LG - 机器学习 CV - 计算机视觉 CL - 计算与语言 AS - 音频与语音 RO - 机器人 GR - 图形学
转自爱可可爱生活
摘要:用掩码扩展语言-图像预训练规模、全始计算量子化学的自注意力拟设、GLOM从模糊部分推断整体能力测试、用区间非对称距离结构嵌入改进不对称距离表示方法、特定实例图像目标导航、面向数据分布漂移的自学习、用于快速多视角视频合成的混合神经体素、基于去噪扩散空白空间模型的零样本图像修复、基于干预的线性因果解缠
1、[CV] Scaling Language-Image Pre-training via Masking
Y Li, H Fan, R Hu, C Feichtenhofer, K He
[Meta AI]
用掩码扩展语言-图像预训练规模
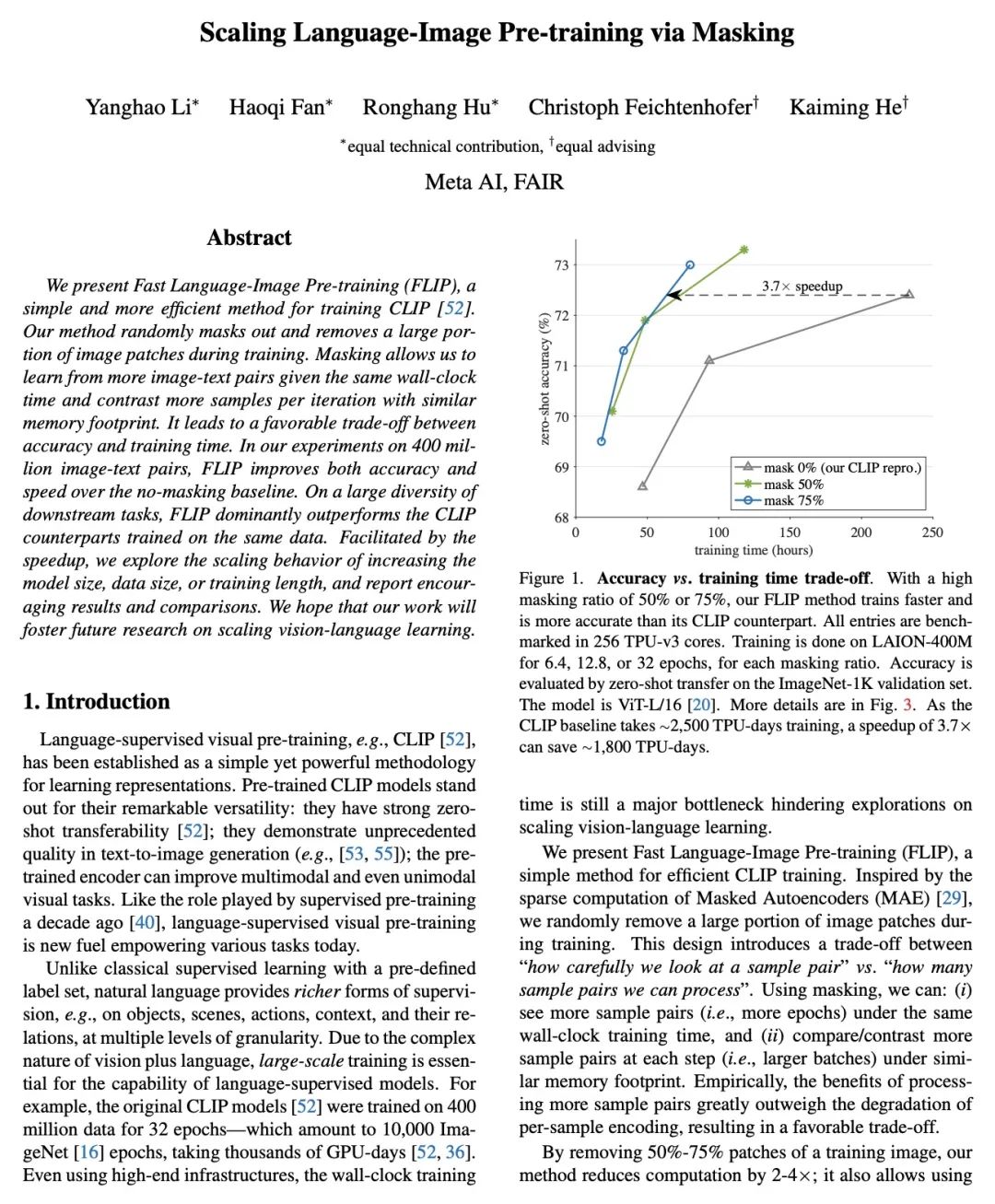
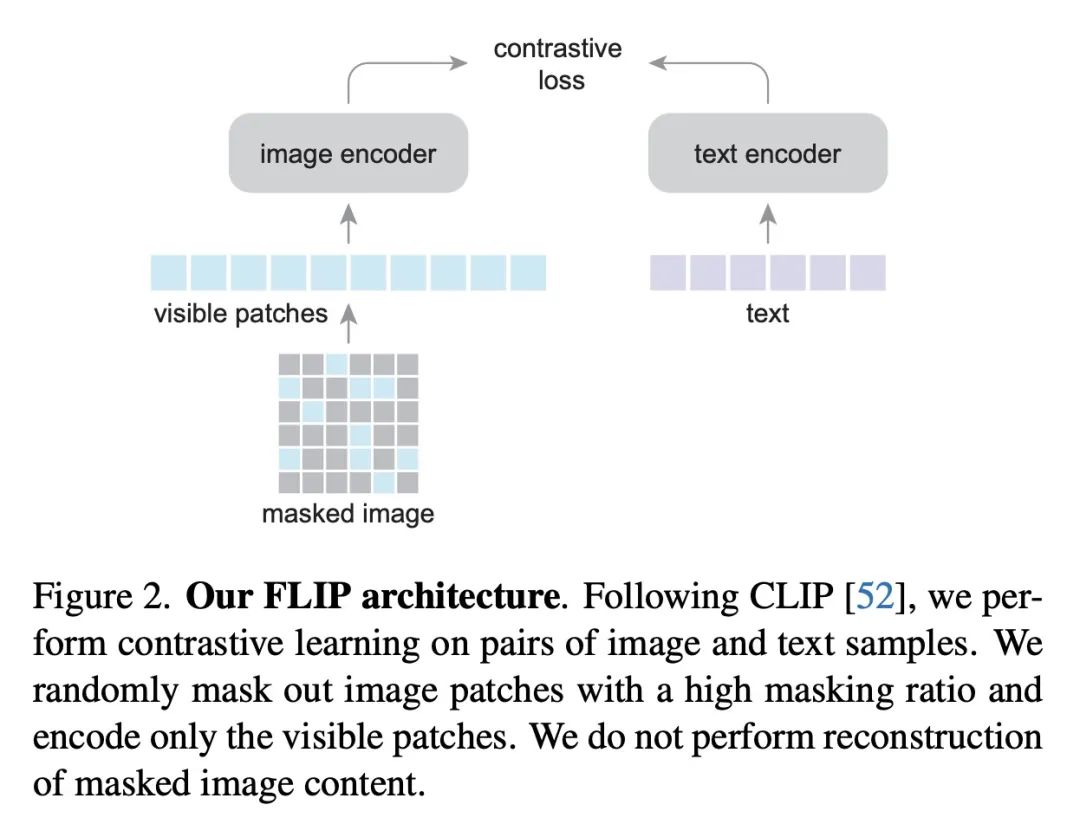
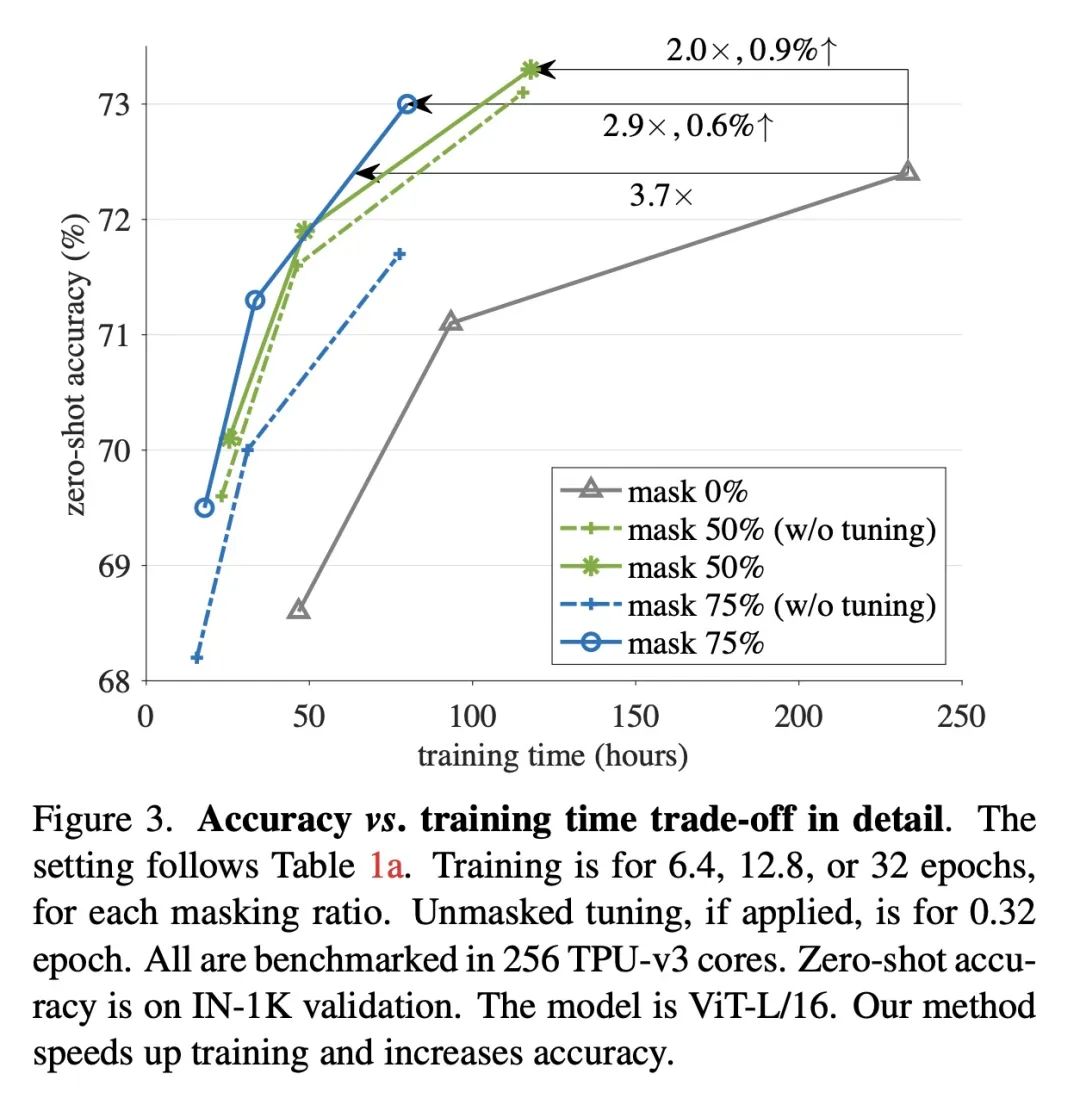
简介:快速语言-图像预训练(FLIP)是训练CLIP(对比语言-图像预训练)模型的一种更高效且有效的方法。训练过程中,FLIP随机掩码并移除一大部分图块,这使得模型在相同的挂壁时间内可以从更多的图像-文本对中学习,且仍然保持相似的内存占用率。FLIP在4亿图像-文本对上进行了测试,发现它在准确性和速度方面都超过了非掩码的基线。本文还提供了当数据大小、模型大小和训练长度增加时模型表现的结果。研究发现,数据扩展是很实用的缩放维度,可以在训练或推理时无需额外成本提高精度。
摘要:本文提出快速语言-图像预训练(FLIP),一种简单且有效的训练CLIP的方法。该方法在训练过程中随机掩码并删除了一大部分的图块。掩码使得能在相同的挂壁时间内从更多的图像-文本对中学习,并且在类似的内存占用下,每次迭代对比更多的样本,带来了准确性和训练时间之间的有利权衡。在对4亿个图像-文本对的实验中,FLIP比非掩码基线提高了精度和速度。在大量的下游任务中,FLIP的表现主要优于在相同数据上训练的CLIP对应模型。在速度提升的推动下,本文探索了增加模型大小、数据大小或训练长度的扩展行为,并报告了令人鼓舞的结果和比较。希望本文工作将促进未来对视觉语言学习的扩展的研究。
We present Fast Language-Image Pre-training (FLIP), a simple and more efficient method for training CLIP. Our method randomly masks out and removes a large portion of image patches during training. Masking allows us to learn from more image-text pairs given the same wall-clock time and contrast more samples per iteration with similar memory footprint. It leads to a favorable trade-off between accuracy and training time. In our experiments on 400 million image-text pairs, FLIP improves both accuracy and speed over the no-masking baseline. On a large diversity of downstream tasks, FLIP dominantly outperforms the CLIP counterparts trained on the same data. Facilitated by the speedup, we explore the scaling behavior of increasing the model size, data size, or training length, and report encouraging results and comparisons. We hope that our work will foster future research on scaling vision-language learning.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.00794
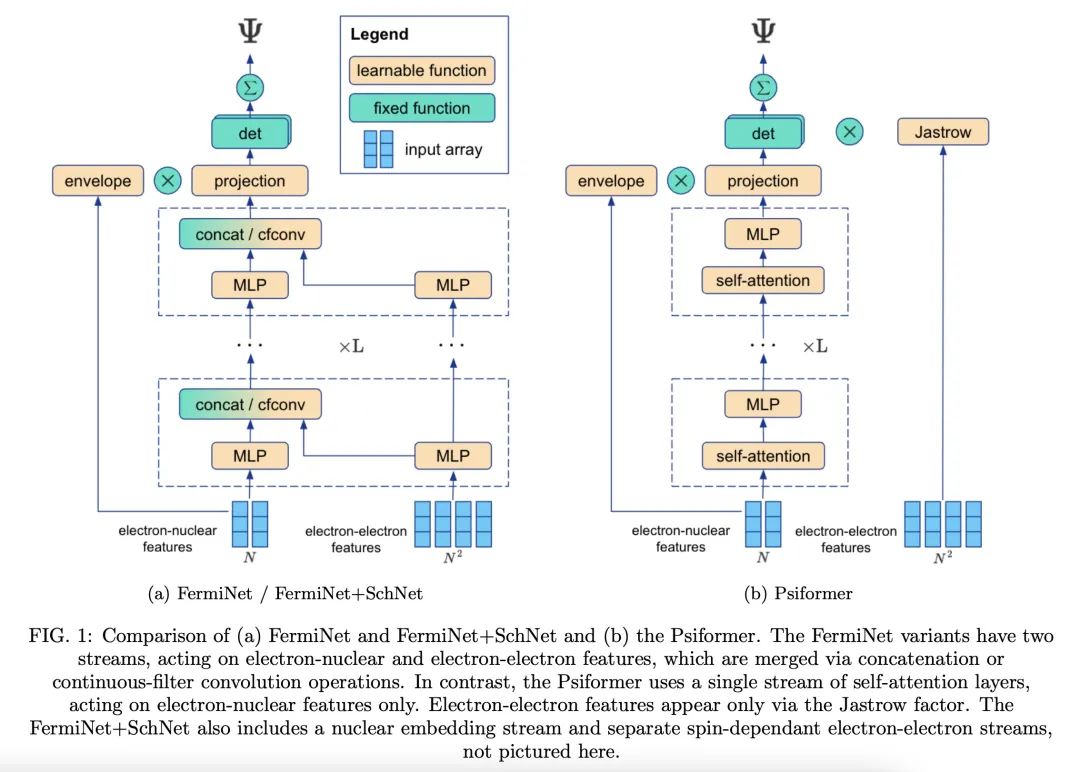
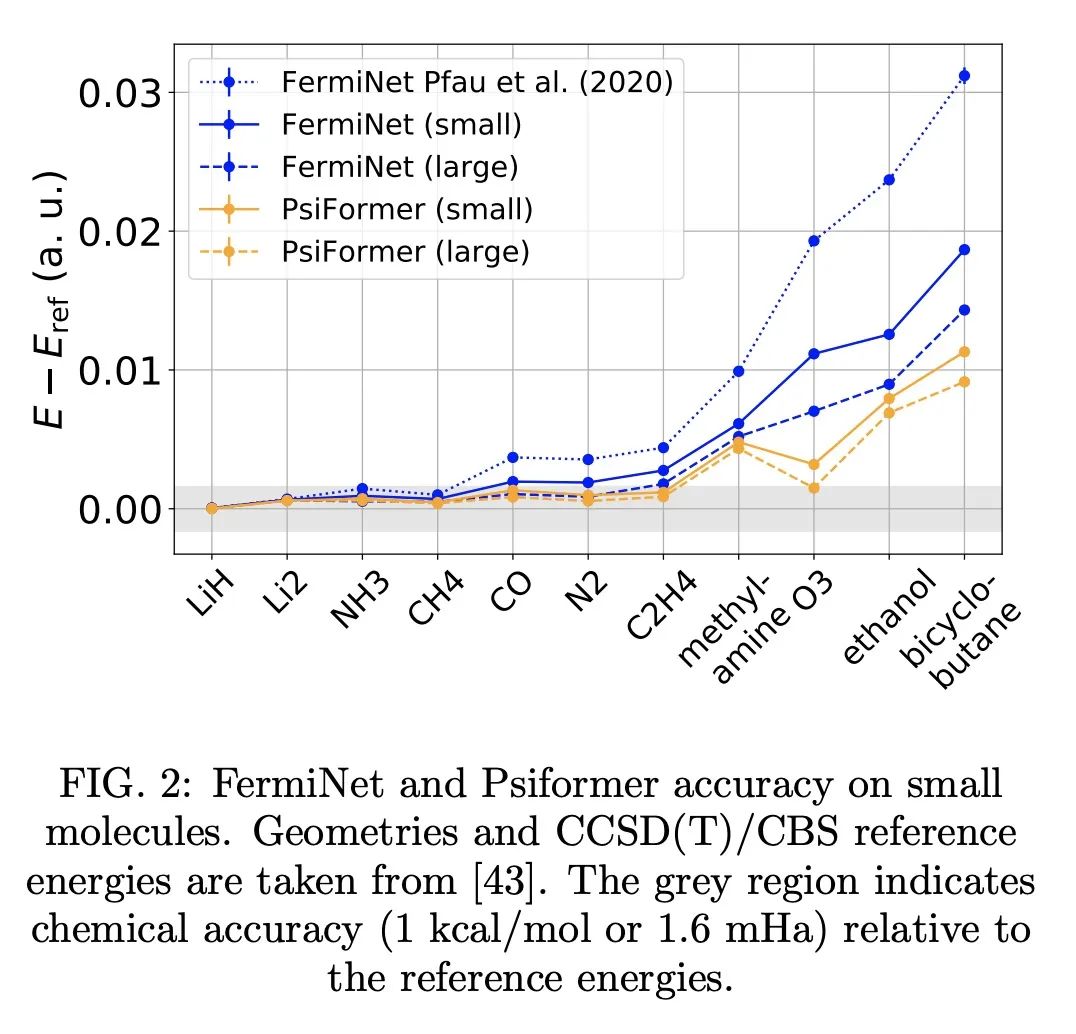
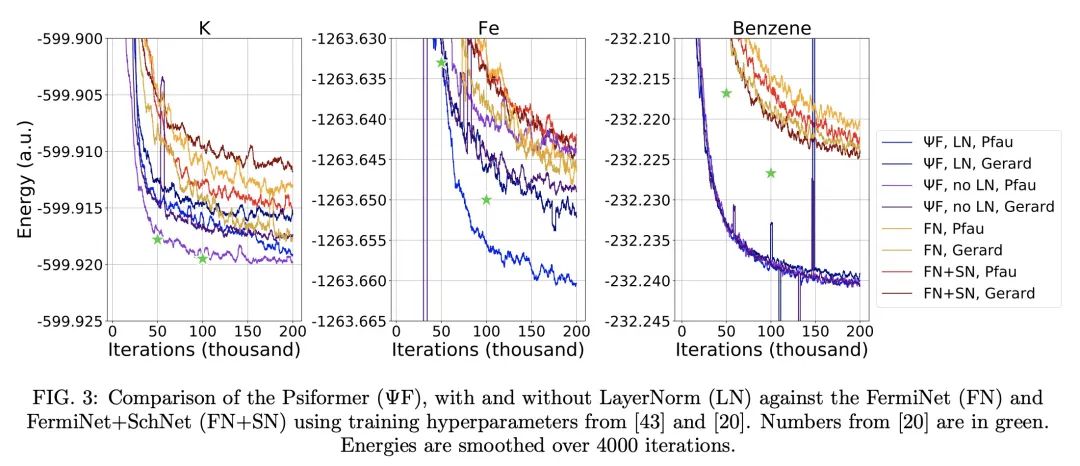
2、[LG] A Self-Attention Ansatz for Ab-initio Quantum Chemistry
I v Glehn, J S. Spencer, D Pfau
[DeepMind]
全始计算量子化学的自注意力拟设
简介:波函数Transformer(Psiformer)是一种新的神经网络结构,使用自注意力,可求解多电子薛定谔方程的近似值(或称拟设(Ansatz)),该方程是量子化学和材料科学的基本方程,可以从第一性原理来求解,而无需外部训练数据。Psiformer可用作其他神经网络的替代品,通常可极大地提高计算的准确性。在较大的分子上,基态能量可以提高几十千卡/摩尔,比之前的方法有很大的改进。这些结果表明,自注意力网络可以学习电子间复杂的量子力学关联,是在更大的系统上达到前所未有的化学计算精度的有希望的途径。全始计算量子化学(Ab-initio quantum chemistry)是量子化学的一个分支,其重点是在没有任何经验输入的情况下从第一性原理计算分子和材料特性。其依赖于用薛定谔方程来描述分子或材料中电子和原子核的行为。全始计算量子化学被用来准确预测诸如能量、力和振动等特性,还被用来研究量子效应,如量子纠缠和叠加,以及理解分子结构和反应性。
摘要:本文提出一种使用自注意力的新的神经网络结构,即波函数Transformer(Psiformer),可用来求解多电子薛定谔方程的近似(或称拟设(Ansatz)),该方程是量子化学和材料科学的基本方程,可以从第一性原理来解决,而无需外部训练数据。近年来,像FermiNet和PauliNet这样的深度神经网络已经被用来显著提高这些第一性原理计算的准确性,但它们缺乏类似于注意力的机制来为电子之间的相互作用把关。本文展示了Psiformer可以作为其他这些神经网络的替代,通常可极大地提高计算的准确性。特别是在大分子上,基态能量可以提高几十千卡/摩尔,比之前的方法有质的飞跃。这表明,自注意力网络可以学习电子之间复杂的量子力学关联,是在更大的系统上达到前所未有的化学计算精度的一条有希望的途径。
We present a novel neural network architecture using self-attention, the Wavefunction Transformer (Psiformer), which can be used as an approximation (or Ansatz) for solving the many-electron Schrödinger equation, the fundamental equation for quantum chemistry and material science. This equation can be solved from first principles, requiring no external training data. In recent years, deep neural networks like the FermiNet and PauliNet have been used to significantly improve the accuracy of these first-principle calculations, but they lack an attention-like mechanism for gating interactions between electrons. Here we show that the Psiformer can be used as a drop-in replacement for these other neural networks, often dramatically improving the accuracy of the calculations. On larger molecules especially, the ground state energy can be improved by dozens of kcal/mol, a qualitative leap over previous methods. This demonstrates that self-attention networks can learn complex quantum mechanical correlations between electrons, and are a promising route to reaching unprecedented accuracy in chemical calculations on larger systems.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.13672

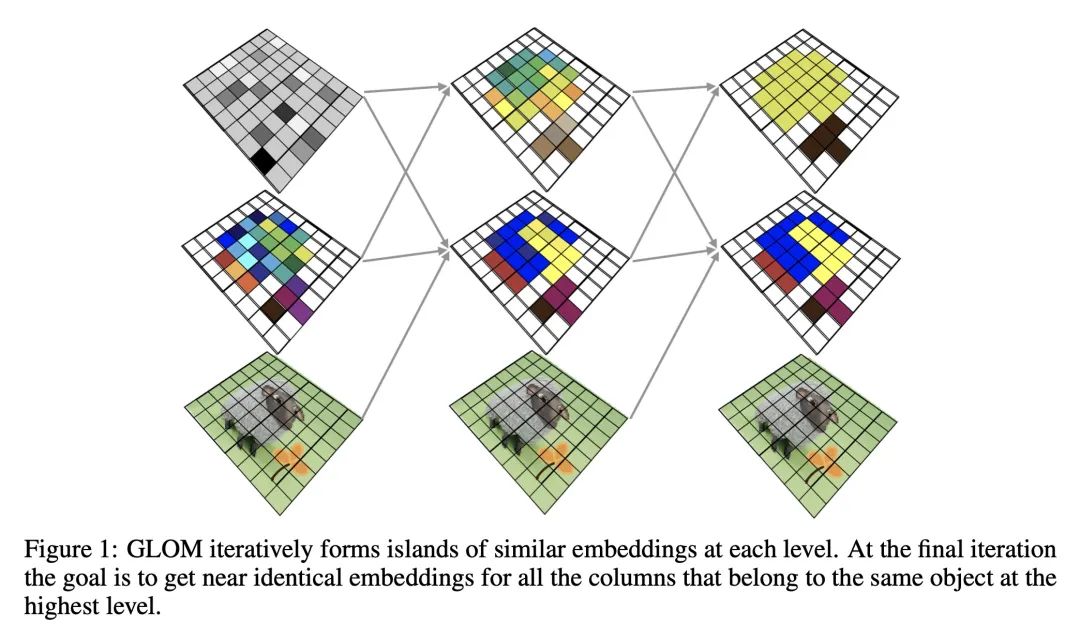
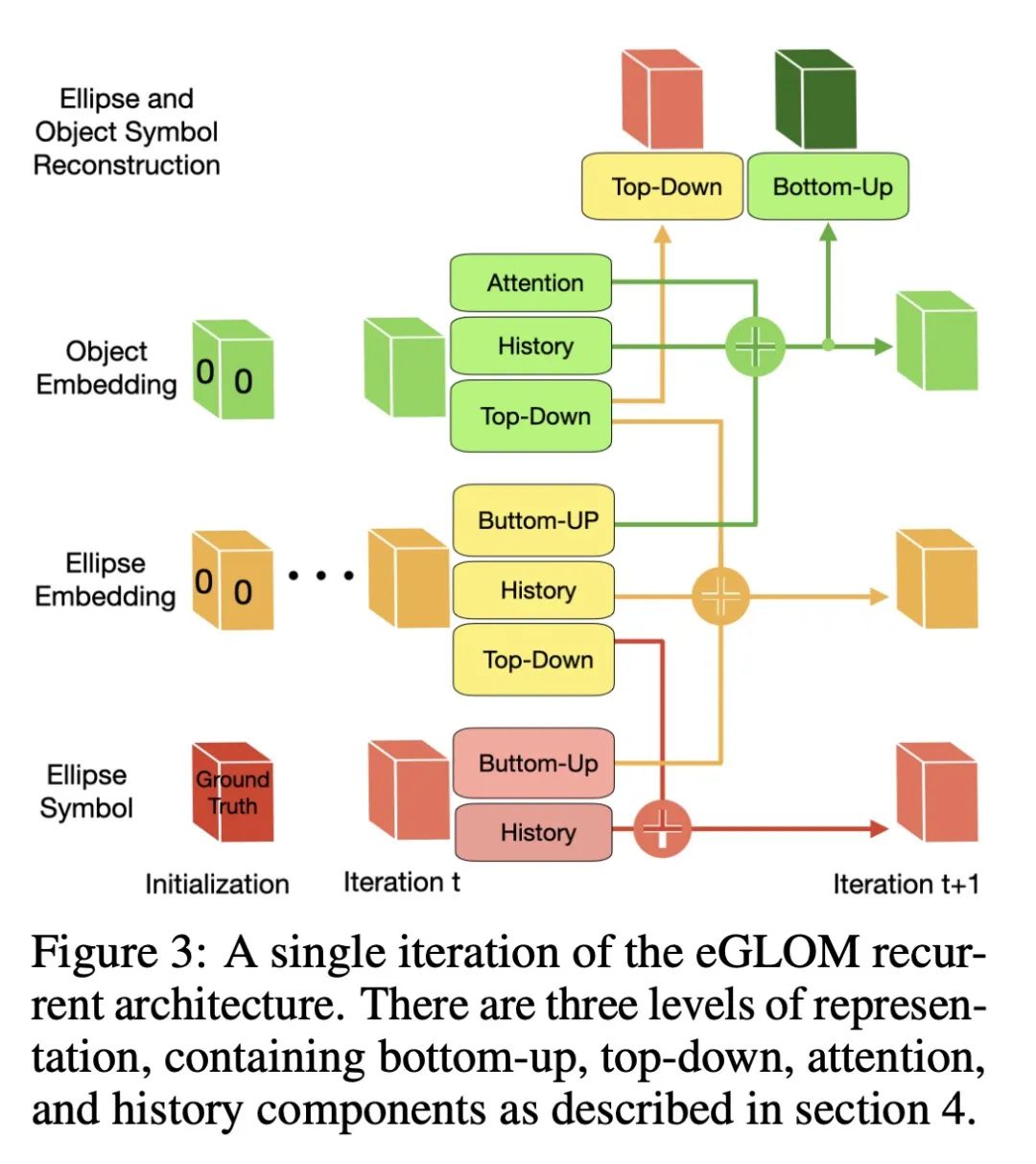
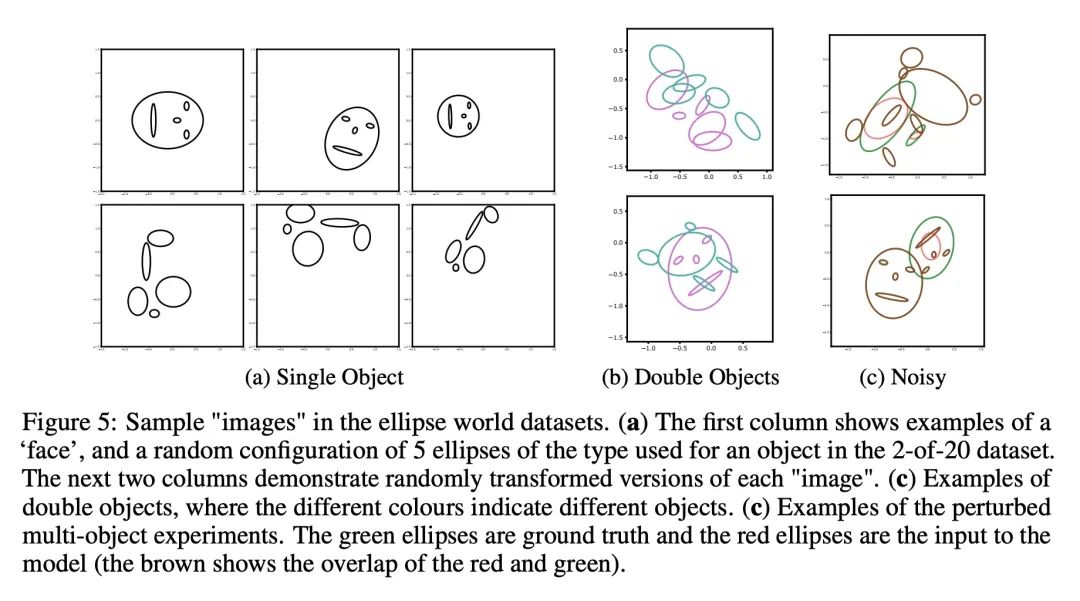
3、[CV] Testing GLOM's ability to infer wholes from ambiguous parts
L Culp, S Sabour, G E. Hinton
[Google AI]
GLOM从模糊部分推断整体能力测试
简介:Hinton提出的GLOM架构[2021]是一个递归神经网络,能将图像解析为整体和部分的层次结构,能通过允许部件对其所属整体的姿态和身份进行多模态预测来解决模糊性,利用对来自其他可能模糊的部件的类似预测的关注来确定一个共同模式。本文描述了一个高度简化的GLOM版本,使得能评估其有效性。通过监督训练,GLOM能成功地对同一物体所占据的所有位置形成非常相似的嵌入向量的岛屿,并且还发现它对输入中的强噪声注入和分布外的输入变换具有鲁棒性。
摘要:Hinton提出的GLOM架构[2021]是一个递归神经网络,用于将图像解析为整体和部分的层次结构。当一个部分是模糊的,GLOM假设模糊性可以通过允许该部分对其所属整体的姿态和身份进行多模态预测来解决,然后利用对来自其他可能模糊的部分的类似预测的关注来确定由几个不同部分预测的共同模式。本文描述了一个高度简化的GLOM版本,使得能评估这种处理模糊性的方式的有效性。结果表明,在有监督的训练下,GLOM能够成功地对同一物体所占据的所有位置形成非常相似的嵌入向量的岛屿,而且它对输入中的强噪声注入和分布外的输入变换也很稳健。
The GLOM architecture proposed by Hinton [2021] is a recurrent neural network for parsing an image into a hierarchy of wholes and parts. When a part is ambiguous, GLOM assumes that the ambiguity can be resolved by allowing the part to make multi-modal predictions for the pose and identity of the whole to which it belongs and then using attention to similar predictions coming from other possibly ambiguous parts to settle on a common mode that is predicted by several different parts. In this study, we describe a highly simplified version of GLOM that allows us to assess the effectiveness of this way of dealing with ambiguity. Our results show that, with supervised training, GLOM is able to successfully form islands of very similar embedding vectors for all of the locations occupied by the same object and it is also robust to strong noise injections in the input and to out-of-distribution input transformations.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16564

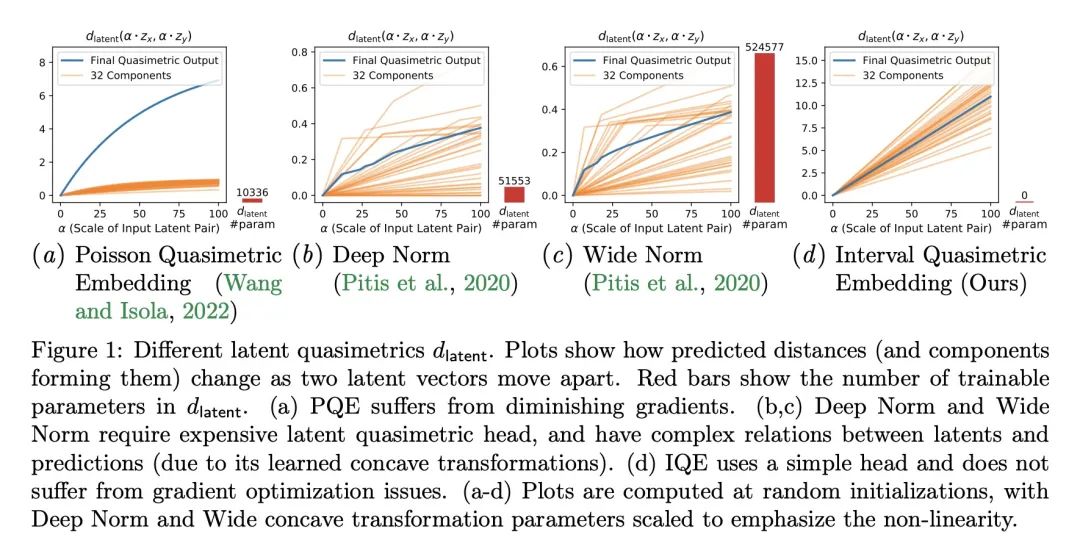
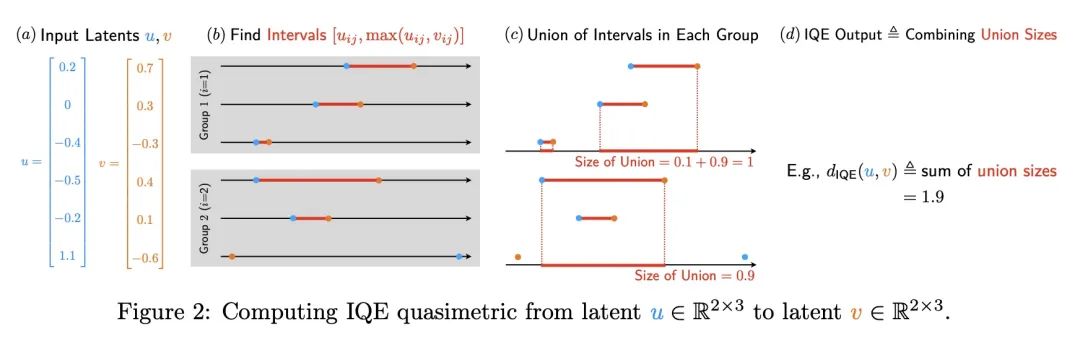
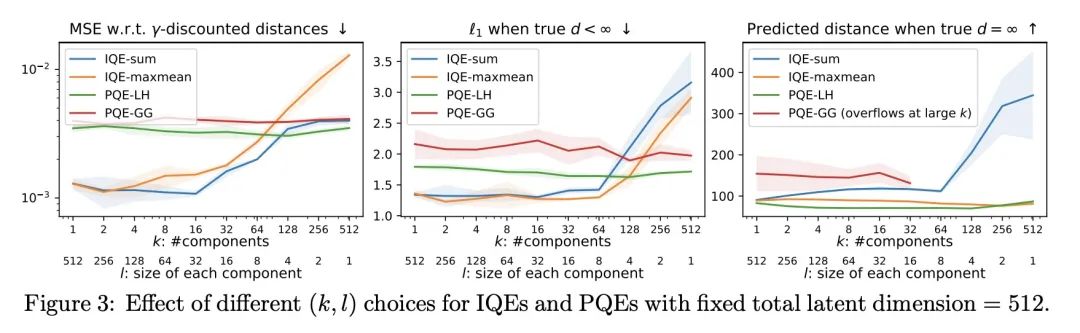
4、[LG] Improved Representation of Asymmetrical Distances with Interval Quasimetric Embeddings
T Wang, P Isola
[MIT CSAIL]
用区间非对称距离结构嵌入改进不对称距离表示方法
简介:非对称距离结构对机器学习的应用是有益的,如强化学习和因果关系学习。本文提出了区间非对称距离结构嵌入(IQE)作为满足非对称距离结构表示四项标准的模型。IQE被证明具有很强的逼近和泛化能力,与之前的方法相比,性能和效率得到了提高。
摘要:非对称距离结构(quasimetrics)在日常无处不在,在机器学习应用中也越来越受到关注。在模型表示中强加这种非对称距离结构已被证明可以改善许多任务,包括强化学习(RL)和因果关系学习。本文提出这种非对称距离结构模型的四个理想属性,并展示了之前的工作如何在这些方面失败。本文提出区间非对称距离结构嵌入(IQE),其目的是为了满足所有四项标准。在三个非对称距离结构学习实验中,IQE表现出很强的逼近和泛化能力,与之前的方法相比,带来了更好的性能和效率的提高。
Asymmetrical distance structures (quasimetrics) are ubiquitous in our lives and are gaining more attention in machine learning applications. Imposing such quasimetric structures in model representations has been shown to improve many tasks, including reinforcement learning (RL) and causal relation learning. In this work, we present four desirable properties in such quasimetric models, and show how prior works fail at them. We propose Interval Quasimetric Embedding (IQE), which is designed to satisfy all four criteria. On three quasimetric learning experiments, IQEs show strong approximation and generalization abilities, leading to better performance and improved efficiency over prior methods.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.15120

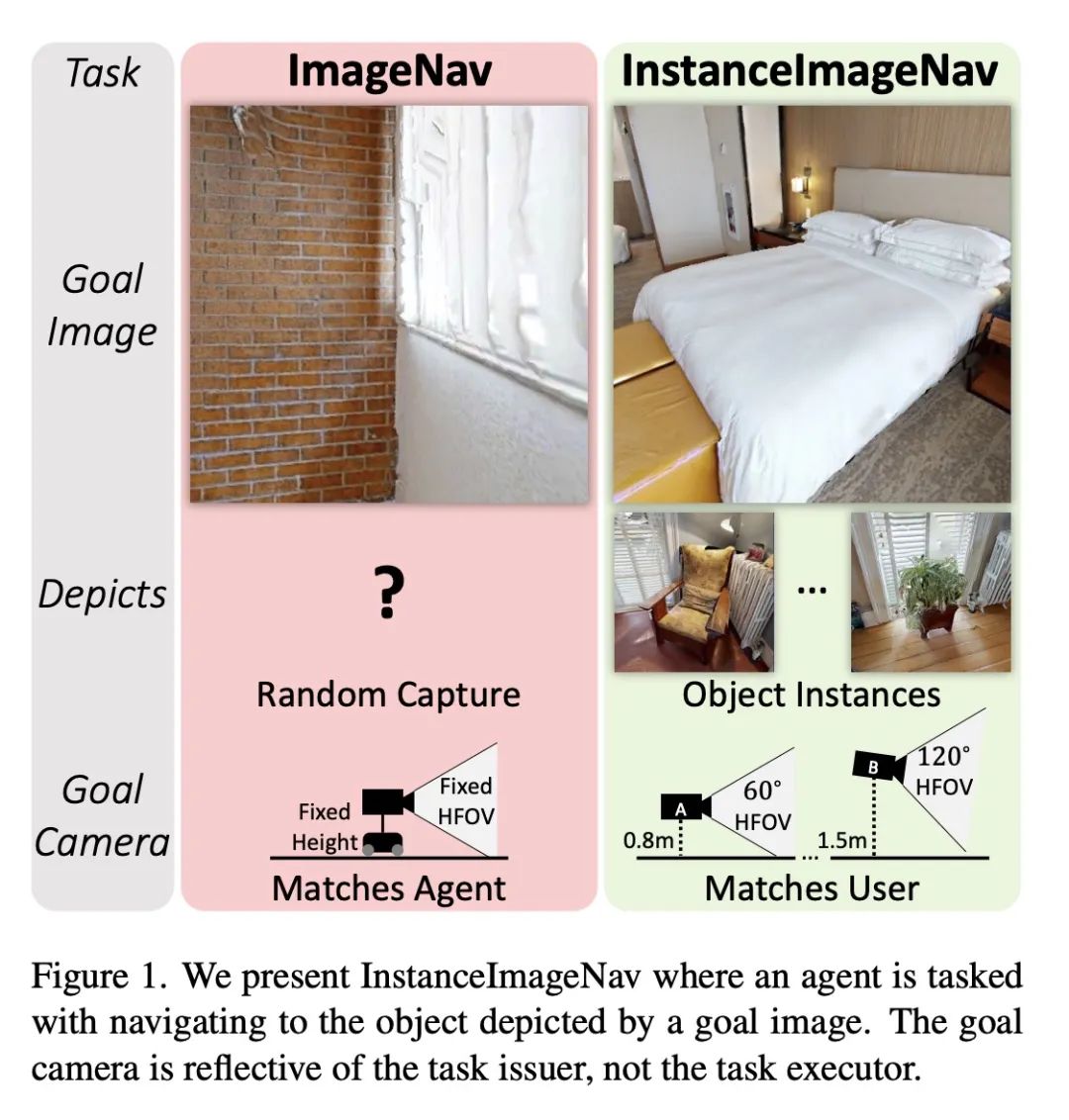
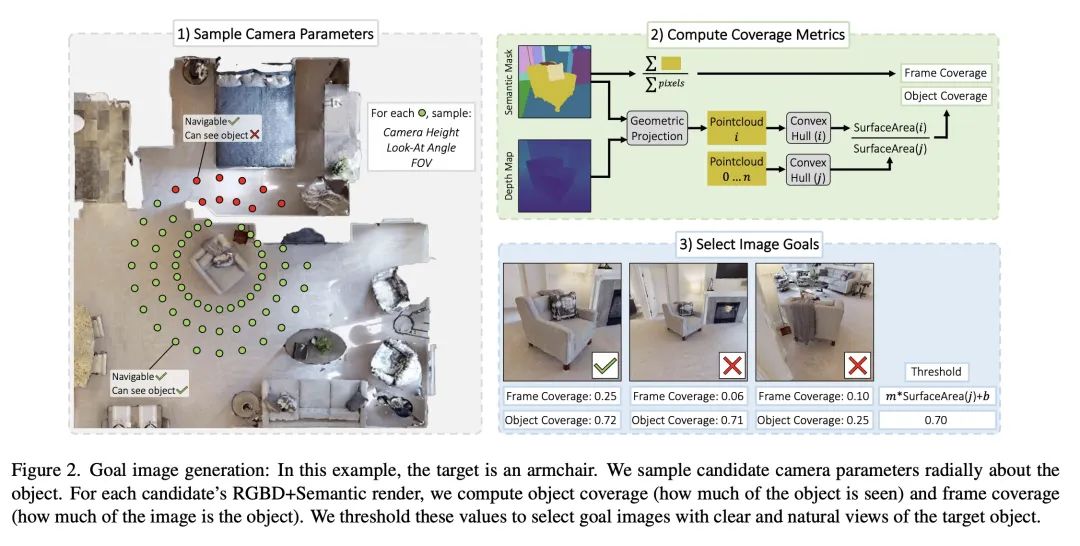
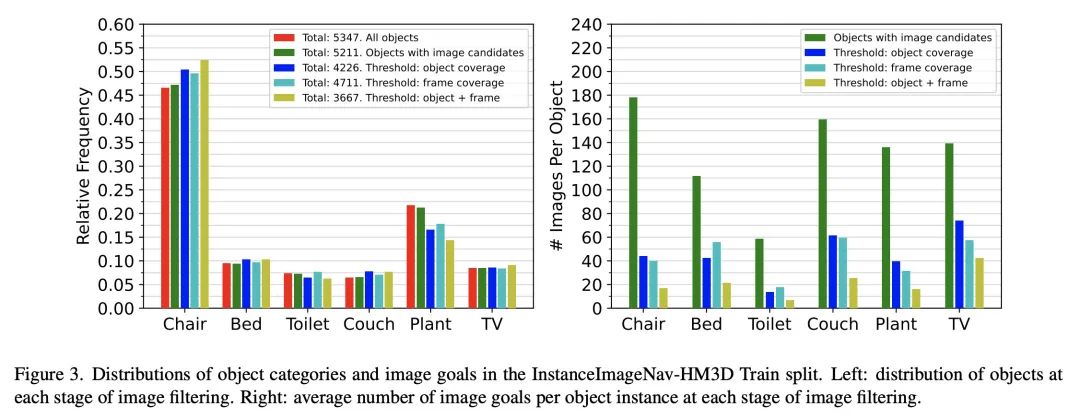
5、[CV] Instance-Specific Image Goal Navigation: Training Embodied Agents to Find Object Instances
J Krantz, S Lee, J Malik, D Batra, D S Chaplot
[Meta AI & Oregon State University]
特定实例图像目标导航:具身智能体寻找目标实例训练
简介:本文提出一个名为InstanceImageNav的新基准,以解决现有导航任务的一些限制。该基准要求图像目标"聚焦"于环境中的一个目标实例,并使用独立于智能体的相机参数进行拍摄。该基准在Habitat模拟器中被实例化,其场景来自于Habitat-Matterport三维数据集,提供了一个标准化的方法来衡量社区在具身视觉导航领域的进展。
摘要:本文考虑给定图像目标的具身视觉导航(ImageNav)问题,在这个问题上,智能体在一个不熟悉的环境中被初始化,任务是导航到一个由图像"描述"的位置。与相关的导航任务不同,ImageNav没有一个标准化的任务定义,这使得不同的方法难以比较。此外,现有的表述有两个问题:(1) 图像目标是从随机位置取样的,这可能会导致模糊性(例如,看墙),以及 (2) 图像目标与相机规格和智能体的具身相匹配;在考虑用户驱动的下游应用时,这种僵化是有限的。本文提出针对具体实例的图像导航任务(InstanceImageNav)来解决这些限制。具体来说,目标图像被"聚焦"在场景中的某些特定目标实例上,并且是用独立于智能体的相机参数拍摄的。使用Habitat-Matterport3D数据集(HM3D)中的场景在Habitat模拟器中实例化InstanceImageNav,并发布了一个标准化的基准来衡量社区的进展。
We consider the problem of embodied visual navigation given an image-goal (ImageNav) where an agent is initialized in an unfamiliar environment and tasked with navigating to a location 'described' by an image. Unlike related navigation tasks, ImageNav does not have a standardized task definition which makes comparison across methods difficult. Further, existing formulations have two problematic properties; (1) image-goals are sampled from random locations which can lead to ambiguity (e.g., looking at walls), and (2) image-goals match the camera specification and embodiment of the agent; this rigidity is limiting when considering user-driven downstream applications. We present the Instance-specific ImageNav task (InstanceImageNav) to address these limitations. Specifically, the goal image is 'focused' on some particular object instance in the scene and is taken with camera parameters independent of the agent. We instantiate InstanceImageNav in the Habitat Simulator using scenes from the Habitat-Matterport3D dataset (HM3D) and release a standardized benchmark to measure community progress.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.15876

另外几篇值得关注的论文:
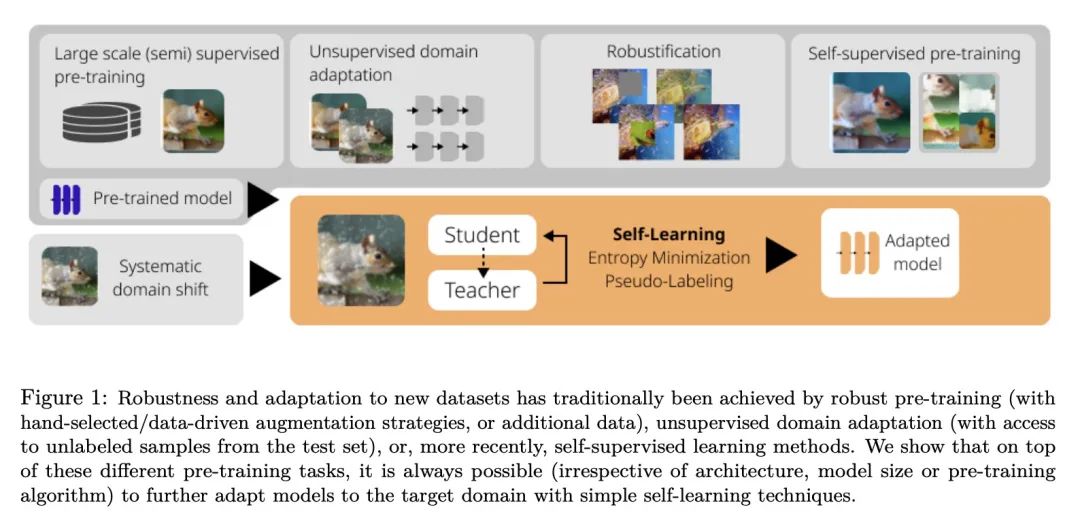
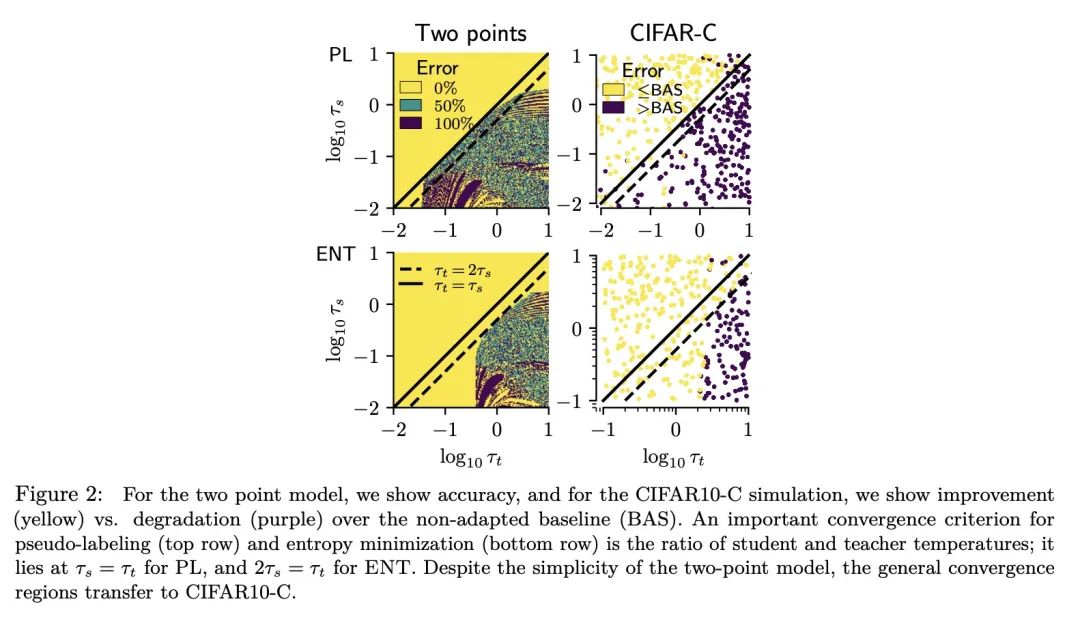
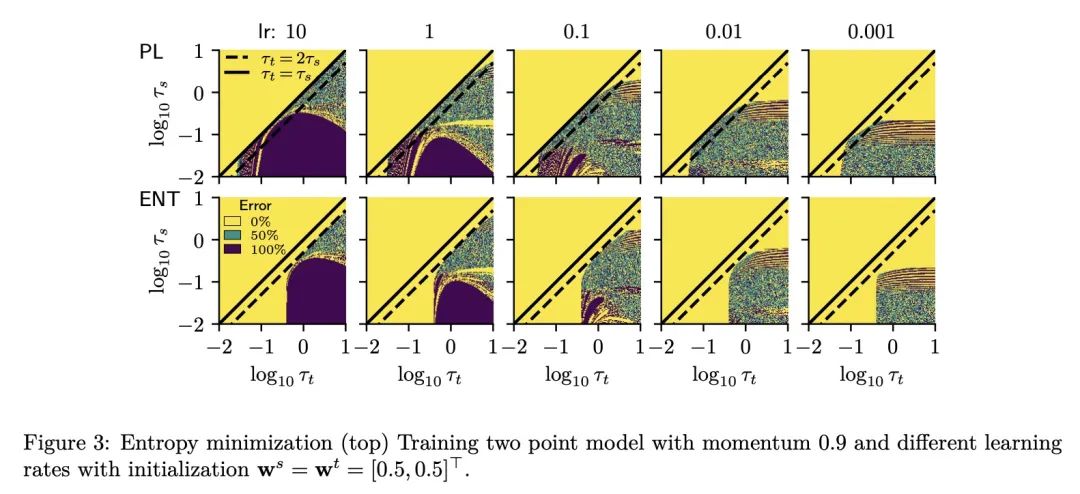
[CV] If your data distribution shifts, use self-learning
E Rusak, S Schneider, G Pachitariu, L Eck, P Gehler, O Bringmann, W Brendel, M Bethge
[University of Tübingen & University of Oxford]
面向数据分布漂移的自学习
简介:像熵最小化和伪标签这样的自学习技术,当存在数据的系统性域漂移时,可简单有效地提高计算机视觉模型性能,且很容易实现,对超参数的选择具有鲁棒性,只需要很少的自适应训练轮次。
https://arxiv.org/abs/2104.12928

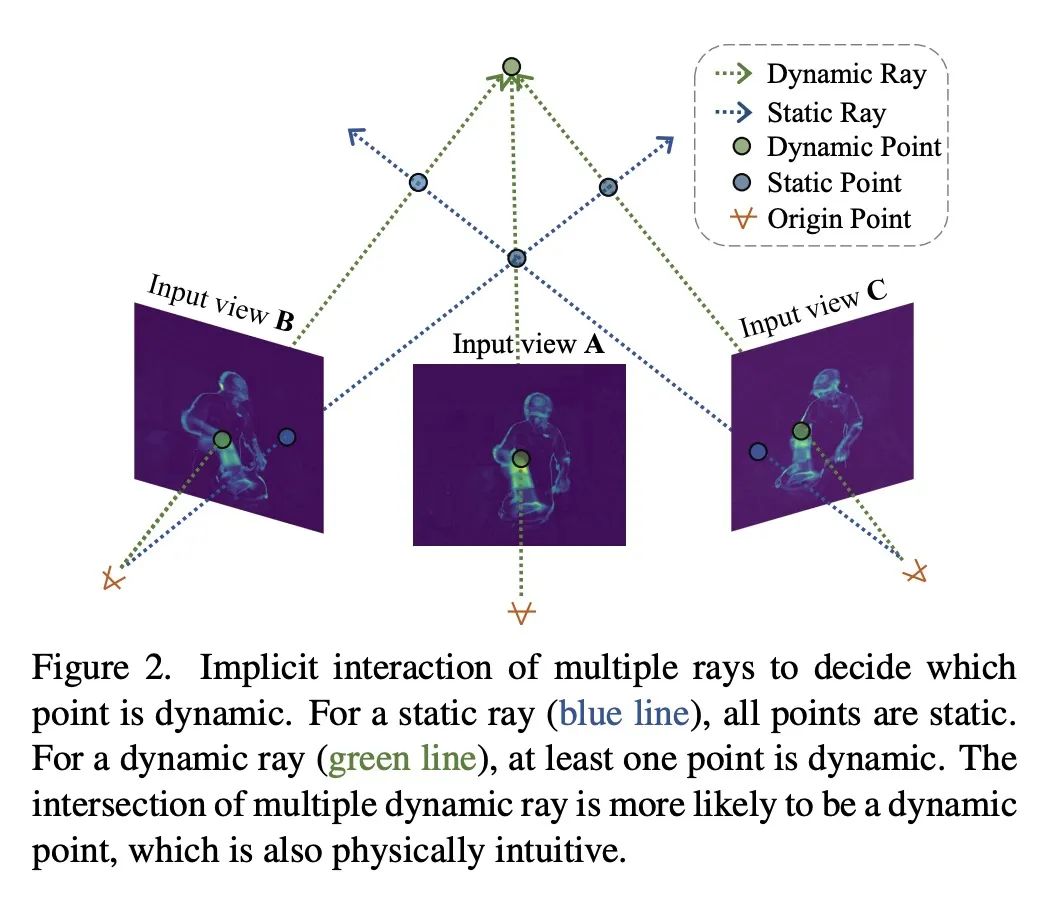
[CV] Mixed Neural Voxels for Fast Multi-view Video Synthesis
F Wang, S Tan, X Li, Z Tian, H Liu
[Tsinghua University & Hong Kong University of Science and Technology]
用于快速多视角视频合成的混合神经体素
简介:MixVoxels是一种有效重建4D动态场景和合成新视角视频的新方法,能用15分钟训练做到这一点,使动态场景渲染更加实用。该方法将3D空间分割成静态和动态部分,然后分别处理以提高性能,还用像素级的时间变化来估计体素级的变化,这是所提出的变化场的基础。
https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.00190


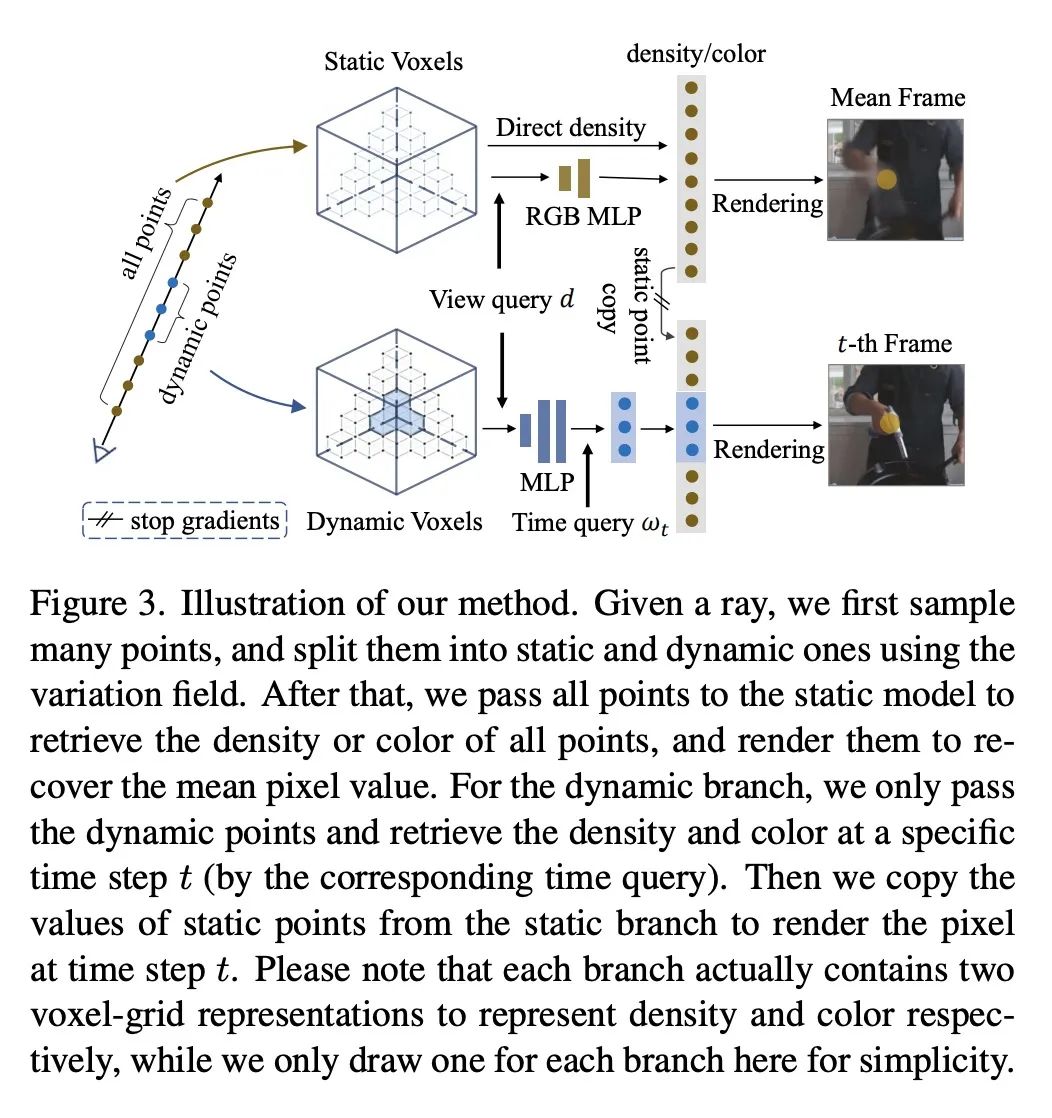
[CV] Zero-Shot Image Restoration Using Denoising Diffusion Null-Space Model
Y Wang, J Yu, J Zhang
[Peking University]
基于去噪扩散空白空间模型的零样本图像修复
简介:去噪扩散空洞空间模型(DDNM)是一种新的零样本框架,适用于任意的线性图像修复(IR)问题。该框架只需要一个预训练好的现成的扩散模型作为生成先验,不需要任何额外的训练或网络修改。通过DDNM+模型进一步增强,可以解决复杂的实际应用,包括图像超分辨率、着色、绘画、压缩感知和去模糊等。
https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.00490


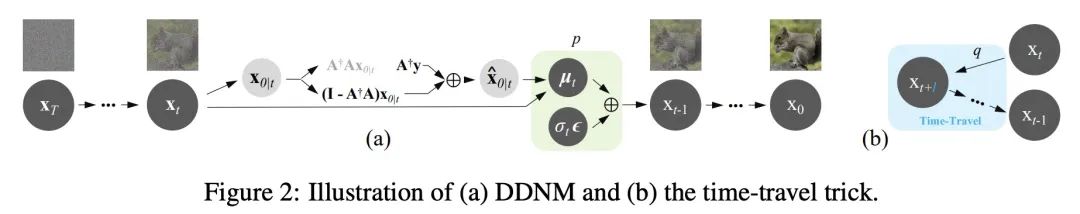

[LG] Linear Causal Disentanglement via Interventions
A Seigal, C Squires, C Uhler
[Broad Institute of MIT and Harvard]
基于干预的线性因果解缠
简介:因果解缠是寻找数据表示的过程,该表示涉及通过因果模型相互关联的潜变量。如果潜模型和从潜变量到观察变量的转换都是唯一的,那么该表述就是可识别的。本文研究了作为线性潜因果模型的线性转换的观察变量,如果一个潜变量缺少干预,就存在无法区分的不同模型。论文还指出,对每个潜变量进行一次干预就足以实现可识别性。本文提出一种能够准确恢复潜因果模型的因果分解方法,这一点得到了理论结果的证实。
https://arxiv.org/abs/2211.16467

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢