LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人
摘要:基于引导扩散模型的无文本逆向真实图像编辑、具有可控表情的语音驱动人像动画、机制模式连接性、用基因组规模语言模型揭示SARS-CoV-2进化动态、基于Bambu的长读RNA-Seq数据上下文感知转录量化、维基百科集体关注网络化主题的有效识别、提示PaLM进行翻译、面向语言结构的提示语言模型、面向细粒度调试与分析的领域专家密集标注皮肤病数据集
1、[CV] Null-text Inversion for Editing Real Images using Guided Diffusion Models
R Mokady, A Hertz, K Aberman, Y Pritch, D Cohen-Or
[Google Research]
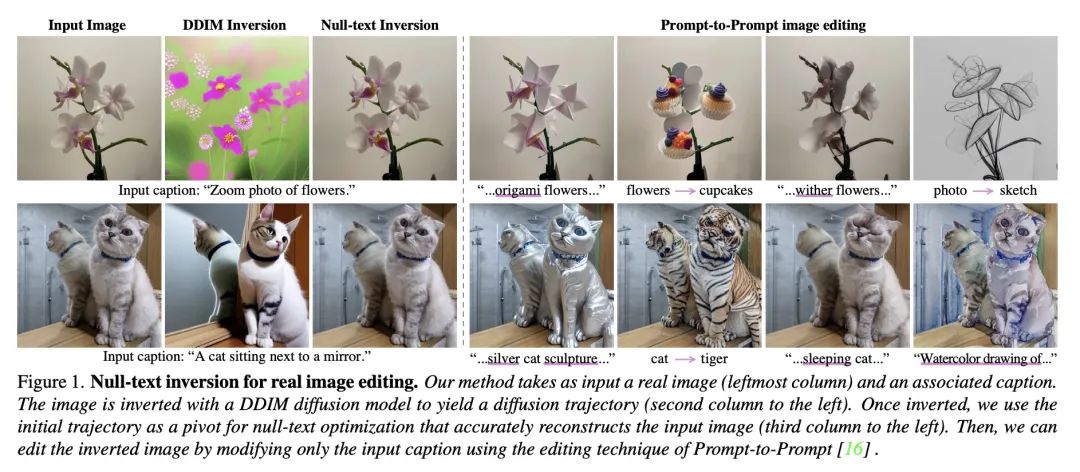
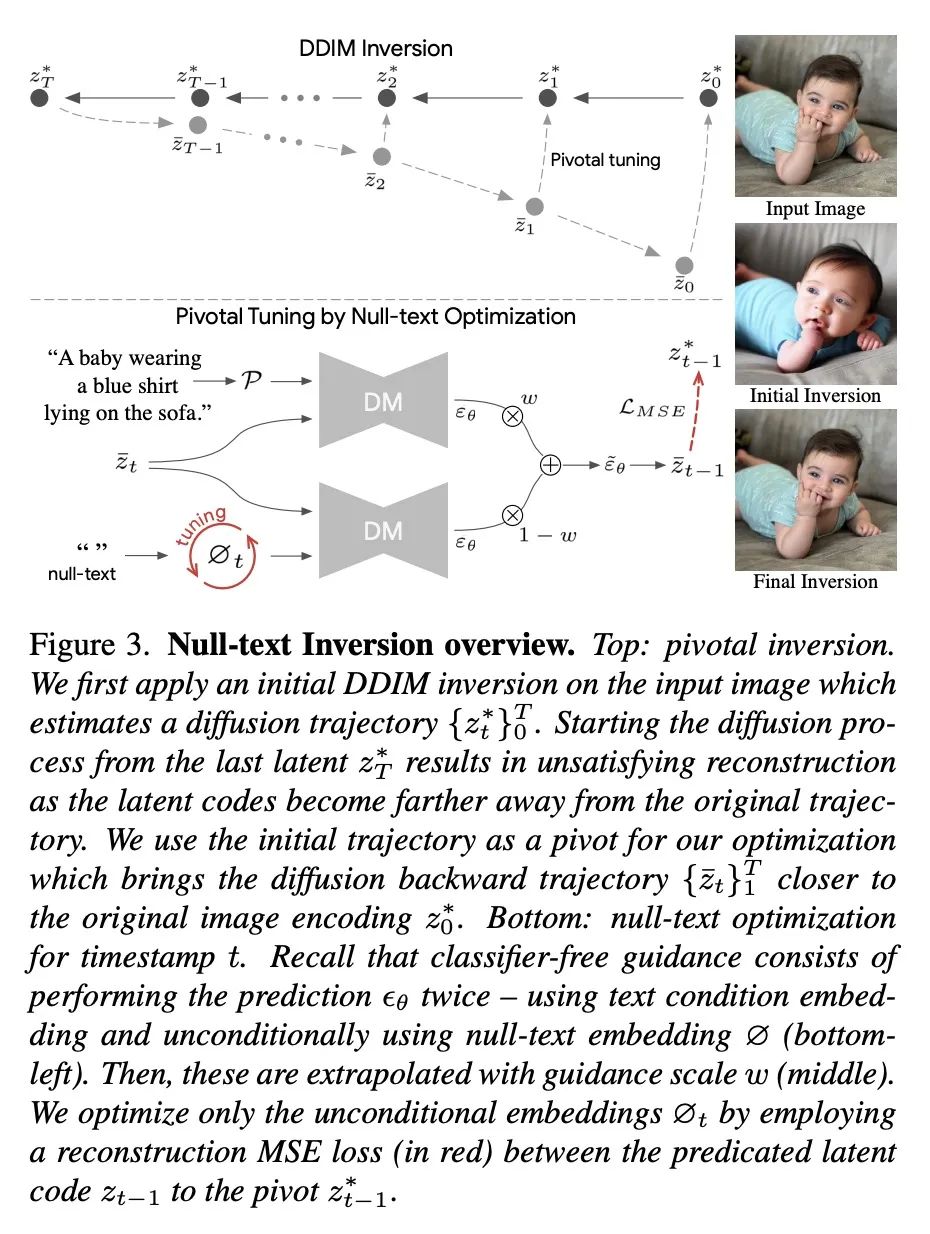
基于引导扩散模型的无文本逆向真实图像编辑。最近的文本引导扩散模型提供了强大的图像生成能力。目前,人们付出了巨大的努力,使这些图像的修改只用文本作为提供直观且多功能的编辑手段。要使用这些最先进的工具来编辑真实的图像,首先必须用有意义的文本提示将图像逆向到预训练模型的域。本文提出一种精确的逆向方法,从而促进了对图像的直观的基于文本的修改。所提出的逆向包括两个新的关键部分。(i) 扩散模型的关键反演。目前的方法旨在将随机噪声样本映射到单幅输入图像,而本文对每个时间戳使用单一的关键噪声矢量,并围绕它进行优化。本文证明,直接逆向本身是不够的,但确实为优化提供了一个良好的锚。(ii) NULL-text优化,只修改用于无分类器指导的无条件文本嵌入,而不是输入文本嵌入。这允许保持模型权重和条件嵌入的完整,因此能应用基于提示的编辑,同时避免了对模型权重的繁琐调整。所提出的Null-text逆向,基于开放的Stable Diffusion模型,在各种图像和提示编辑上进行了广泛的评估,显示了对真实图像的高保真编辑。
Recent text-guided diffusion models provide powerful image generation capabilities. Currently, a massive effort is given to enable the modification of these images using text only as means to offer intuitive and versatile editing. To edit a real image using these state-of-the-art tools, one must first invert the image with a meaningful text prompt into the pretrained model's domain. In this paper, we introduce an accurate inversion technique and thus facilitate an intuitive text-based modification of the image. Our proposed inversion consists of two novel key components: (i) Pivotal inversion for diffusion models. While current methods aim at mapping random noise samples to a single input image, we use a single pivotal noise vector for each timestamp and optimize around it. We demonstrate that a direct inversion is inadequate on its own, but does provide a good anchor for our optimization. (ii) NULL-text optimization, where we only modify the unconditional textual embedding that is used for classifier-free guidance, rather than the input text embedding. This allows for keeping both the model weights and the conditional embedding intact and hence enables applying prompt-based editing while avoiding the cumbersome tuning of the model's weights. Our Null-text inversion, based on the publicly available Stable Diffusion model, is extensively evaluated on a variety of images and prompt editing, showing high-fidelity editing of real images.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09794


2、[CV] SPACEx: Speech-driven Portrait Animation with Controllable Expression
S Gururani, A Mallya, T Wang, R Valle, M Liu
[NVIDIA]
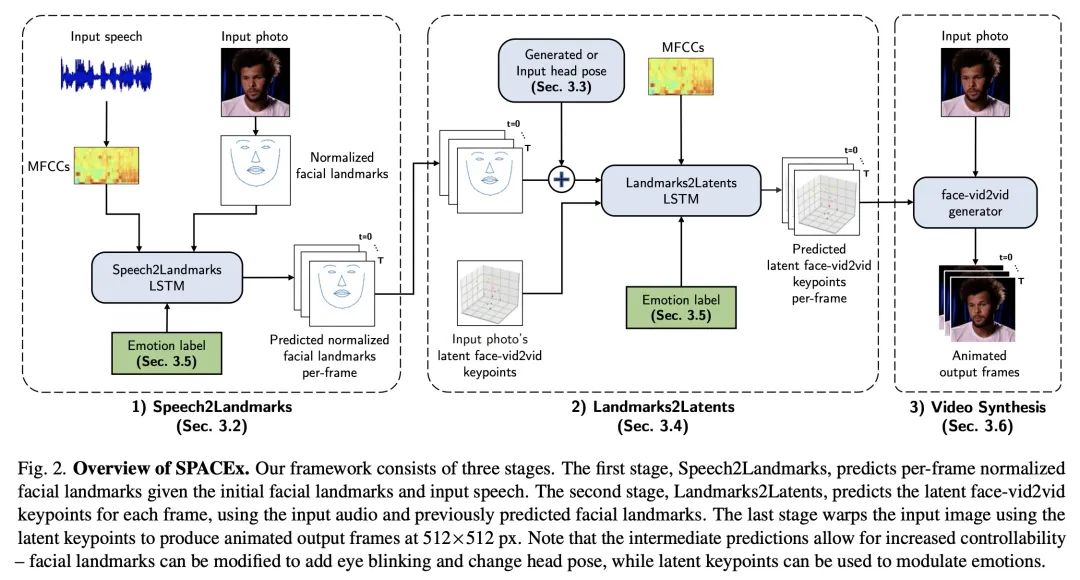
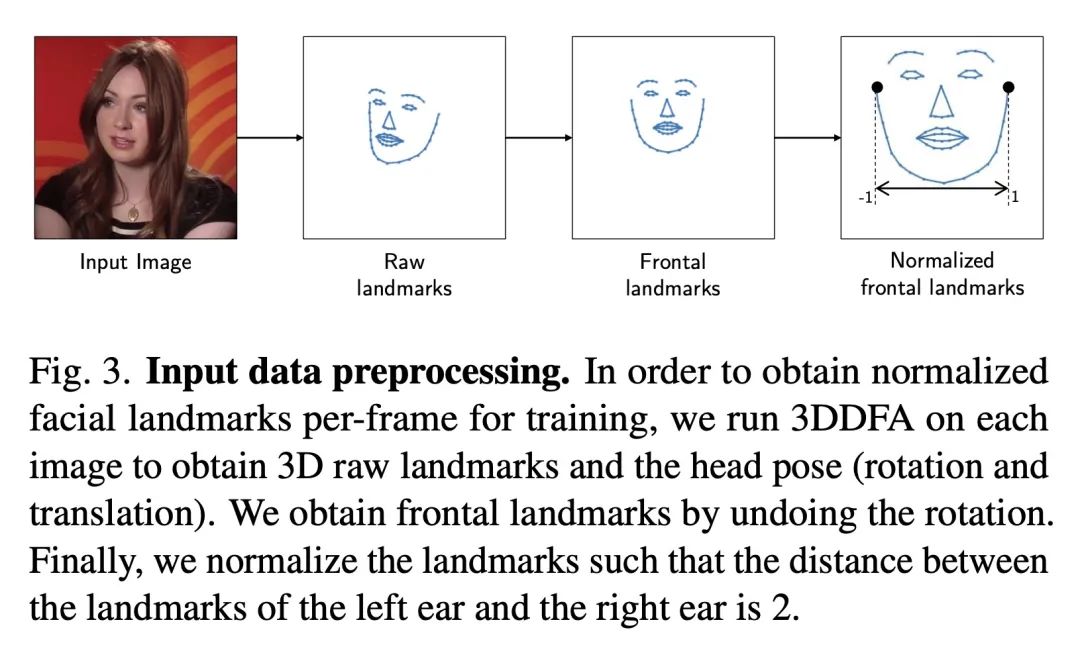
SPACEx:具有可控表情的语音驱动人像动画。近年来,用语音制作人像动画受到越来越多的关注,有各种创造性和实用性的用例。一个理想的生成视频应该与音频有良好的唇语同步,有自然的人脸表情和头部动作,并且有较高的帧质量。本文提出SPACEx,使用语音和单幅图像来生成高分辨率的、具有真实头部姿态具有表现力的视频,而不需要驱动视频。其采用了一种多阶段方法,将人脸特征点的可控性与预训练的人脸生成器的高质量合成能力相结合。SPACEx还允许控制情绪及其强度。所提出方法在图像质量和人脸运动的客观指标方面优于之前的方法,并且在配对比较中受到用户的强烈青睐。
Animating portraits using speech has received growing attention in recent years, with various creative and practical use cases. An ideal generated video should have good lip sync with the audio, natural facial expressions and head motions, and high frame quality. In this work, we present SPACEx, which uses speech and a single image to generate high-resolution, and expressive videos with realistic head pose, without requiring a driving video. It uses a multi-stage approach, combining the controllability of facial landmarks with the high-quality synthesis power of a pretrained face generator. SPACEx also allows for the control of emotions and their intensities. Our method outperforms prior methods in objective metrics for image quality and facial motions and is strongly preferred by users in pair-wise comparisons. The project website is available at this https URL
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09809
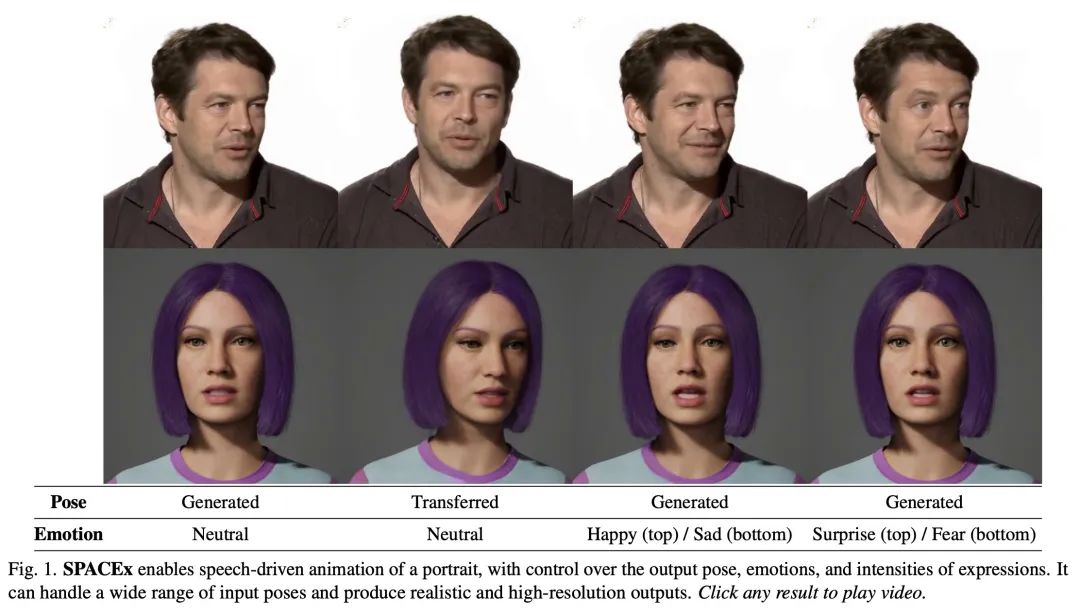


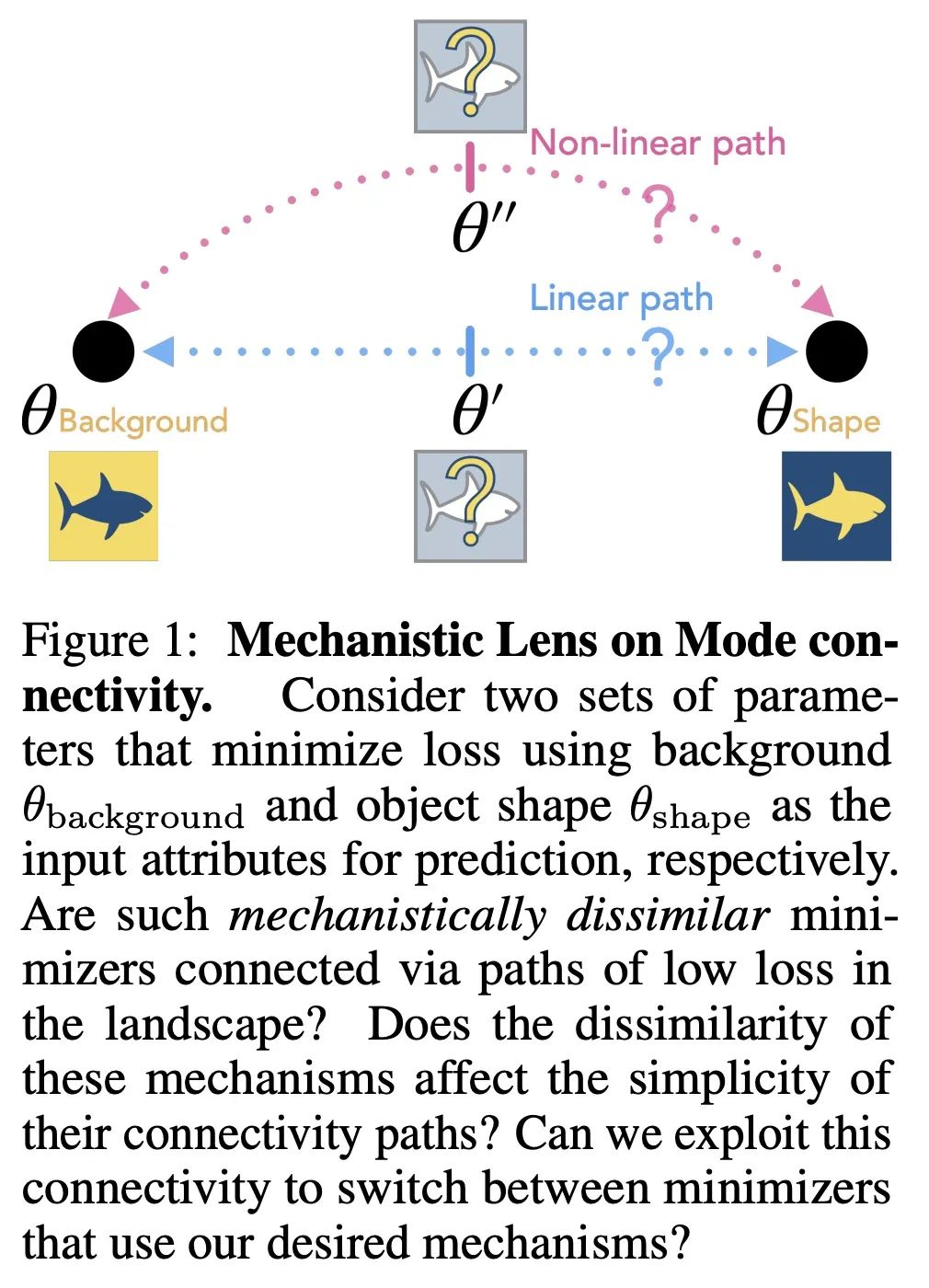
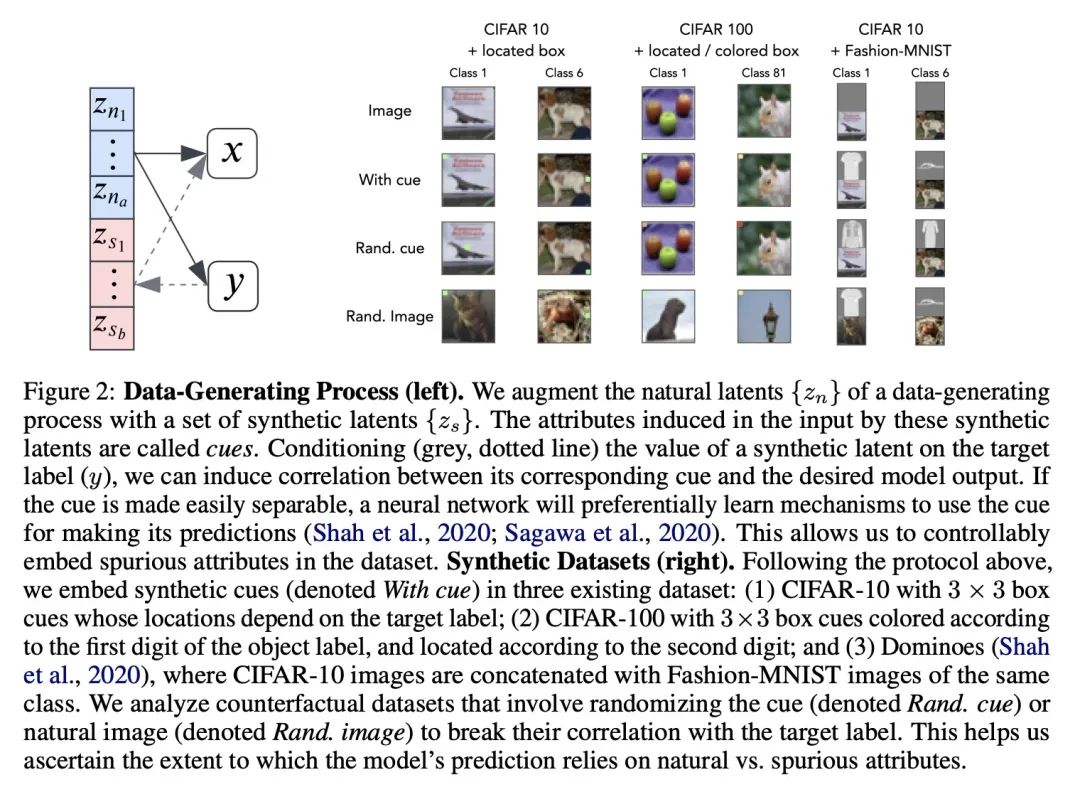
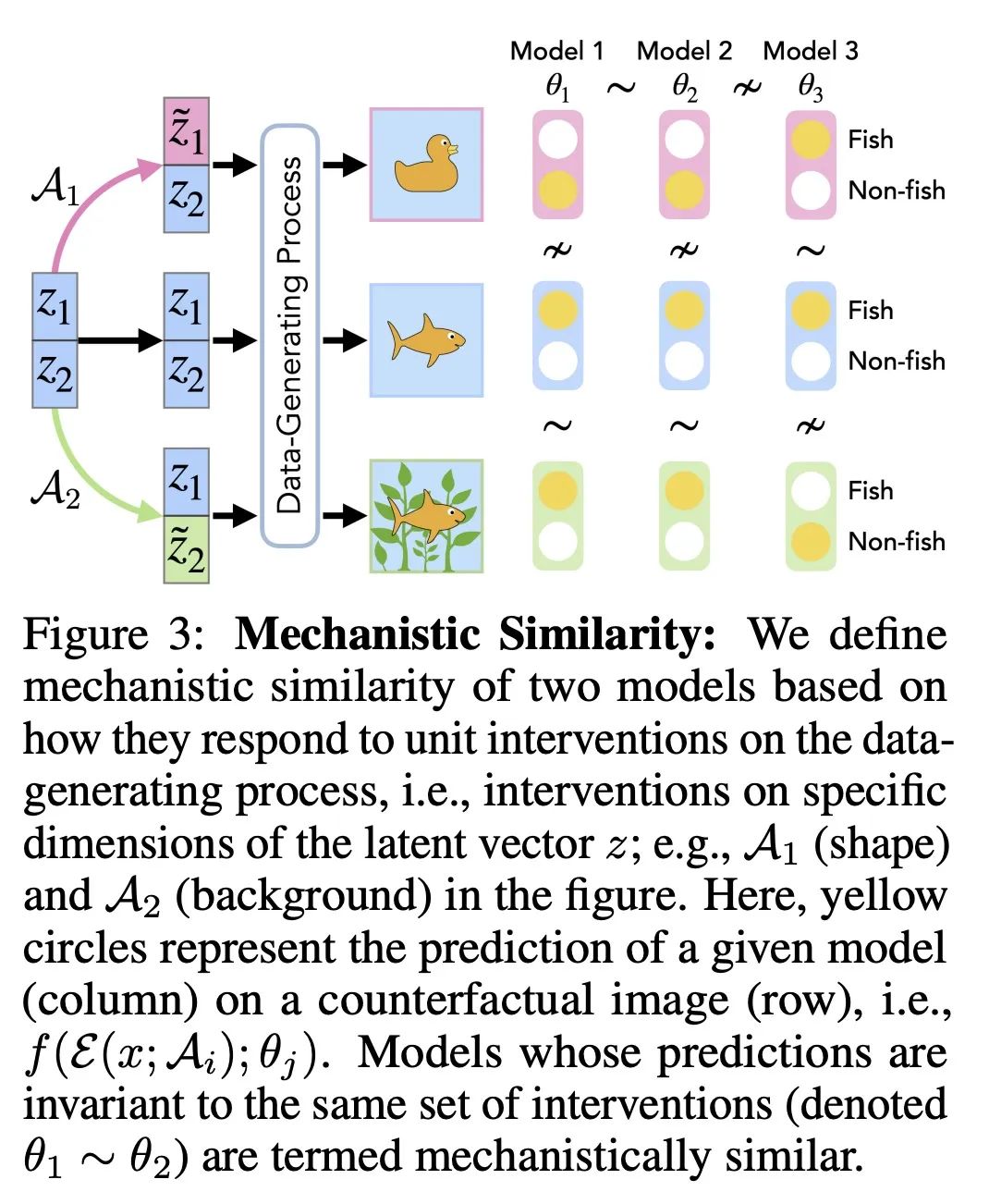
3、[LG] Mechanistic Mode Connectivity
E S Lubana, E J. Bigelow, R P. Dick, D Krueger, H Tanaka
[University of Michigan & Harvard University & University of Cambridge]
机制模式连接性。众所周知,神经网络偏向于有助于识别虚假属性的学习机制,产生的特征在分布变化的情况下不能很好地泛化。为理解和解决这一局限性,本文通过模式连接性的视角来研究神经网络损失景观几何,模式连接性是指神经网络的最小化器通过低损失的简单路径连接。本文工作涉及两个问题:(i) 编码不同机制的最小化器是否通过简单的低损失路径连接?(ii)对预训练模型进行微调是否有助于在这些最小化器之间进行切换?本文定义了一个机制相似性的概念,并证明两个最小化器之间缺乏线性连接意味着相应的模型使用不同的机制来进行预测。这一特性辅助证明了,单纯的微调可能无法消除模型对虚假属性的依赖。因此,本文提出一种改变模型机制的方法,称为基于连接的微调,并通过归纳对虚假属性不变的模型来验证其有用性。
Neural networks are known to be biased towards learning mechanisms that help identify spuriousattributes, yielding features that do not generalize well under distribution shifts. To understand and address this limitation, we study the geometry of neural network loss landscapes through the lens of modeconnectivity, the observation that minimizers of neural networks are connected via simple paths of low loss. Our work addresses two questions: (i) do minimizers that encode dissimilar mechanisms connect via simple paths of low loss? (ii) can fine-tuning a pretrained model help switch between such minimizers? We define a notion of mechanistic similarity and demonstrate that lack of linear connectivity between two minimizers implies the corresponding models use dissimilar mechanisms for making their predictions. This property helps us demonstrate that naïve fine-tuning can fail to eliminate a model's reliance on spurious attributes. We thus propose a method for altering a model's mechanisms, named connectivity-based fine-tuning, and validate its usefulness by inducing models invariant to spurious attributes.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.08422

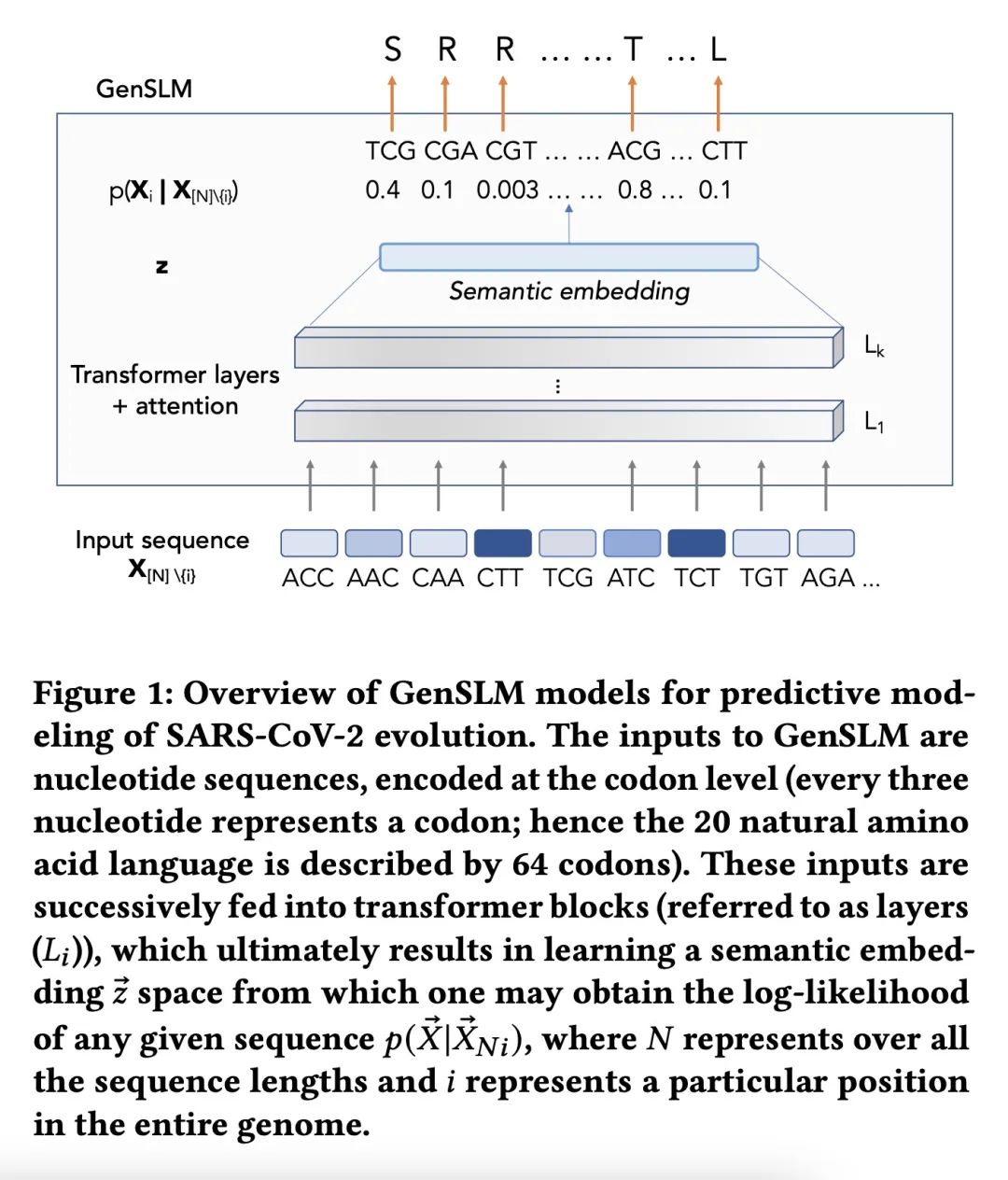
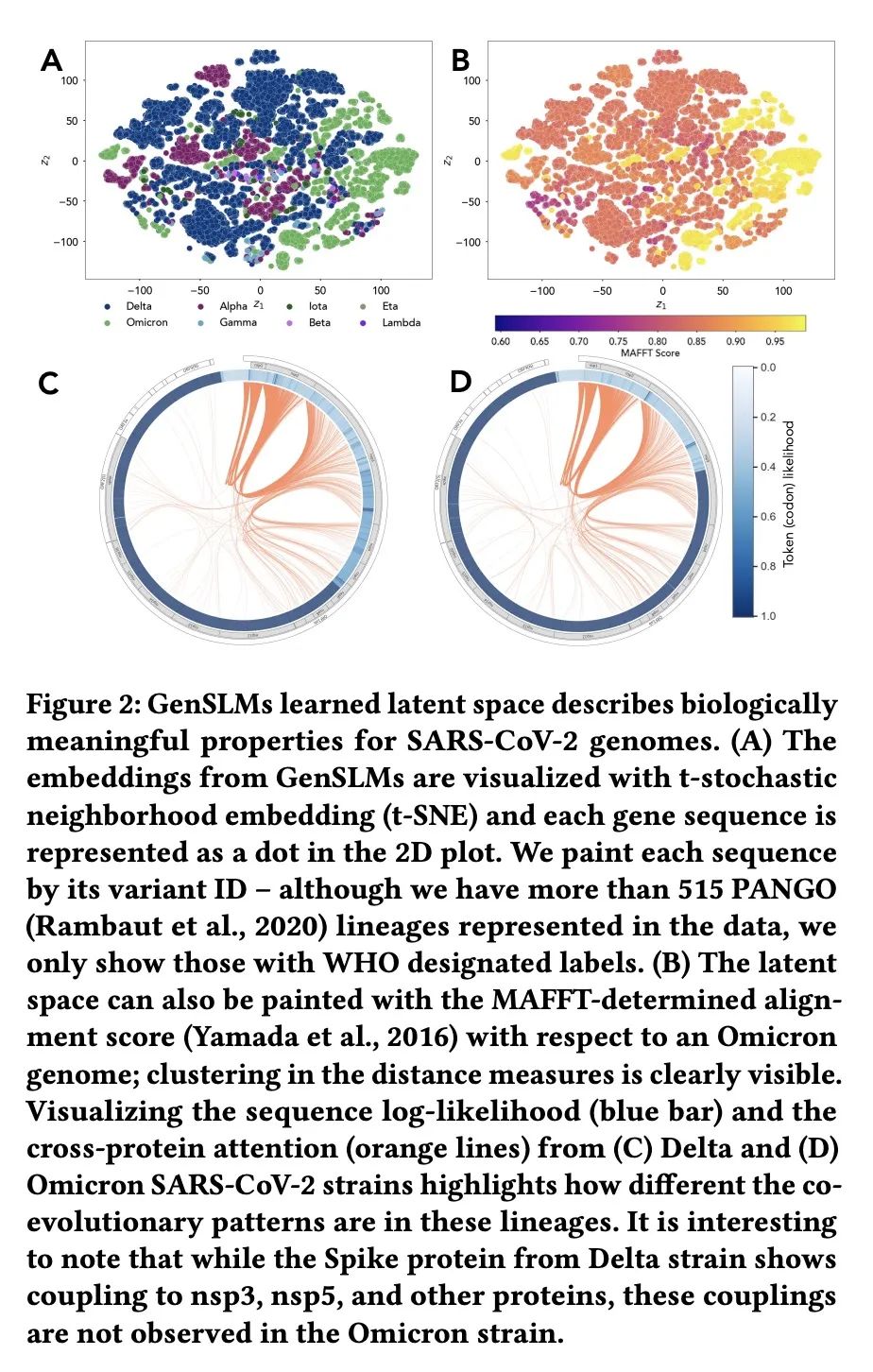
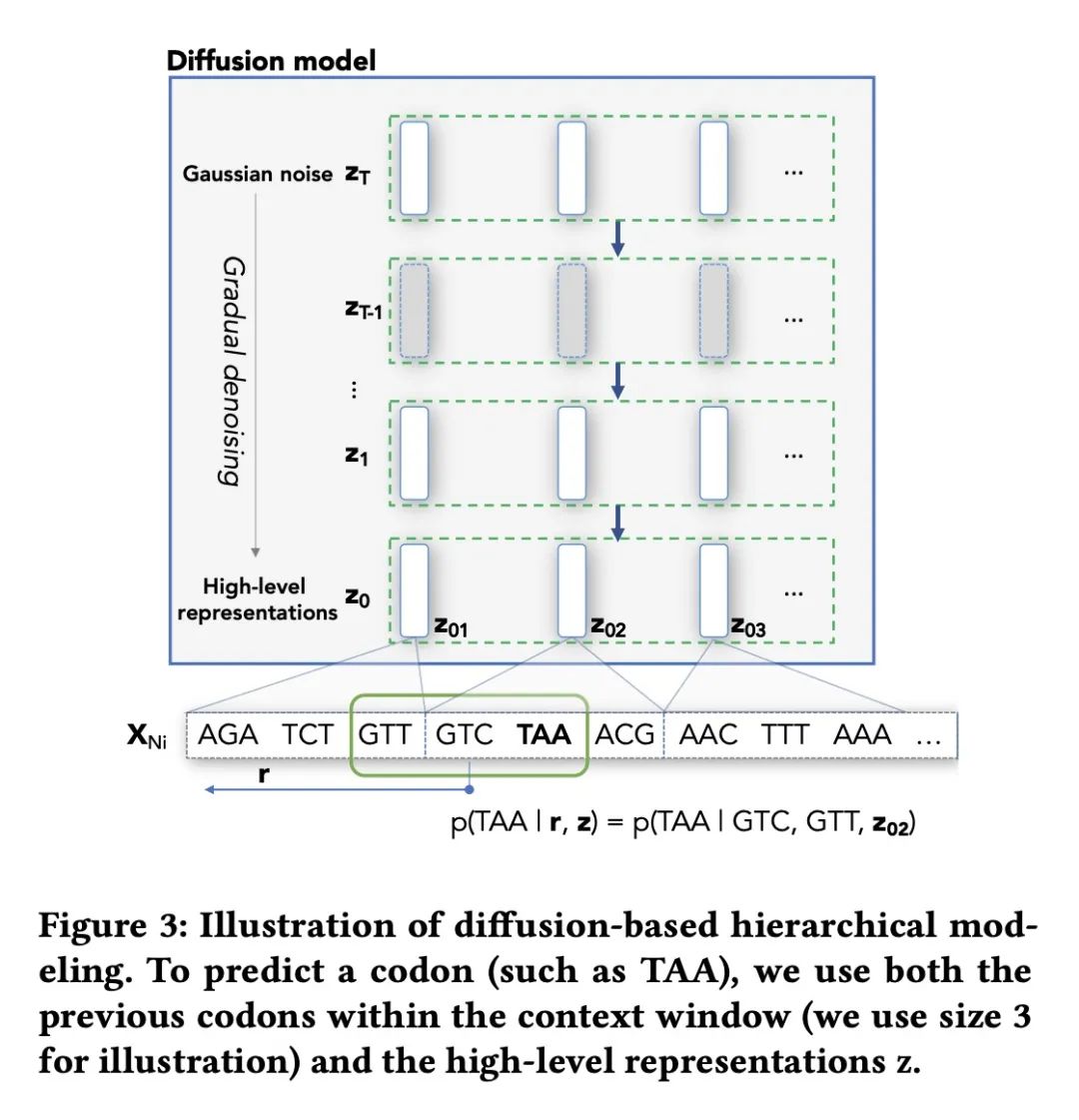
4、[LG] GenSLMs: Genome-scale language models reveal SARS-CoV-2 evolutionary dynamics
MT Zvyagin, A Brace, K Hippe, Y Deng, B Zhang…
[Argonne National Laboratory & NVIDIA Inc & Cerebras Inc & University of Chicago...]
GenSLMs: 用基因组规模语言模型揭示SARS-CoV-2进化动态。本文工作旨在改变导致大流行的病毒,特别是SARS-CoV-2的新的和不断涌现变种的识别和分类方式。通过面向基因组数据训练大型语言模型(LLM),建立了基因组规模的语言模型(GenSLMs),可以学习SARS-CoV-2基因组的进化图景。通过对超过1.1亿个原核生物基因序列进行预训练,在150万个基因组上对SARS-CoV-2的特定模型进行微调,结果表明GenSLM能准确和快速地识别令人担忧的变体。GenSLM代表了第一批全基因组规模的基础模型之一,可以推广到其他预测任务。本文展示了GenSLMs在基于GPU的超级计算机和AI硬件加速器上的扩展性,在训练运行中实现了超过1.54 zettaflops。本文介绍了在跟踪SARS-CoV-2的进化动态中研究GenSLMs所获得的初步科学见解,并指出它在大型生物数据上的全部潜力还有待实现。
Our work seeks to transform how new and emergent variants of pandemic causing viruses, specially SARS-CoV-2, are identified and classified. By adapting large language models (LLMs) for genomic data, we build genome-scale language models (GenSLMs) which can learn the evolutionary landscape of SARS-CoV-2 genomes. By pretraining on over 110 million prokaryotic gene sequences, and then finetuning a SARS-CoV-2 specific model on 1.5 million genomes, we show that GenSLM can accurately and rapidly identify variants of concern. Thus, to our knowledge, GenSLM represents one of the first whole genome scale foundation models which can generalize to other prediction tasks. We demonstrate the scaling of GenSLMs on both GPU-based supercomputers and AI-hardware accelerators, achieving over 1.54 zettaflops in training runs. We present initial scientific insights gleaned from examining GenSLMs in tracking the evolutionary dynamics of SARS-CoV-2, noting that its full potential on large biological data is yet to be realized.
https://biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.10.10.511571v1

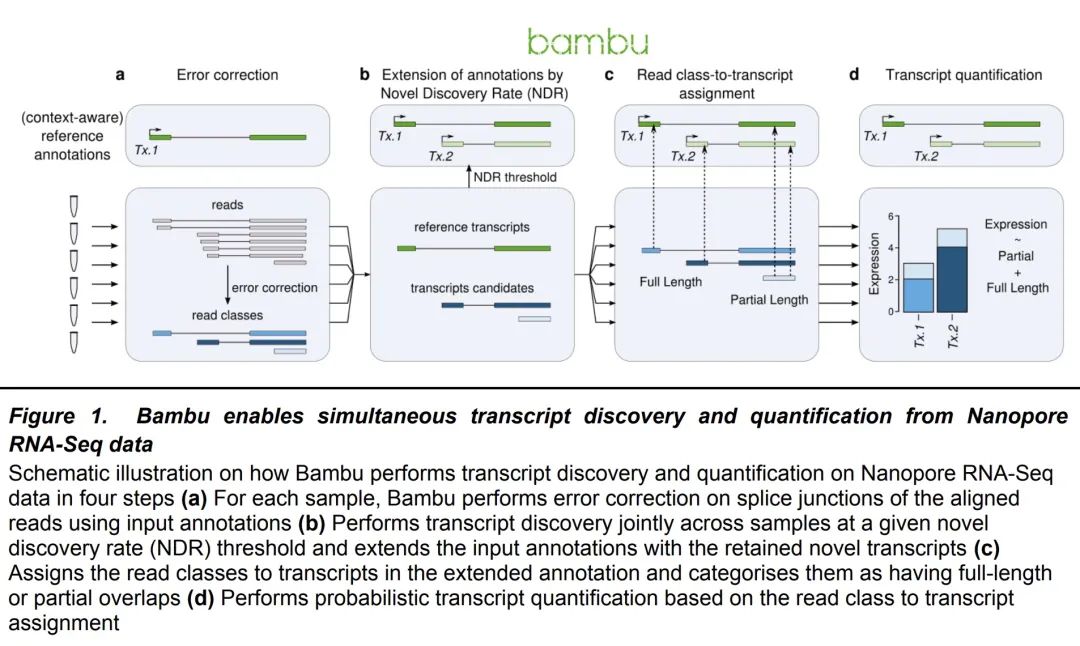
5、[LG] Context-Aware Transcript Quantification from Long Read RNA-Seq data with Bambu
Y Chen, AD Sim, YK Wan, K Yeo, JJX Lee, MH Ling…
[Genome Institute of Singapore & University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill]
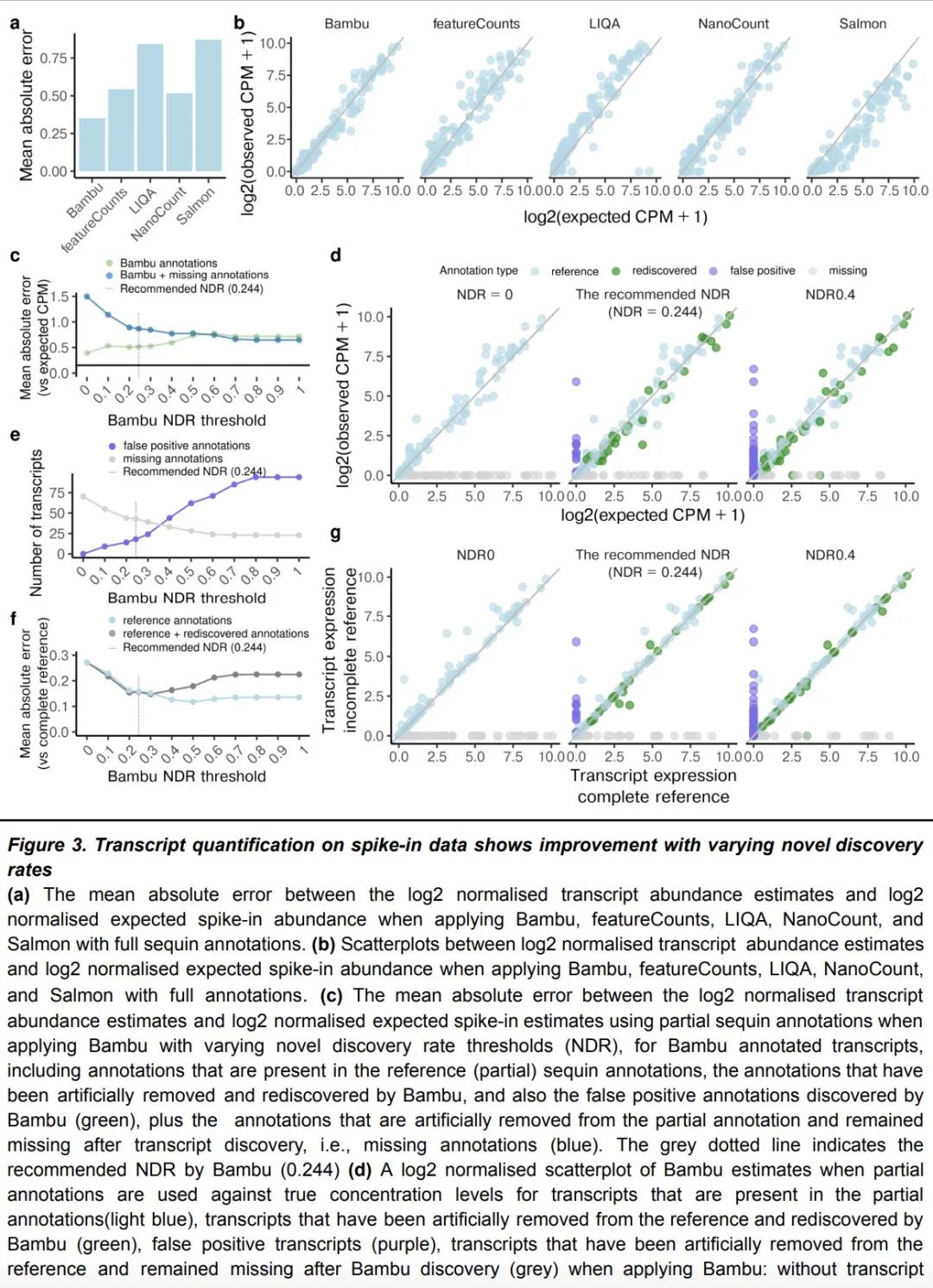
基于Bambu的长读RNA-Seq数据上下文感知转录量化。大多数转录量化方法依赖于固定的参考标注。然而,转录组是动态的,根据不同的环境,这种静态标注包含一些基因的非活性异构体,而对其他基因则是不完整的。为解决该问题,本文开发了Bambu,一种执行基于机器学习的转录发现方法,以便利用长读RNA-Seq数据对感兴趣的环境进行针对性量化。为了识别新的转录本,Bambu采用了一个以精度为重点的阈值,称为新颖发现率(NDR),用一个可解释的参数取代了任意的每样本阈值。Bambu保留了全长和独特的读数,从而能在非活性异构体存在的情况下进行准确的量化。与现有的转录本发现方法相比,Bambu在不牺牲灵敏度的情况下实现了更高的精度。本文表明,上下文感知标注提高了对新的和已知转录的丰度估计。将Bambu应用于人类胚胎干细胞,对重复的HERVH-LTR7逆转录基因的异构体进行量化,证明其有能力估计特定于相关上下文的转录物表达。
Most approaches to transcript quantification rely on fixed reference annotations. However, the transcriptome is dynamic, and depending on the context, such static annotations contain inactive isoforms for some genes while they are incomplete for others. To address this, we have developed Bambu, a method that performs machine-learning based transcript discovery to enable quantification specific to the context of interest using long-read RNA-Seq data. To identify novel transcripts, Bambu employs a precision-focused threshold referred to as the novel discovery rate (NDR), which replaces arbitrary per-sample thresholds with a single interpretable parameter. Bambu retains the full-length and unique read counts, enabling accurate quantification in presence of inactive isoforms. Compared to existing methods for transcript discovery, Bambu achieves greater precision without sacrificing sensitivity. We show that context-aware annotations improve abundance estimates for both novel and known transcripts. We apply Bambu to human embryonic stem cells to quantify isoforms from repetitive HERVH-LTR7 retrotransposons, demonstrating the ability to estimate transcript expression specific to the context of interest.
https://biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.11.14.516358v2

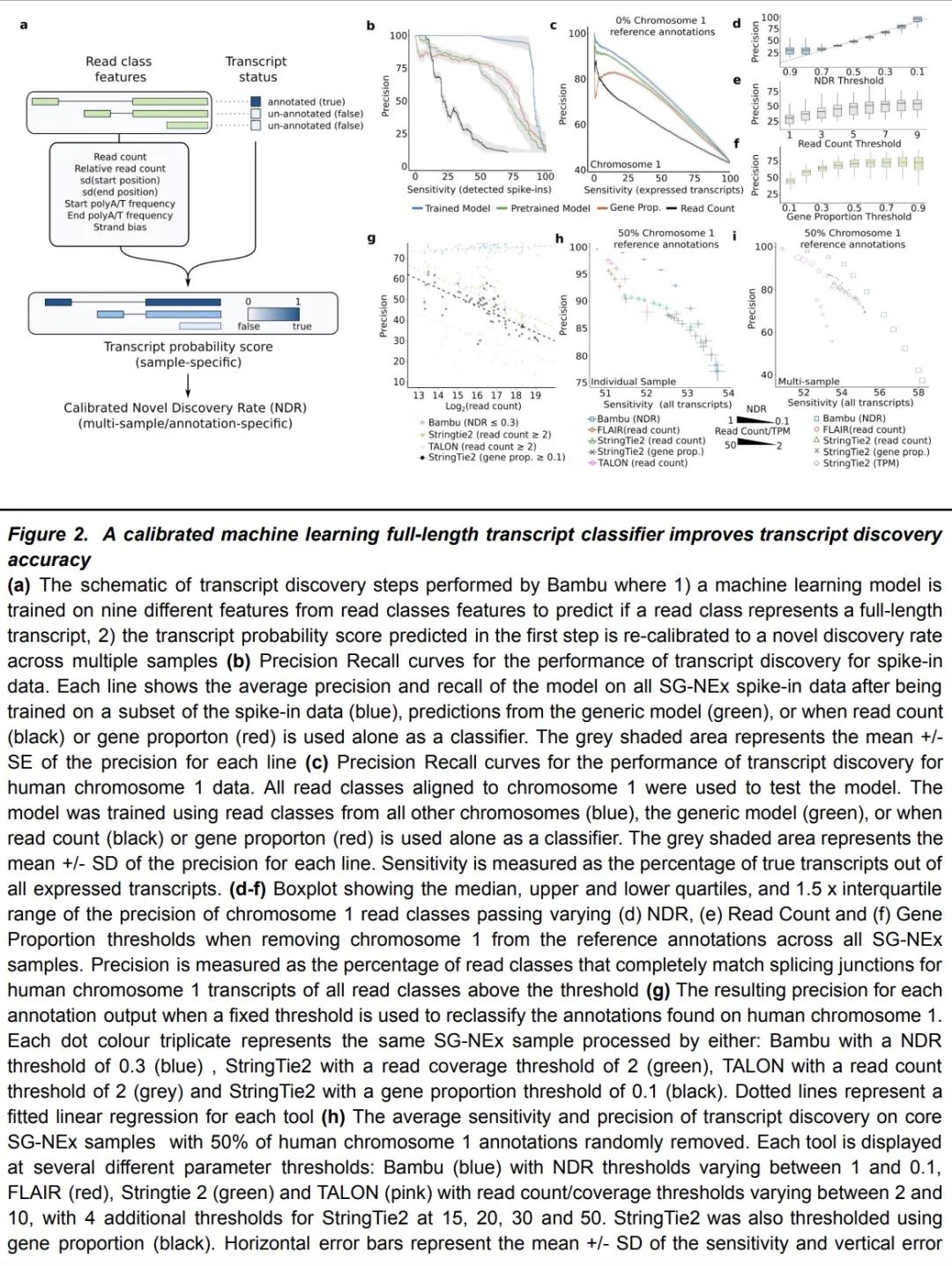
另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[SI] Between News and History: Identifying Networked Topics of Collective Attention on Wikipedia
新闻与历史:维基百科集体关注网络化主题的有效识别
P Gildersleve...
[London School of Economics and Political Science & University of Oxford & University College Dublin]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.07616

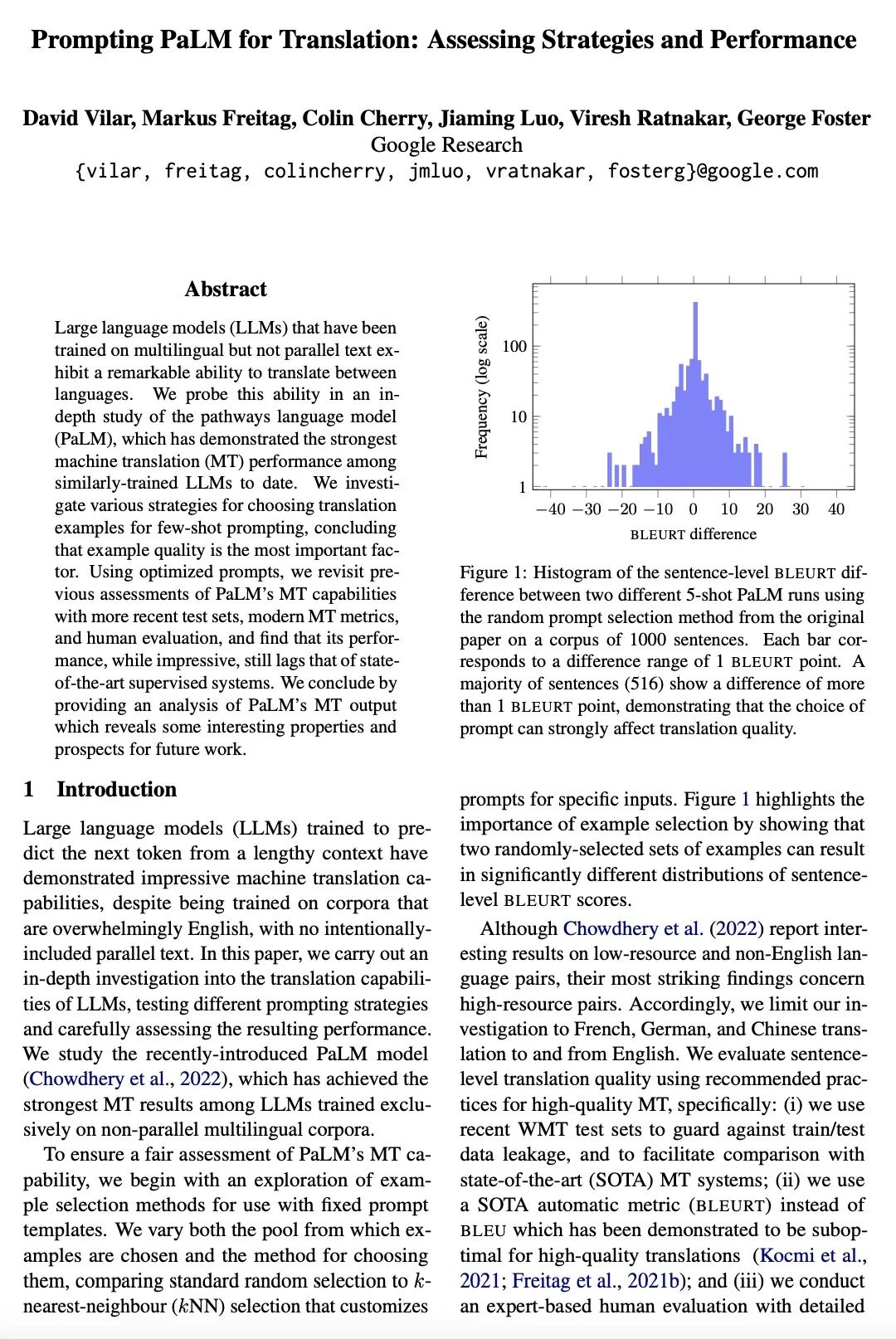
[CL] Prompting PaLM for Translation: Assessing Strategies and Performance
提示PaLM进行翻译:评估策略与性能
D Vilar, M Freitag, C Cherry, J Luo, V Ratnakar, G Foster
[Google Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.09102
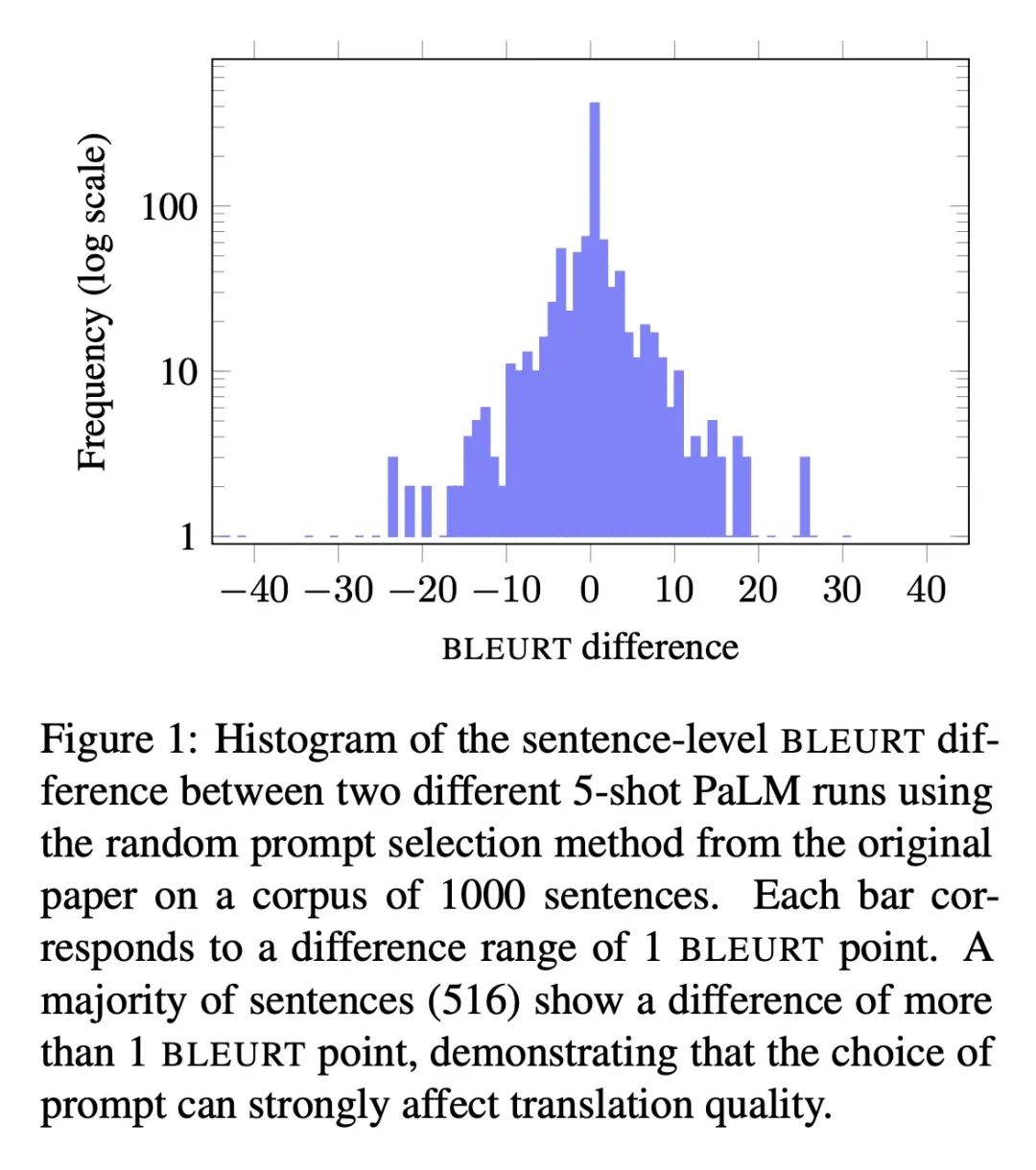
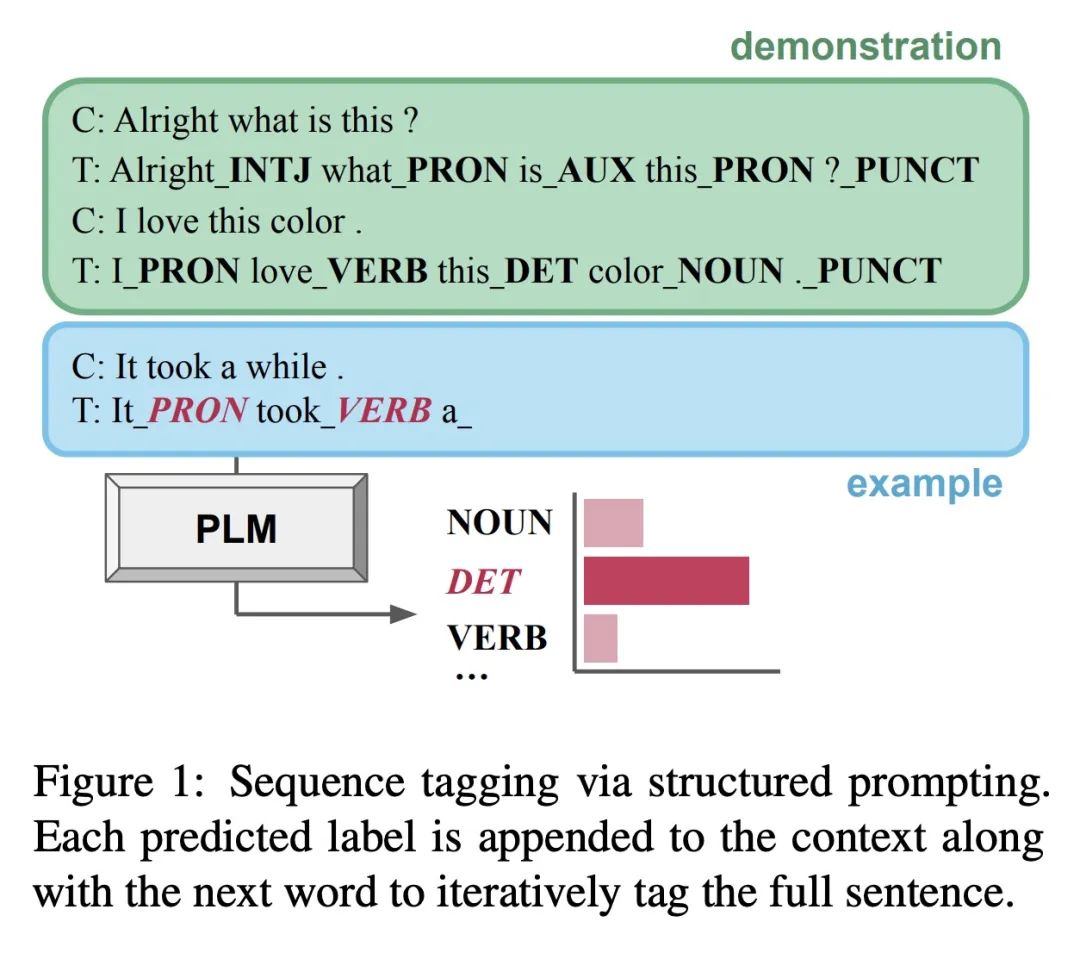
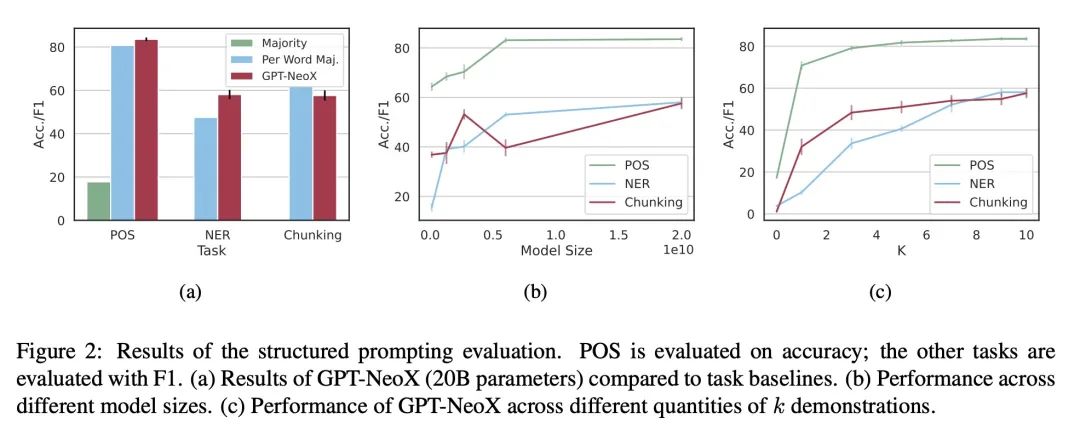
[CL] Prompting Language Models for Linguistic Structure
面向语言结构的提示语言模型
T Blevins, H Gonen, L Zettlemoyer
[University of Washington]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.07830

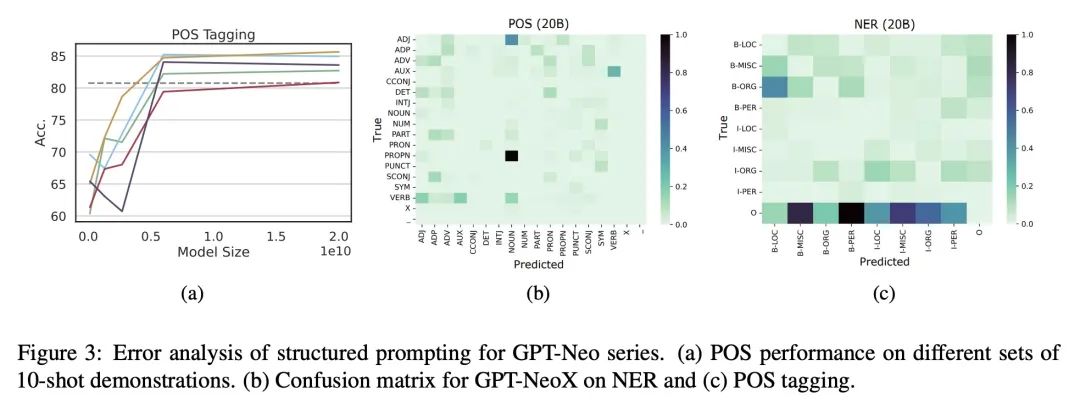
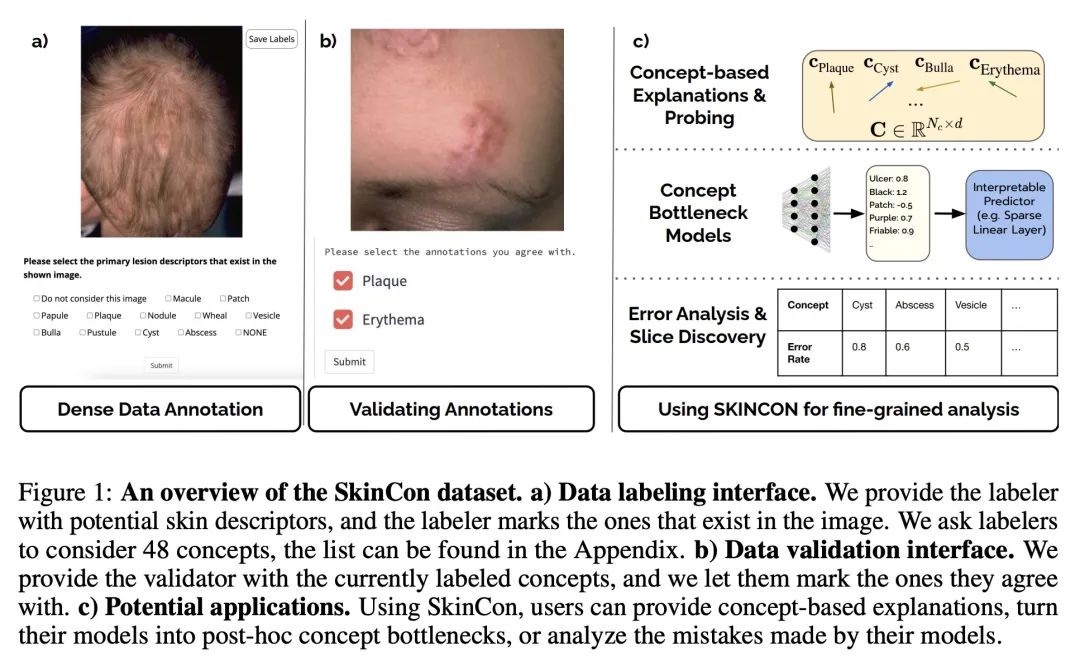
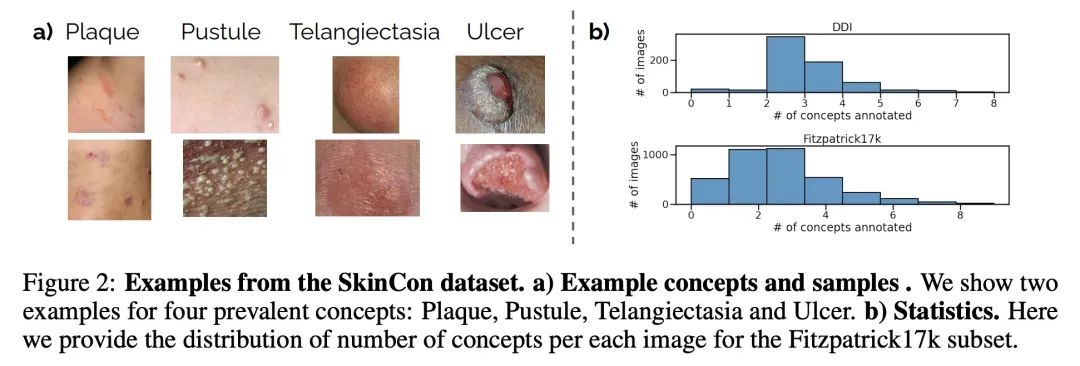
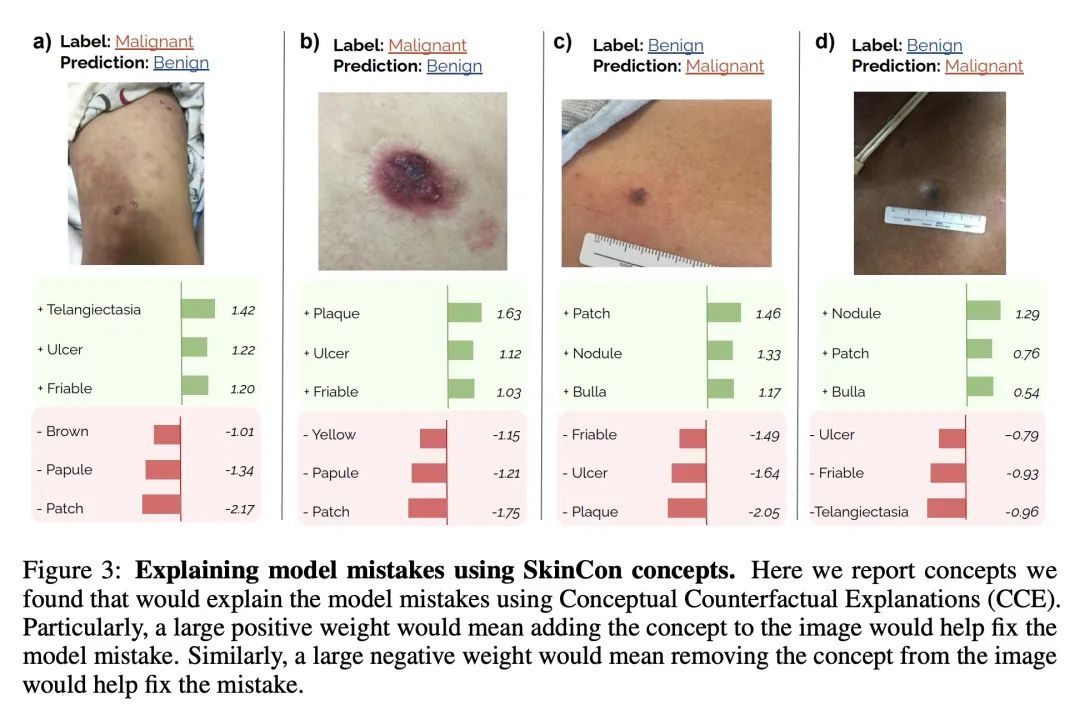
[CV] SkinCon: A skin disease dataset densely annotated by domain experts for fine-grained debugging and analysis
SkinCon:面向细粒度调试与分析的领域专家密集标注皮肤病数据集
R Daneshjou, M Yuksekgonul, ZR Cai…
[Stanford University]
https://openreview.net/forum?id=gud0qopqJc4

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢