LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:学习遵循图像编辑指令、面向目标检测的扩散模型、通过扩大规模训练通用习得优化器、只用语言数据学习视觉任务、基于指令的任务感知检索、基于对齐感知训练的高保真神经辐射场、扩散模型的置信区间、通过从扩散模型学习文本嵌入进行极端生成式图像压缩、大规模视觉和视觉-语言任务通才模型
1、[CV] InstructPix2Pix: Learning to Follow Image Editing Instructions
T Brooks, A Holynski, A A. Efros
[UC Berkeley]
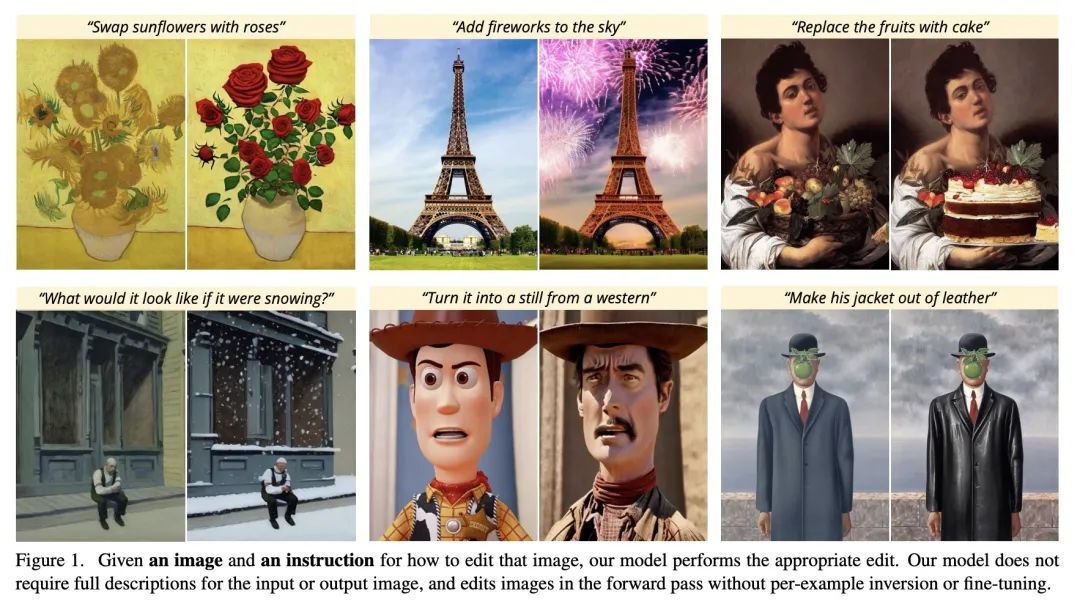
InstructPix2Pix:学习遵循图像编辑指令。本文提出一种根据人的指令编辑图像的方法:给定一幅输入图像以及告诉模型该做什么的书面指令,所提出的模型可以按这些指令完成图像编辑。为了获得这个问题的训练数据,本文结合了两个大型预训练模型的知识——一个语言模型(GPT-3)和一个文本到图像模型(Stable Diffusion)——来生成一个大型的图像编辑实例数据集。条件扩散模型InstructPix2Pix是在生成的数据上训练的,并在推理时推广到真实图像和用户编写的指令。由于它在正向传递中进行编辑,不需要对每个样本进行微调或逆转,该模型可以在几秒钟内快速编辑图像。本文展示了对各种输入图像和书面指令的引人注目的编辑结果。
We propose a method for editing images from human instructions: given an input image and a written instruction that tells the model what to do, our model follows these instructions to edit the image. To obtain training data for this problem, we combine the knowledge of two large pretrained models -- a language model (GPT-3) and a text-to-image model (Stable Diffusion) -- to generate a large dataset of image editing examples. Our conditional diffusion model, InstructPix2Pix, is trained on our generated data, and generalizes to real images and user-written instructions at inference time. Since it performs edits in the forward pass and does not require per example fine-tuning or inversion, our model edits images quickly, in a matter of seconds. We show compelling editing results for a diverse collection of input images and written instructions.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09800



2、[CV] DiffusionDet: Diffusion Model for Object Detection
S Chen, P Sun, Y Song, P Luo
[The University of Hong Kong & Tencent AI Lab]
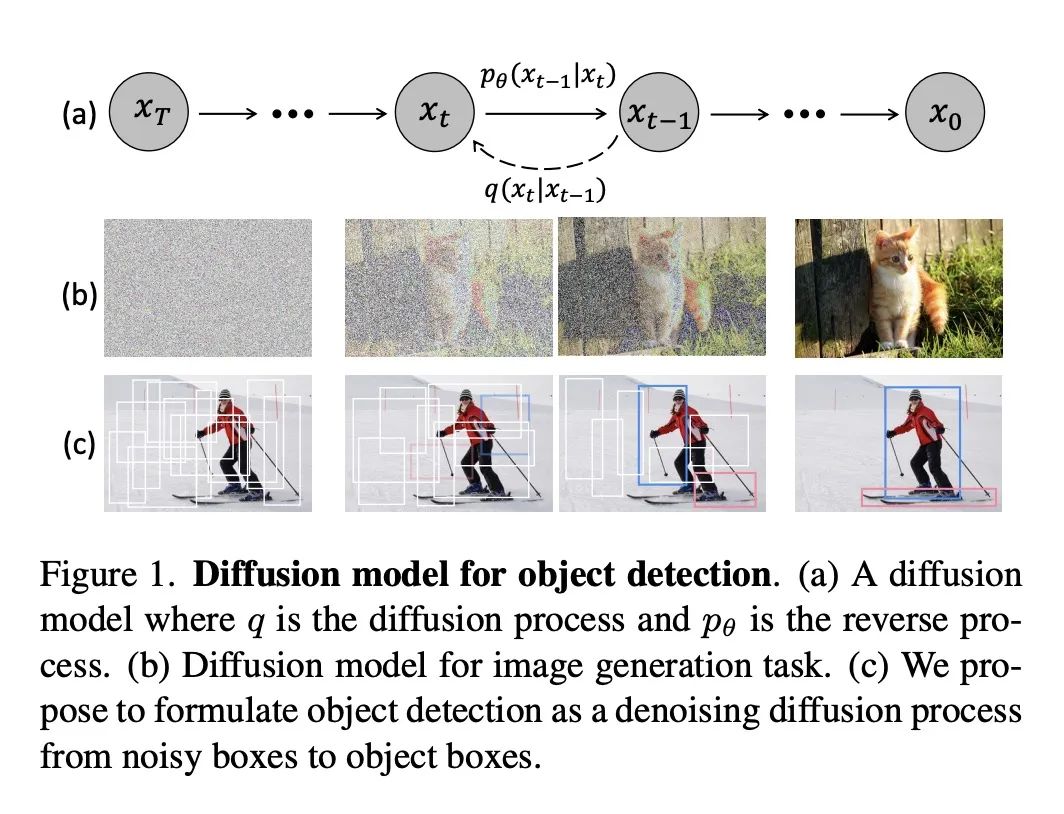
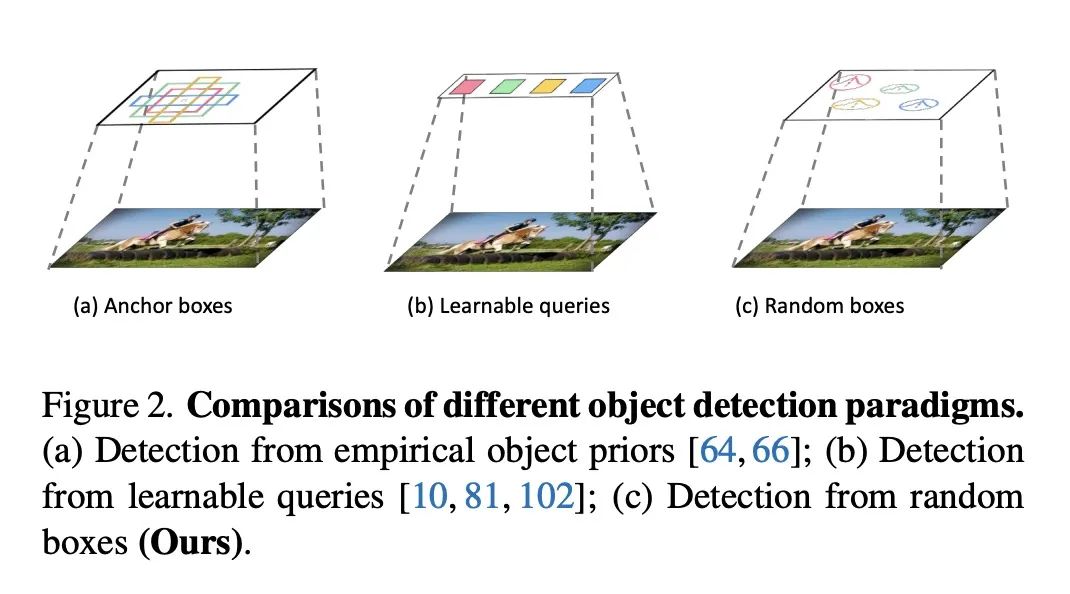
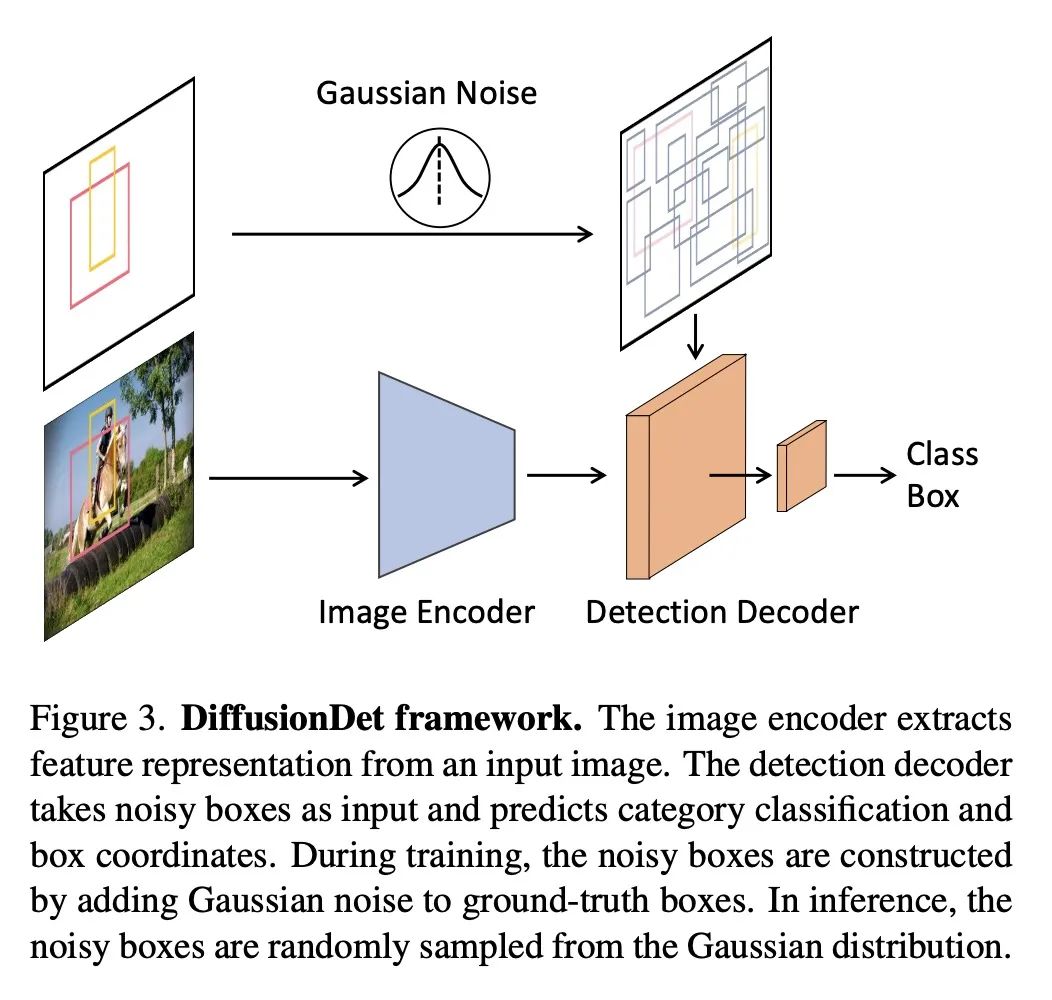
DiffusionDet: 面向目标检测的扩散模型。本文提出DiffusionDet,一种新的框架,将目标检测表述为一个从噪声框到目标框的去噪扩散过程。在训练阶段,目标框从真实的框扩散到随机分布,模型学习逆转这一噪声过程。在推理中,该模型以渐进的方式将一组随机生成的框细化为输出结果。对标准基准的广泛评估,包括MS-COCO和LVIS,表明DiffusionDet与之前成熟的检测器相比取得了良好的性能。本文工作带来了目标检测方面的两个重要发现。首先,随机框虽然与预定义的锚或学习的查询有很大的不同,但也是有效的目标候选。第二,作为代表性的感知任务之一,目标检测可以通过生成的方式来解决。
We propose DiffusionDet, a new framework that formulates object detection as a denoising diffusion process from noisy boxes to object boxes. During training stage, object boxes diffuse from ground-truth boxes to random distribution, and the model learns to reverse this noising process. In inference, the model refines a set of randomly generated boxes to the output results in a progressive way. The extensive evaluations on the standard benchmarks, including MS-COCO and LVIS, show that DiffusionDet achieves favorable performance compared to previous well-established detectors. Our work brings two important findings in object detection. First, random boxes, although drastically different from pre-defined anchors or learned queries, are also effective object candidates. Second, object detection, one of the representative perception tasks, can be solved by a generative way. Our code is available at this https URL.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09788

3、[LG] VeLO: Training Versatile Learned Optimizers by Scaling Up
L Metz, J Harrison, C. D Freeman, A Merchant, L Beyer, J Bradbury, N Agrawal, B Poole, I Mordatch, A Roberts, J Sohl-Dickstein
[Google Research]
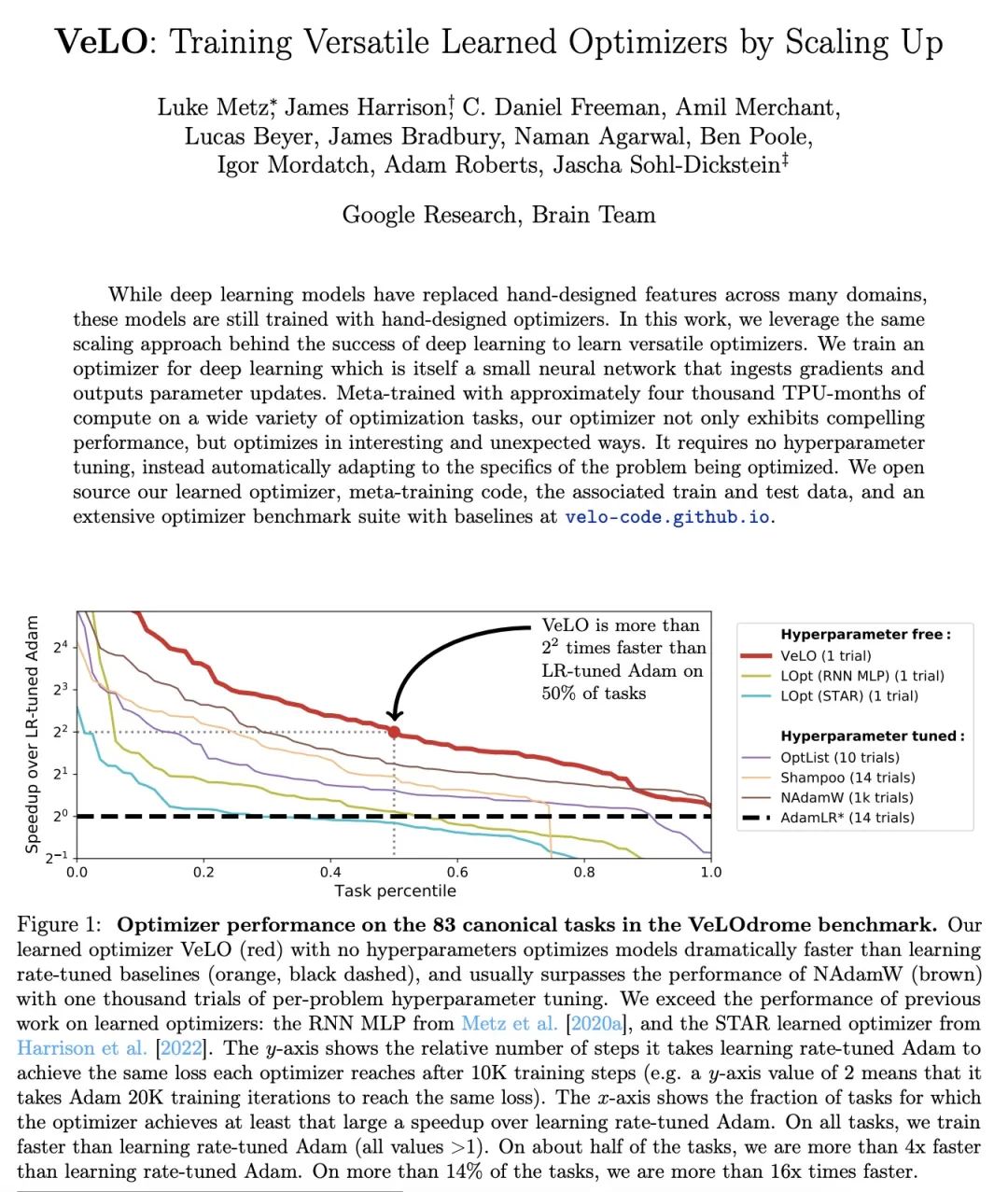
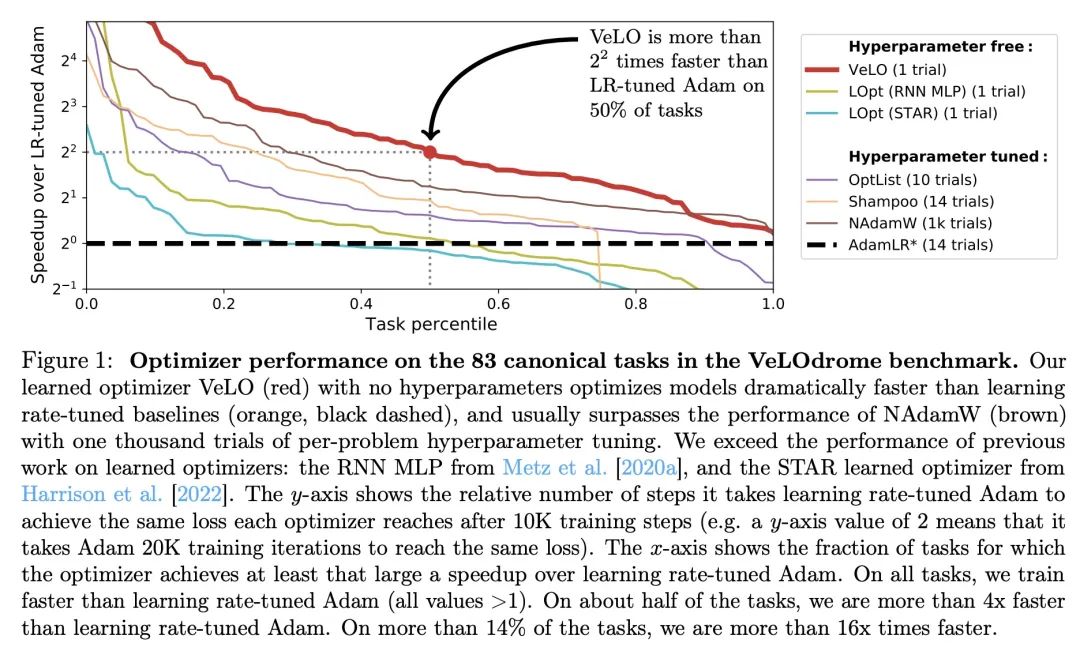
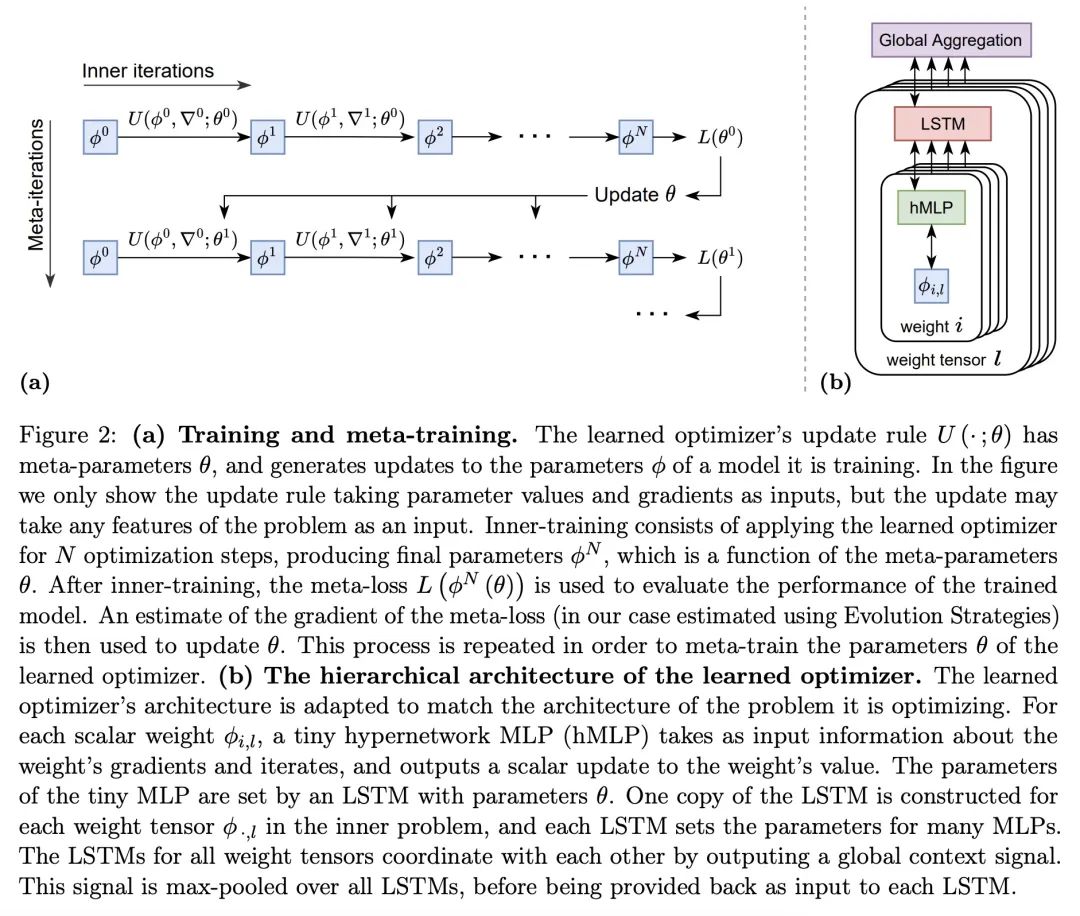
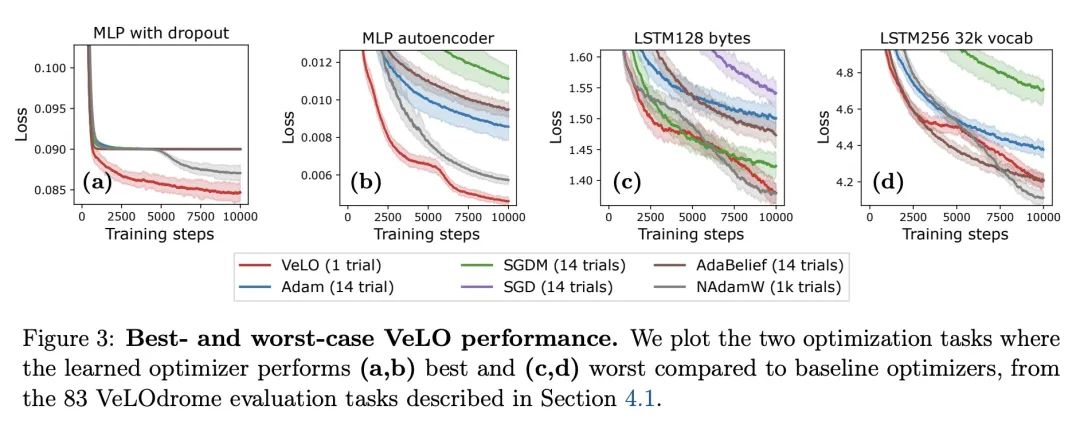
VeLO:通过扩大规模训练通用习得优化器。虽然深度学习模型在许多领域已经取代了手工设计的特征,但这些模型仍然是用手工设计的优化器训练的。本文利用深度学习成功背后的同样的扩展方法来学习多功能的优化器。本文为深度学习训练了一个优化器,其本身就是一个小型的神经网络,可以摄入梯度并输出参数更新。在各种各样的优化任务中,用大约四千个TPU月的计算进行元训练,该优化器不仅表现出引人注目的性能,而且以有趣和意想不到的方式进行优化。它不需要调整超参数,而是自动适应被优化问题的具体情况。
While deep learning models have replaced hand-designed features across many domains, these models are still trained with hand-designed optimizers. In this work, we leverage the same scaling approach behind the success of deep learning to learn versatile optimizers. We train an optimizer for deep learning which is itself a small neural network that ingests gradients and outputs parameter updates. Meta-trained with approximately four thousand TPU-months of compute on a wide variety of optimization tasks, our optimizer not only exhibits compelling performance, but optimizes in interesting and unexpected ways. It requires no hyperparameter tuning, instead automatically adapting to the specifics of the problem being optimized. We open source our learned optimizer, meta-training code, the associated train and test data, and an extensive optimizer benchmark suite with baselines at this http URL.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09760
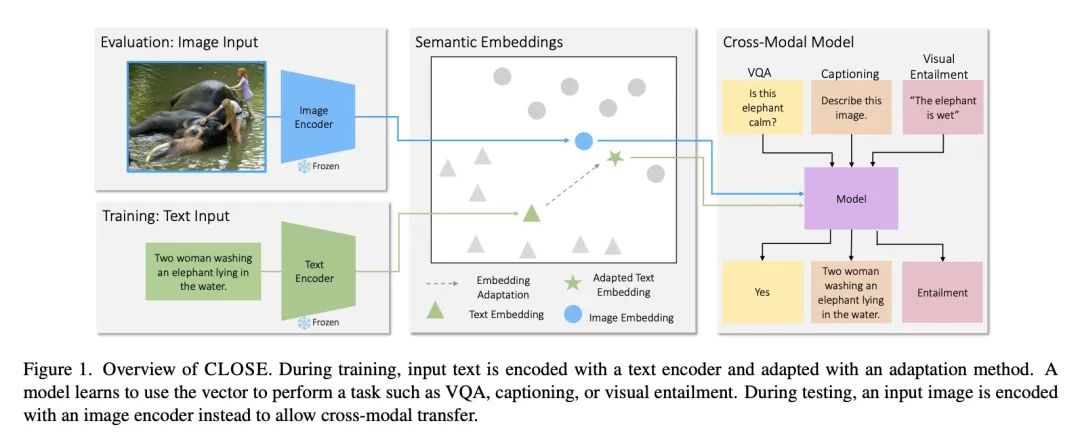
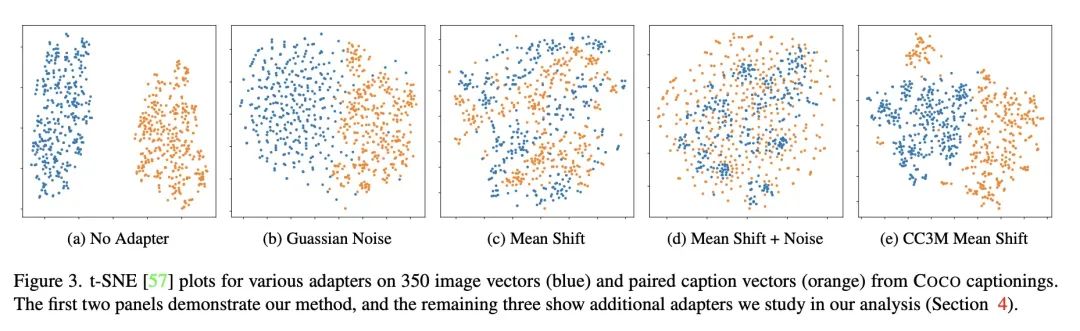
4、[CV] I Can't Believe There's No Images! Learning Visual Tasks Using only Language Data
S Gu, C Clark, A Kembhavi
[Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence]
只用语言数据学习视觉任务。计算机视觉任务所需要的许多高级技能,如解析问题、比较和对比语义以及生成描述等,在其他领域如自然语言处理中也是需要的。本文询问这是否使得从文本数据中学习这些技能成为可能,然后用它们来完成视觉任务,而不需要在视觉训练数据上进行训练。该方法的关键是利用对比训练的视觉和语言编码器的联合嵌入空间。在实践中,不同模态的嵌入空间在对比模型中可能存在系统性差异,本文分析了这些差异是如何影响所提出方法的,并研究了各种策略来缓解这一问题。在三个任务上只用文本训练数据来制作模型:图像描述、视觉蕴含和视觉问答,并在使用图像的标准基准上对它们进行评估。结果发现,这种迁移是可能的,而且相对于在图像上训练的模型,这种迁移只导致了性能的小幅下降。本文还展示了各种风格化的图像描述模型,这些模型没有使用图像数据和人工策划的语言数据,而是采用来自书籍、网络或语言模型的文本数据进行训练。
Many high-level skills that are required for computer vision tasks, such as parsing questions, comparing and contrasting semantics, and writing descriptions, are also required in other domains such as natural language processing. In this paper, we ask whether this makes it possible to learn those skills from text data and then use them to complete vision tasks without ever training on visual training data. Key to our approach is exploiting the joint embedding space of contrastively trained vision and language encoders. In practice, there can be systematic differences between embedding spaces for different modalities in contrastive models, and we analyze how these differences affect our approach and study a variety of strategies to mitigate this concern. We produce models using only text training data on three tasks: image captioning, visual entailment and visual question answering, and evaluate them on standard benchmarks using images. We find that this kind of transfer is possible and results in only a small drop in performance relative to models trained on images. We also showcase a variety of stylistic image captioning models that were trained using no image data and no human-curated language data, but instead text data from books, the web, or language models.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09778


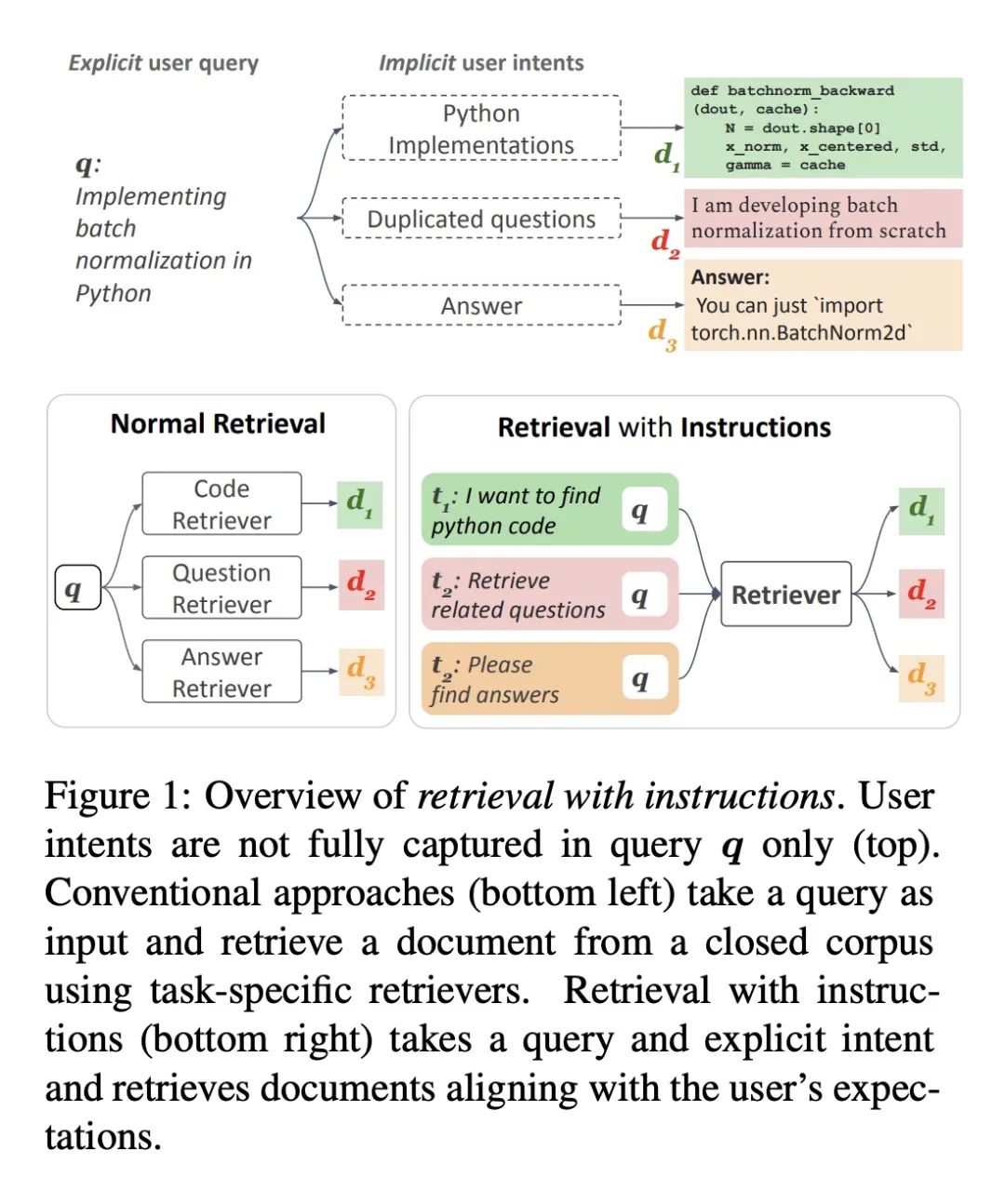
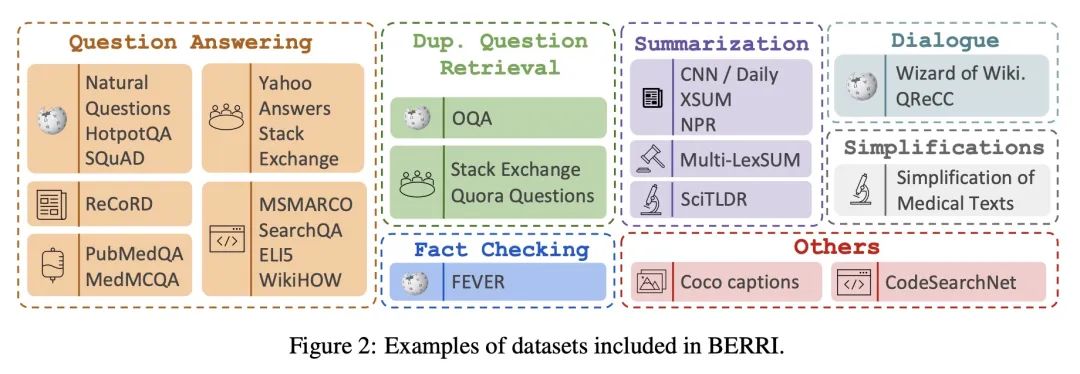
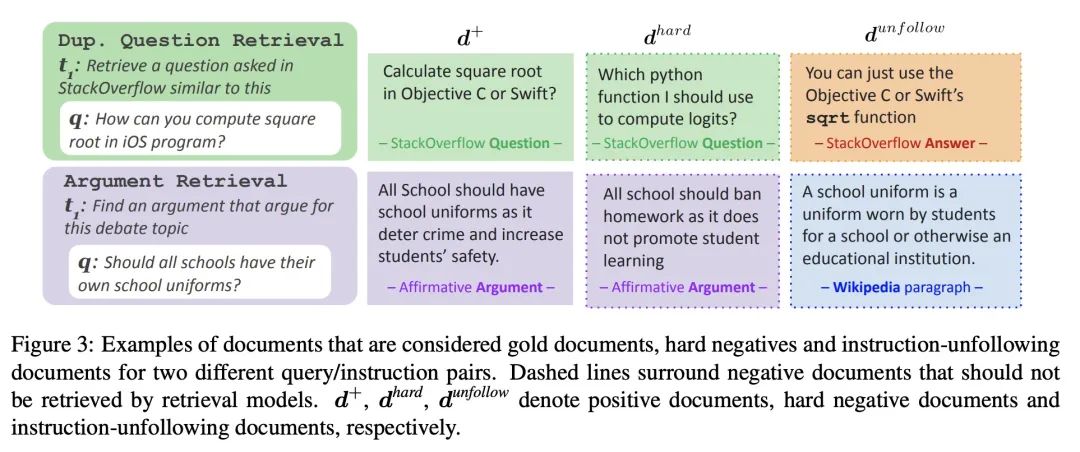
5、[CL] Task-aware Retrieval with Instructions
A Asai, T Schick, P Lewis, X Chen, G Izacard, S Riedel, H Hajishirzi, W Yih
[Meta AI & University College London & University of Washington]
基于指令的任务感知检索。本文研究基于指令的检索问题,即检索系统的用户在查询的同时明确描述他们的意图,使系统具有任务感知。本文的目标是开发一个通用的任务感知检索系统,该系统用多任务指令调整,能够遵循人工写的指令,为给定的查询找到最佳文档。为此,本文引入了第一个大规模的约40个带有指令的检索数据集,并提出了TART,一个在基于指令的不同检索任务上训练的多任务检索系统。TART展示了通过指令适应新任务的强大能力,并在BEIR和LOTTE这两个零样本检索基准上推动了技术水平的提高,其性能超过了最多三倍的模型。本文进一步引入了一个新的评估设置,以更好地反映现实世界的情况,汇集了不同的文档和任务。在这个设置中,TART明显优于竞争基准,进一步证明了用指令指导检索的有效性。
We study the problem of retrieval with instructions, where users of a retrieval system explicitly describe their intent along with their queries, making the system task-aware. We aim to develop a general-purpose task-aware retrieval systems using multi-task instruction tuning that can follow human-written instructions to find the best documents for a given query. To this end, we introduce the first large-scale collection of approximately 40 retrieval datasets with instructions, and present TART, a multi-task retrieval system trained on the diverse retrieval tasks with instructions. TART shows strong capabilities to adapt to a new task via instructions and advances the state of the art on two zero-shot retrieval benchmarks, BEIR and LOTTE, outperforming models up to three times larger. We further introduce a new evaluation setup to better reflect real-world scenarios, pooling diverse documents and tasks. In this setup, TART significantly outperforms competitive baselines, further demonstrating the effectiveness of guiding retrieval with instructions.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09260

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
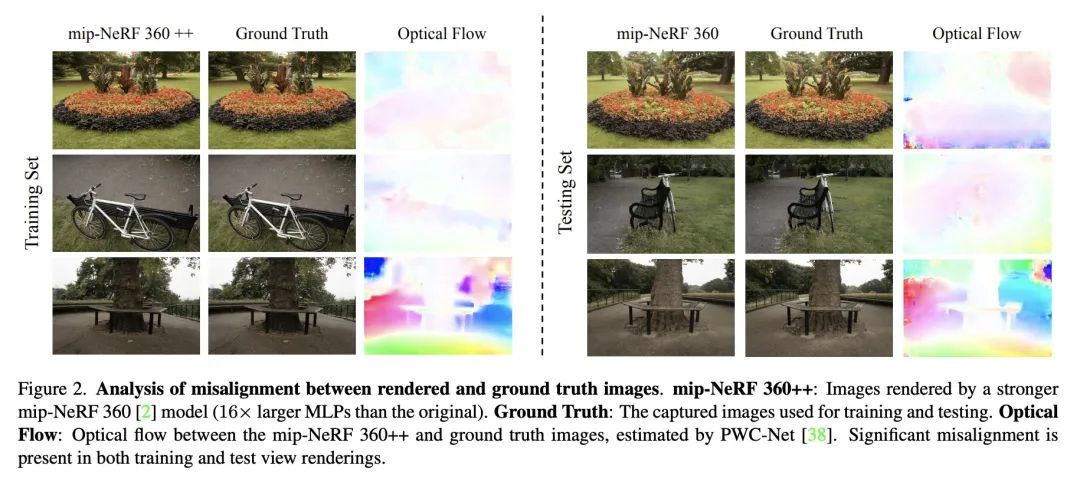
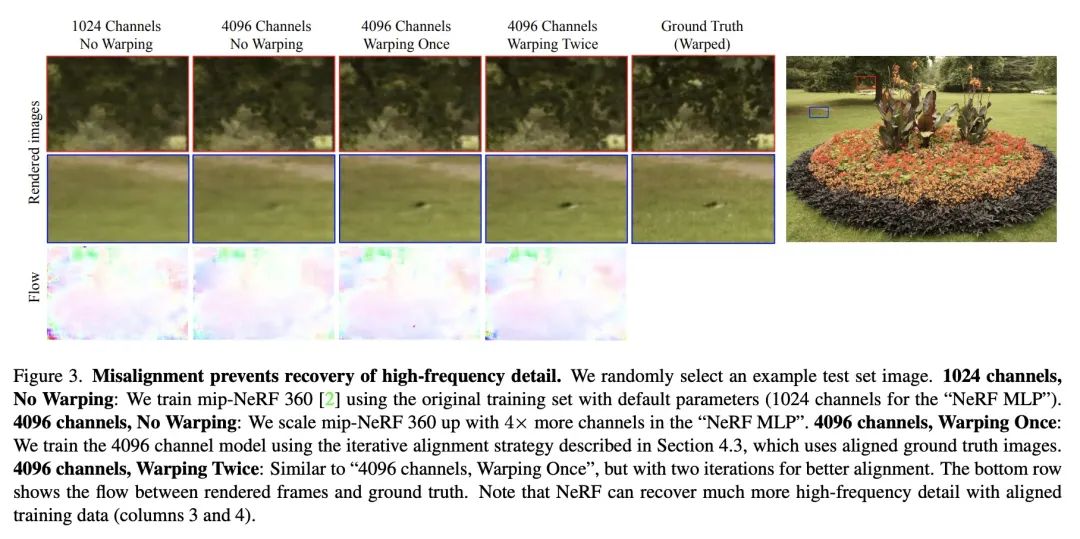
[CV] AligNeRF: High-Fidelity Neural Radiance Fields via Alignment-Aware Training
AligNeRF:基于对齐感知训练的高保真神经辐射场
Y Jiang, P Hedman, B Mildenhall...
[Google Research & University of Texas at Austin & The Chinese University of Hong Kong]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09682




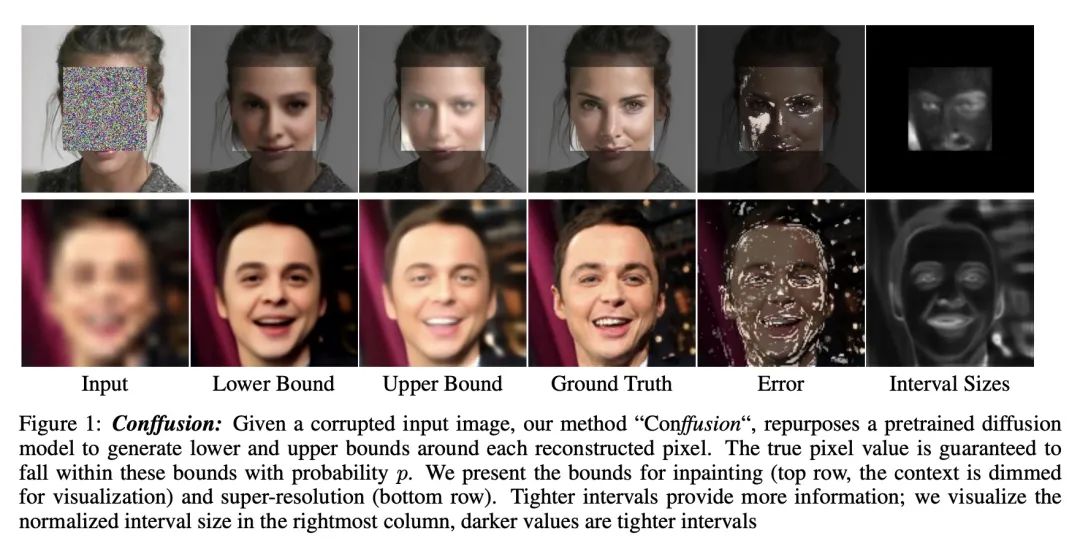
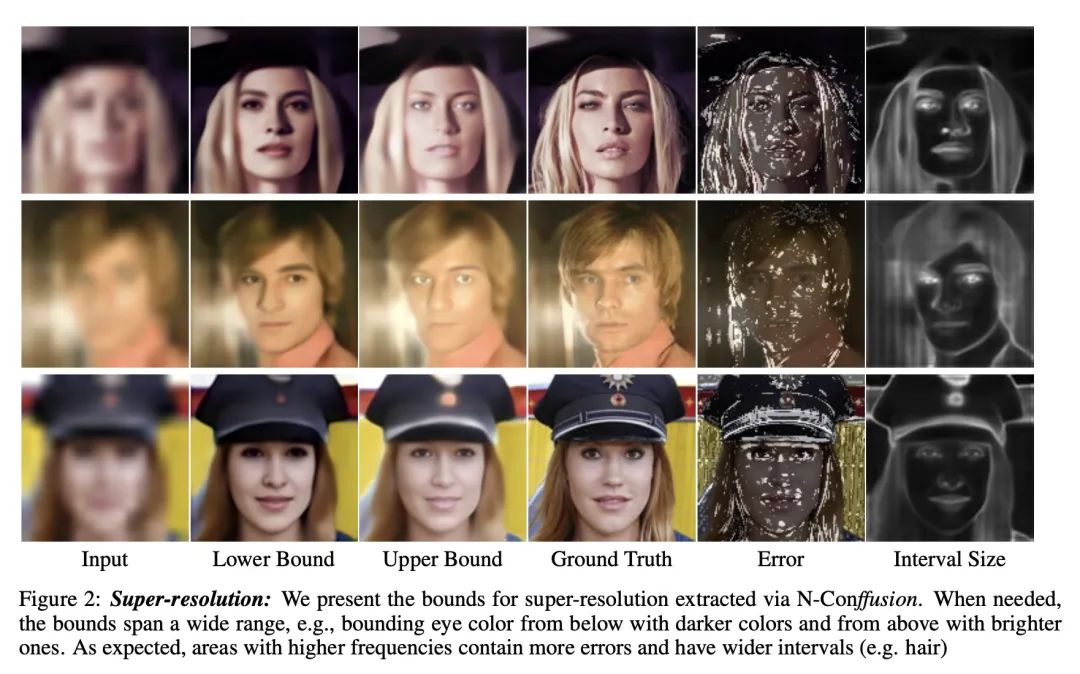
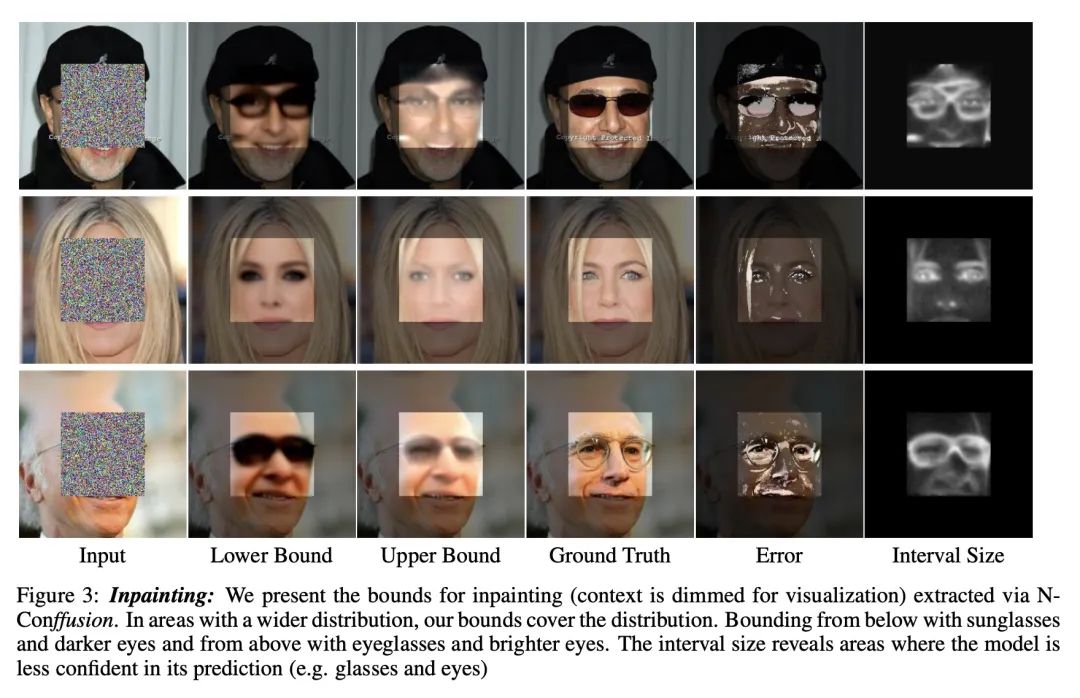
[CV] Conffusion: Confidence Intervals for Diffusion Models
Conffusion:扩散模型的置信区间
E Horwitz, Y Hoshen
[The Hebrew University of Jerusalem]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09795




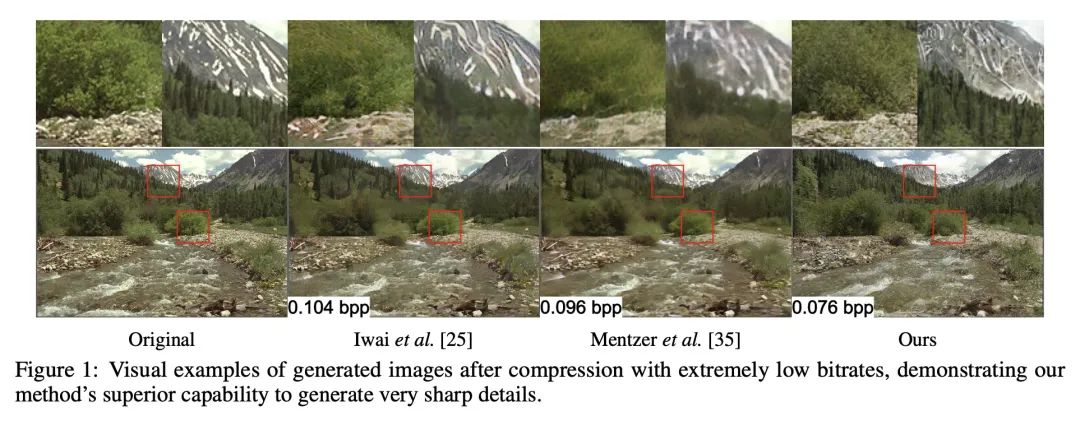
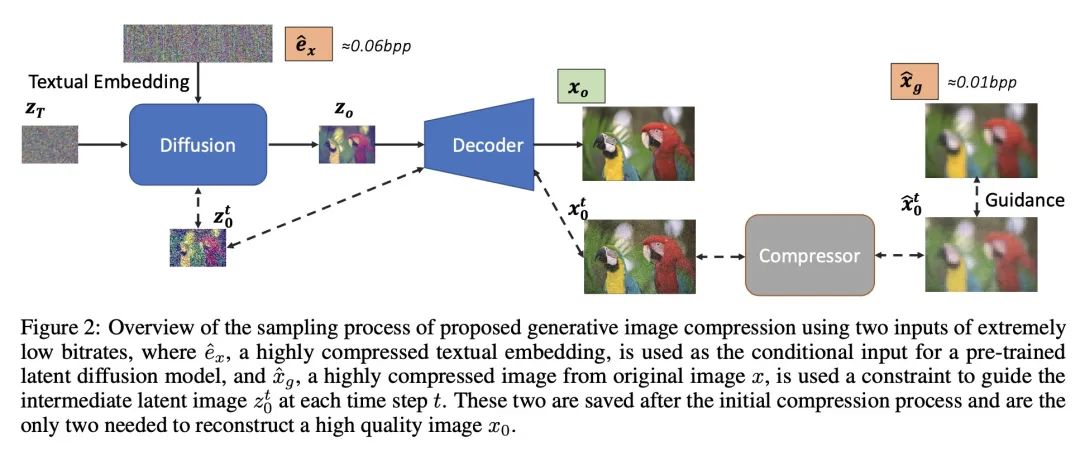
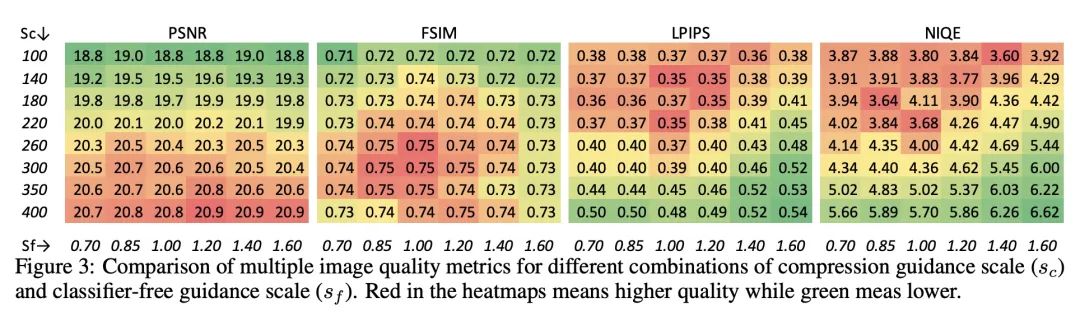
[CV] Extreme Generative Image Compression by Learning Text Embedding from Diffusion Models
通过从扩散模型学习文本嵌入进行极端生成式图像压缩
Z Pan, X Zhou, H Tian
[Baidu Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.07793


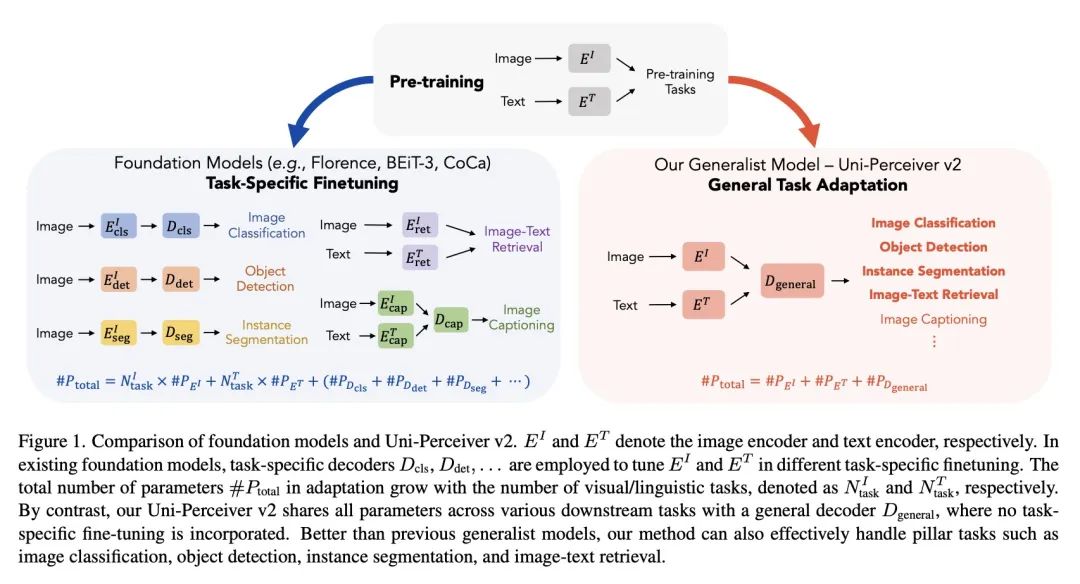
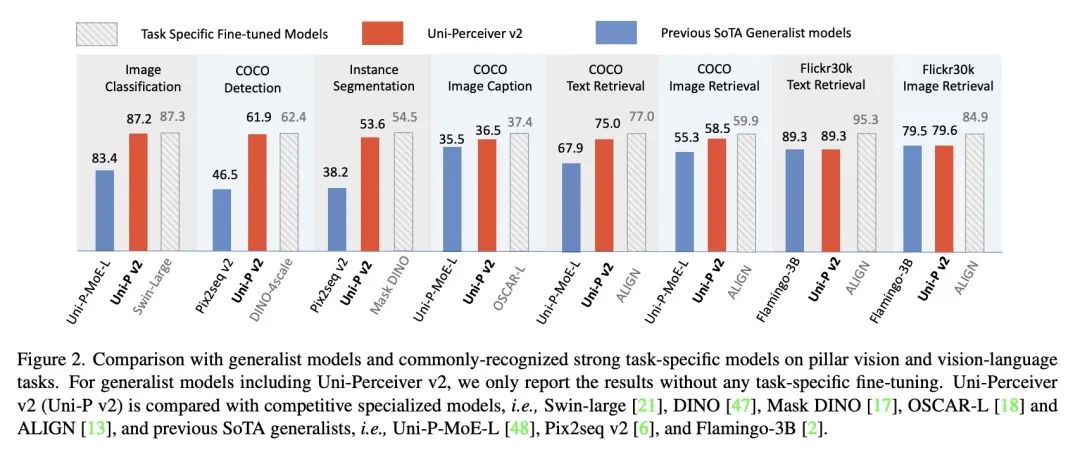
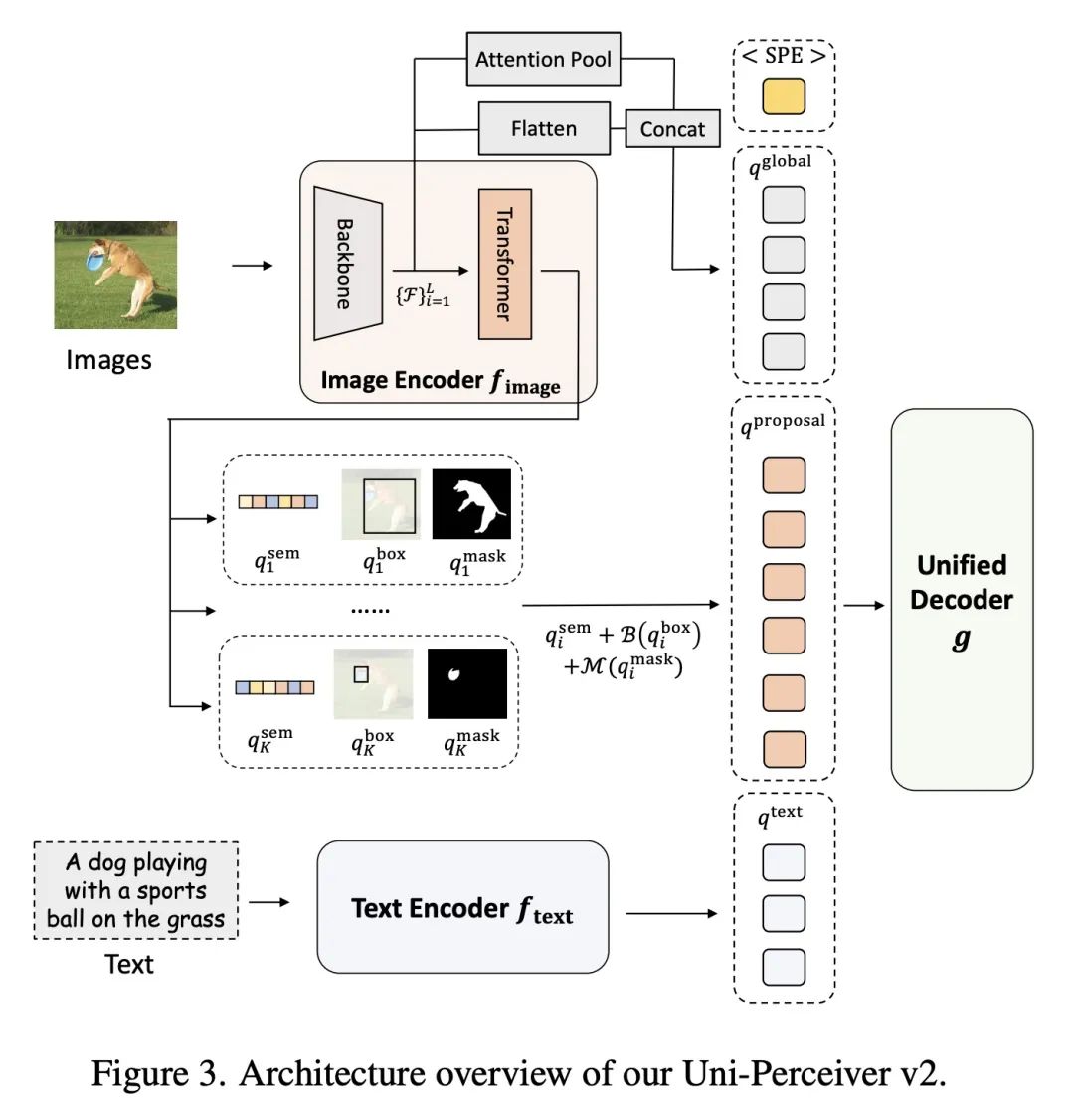
[CV] Uni-Perceiver v2: A Generalist Model for Large-Scale Vision and Vision-Language Tasks
Uni-Perceiver v2:大规模视觉和视觉-语言任务通才模型
H Li, J Zhu, X Jiang...
[The Chinese University of Hong Kong & Xi’an Jiaotong University & Tsinghua University & SenseTime Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09808

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢