转自爱可可爱生活
LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 GR - 图形学
摘要:微调语言模型帮不同意见人群找到一致意见、面向3D生成的提升预训练2D扩散模型、可解释的防泄漏的基于概念模型、深度可微逻辑门网络、分布不匹配下的半监督异常检测、将3D GAN用于艺术绘画、单幅图像去噪扩散模型、基于文本到图像扩散3D生成模型的多样性保持域自适应、分子表示生成式掩码语言模型
1、[LG] Fine-tuning language models to find agreement among humans with diverse preferences
M A. Bakker, M J. Chadwick, H R. Sheahan, M H Tessler...
[DeepMind]
微调语言模型帮不同意见人群找到一致意见
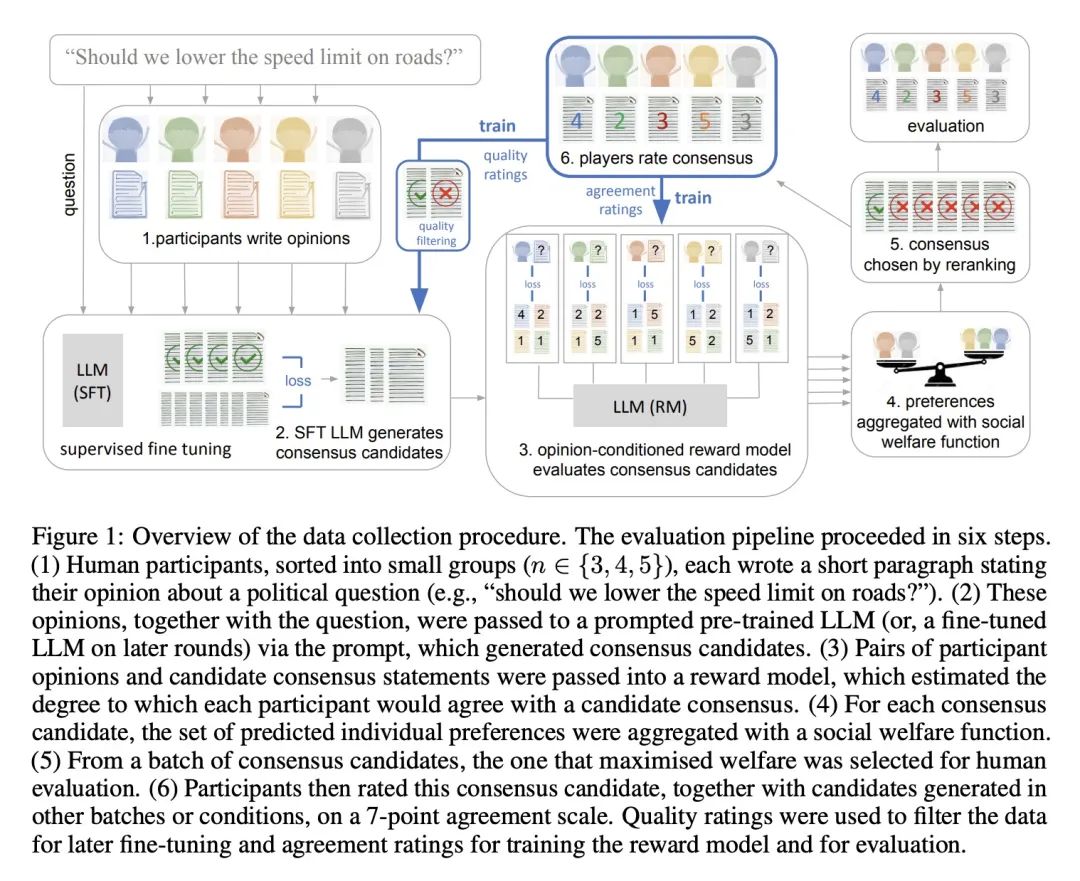
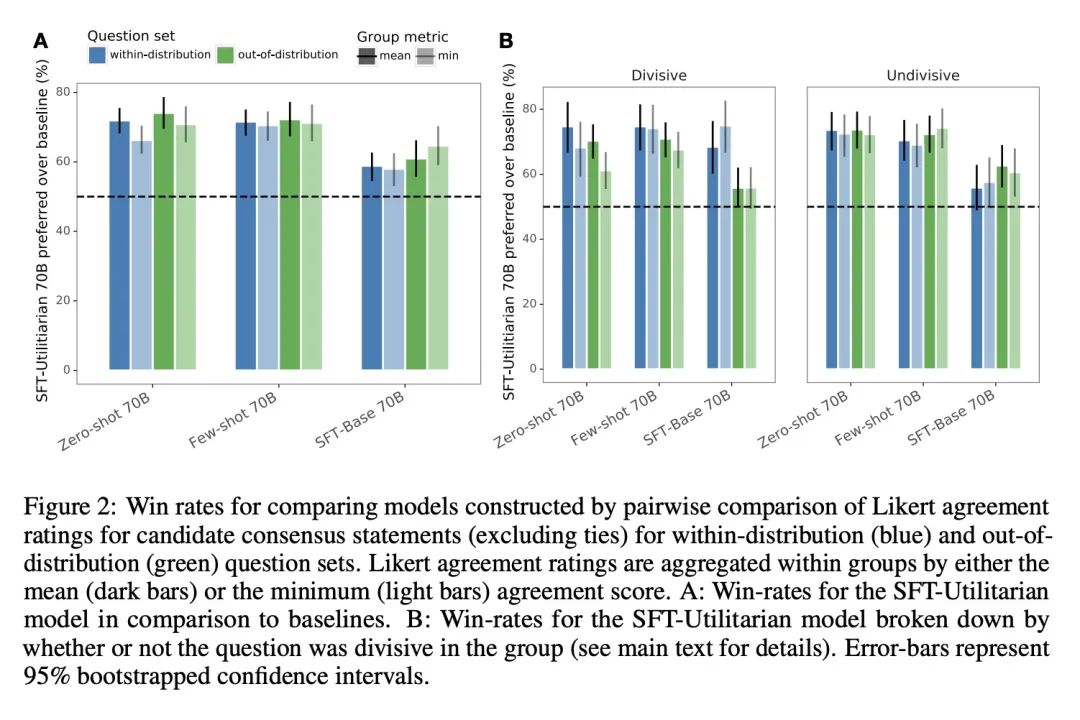
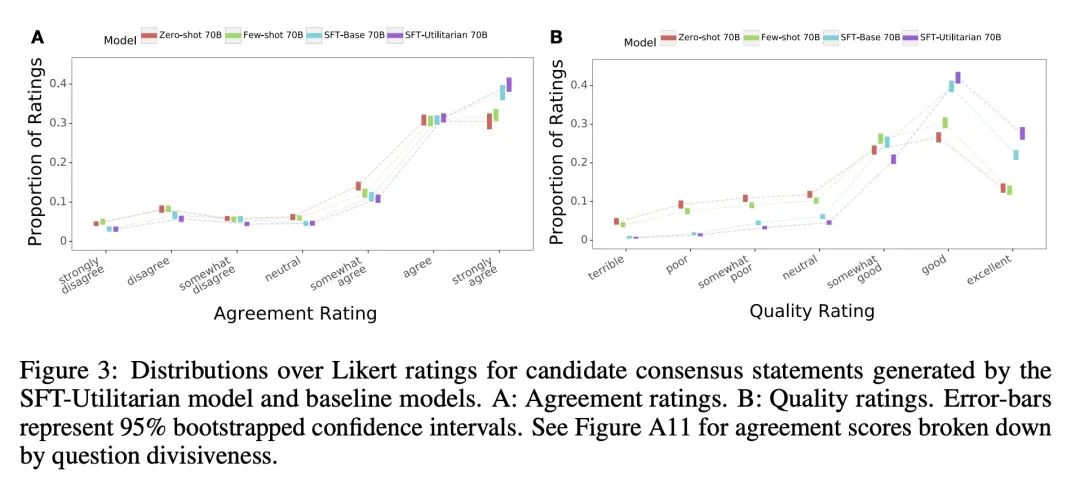
简介:用大型语言模型来帮助具有不同意见的人群找到一致意见。本文显示,当模型被微调时,可以产生共识声明,这些声明比提示语言模型的声明更受人类用户欢迎。当共识声明是由小组成员的一个子集创建的时候,那些被排除在外的人更有可能提出异议。该模型的共识声明被发现比人类产生的最佳意见更受青睐。本文使用700亿参数的LLM来生成语句,使一群有潜在不同意见的人的预期认可度最大化。通过对参与者对数千个问题的回答进行奖励模型训练来做到这一点,这使得它能够根据对整个群体的吸引力对共识声明进行量化和排序。
摘要:最近在大型语言建模(LLM)方面的工作使用了微调来使输出与典型用户的偏好相一致。这项工作假定人的偏好是静态的,并且在不同个体间是同质的,因此,与一个"通用"用户对齐将赋予更普遍的对齐。本文承认人偏好的异质性,思考一种不同的挑战:机器如何帮助具有不同观点的人找到一致?本文对700亿参数的LLM进行了微调,以生成对具有潜在不同意见的一群人的预期赞成最大化的声明。人工参与者就上千个涉及道德和政治的问题提供书面意见(例如,"应该对富人加税吗?"),并对LLM生成的候选共识声明的一致性和质量进行评分。然后训练一个奖励模型来预测个人偏好,使其能根据不同的聚合(社会福利)函数定义的对整体群体的吸引力,对共识声明进行量化和排名。该模型产生的共识声明被人工用户判定优于来自提示LLM的声明(>70%),且明显优于缺乏最终排名步骤的严格微调基线。此外,所得到的最佳模型的共识声明比人工生成的最佳意见更受青睐(>65%)。当只从小组成员的一个子集中默默地构建共识声明时,那些被排除在外的成员更有可能提出异议,这揭示了共识对个人贡献的敏感性。这些结果强调了使用LLM来帮助人类群体相互协调其价值观的潜力。
Recent work in large language modeling (LLMs) has used fine-tuning to align outputs with the preferences of a prototypical user. This work assumes that human preferences are static and homogeneous across individuals, so that aligning to a a single "generic" user will confer more general alignment. Here, we embrace the heterogeneity of human preferences to consider a different challenge: how might a machine help people with diverse views find agreement? We fine-tune a 70 billion parameter LLM to generate statements that maximize the expected approval for a group of people with potentially diverse opinions. Human participants provide written opinions on thousands of questions touching on moral and political issues (e.g., "should we raise taxes on the rich?"), and rate the LLM's generated candidate consensus statements for agreement and quality. A reward model is then trained to predict individual preferences, enabling it to quantify and rank consensus statements in terms of their appeal to the overall group, defined according to different aggregation (social welfare) functions. The model produces consensus statements that are preferred by human users over those from prompted LLMs (>70%) and significantly outperforms a tight fine-tuned baseline that lacks the final ranking step. Further, our best model's consensus statements are preferred over the best human-generated opinions (>65%). We find that when we silently constructed consensus statements from only a subset of group members, those who were excluded were more likely to dissent, revealing the sensitivity of the consensus to individual contributions. These results highlight the potential to use LLMs to help groups of humans align their values with one another.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.15006

2、[CV] Score Jacobian Chaining: Lifting Pretrained 2D Diffusion Models for 3D Generation
H Wang, X Du, J Li, R A. Yeh, G Shakhnarovich
[TTI-Chicago & Purdue University]
得分Jacobian链:面向3D生成的提升预训练2D扩散模型
简介:本文提出一种基于2D图像而非3D数据集的3D生成建模方法,用一个可微渲染器将多个视图上的2D图像梯度聚合成一个3D梯度,并将生成模型从2D提升到3D。
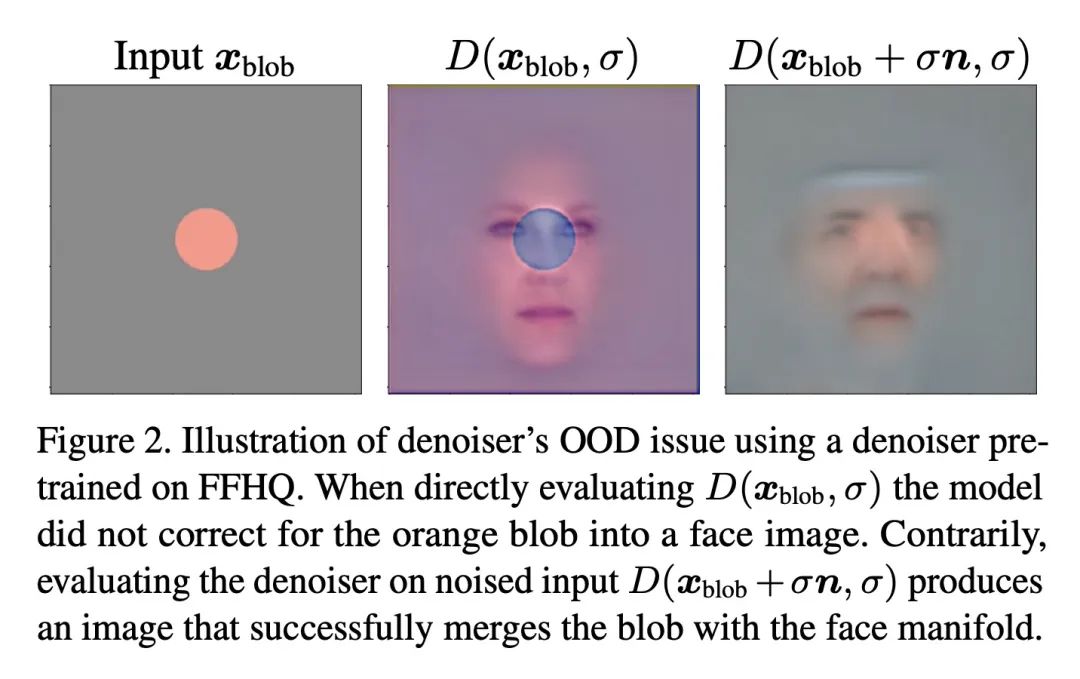
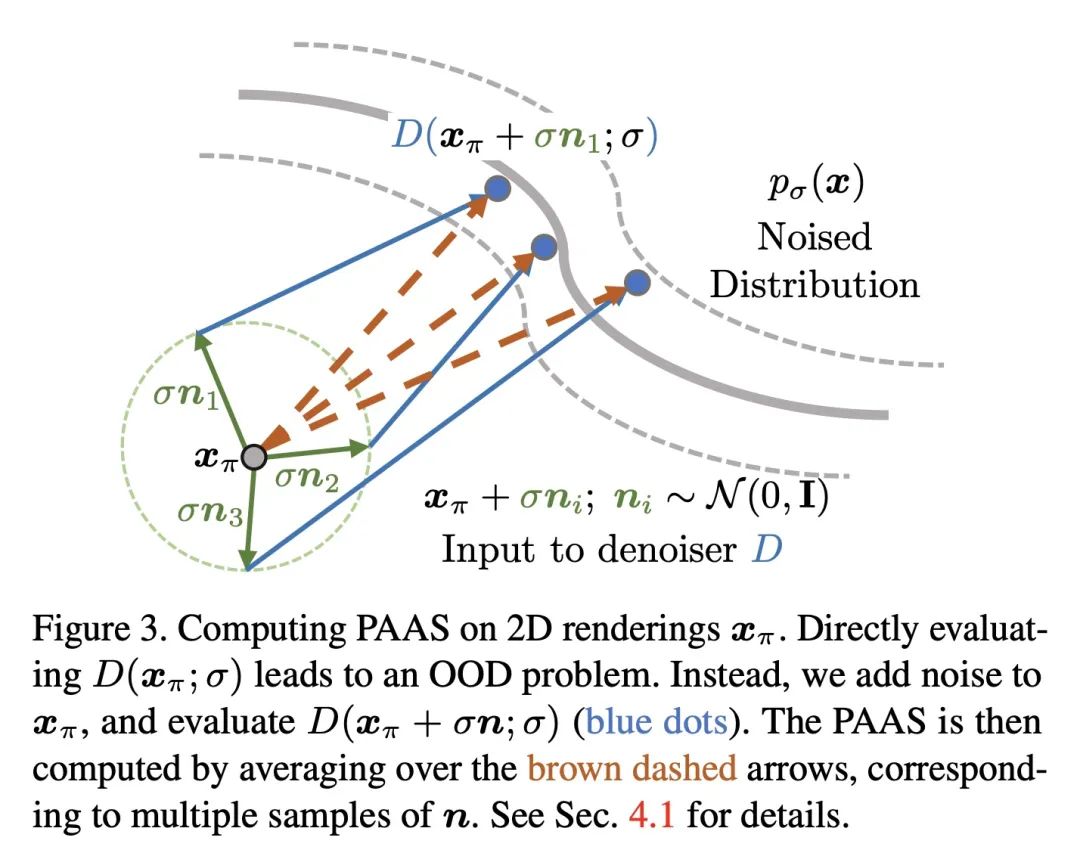
摘要:扩散模型学习预测梯度的矢量场。本文提出在学习到的梯度上应用链式规则,并通过可微渲染器的Jacobian反向传播扩散模型的得分,将其实例化为一个体辐射场。这种设置将多个相机视图的2D分数汇总为3D分数,并将预训练的2D模型重新用于3D数据的生成。本文确定了这一应用中出现的分布不匹配的技术挑战,并提出了一种新的估计机制来解决这一问题。在几个现成的扩散图像生成模型上运行该算法,包括最近发布的在大规模LAION数据集上训练的Stable Diffusion模型。
A diffusion model learns to predict a vector field of gradients. We propose to apply chain rule on the learned gradients, and back-propagate the score of a diffusion model through the Jacobian of a differentiable renderer, which we instantiate to be a voxel radiance field. This setup aggregates 2D scores at multiple camera viewpoints into a 3D score, and repurposes a pretrained 2D model for 3D data generation. We identify a technical challenge of distribution mismatch that arises in this application, and propose a novel estimation mechanism to resolve it. We run our algorithm on several off-the-shelf diffusion image generative models, including the recently released Stable Diffusion trained on the large-scale LAION dataset.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.00774



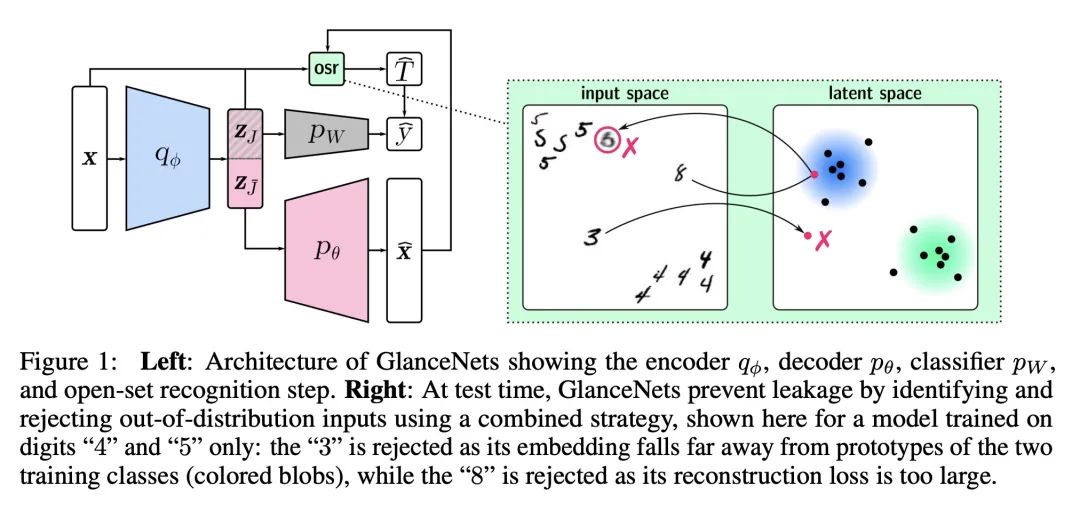
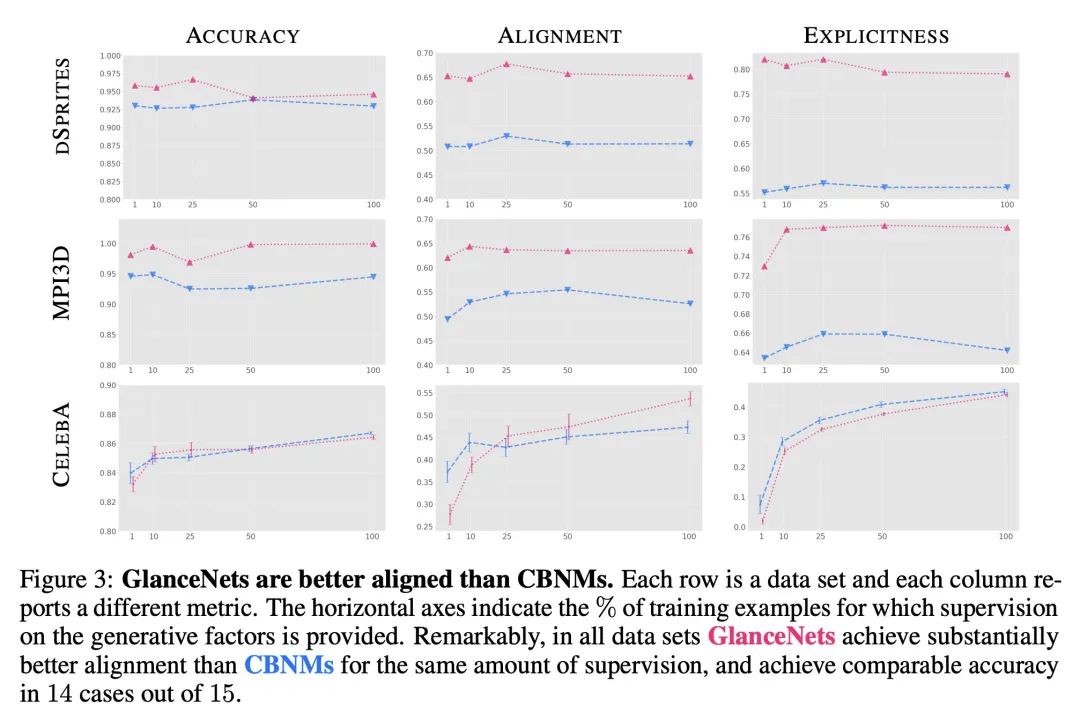
3、[LG] GlanceNets: Interpretabile, Leak-proof Concept-based Models
E Marconato, A Passerini, S Teso
[University of Trento]
GlanceNets:可解释的、防泄漏的基于概念模型。
简介:本文通过在模型的表征和底层数据生成过程的一致性方面对可解释性进行明确的定义,并提出GlanceNets,一种新的基于概念模型,使用来自解缠表示学习和开放集识别的技术来实现更好的一致性,提高所学概念的可解释性。解缠表示学习是机器学习的一种类型,其目标是学习不互相纠缠的数据表示,而开放集识别是一个系统识别不属于任何已知类别的数据点的能力。。
摘要:人们对基于概念的模型(CBMs)越来越感兴趣,这些模型通过获取和推理高层次的概念词汇来结合高性能和可解释性。一个关键的需求是,这些概念是可解释的。现有的CBM使用各种基于不明确的可解释性概念的启发式方法来处理这一要求,并且未能获得具有预期语义的概念。本文通过在模型的表示和底层数据生成过程的一致性方面提供一个明确的可解释性定义来解决这个问题,提出GlanceNets,一种新的CBM,利用来自解缠表示学习和开放及识别的技术来实现一致性,从而提高了所学概念的可解释性。GlanceNets与概念级监督相结合,实现了比最先进方法更好的一致性,同时防止虚假信息意外地泄露到所学概念中。
There is growing interest in concept-based models (CBMs) that combine high-performance and interpretability by acquiring and reasoning with a vocabulary of high-level concepts. A key requirement is that the concepts be interpretable. Existing CBMs tackle this desideratum using a variety of heuristics based on unclear notions of interpretability, and fail to acquire concepts with the intended semantics. We address this by providing a clear definition of interpretability in terms of alignment between the model's representation and an underlying data generation process, and introduce GlanceNets, a new CBM that exploits techniques from disentangled representation learning and open-set recognition to achieve alignment, thus improving the interpretability of the learned concepts. We show that GlanceNets, paired with concept-level supervision, achieve better alignment than state-of-the-art approaches while preventing spurious information from unintendedly leaking into the learned concepts.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.15612

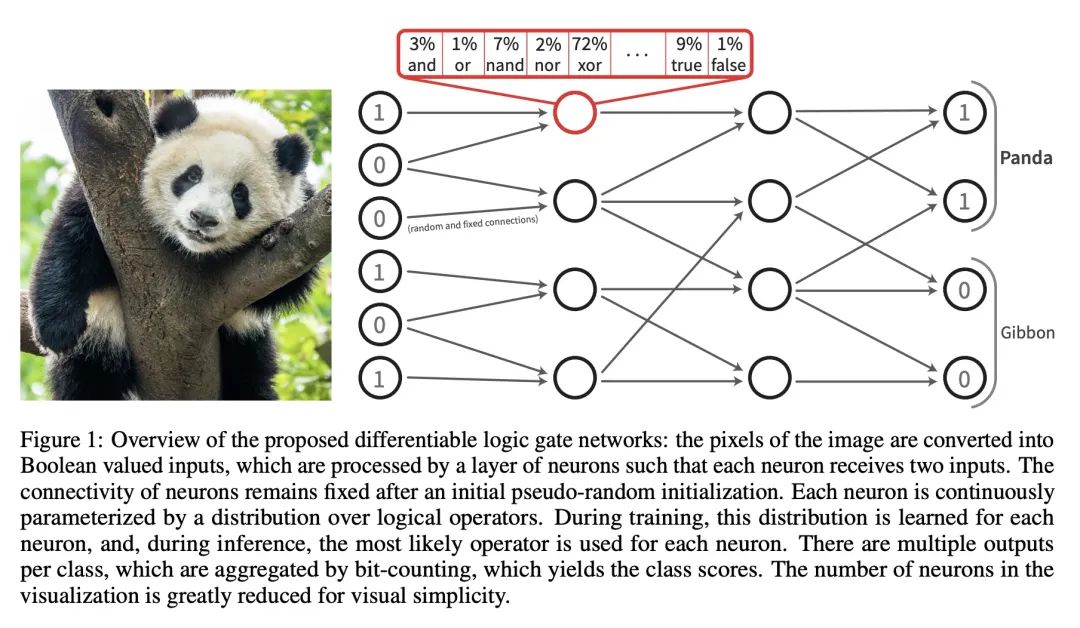
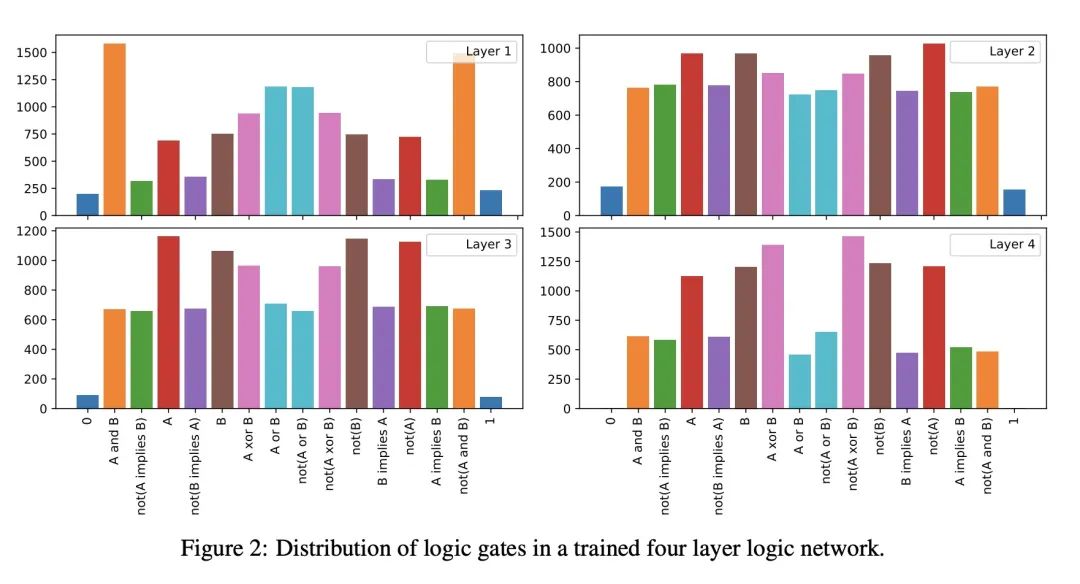
4、[LG] Deep Differentiable Logic Gate Networks
F Petersen, C Borgelt, H Kuehne, O Deussen
[Stanford University & University of Salzburg & University of Frankfurt & University of Konstanz]
深度可微逻辑门网络
简介:通过结合实值逻辑和逻辑门网络的连续参数化松弛,创建一个可微的逻辑门网络,使得梯度下降的高效训练和快速推理速度成为可能。
摘要:最近,研究越来越集中在开发高效的神经网络架构上。本文通过逻辑门组合学习来探索面向机器学习任务的逻辑门网络。这些网络由"AND"和"XOR"等逻辑门组成,可以非常快速的执行。逻辑门网络学习的困难在于,其在传统上是不可微的,无法用梯度下降进行训练。为了实现有效训练,本文提出可微逻辑门网络,一种结合了实值逻辑和网络连续参数化松弛的架构。由此产生的可微逻辑门网络实现了快速的推理速度,在单个CPU核心上每秒处理超过一百万张MNIST图像。
Recently, research has increasingly focused on developing efficient neural network architectures. In this work, we explore logic gate networks for machine learning tasks by learning combinations of logic gates. These networks comprise logic gates such as "AND" and "XOR", which allow for very fast execution. The difficulty in learning logic gate networks is that they are conventionally non-differentiable and therefore do not allow training with gradient descent. Thus, to allow for effective training, we propose differentiable logic gate networks, an architecture that combines real-valued logics and a continuously parameterized relaxation of the network. The resulting discretized logic gate networks achieve fast inference speeds, e.g., beyond a million images of MNIST per second on a single CPU core.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.08277

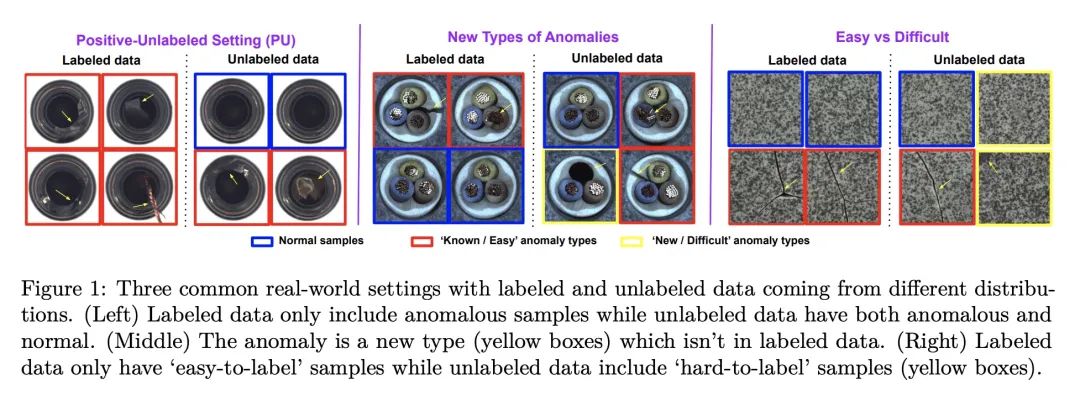
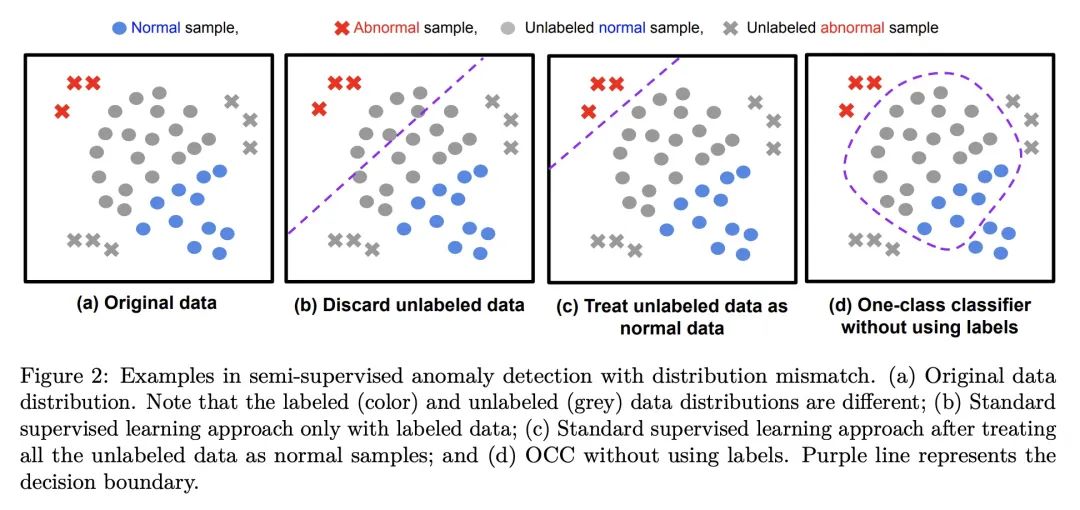
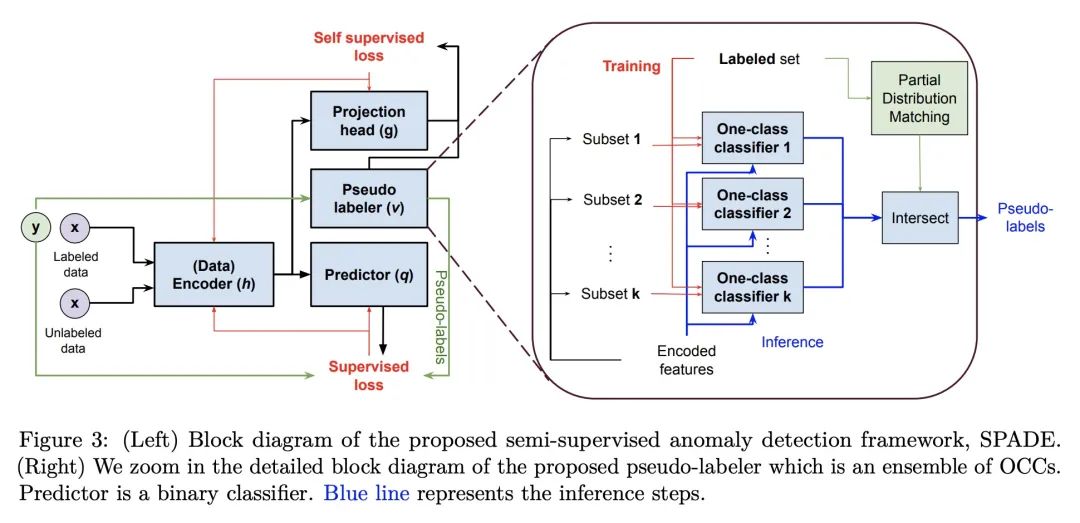
5、[LG] SPADE: Semi-supervised Anomaly Detection under Distribution Mismatch
J Yoon, K Sohn, C Li, S O. Arik, T Pfister
[Google Cloud AI]
SPADE:分布不匹配下的半监督异常检测
简介:SPADE (基于集成的半监督伪标签异常检测)是一种新的半监督异常检测框架,主要面向标记和未标记数据来自不同分布的情况。SPADE使用单类分类器的集成作为伪标签器,来提高分布不匹配的鲁棒性。此外,SPADE还提出使用部分匹配来自动选择伪标签的关键超参数,而不需要验证数据。SPADE显示了最先进的半监督异常检测性能,包括表格和图像领域等各种分布不匹配的场景。
摘要:半监督异常检测是一个常见问题,因为包含异常的数据集往往是部分标记的。本文提出一个标准化框架。基于集成的半监督伪标签异常检测(SPADE),不受标记和未标记数据来自同一分布的假设的限制。事实上,该假设在许多应用中经常无法满足——例如,标记数据可能只包含与未标记数据不同的异常,或者未标记数据可能包含不同类型的异常,或者标记的数据可能只包含"容易标记的"样本。SPADE利用一类分类器的集成作为伪标签器来提高分布不匹配的伪标签的鲁棒性。部分匹配被提出用于自动选择关键的超参数进行伪标注,而不需要验证数据,这在有限的标记数据中是至关重要的。SPADE在表格和图像领域等分布不匹配的广泛场景中显示了最先进的半监督异常检测性能。在一些常见的现实环境中,如面对新的无标签异常情况的模型,SPADE的AUC平均比最先进的替代方案高出5%。
Semi-supervised anomaly detection is a common problem, as often the datasets containing anomalies are partially labeled. We propose a canonical framework: Semi-supervised Pseudo-labeler Anomaly Detection with Ensembling (SPADE) that isn't limited by the assumption that labeled and unlabeled data come from the same distribution. Indeed, the assumption is often violated in many applications - for example, the labeled data may contain only anomalies unlike unlabeled data, or unlabeled data may contain different types of anomalies, or labeled data may contain only 'easy-to-label' samples. SPADE utilizes an ensemble of one class classifiers as the pseudo-labeler to improve the robustness of pseudo-labeling with distribution mismatch. Partial matching is proposed to automatically select the critical hyper-parameters for pseudo-labeling without validation data, which is crucial with limited labeled data. SPADE shows state-of-the-art semi-supervised anomaly detection performance across a wide range of scenarios with distribution mismatch in both tabular and image domains. In some common real-world settings such as model facing new types of unlabeled anomalies, SPADE outperforms the state-of-the-art alternatives by 5% AUC in average.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.00173

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
[CV] Dr.3D: Adapting 3D GANs to Artistic Drawings
Dr.3D:将3D GAN用于艺术绘画
简介:Dr.3D是一种新的3D GAN自适应方法,从真实的人像到艺术绘画,首次成功地将3D GAN适应于绘画。通过交替适应姿态估计和图像合成、变形感知网络和几何先验来处理图画的内在几何模糊性。Dr.3D允许对艺术图画进行语义编辑,考虑其3D几何结构和内容语义。3D GAN是生成模型,可以从给定输入生成3D场景。姿态估计是确定图像中物体的方向和位置的过程。变形感知网络是能处理图像中变形的神经网络,如形状或大小的变化。几何先验是一组假设,用于推断3D物体的属性。
W Jin, N Ryu, G Kim, S Baek, S Cho
[POSTECH]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16798



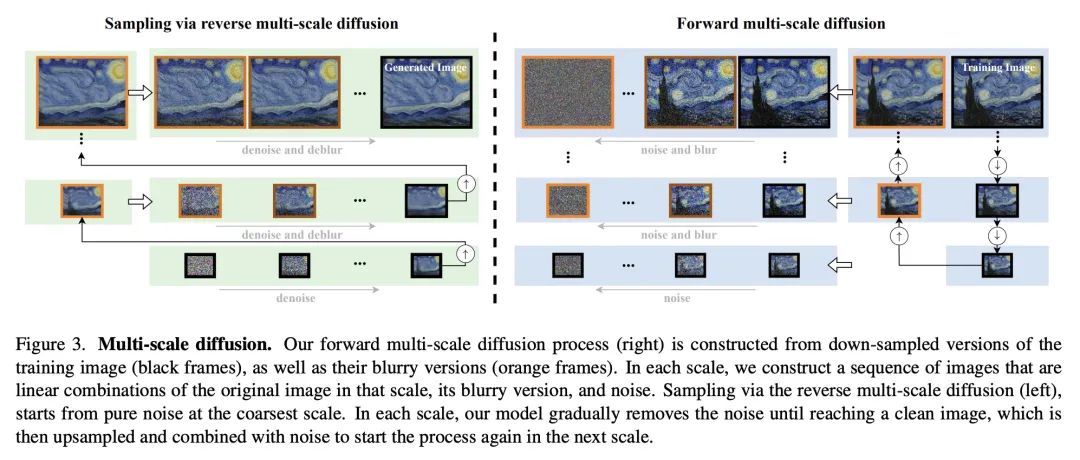
[CV] SinDDM: A Single Image Denoising Diffusion Model
SinDDM:单幅图像去噪扩散模型
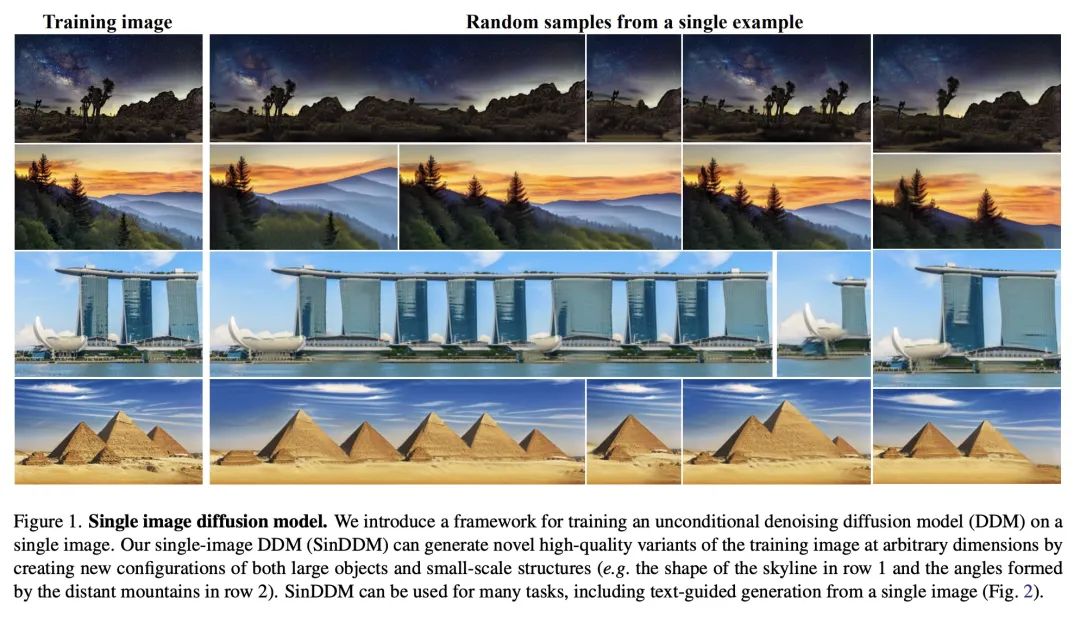
简介:提出SinDDM(单幅图像扩散模型)框架,可在任意尺度上生成训练图像的新的高质量变体,可用于诸如基于单幅图像的文本指导生成任务,允许用户控制生成内容和风格。
V Kulikov, S Yadin, M Kleiner, T Michaeli
[Technion–IsraelInstituteofTechnology]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16582



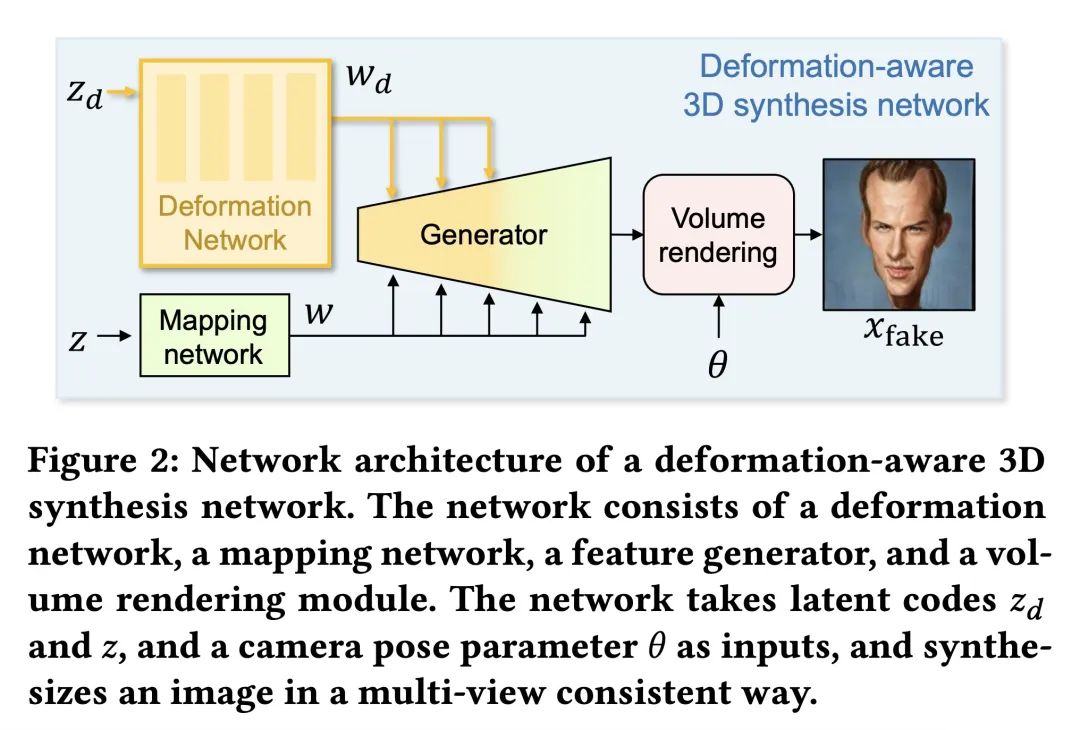
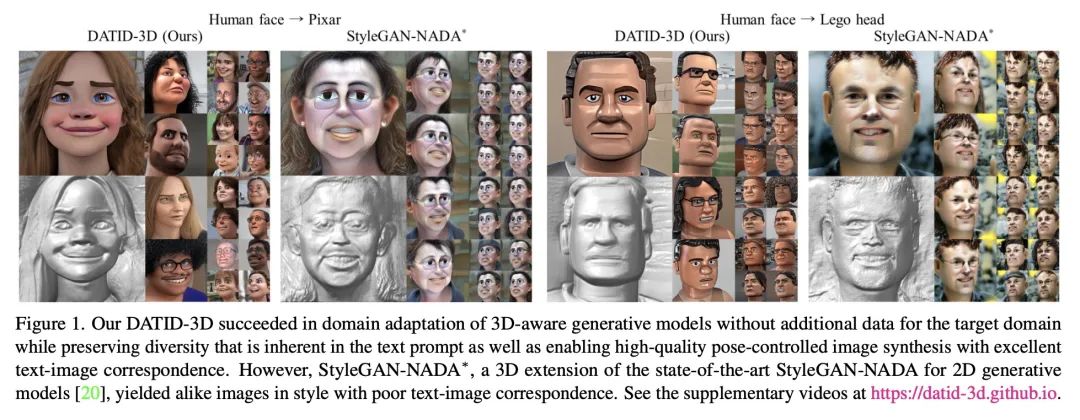
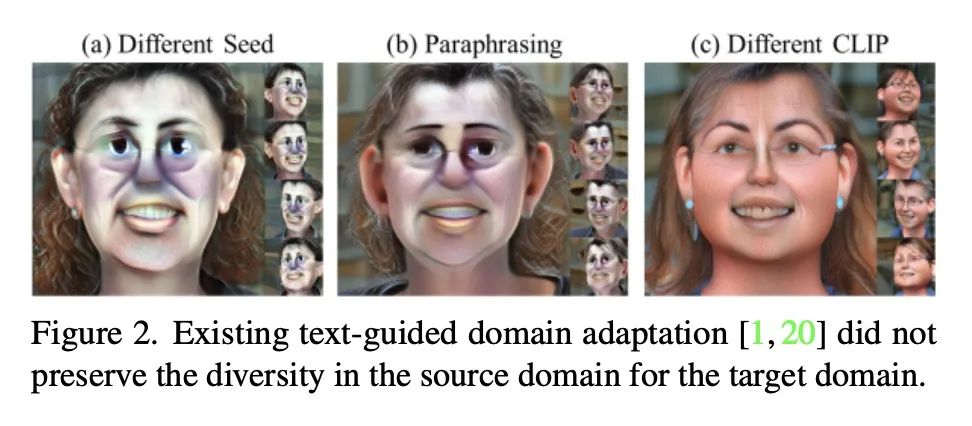
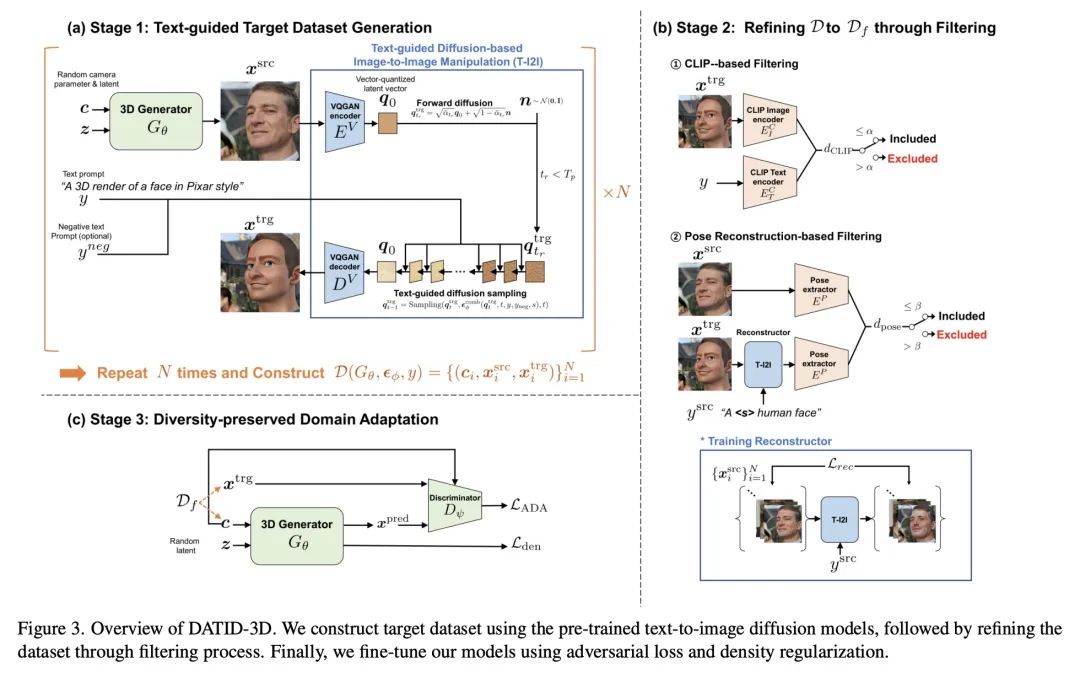
[CV] DATID-3D: Diversity-Preserved Domain Adaptation Using Text-to-Image Diffusion for 3D Generative ModelDATID-3D:基于文本到图像扩散3D生成模型的多样性保持域自适应
简介:DATID-3D是一种有效的3D感知生成模型域自适应技术,能产生高质量的姿态受控图像,并具有良好的文本-图像对应关系,不需要目标域的额外数据。为了确保生成的图像的准确性和一致性,论文提出两种过滤过程:基于CLIP的过滤和基于姿态重建的过滤。基于CLIP的过滤是一个使用潜在目标图像和文本提示之间CLIP空间余弦距离的过程。基于姿态重建的过滤是一个检查相机姿态在随机过程中是否改变的过程。
G Kim, S Y Chun
[Seoul National University]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16374

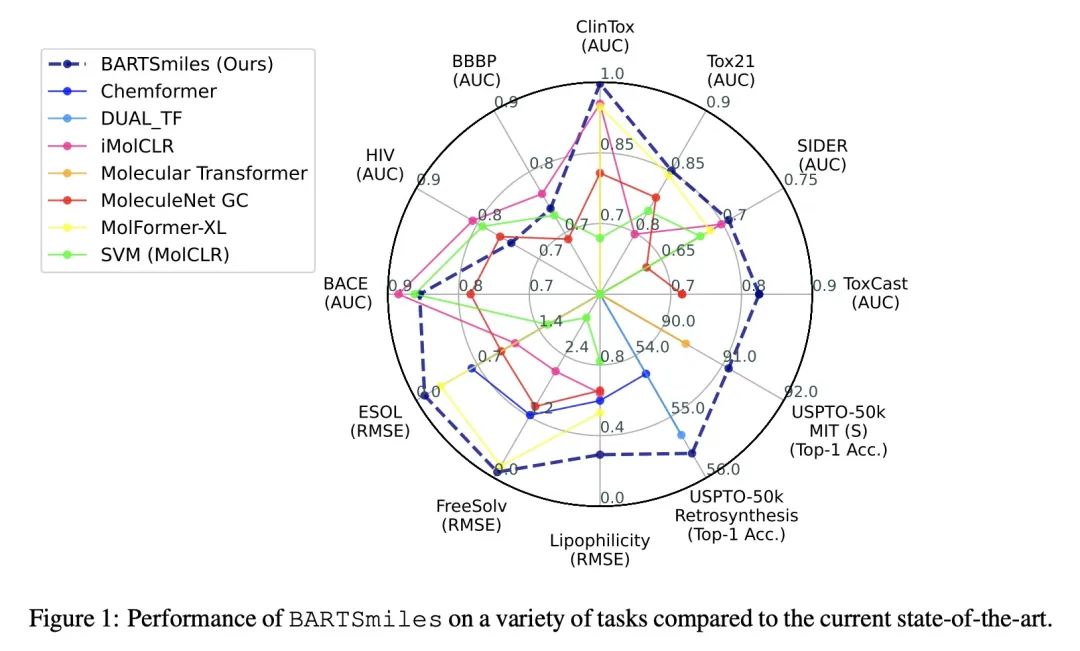
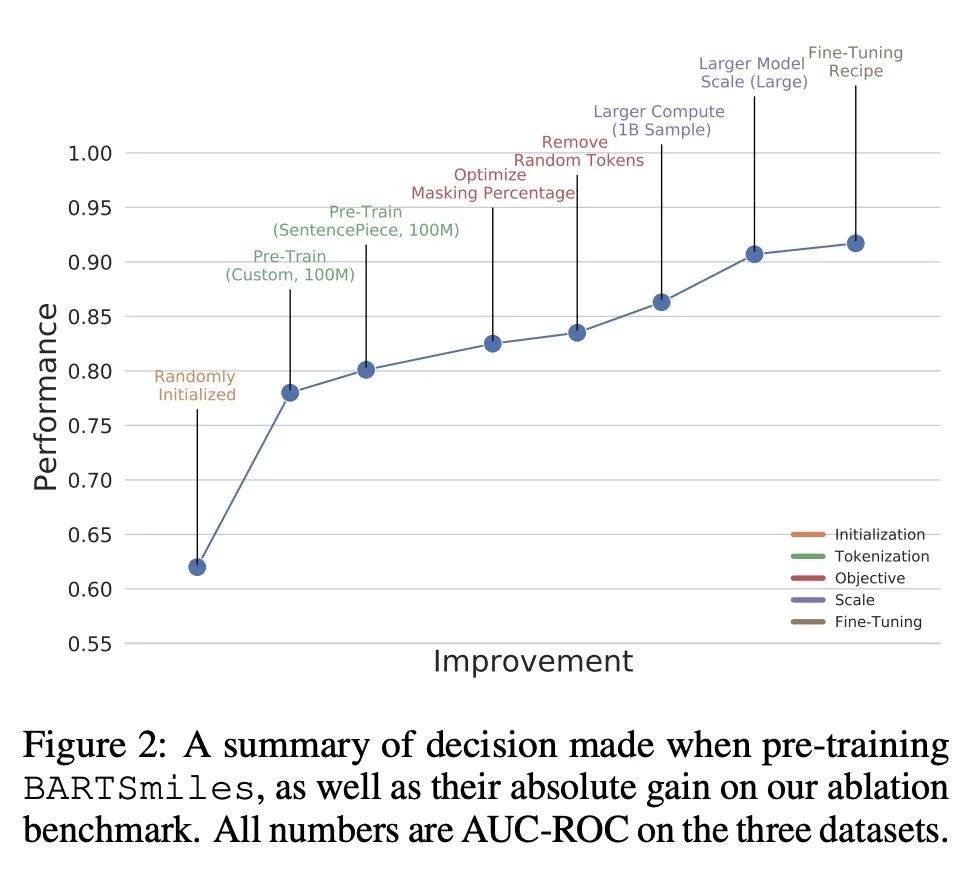
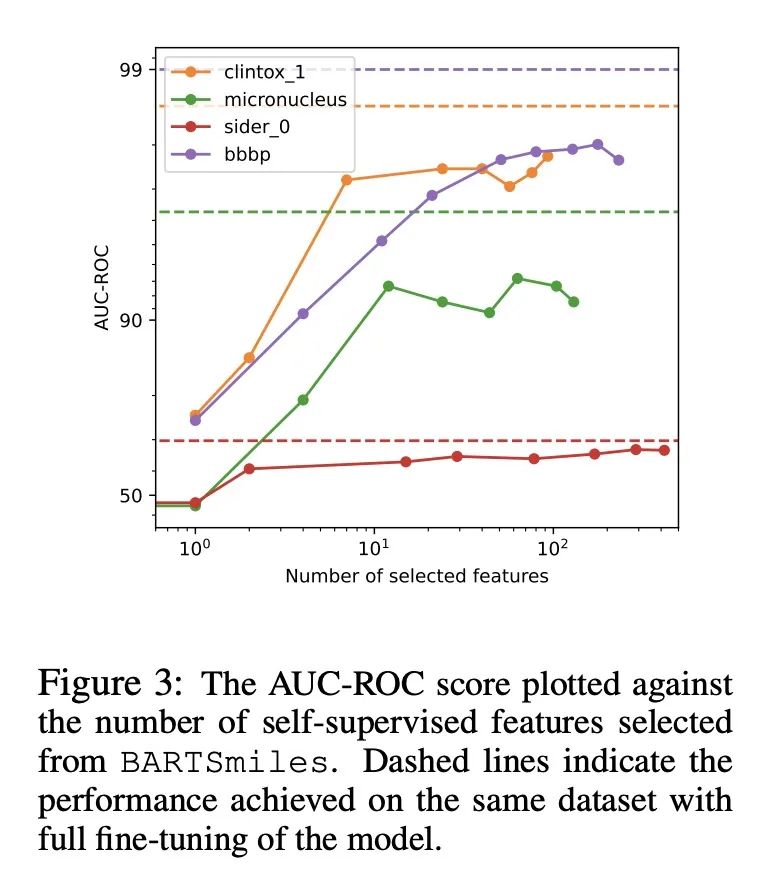
[LG] BARTSmiles: Generative Masked Language Models for Molecular RepresentationsBARTSmiles:分子表示生成式掩码语言模型
简介:一种针对分子表示的自监督策略,用于生成式掩码语言模型,以获得比其他自监督表示更好的结果,该策略称为BARTSmiles,类似于BART,在训练时比之前的自监督分子表示多了一个数量级的计算量。研究发现,当应用于分子领域时,BART目标学习的表示隐性编码了下游感兴趣的任务。当应用于BARTSmiles时,标准的归因可解释性方法突出了化学家用来解释分子特定属性的某些子结构。
G Chilingaryan, H Tamoyan, A Tevosyan...
[YerevaNN & NAS RA & Meta AI Research]
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16349

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢