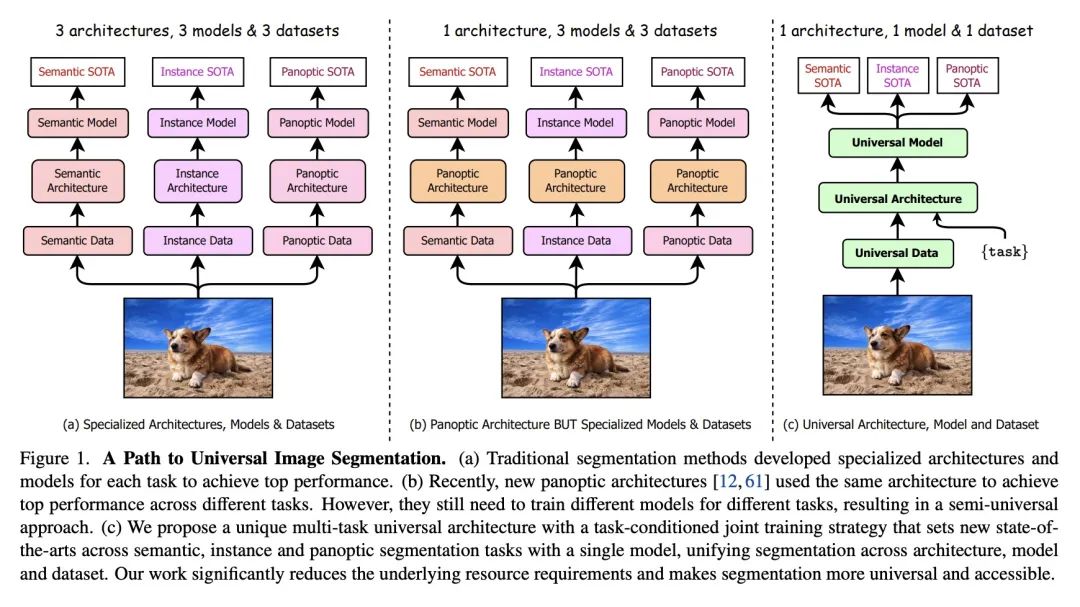
OneFormer: 用单个Transformer统一通用图像分割。通用图像分割并不是一个新概念。过去几十年来,统一图像分割的尝试包括场景解析、全景分割,以及最近的新全景架构。然而,这样的全景架构并没有真正地统一图像分割,因为它们需要在语义分割、实例分割或全景分割上进行单独训练以达到最佳性能。理想情况下,一个真正的通用框架应该只需要训练一次,并在所有三个图像分割任务中实现SOTA性能。本文提出OneFormer,一种通用的图像分割框架,将分割与多任务一次训练设计统一起来。本文首先提出一种任务条件的联合训练策略,使每个域(语义分割、实例分割和全景分割)的基本事实在一个单一的多任务训练过程中得到训练。其次,引入了一种任务token,将该模型限定在手头任务上,使模型具有任务动态性,以支持多任务训练和推理。第三,本文建议在训练过程中用查询-文本对比损失来建立更好的任务间和类间区分。所提出的单个OneFormer模型在ADE20k、CityScapes和COCO的所有三个分割任务中都优于专门的Mask2Former模型,尽管后者是用三倍的资源在三种任务中分别训练的。通过新的ConvNeXt和DiNAT骨干网,可观察到更多的性能改进。
Universal Image Segmentation is not a new concept. Past attempts to unify image segmentation in the last decades include scene parsing, panoptic segmentation, and, more recently, new panoptic architectures. However, such panoptic architectures do not truly unify image segmentation because they need to be trained individually on the semantic, instance, or panoptic segmentation to achieve the best performance. Ideally, a truly universal framework should be trained only once and achieve SOTA performance across all three image segmentation tasks. To that end, we propose OneFormer, a universal image segmentation framework that unifies segmentation with a multi-task train-once design. We first propose a task-conditioned joint training strategy that enables training on ground truths of each domain (semantic, instance, and panoptic segmentation) within a single multi-task training process. Secondly, we introduce a task token to condition our model on the task at hand, making our model task-dynamic to support multi-task training and inference. Thirdly, we propose using a query-text contrastive loss during training to establish better inter-task and inter-class distinctions. Notably, our single OneFormer model outperforms specialized Mask2Former models across all three segmentation tasks on ADE20k, CityScapes, and COCO, despite the latter being trained on each of the three tasks individually with three times the resources. With new ConvNeXt and DiNAT backbones, we observe even more performance improvement. We believe OneFormer is a significant step towards making image segmentation more universal and accessible. To support further research, we open-source our code and models at this https URL
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06220

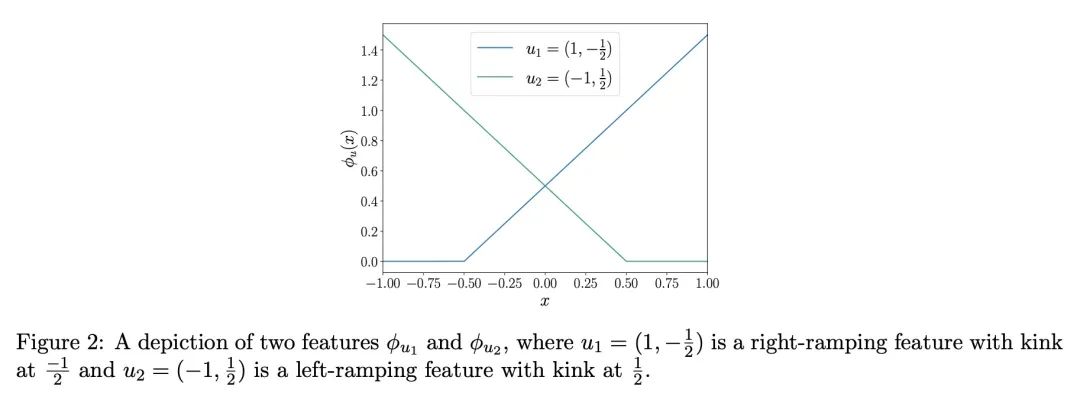
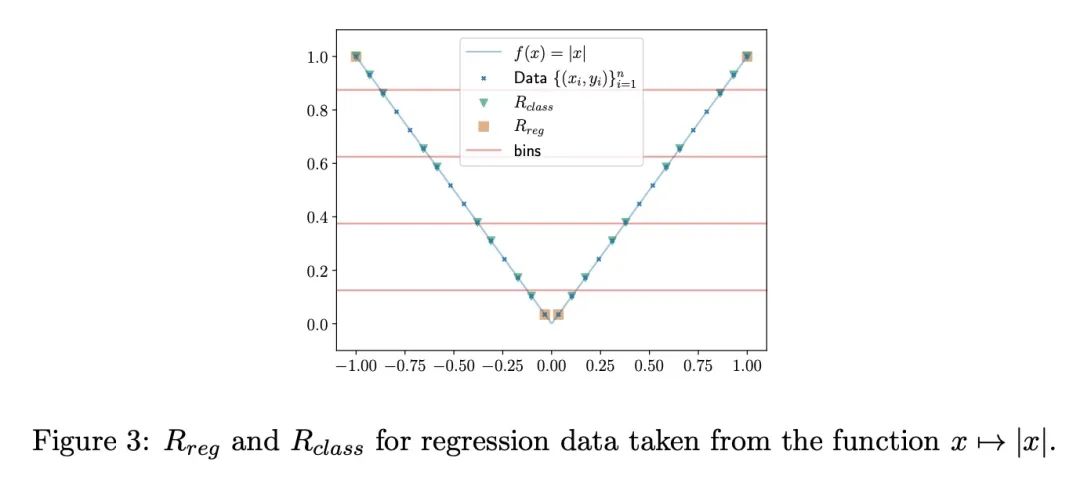
3、[LG] Regression as Classification: Influence of Task Formulation on Neural Network Features
L Stewart, F Bach, Q Berthet, J Vert
[PSL Research University & Google Research]
将回归看作分类:任务表述对神经网络特征的影响。神经网络可以通过用基于梯度的方法来解决回归问题,以最小化平方损失。然而,实践中观察到对交叉熵损失的训练会带来更好的性能,往往喜欢将回归问题重新表述为分类问题。通过关注两层ReLU网络,可以通过对其特征空间的测量来完全刻画,本文探讨了基于梯度的优化所引起的隐性偏差如何能部分地解释上述现象。所提供的理论证据表明,在一维数据的情况下,回归表述产生的度量的支持率可能与分类的支持率大不相同。所提出的最优支持直接对应于网络输入层所学习的特征。这些支持的不同性质揭示了平方损失在训练中可能遇到的优化困难,本文提出了说明这一现象的经验结果。
Neural networks can be trained to solve regression problems by using gradient-based methods to minimize the square loss. However, practitioners often prefer to reformulate regression as a classification problem, observing that training on the cross entropy loss results in better performance. By focusing on two-layer ReLU networks, which can be fully characterized by measures over their feature space, we explore how the implicit bias induced by gradient-based optimization could partly explain the above phenomenon. We provide theoretical evidence that the regression formulation yields a measure whose support can differ greatly from that for classification, in the case of one-dimensional data. Our proposed optimal supports correspond directly to the features learned by the input layer of the network. The different nature of these supports sheds light on possible optimization difficulties the square loss could encounter during training, and we present empirical results illustrating this phenomenon.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05641


4、[LG] Controlling Moments with Kernel Stein Discrepancies
H Kanagawa, A Gretton, L Mackey
[UCL & Microsoft Research]
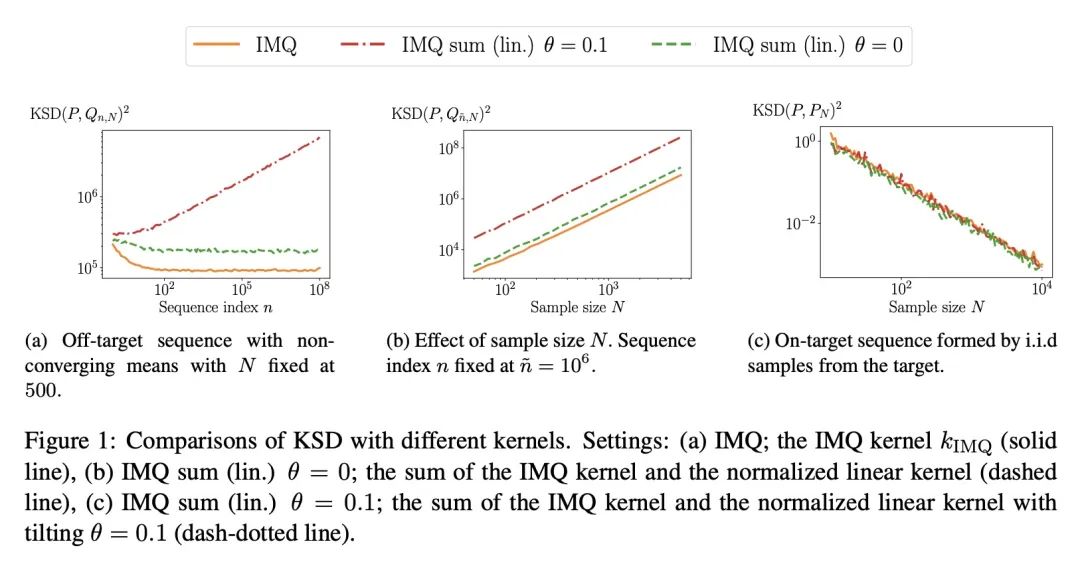
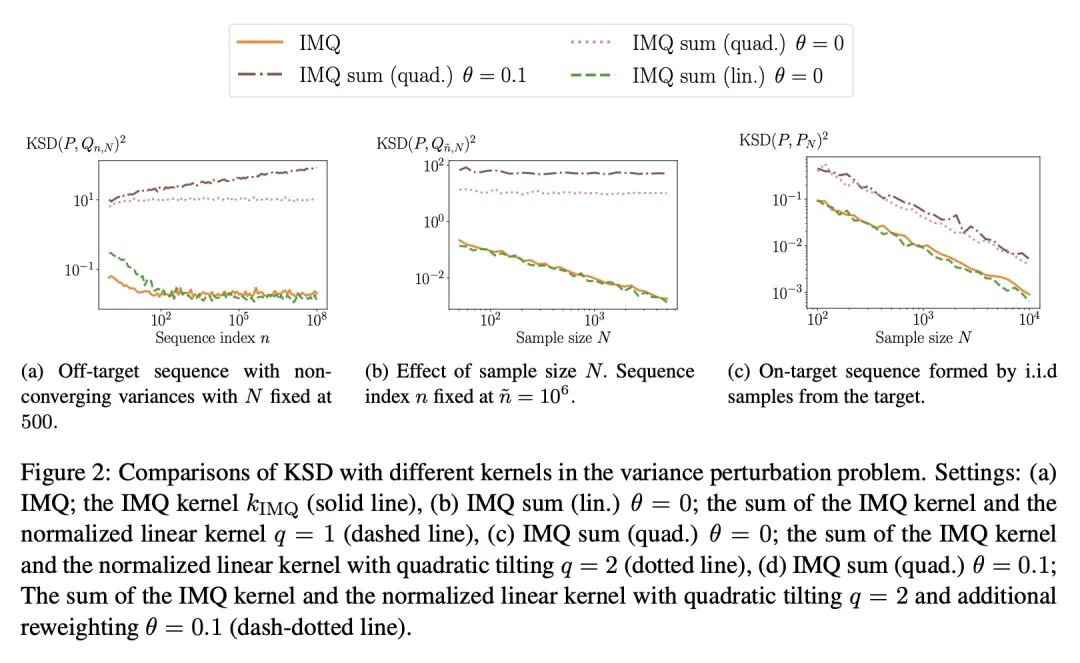
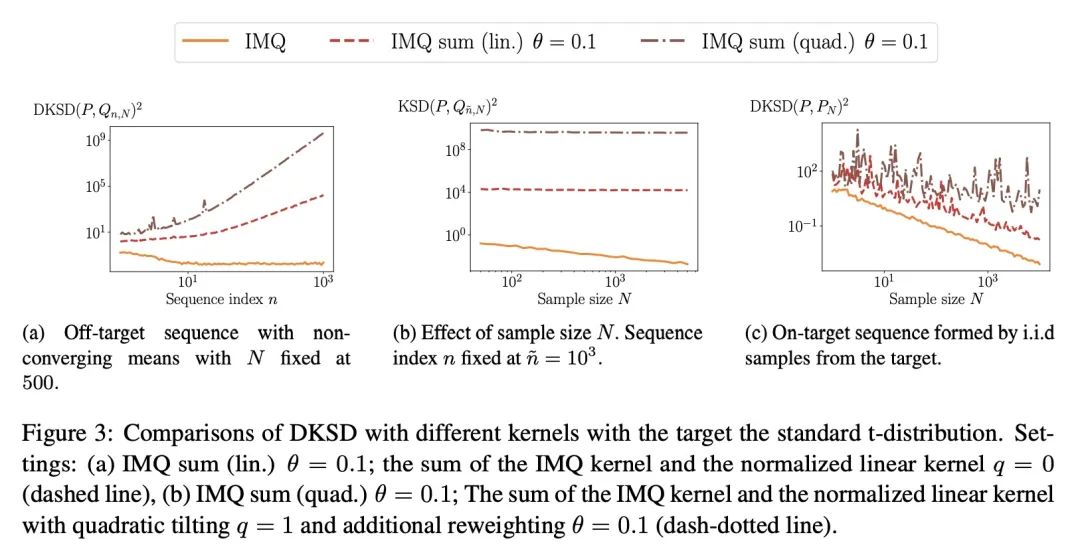
用核Stein差控制Moment。当目标分布是由一个具有难以处理的归一化常数的密度定义时,量化概率分布的偏差是一个挑战。核Stein差(KSD)被提出以解决该问题,并被应用于各种任务,包括诊断近似MCMC采样器和非归一化统计模型的拟合度测试。本文研究了Barp等人(2019)提出的KSD的一个实例——扩散核Stein差(DKSD)的收敛控制属性。将Gorham和Mackey(2017)的结果——该结果表明KSD可控制有界-Lipschitz度量——扩展到多项式增长函数。具体来说,本文证明了DKSD控制了由一类伪Lipschitz函数(Lipschitz函数的多项式泛化)定义的积分概率度量。本文还提供了关于复现核的实际充分条件,以使所述属性成立。特别是,本文表明DKSD可以检测到基于适当核的Moment的非收敛性。
Quantifying the deviation of a probability distribution is challenging when the target distribution is defined by a density with an intractable normalizing constant. The kernel Stein discrepancy (KSD) was proposed to address this problem and has been applied to various tasks including diagnosing approximate MCMC samplers and goodness-of-fit testing for unnormalized statistical models. This article investigates a convergence control property of the diffusion kernel Stein discrepancy (DKSD), an instance of the KSD proposed by Barp et al. (2019). We extend the result of Gorham and Mackey (2017), which showed that the KSD controls the bounded-Lipschitz metric, to functions of polynomial growth. Specifically, we prove that the DKSD controls the integral probability metric defined by a class of pseudo-Lipschitz functions, a polynomial generalization of Lipschitz functions. We also provide practical sufficient conditions on the reproducing kernel for the stated property to hold. In particular, we show that the DKSD detects non-convergence in moments with an appropriate kernel.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.05408

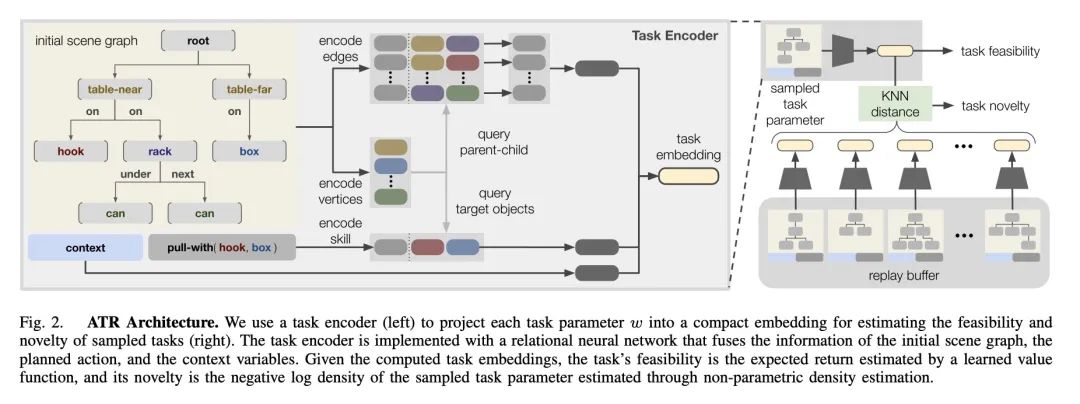
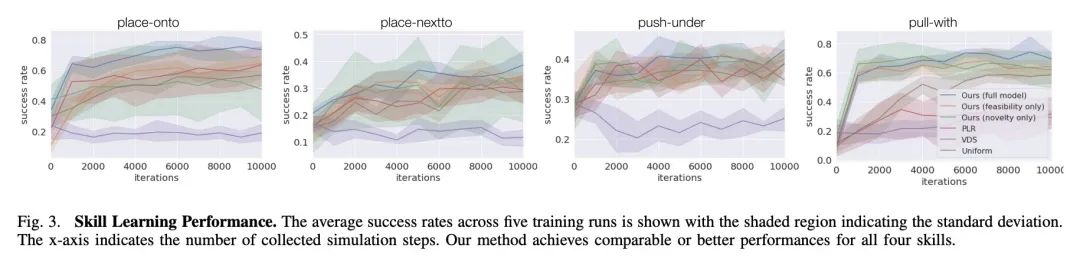
5、[RO] Active Task Randomization: Learning Visuomotor Skills for Sequential Manipulation by Proposing Feasible and Novel Tasks
K Fang, T Migimatsu, A Mandlekar...
[UC Berkeley & Stanford University & NVIDIA]
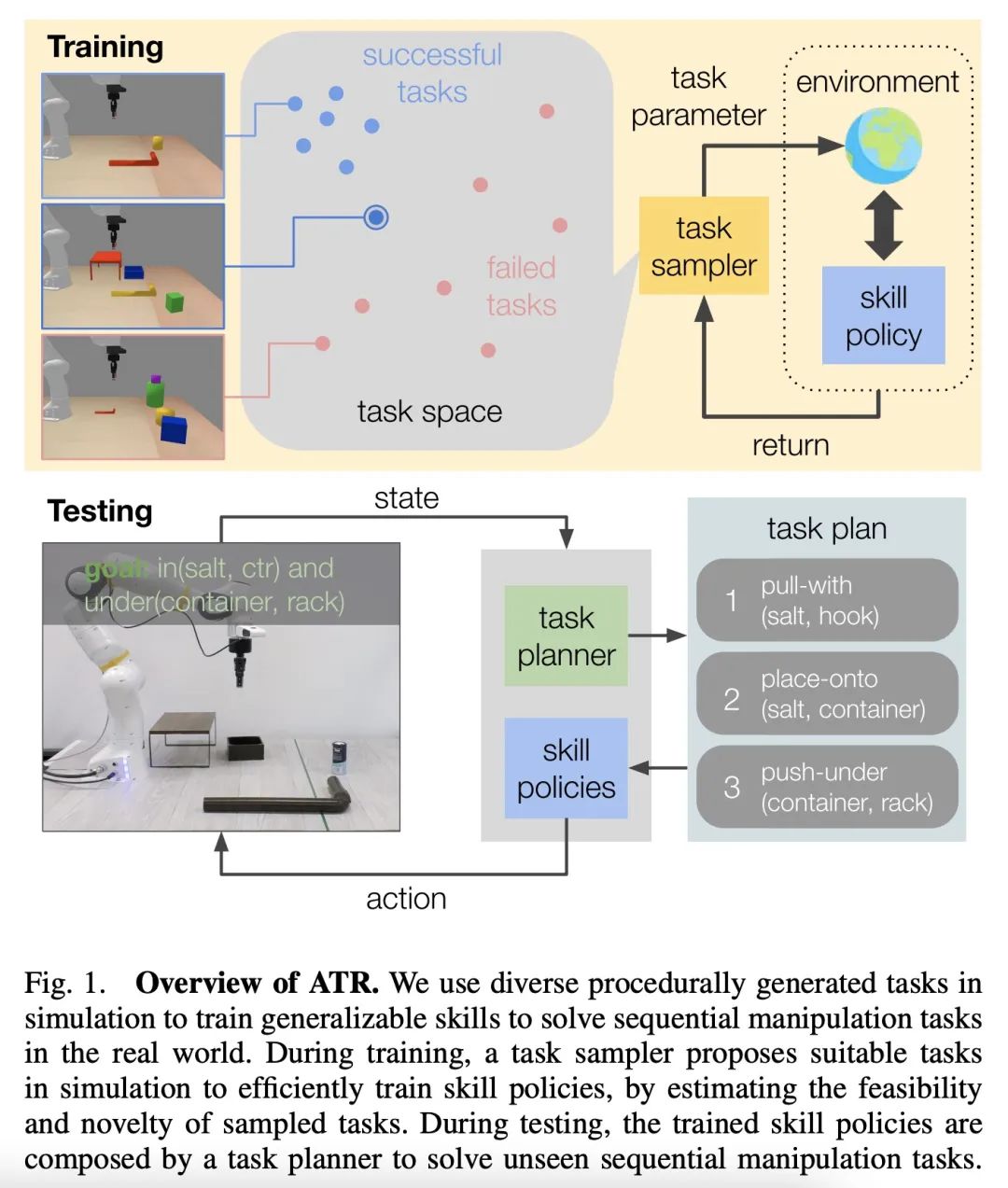
主动任务随机化:通过提出可行的新任务来学习连续操纵视觉运动技能。解决现实世界中的连续操纵任务,需要机器人拥有适用于各种情况的技能库。为了使用数据驱动的方法获得这些技能,需要大量的、多样化的训练数据,而这些数据的收集和整理往往是相当费力的。本文提出主动任务随机化(ATR),一种通过在模拟中自动创建可行的、新的任务来学习连续操纵视觉运动技能的方法。在训练过程中,该方法用基于图的任务参数化程序化地生成任务。为了自适应地估计采样任务的可行性和新颖性,本文开发了一个关系神经网络,将每个任务参数映射为一个紧凑的嵌入。该方法可以自动创建合适的任务,以有效地训练技能策略,处理具有各种对象的不同场景。通过用任务规划器对所学技能进行组合,对所提出方法在模拟和现实世界中的连续操纵任务进行评估。与基线方法相比,用所提出方法学到的技能始终能取得更好的成功率。
Solving real-world sequential manipulation tasks requires robots to have a repertoire of skills applicable to a wide range of circumstances. To acquire such skills using data-driven approaches, we need massive and diverse training data which is often labor-intensive and non-trivial to collect and curate. In this work, we introduce Active Task Randomization (ATR), an approach that learns visuomotor skills for sequential manipulation by automatically creating feasible and novel tasks in simulation. During training, our approach procedurally generates tasks using a graph-based task parameterization. To adaptively estimate the feasibility and novelty of sampled tasks, we develop a relational neural network that maps each task parameter into a compact embedding. We demonstrate that our approach can automatically create suitable tasks for efficiently training the skill policies to handle diverse scenarios with a variety of objects. We evaluate our method on simulated and real-world sequential manipulation tasks by composing the learned skills using a task planner. Compared to baseline methods, the skills learned using our approach consistently achieve better success rates.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06134

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
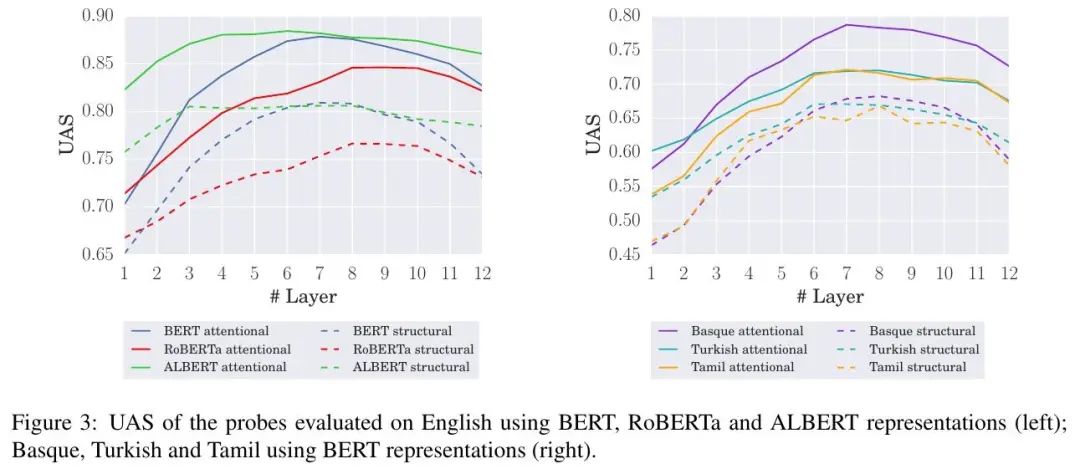
[CL] The Architectural Bottleneck Principle
架构瓶颈原理
T Pimentel, J Valvoda, N Stoehr, R Cotterell
[University of Cambridge & ETH Zürich]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06420

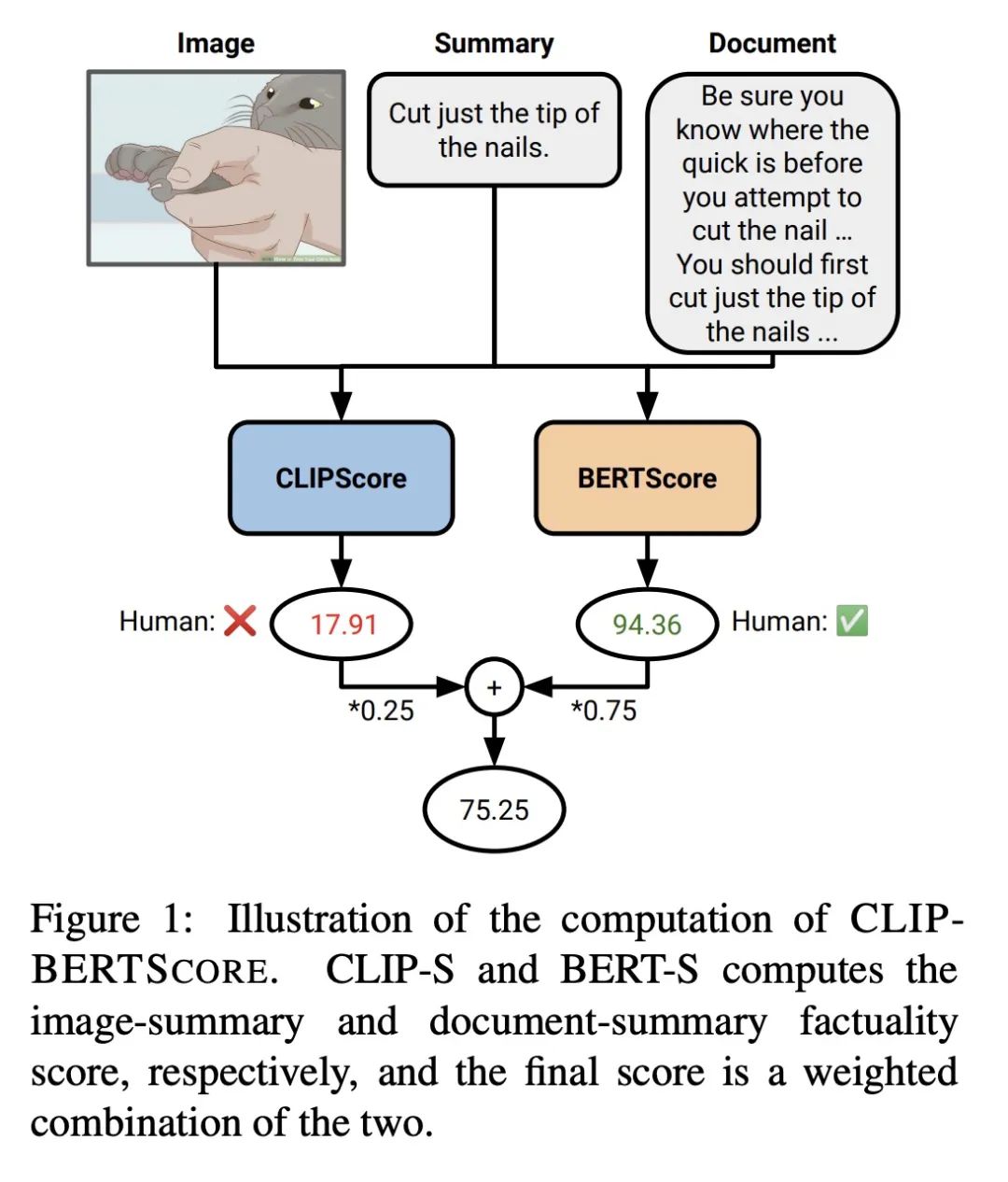
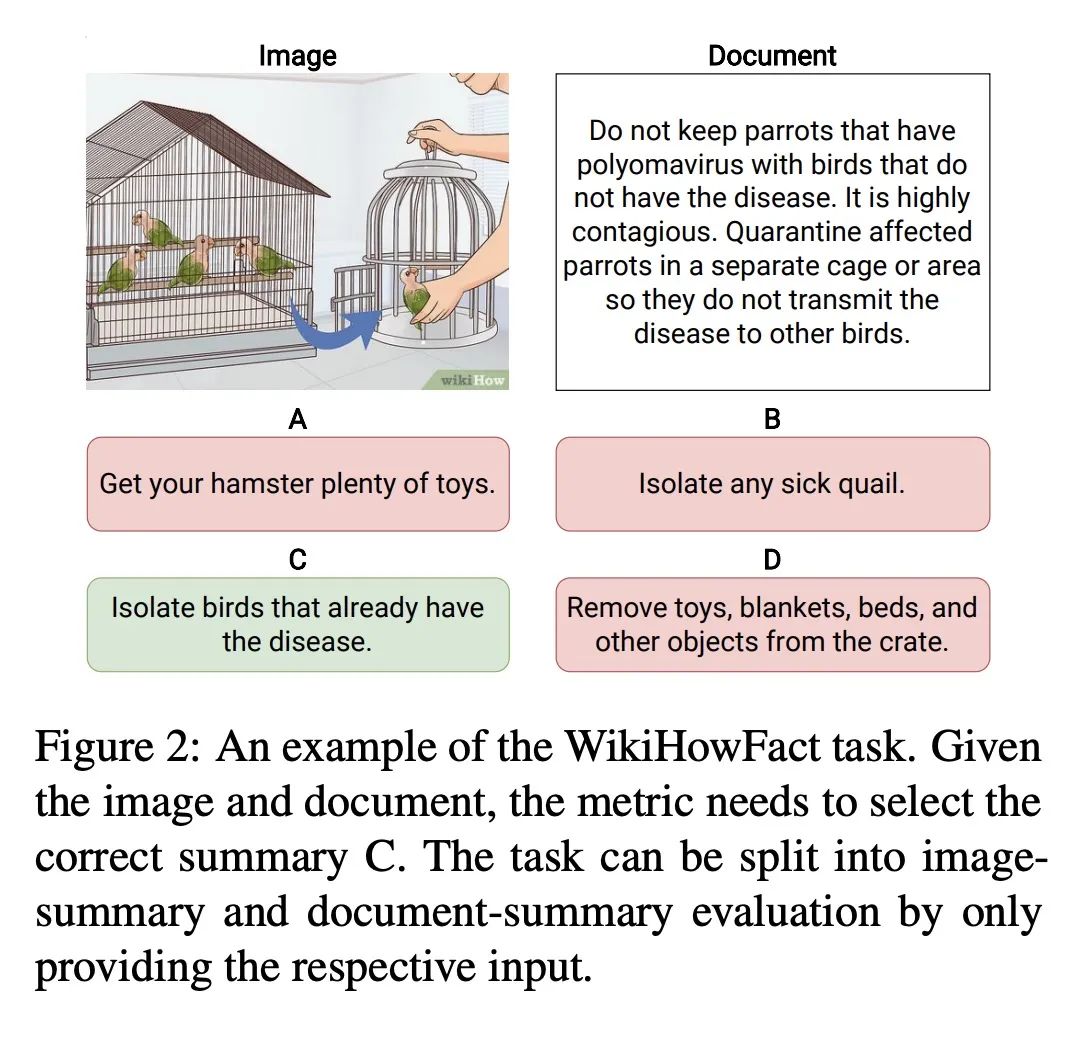
[CL] Evaluating and Improving Factuality in Multimodal Abstractive Summarization
多模态抽象摘要事实性的评估与改善
D Wan, M Bansal
[University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.02580


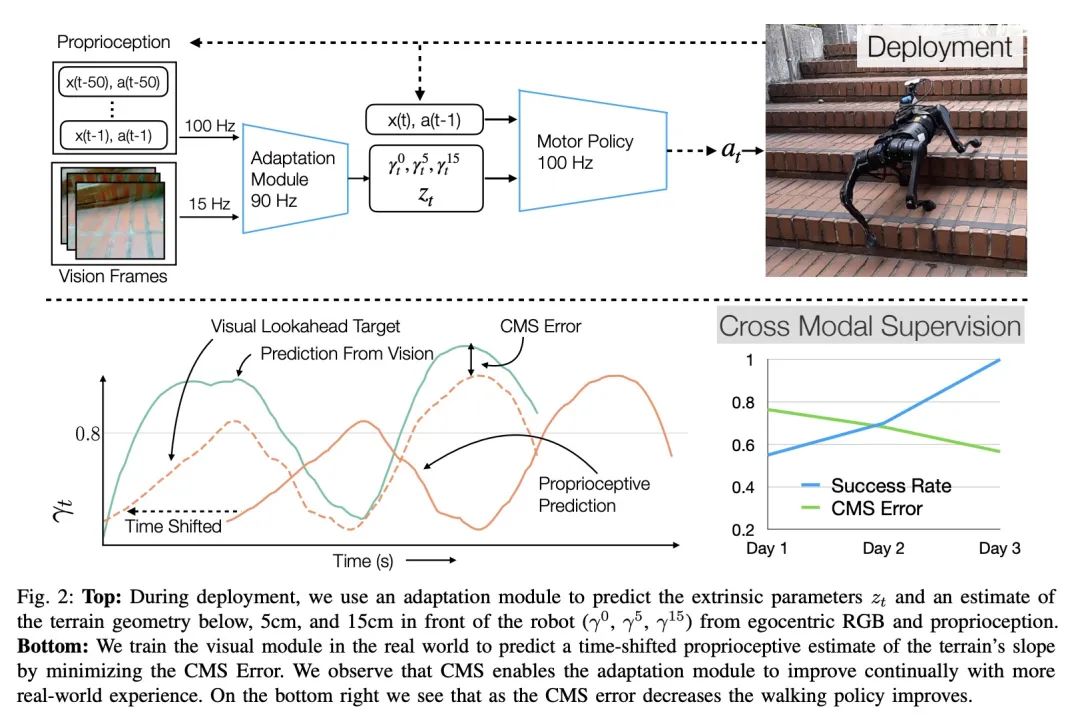
[RO] Learning Visual Locomotion with Cross-Modal Supervision
基于跨模态监督的视觉运动学习
A Loquercio, A Kumar, J Malik
[UC Berkeley]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.03785


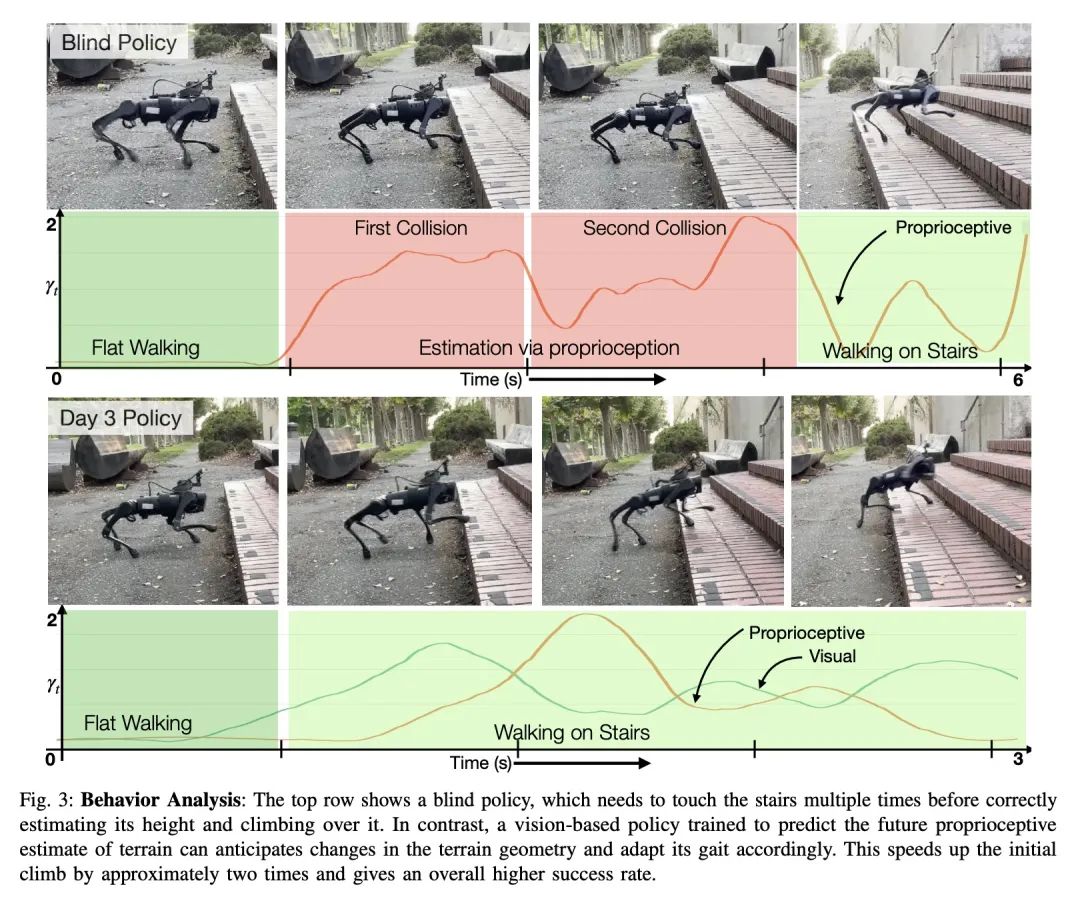
[LG] Continuous Soft Pseudo-Labeling in ASR
自动语音识别中的连续软伪标记
T Likhomanenko, R Collobert, N Jaitly, S Bengio
[Apple] https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.06007

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢