来自爱可可AI前沿推介
1、[LG] Compute-Efficient Deep Learning: Algorithmic Trends and Opportunities
B R. Bartoldson, B Kailkhura, D Blalock
[Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory & MosaicML]
计算高效深度学习:算法趋势与机遇
简介:全面概述了算法高效的深度学习,旨在降低训练成本,提出一种分类方法,对 200 多种深度学习加速方法进行了分类,探讨了算法效率评估的最佳实践,强调了该领域尚未解决的研究挑战。
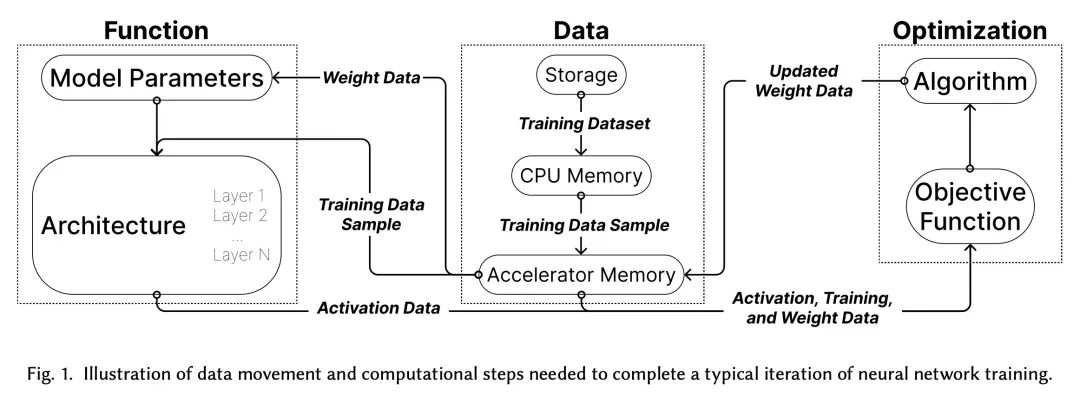
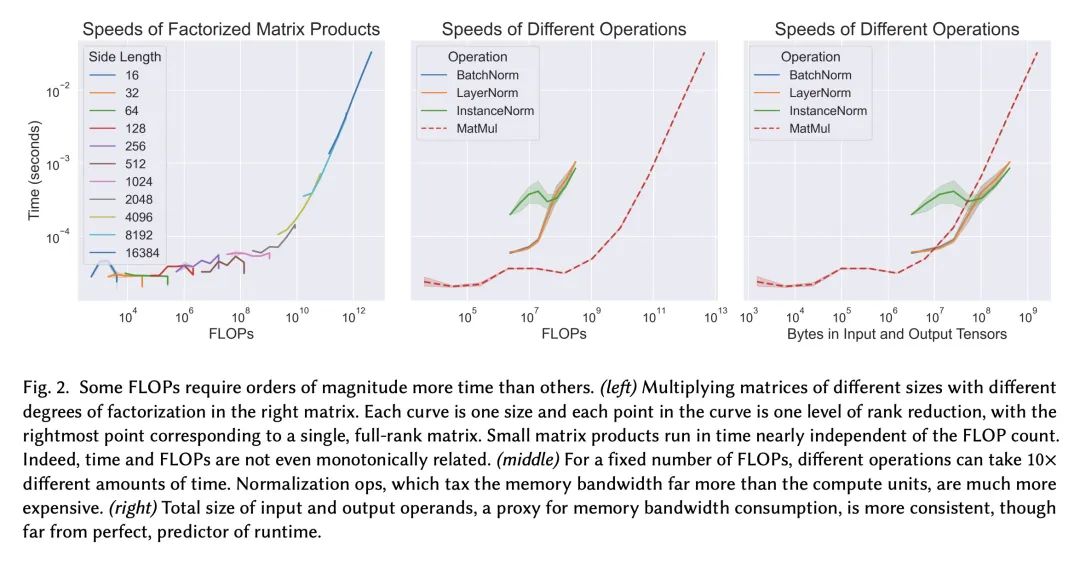
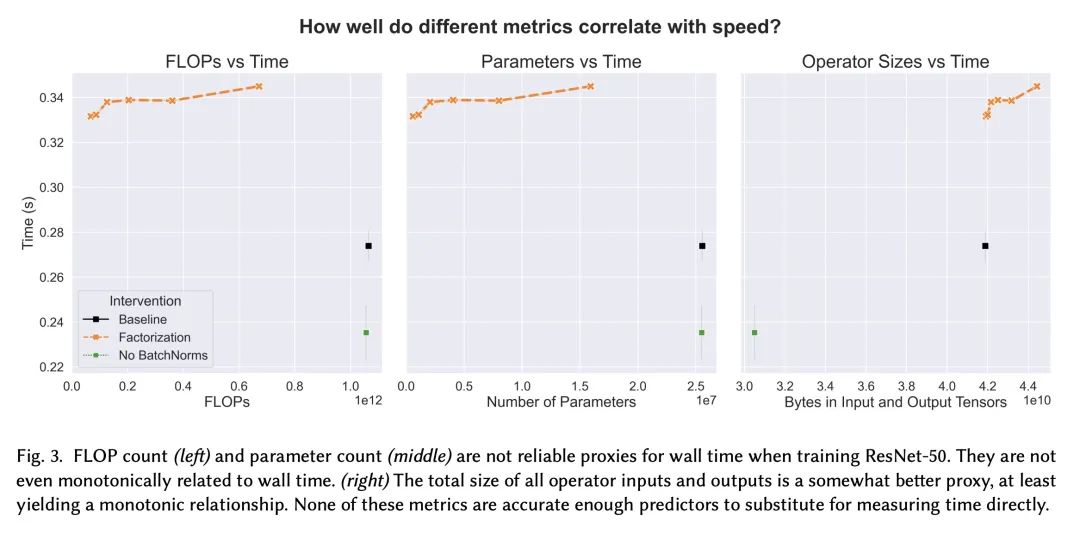
摘要:尽管深度学习近年来取得了长足进步,但训练神经网络的爆炸性经济与环境成本正变得难以为继。为了解决这个问题,本文对*算法高效深度学习* 进行了大量研究,旨在通过改变训练程序的语义来降低训练成本,而不是在硬件或实现层面。在本文中,我们对该领域的研究进行了结构化和全面的概述。首先,将*算法加速*问题形式化,然后我们使用算法高效训练的基本构建块来开发分类法。所述分类突出了看似不同方法的共性,并揭示了当前的研究差距。接下来,本文展示了评估最佳实践,以实现对加速技术的全面、公平和可靠的比较。为了进一步帮助研究和应用,讨论了训练管道中的常见瓶颈(通过实验说明)并为它们提供了分类缓解策略。最后,强调了一些尚未解决的研究挑战,并提出了有希望的未来方向。
https://arxiv.org/abs/2210.06640
Although deep learning has made great progress in recent years, the exploding economic and environmental costs of training neural networks are becoming unsustainable. To address this problem, there has been a great deal of research on *algorithmically-efficient deep learning*, which seeks to reduce training costs not at the hardware or implementation level, but through changes in the semantics of the training program. In this paper, we present a structured and comprehensive overview of the research in this field. First, we formalize the *algorithmic speedup* problem, then we use fundamental building blocks of algorithmically efficient training to develop a taxonomy. Our taxonomy highlights commonalities of seemingly disparate methods and reveals current research gaps. Next, we present evaluation best practices to enable comprehensive, fair, and reliable comparisons of speedup techniques. To further aid research and applications, we discuss common bottlenecks in the training pipeline (illustrated via experiments) and offer taxonomic mitigation strategies for them. Finally, we highlight some unsolved research challenges and present promising future directions.


内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢