转自爱可可爱生活
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 GR - 图形学
摘要:语言模型与战略推理相结合在《外交风云》游戏中达到人类水平、在单个图像或视频上训练扩散模型、基于语言抽象改善内在探索、任意级别描述的语义图像合成、面向目标发现的复数值自编码器、基于人工反馈强化学习改进多模态交互式智能体、人工评价的原真性差距、面向图像描述的离散扩散模型探索、用基于图的深度生成模型从头设计PROTAC
1、[LG] Human-level play in the game of Diplomacy by combining language models with strategic reasoning
A Bakhtin, N Brown, E Dinan...
[Meta AI(FAIR)]
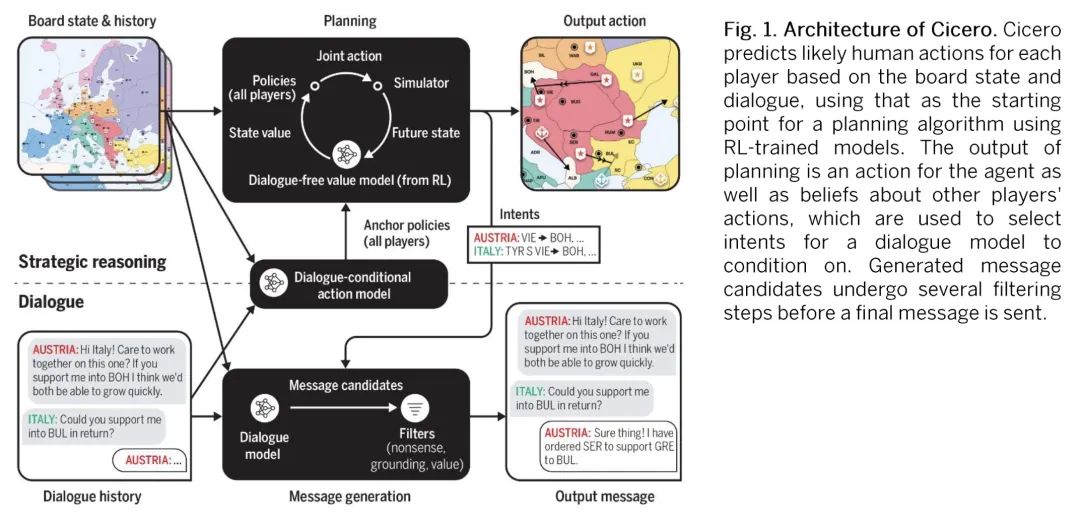
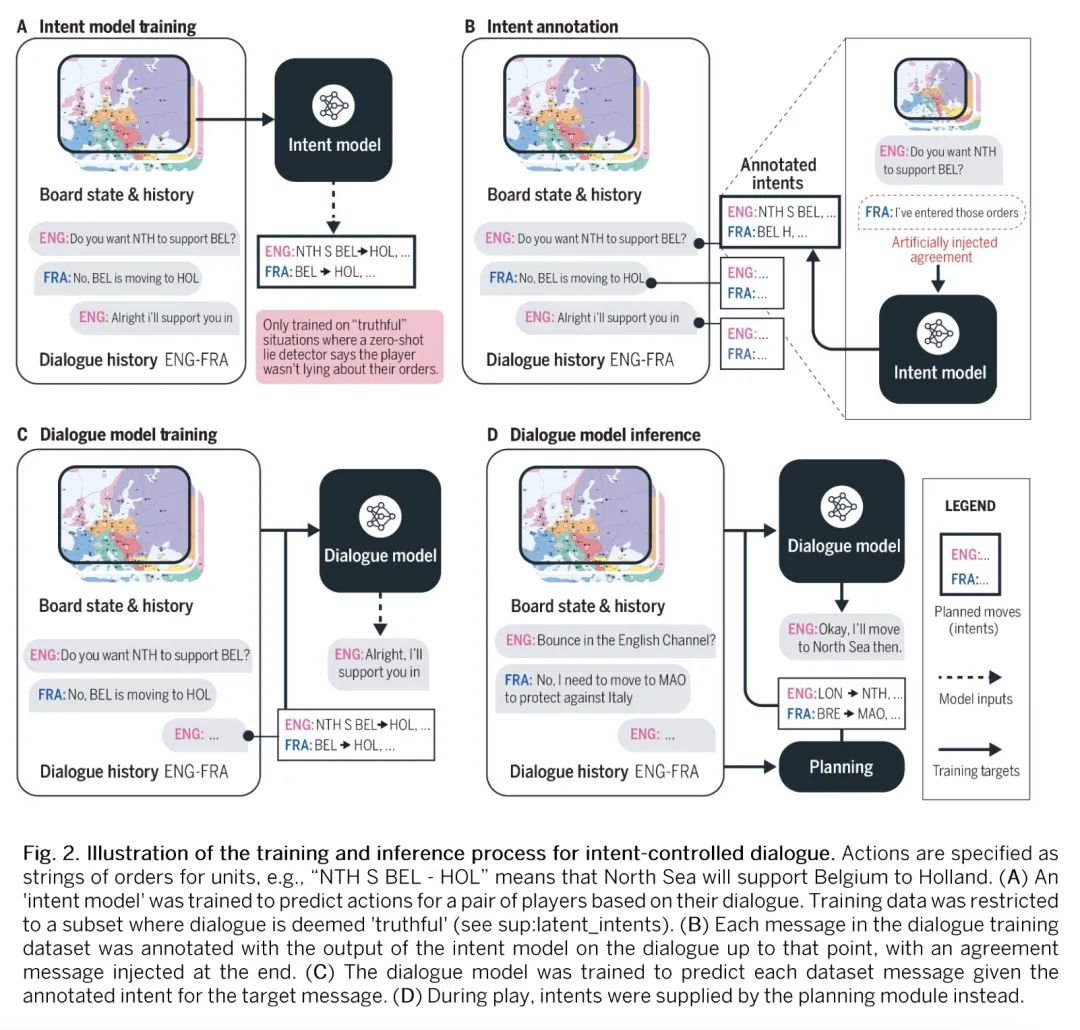
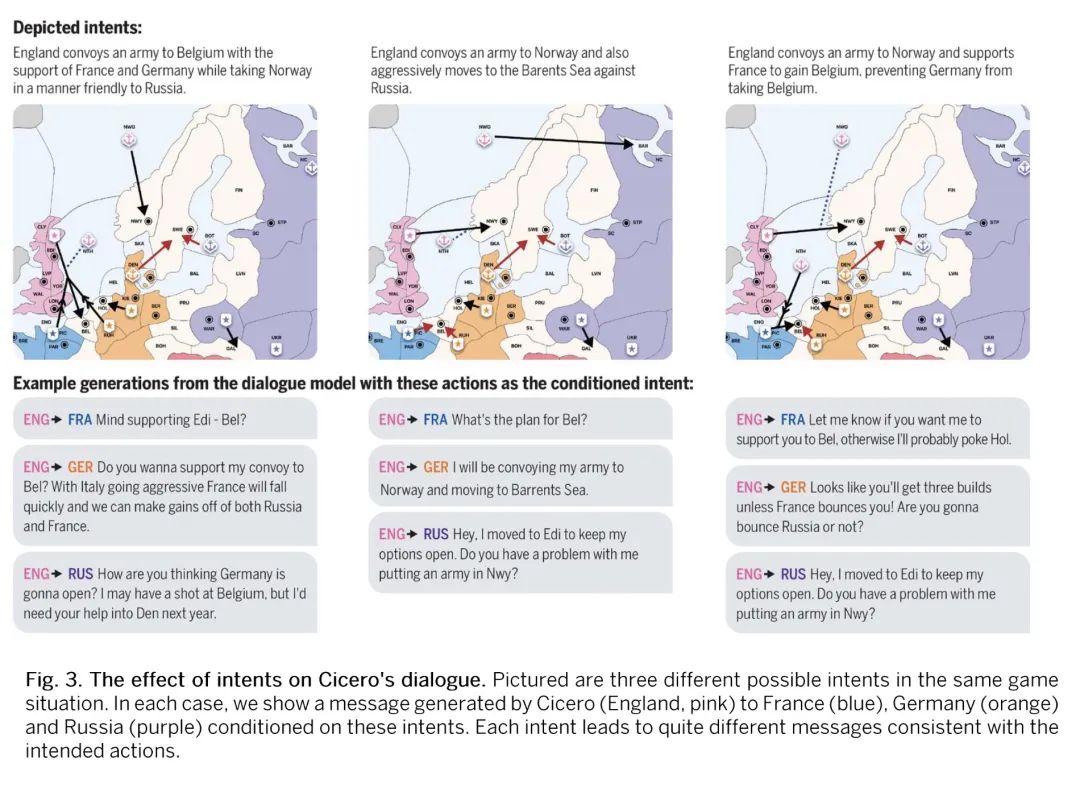
语言模型与战略推理相结合在《外交风云》游戏中达到人类水平。尽管在训练AI系统模仿人类语言方面取得了很大进展,但建立在交互环境中用语言与人类有意沟通的智能体仍然是一个重大挑战。本文提出Cicero,第一个在《外交风云(Diplomacy)》中达到人类水平的AI智能体,《外交风云》是一个涉及合作和竞争的战略游戏,强调七个玩家之间的自然语言谈判和战术协调。Cicero将语言模型与规划和强化学习算法结合起来,从其对话中推断出玩家的信念和意图,并产生对话以实现其规划。在匿名的在线外交风云的40场比赛中,Cicero取得了比人类玩家的平均分数高一倍以上的成绩,并且在参加过不止一场比赛的参与者中排名前10%。
Despite much progress in training AI systems to imitate human language, building agents that use language to communicate intentionally with humans in interactive environments remains a major challenge. We introduce Cicero, the first AI agent to achieve human-level performance in Diplomacy, a strategy game involving both cooperation and competition that emphasizes natural language negotiation and tactical coordination between seven players. Cicero integrates a language model with planning and reinforcement learning algorithms by inferring players' beliefs and intentions from its conversations and generating dialogue in pursuit of its plans. Across 40 games of an anonymous online Diplomacy league, Cicero achieved more than double the average score of the human players and ranked in the top 10% of participants who played more than one game.
https://science.org/doi/10.1126/science.ade9097

2、[CV] SinFusion: Training Diffusion Models on a Single Image or Video
Y Nikankin, N Haim, M Irani
[Weizmann Institute of Science]
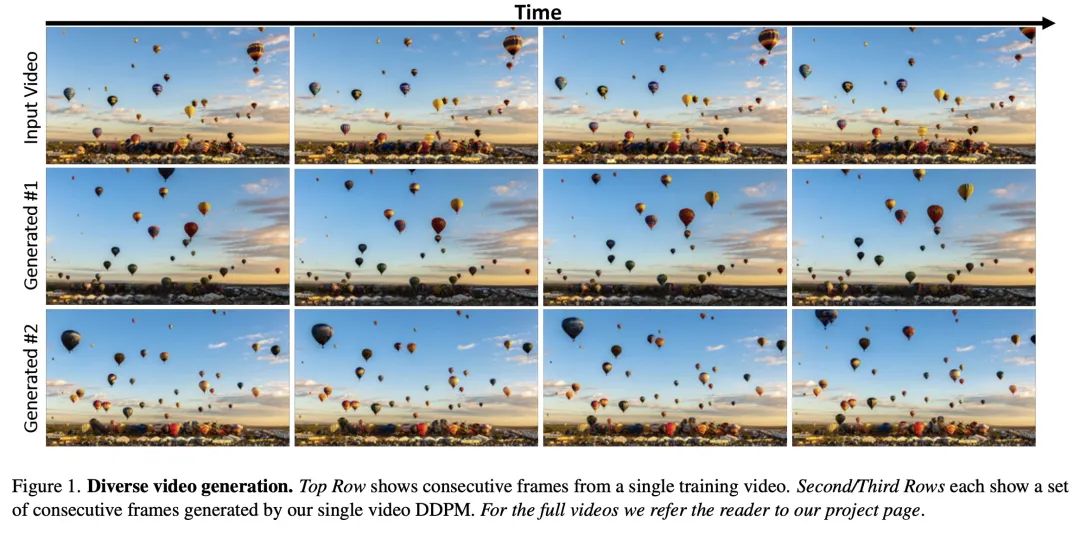
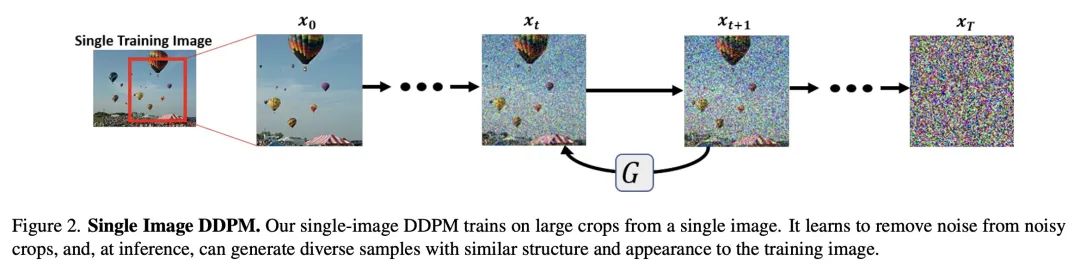
SinFusion: 在单个图像或视频上训练扩散模型。扩散模型在图像和视频生成方面取得了巨大的进步,在质量和多样性方面超过了GAN。然而,它们通常是在非常大的数据集上训练的,并不自然适应于处理一个给定的输入图像或视频。本文展示了如何通过在单个输入图像或视频上训练扩散模型来解决该问题。所提出的图像/视频专用扩散模型(SinFusion)学习单个图像或视频的外观和动态,同时利用扩散模型的调节能力。可以解决广泛的图像/视频特定操纵任务。特别是,该模型可以从少数帧中学习单个输入视频的运动和动态,可以生成同一动态场景的不同的新视频样本,将短视频推断为长视频(在时间上向前和向后),并进行视频升采样。当对单个图像进行训练时,所提出模型在各种图像处理任务中表现出与之前的单图像模型相当的性能和能力。
Diffusion models exhibited tremendous progress in image and video generation, exceeding GANs in quality and diversity. However, they are usually trained on very large datasets and are not naturally adapted to manipulate a given input image or video. In this paper we show how this can be resolved by training a diffusion model on a single input image or video. Our image/video-specific diffusion model (SinFusion) learns the appearance and dynamics of the single image or video, while utilizing the conditioning capabilities of diffusion models. It can solve a wide array of image/video-specific manipulation tasks. In particular, our model can learn from few frames the motion and dynamics of a single input video. It can then generate diverse new video samples of the same dynamic scene, extrapolate short videos into long ones (both forward and backward in time) and perform video upsampling. When trained on a single image, our model shows comparable performance and capabilities to previous single-image models in various image manipulation tasks.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.11743


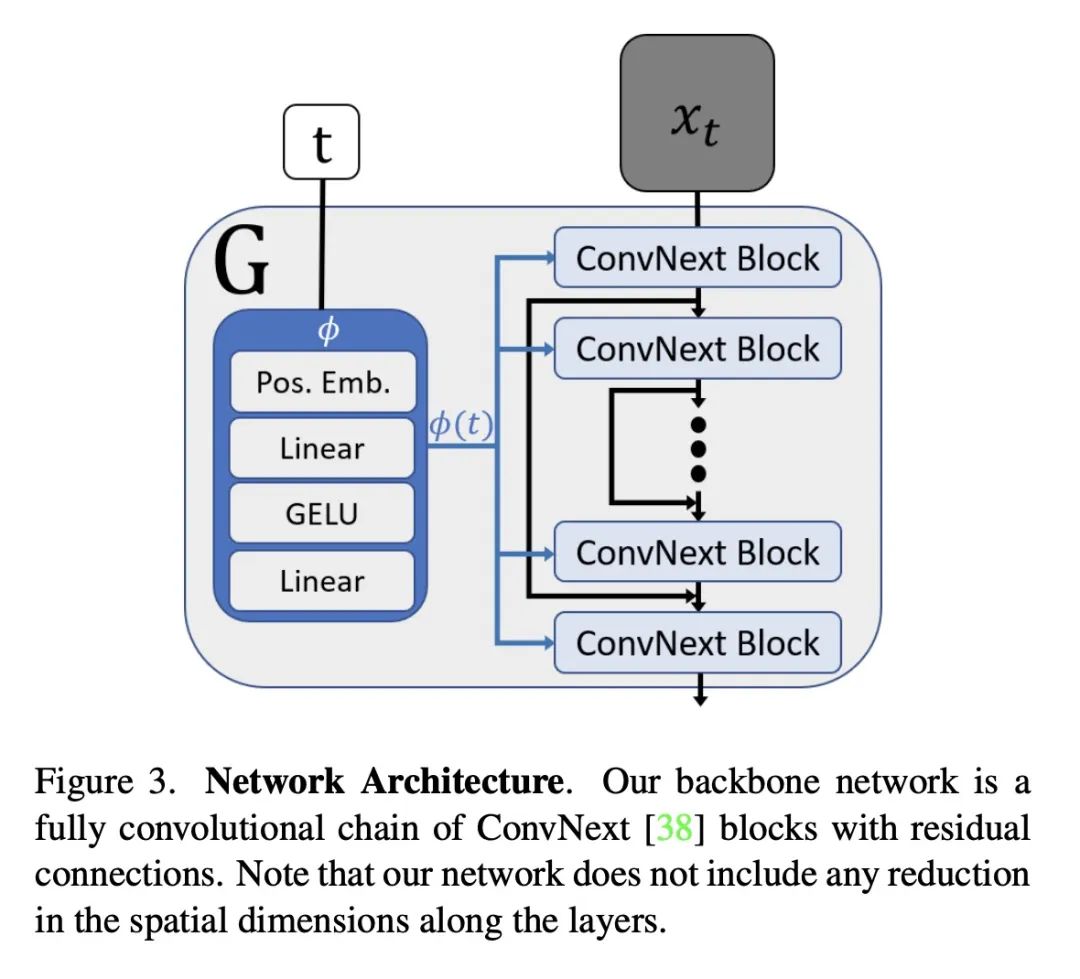
3、[LG] Improving Intrinsic Exploration with Language Abstractions
J Mu, V Zhong, R Raileanu, M Jiang, N Goodman, T Rocktäschel, E Grefenstette
[Stanford University & University of Washington & Meta AI]
基于语言抽象改善内在探索。当奖励稀少时,强化学习(RL)智能体特别难以训练。一个常见的解决方案是用内在奖励来鼓励代理探索其环境。然而,最近的内在探索方法经常用基于状态的新奇度量,奖励低层次的探索,可能无法扩展到需要更多抽象技能的领域。本文将自然语言作为一种一般媒介来探索,以突出环境中的相关抽象概念。与之前的工作不同,本文通过直接扩展(并相较于)有竞争力的内在探索基线,评估语言是否可以改善现有的探索方法。这些基于语言的变体在MiniGrid和MiniHack环境套件的13个具有挑战性的任务中的表现优于其非语言形式45-85%。
Reinforcement learning (RL) agents are particularly hard to train when rewards are sparse. One common solution is to use intrinsic rewards to encourage agents to explore their environment. However, recent intrinsic exploration methods often use state-based novelty measures which reward low-level exploration and may not scale to domains requiring more abstract skills. Instead, we explore natural language as a general medium for highlighting relevant abstractions in an environment. Unlike previous work, we evaluate whether language can improve over existing exploration methods by directly extending (and comparing to) competitive intrinsic exploration baselines: AMIGo (Campero et al., 2021) and NovelD (Zhang et al., 2021). These language-based variants outperform their non-linguistic forms by 45-85% across 13 challenging tasks from the MiniGrid and MiniHack environment suites.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2202.08938

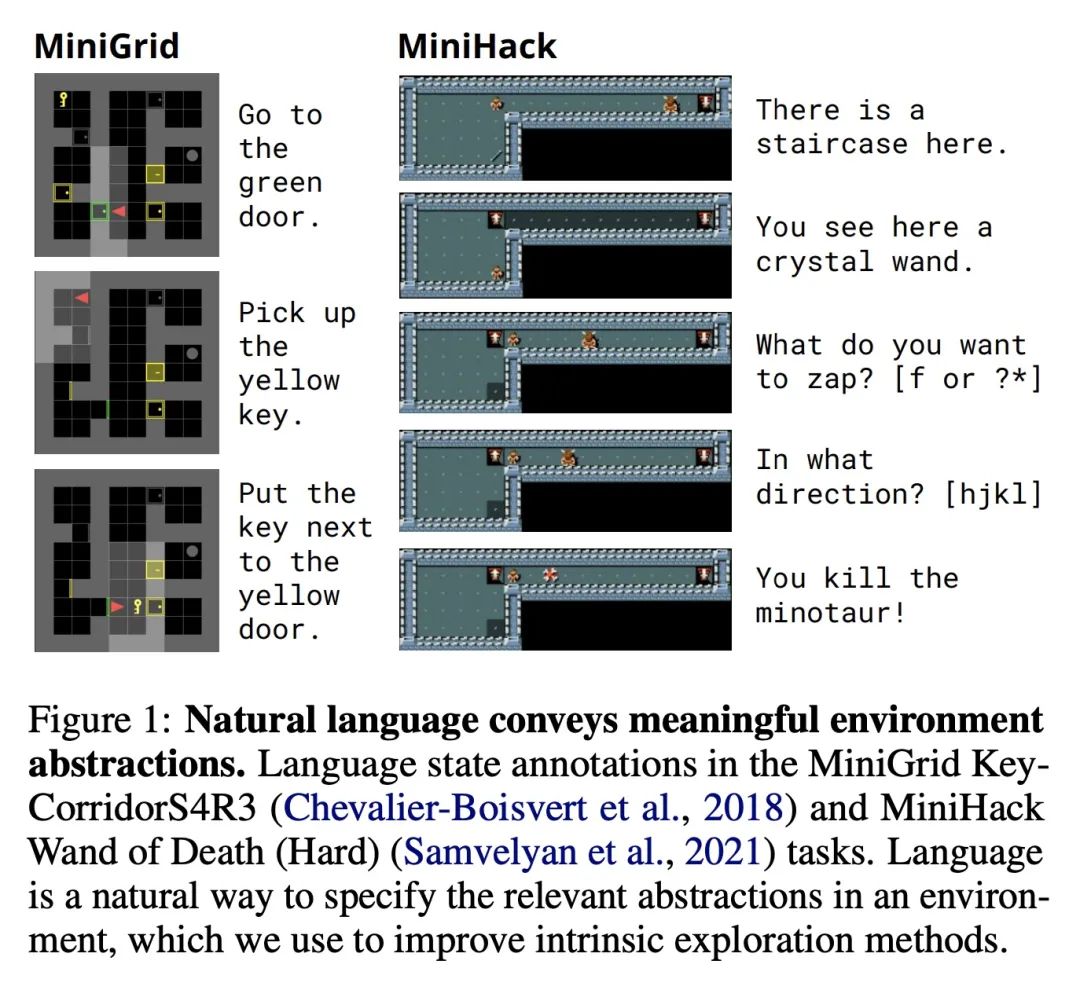
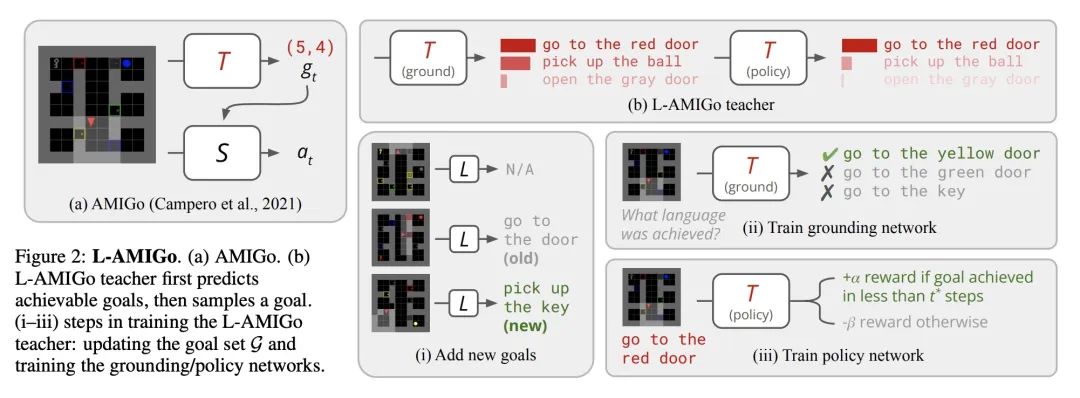
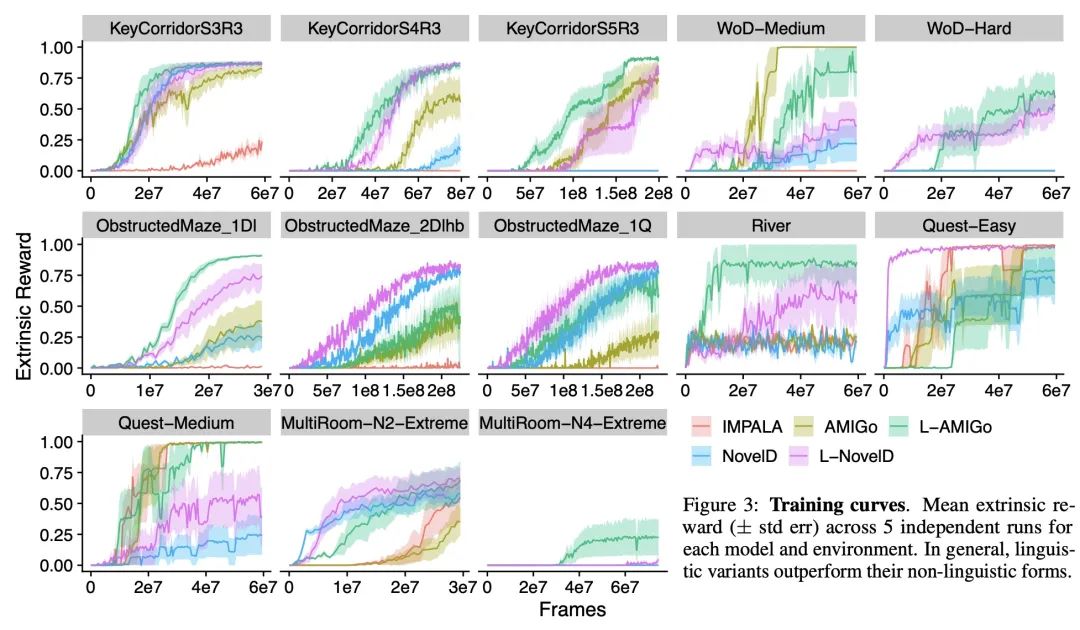
4、[CV] SceneComposer: Any-Level Semantic Image Synthesis
Y Zeng, Z Lin, J Zhang, Q Liu, J Collomosse, J Kuen, V M. Patel
[Johns Hopkins University & Adobe Research]
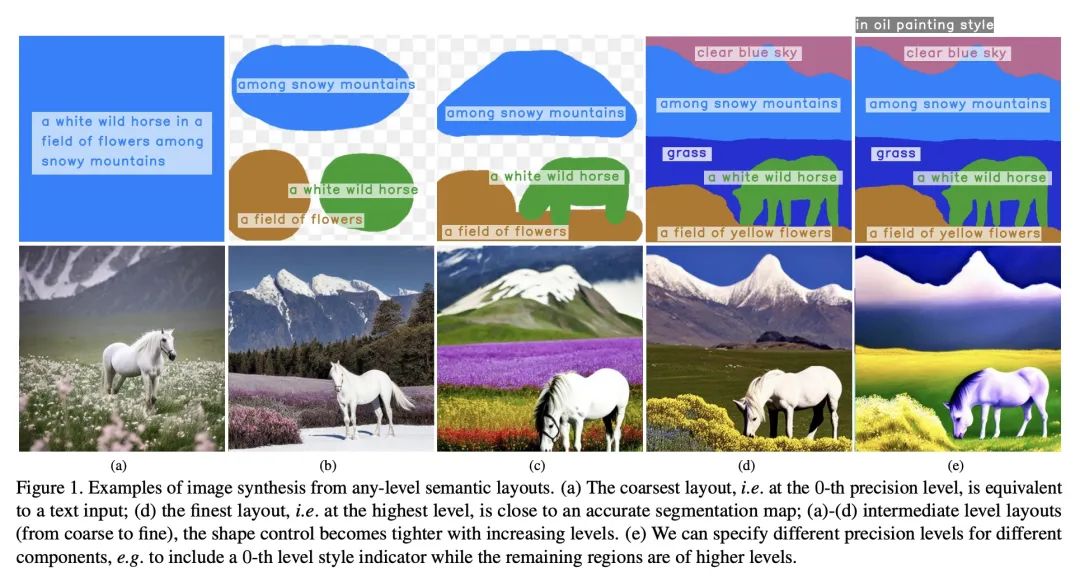
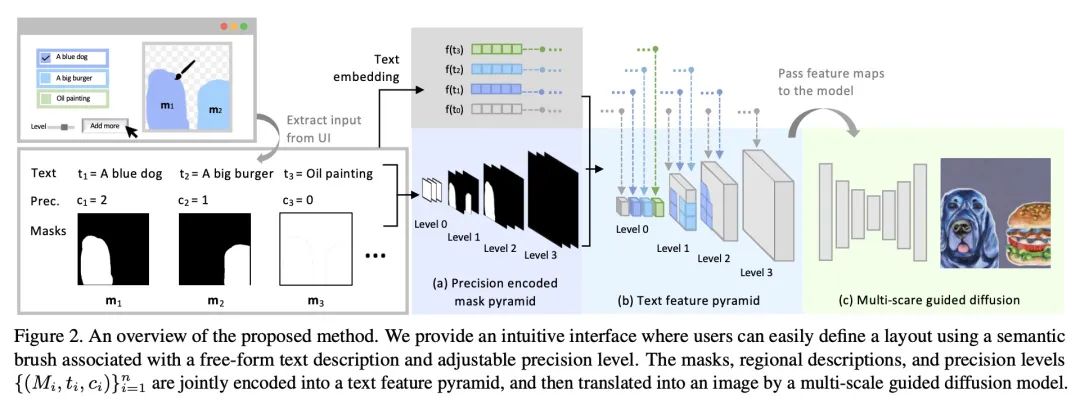
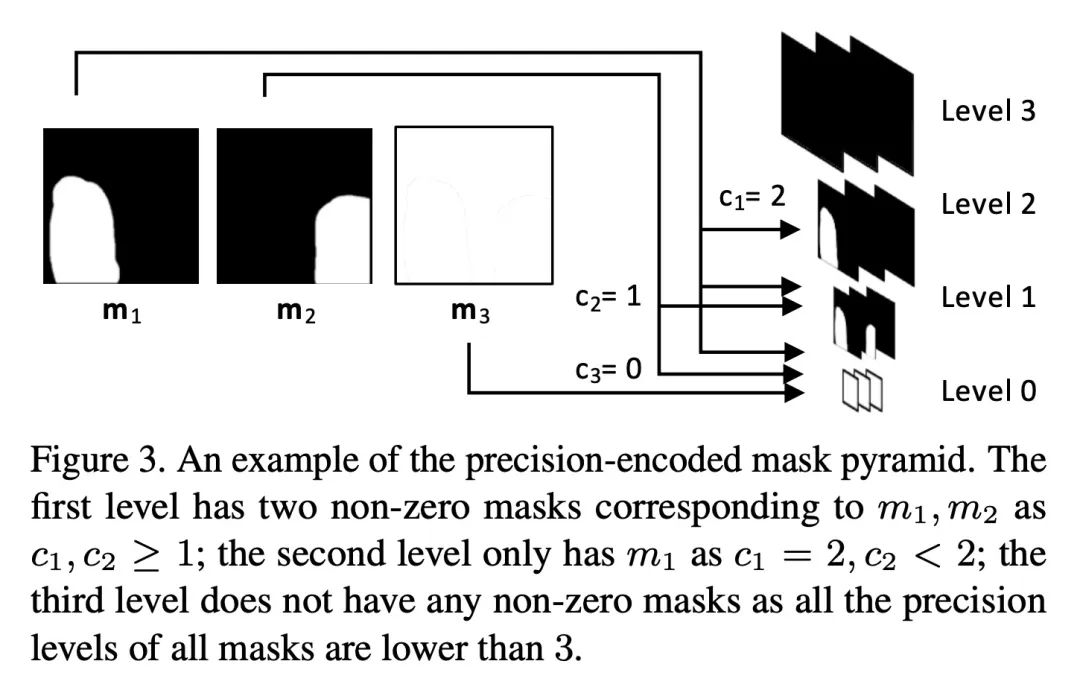
SceneComposer: 任意级别描述的语义图像合成。本文提出一种新框架,用于从任何精度级别的语义布局中进行条件性图像合成,范围从纯文本到具有精确形状的2D语义画布。更具体地说,输入布局由一个或多个语义区域组成,这些区域具有自由形式的文本描述和可调整的精度级,可以根据所需的可控性来设置。该框架在没有形状信息的情况下,在最低层次上自然削减为文本到图像(T2I),而在最高层则成为分割到图像(S2I)。通过支持两者之间的层次,所提出框架可以灵活地帮助不同绘画专长的用户和他们创作工作流程中的不同阶段。本文提出一些新技术来解决这个新设置带来的挑战,包括收集训练数据的管线;一个精确编码的掩码金字塔和一个文本特征图表示,以共同编码精确水平、语义和组成信息;以及一个多尺度引导扩散模型来合成图像。为了评估所提出的方法,本文收集了一个测试数据集,其中包含用户绘制的不同场景和风格的布局。实验结果表明,所提出的方法可以在给定精度下按照布局生成高质量的图像,并且与现有的方法相比更有优势。
We propose a new framework for conditional image synthesis from semantic layouts of any precision levels, ranging from pure text to a 2D semantic canvas with precise shapes. More specifically, the input layout consists of one or more semantic regions with free-form text descriptions and adjustable precision levels, which can be set based on the desired controllability. The framework naturally reduces to text-to-image (T2I) at the lowest level with no shape information, and it becomes segmentation-to-image (S2I) at the highest level. By supporting the levels in-between, our framework is flexible in assisting users of different drawing expertise and at different stages of their creative workflow. We introduce several novel techniques to address the challenges coming with this new setup, including a pipeline for collecting training data; a precision-encoded mask pyramid and a text feature map representation to jointly encode precision level, semantics, and composition information; and a multi-scale guided diffusion model to synthesize images. To evaluate the proposed method, we collect a test dataset containing user-drawn layouts with diverse scenes and styles. Experimental results show that the proposed method can generate high-quality images following the layout at given precision, and compares favorably against existing methods. Project page \url{this https URL}
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.11742

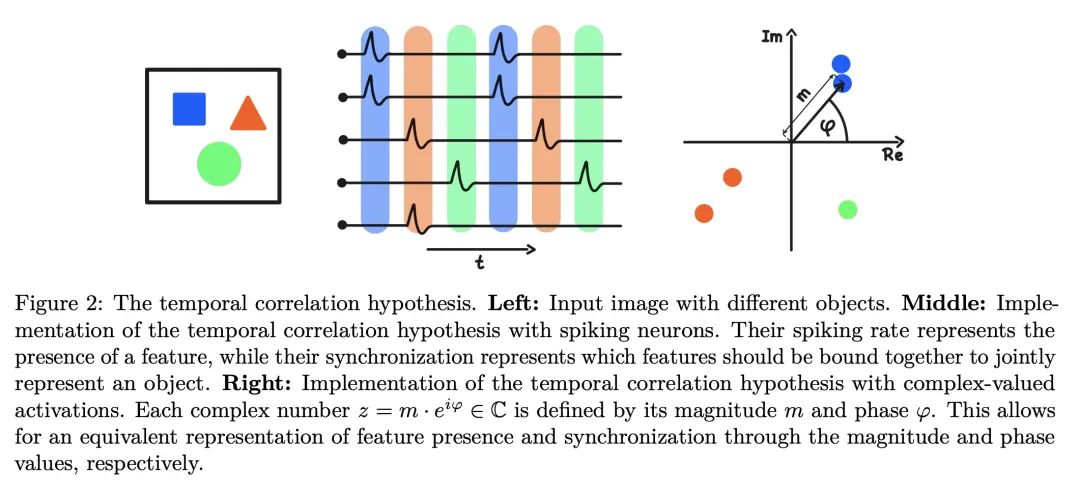
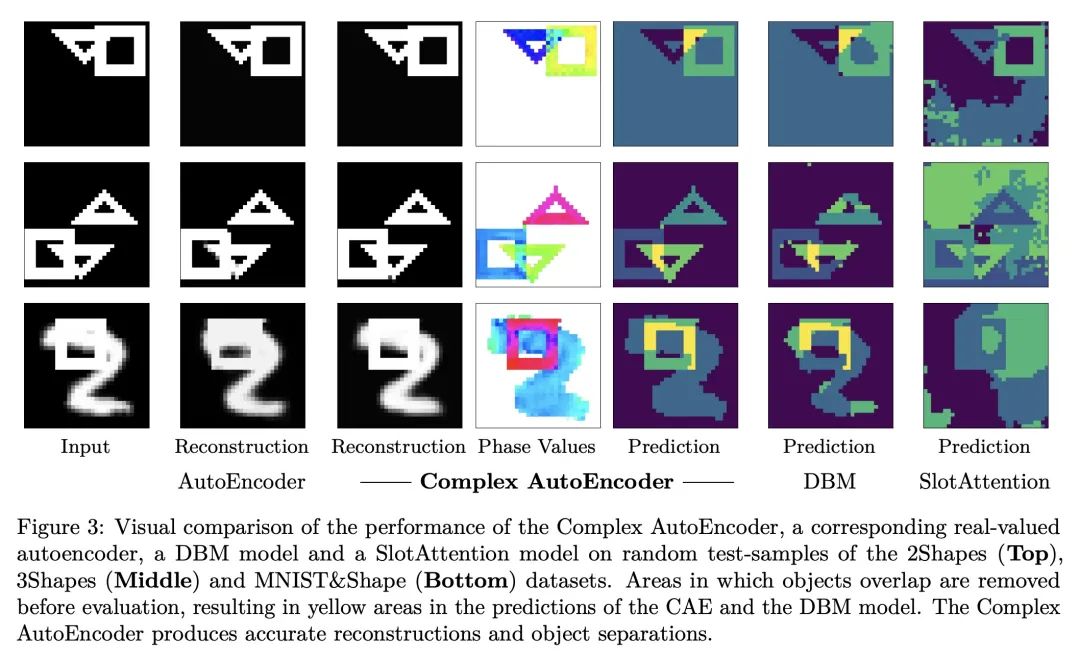
5、[LG] Complex-Valued Autoencoders for Object Discovery
S Löwe, P Lippe, M Rudolph, M Welling
[University of Amsterdam]
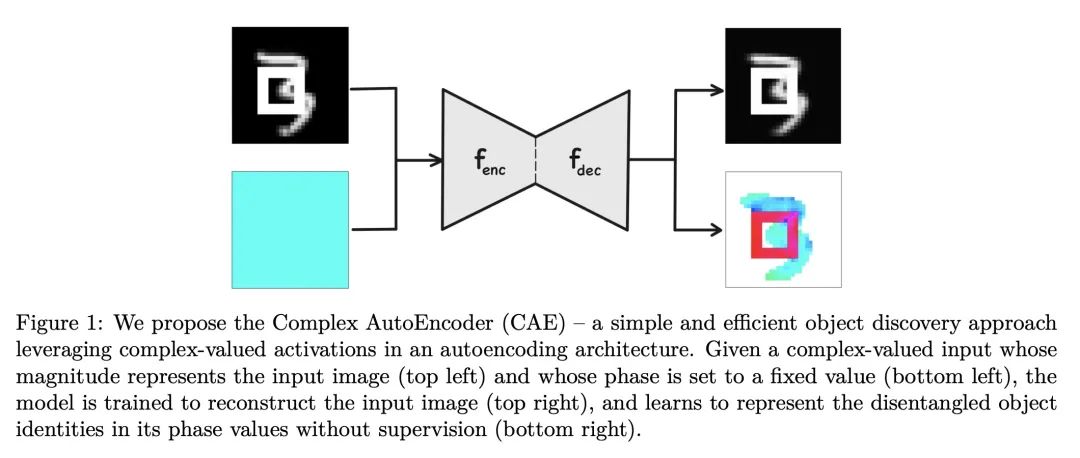
面向目标发现的复数值自编码器。以目标为中心的表示是人类感知的基础,它使我们能对世界进行推理并系统地泛化到新设置下。目前,大多数关于无监督目标发现的工作都集中在基于槽的方法,这些方法明确地将单个物体的潜表示分开。虽然结果很容易解释,但通常需要设计相关的架构。本文提出一种相对简单的方法——复数自编码器(CAE)——创建以目标为中心的分布式表征。遵循一种被认为是生物神经元中目标表示基础的编码方案,其复数值激活代表了两个信息:其大小表达了一种特征的存在,而神经元间的相对相位差表达了哪些特征应该被结合在一起以创建联合目标表示。与之前使用复数值激活来发现目标的方法相比,本文提出一种完全无监督的方法,进行端到端的训练——导致性能和效率的显著提高。本文表明,与最先进的基于槽的方法相比,CAE在简单的多目标数据集上实现了有竞争力的或更好的无监督目标发现性能,同时训练速度快100倍。
Object-centric representations form the basis of human perception, and enable us to reason about the world and to systematically generalize to new settings. Currently, most works on unsupervised object discovery focus on slot-based approaches, which explicitly separate the latent representations of individual objects. While the result is easily interpretable, it usually requires the design of involved architectures. In contrast to this, we propose a comparatively simple approach - the Complex AutoEncoder (CAE) - that creates distributed object-centric representations. Following a coding scheme theorized to underlie object representations in biological neurons, its complex-valued activations represent two messages: their magnitudes express the presence of a feature, while the relative phase differences between neurons express which features should be bound together to create joint object representations. In contrast to previous approaches using complex-valued activations for object discovery, we present a fully unsupervised approach that is trained end-to-end - resulting in significant improvements in performance and efficiency. Further, we show that the CAE achieves competitive or better unsupervised object discovery performance on simple multi-object datasets compared to a state-of-the-art slot-based approach while being up to 100 times faster to train.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.02075

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
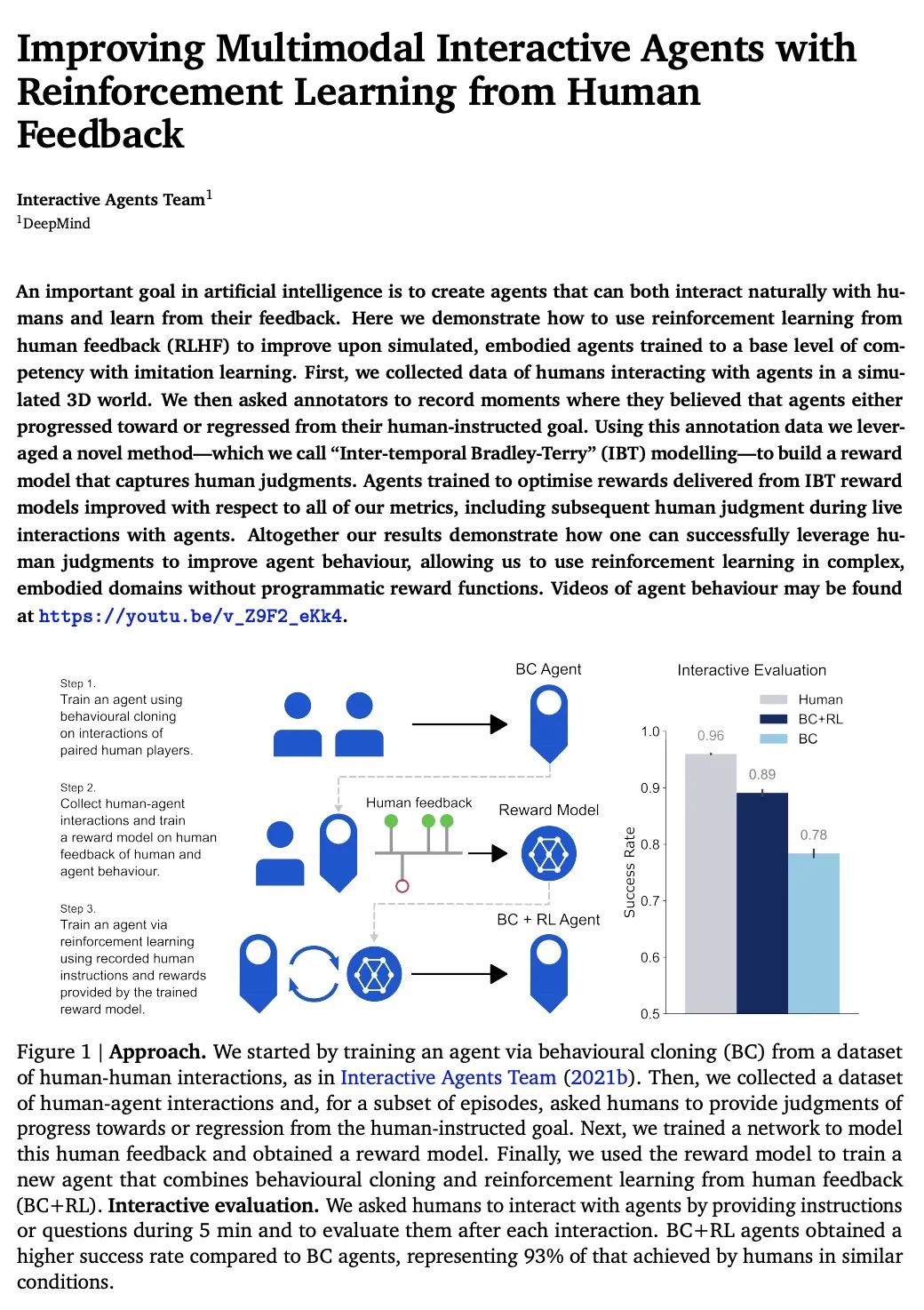
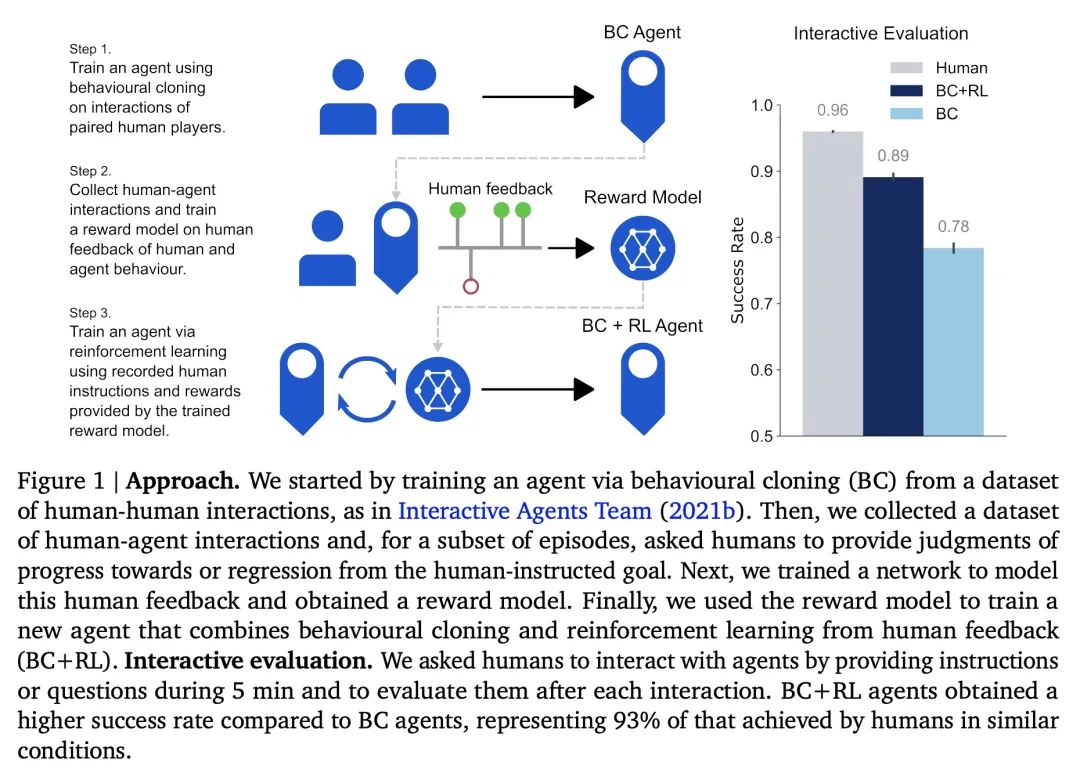
[LG] Improving Multimodal Interactive Agents with Reinforcement Learning from Human Feedback
基于人工反馈强化学习改进多模态交互式智能体
J Abramson, A Ahuja, F Carnevale, P Georgiev...
[DeepMind]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.11602

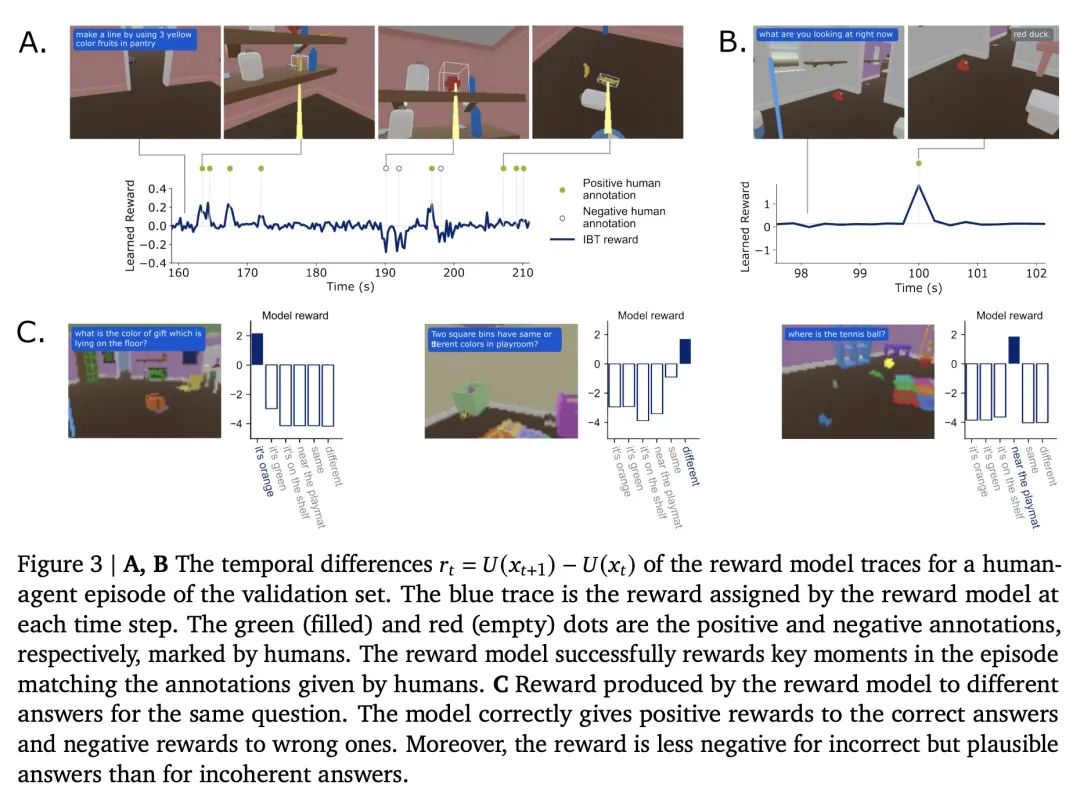
[CL] The Authenticity Gap in Human Evaluation
人工评价的原真性差距
K Ethayarajh, D Jurafsky
[Stanford University]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.11930



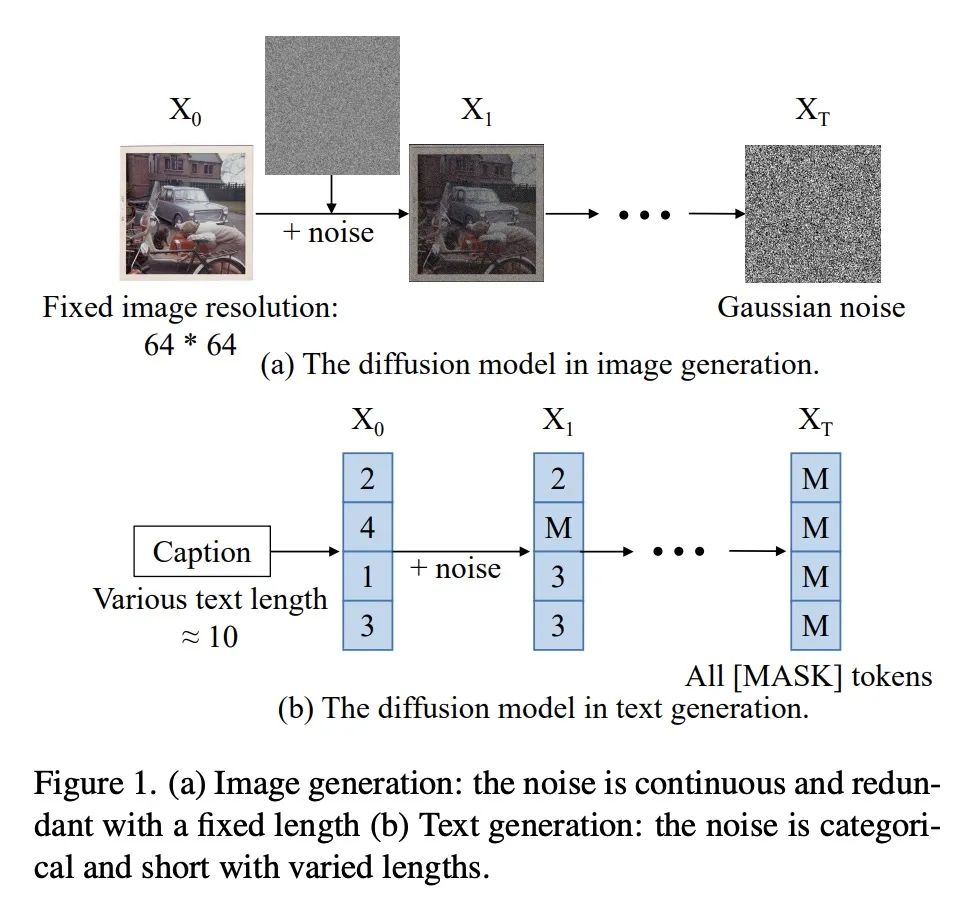
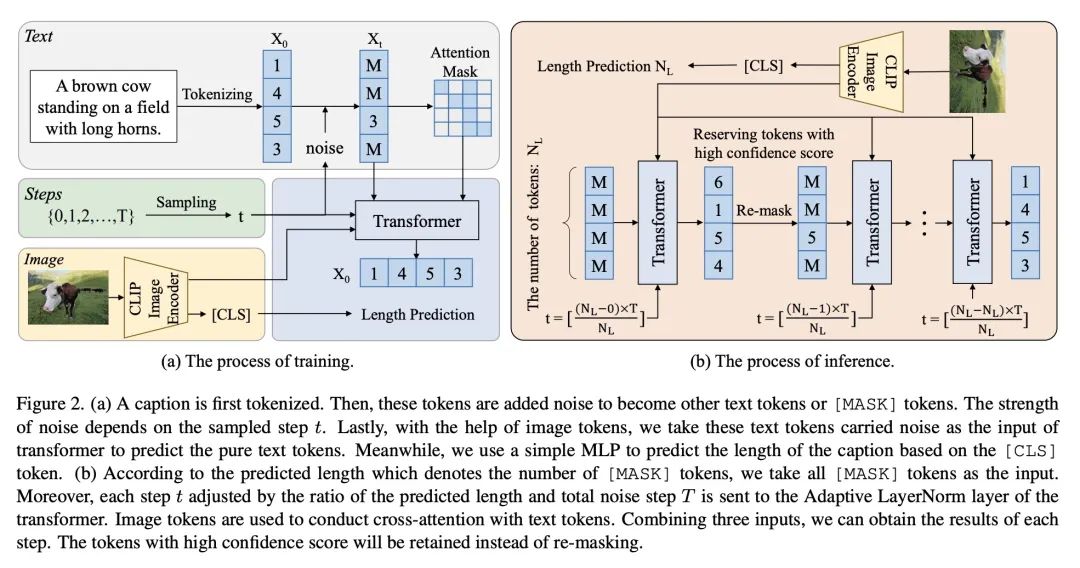
[CV] Exploring Discrete Diffusion Models for Image Captioning
面向图像描述的离散扩散模型探索
Z Zhu, Y Wei, J Wang, Z Gan, Z Zhang, L Wang, G Hua, L Wang, Z Liu, H Hu
[Microsoft & Xi’an Jiaotong University & Tsinghua University]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.11694

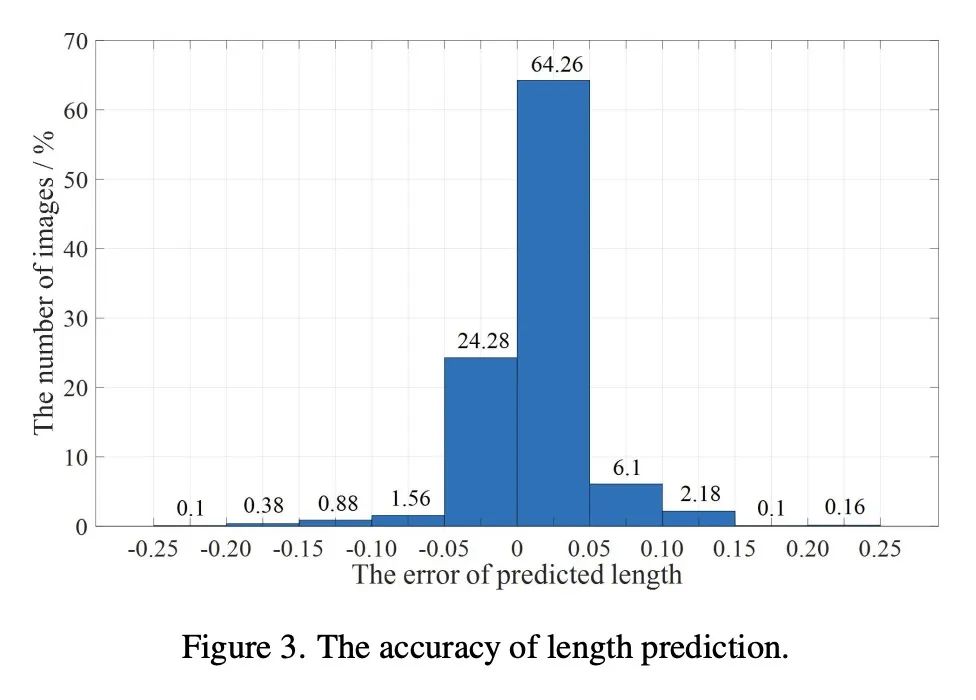
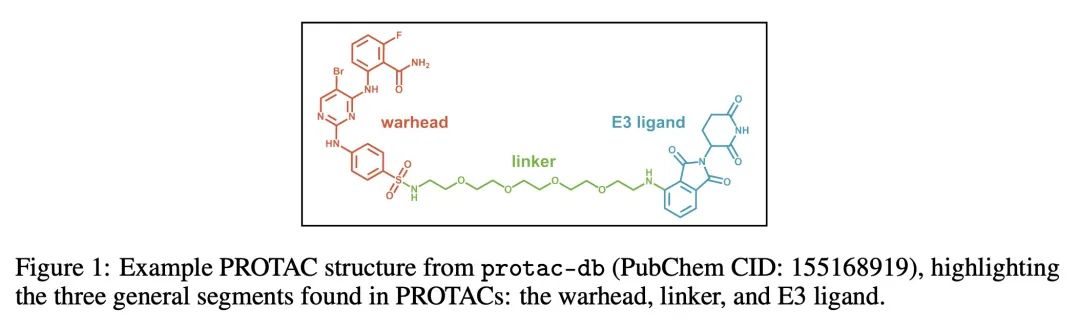
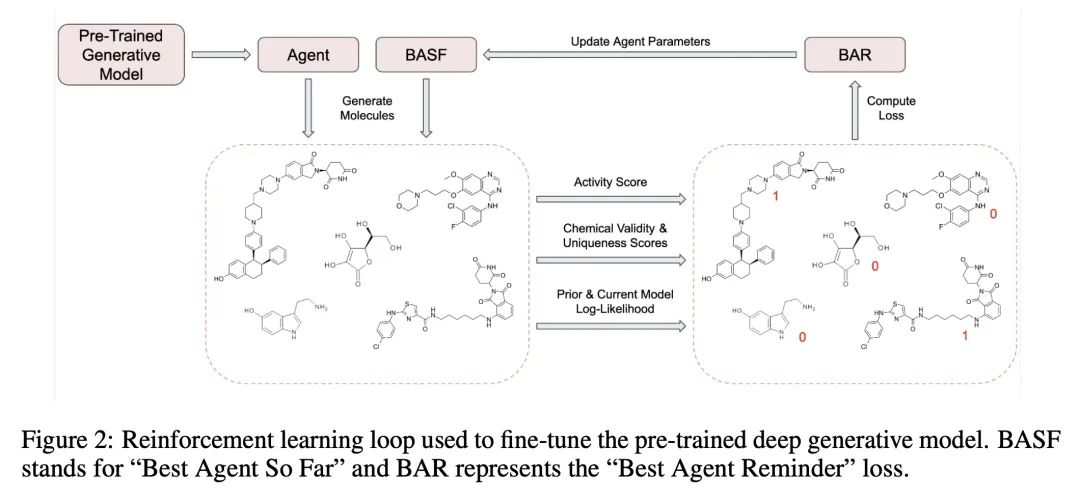
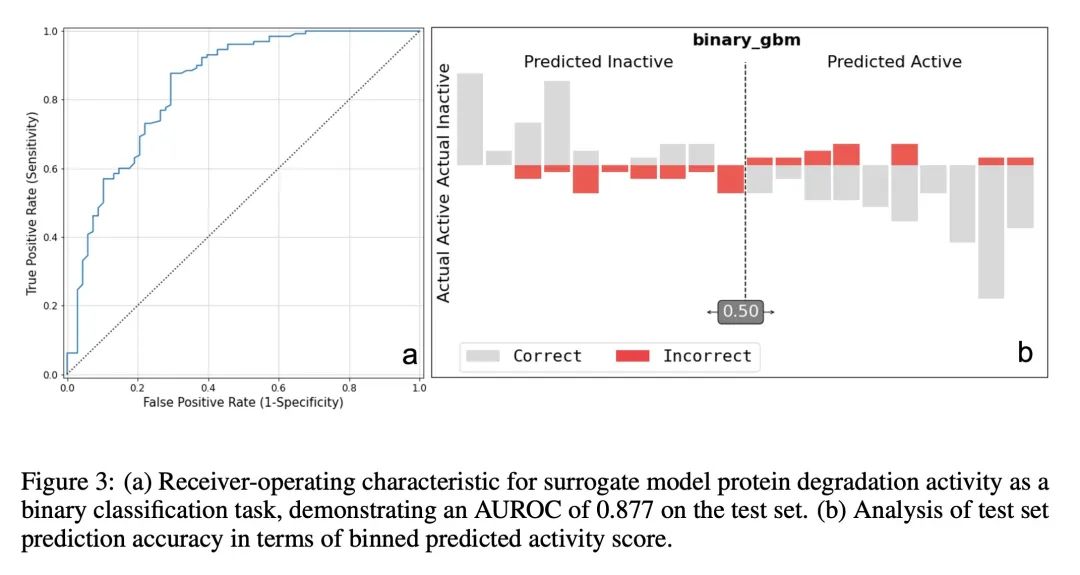
[LG] De novo PROTAC design using graph-based deep generative models
用基于图的深度生成模型从头设计PROTAC
D Nori, C W. Coley, R Mercado
[MIT]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.02660

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢