来自今天的爱可可AI前沿推介
[CV] LADIS: Language Disentanglement for 3D Shape Editing
I Huang, P Achlioptas, T Zhang, S Tulyakov, M Sung, L Guibas
[Stanford University & Snap Research & KAIST]
LADIS: 面向3D形状编辑的语言解缠
要点:
-
提出了一套互补工具集,包括新的网络架构、解缠损失和新的编辑程序; -
定义了一个新的指标,部分编辑精度,来衡量编辑局部性。
摘要:
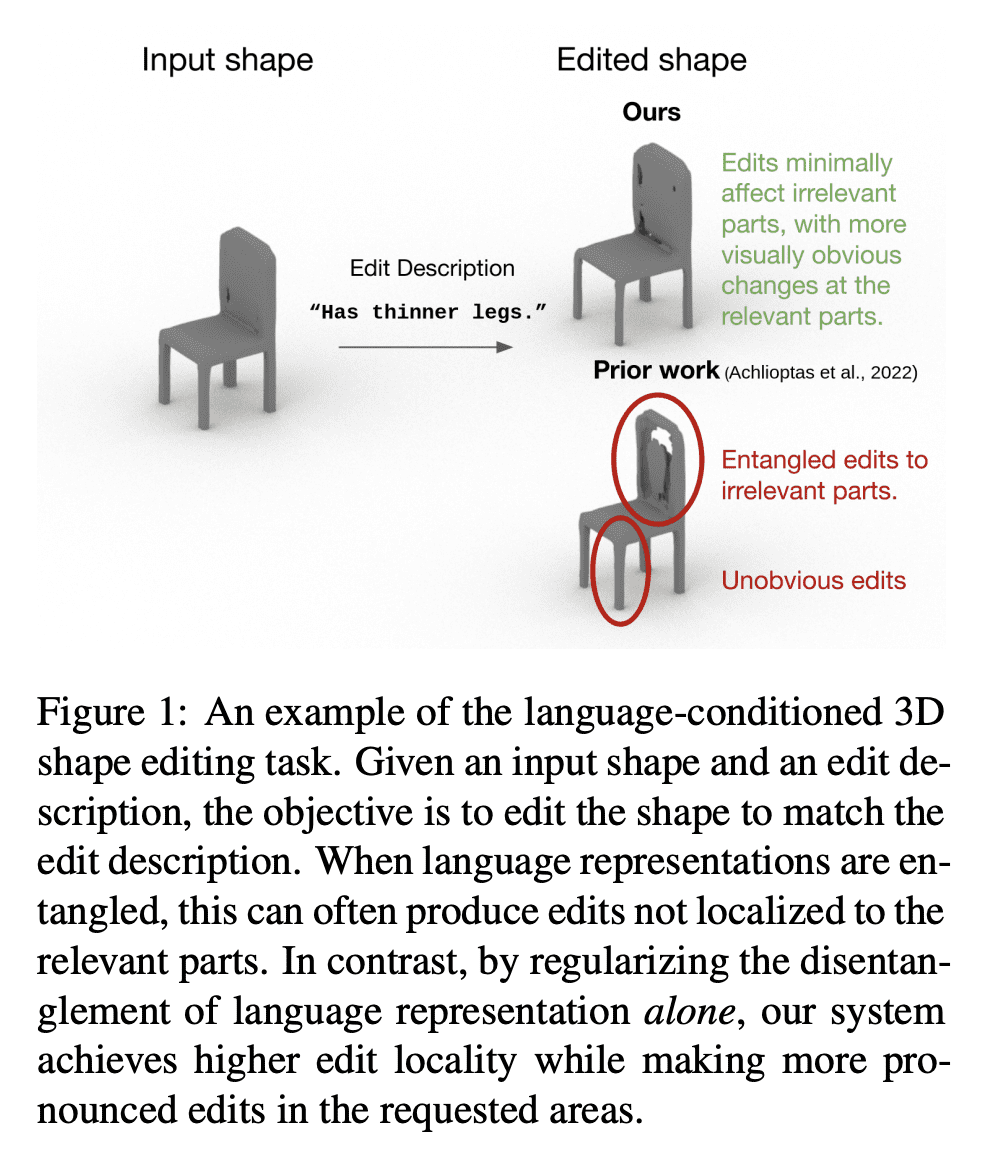
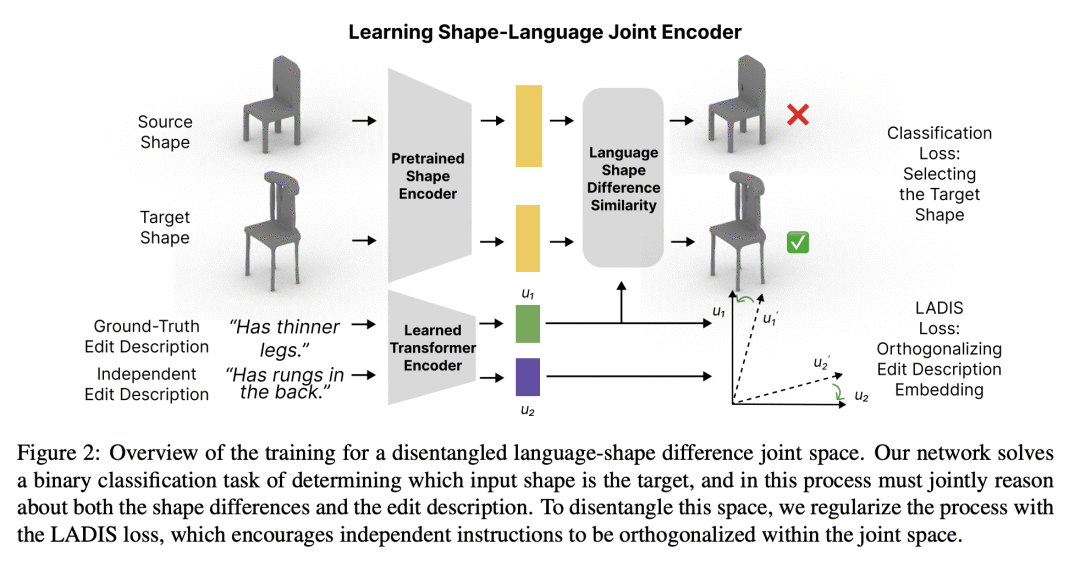
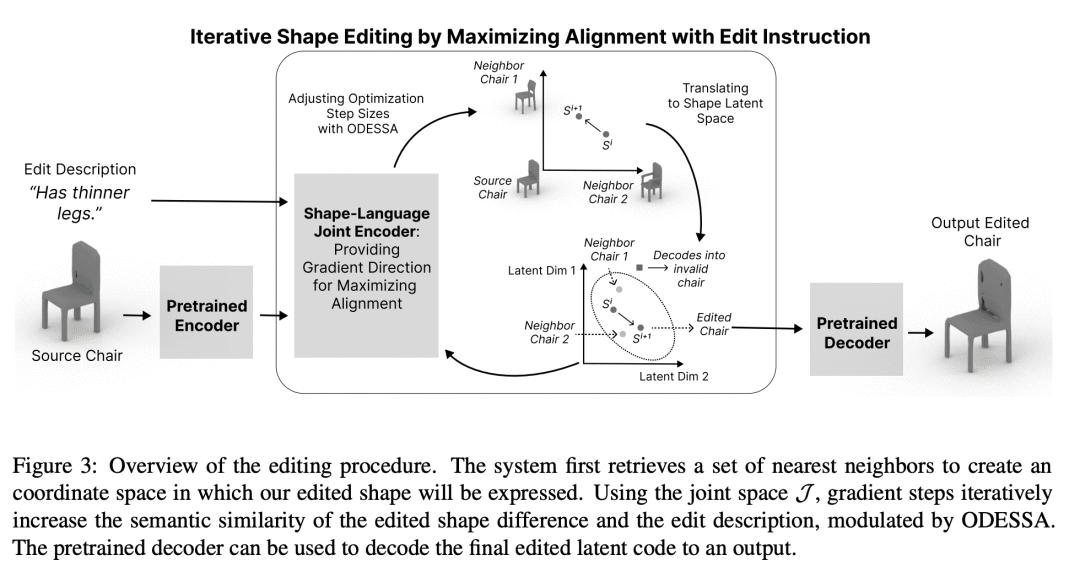
自然语言交互是3D形状设计大众化的一个有希望的方向。然而,现有的文本驱动的3D形状编辑方法在对3D形状进行解耦、局部编辑时面临挑战。本文通过学习解缠的潜在表征来解决这个问题,这些表征将语言置于3D几何中。提出一个互补的工具集,包括一个新的网络结构、一个解缠损失和一个新的编辑程序。此外,为了衡量编辑的局部性,定义了一种新的指标,称为部分编辑精度。所提出方法在编辑定位方面优于现有的SOTA方法20%,而在语言参考解决精度方面优于6.6%。通过单纯地拆分语言表征,下游的3D形状编辑可以变得对相关部分更加局部化,即使该模型从未被给予明确的基于部分的监督。
Natural language interaction is a promising direction for democratizing 3D shape design. However, existing methods for text-driven 3D shape editing face challenges in producing decoupled, local edits to 3D shapes. We address this problem by learning disentangled latent representations that ground language in 3D geometry. To this end, we propose a complementary tool set including a novel network architecture, a disentanglement loss, and a new editing procedure. Additionally, to measure edit locality, we define a new metric that we call part-wise edit precision. We show that our method outperforms existing SOTA methods by 20% in terms of edit locality, and up to 6.6% in terms of language reference resolution accuracy. Our work suggests that by solely disentangling language representations, downstream 3D shape editing can become more local to relevant parts, even if the model was never given explicit part-based supervision.
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.05011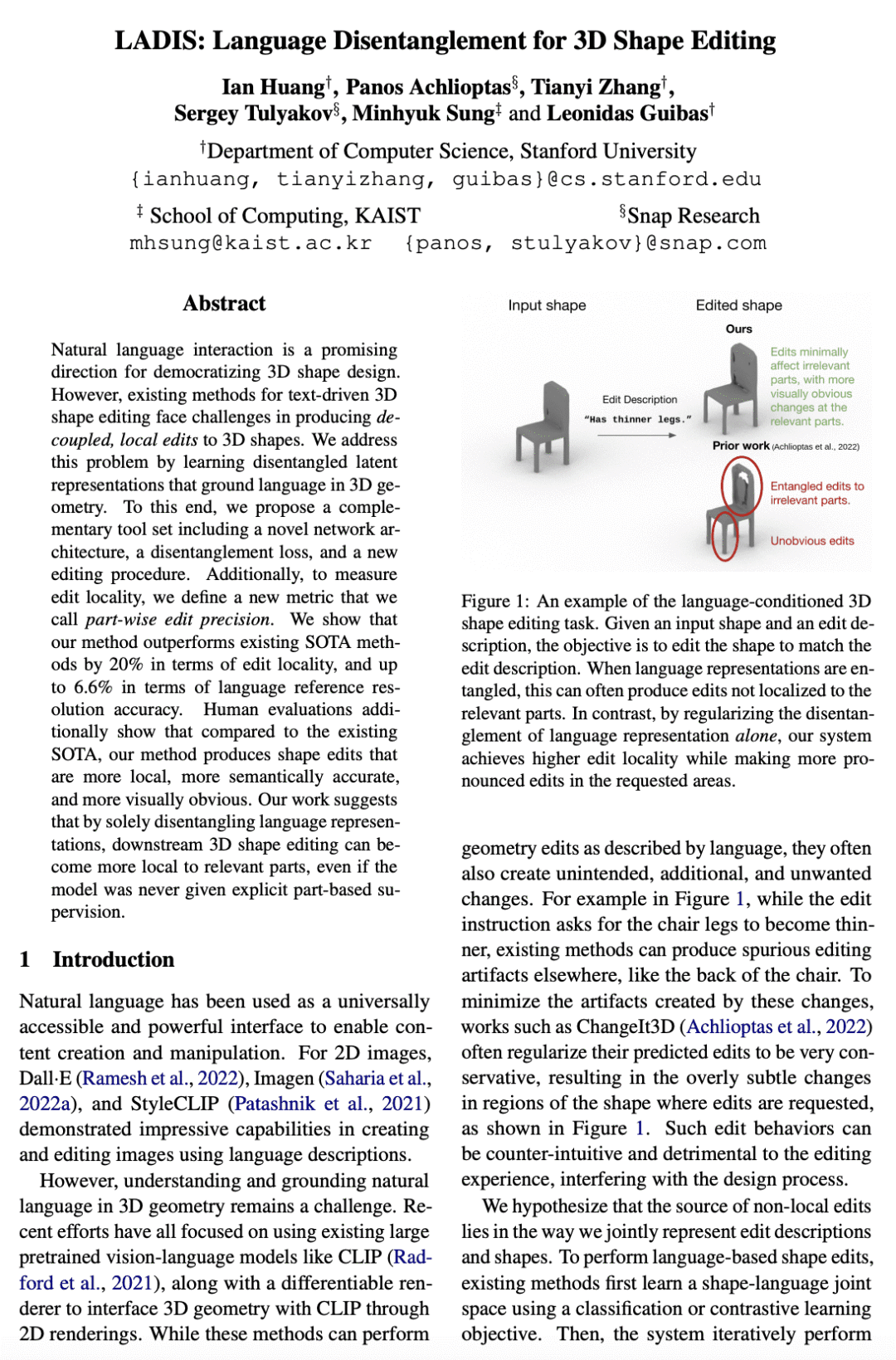
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢