转自爱可可爱生活
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 GR - 图形学
摘要:最小解码JPEG视觉Transformer、基于多头蒸馏的去中心化分散学习、将体辐射场压缩到1MB、面向快速DTI预测的蛋白质语言模型自适应、连续神经算法规划器、开放词表3D场景理解、将真实场景2D照片提升为具有360°视图的3D对象、用反事实仿真测试发现Transformer和ConvNet间差异、多语言数据集构建及必要资源综述
1、[CV] RGB no more: Minimally-decoded JPEG Vision Transformers
J Park, J Johnson
[University of Michigan]
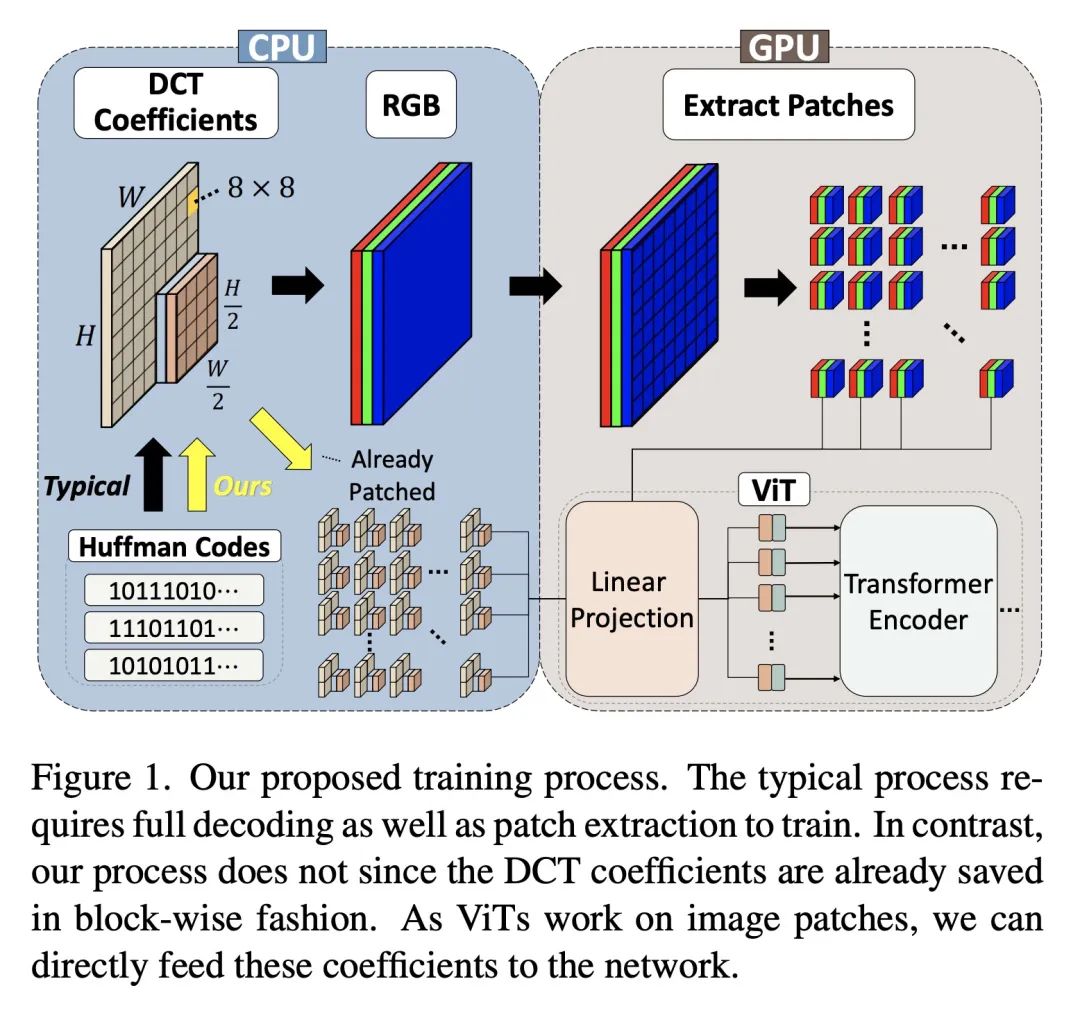
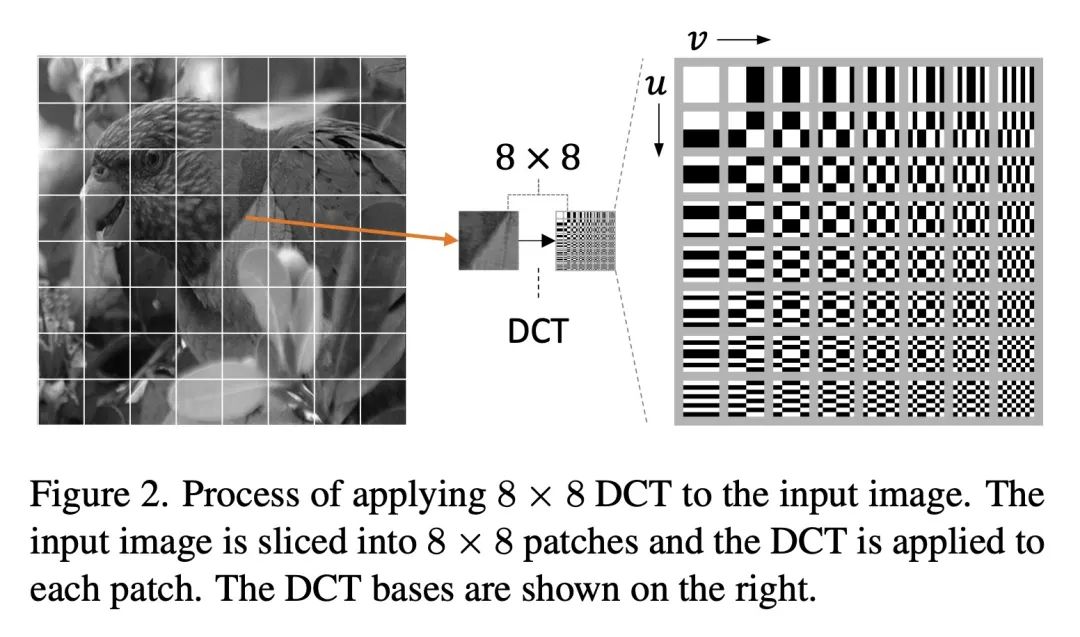
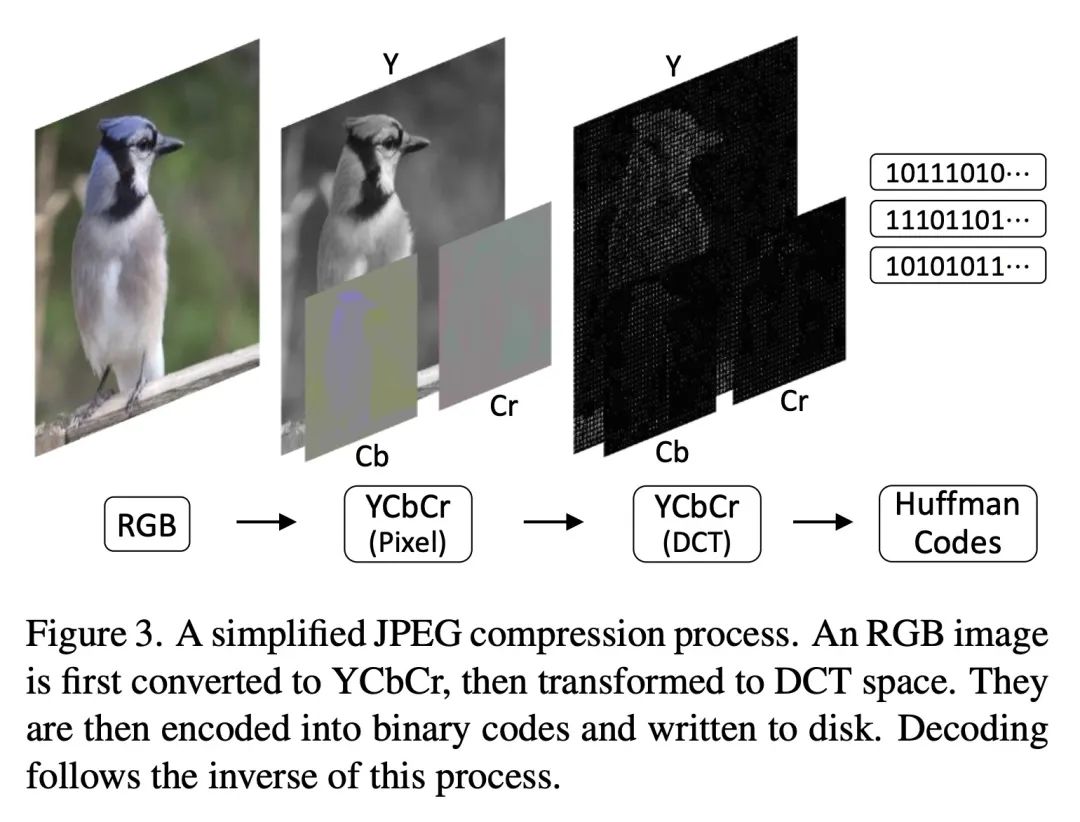
最小解码JPEG视觉Transformer。大多数计算机视觉的神经网络被设计为使用RGB图像进行推断。然而,这些RGB图像在保存到磁盘之前通常是用JPEG编码的;对它们进行解码会给RGB网络带来不可避免的开销。相本文的工作重点是直接从JPEG的编码特征中训练视觉Transformer(ViT),可以避免大部分的解码开销,加速数据加载。现有工作已经研究了这方面的问题,但它们集中在CNN上。由于这些编码特征的结构方式,CNN需要对其架构进行大量修改以接受这些数据。本文表明ViT的情况并非如此,可直接解决这些编码特征的数据增强问题,这种情况下的训练还没有得到深入的探索。通过这两项改进——ViT和数据增强——本文表明,与RGB模型相比,所提出的ViT-Ti模型训练速度提高了39.2%、推理速度提高了17.9%,并且没有精度损失。
Most neural networks for computer vision are designed to infer using RGB images. However, these RGB images are commonly encoded in JPEG before saving to disk; decoding them imposes an unavoidable overhead for RGB networks. Instead, our work focuses on training Vision Transformers (ViT) directly from the encoded features of JPEG. This way, we can avoid most of the decoding overhead, accelerating data load. Existing works have studied this aspect but they focus on CNNs. Due to how these encoded features are structured, CNNs require heavy modification to their architecture to accept such data. Here, we show that this is not the case for ViTs. In addition, we tackle data augmentation directly on these encoded features, which to our knowledge, has not been explored in-depth for training in this setting. With these two improvements -- ViT and data augmentation -- we show that our ViT-Ti model achieves up to 39.2% faster training and 17.9% faster inference with no accuracy loss compared to the RGB counterpart.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16421

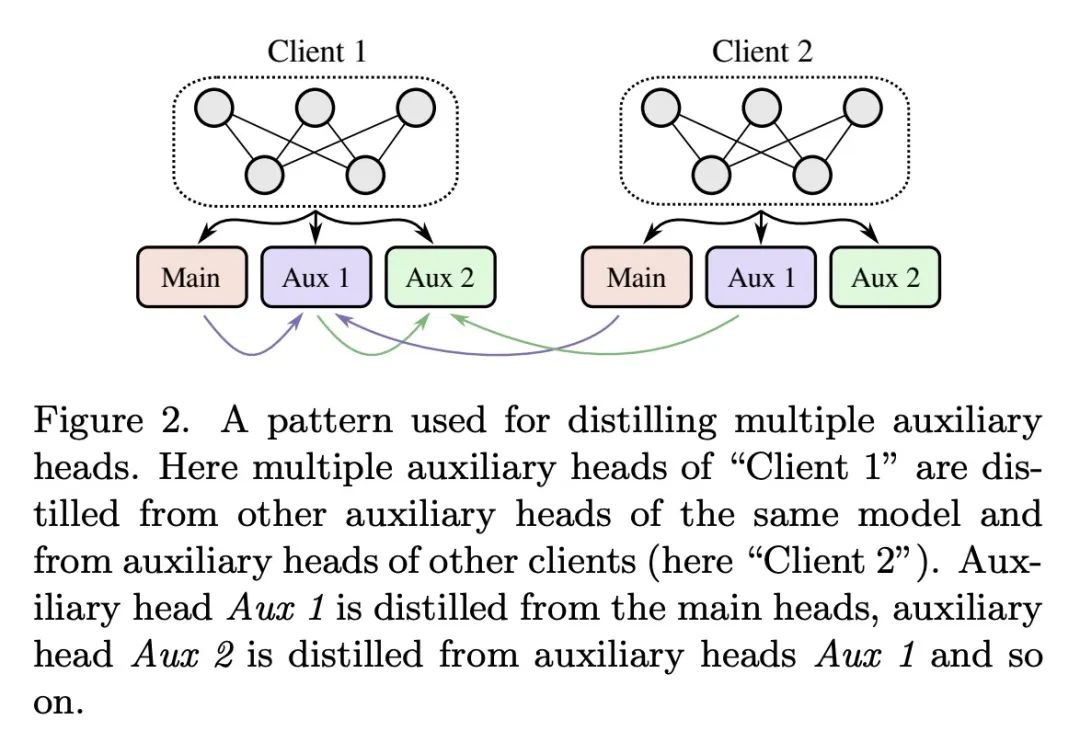
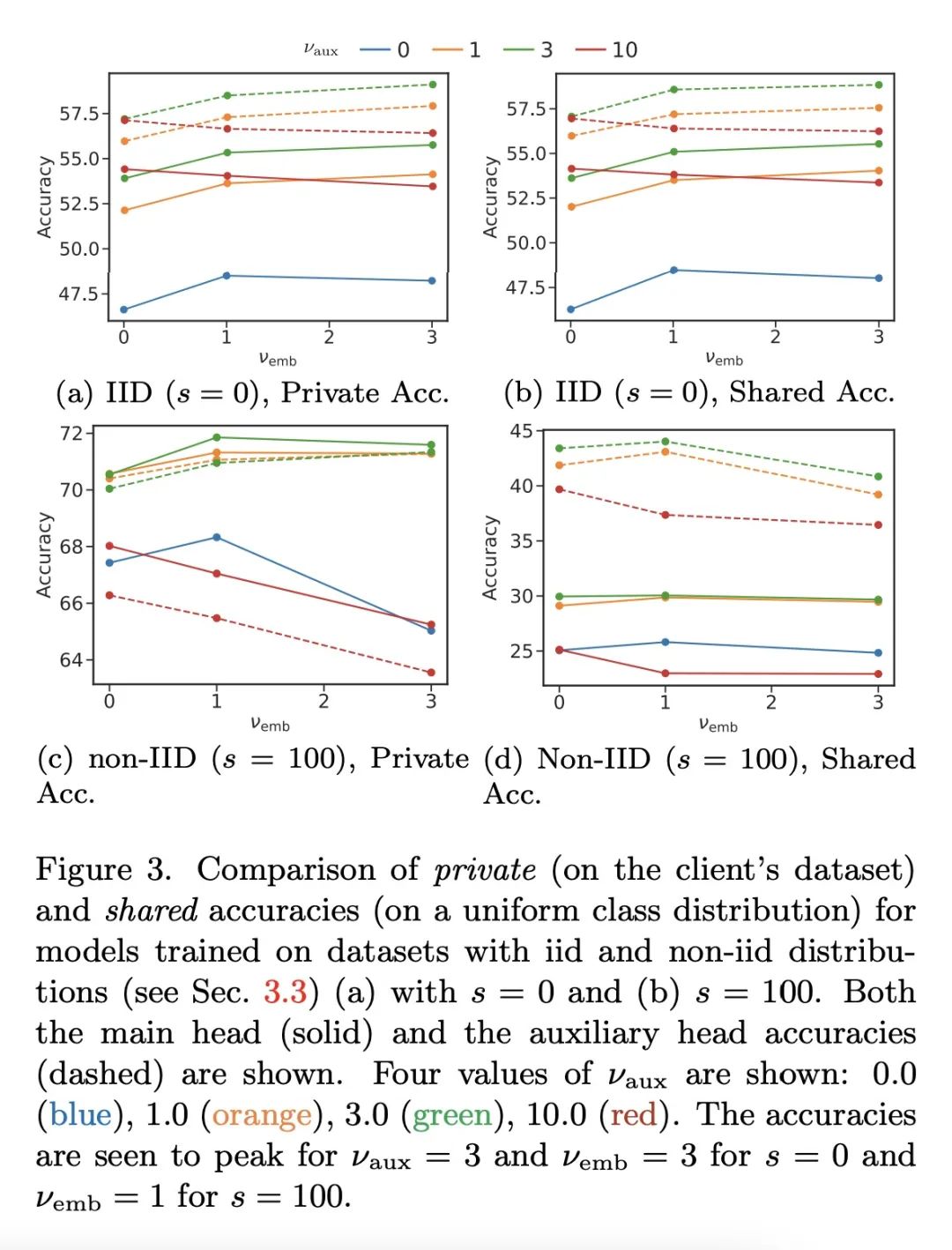
2、[LG] Decentralized Learning with Multi-Headed Distillation
A Zhmoginov, M Sandler, N Miller, G Kristiansen, M Vladymyrov
[Google Research]
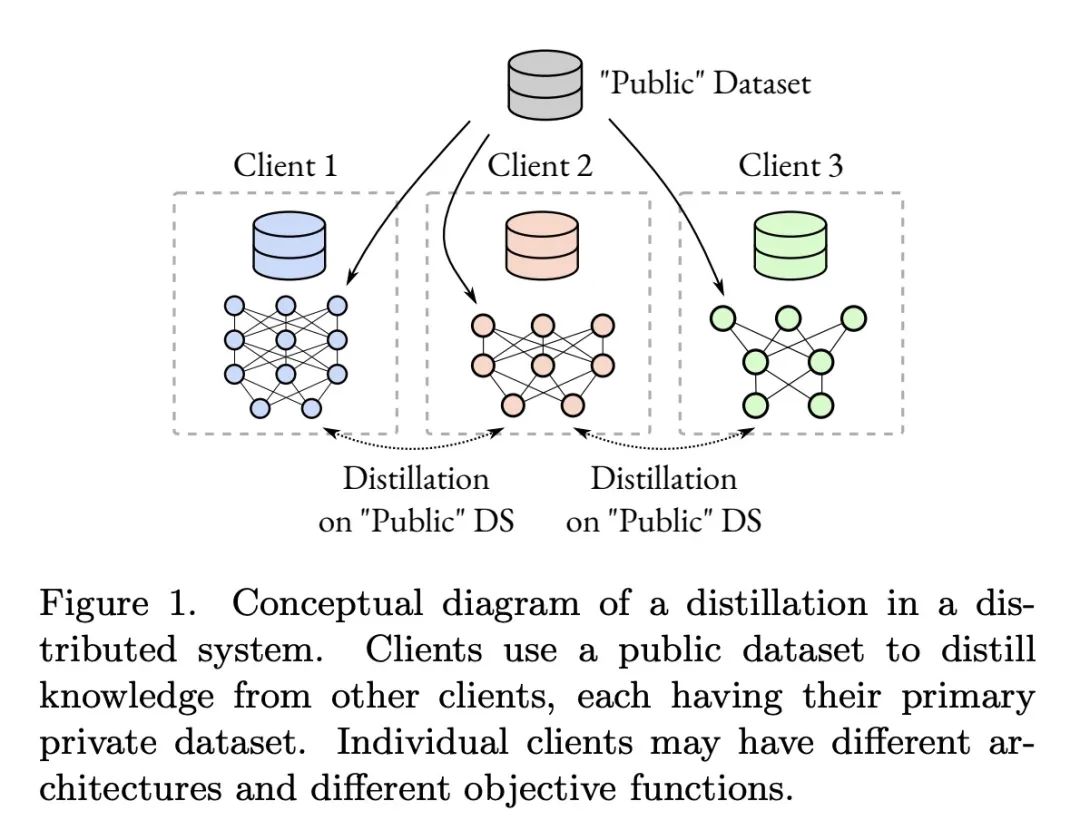
基于多头蒸馏的去中心化分散学习。用私有数据进行去中心化分散学习是机器学习的一个核心问题。本文提出一种新的基于蒸馏的分散学习技术,允许具有私有非iid数据的多个代理相互学习,而不需要分享其数据、权重或权重更新。该方法通信高效,利用无标签公共数据集,为每个客户端使用多个辅助头,在异质数据情况下大大提高了训练效率。该方法允许单个模型保持并提高其私有任务的性能,同时也极大地提高其在全局聚合数据分布上的性能。本文研究了数据和模型结构异质性的影响,以及底层通信图拓扑对学习效率的影响,并表明该方法的代理与孤立学习相比,可以显著提高其性能。
Decentralized learning with private data is a central problem in machine learning. We propose a novel distillation-based decentralized learning technique that allows multiple agents with private non-iid data to learn from each other, without having to share their data, weights or weight updates. Our approach is communication efficient, utilizes an unlabeled public dataset and uses multiple auxiliary heads for each client, greatly improving training efficiency in the case of heterogeneous data. This approach allows individual models to preserve and enhance performance on their private tasks while also dramatically improving their performance on the global aggregated data distribution. We study the effects of data and model architecture heterogeneity and the impact of the underlying communication graph topology on learning efficiency and show that our agents can significantly improve their performance compared to learning in isolation.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.15774

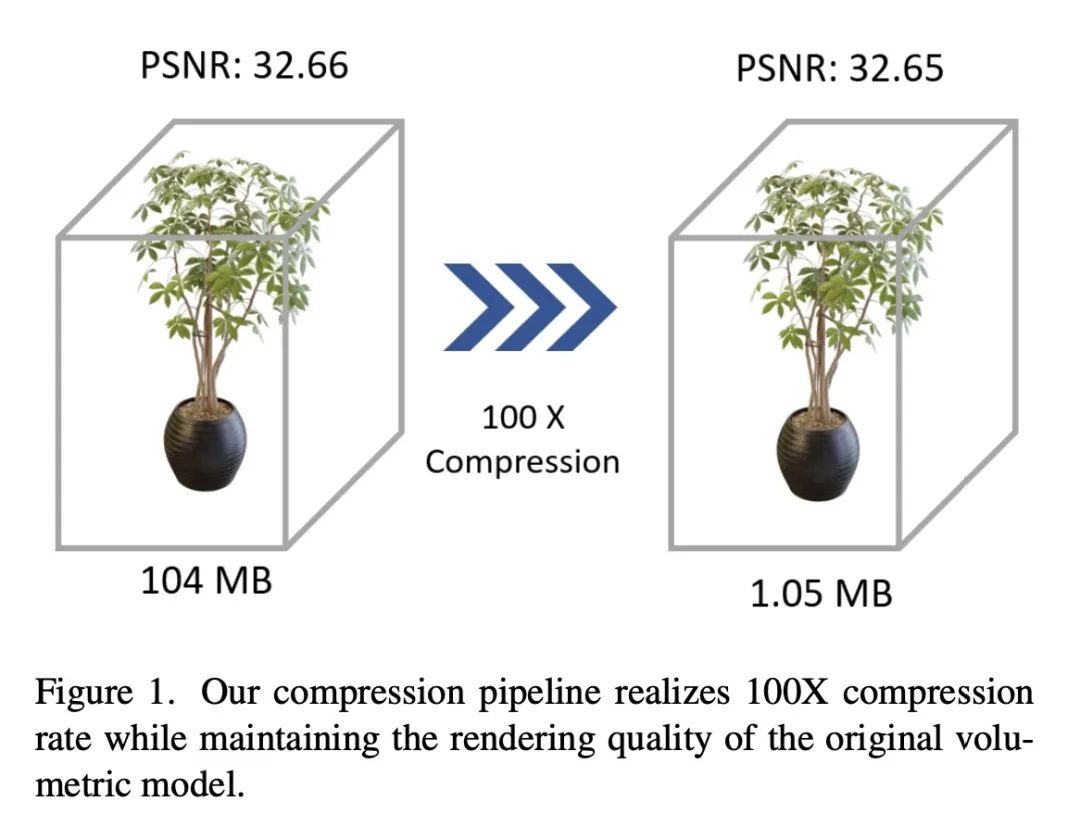
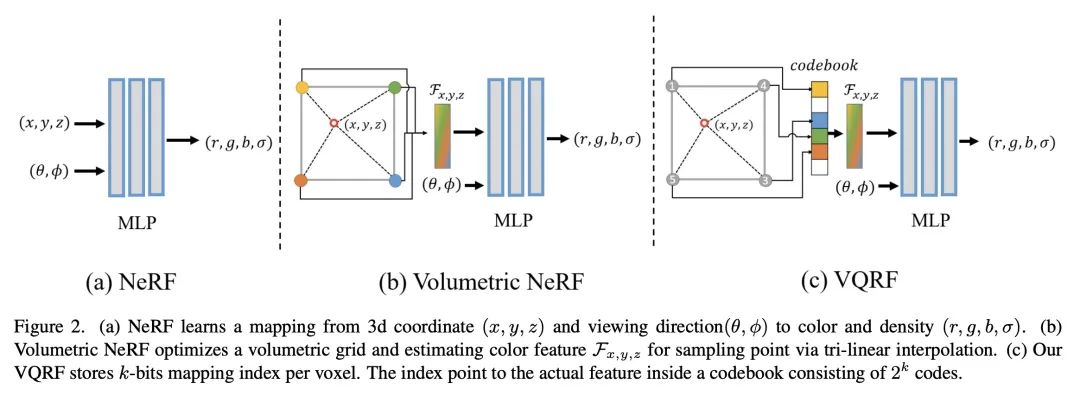
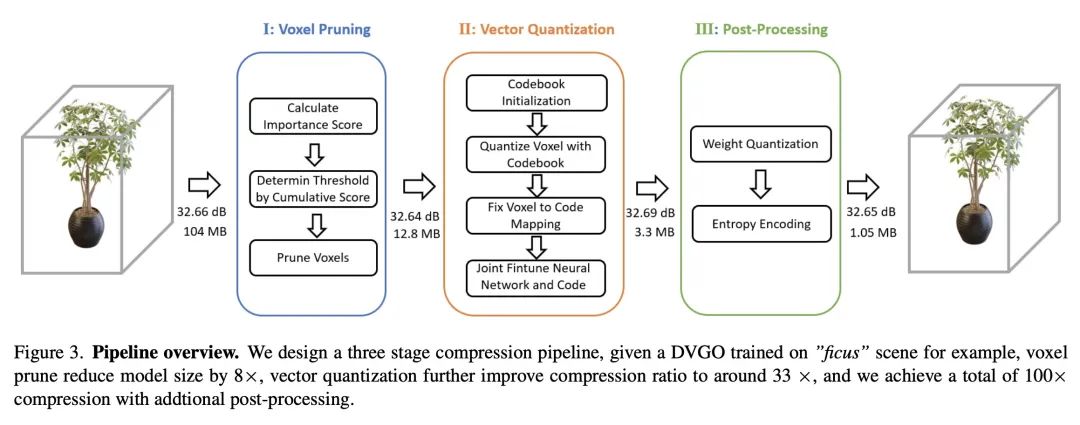
3、[CV] Compressing Volumetric Radiance Fields to 1 MB
L Li, Z Shen, Z Wang, L Shen, L Bo
[Alibaba Group]
将体辐射场压缩到1MB。用体网格逼近辐射场是改进NeRF的一个很有前途的方向,其代表方法是Plenoxels和DVGO,可实现超快的训练收敛和实时渲染。然而,这些方法通常需要巨大的存储开销,单个场景的磁盘空间和运行时内存成本高达数百兆。本文提出一种简单而有效的框架来解决该问题,该框架称为矢量量化辐射场(VQRF),用于压缩这些基于体网格的辐射场。本文首先提出一种鲁棒和自适应的指标,用于估计网格模型中的冗余,并通过更好地探索体渲染的中间输出来进行体素修剪。进一步提出一种可训练的矢量量化,以提高网格模型的紧凑性。结合有效的联合调整策略和后处理,所提出方法可实现100倍的压缩率,将整体模型缩小到1MB,视觉质量上的损失可忽略不计。广泛的实验表明,所提出的框架能在具有不同体结构的多种方法中实现优秀的性能和良好的通用性,促进了体辐射场方法在现实世界中的广泛使用。
Approximating radiance fields with volumetric grids is one of promising directions for improving NeRF, represented by methods like Plenoxels and DVGO, which achieve super-fast training convergence and real-time rendering. However, these methods typically require a tremendous storage overhead, costing up to hundreds of megabytes of disk space and runtime memory for a single scene. We address this issue in this paper by introducing a simple yet effective framework, called vector quantized radiance fields (VQRF), for compressing these volume-grid-based radiance fields. We first present a robust and adaptive metric for estimating redundancy in grid models and performing voxel pruning by better exploring intermediate outputs of volumetric rendering. A trainable vector quantization is further proposed to improve the compactness of grid models. In combination with an efficient joint tuning strategy and post-processing, our method can achieve a compression ratio of 100× by reducing the overall model size to 1 MB with negligible loss on visual quality. Extensive experiments demonstrate that the proposed framework is capable of achieving unrivaled performance and well generalization across multiple methods with distinct volumetric structures, facilitating the wide use of volumetric radiance fields methods in real-world applications. Code Available at this https URL
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16386

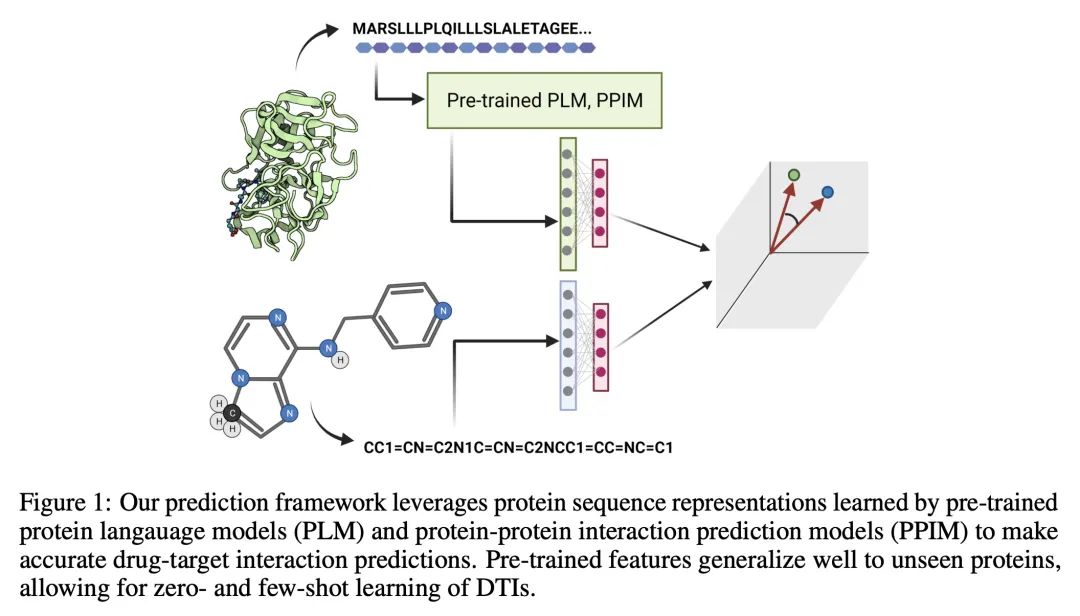
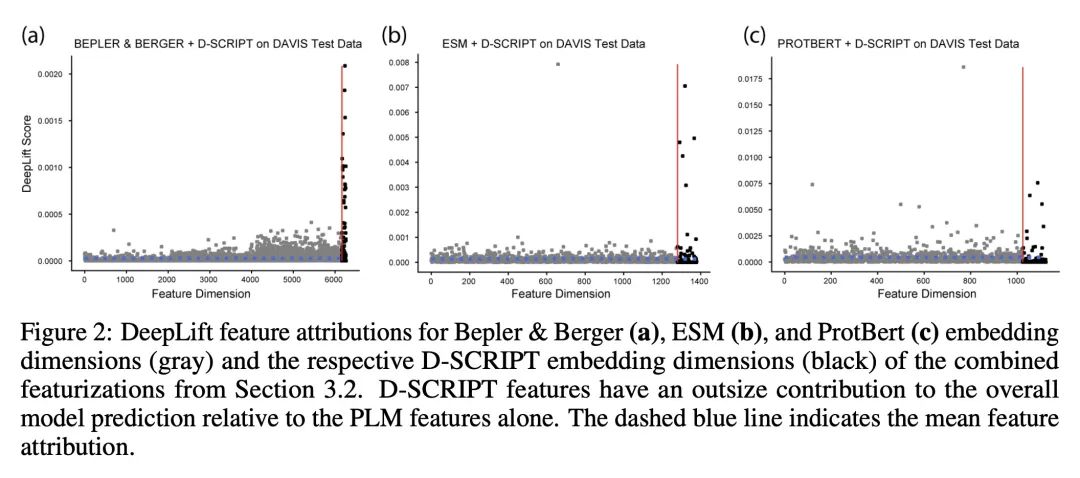
4、[LG] Adapting protein language models for rapid DTI prediction
S Sledzieski, R Singh, L Cowen, B Berger
[MIT & Tufts University]
面向快速DTI预测的蛋白质语言模型自适应。本文考虑基于序列的药物-目标相互作用(DTI)预测问题,表明一个直接的深度学习架构,利用预训练的蛋白质语言模型(PLM)进行蛋白质嵌入,优于现有的方法,实现了更高的精度,扩大了通用性,并且训练速度快了一个数量级。PLM嵌入被发现包含通用的信息,这些信息在少样本(小的训练数据集)和零样本情况下(未见过的蛋白质或药物)特别有用。此外,PLM嵌入可以通过特定任务的预训练来增强特征,本文发现这些特定任务的特征比PLM基线特征更有信息量。预计这种迁移学习方法将促进DTI模型的快速原型化,特别是在低N场景下。
We consider the problem of sequence-based drug-target interaction (DTI) prediction, showing that a straightforward deep learning architecture that leverages pre-trained protein language models (PLMs) for protein embedding outperforms state of the art approaches, achieving higher accuracy, expanded generalizability, and an order of magnitude faster training. PLM embeddings are found to contain general information that is especially useful in few-shot (small training data set) and zero-shot instances (unseen proteins or drugs). Additionally, the PLM embeddings can be augmented with features tuned by task-specific pre-training, and we find that these task-specific features are more informative than baseline PLM features. We anticipate such transfer learning approaches will facilitate rapid prototyping of DTI models, especially in low-N scenarios.
https://biorxiv.org/content/10.1101/2022.11.03.515084v1

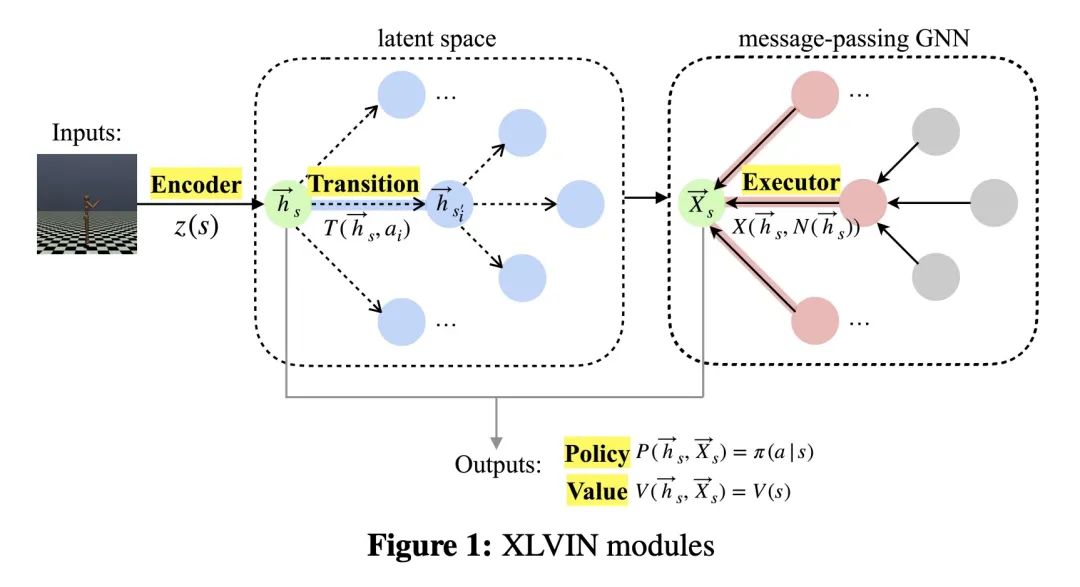
5、[LG] Continuous Neural Algorithmic Planners
Y He, P Veličković, P Liò, A Deac
[University of Cambridge & DeepMind & Université de Montréal]
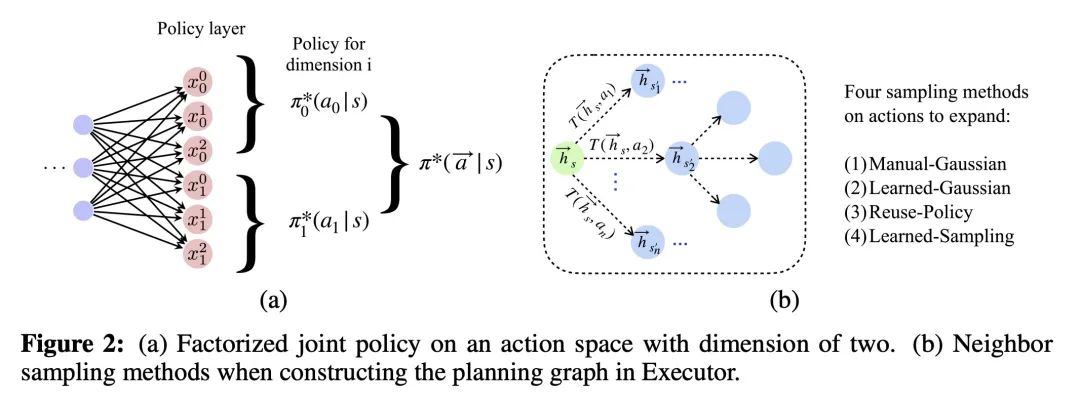
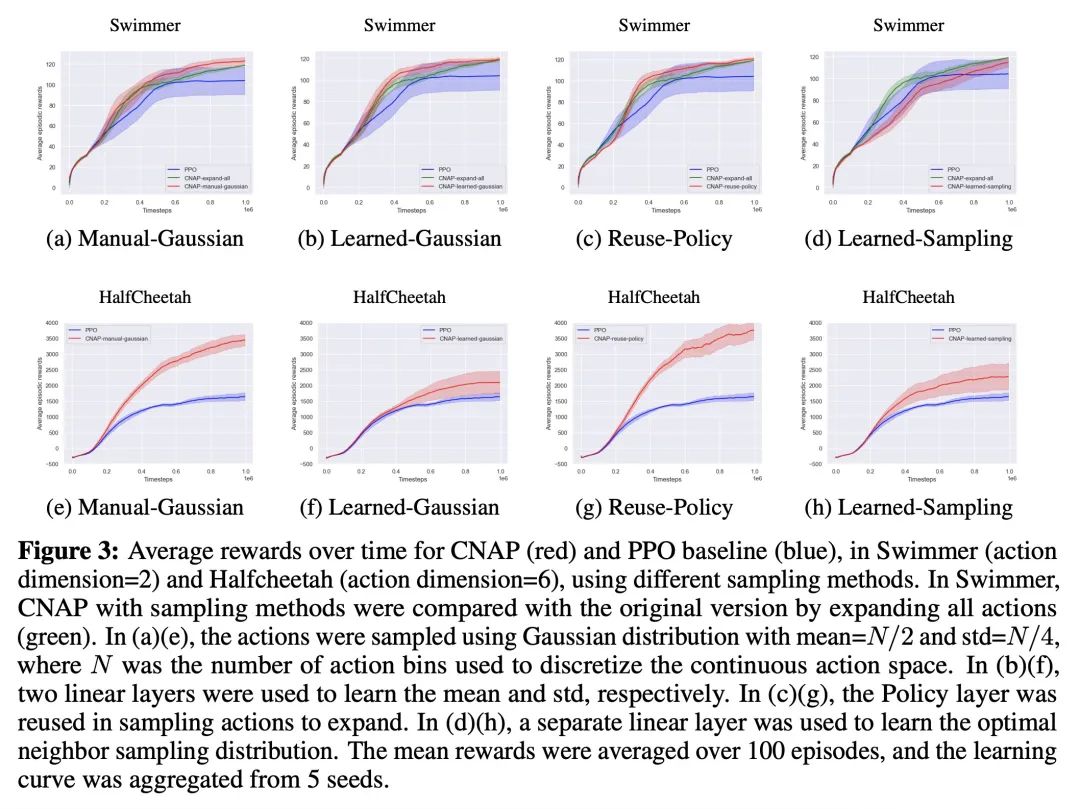
连续神经算法规划器。神经算法推理研究的是用神经网络学习算法的问题,特别是用图结构学习算法。最近的一个提议,XLVIN,收获了用图神经网络模拟深度强化学习智能体中价值迭代算法的好处,允许无模型规划,而不需要获得关于环境的特权信息,这通常是不可用的。然而,XLVIN只支持离散的行动空间,因此无法适用于现实世界中的大多数任务。本文通过离散化将XLVIN扩展到连续行动空间,评估了几种选择性的扩展策略来处理大型规划图。本文的建议,即CNAP,展示了神经算法推理如何在更高维度的连续控制环境中产生可衡量的影响,如MuJoCo,在低数据环境中带来收益,并优于无模型基线。
Neural algorithmic reasoning studies the problem of learning algorithms with neural networks, especially with graph architectures. A recent proposal, XLVIN, reaps the benefits of using a graph neural network that simulates the value iteration algorithm in deep reinforcement learning agents. It allows model-free planning without access to privileged information about the environment, which is usually unavailable. However, XLVIN only supports discrete action spaces, and is hence nontrivially applicable to most tasks of real-world interest. We expand XLVIN to continuous action spaces by discretization, and evaluate several selective expansion policies to deal with the large planning graphs. Our proposal, CNAP, demonstrates how neural algorithmic reasoning can make a measurable impact in higher-dimensional continuous control settings, such as MuJoCo, bringing gains in low-data settings and outperforming model-free baselines.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.15839

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
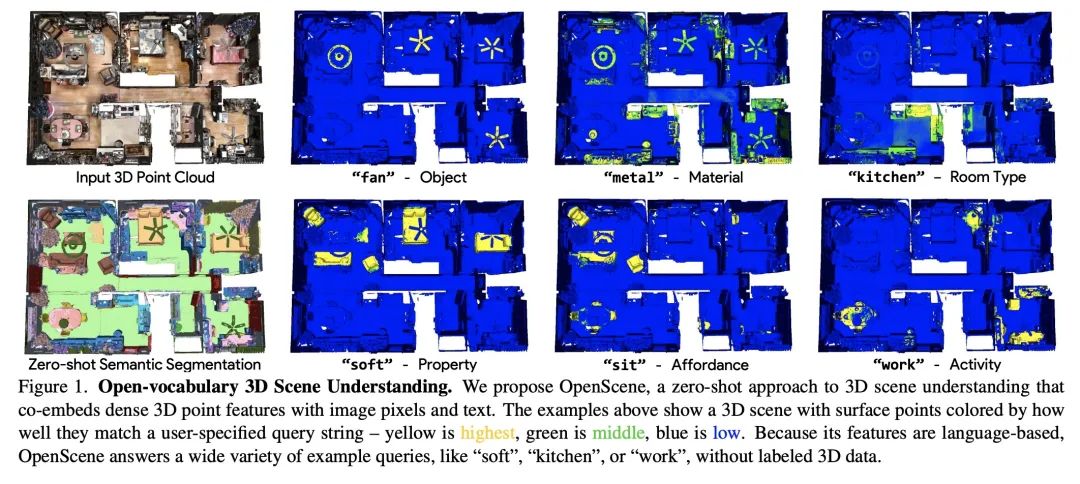
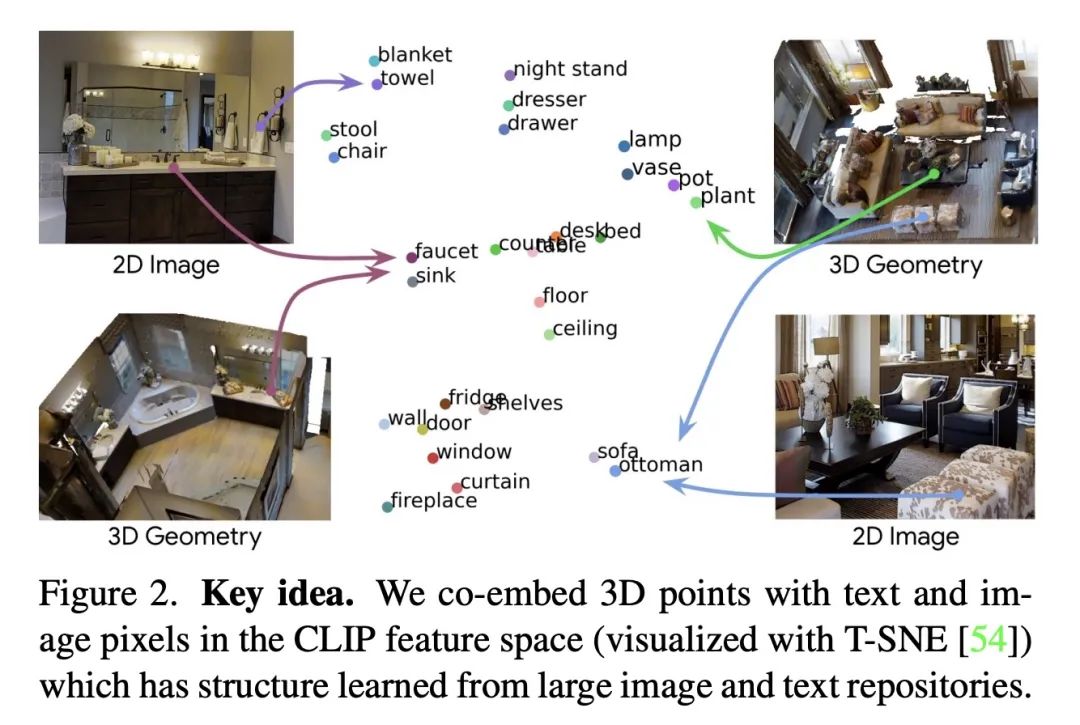
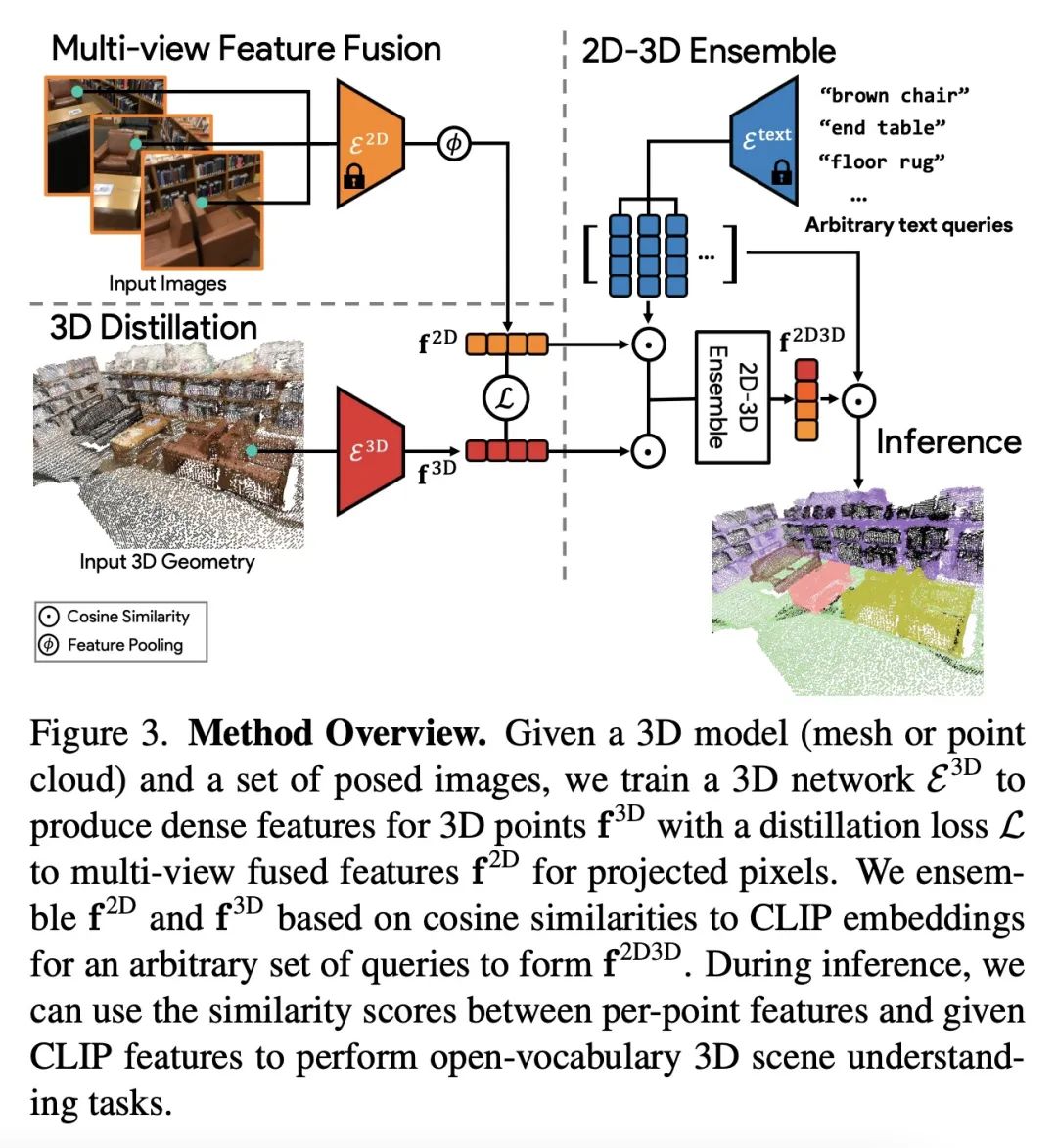
[CV] OpenScene: 3D Scene Understanding with Open Vocabularies
OpenScene:开放词表3D场景理解
S Peng, K Genova, C M Jiang, A Tagliasacchi, M Pollefeys, T Funkhouser
[Google Research & Waymo LLC & ETH Zurich]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.15654

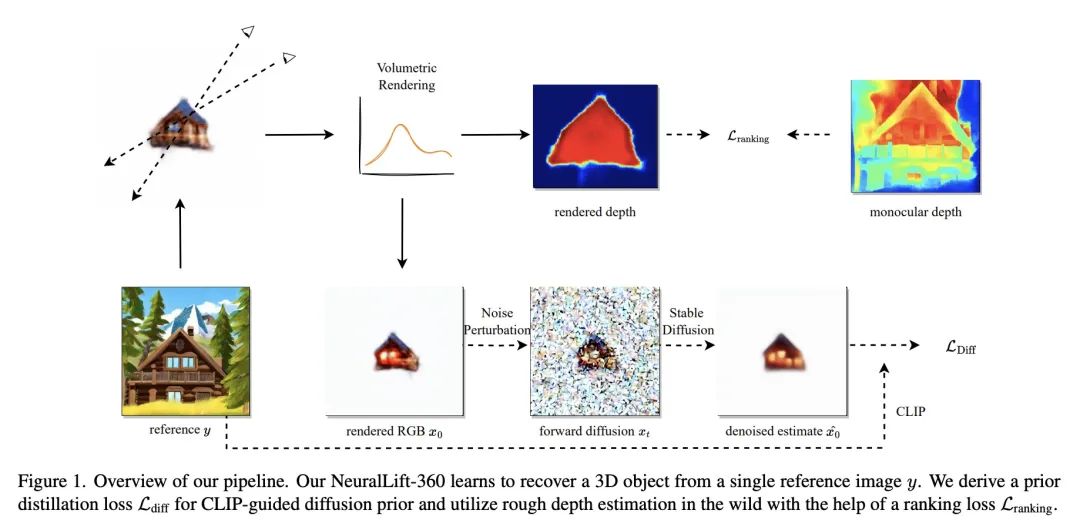
[CV] NeuralLift-360: Lifting An In-the-wild 2D Photo to A 3D Object with 360° Views
NeuralLift-360:将真实场景2D照片提升为具有360°视图的3D对象
D Xu, Y Jiang, P Wang, Z Fan, Y Wang, Z Wang
[University of Texas at Austin]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16431



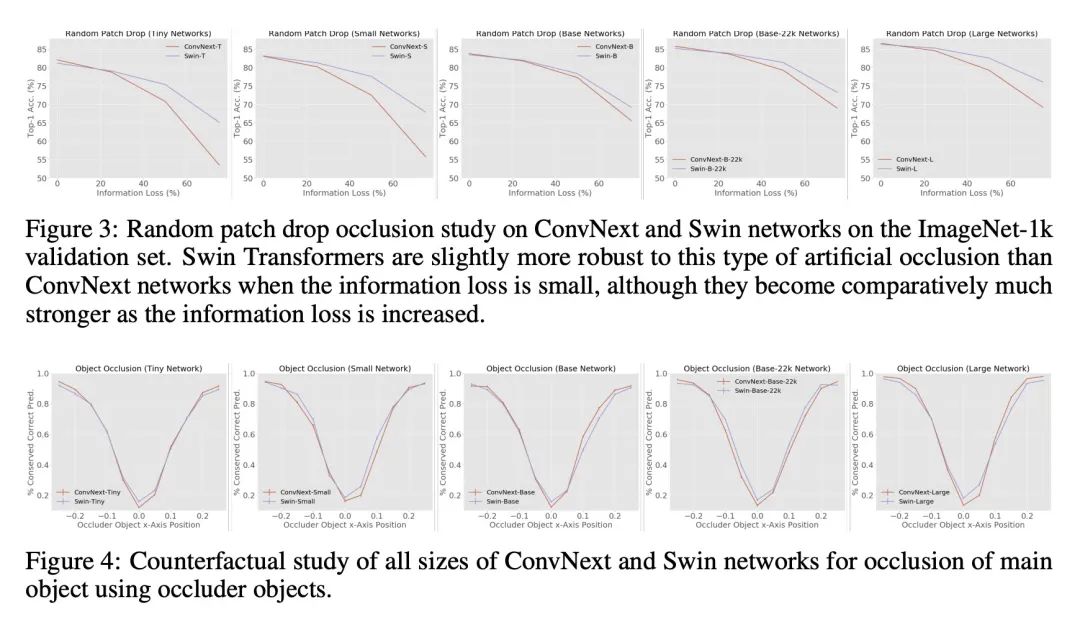
[LG] Finding Differences Between Transformers and ConvNets Using Counterfactual Simulation Testing
用反事实仿真测试发现Transformer和ConvNet间差异
N Ruiz, S A Bargal, C Xie...
[Boston University & Georgetown University & University of California, Santa Cruz]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16499



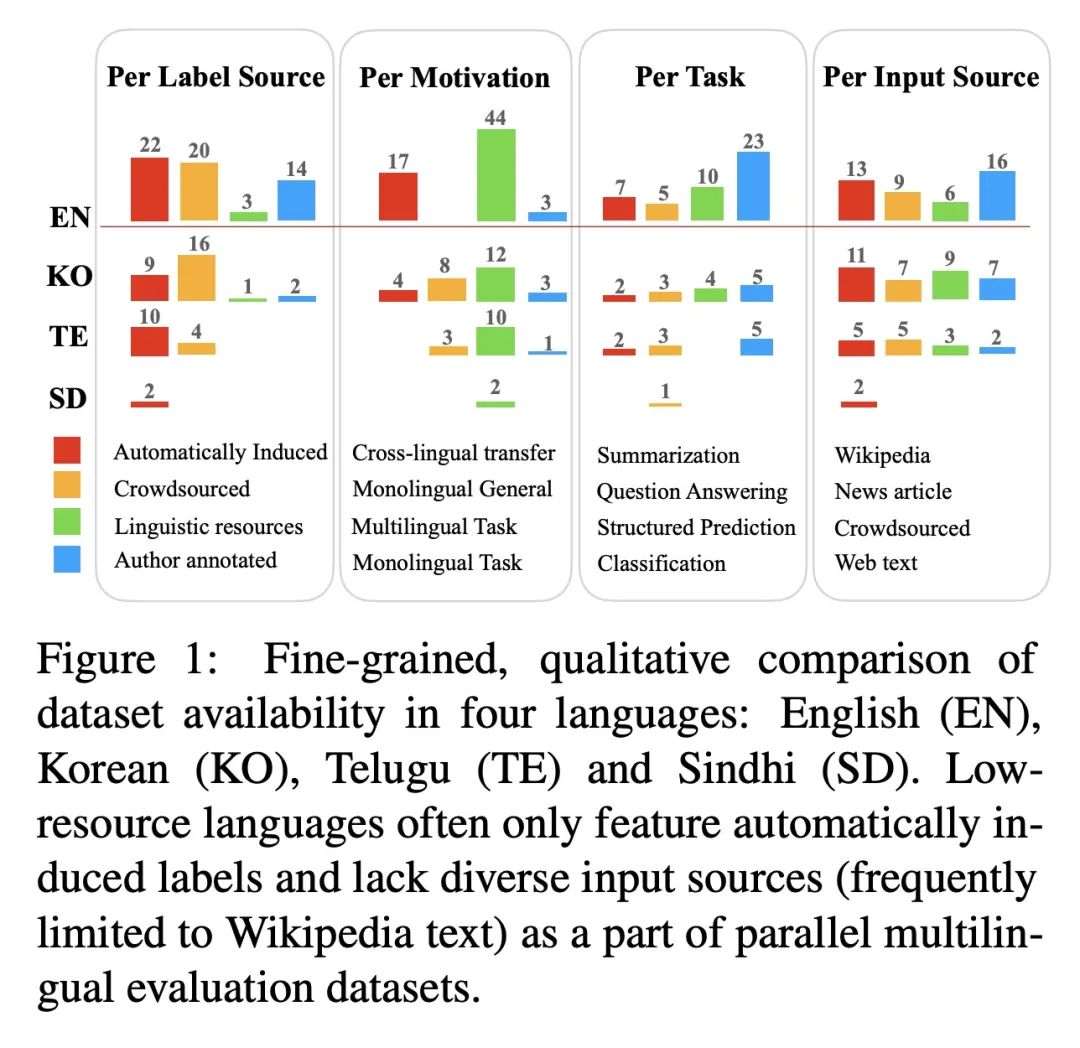
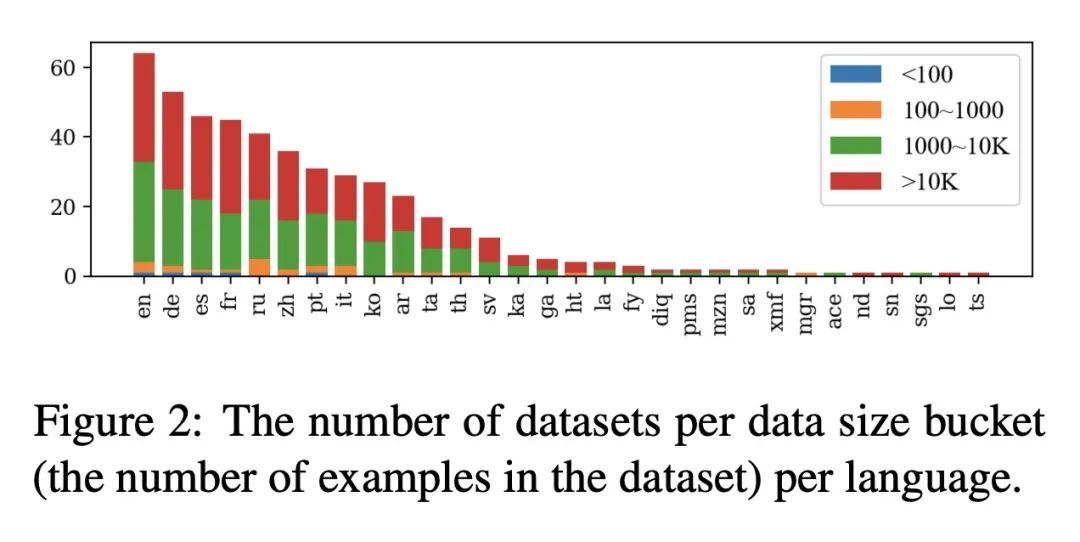
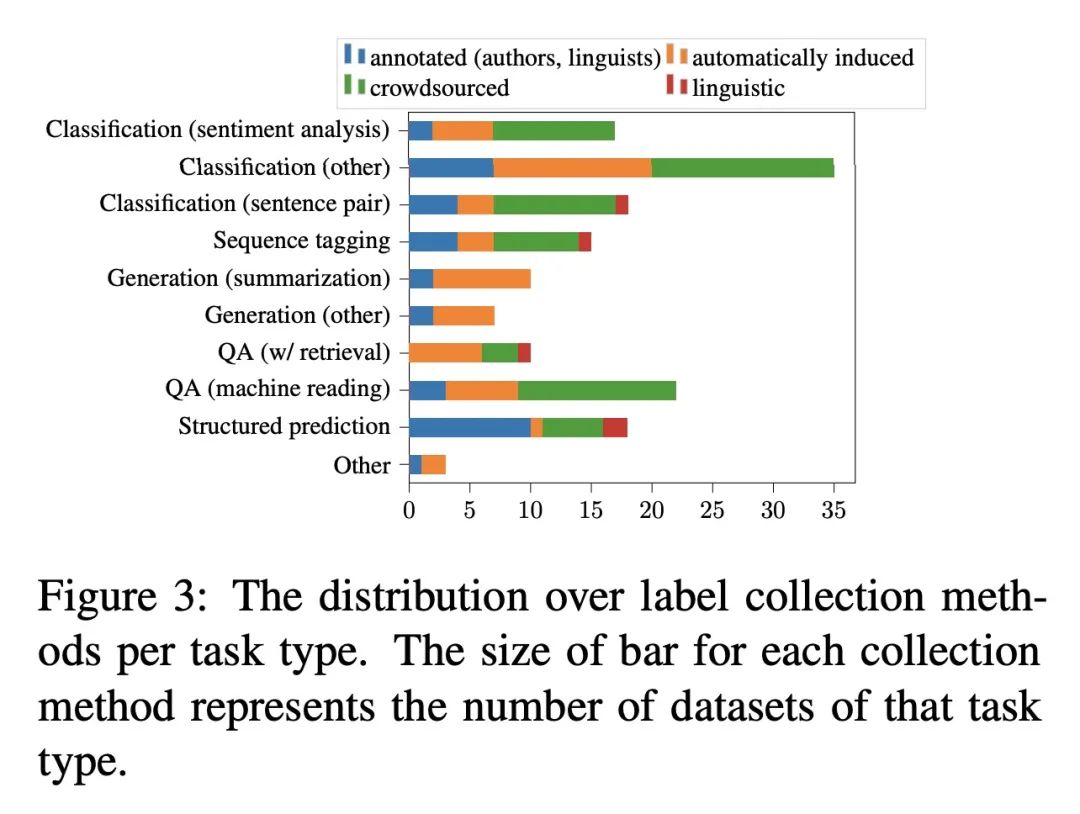
[CL] Beyond Counting Datasets: A Survey of Multilingual Dataset Construction and Necessary Resources
超越计数数据集:多语言数据集构建及必要资源综述
X V Yu, A Asai, T Chatterjee, J Hu, E Choi
[University of Washington & The University of Texas at Austin & The University of Wisconsin-Madison]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.15649

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢