转自爱可可爱生活
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 GR - 图形学
摘要:重新训练AlphaFold2对其学习机制和泛化能力产生新见解、无需反向传播的大型语言模型自适应、从消息传递角度重新审视因式分解模型、用基于像素扩散模型抽象实现从文本到SVG合成、从单幅自然图像学习扩散模型、开源大规模Transformer工具包、面向通用音频表示的音频谱视觉Transformer、面向任意长度高保真视频生成的潜视频扩散模型、动态足式机器人的基于优化控制
1、[LG] OpenFold: Retraining AlphaFold2 yields new insights into its learning mechanisms and capacity for generalization
G Ahdritz, N Bouatta, S Kadyan...
[Columbia University & Harvard Medical School...]
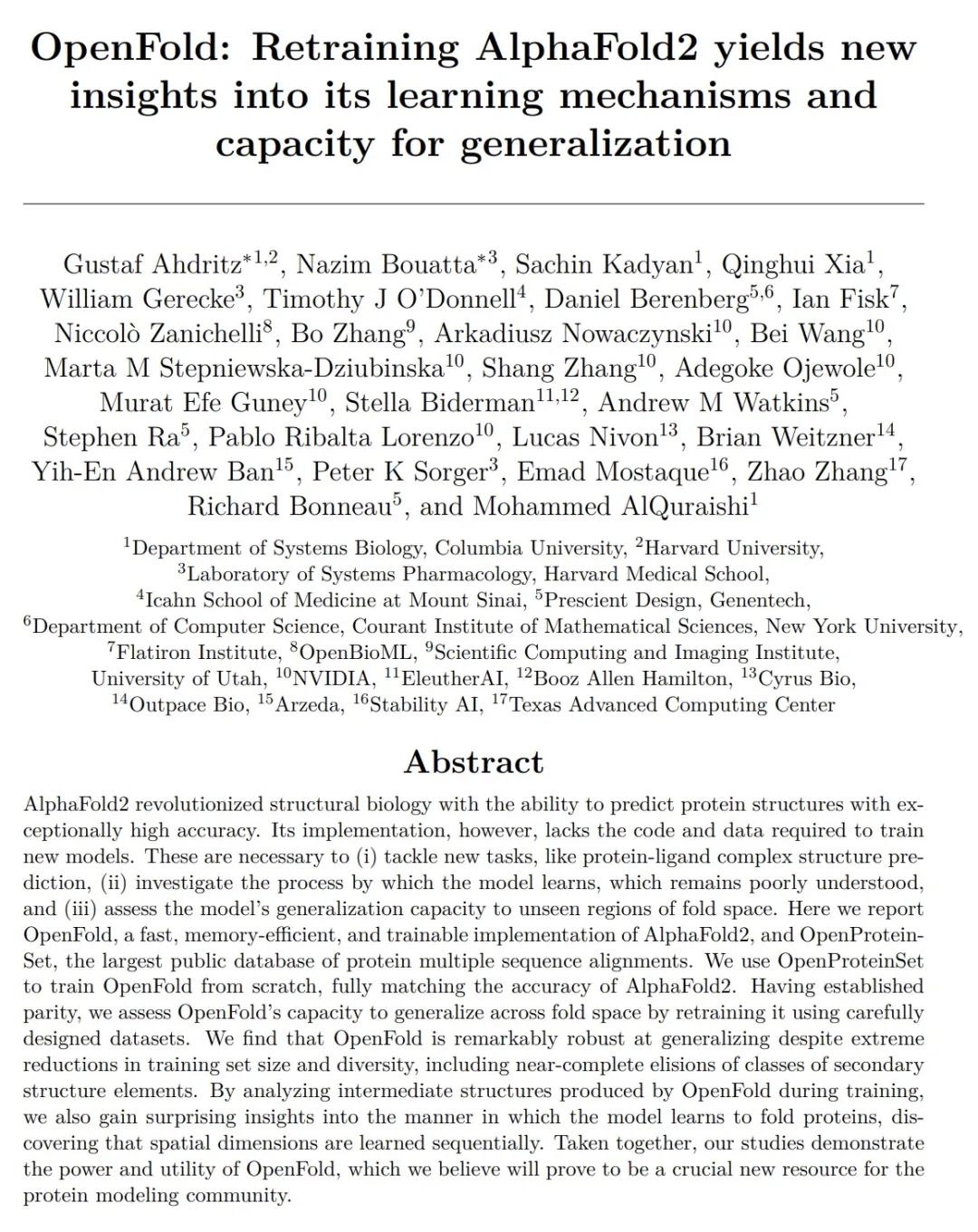
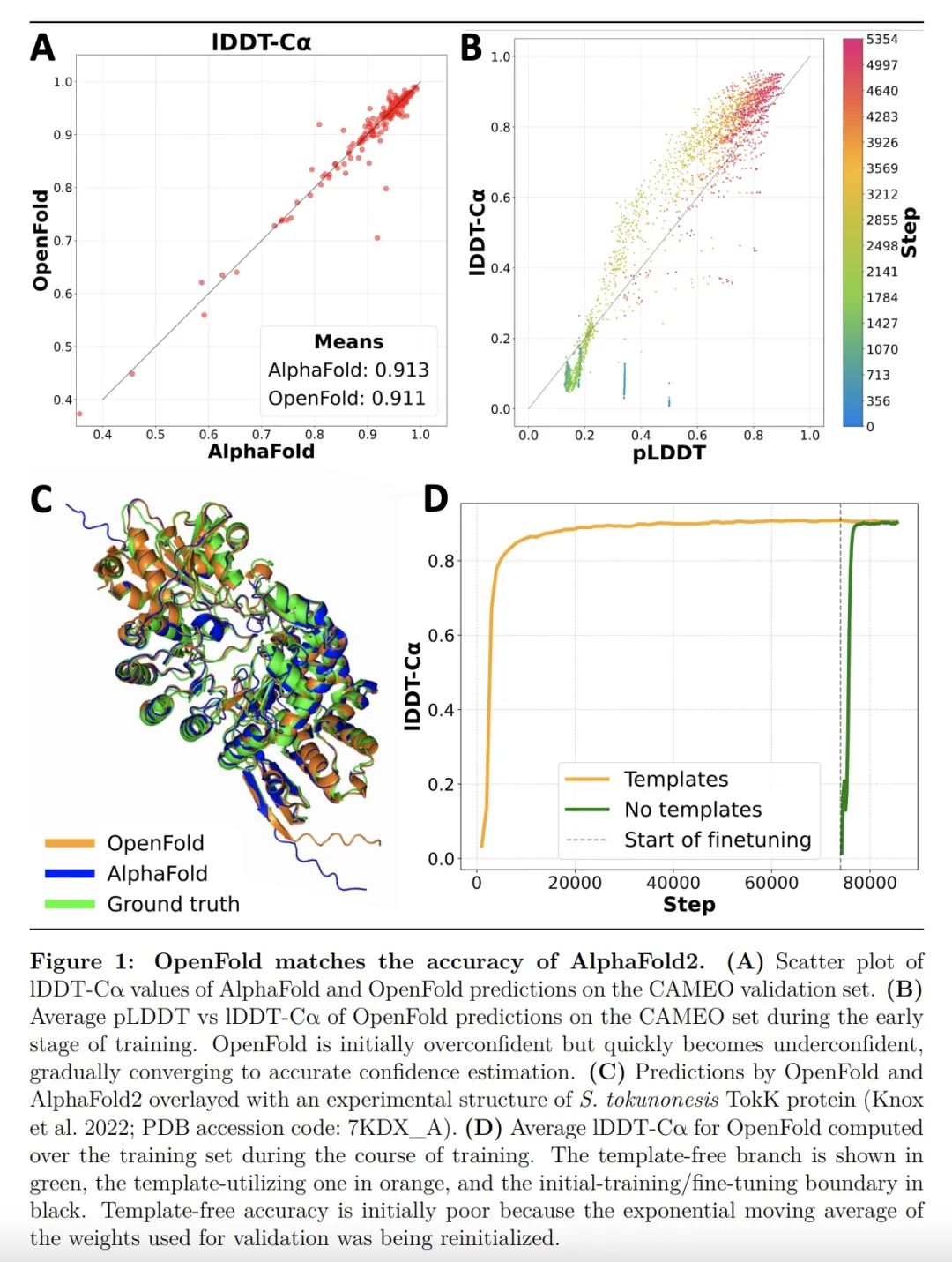
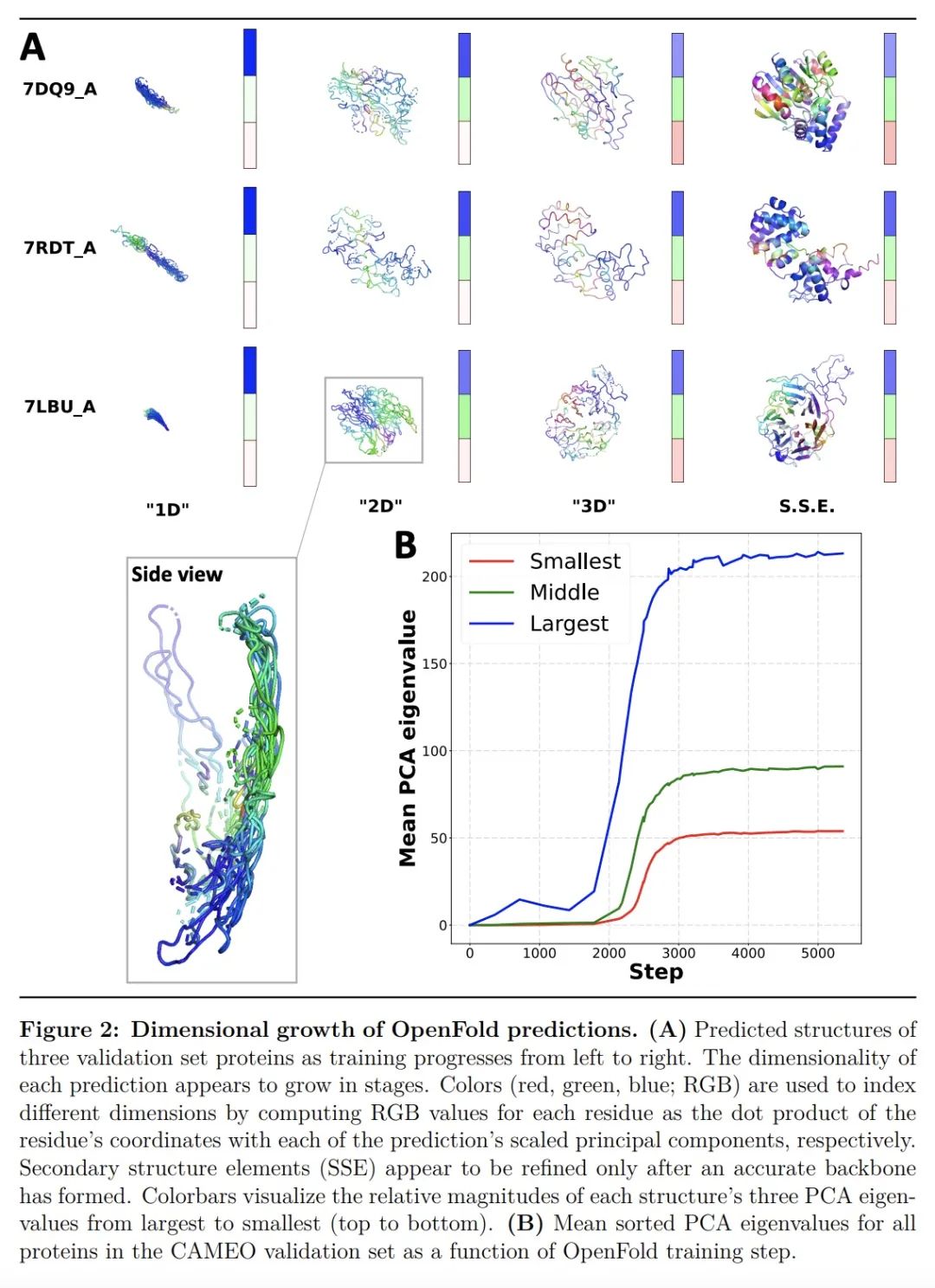
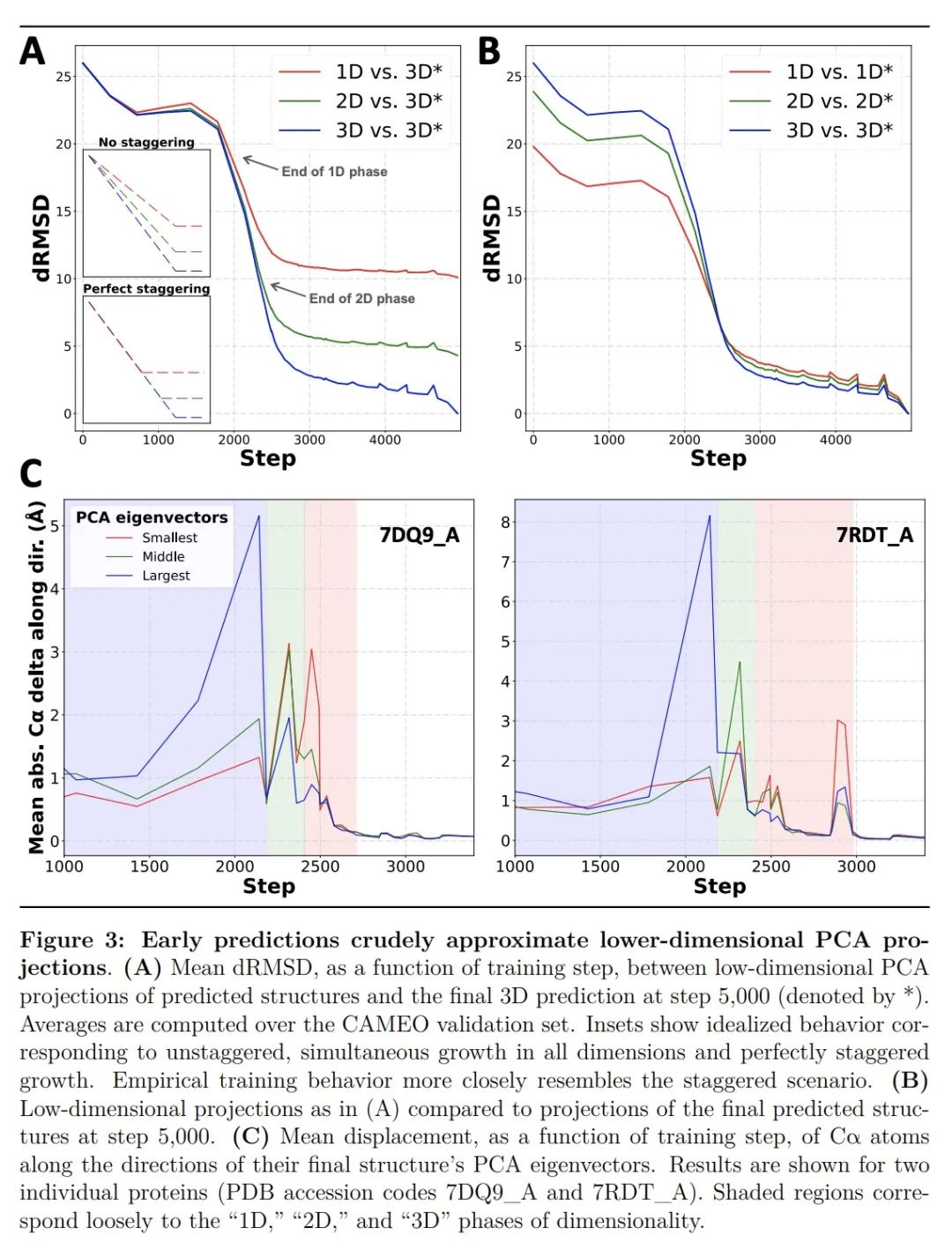
OpenFold:重新训练AlphaFold2对其学习机制和泛化能力产生新见解。AlphaFold2彻底改变了结构生物学,能以特别高的精度预测蛋白质结构。然而,其实施缺乏训练新模型所需的代码和数据。这些都是必要的,以 (i)处理新任务,如蛋白质-配体复合物结构预测,(ii)研究模型的学习过程,这一点仍然知之甚少,以及(iii)评估模型对折叠空间的未见区域的泛化能力。在此,本文发布OpenFold,AlphaFold2的一种快速、高效记忆和可训练的实现,以及OpenProteinSet,最大的蛋白质多序列比对开放数据库。用OpenProteinSet从头开始训练OpenFold,完全匹配了AlphaFold2的准确性。在建立了平价性之后,通过使用精心设计的数据集对OpenFold进行再训练,评估其在折叠空间中的泛化能力。结果发现,尽管训练集规模和多样性极度减少,包括二级结构元素类别的近乎完全删除,但OpenFold的泛化能力还是非常强大。通过分析OpenFold在训练过程中产生的中间结构,本文还对该模型学习蛋白质折叠的方式有了惊人的认识,发现空间尺寸是按顺序学习的。总之,本文研究证明了OpenFold的力量和效用,相信它将被证明是蛋白质建模界的一个重要的新资源。
AlphaFold2 revolutionized structural biology with the ability to predict protein structures with exceptionally high accuracy. Its implementation, however, lacks the code and data required to train new models. These are necessary to (i) tackle new tasks, like protein-ligand complex structure prediction, (ii) investigate the process by which the model learns, which remains poorly understood, and (iii) assess the model's generalization capacity to unseen regions of fold space. Here we report OpenFold, a fast, memory-efficient, and trainable implementation of AlphaFold2, and OpenProteinSet, the largest public database of protein multiple sequence alignments. We use OpenProteinSet to train OpenFold from scratch, fully matching the accuracy of AlphaFold2. Having established parity, we assess OpenFold's capacity to generalize across fold space by retraining it using carefully designed datasets. We find that OpenFold is remarkably robust at generalizing despite extreme reductions in training set size and diversity, including near-complete elisions of classes of secondary structure elements. By analyzing intermediate structures produced by OpenFold during training, we also gain surprising insights into the manner in which the model learns to fold proteins, discovering that spatial dimensions are learned sequentially. Taken together, our studies demonstrate the power and utility of OpenFold, which we believe will prove to be a crucial new resource for the protein modeling community.
https://biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.11.20.517210v1
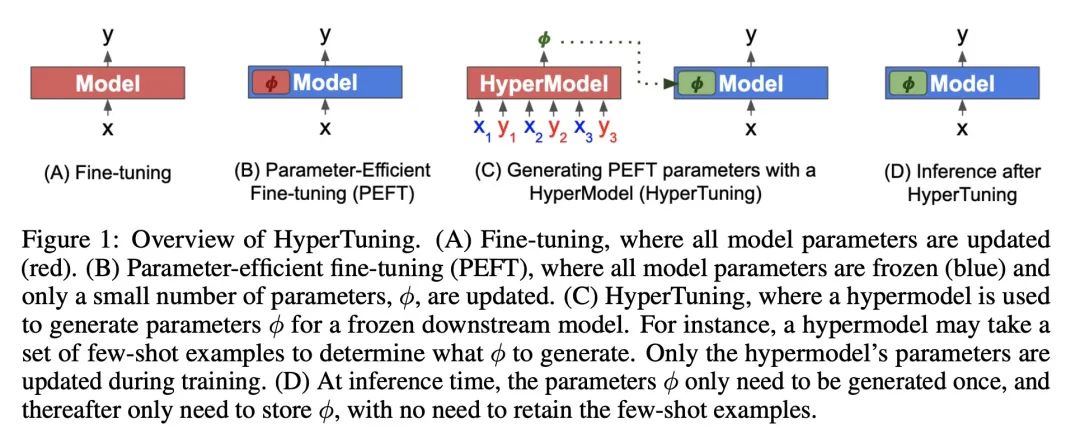
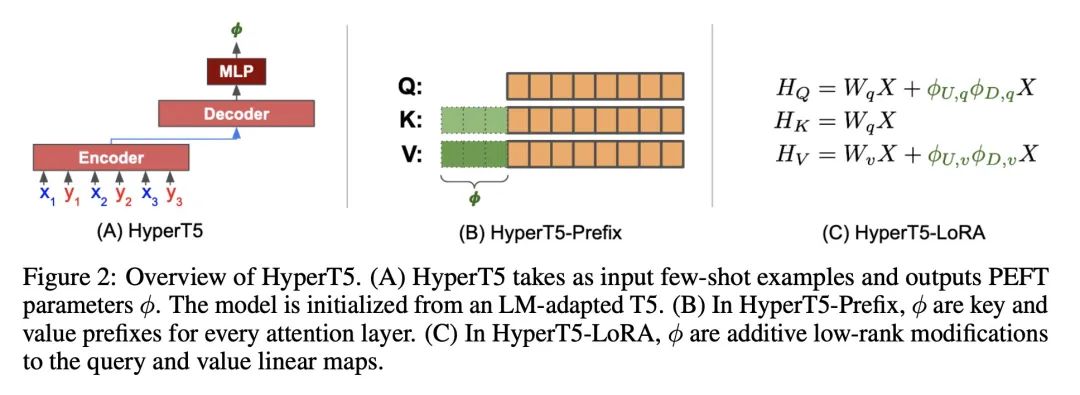
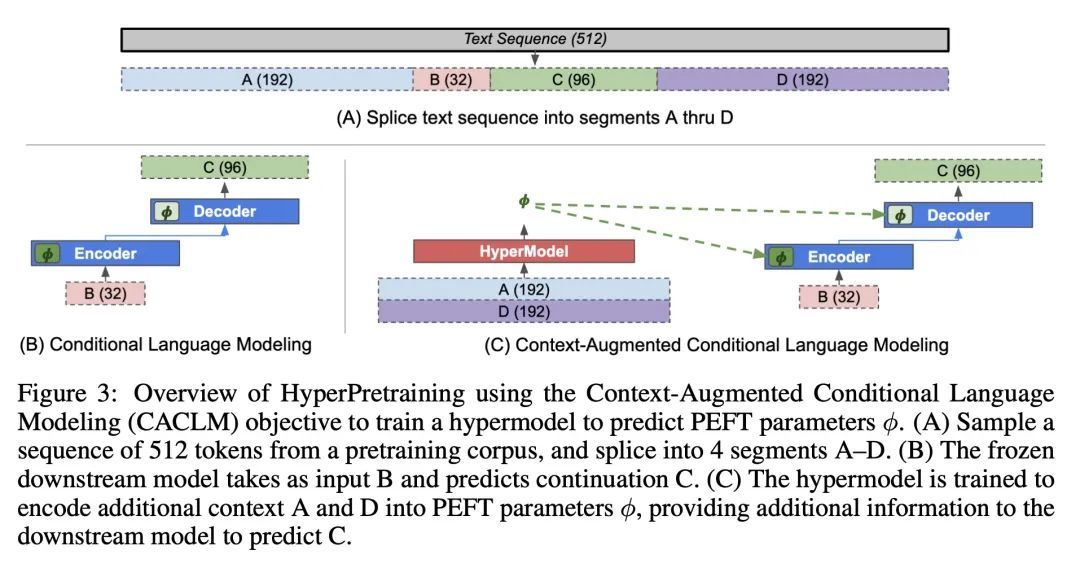
2、[CL] HyperTuning: Toward Adapting Large Language Models without Back-propagation
J Phang, Y Mao, P He, W Chen
[New York University & Microsoft Azure AI]
HyperTuning:无需反向传播的大型语言模型自适应。针对不同任务对大型语言模型进行微调可能是昂贵而低效的,即使是减少调整参数数量的方法也需要基于梯度的完全优化。本文提出HyperTuning,一种新的模型自适应方法,用超模型为固定的下游模型生成特定的任务参数。用HyperT5演示了一个简单的HyperTuning设置,HyperT5是一个基于T5的超模型,能从少样本中为一个冻结的T5模型产生软前缀或LoRA参数。分两个阶段训练HyperT5:首先,用修改过的条件语言建模目标进行超训练,训练超模型产生参数;其次,在大量不同的语言任务上进行多任务微调(MTF)。在P3、MetaICL和Super-NaturalInstructions数据集上评估了HyperT5,并表明其能有效地生成未见任务的参数。使用超模型生成的参数作为初始化,可进一步提高参数高效微调性能。因此,HyperTuning是一种灵活、高效的方式,可将大型语言模型用于不同的下游应用。
Fine-tuning large language models for different tasks can be costly and inefficient, and even methods that reduce the number of tuned parameters still require full gradient-based optimization. We propose HyperTuning, a novel approach to model adaptation that uses a hypermodel to generate task-specific parameters for a fixed downstream model. We demonstrate a simple setup for hypertuning with HyperT5, a T5-based hypermodel that produces soft prefixes or LoRA parameters for a frozen T5 model from few-shot examples. We train HyperT5 in two stages: first, hyperpretraining with a modified conditional language modeling objective that trains a hypermodel to generate parameters; second, multi-task fine-tuning (MTF) on a large number of diverse language tasks. We evaluate HyperT5 on P3, MetaICL and Super-NaturalInstructions datasets, and show that it can effectively generate parameters for unseen tasks. Moreover, we show that using hypermodel-generated parameters as initializations for further parameter-efficient fine-tuning improves performance. HyperTuning can thus be a flexible and efficient way to leverage large language models for diverse downstream applications.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.12485

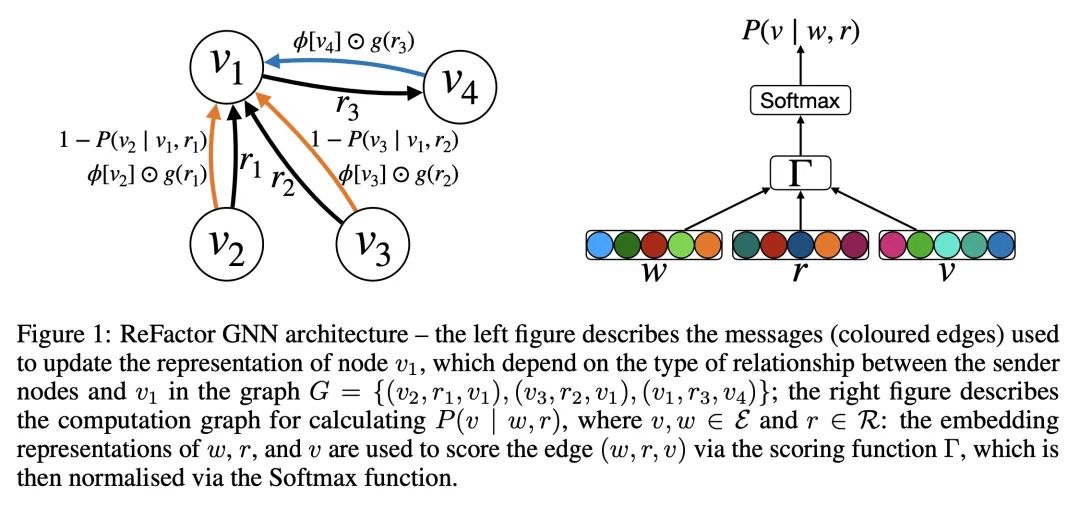
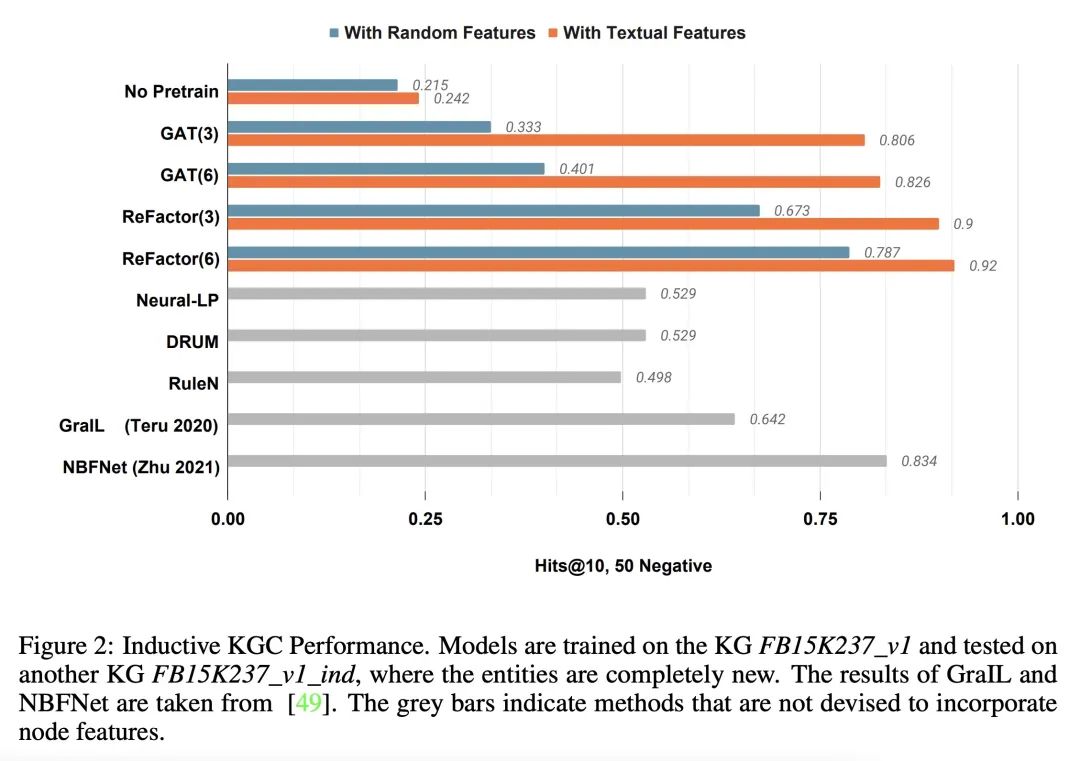
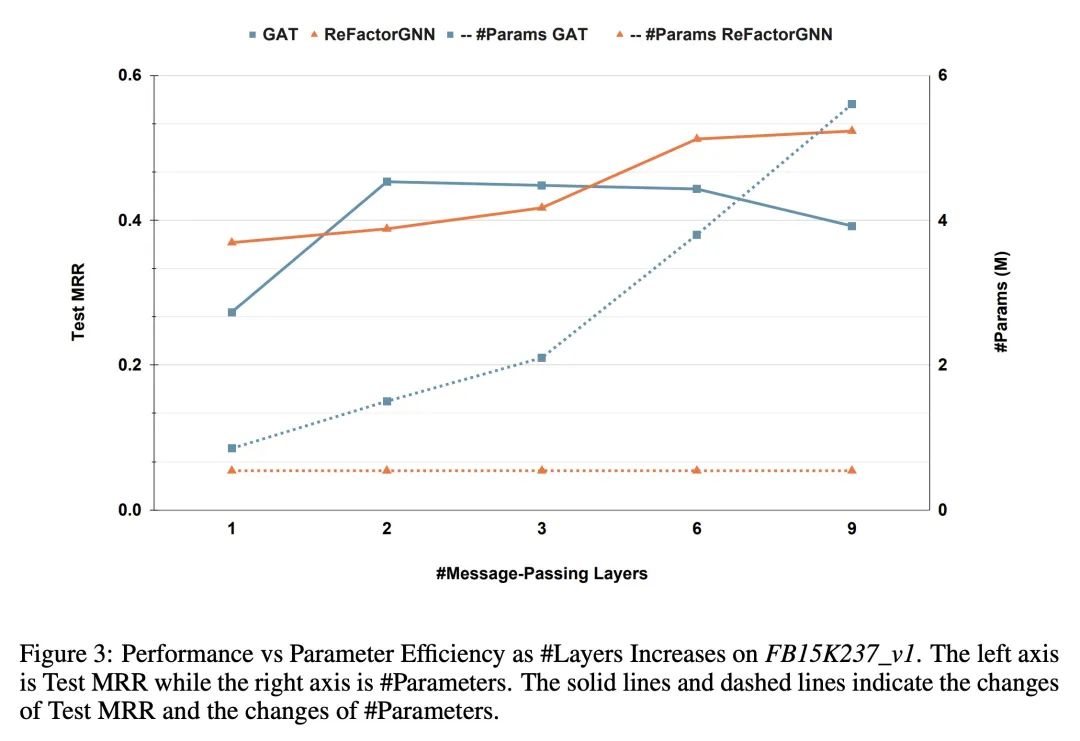
3、[LG] ReFactor GNNs: Revisiting Factorisation-based Models from a Message-Passing Perspective
Y Chen, P Mishra, L Franceschi, P Minervini, P Stenetorp, S Riedel
[UCL & Meta AI & Amazon Web Services]
ReFactor GNN: 从消息传递角度重新审视因式分解模型。基于因式分解的模型(FM),如DistMult,在知识图谱补全(KGC)任务中取得了持久的成功,其表现往往超过图神经网络(GNN)。然而,与图神经网络不同的是,FM模型在纳入节点特征和归纳出未见节点方面遇到了困难。本文提出ReFactor GNN以弥补FM和GNN之间的差距。这种新架构借鉴了两种建模范式,而之前这两种范式被认为是不相干的。通过使用消息传递形式,本文展示了如何通过将梯度下降过程重新表述为消息传递操作,将FM投射到GNN中,这构成了所提出ReFactor GNN的基础。在众多成熟的KGC基准中,ReFactor GNN实现了与FM相当的传递性能,以及最先进的泛化性能,同时使用的参数少了一个数量级。
Factorisation-based Models (FMs), such as DistMult, have enjoyed enduring success for Knowledge Graph Completion (KGC) tasks, often outperforming Graph Neural Networks (GNNs). However, unlike GNNs, FMs struggle to incorporate node features and generalise to unseen nodes in inductive settings. Our work bridges the gap between FMs and GNNs by proposing ReFactor GNNs. This new architecture draws upon both modelling paradigms, which previously were largely thought of as disjoint. Concretely, using a message-passing formalism, we show how FMs can be cast as GNNs by reformulating the gradient descent procedure as message-passing operations, which forms the basis of our ReFactor GNNs. Across a multitude of well-established KGC benchmarks, our ReFactor GNNs achieve comparable transductive performance to FMs, and state-of-the-art inductive performance while using an order of magnitude fewer parameters.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2207.09980

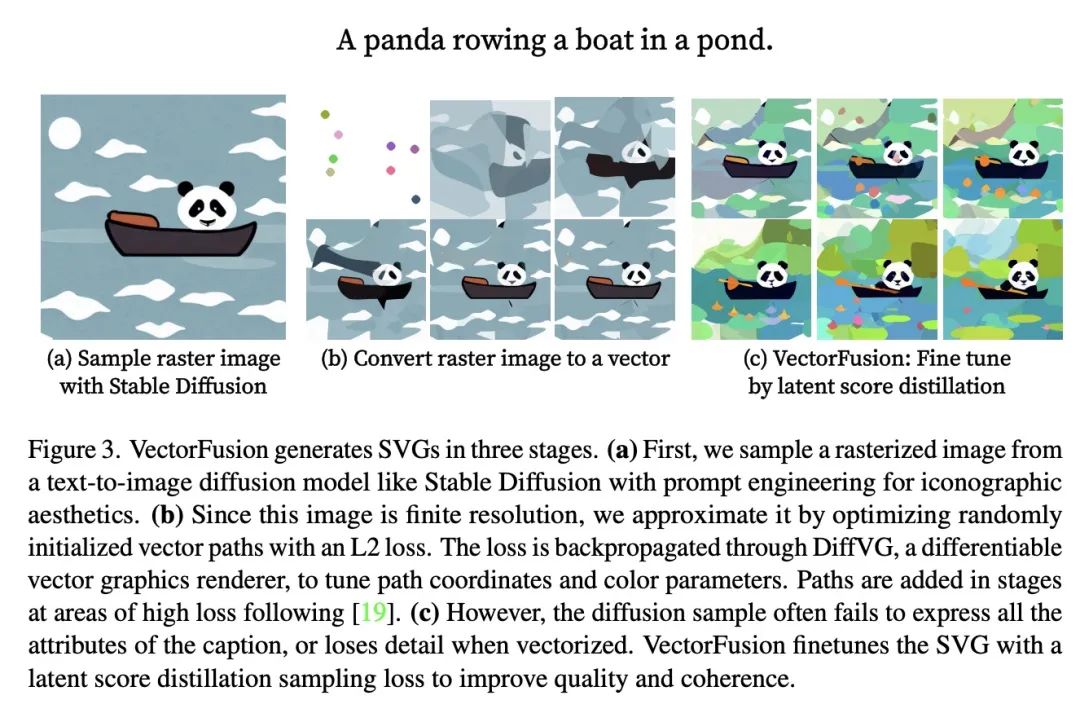
4、[CV] VectorFusion: Text-to-SVG by Abstracting Pixel-Based Diffusion Models
A Jain, A Xie, P Abbeel
[UC Berkeley]
VectorFusion: 用基于像素扩散模型抽象实现从文本到SVG合成。扩散模型在文本到图像的合成中显示了令人印象深刻的结果。使用大量的描述图像数据集,扩散模型学会了生成高多样化的物体和场景的光栅图像。然而,设计师经常使用图像的矢量表示,如可扩展矢量图形(SVG),用于数字图标或艺术。矢量图形可被缩放到任意尺寸,且结构紧凑。本文表明,在图像像素表示上训练的文本条件扩散模型可用来生成SVG-可导出矢量图。这样做不需要获得大规模的带描述的SVG数据集。通过优化可微矢量图形光栅,所提出方法VectorFusion从预训练扩散模型中提炼出抽象语义知识。受最近文本到3D工作的启发,本文用分数提炼采样法学习与描述一致的SVG。为了加速生成并提高保真度,VectorFusion也从一个图像样本中初始化。实验显示比之前的工作质量更高,并展示了一系列的风格,包括像素艺术和草图。
Diffusion models have shown impressive results in text-to-image synthesis. Using massive datasets of captioned images, diffusion models learn to generate raster images of highly diverse objects and scenes. However, designers frequently use vector representations of images like Scalable Vector Graphics (SVGs) for digital icons or art. Vector graphics can be scaled to any size, and are compact. We show that a text-conditioned diffusion model trained on pixel representations of images can be used to generate SVG-exportable vector graphics. We do so without access to large datasets of captioned SVGs. By optimizing a differentiable vector graphics rasterizer, our method, VectorFusion, distills abstract semantic knowledge out of a pretrained diffusion model. Inspired by recent text-to-3D work, we learn an SVG consistent with a caption using Score Distillation Sampling. To accelerate generation and improve fidelity, VectorFusion also initializes from an image sample. Experiments show greater quality than prior work, and demonstrate a range of styles including pixel art and sketches. See our project webpage at this https URL .
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.11319



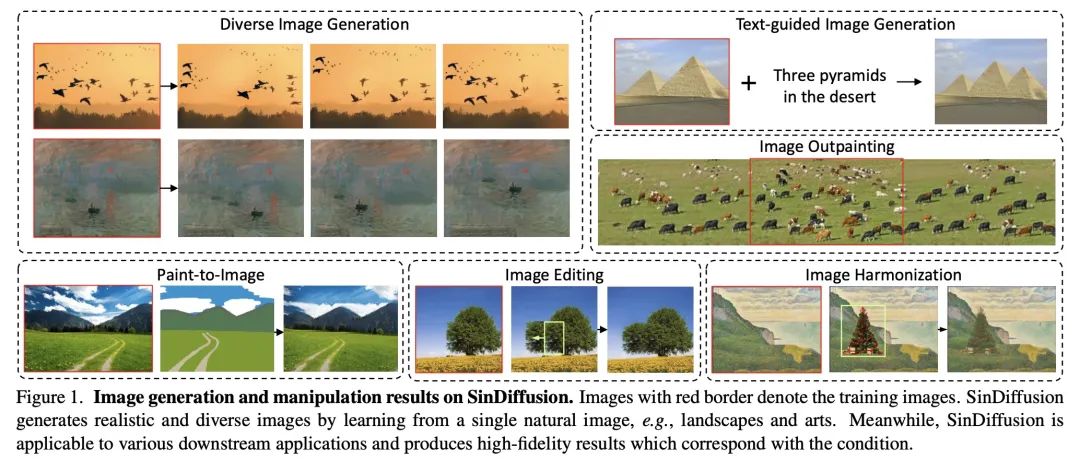
5、[CV] SinDiffusion: Learning a Diffusion Model from a Single Natural Image
W Wang, J Bao, W Zhou, D Chen, D Chen, L Yuan, H Li
[University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) & Microsoft Research Asia]
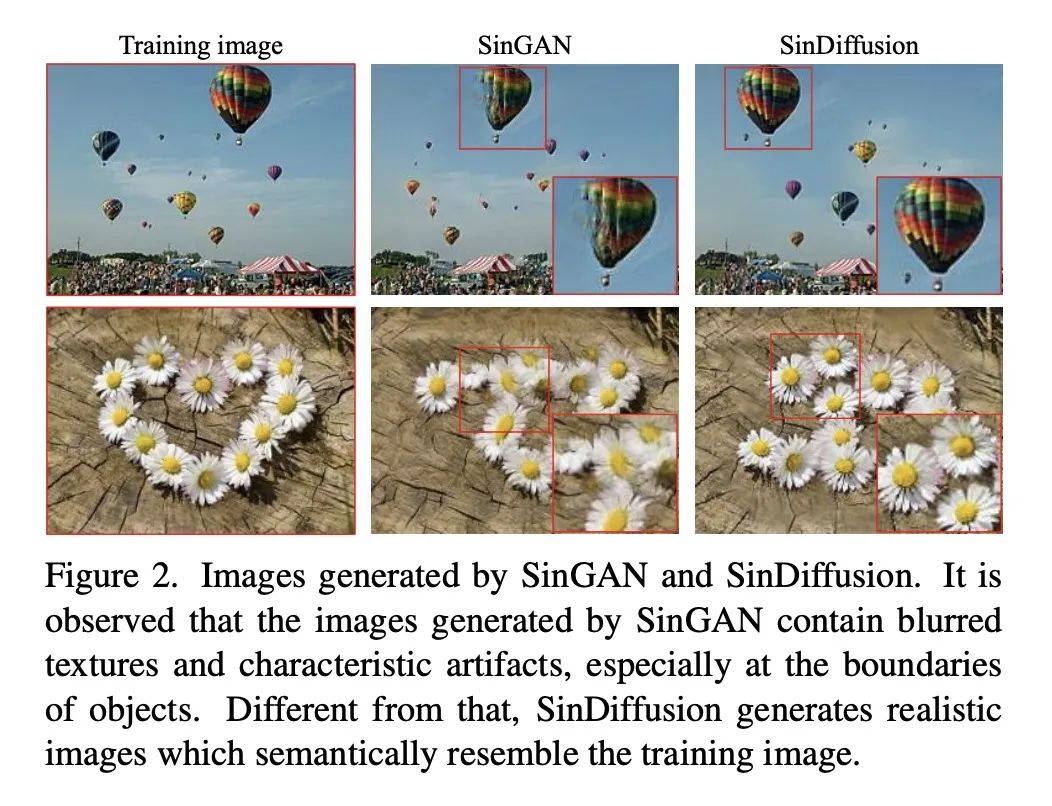
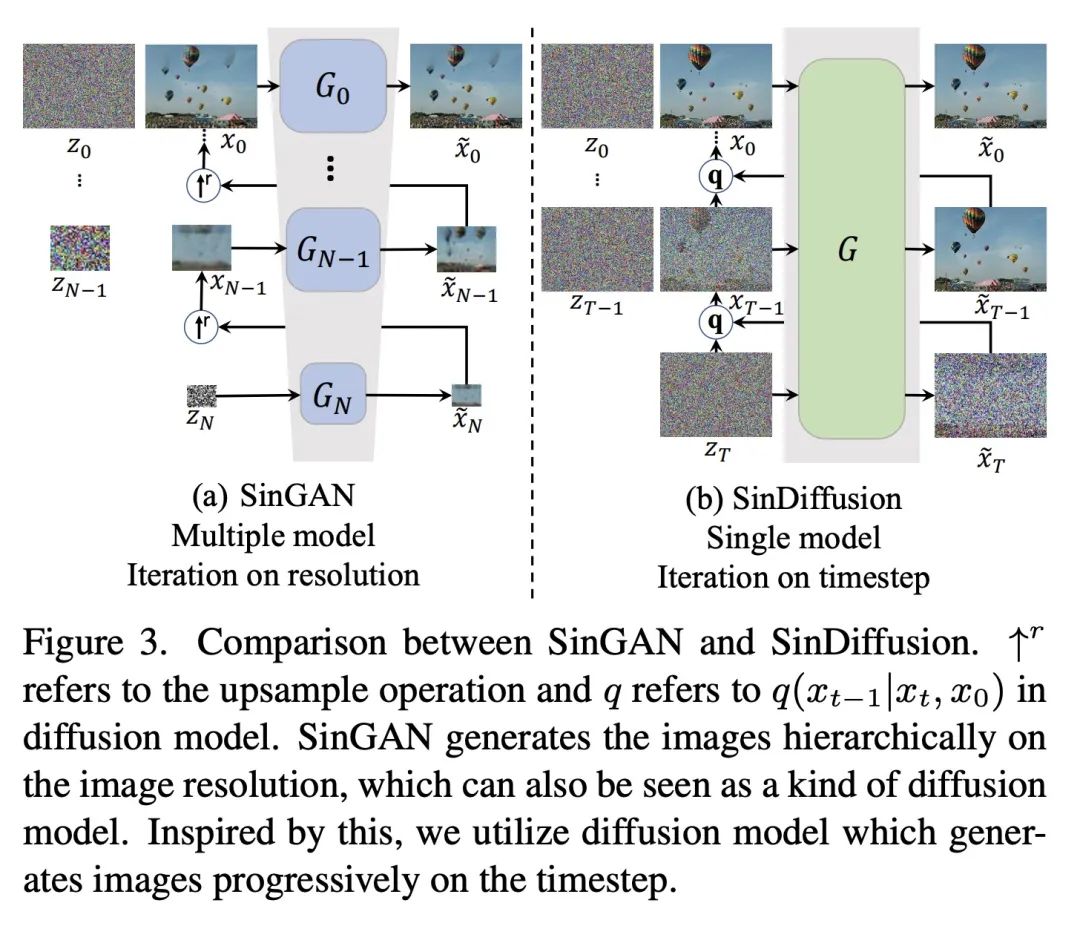
SinDiffusion: 从单幅自然图像学习扩散模型。本文提出SinDiffusion,利用去噪扩散模型捕捉单幅自然图像中图块的内部分布。与现有基于GAN的方法相比,SinDiffusion明显提高了生成样本的质量和多样性。其基于两个核心设计。首先,SinDiffusion是用一个单一模型来训练的,而不是像之前工作中默认的用多个模型来训练的。这就避免了错误的积累,而错误的积累会导致生成结果出现特征性伪影。其次,本文发现扩散网络的图块级感受野对于捕捉图像的图块统计至关重要,而且很有效,因此本文重新设计了扩散模型的网络结构。耦合这两种设计使得能从单幅图像中生成逼真和多样化的图像。此外,由于扩散模型的固有能力,SinDiffusion可用于各种应用,即文本指导的图像生成,以及图像补全。在广泛的图像上进行的广泛实验证明了所提出方法在为图块分布建模方面的优越性。
We present SinDiffusion, leveraging denoising diffusion models to capture internal distribution of patches from a single natural image. SinDiffusion significantly improves the quality and diversity of generated samples compared with existing GAN-based approaches. It is based on two core designs. First, SinDiffusion is trained with a single model at a single scale instead of multiple models with progressive growing of scales which serves as the default setting in prior work. This avoids the accumulation of errors, which cause characteristic artifacts in generated results. Second, we identify that a patch-level receptive field of the diffusion network is crucial and effective for capturing the image's patch statistics, therefore we redesign the network structure of the diffusion model. Coupling these two designs enables us to generate photorealistic and diverse images from a single image. Furthermore, SinDiffusion can be applied to various applications, i.e., text-guided image generation, and image outpainting, due to the inherent capability of diffusion models. Extensive experiments on a wide range of images demonstrate the superiority of our proposed method for modeling the patch distribution.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.12445

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[LG] TorchScale: Transformers at Scale
TorchScale:开源大规模Transformer工具包
S Ma, H Wang, S Huang, W Wang, Z Chi, L Dong, A Benhaim, B Patra, V Chaudhary, X Song, F Wei
[Microsoft]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13184

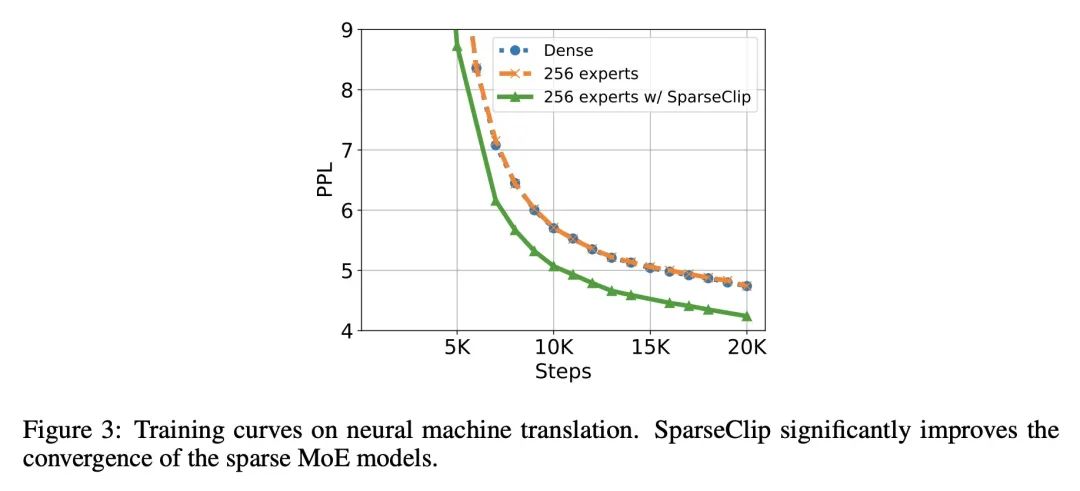
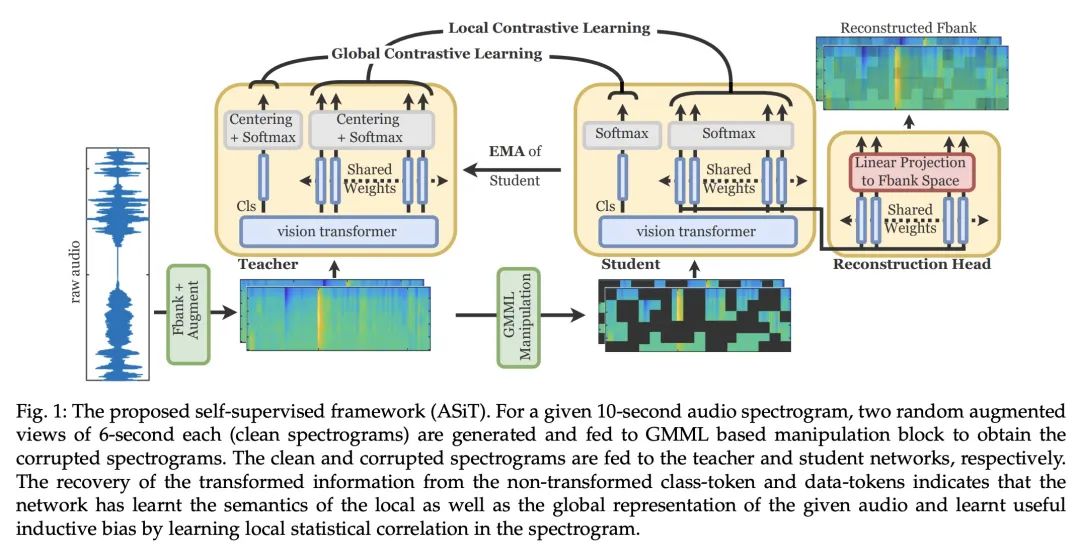
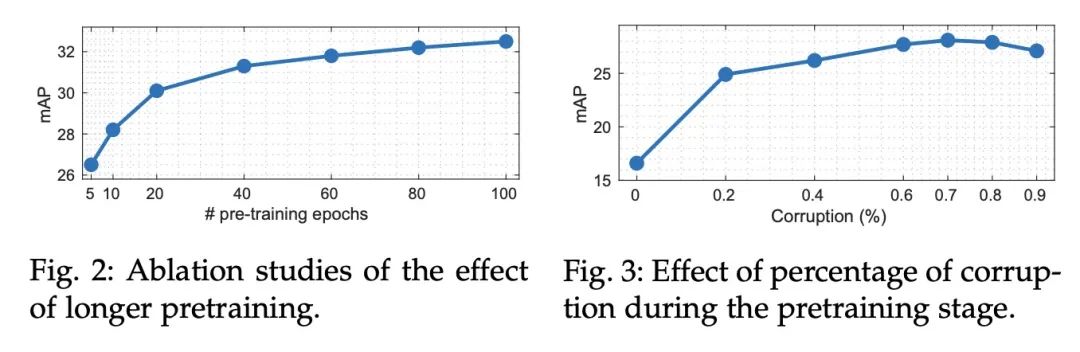
[AS] ASiT: Audio Spectrogram vIsion Transformer for General Audio Representation
ASiT:面向通用音频表示的音频谱视觉Transformer
S Atito, M Awais, W Wang, M D Plumbley, J Kittler
[University of Surrey]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13189

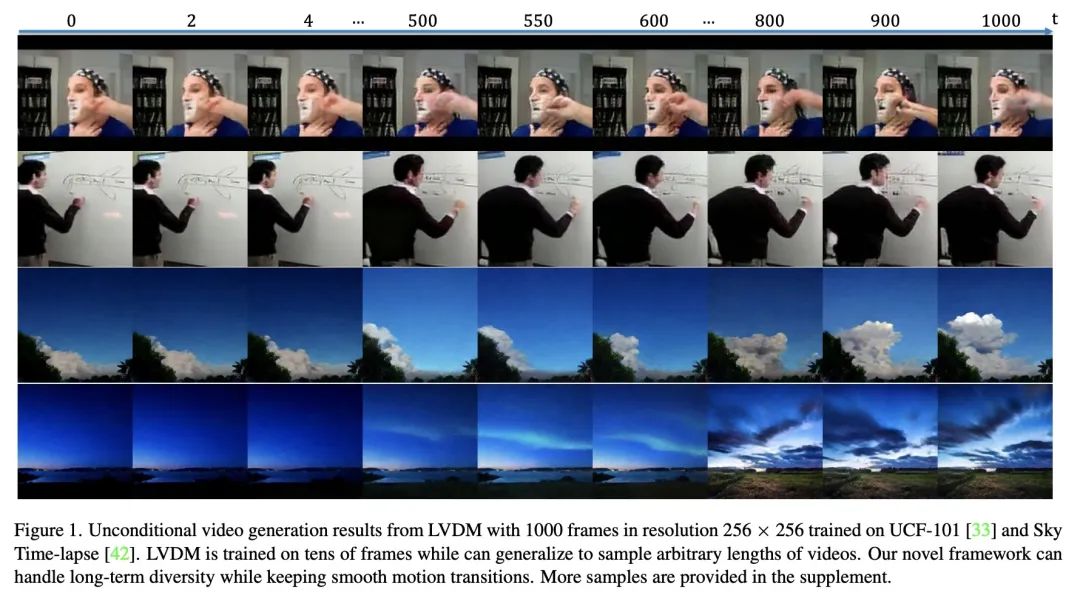
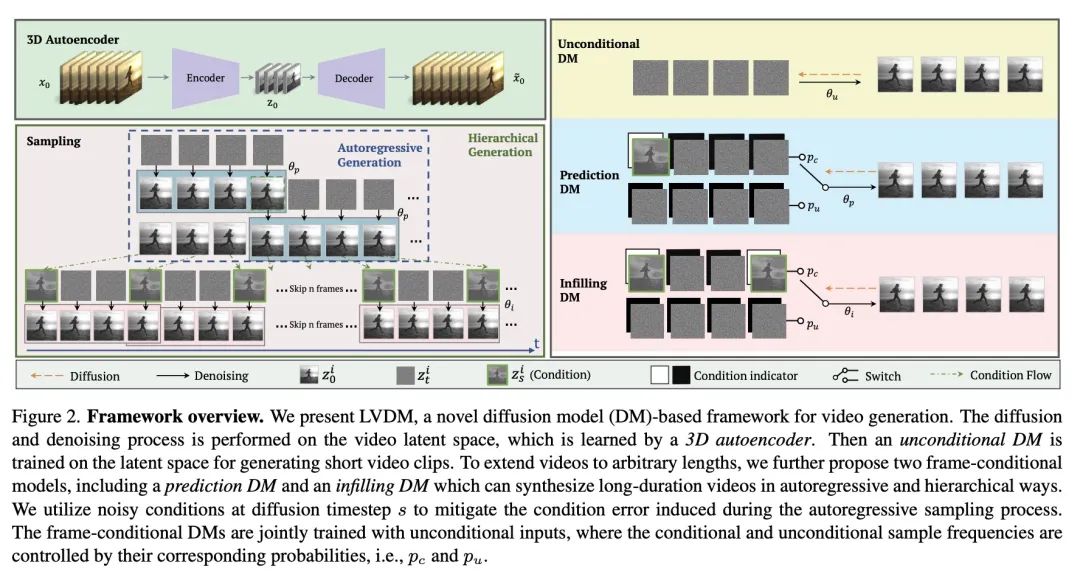
[CV] Latent Video Diffusion Models for High-Fidelity Video Generation with Arbitrary Lengths
面向任意长度高保真视频生成的潜视频扩散模型
Y He, T Yang, Y Zhang, Y Shan, Q Chen
[The Hong Kong University of Science and Technology & Tencent AI Lab]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13221



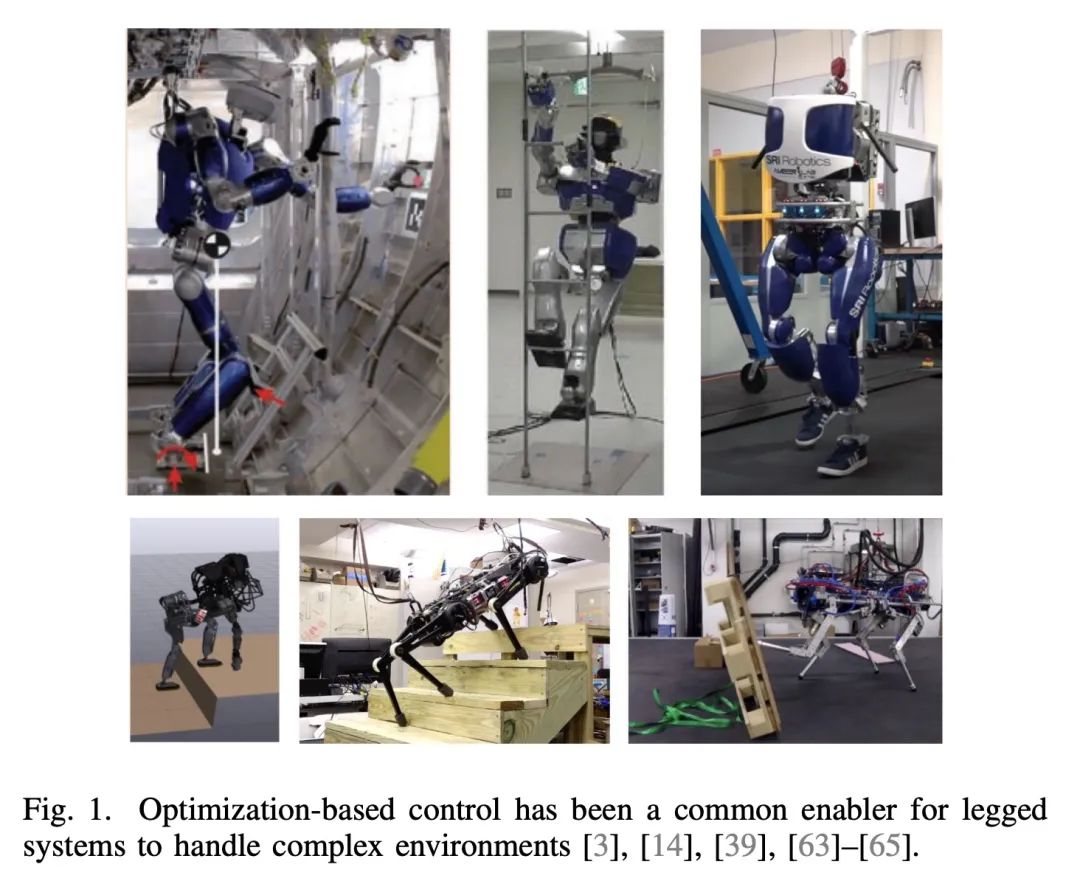
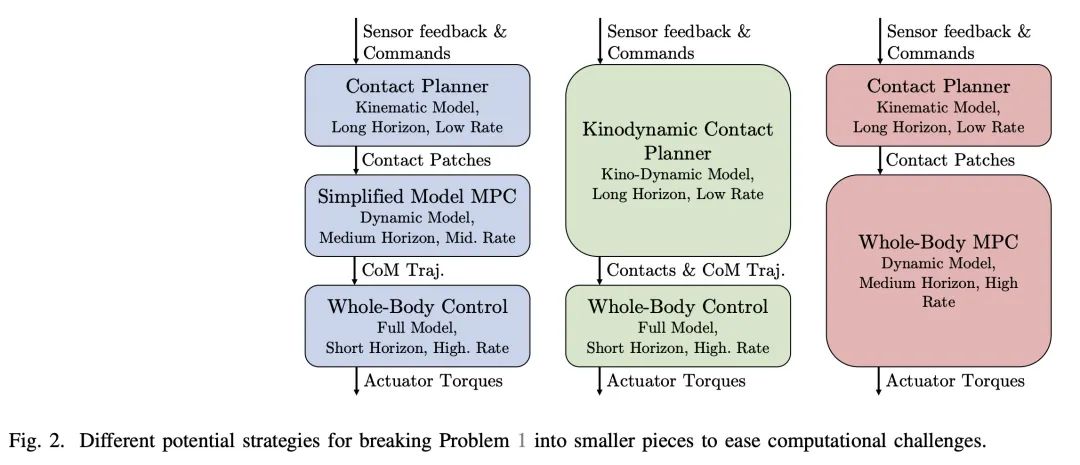
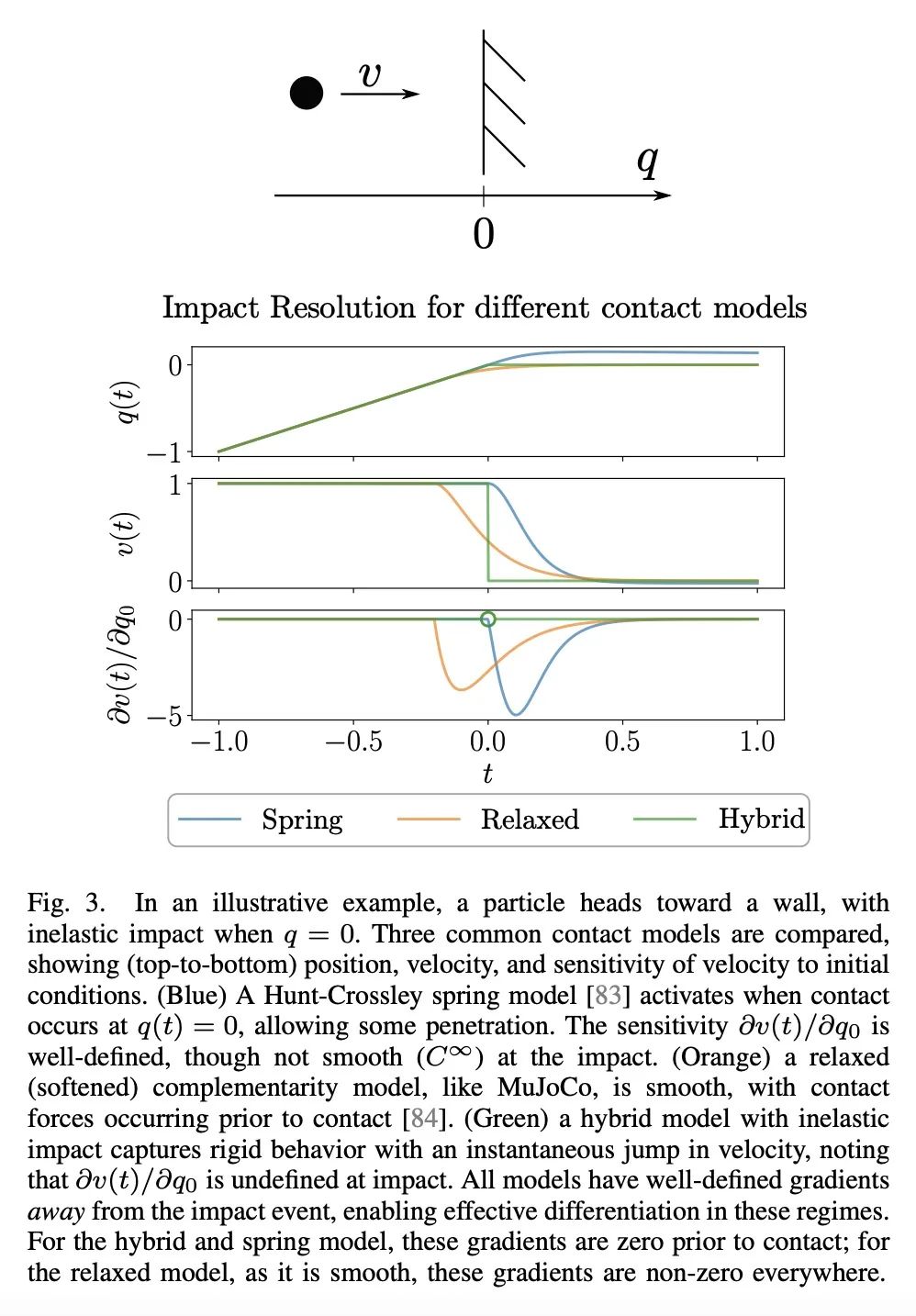
[RO] Optimization-Based Control for Dynamic Legged Robots
动态足式机器人的基于优化控制
P M. Wensing, M Posa, Y Hu...
[University of Notre Dame & University of Pennsylvania & University of Waterloo & INRIA & LAAS-CNRS & University of Trento]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.11644

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢