转自爱可可爱生活
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 GR - 图形学
摘要:基于三平面扩散的3D神经场生成、视觉语言模型利用分类名称进行初始化的少样本分类、基于推测性解码的Transformer快速推断、虚假前提开放域问答、面向基于结构药物设计的强化遗传算法、用渐进体蒸馏缩短神经辐射场架构间的差距、代码生成的代码审计重排、不同类型和抽象层次的场景草图生成、分布外检测不足以保证系统安全
1、[CV] 3D Neural Field Generation using Triplane Diffusion
J. R Shue, E R Chan, R Po, Z Ankner, J Wu, G Wetzstein
[Milton Academy & Stanford University & MIT]
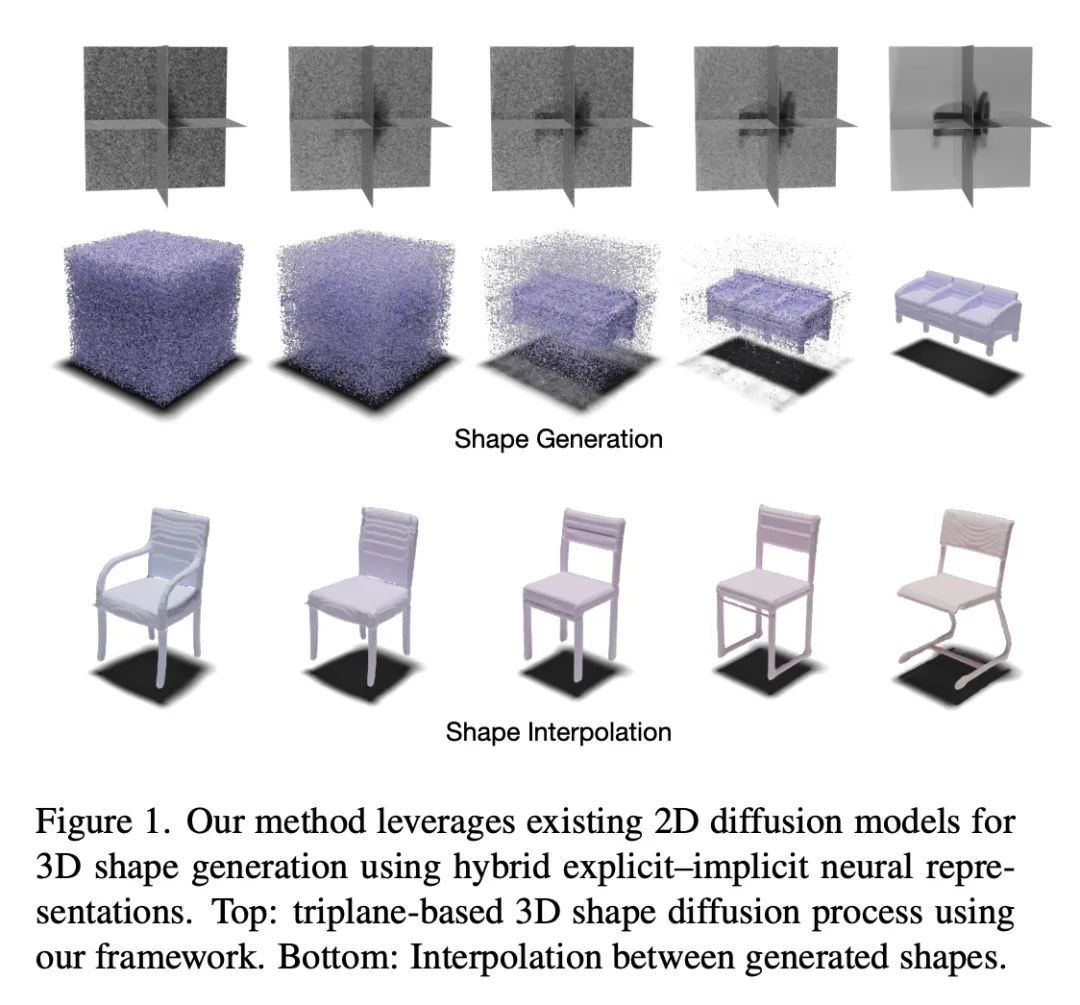
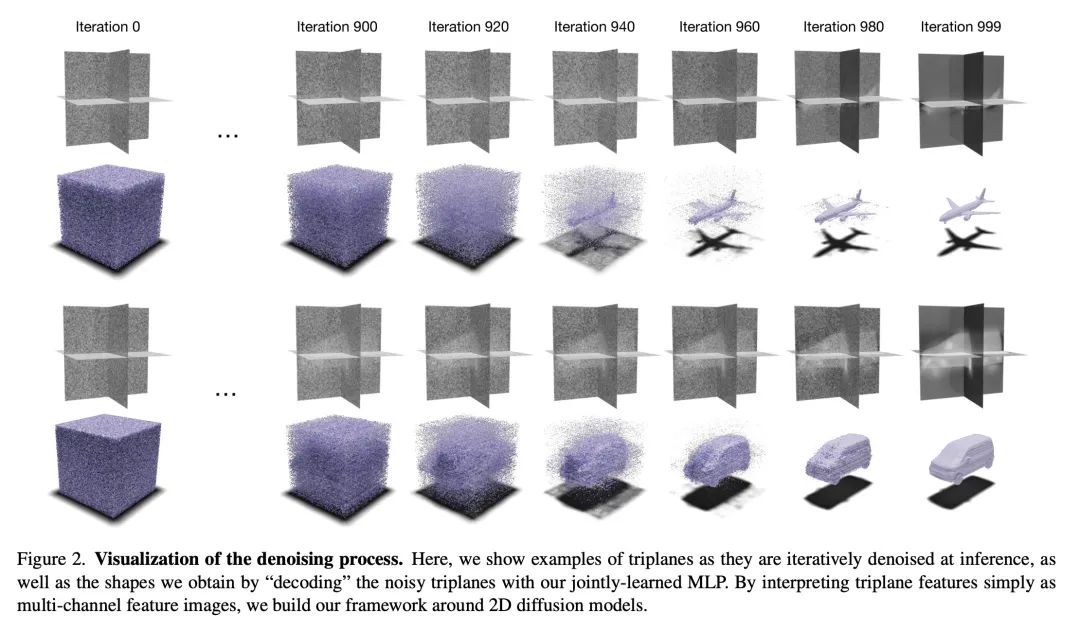
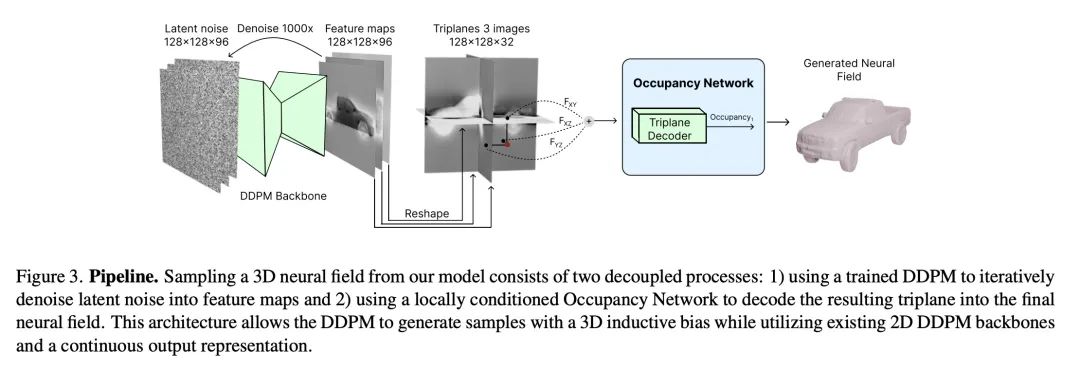
基于三平面扩散的3D神经场生成。扩散模型已成为图像生成和其他任务的最先进技术。本文提出一种高效的基于扩散的模型,用于3D感知神经场生成。该方法对训练数据,如ShapeNet网格,进行预处理,将其转换为连续覆盖场,并将其分解为一组轴对齐的三平面特征表示。因此,所提出的3D训练场景都是由2D特征平面表示的,可以直接在这些表示上训练现有的2D扩散模型,生成具有高质量和多样性的3D神经场,优于其他3D感知生成方法。该方法需要对现有的三平面分解管线进行必要的修改,以使产生的特征易于被扩散模型学习。本文在ShapeNet的几个物体类别上展示了最先进的3D生成结果。
Diffusion models have emerged as the state-of-the-art for image generation, among other tasks. Here, we present an efficient diffusion-based model for 3D-aware generation of neural fields. Our approach pre-processes training data, such as ShapeNet meshes, by converting them to continuous occupancy fields and factoring them into a set of axis-aligned triplane feature representations. Thus, our 3D training scenes are all represented by 2D feature planes, and we can directly train existing 2D diffusion models on these representations to generate 3D neural fields with high quality and diversity, outperforming alternative approaches to 3D-aware generation. Our approach requires essential modifications to existing triplane factorization pipelines to make the resulting features easy to learn for the diffusion model. We demonstrate state-of-the-art results on 3D generation on several object classes from ShapeNet.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16677

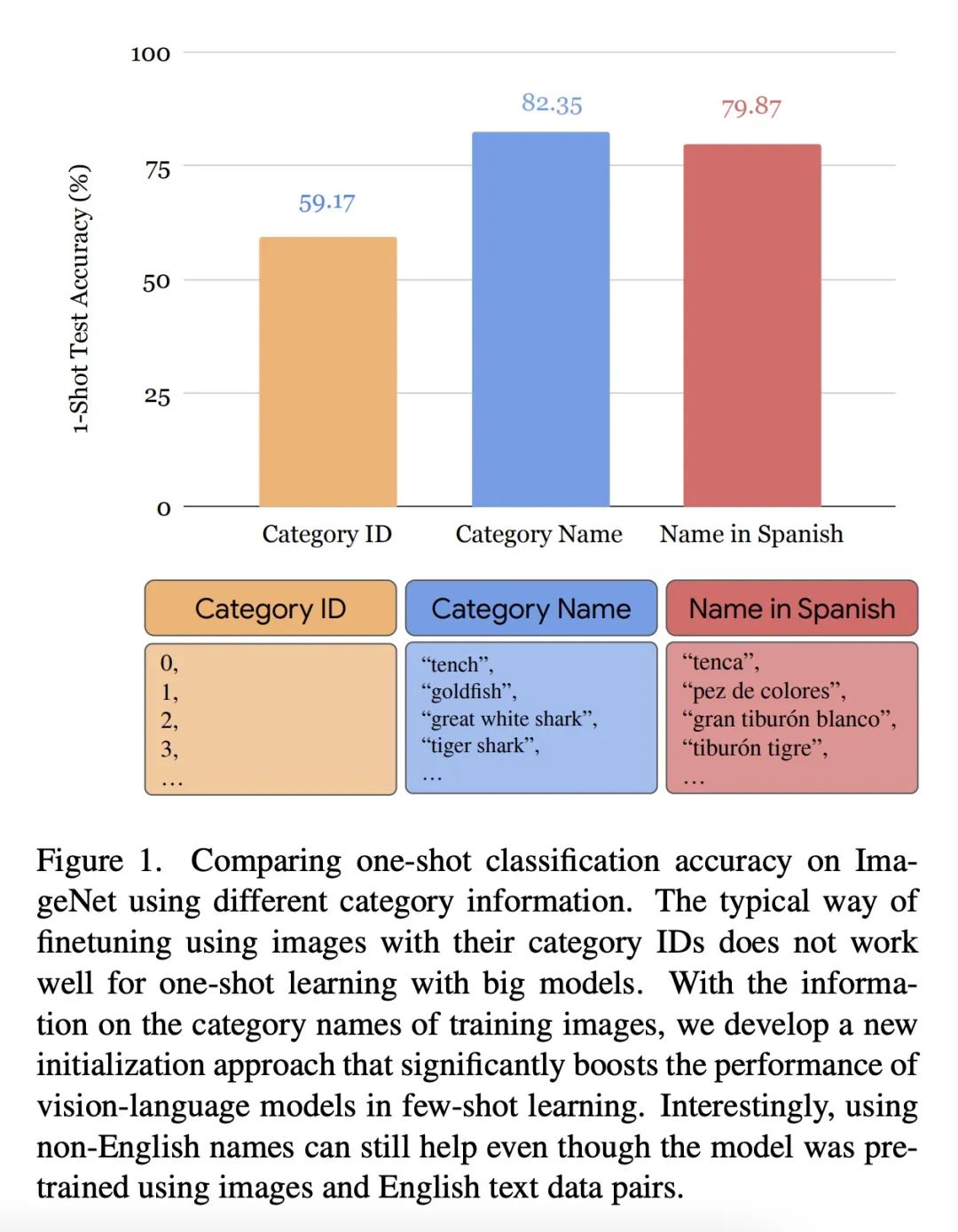
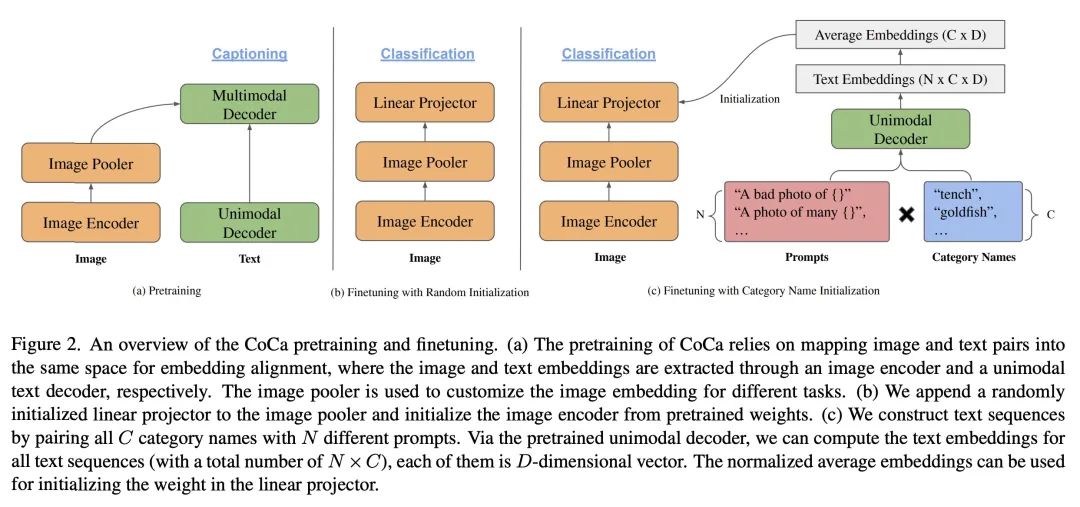
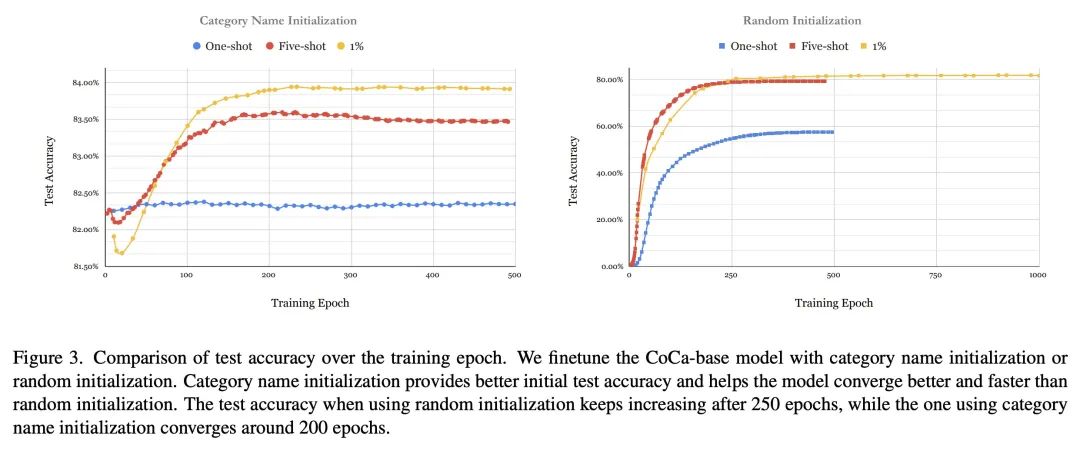
2、[CV] Exploiting Category Names for Few-Shot Classification with Vision-Language Models
T Xiao, Z Wang, L Cao, J Yu, S Dai, M Yang
[Google & University of California, Merced & Apple]
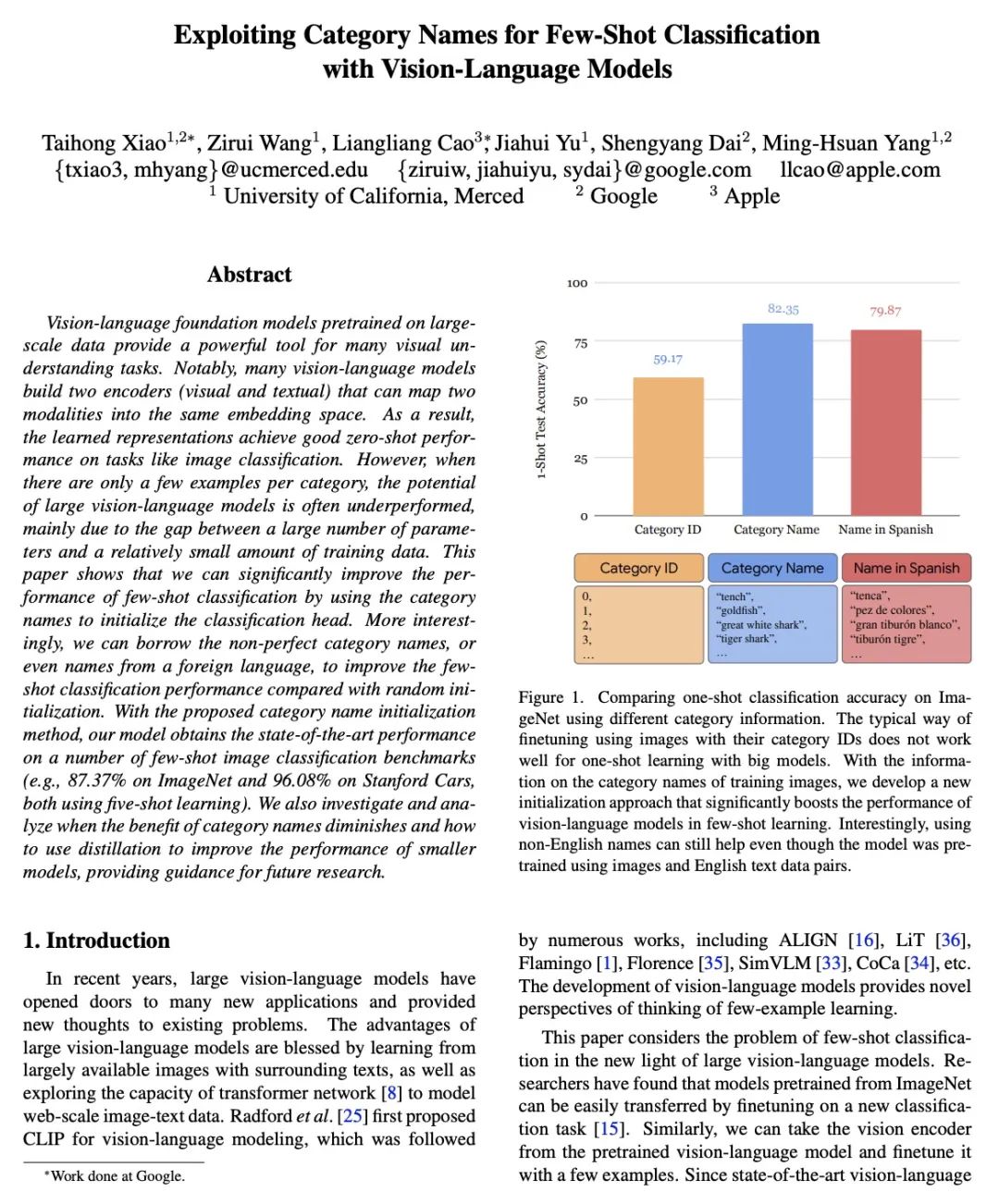
视觉语言模型利用分类名称进行初始化的少样本分类。在大规模数据上预训练的视觉语言基础模型,为许多视觉理解任务提供了一个强大的工具。值得注意的是,许多视觉语言模型建立了两个编码器(视觉和文本),可以将两种模态映射到同一嵌入空间。因此,学到的表示在图像分类等任务上取得了良好的零样本性能。然而,当每类别只有几个样本时,大型视觉-语言模型的潜力往往表现不佳,这主要是由于大量的参数和相对较少的训练数据之间的差距。本文表明,可以通过利用分类名称来初始化分类头,从而显著提高少样本分类性能。更有趣的是,与随机初始化相比,可以借用非完美的分类名称,甚至是来自外语的名称,来提高少样本分类性能。通过所提出的分类名称初始化方法,所提出模型在一些少样本图片分类基准上获得了最先进的性能(例如,在ImageNet上获得87.37%,在Stanford Cars上获得96.08%,都是用五张图片进行学习)。本文还调查和分析了分类名称的收益何时减少,以及如何用蒸馏来提高小型模型的性能,为未来的研究提供了指导。
Vision-language foundation models pretrained on large-scale data provide a powerful tool for many visual understanding tasks. Notably, many vision-language models build two encoders (visual and textual) that can map two modalities into the same embedding space. As a result, the learned representations achieve good zero-shot performance on tasks like image classification. However, when there are only a few examples per category, the potential of large vision-language models is often underperformed, mainly due to the gap between a large number of parameters and a relatively small amount of training data. This paper shows that we can significantly improve the performance of few-shot classification by using the category names to initialize the classification head. More interestingly, we can borrow the non-perfect category names, or even names from a foreign language, to improve the few-shot classification performance compared with random initialization. With the proposed category name initialization method, our model obtains the state-of-the-art performance on a number of few-shot image classification benchmarks (e.g., 87.37\% on ImageNet and 96.08\% on Stanford Cars, both using five-shot learning). We also investigate and analyze when the benefit of category names diminishes and how to use distillation to improve the performance of smaller models, providing guidance for future research.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16594
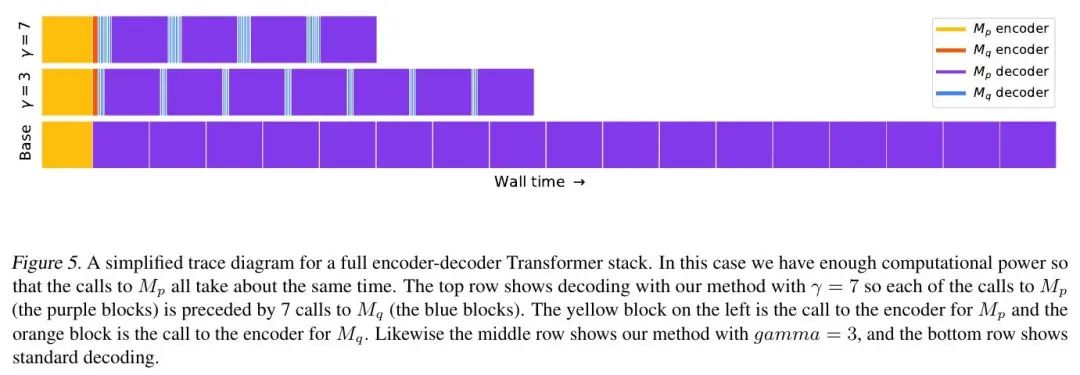
3、[LG] Fast Inference from Transformers via Speculative Decoding
Y Leviathan, M Kalman, Y Matias
[Google Research]
基于推测性解码的Transformer快速推断。从大型自回归模型(如Transformer)进行推断是很慢的——对K个Token进行解码需要对模型进行K次连续运行。本文提出推测性解码——一种在不改变输出的情况下通过并行计算多个Token从自回归模型快速采样的算法。该方法的核心是:(1) 困难的语言建模任务通常包括较容易的子任务,这些子任务可以由更有效的模型来近似,以及(2) 用推测性执行和新的采样方法,可以使大型模型的精确解码更快,通过在近似模型的输出上并行运行,能同时产生多个Token,并且不改变分布。该方法支持现有的模型,无需重新训练或改变结构。本文在T5-XXL上进行了演示,与标准的T5X实现相比,在输出相同的情况下,显示了2倍到3倍的加速。
Inference from large autoregressive models like Transformers is slow - decoding K tokens takes K serial runs of the model. In this work we introduce speculative decoding - an algorithm to sample from autoregressive models faster without any changes to the outputs, by computing several tokens in parallel. At the heart of our approach lie the observations that (1) hard language-modeling tasks often include easier subtasks that can be approximated well by more efficient models, and (2) using speculative execution and a novel sampling method, we can make exact decoding from the large models faster, by running them in parallel on the outputs of the approximation models, potentially generating several tokens concurrently, and without changing the distribution. Our method supports existing off-the-shelf models without retraining or architecture changes. We demonstrate it on T5-XXL and show a 2X-3X acceleration compared to the standard T5X implementation, with identical outputs.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.17192


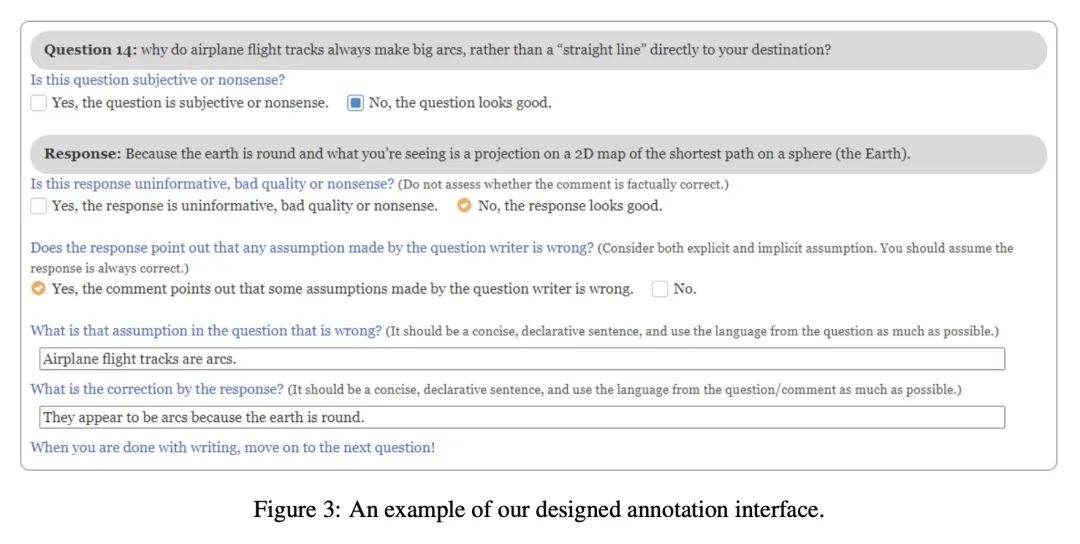
4、[CL] CREPE: Open-Domain Question Answering with False Presuppositions
X V Yu, S Min, L Zettlemoyer, H Hajishirzi
[University of Washington & Allen Institute for Artificial Intelligence]
CREPE:虚假前提开放域问答。寻求信息的用户经常提出带有错误前提的问题,特别是在询问不熟悉的主题时。相反,大多数现有的问答(QA)数据集都假定所有问题都有明确的答案。本文提出CREPE,一种包含来自在线信息搜索论坛的前提失败的自然分布的QA数据集。本文发现25%的问题包含错误的前提,并为这些前提及其更正提供标注。广泛的基线实验表明,现有的开放域质量保证模型的改编可以适度地找到前提,但在预测前提是否符合事实时却很困难。这在很大程度上是由于难以从大型文本语料库中检索出相关的证据段落。CREPE为研究实际场景问答提供了一个基准,本文的分析为今后更好地建模和进一步研究这一任务提供了途径。
Information seeking users often pose questions with false presuppositions, especially when asking about unfamiliar topics. Most existing question answering (QA) datasets, in contrast, assume all questions have well defined answers. We introduce CREPE, a QA dataset containing a natural distribution of presupposition failures from online information-seeking forums. We find that 25% of questions contain false presuppositions, and provide annotations for these presuppositions and their corrections. Through extensive baseline experiments, we show that adaptations of existing open-domain QA models can find presuppositions moderately well, but struggle when predicting whether a presupposition is factually correct. This is in large part due to difficulty in retrieving relevant evidence passages from a large text corpus. CREPE provides a benchmark to study question answering in the wild, and our analyses provide avenues for future work in better modeling and further studying the task.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.17257



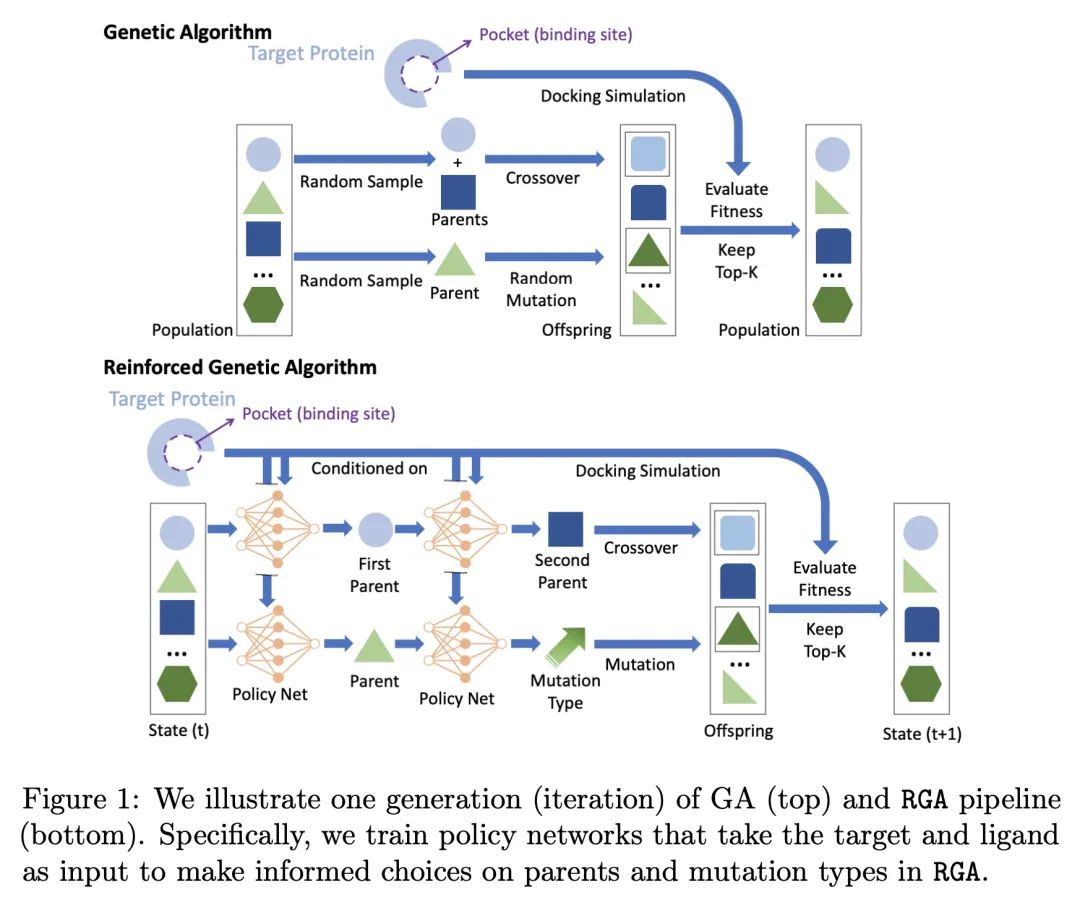
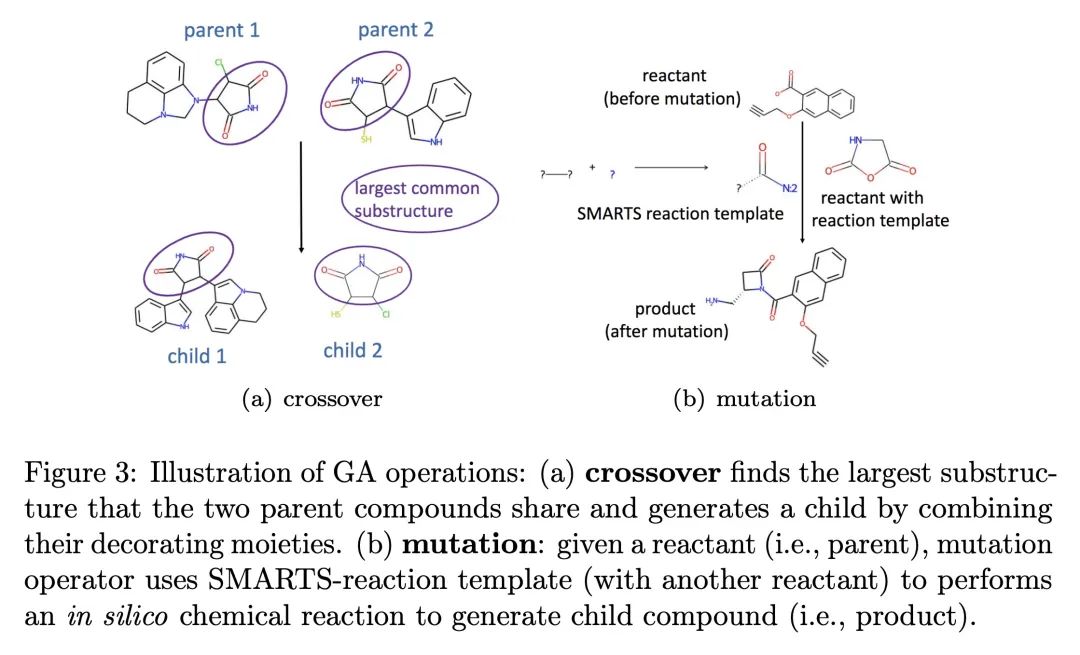
5、[LG] Reinforced Genetic Algorithm for Structure-based Drug Design
T Fu, W Gao, C W. Coley, J Sun
[Georgia Institute of Technology & MIT & University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign]
面向基于结构药物设计的强化遗传算法。基于结构的药物设计(SBDD)旨在通过寻找与疾病相关蛋白(目标)紧密结合的分子(配体)来发现候选药物,这是计算机辅助药物发现的主要方法。最近,应用以蛋白质袋为条件的3D分子设计的深度生成模型来解决SBDD已经引起了广泛的关注,但其作为概率模型的表述往往导致优化性能不尽人意。另一方面,传统的组合优化方法,如遗传算法(GA),在各种分子优化任务中表现出最先进的性能。然而,它们没有利用蛋白质目标结构来告知设计步骤,而是依赖于随机游走式的探索,这导致了不稳定的性能和不同任务之间没有知识迁移,尽管有类似的结合物理。为了实现更稳定和高效的SBDD,本文提出强化遗传算法(RGA),用神经模型来确定有用的设计步骤的优先次序,并抑制随机游走行为。神经模型将目标和配体的3D结构作为输入,利用本地复杂结构进行预训练,以利用不同目标的共享结合物理知识,在优化期间进行微调。本文对优化与各种疾病目标的结合亲和力进行了全面的实证研究,结果表明,RGA在对接分数方面优于基线,对随机初始化更稳定。消融研究还表明,对不同目标的训练有助于利用结合过程中的共享基础物理学来提高性能。
Structure-based drug design (SBDD) aims to discover drug candidates by finding molecules (ligands) that bind tightly to a disease-related protein (targets), which is the primary approach to computer-aided drug discovery. Recently, applying deep generative models for three-dimensional (3D) molecular design conditioned on protein pockets to solve SBDD has attracted much attention, but their formulation as probabilistic modeling often leads to unsatisfactory optimization performance. On the other hand, traditional combinatorial optimization methods such as genetic algorithms (GA) have demonstrated state-of-the-art performance in various molecular optimization tasks. However, they do not utilize protein target structure to inform design steps but rely on a random-walk-like exploration, which leads to unstable performance and no knowledge transfer between different tasks despite the similar binding physics. To achieve a more stable and efficient SBDD, we propose Reinforced Genetic Algorithm (RGA) that uses neural models to prioritize the profitable design steps and suppress random-walk behavior. The neural models take the 3D structure of the targets and ligands as inputs and are pre-trained using native complex structures to utilize the knowledge of the shared binding physics from different targets and then fine-tuned during optimization. We conduct thorough empirical studies on optimizing binding affinity to various disease targets and show that RGA outperforms the baselines in terms of docking scores and is more robust to random initializations. The ablation study also indicates that the training on different targets helps improve performance by leveraging the shared underlying physics of the binding processes. The code is available at this https URL.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16508


另外几篇值得关注的论文:
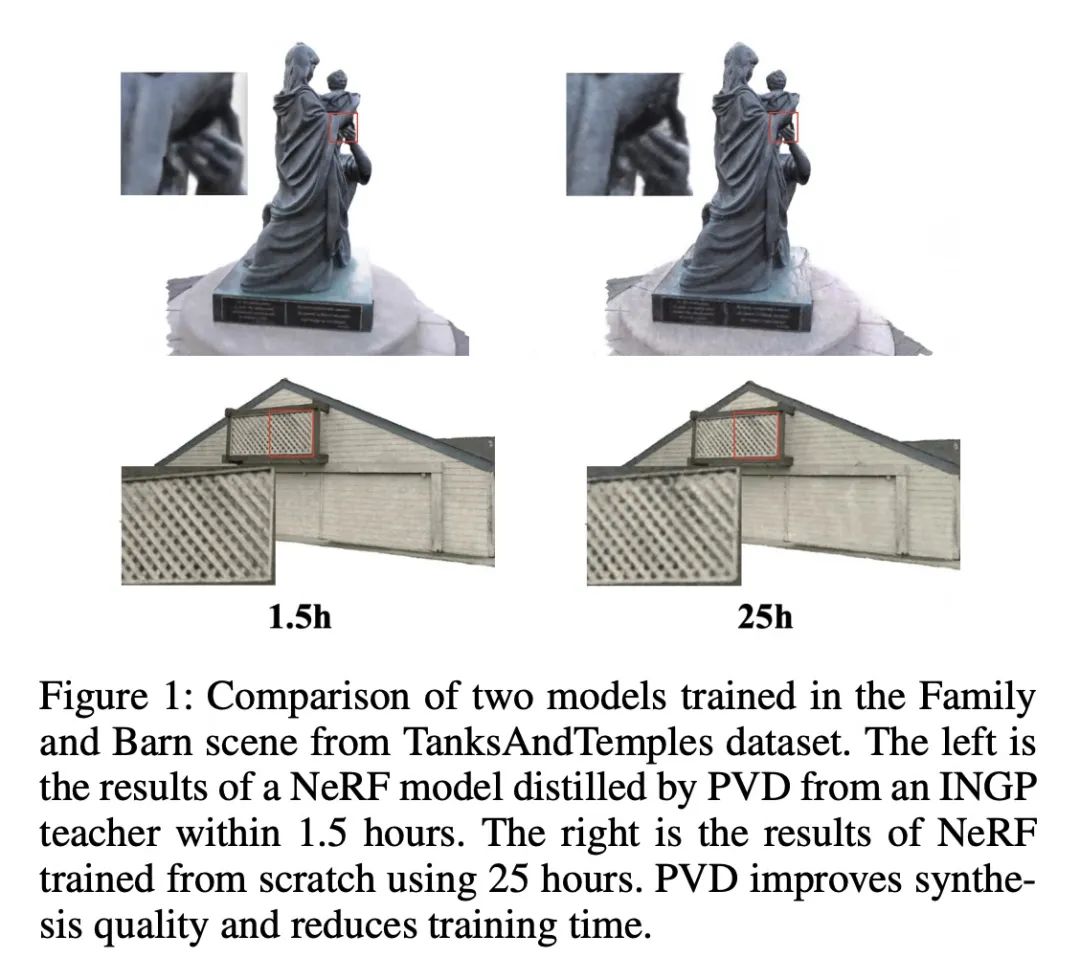
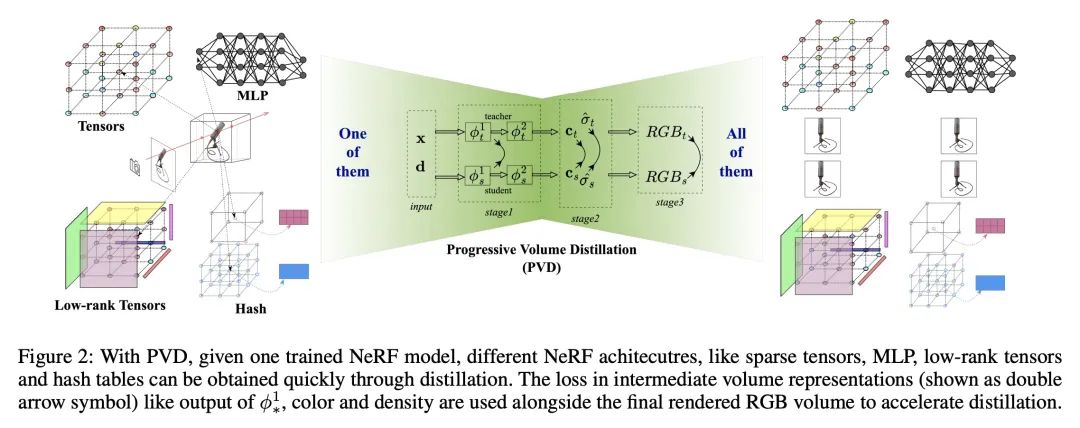
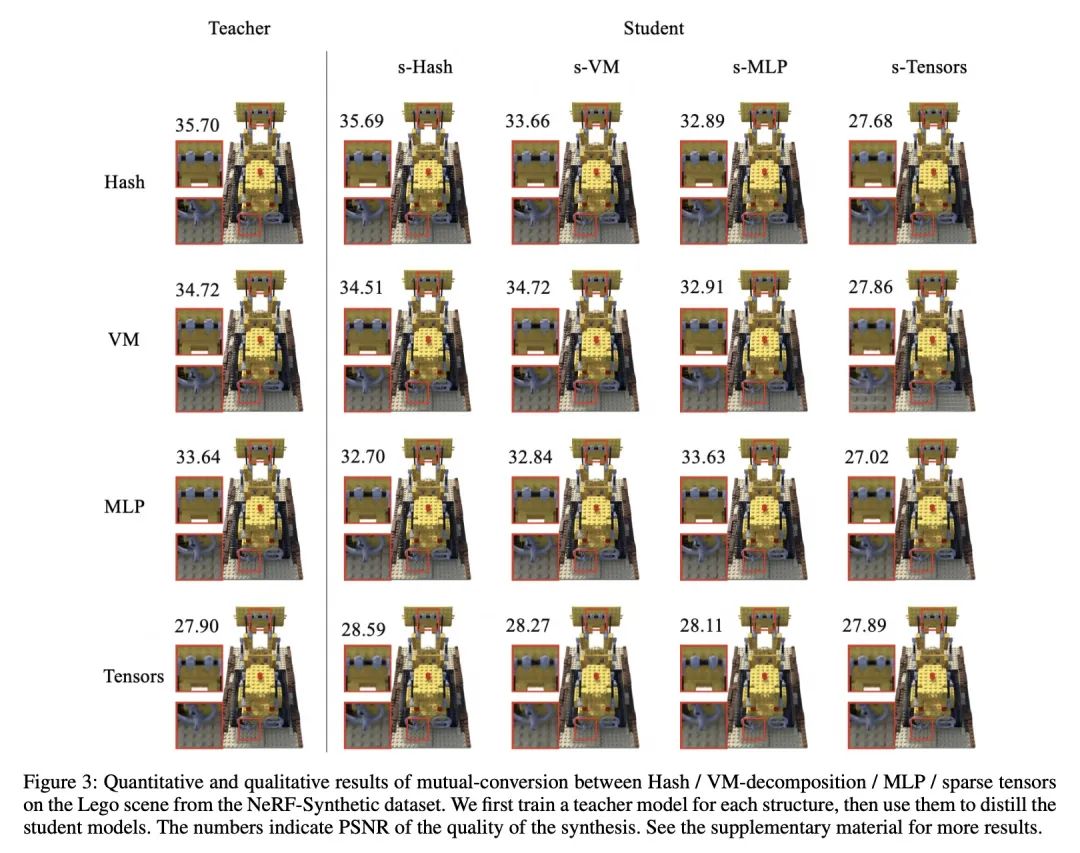
[CV] One is All: Bridging the Gap Between Neural Radiance Fields Architectures with Progressive Volume Distillation
用渐进体蒸馏缩短神经辐射场架构间的差距
S Fang, W Xu, H Wang, Y Yang, Y Wang, S Zhou
[Beihang University & Megvii Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.15977


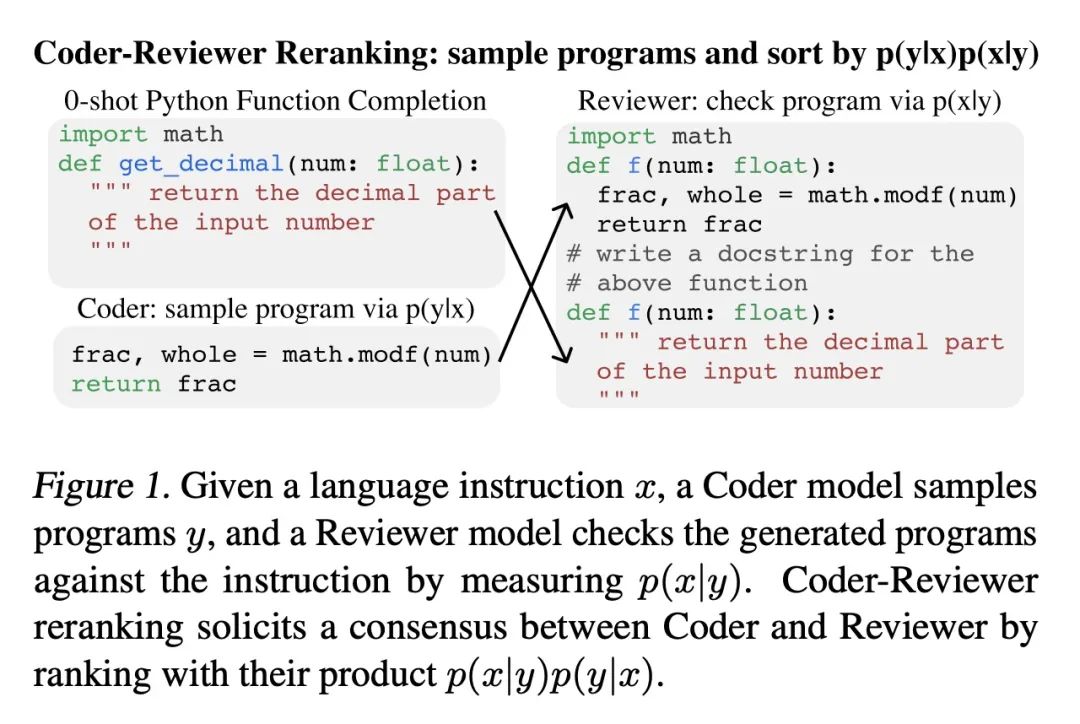
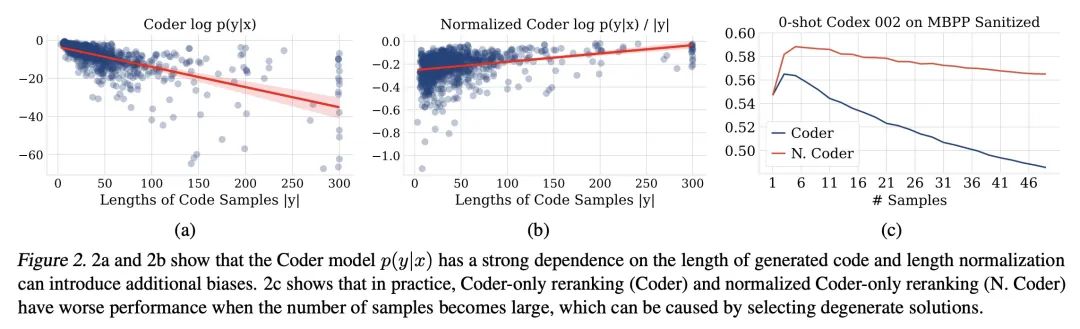
[LG] Coder Reviewer Reranking for Code Generation
代码生成的代码审计重排
T Zhang, T Yu, T B. Hashimoto, M Lewis, W Yih, D Fried, S I. Wang
[Meta AI & Stanford University &The University of Hong Kong & CMU]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16490


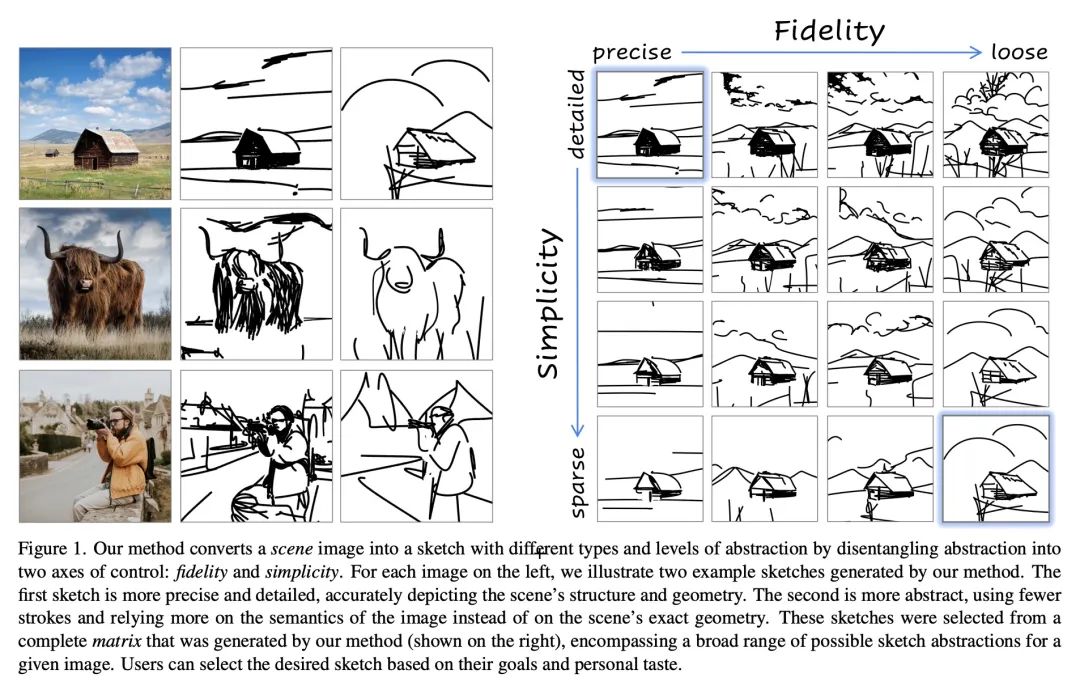
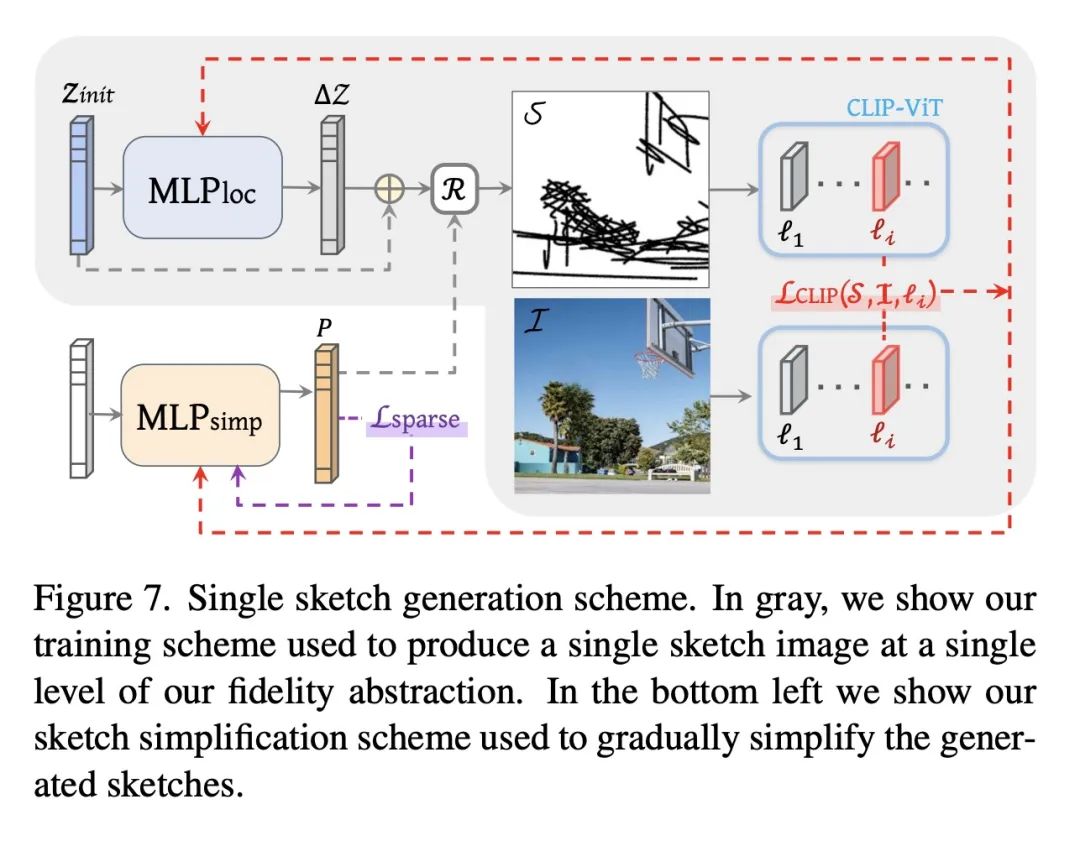
[CV] CLIPascene: Scene Sketching with Different Types and Levels of Abstraction
CLIPascene:不同类型和抽象层次的场景草图生成
Y Vinker, Y Alaluf, D Cohen-Or, A Shamir
[Tel Aviv University & Reichman University]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.17256


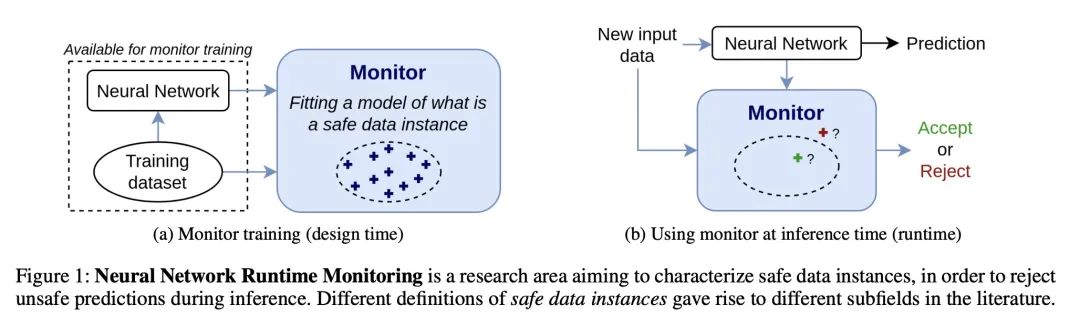
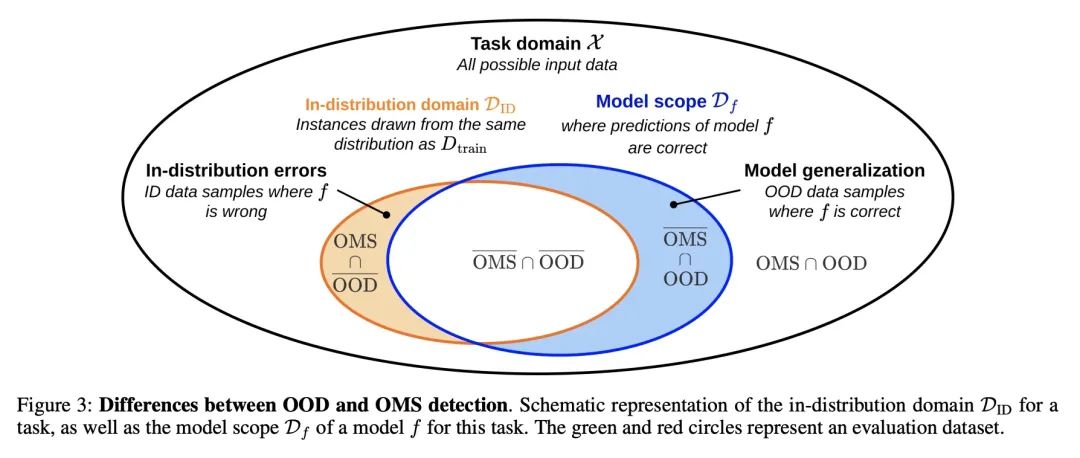
[LG] Out-Of-Distribution Detection Is Not All You Need
分布外检测不足以保证系统安全
J Guerin, K Delmas, R S Ferreira, J Guiochet
[Universite de Toulouse & ONERA]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16158


内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢