转自爱可可爱生活
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 GR - 图形学
摘要:基于压缩目标的选择学习、用PAC-Bayes紧确压缩界解释泛化问题、草图引导文本-图像扩散模型、面向可控图像生成的空间-文本表示、视觉记忆条件一致故事生成、通过基于过程反馈和基于结果反馈求解数学应用题、基于算子学习的扩散模型快速采样、从无姿态照片学习潜神经场景表示、神经泊松神经场指示函数
1、[LG] Learning Options via Compression
Y Jiang, EZ Liu, B Eysenbach, JZ Kolter…
[CMU & Stanford University]
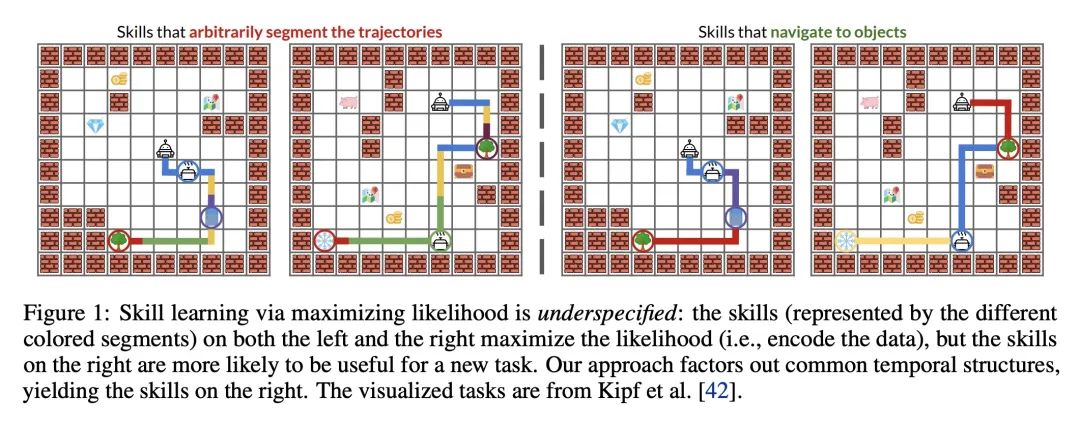
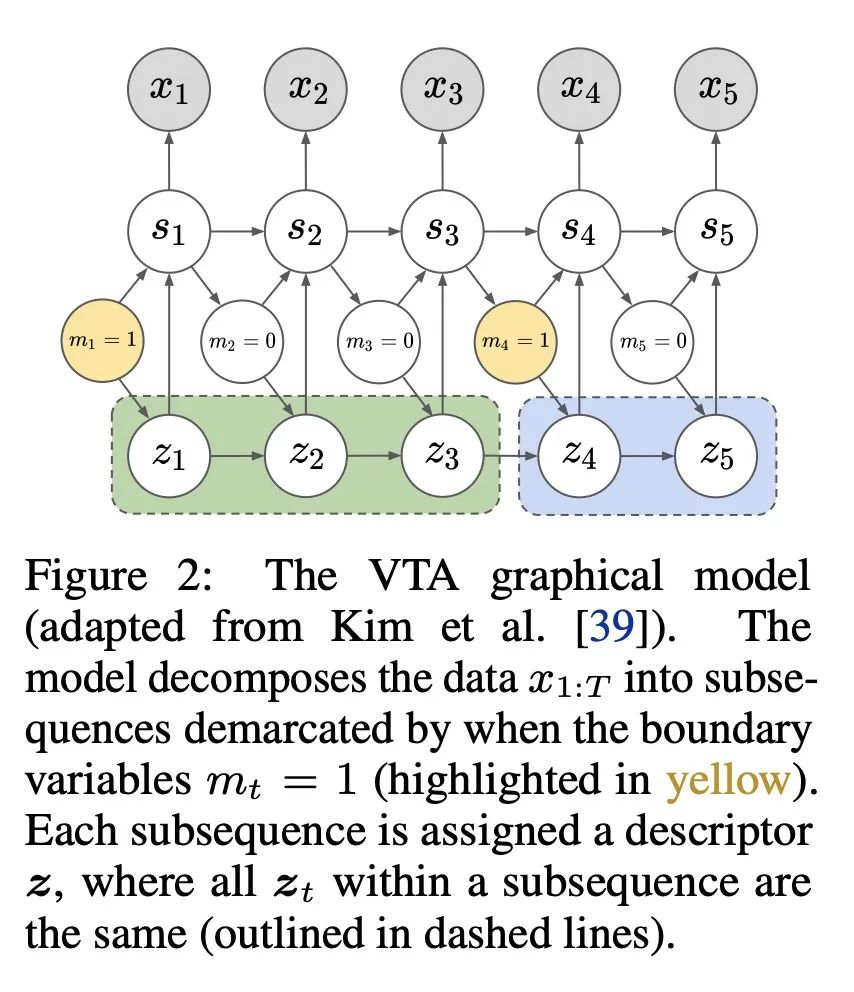
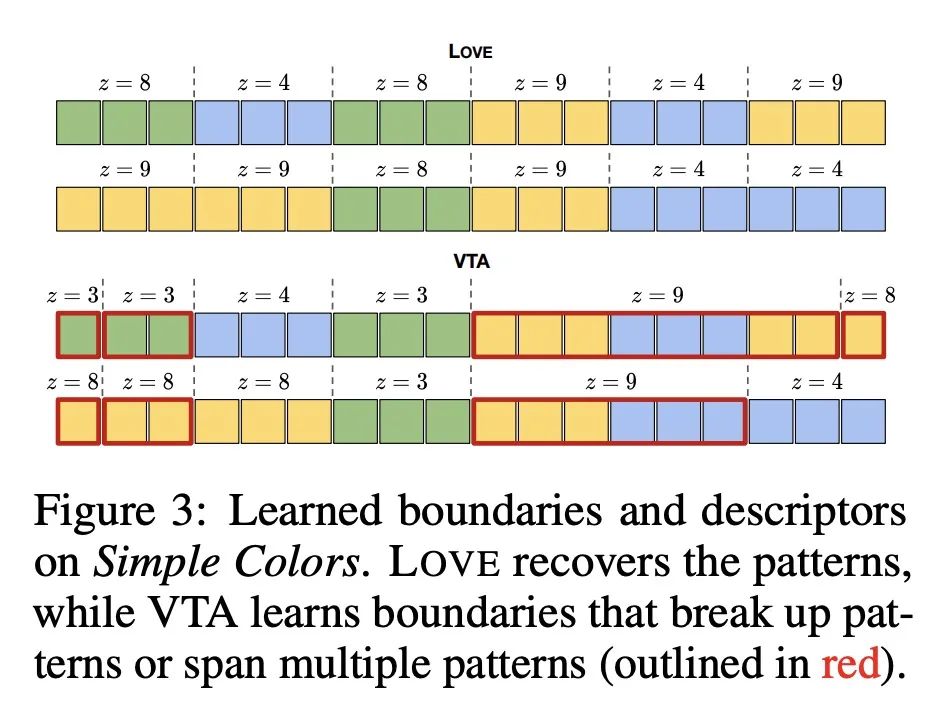
基于压缩目标的选择学习。识别多任务强化学习中某些任务解决方案的统计规律性,可以加速新任务的学习。技能学习通过将预先收集的经验分解为一连串的技能,提供了一种识别这些规律性的方法。一种流行的技能学习方法,是用潜变量模型最大化预收集的经验的可能性。其中潜变量代表技能。然而,通常有许多解决方案可以同样最大化可能性,包括退化的解决方案。为了解决该问题,本文提出一种新目标,将最大似然目标与技能描述长度惩罚结合起来。这种惩罚激励技能从经验中最大限度地提取共同结构。从经验上看,该目标所学习的技能与仅从最大似然中学习的技能相比,能用更少的样本解决下游任务。此外,在离线多任务设置中,大多数之前的工作侧重于低维观察的任务,而本文目标可扩展到具有高维图像观察的挑战性任务。
Identifying statistical regularities in solutions to some tasks in multi-task reinforcement learning can accelerate the learning of new tasks. Skill learning offers one way of identifying these regularities by decomposing pre-collected experiences into a sequence of skills. A popular approach to skill learning is maximizing the likelihood of the pre-collected experience with latent variable models, where the latent variables represent the skills. However, there are often many solutions that maximize the likelihood equally well, including degenerate solutions. To address this underspecification, we propose a new objective that combines the maximum likelihood objective with a penalty on the description length of the skills. This penalty incentivizes the skills to maximally extract common structures from the experiences. Empirically, our objective learns skills that solve downstream tasks in fewer samples compared to skills learned from only maximizing likelihood. Further, while most prior works in the offline multi-task setting focus on tasks with low-dimensional observations, our objective can scale to challenging tasks with high-dimensional image observations.
https://openreview.net/forum?id=D4fuQ1MveDM

2、[LG] PAC-Bayes Compression Bounds So Tight That They Can Explain Generalization
S Lotfi, M Finzi, S Kapoor, A Potapczynski, M Goldblum, A G Wilson
[New York University]
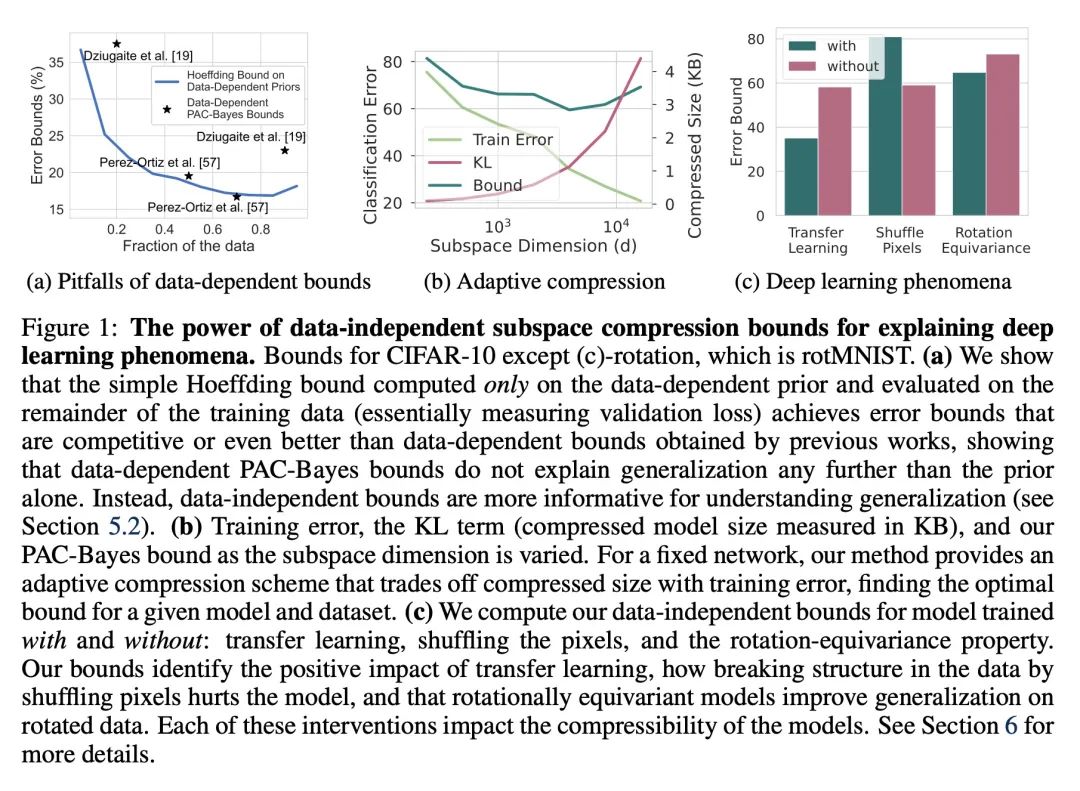
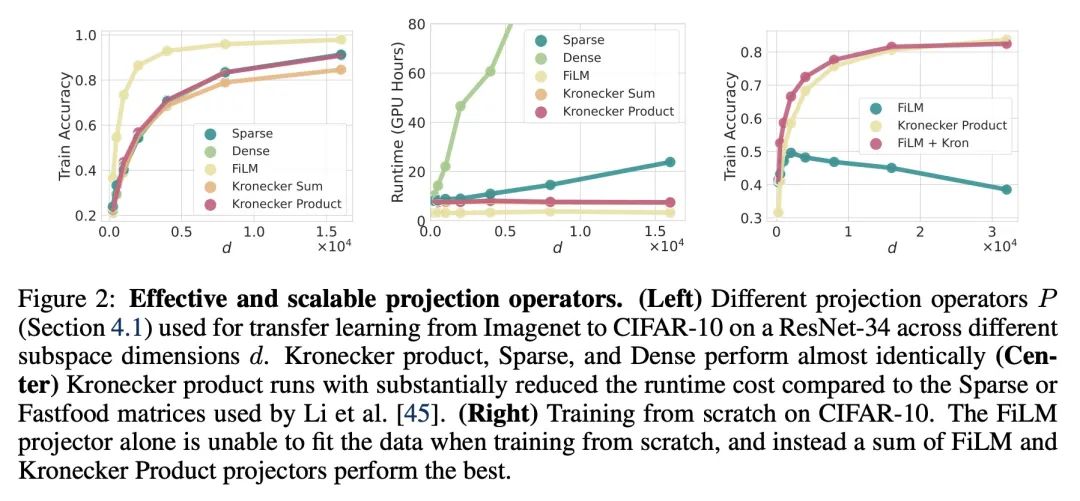
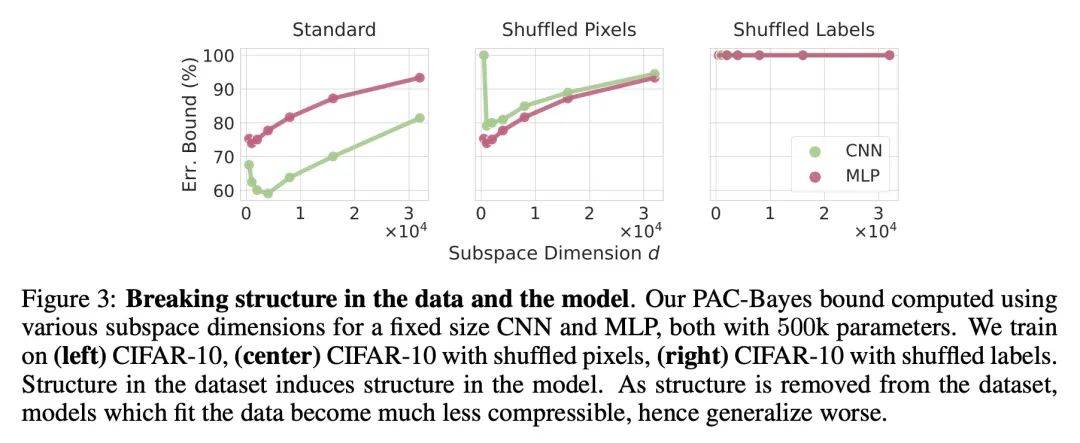
用PAC-Bayes紧确压缩界解释泛化问题。虽然在开发深度神经网络的非空泛化界方面取得了进展,但这些界往往不能说明深度学习有效的原因。本文提出一种基于在线性子空间中量化神经网络参数的压缩方法,对模型和训练数据集具有很强的自适应性,深刻地改进了之前的结果,在各种任务上提供了最先进的泛化界,包括迁移学习。本文用这些严格的界来更好地理解模型大小、等变性和优化的隐性偏差在深度学习中的作用。本文发现大模型可以被压缩到比之前已知的更大的程度。本文还论证了在解释泛化时与数据无关的界。
While there has been progress in developing non-vacuous generalization bounds for deep neural networks, these bounds tend to be uninformative about why deep learning works. In this paper, we develop a compression approach based on quantizing neural network parameters in a linear subspace, profoundly improving on previous results to provide state-of-the-art generalization bounds on a variety of tasks, including transfer learning. We use these tight bounds to better understand the role of model size, equivariance, and the implicit biases of optimization, for generalization in deep learning. Notably, we find large models can be compressed to a much greater extent than previously known, encapsulating Occam's razor. We also argue for data-independent bounds in explaining generalization.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13609

3、[CV] Sketch-Guided Text-to-Image Diffusion Models
A Voynov, K Aberman, D Cohen-Or
[Google Research]
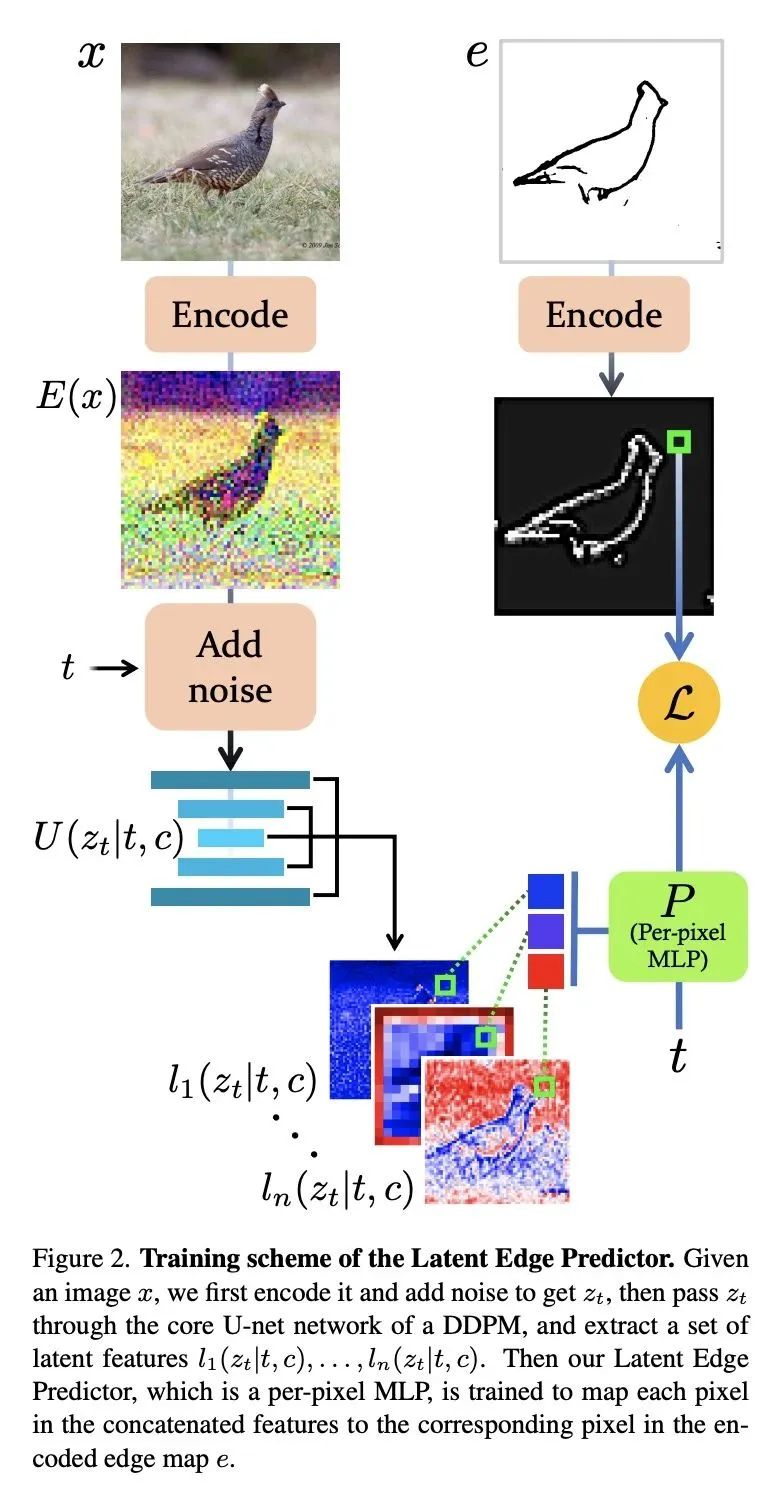
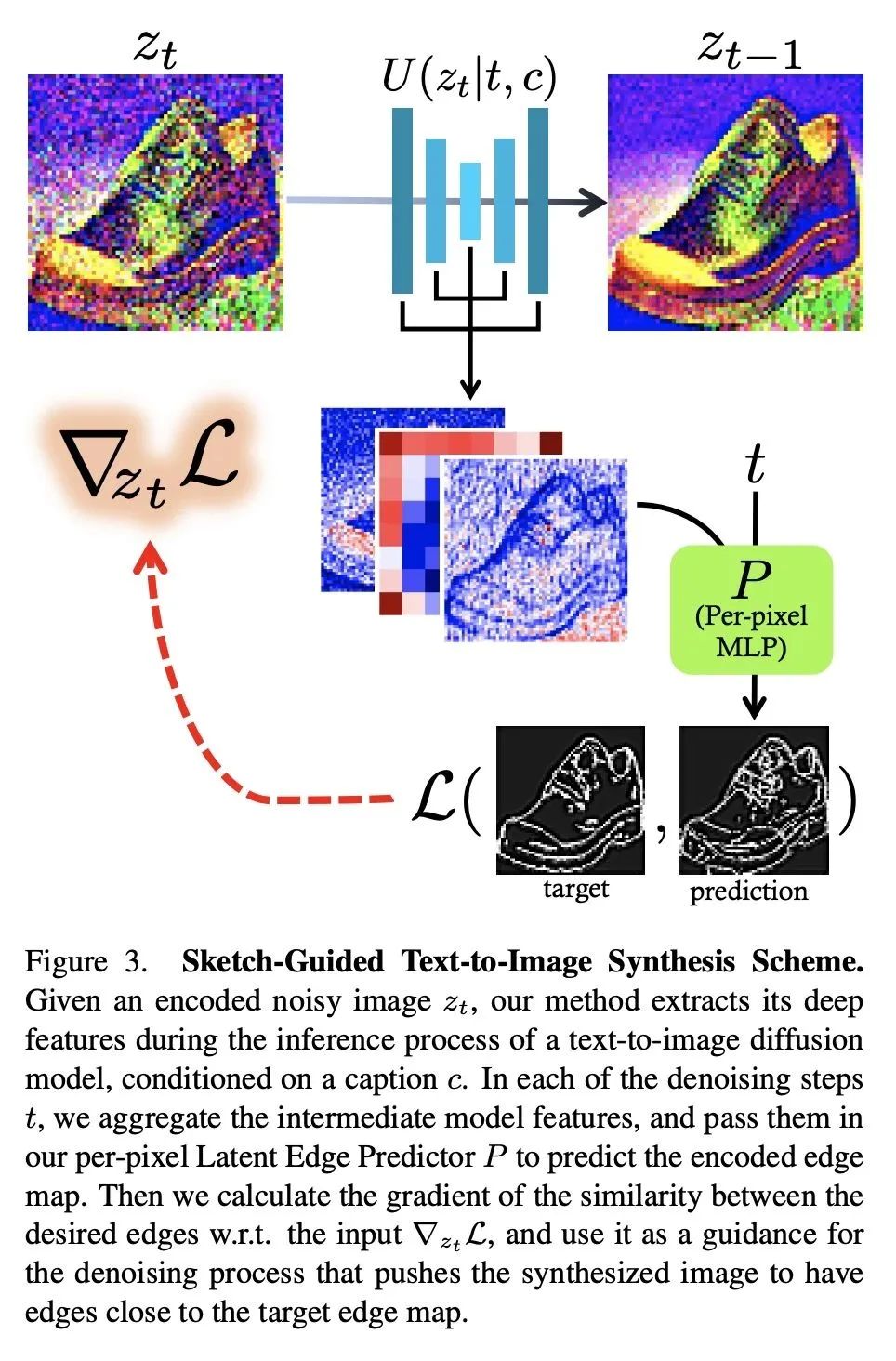
草图引导文本-图像扩散模型。文本-图像模型在机器学习的发展过程中带来了显著的飞跃,展示了从给定文本提示中合成高质量图像的能力。然而,这些强大的预训练模型仍然缺乏能指导合成图像的空间属性的控制柄。本文提出一种通用方法来指导预训练文本到图像扩散模型,在推理时间内用来自另一个域(例如,草图)的空间图。与之前的工作不同,所提出方法不需要为该任务训练一个专门的模型或编码器。其关键想法是训练一个潜导预测器(LGP)——一个小的、每像素多层感知器(MLP),将噪声图像的潜特征映射到空间图,其中深度特征是从核心去噪扩散概率模型(DDPM)网络中提取的。LGP只在几千张图像上进行训练,并构成一个可微引导图预测器,在此基础上计算损失并向后传播,以推动中间图像与空间图一致。每个像素的训练提供了灵活性和定位性,使该技术在域外草图上表现良好,包括自由手绘风格的图画。本文特别关注草图到图像的翻译任务,揭示了一种强大的、富有表现力的方法,可以按照任意风格或领域草图的指导来生成图像。
Text-to-Image models have introduced a remarkable leap in the evolution of machine learning, demonstrating high-quality synthesis of images from a given text-prompt. However, these powerful pretrained models still lack control handles that can guide spatial properties of the synthesized images. In this work, we introduce a universal approach to guide a pretrained text-to-image diffusion model, with a spatial map from another domain (e.g., sketch) during inference time. Unlike previous works, our method does not require to train a dedicated model or a specialized encoder for the task. Our key idea is to train a Latent Guidance Predictor (LGP) - a small, per-pixel, Multi-Layer Perceptron (MLP) that maps latent features of noisy images to spatial maps, where the deep features are extracted from the core Denoising Diffusion Probabilistic Model (DDPM) network. The LGP is trained only on a few thousand images and constitutes a differential guiding map predictor, over which the loss is computed and propagated back to push the intermediate images to agree with the spatial map. The per-pixel training offers flexibility and locality which allows the technique to perform well on out-of-domain sketches, including free-hand style drawings. We take a particular focus on the sketch-to-image translation task, revealing a robust and expressive way to generate images that follow the guidance of a sketch of arbitrary style or domain. Project page: this http URL
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13752


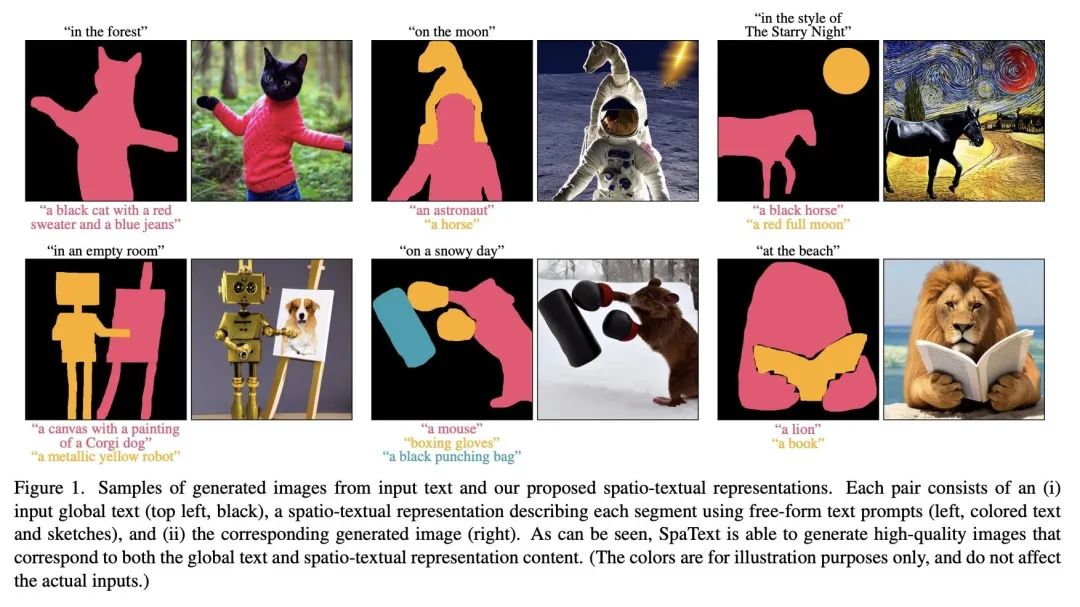
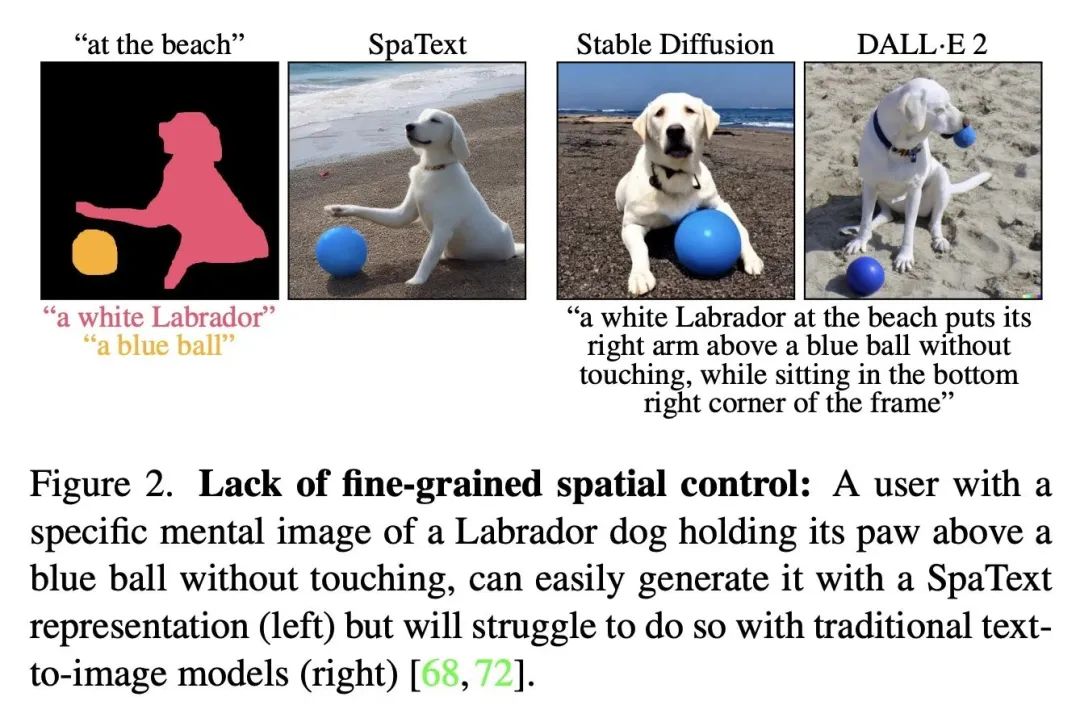
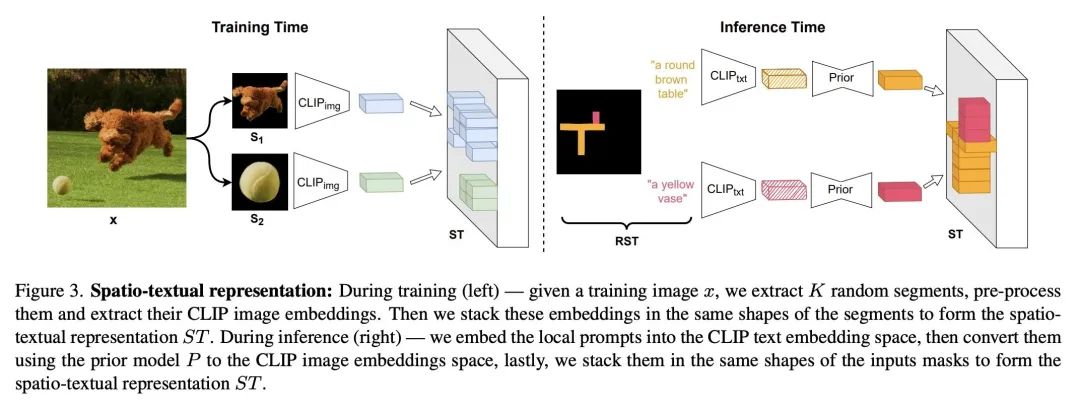
4、[CV] SpaText: Spatio-Textual Representation for Controllable Image Generation
O Avrahami, T Hayes, O Gafni, S Gupta, Y Taigman...
[Meta AI & The Hebrew University of Jerusalem & Reichman University]
SpaText: 面向可控图像生成的空间-文本表示。最近的文本到图像扩散模型能产生质量空前的令人信服的结果。然而,几乎不可能以精细方式控制不同区域/目标的形状或其布局。之前提供这种控制的尝试因其对一组固定标签的依赖而受到阻碍。本文提出SpaText——一种使用开放词汇的场景控制进行文本到图像生成的新方法。除了描述整个场景的全局文本提示外,用户还提供一个分割图,其中每个感兴趣的区域都由自由形式的自然语言描述来标注。由于缺乏大规模数据集,对图像中每区域都有详细的文本描述,本文选择利用目前大规模的文本到图像数据集,并将该方法建立在一个新的基于CLIP的空间-文本表示上,并在两个最先进的扩散模型上显示其有效性:基于像素和基于潜空间。本文展示了如何将扩散模型中的无分类指导方法扩展到多条件情况,并提出一种替代的加速推理算法。本文提供了几个自动评估指标,除了FID分数和用户研究外,还用这些指标来评估所提出方法,并表明它在具有自由格式文本场景控制的图像生成方面取得了最先进的结果。
Recent text-to-image diffusion models are able to generate convincing results of unprecedented quality. However, it is nearly impossible to control the shapes of different regions/objects or their layout in a fine-grained fashion. Previous attempts to provide such controls were hindered by their reliance on a fixed set of labels. To this end, we present SpaText - a new method for text-to-image generation using open-vocabulary scene control. In addition to a global text prompt that describes the entire scene, the user provides a segmentation map where each region of interest is annotated by a free-form natural language description. Due to lack of large-scale datasets that have a detailed textual description for each region in the image, we choose to leverage the current large-scale text-to-image datasets and base our approach on a novel CLIP-based spatio-textual representation, and show its effectiveness on two state-of-the-art diffusion models: pixel-based and latent-based. In addition, we show how to extend the classifier-free guidance method in diffusion models to the multi-conditional case and present an alternative accelerated inference algorithm. Finally, we offer several automatic evaluation metrics and use them, in addition to FID scores and a user study, to evaluate our method and show that it achieves state-of-the-art results on image generation with free-form textual scene control.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.14305

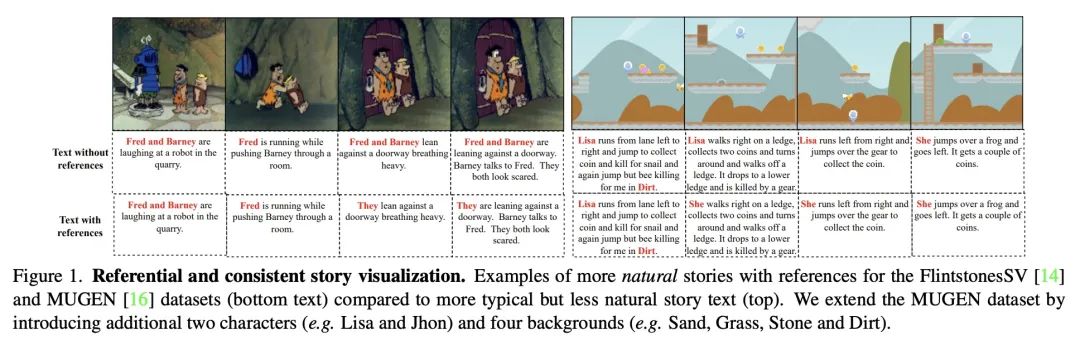
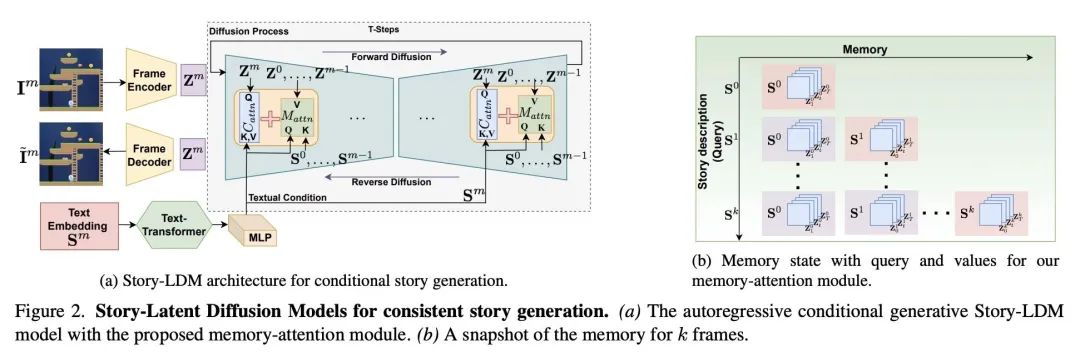
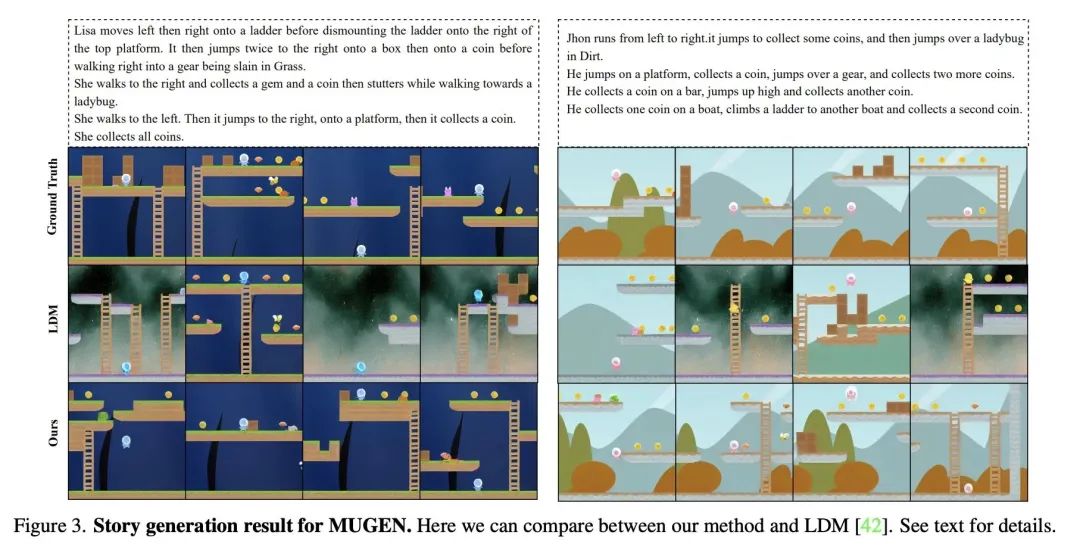
5、[CV] Make-A-Story: Visual Memory Conditioned Consistent Story Generation
T Rahman, H Lee, J Ren, S Tulyakov, S Mahajan, L Sigal
[University of British Columbia & Snap Inc]
Make-A-Story:视觉记忆条件一致故事生成。最近,令人印象深刻的生成模型激增,可以根据文本描述产生高质量的图像(或视频)。然而,所有这些方法都依赖于包含场景和主要角色的明确描述的条件句子。因此,将这样的模型用于更复杂的故事可视化任务,其中自然存在引用和共引,并且需要根据故事的进展来推理何时保持各帧/场景中角色和上下文的一致性,以及何时不这样做,这仍然是一个挑战。本文解决了上述挑战,提出一种新的基于自回归扩散的框架,该框架有一个视觉记忆模块,隐性捕捉了角色和上下文在生成的框架中的上下文。记忆中句子条件软注意力能有效地解决引用问题,并在需要时学会保持场景和角色的一致性。为验证该方法的有效性,本文扩展了MUGEN数据集,并在多句子故事情节中引入了额外的人物、上下文和引用。在MUGEN和FlintstonesSV数据集上进行的故事生成实验表明,所提出方法不仅在生成具有高视觉质量、与故事一致的帧方面优于之前的最先进的方法,而且还在人物和上下文之间建立了适当的对应关系。
There has been a recent explosion of impressive generative models that can produce high quality images (or videos) conditioned on text descriptions. However, all such approaches rely on conditional sentences that contain unambiguous descriptions of scenes and main actors in them. Therefore employing such models for more complex task of story visualization, where naturally references and co-references exist, and one requires to reason about when to maintain consistency of actors and backgrounds across frames/scenes, and when not to, based on story progression, remains a challenge. In this work, we address the aforementioned challenges and propose a novel autoregressive diffusion-based framework with a visual memory module that implicitly captures the actor and background context across the generated frames. Sentence-conditioned soft attention over the memories enables effective reference resolution and learns to maintain scene and actor consistency when needed. To validate the effectiveness of our approach, we extend the MUGEN dataset and introduce additional characters, backgrounds and referencing in multi-sentence storylines. Our experiments for story generation on the MUGEN and the FlintstonesSV dataset show that our method not only outperforms prior state-of-the-art in generating frames with high visual quality, which are consistent with the story, but also models appropriate correspondences between the characters and the background.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13319

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
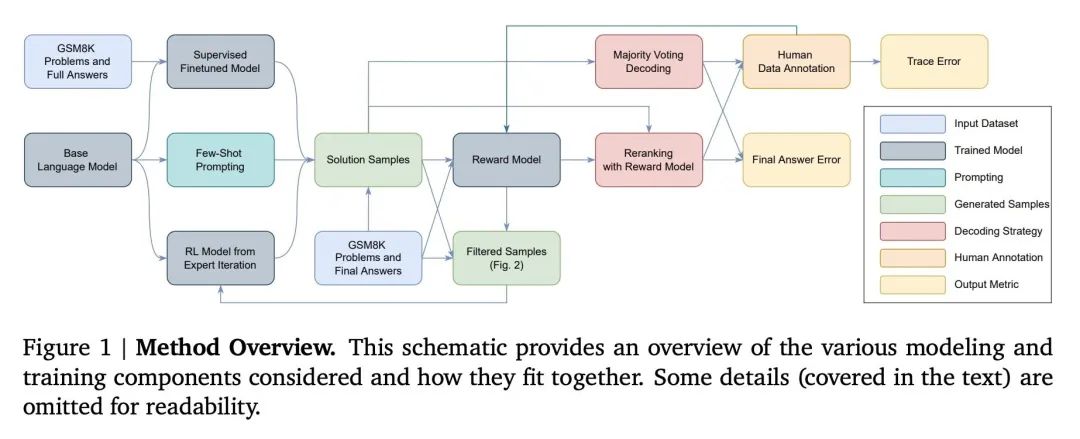
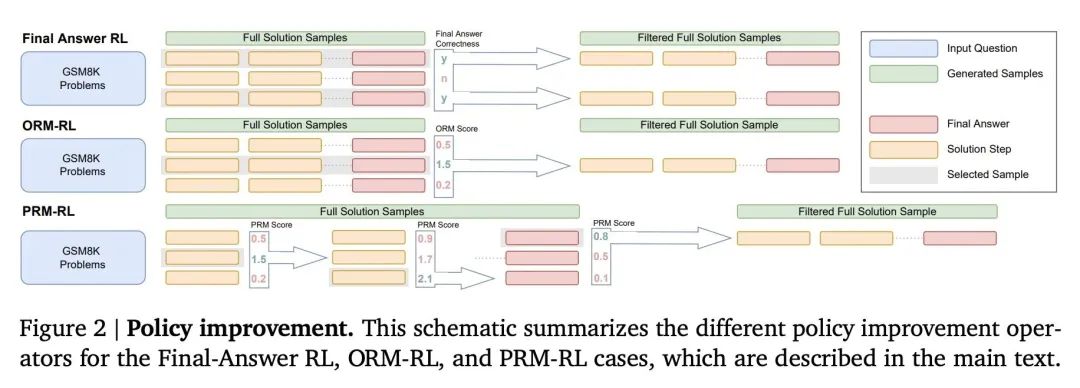
[LG] Solving math word problems with process- and outcome-based feedback
通过基于过程反馈和基于结果反馈求解数学应用题
J Uesato, N Kushman, R Kumar, F Song, N Siegel, L Wang, A Creswell, G Irving, I Higgins
[DeepMind]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.14275

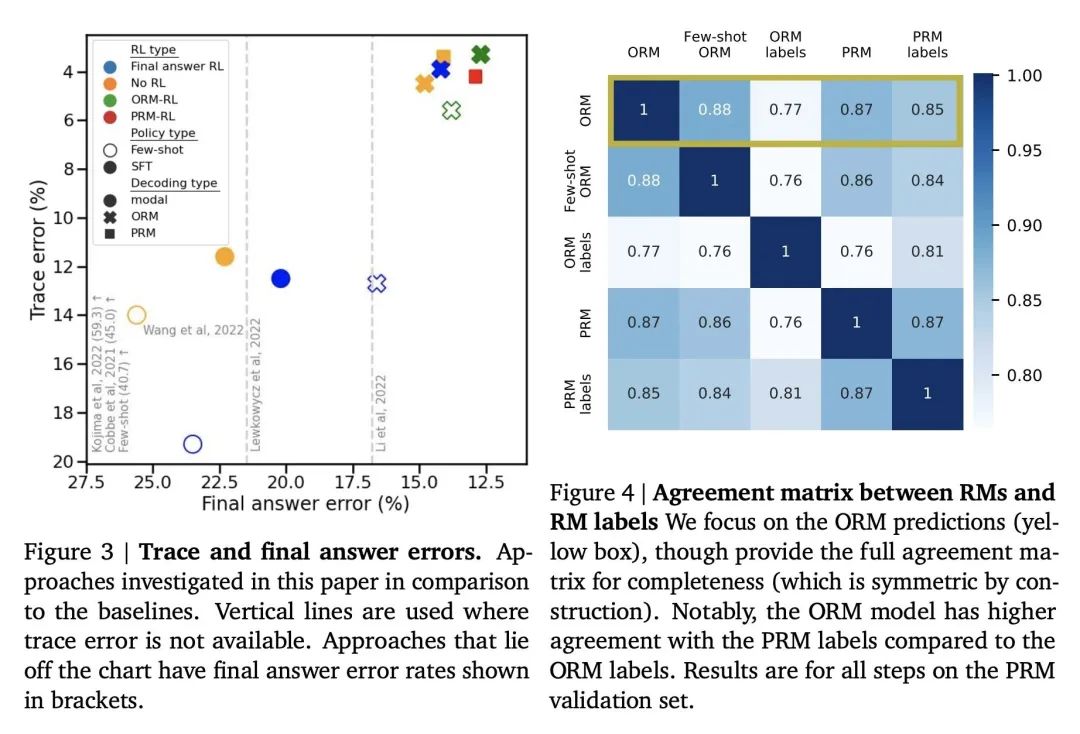
[LG] Fast Sampling of Diffusion Models via Operator Learning
基于算子学习的扩散模型快速采样
H Zheng, W Nie, A Vahdat, K Azizzadenesheli, A Anandkumar
[Caltech & NVIDIA]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13449

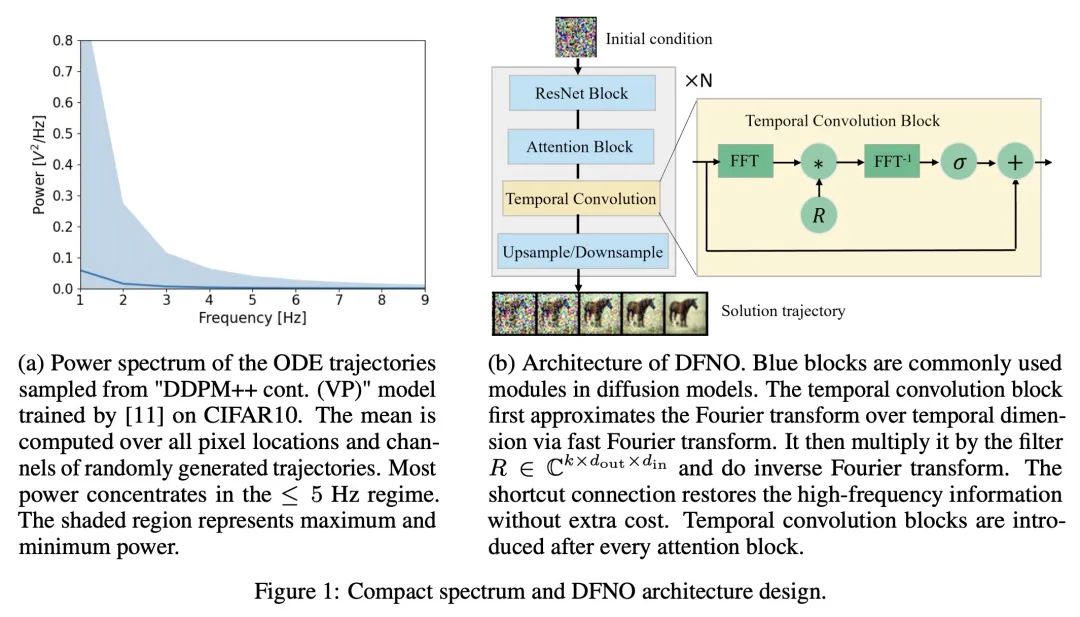
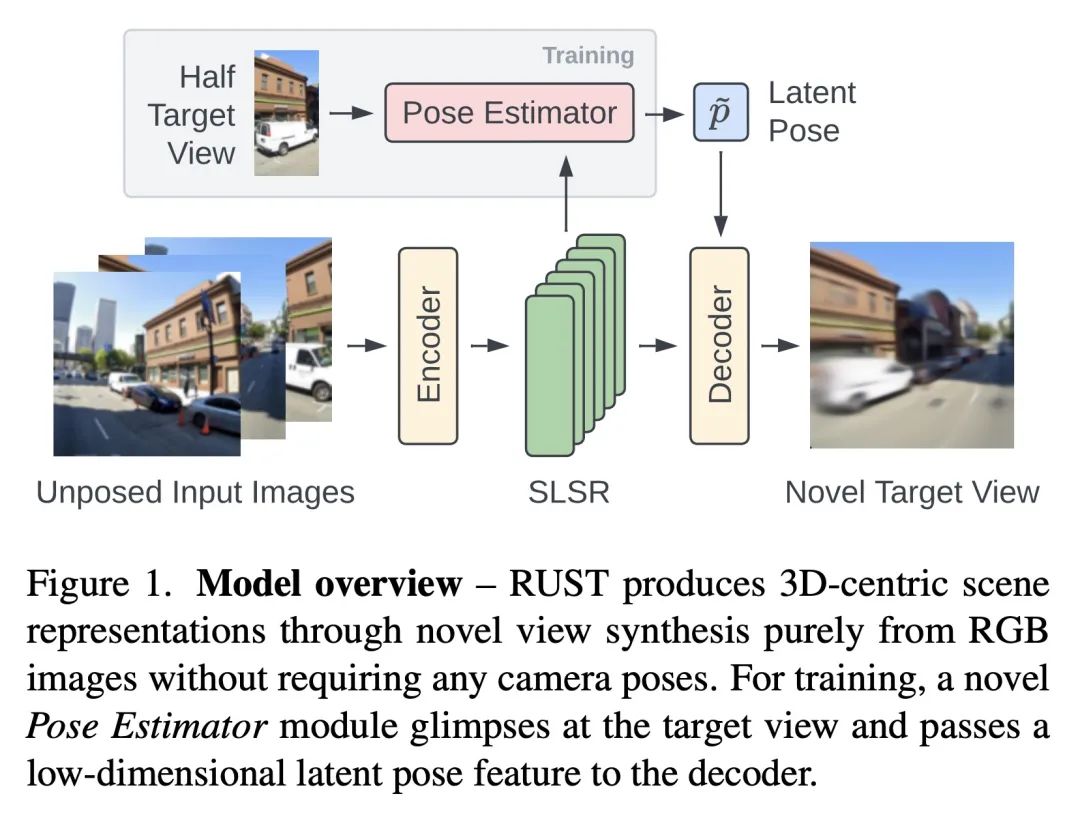
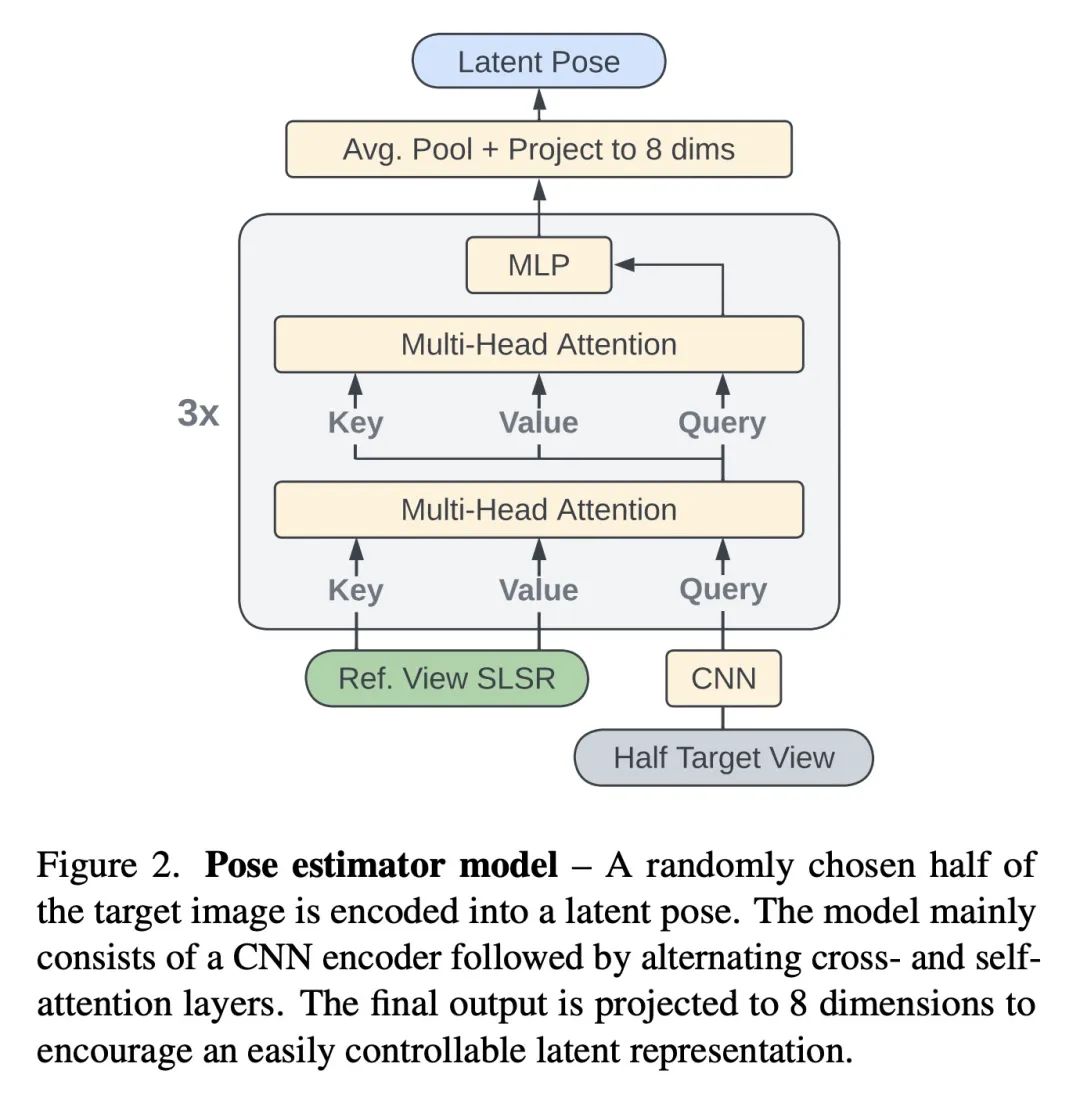
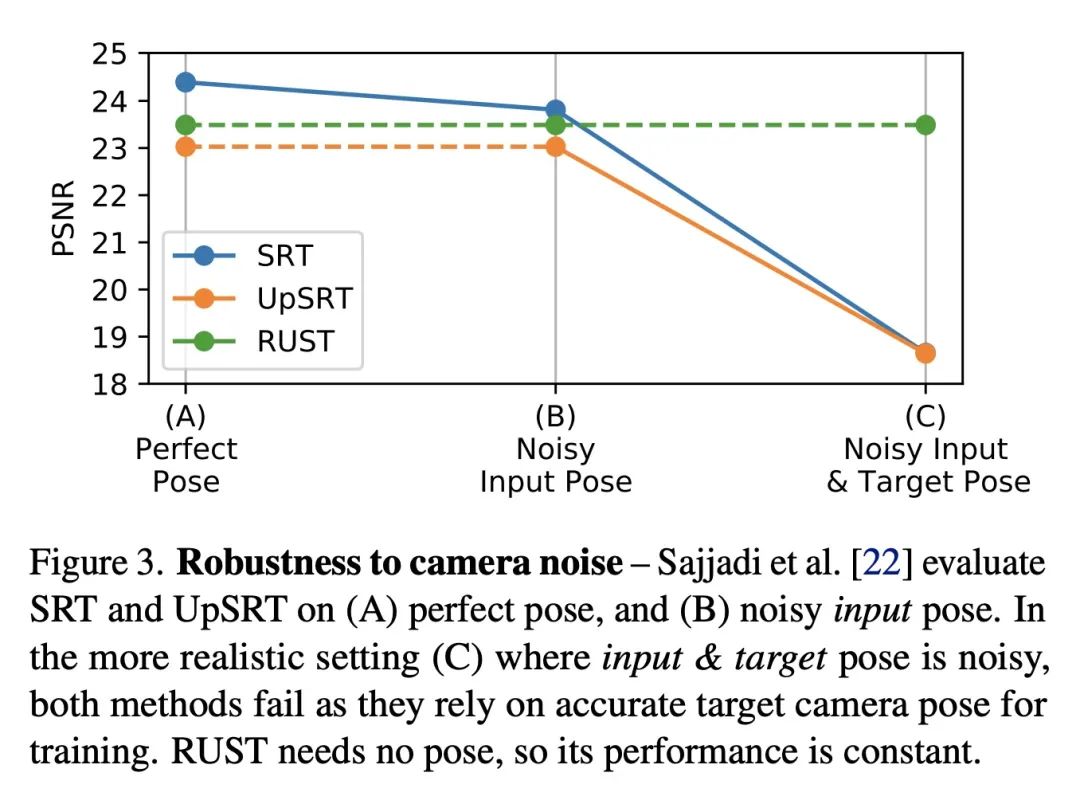
[CV] RUST: Latent Neural Scene Representations from Unposed Imagery
RUST:从无姿态照片学习潜神经场景表示
M S. M. Sajjadi, A Mahendran, T Kipf, E Pot, D Duckworth, M Lucic, K Greff
[Google Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.14306

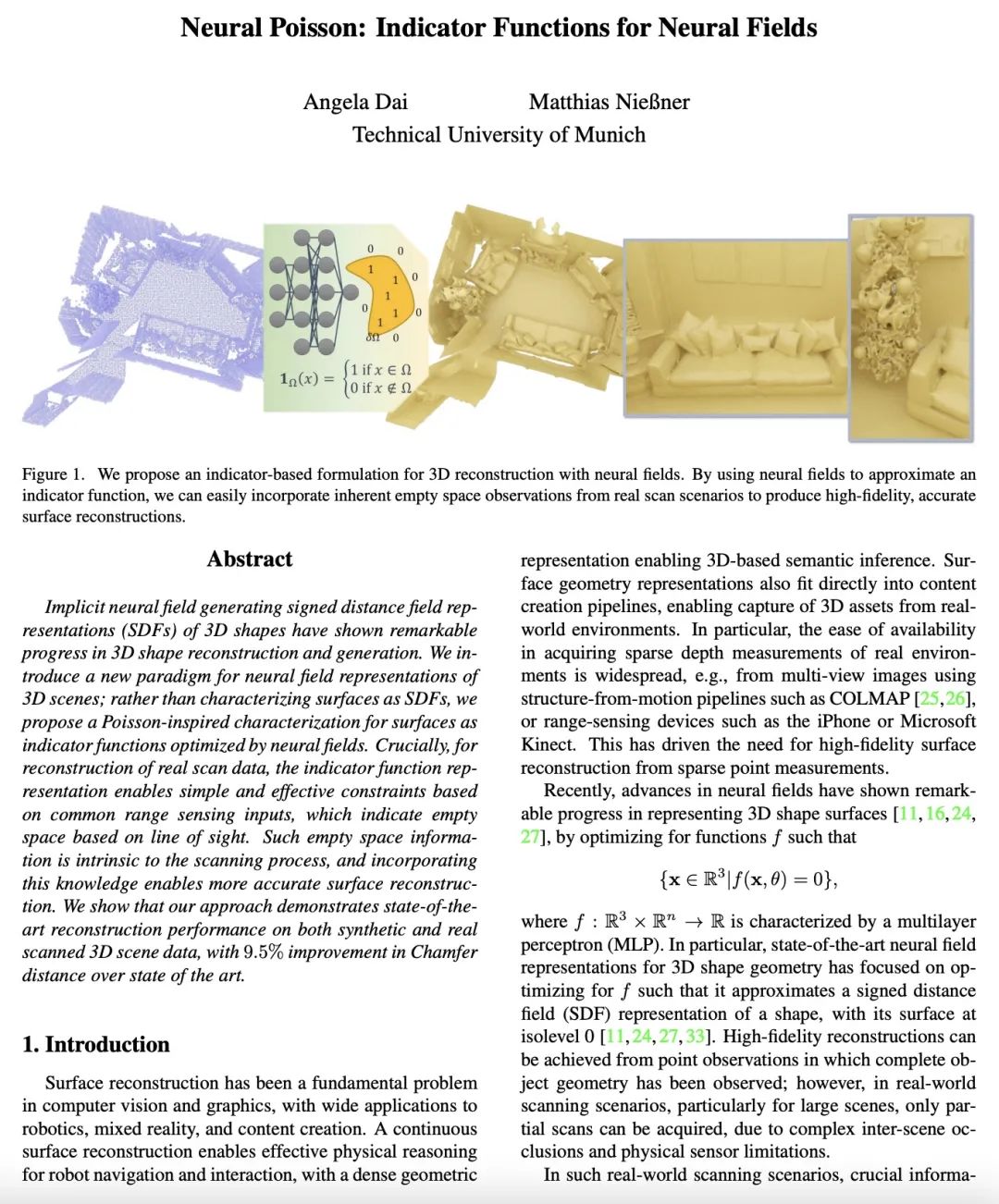
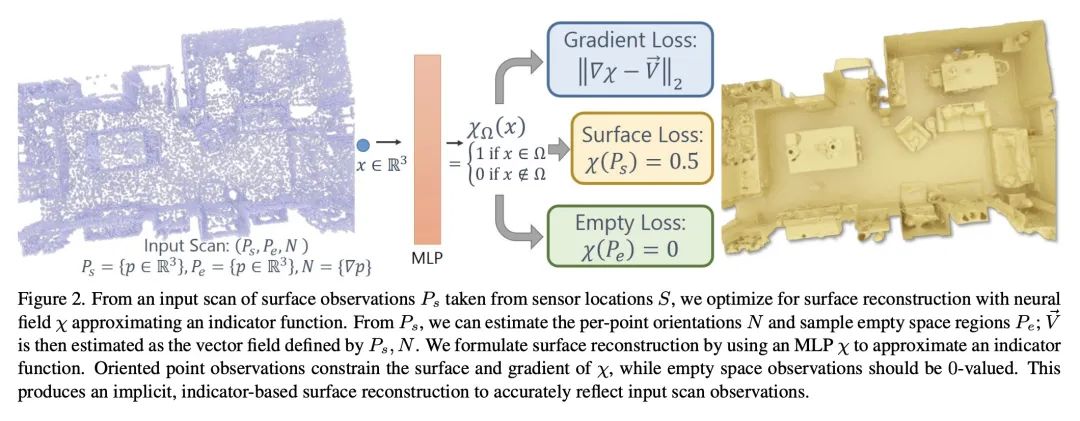
[CV] Neural Poisson: Indicator Functions for Neural Fields
神经泊松:神经场指示函数
A Dai, M Nießner
[Technical University of Munich]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.14249
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢