转自爱可可爱生活
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 GR - 图形学
摘要:面向分子交联剂设计的等变3D条件扩散模型、用凸化改善Transformer网络的优化和理解、分布外检测可学习性研究、SGD高维极限定理、基于强化学习的测试时提示、面向文本驱动图像到图像翻译的即插即用扩散特征、公平会增加对抗脆弱性、端到端多阶段文本-知识图谱生成、基于视觉-语言模型的指令增强机器人技能学习
1、[LG] Equivariant 3D-Conditional Diffusion Models for Molecular Linker Design
I Igashov, H Stärk, C Vignac, V G Satorras...
[EPFL & MIT & Microsoft Research AI4Science & University of Oxford]
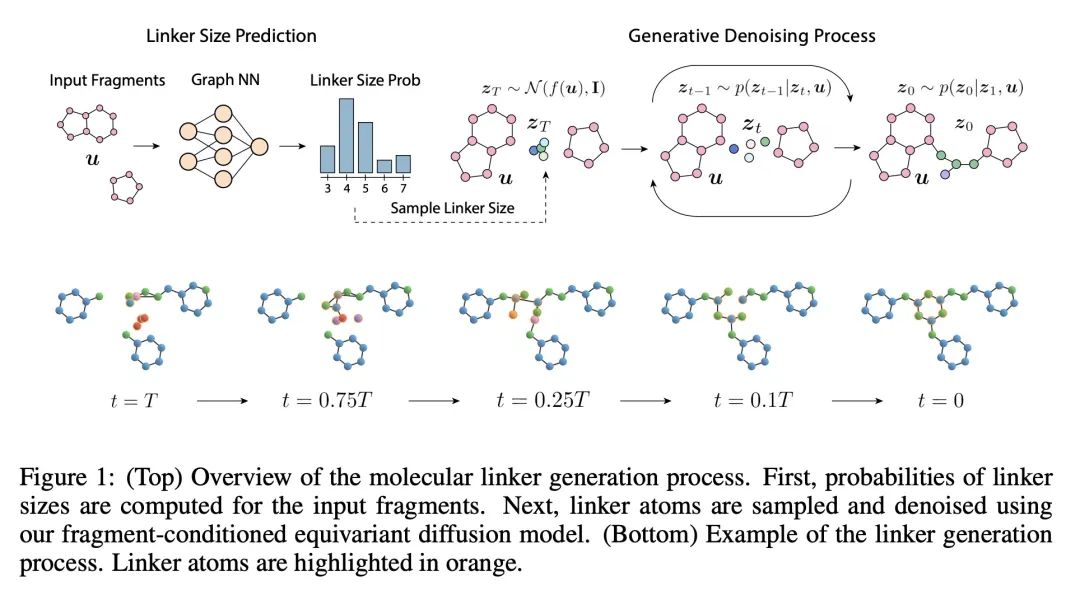
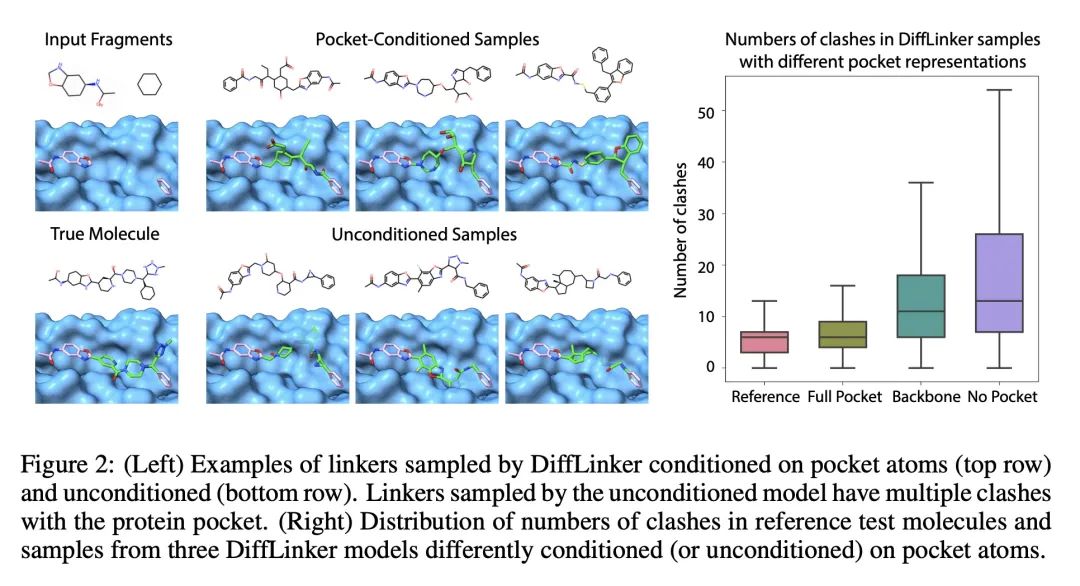
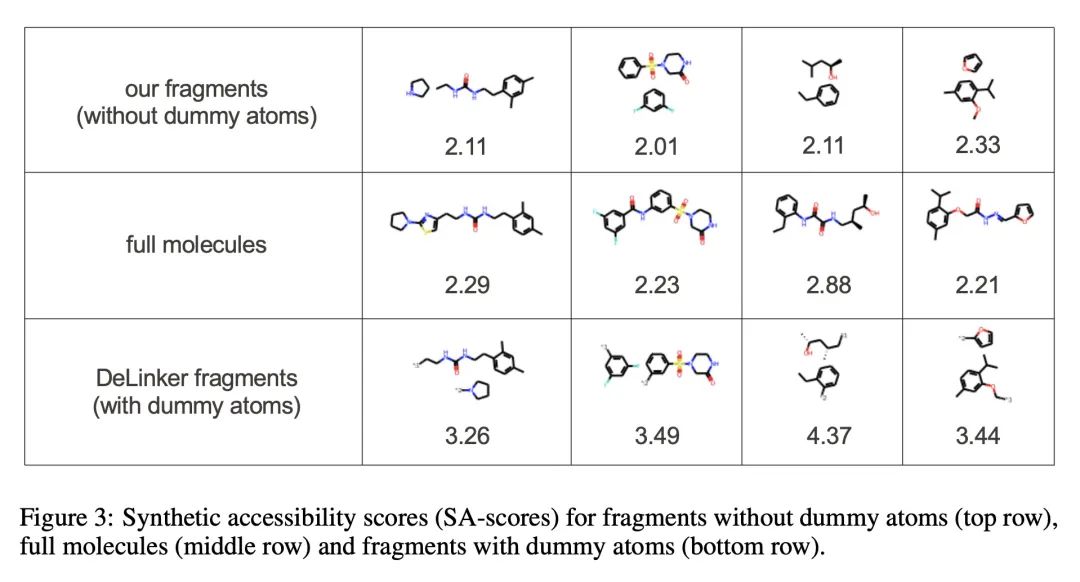
面向分子交联剂设计的等变3D条件扩散模型。基于片段的药物发现一直是早期药物开发的一个有效范式。这一领域的一个公开挑战是在感兴趣的不相连的分子片段间设计交联剂,以获得化学上相关的候选药物分子。本文提出DiffLinker,一种用于分子交联剂设计的E(3)-等变3D条件扩散模型。给定一组不相连的片段,该模型将缺失的原子放在中间,并设计一个包含所有初始片段的分子。与以往只能连接成对分子片段的方法不同,所提出方法可以连接任意数量的片段。此外,该模型还自动确定交联剂的原子数以及它与输入片段的连接点。本文证明DiffLinker在标准数据集上的表现优于其他方法,这些数据集产生了更多多样化的可合成分子。此外,在现实世界的应用中对所提出方法进行了实验测试,表明它可以成功地生成以目标蛋白袋为条件的有效交联剂。
Fragment-based drug discovery has been an effective paradigm in early-stage drug development. An open challenge in this area is designing linkers between disconnected molecular fragments of interest to obtain chemically-relevant candidate drug molecules. In this work, we propose DiffLinker, an E(3)-equivariant 3D-conditional diffusion model for molecular linker design. Given a set of disconnected fragments, our model places missing atoms in between and designs a molecule incorporating all the initial fragments. Unlike previous approaches that are only able to connect pairs of molecular fragments, our method can link an arbitrary number of fragments. Additionally, the model automatically determines the number of atoms in the linker and its attachment points to the input fragments. We demonstrate that DiffLinker outperforms other methods on the standard datasets generating more diverse and synthetically-accessible molecules. Besides, we experimentally test our method in real-world applications, showing that it can successfully generate valid linkers conditioned on target protein pockets.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.05274

2、[LG] Convexifying Transformers: Improving optimization and understanding of transformer networks
T Ergen, B Neyshabur, H Mehta
[Google Research & Stanford Universtiy]
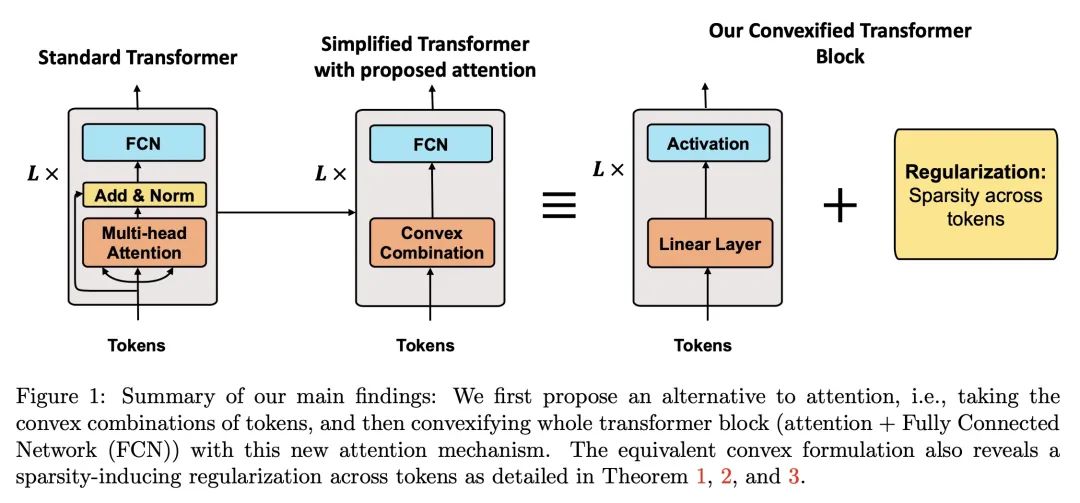
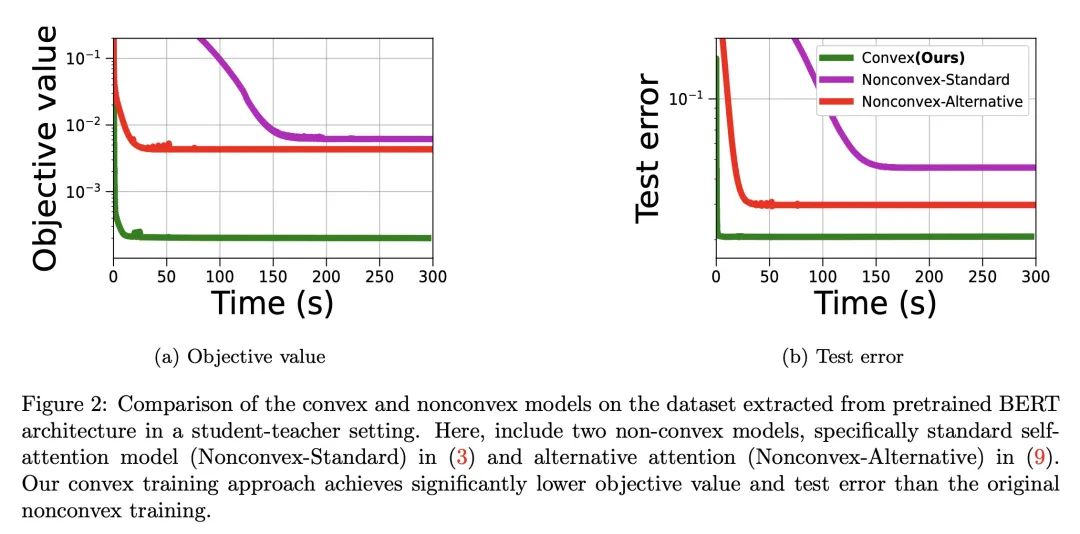
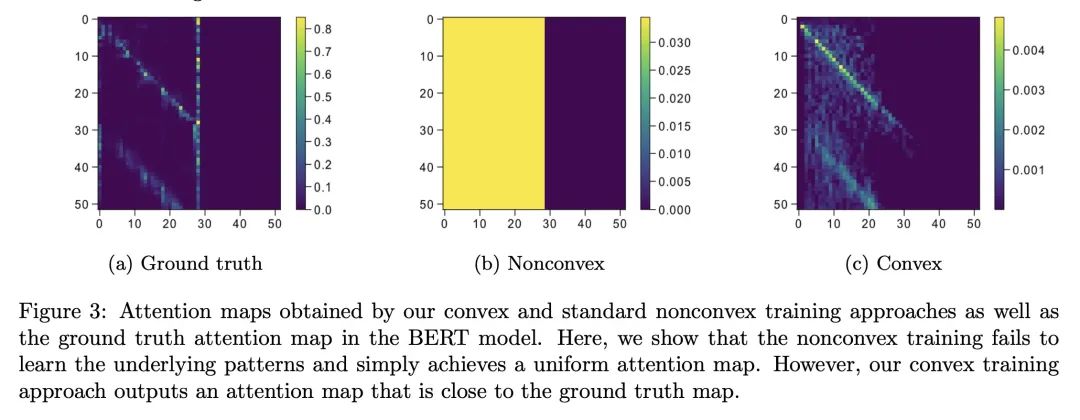
Transformer凸化:改善Transformer网络的优化和理解。理解Transformer网络成功背后的基本机制,仍然是深度学习文献中的一个开放问题。尽管其优秀表现大多归功于自注意力机制,但文献中仍然缺乏对这些网络的扎实分析和对它们所学函数的解释。本文研究了注意力/Transformer网络的训练问题,并引入了一种新的凸分析方法来提高对这些网络的理解和优化。本文提出了一种替代自注意力机制的凸方法,用该替代凸注意力来重新表述Transformer网络的正则化训练问题。将该重构问题作为一个可解释的、更容易优化的凸优化问题。此外,作为凸分析的副产品,本文揭示了一个隐正则化机制,促进了跨token的稀疏性。因此,本文不仅改进了注意力/Transformer网络的优化,而且还对它们所学习的函数提供了坚实的理论理解。本文还通过几个数字实验证明了所提出理论的有效性。
Understanding the fundamental mechanism behind the success of transformer networks is still an open problem in the deep learning literature. Although their remarkable performance has been mostly attributed to the self-attention mechanism, the literature still lacks a solid analysis of these networks and interpretation of the functions learned by them. To this end, we study the training problem of attention/transformer networks and introduce a novel convex analytic approach to improve the understanding and optimization of these networks. Particularly, we first introduce a convex alternative to the self-attention mechanism and reformulate the regularized training problem of transformer networks with our alternative convex attention. Then, we cast the reformulation as a convex optimization problem that is interpretable and easier to optimize. Moreover, as a byproduct of our convex analysis, we reveal an implicit regularization mechanism, which promotes sparsity across tokens. Therefore, we not only improve the optimization of attention/transformer networks but also provide a solid theoretical understanding of the functions learned by them. We also demonstrate the effectiveness of our theory through several numerical experiments.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.11052

3、[LG] Is Out-of-Distribution Detection Learnable?
Z Fang, Y Li, J Lu, J Dong, B Han, F Liu
[University of Technology Sydney & University of Wisconsin-Madison & Chinese Academy of Sciences]
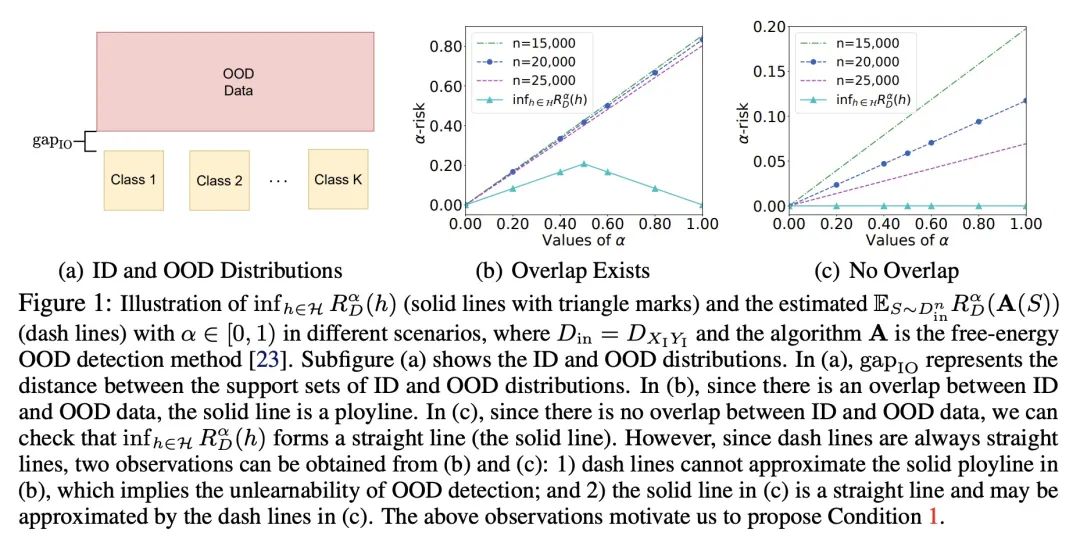
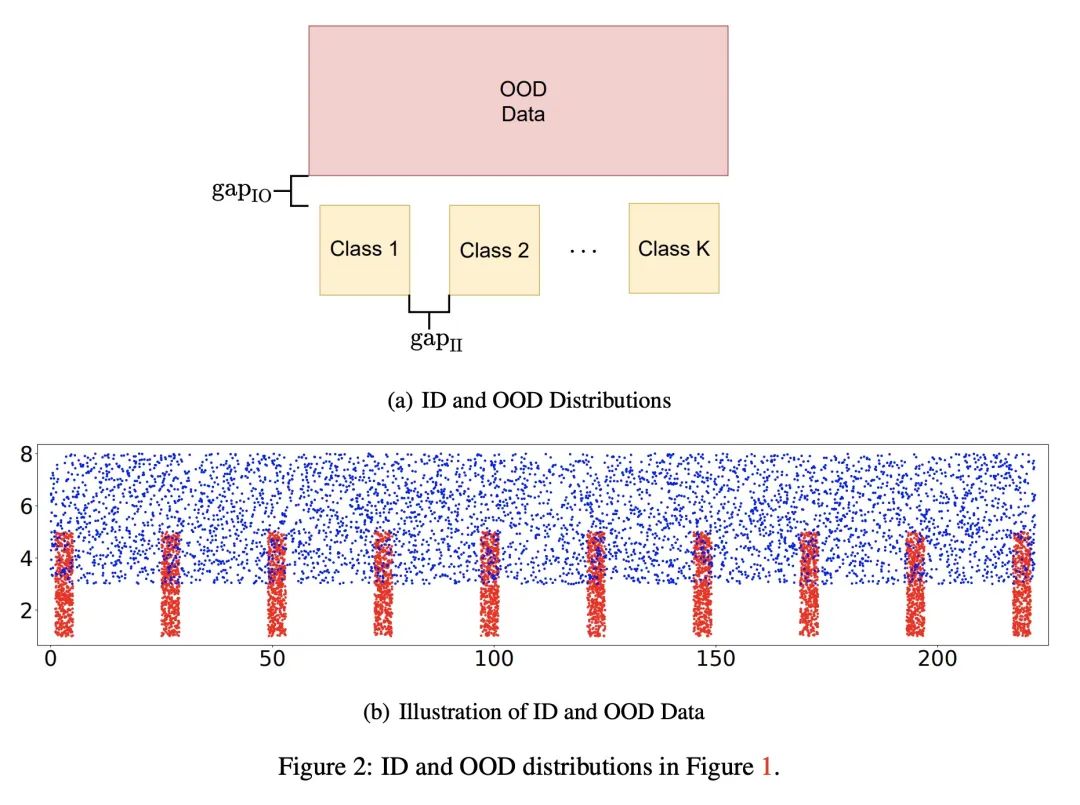
分布外检测可学习性研究。监督学习的目的是在训练数据和测试数据同分布的假设下训练一个分类器。为了缓解上述假设,研究人员研究了一个更现实的环境:分布外(OOD)检测,其中测试数据可能来自训练时未知的类别(即OOD数据)。由于OOD数据的不可用性和多样性,良好的泛化能力对于有效的OOD检测算法至关重要。为了研究OOD检测的泛化问题,本文研究了OOD检测的可能近似正确(PAC)学习理论,该理论被研究人员作为一个开放性问题提出。本文为OOD检测的可学习性找到一个必要条件。然后,利用该条件,本文证明了在某些情况下OOD检测的可学习性的几个不可能定理。尽管这些不可能定理是令人沮丧的,但本文发现这些不可能定理的某些条件在某些实际情况下可能不成立。基于这一观察,本文给出了几个必要和充分的条件来描述OOD检测在某些实际场景下的可学习性。最后,本文还基于所提出的OOD理论为几个有代表性的OOD检测工作提供了理论支持。
Supervised learning aims to train a classifier under the assumption that training and test data are from the same distribution. To ease the above assumption, researchers have studied a more realistic setting: out-of-distribution (OOD) detection, where test data may come from classes that are unknown during training (i.e., OOD data). Due to the unavailability and diversity of OOD data, good generalization ability is crucial for effective OOD detection algorithms. To study the generalization of OOD detection, in this paper, we investigate the probably approximately correct (PAC) learning theory of OOD detection, which is proposed by researchers as an open problem. First, we find a necessary condition for the learnability of OOD detection. Then, using this condition, we prove several impossibility theorems for the learnability of OOD detection under some scenarios. Although the impossibility theorems are frustrating, we find that some conditions of these impossibility theorems may not hold in some practical scenarios. Based on this observation, we next give several necessary and sufficient conditions to characterize the learnability of OOD detection in some practical scenarios. Lastly, we also offer theoretical supports for several representative OOD detection works based on our OOD theory.
https://openreview.net/forum?id=sde_7ZzGXOE

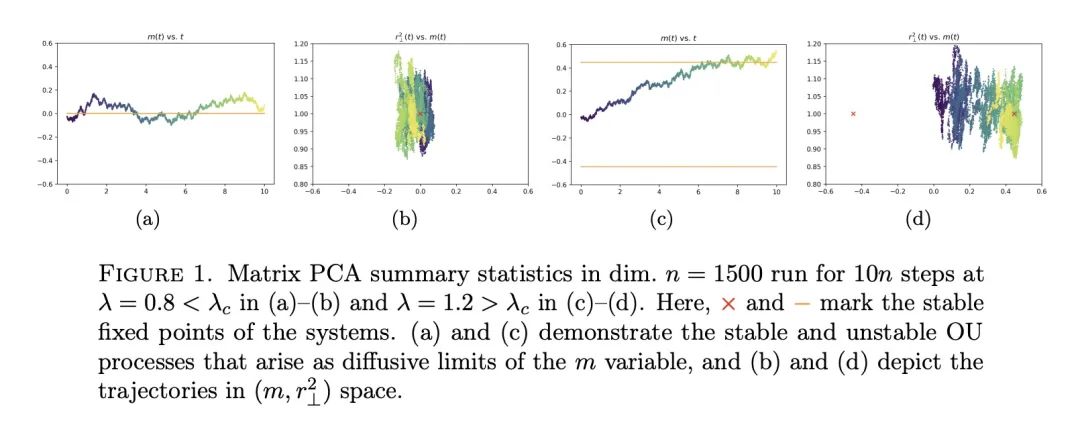
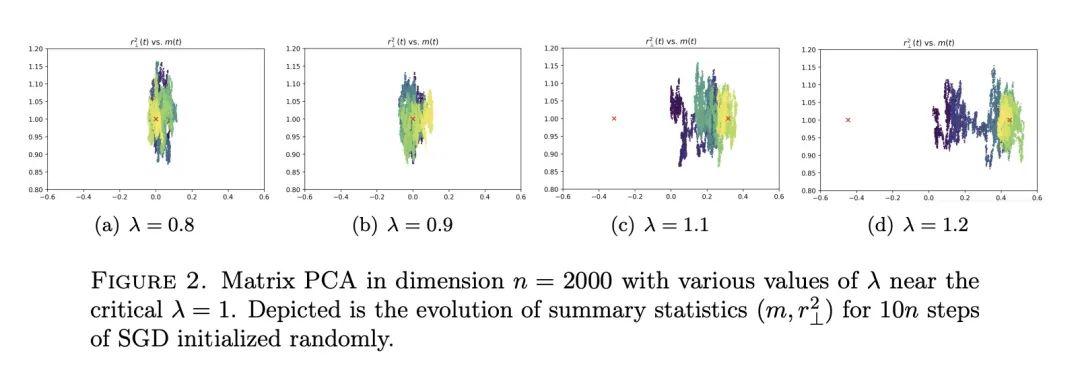
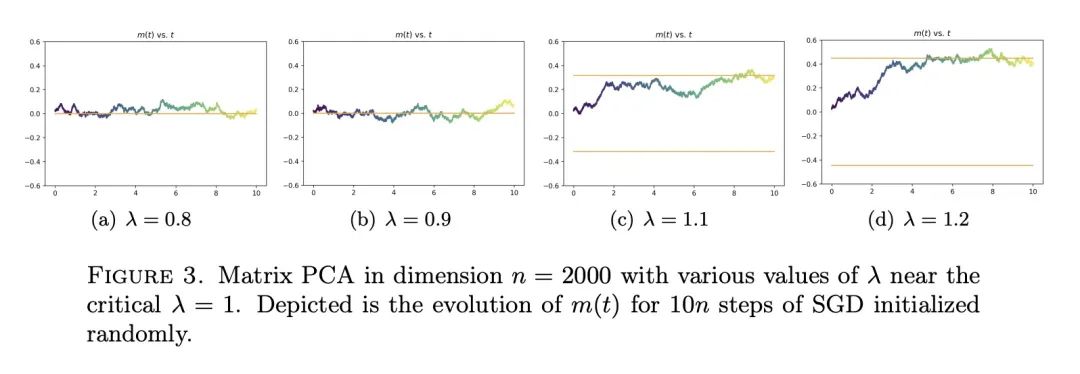
4、[LG] High-dimensional limit theorems for SGD: Effective dynamics and critical scaling
G B Arous, R Gheissari, A Jagannath
[New York University & Northwestern University & University of Waterloo]
SGD高维极限定理:有效动力学与临界扩展。本文研究了高维系统中步长不变的随机梯度下降(SGD)的扩展极限,证明了SGD的汇总统计(即有限维函数)在维度达到无穷大时的轨迹的极限定理。所提出方法允许选择被跟踪的汇总统计量、初始化和步长。它产生了发射(ODE)和扩散(SDE)两种极限,极限极大地取决于前者的选择。本文展示了步长的一个临界比例机制,在该机制下,有效的发射动力学与群体损失的梯度流相匹配,但在该机制下,一个新的修正项出现,改变了相图。关于这个有效动力学的固定点,相应的扩散极限可能是相当复杂的,甚至是退化的。本文在流行的例子上展示了所提出的方法,包括对尖峰矩阵和张量模型的估计,以及通过两层网络对二元和XOR型高斯混合模型的分类。这些例子表现出令人惊讶的现象,包括收敛的多模态时间尺度,以及从随机(如高斯)初始化中以远离零的概率收敛到次优解。本文证明了过参数化的好处,即随着第二层宽度的增加,后者的概率归零。
We study the scaling limits of stochastic gradient descent (SGD) with constant step-size in the high-dimensional regime. We prove limit theorems for the trajectories of summary statistics (i.e., finite-dimensional functions) of SGD as the dimension goes to infinity. Our approach allows one to choose the summary statistics that are tracked, the initialization, and the step-size. It yields both ballistic (ODE) and diffusive (SDE) limits, with the limit depending dramatically on the former choices. We show a critical scaling regime for the step-size, below which the effective ballistic dynamics matches gradient flow for the population loss, but at which, a new correction term appears which changes the phase diagram. About the fixed points of this effective dynamics, the corresponding diffusive limits can be quite complex and even degenerate. We demonstrate our approach on popular examples including estimation for spiked matrix and tensor models and classification via two-layer networks for binary and XOR-type Gaussian mixture models. These examples exhibit surprising phenomena including multimodal timescales to convergence as well as convergence to sub-optimal solutions with probability bounded away from zero from random (e.g., Gaussian) initializations. At the same time, we demonstrate the benefit of overparametrization by showing that the latter probability goes to zero as the second layer width grows.
https://openreview.net/forum?id=Q38D6xxrKHe

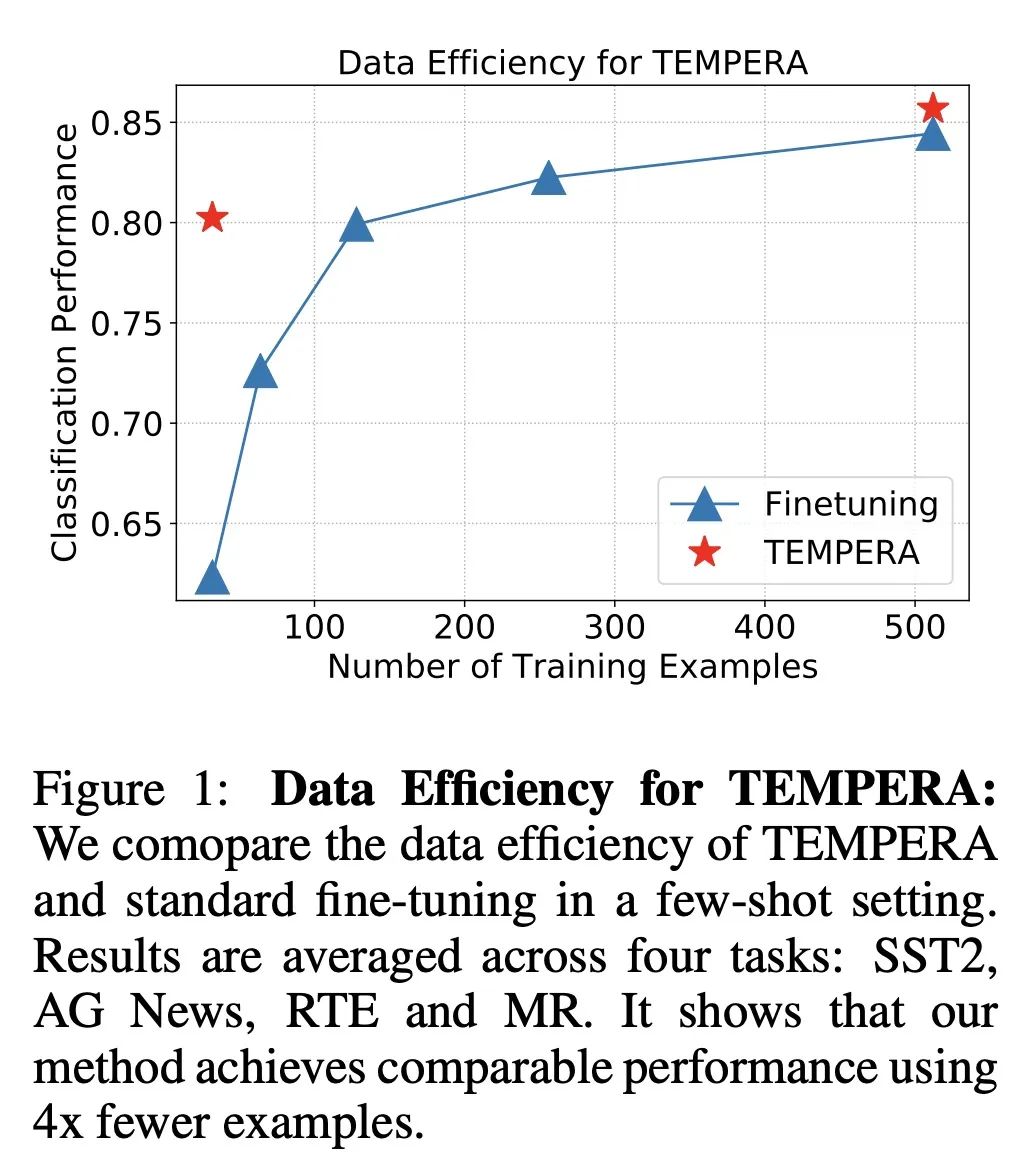
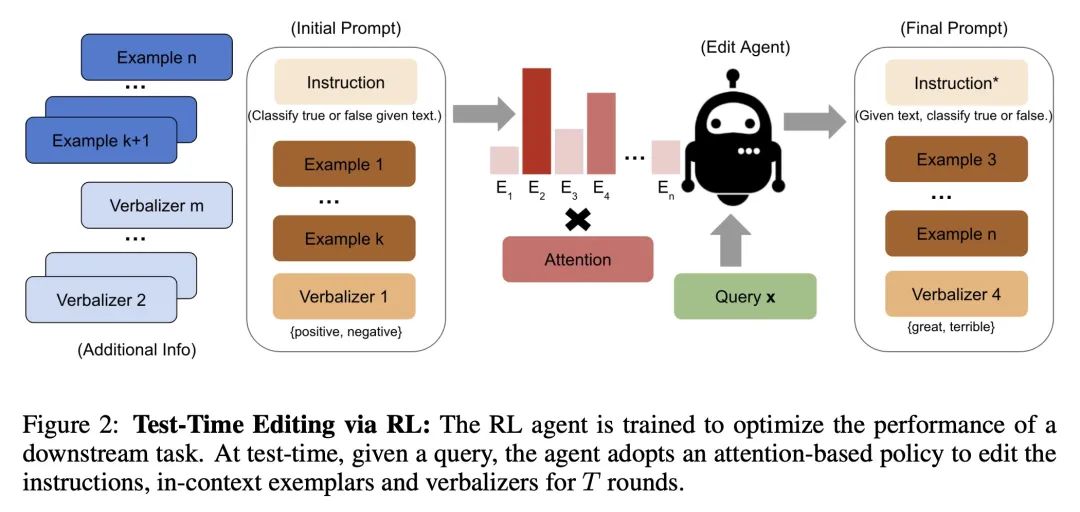
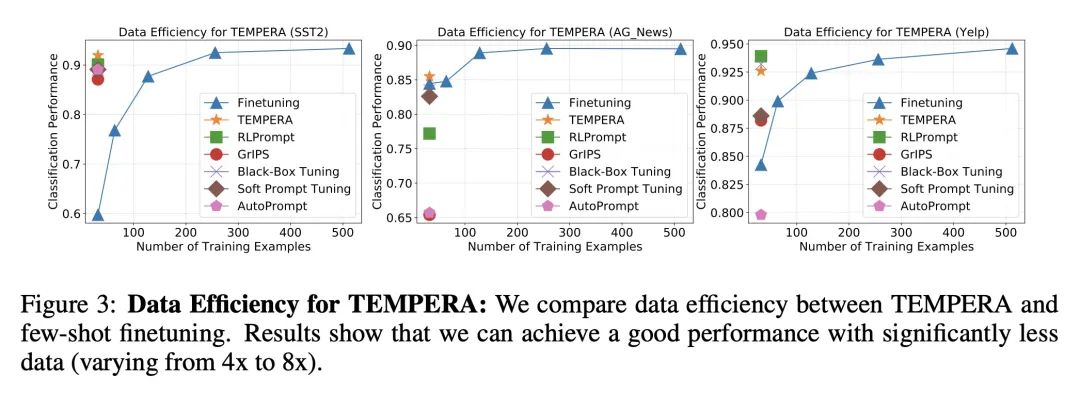
5、[CL] TEMPERA: Test-Time Prompting via Reinforcement Learning
T Zhang, X Wang, D Zhou, D Schuurmans, J E. Gonzalez
[UC Berkeley & Google Research]
TEMPERA:基于强化学习的测试时提示。仔细的提示设计对于大型语言模型在零样本学习或少样本学习中的使用至关重要。因此,人们对设计最佳提示的自动化方法越来越感兴趣。本文提出基于强化学习的测试时提示编辑(TEMPERA)。与之前的提示生成方法相比,TEMPERA可有效地利用先前知识,自适应不同的查询,并为每个查询提供一个可解释的提示。为实现这一点,本文设计了一个新的行动空间,允许灵活地编辑初始提示,涵盖了广泛的常用组件,如指令、少样本示例和言语者。与最近的SoTA方法(如提示微调、AutoPrompt和RLPrompt)相比,所提出方法在各种任务(包括情感分析、话题分类、自然语言推理和阅读理解)中取得了显著的收益。与传统微调方法相比,所提出方法实现了平均5.33倍的样本效率提升。
Careful prompt design is critical to the use of large language models in zero-shot or few-shot learning. As a consequence, there is a growing interest in automated methods to design optimal prompts. In this work, we propose Test-time Prompt Editing using Reinforcement learning (TEMPERA). In contrast to prior prompt generation methods, TEMPERA can efficiently leverage prior knowledge, is adaptive to different queries and provides an interpretable prompt for every query. To achieve this, we design a novel action space that allows flexible editing of the initial prompts covering a wide set of commonly-used components like instructions, few-shot exemplars, and verbalizers. The proposed method achieves significant gains compared with recent SoTA approaches like prompt tuning, AutoPrompt, and RLPrompt, across a variety of tasks including sentiment analysis, topic classification, natural language inference, and reading comprehension. Our method achieves 5.33x on average improvement in sample efficiency when compared to the traditional fine-tuning methods.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.11890

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
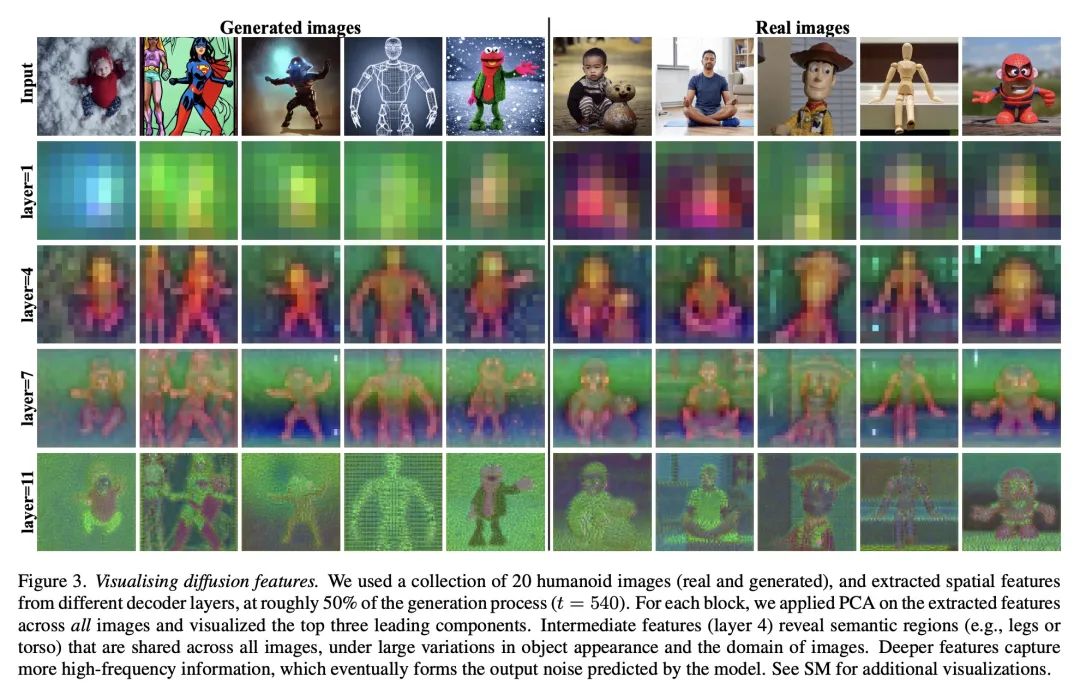
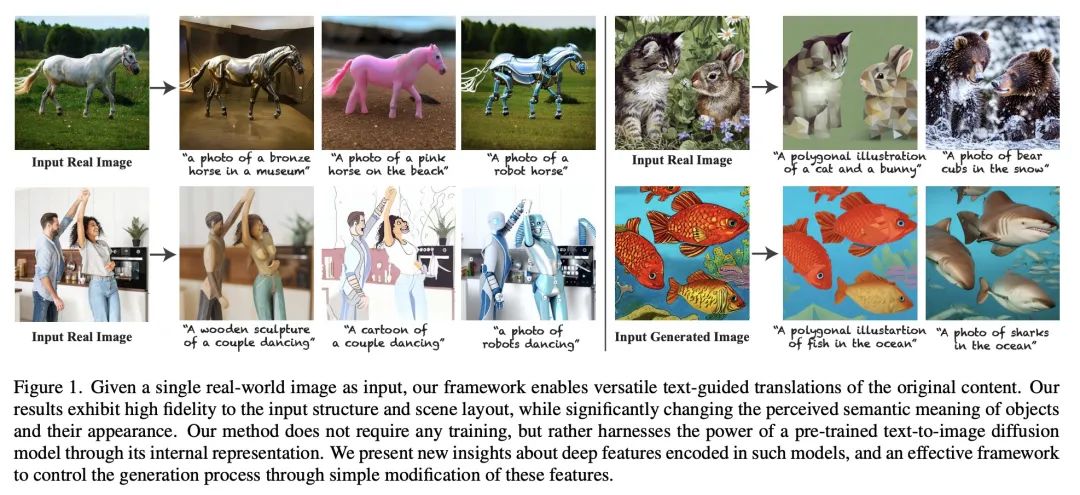
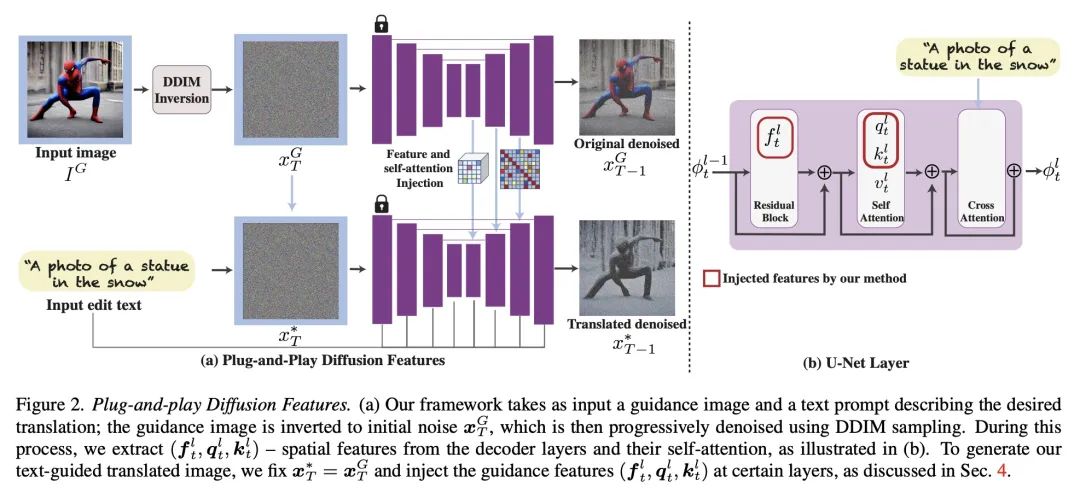
[CV] Plug-and-Play Diffusion Features for Text-Driven Image-to-Image Translation
面向文本驱动图像到图像翻译的即插即用扩散特征
N Tumanyan, M Geyer, S Bagon, T Dekel
[Weizmann Institute of Science]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.12572


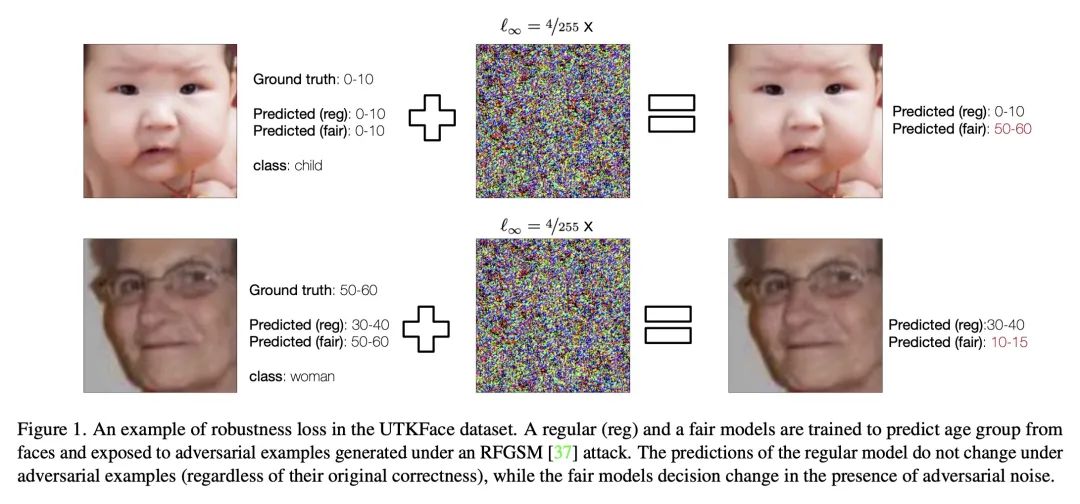
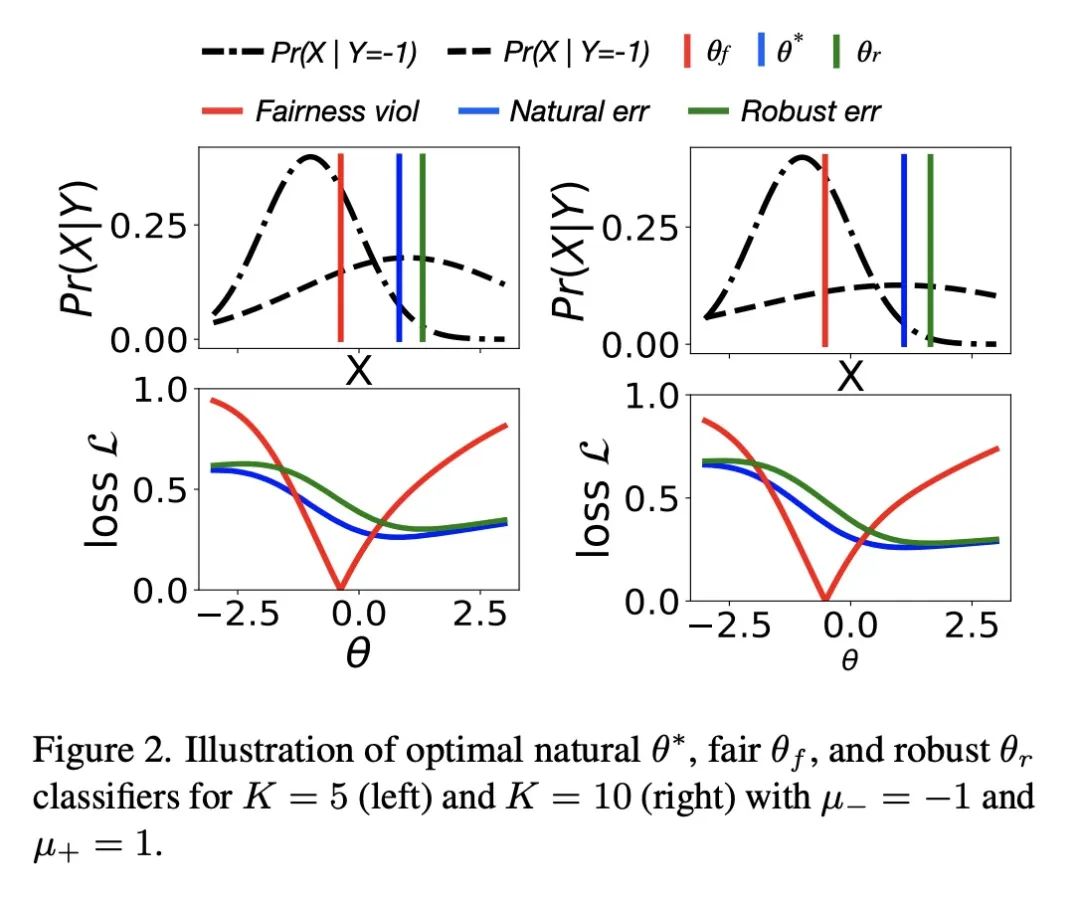
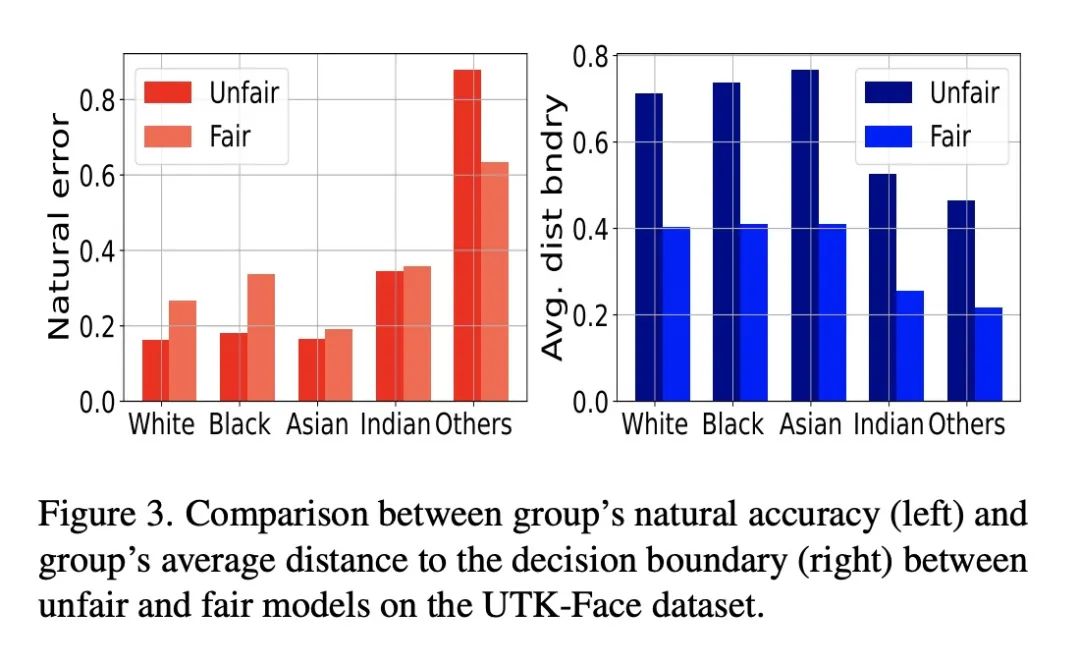
[LG] Fairness Increases Adversarial Vulnerability
公平会增加对抗脆弱性
C Tran, K Zhu, F Fioretto, P V Hentenryck
[Syracuse University & Georgia Tech]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.11835

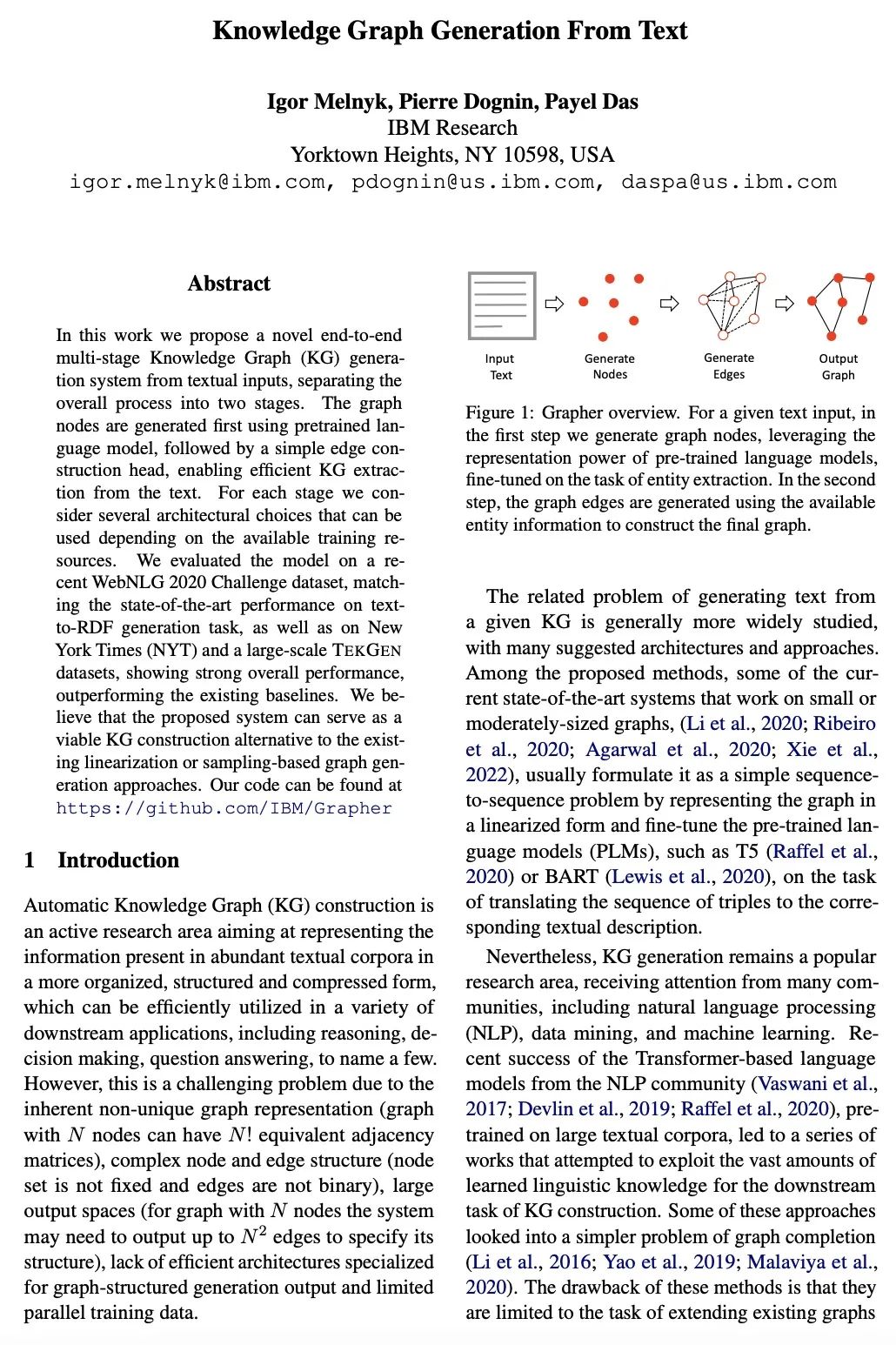
[CL] Knowledge Graph Generation From Text
端到端多阶段文本-知识图谱生成
I Melnyk, P Dognin, P Das
[IBM Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.10511
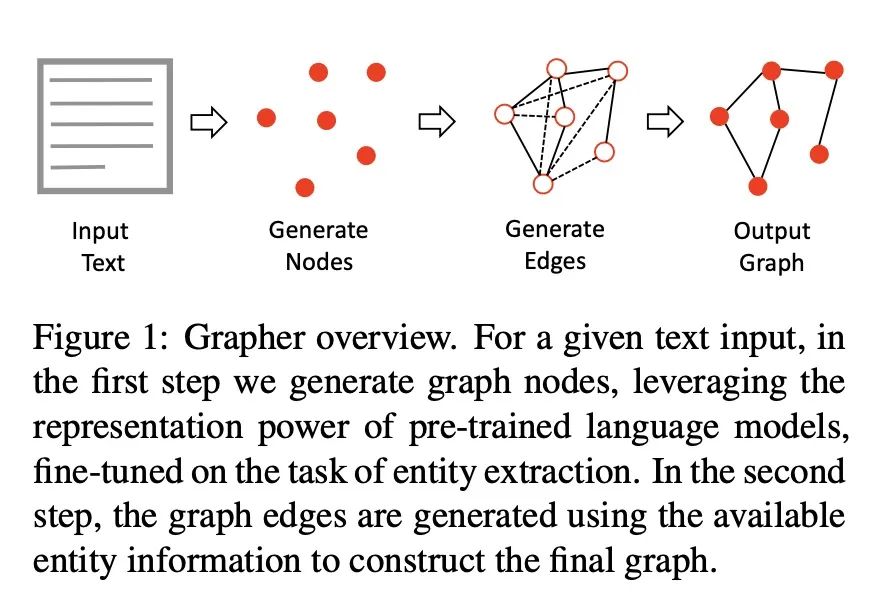
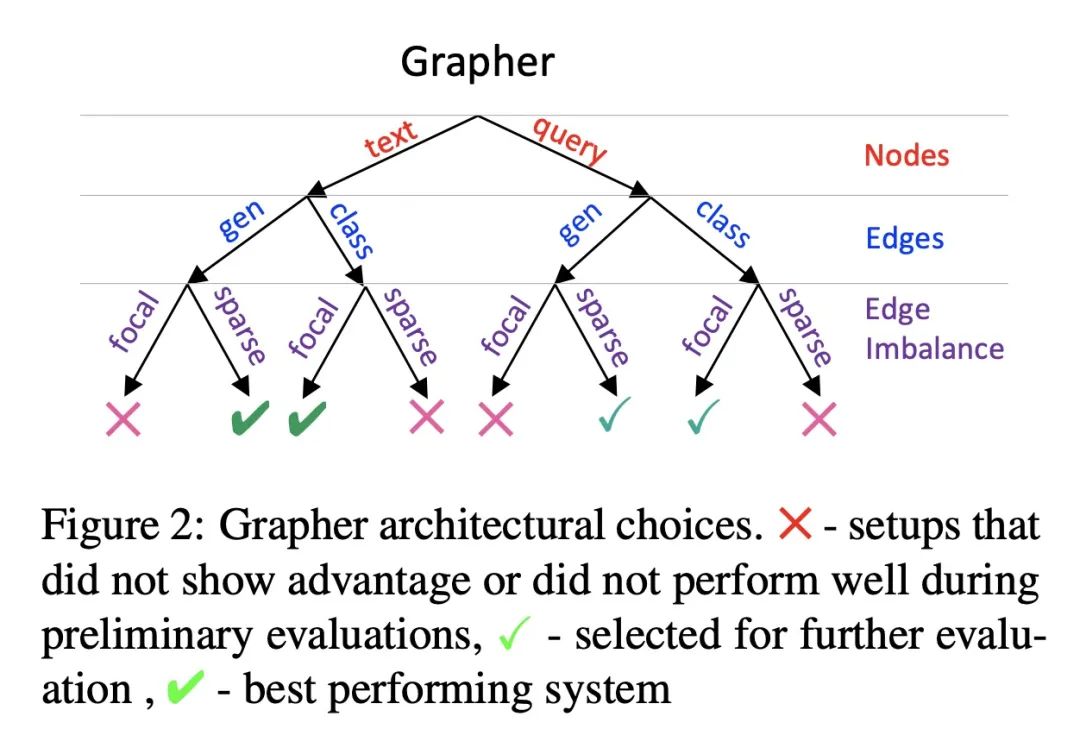
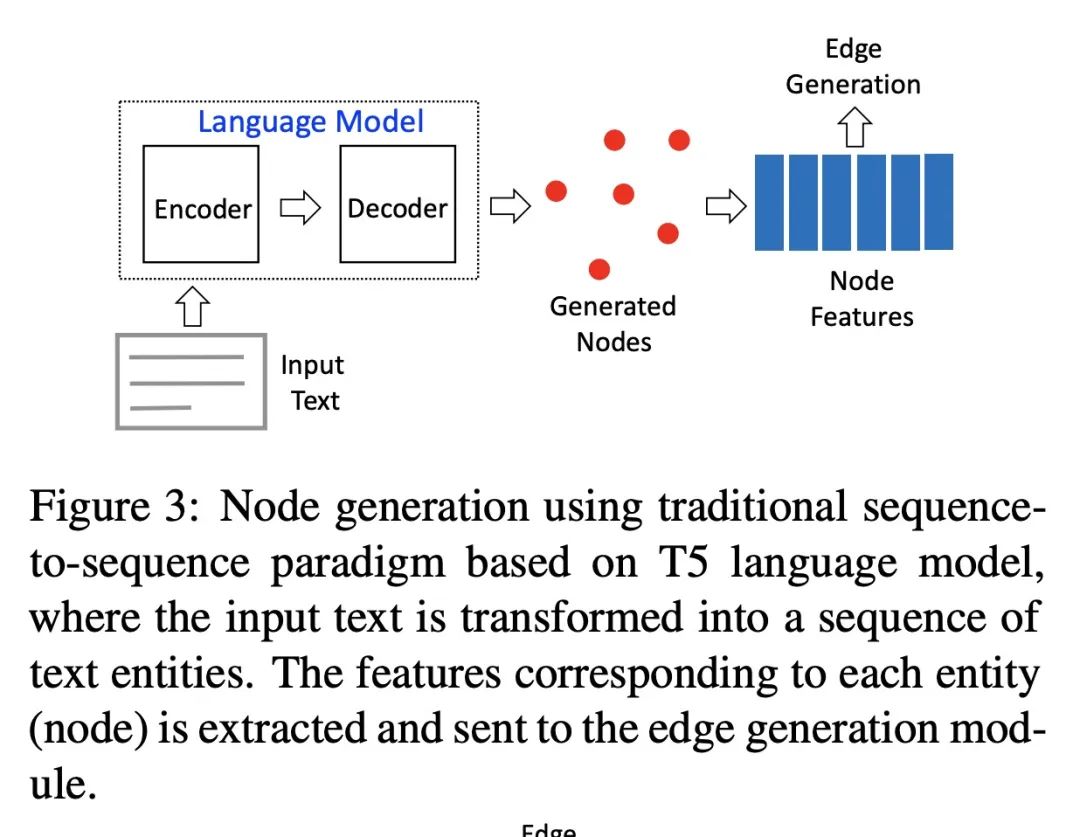
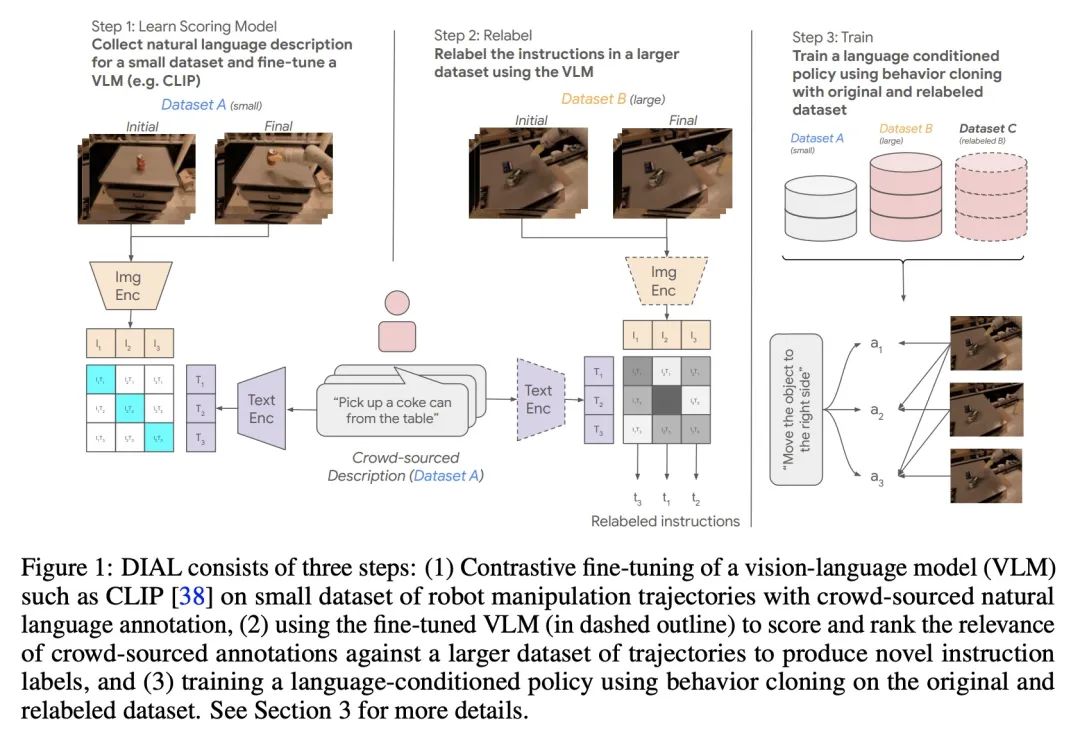
[RO] Robotic Skill Acquisition via Instruction Augmentation with Vision-Language Models
基于视觉-语言模型的指令增强机器人技能学习
T Xiao, H Chan, P Sermanet, A Wahid, A Brohan, K Hausman, S Levine, J Tompson
[Robotics at Google]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.11736


内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢