来自今天的爱可可AI前沿推介
[CL] Why Can GPT Learn In-Context? Language Models Secretly Perform Gradient Descent as Meta-Optimizers
D Dai, Y Sun, L Dong, Y Hao, Z Sui, F Wei
[Microsoft Research & Peking University & Tsinghua University]
为什么 GPT 可以在上下文中学习? 语言模型作为元优化器秘密执行梯度下降
要点:
-
找出了Transformer注意力和基于梯度下降优化之间的双重形式,并将语言模型解释为元优化器; -
在上下文学习(ICL)和显式微调之间建立联系,提出将ICL理解为一种隐式微调; -
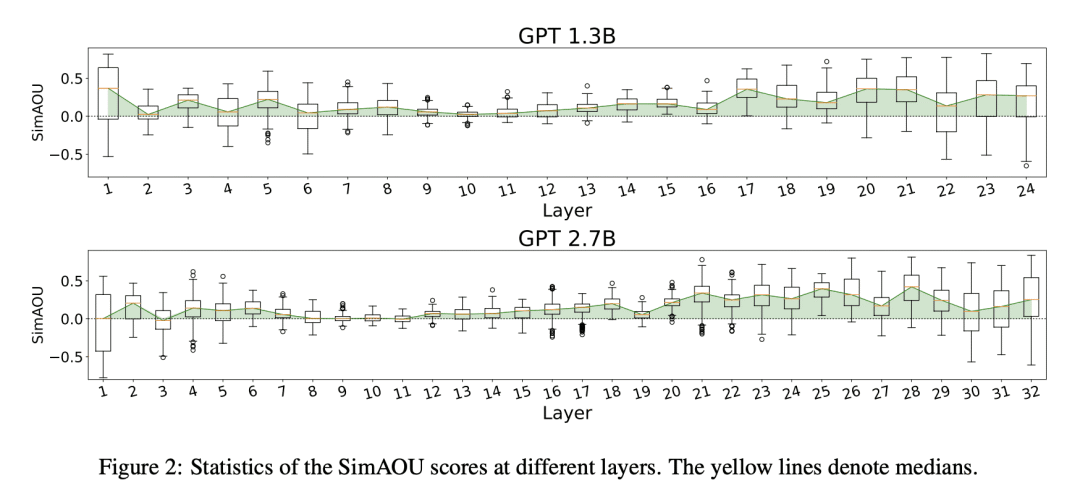
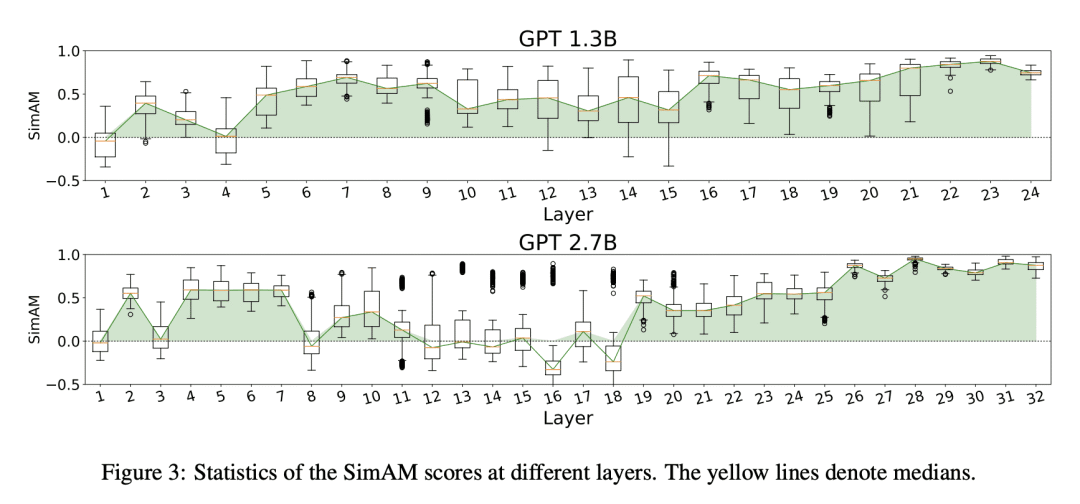
从理论上和实证上,证明ICL的行为类似于显式微调; -
设计了一种基于动量的注意力,以实现一致的性能改进。
摘要:
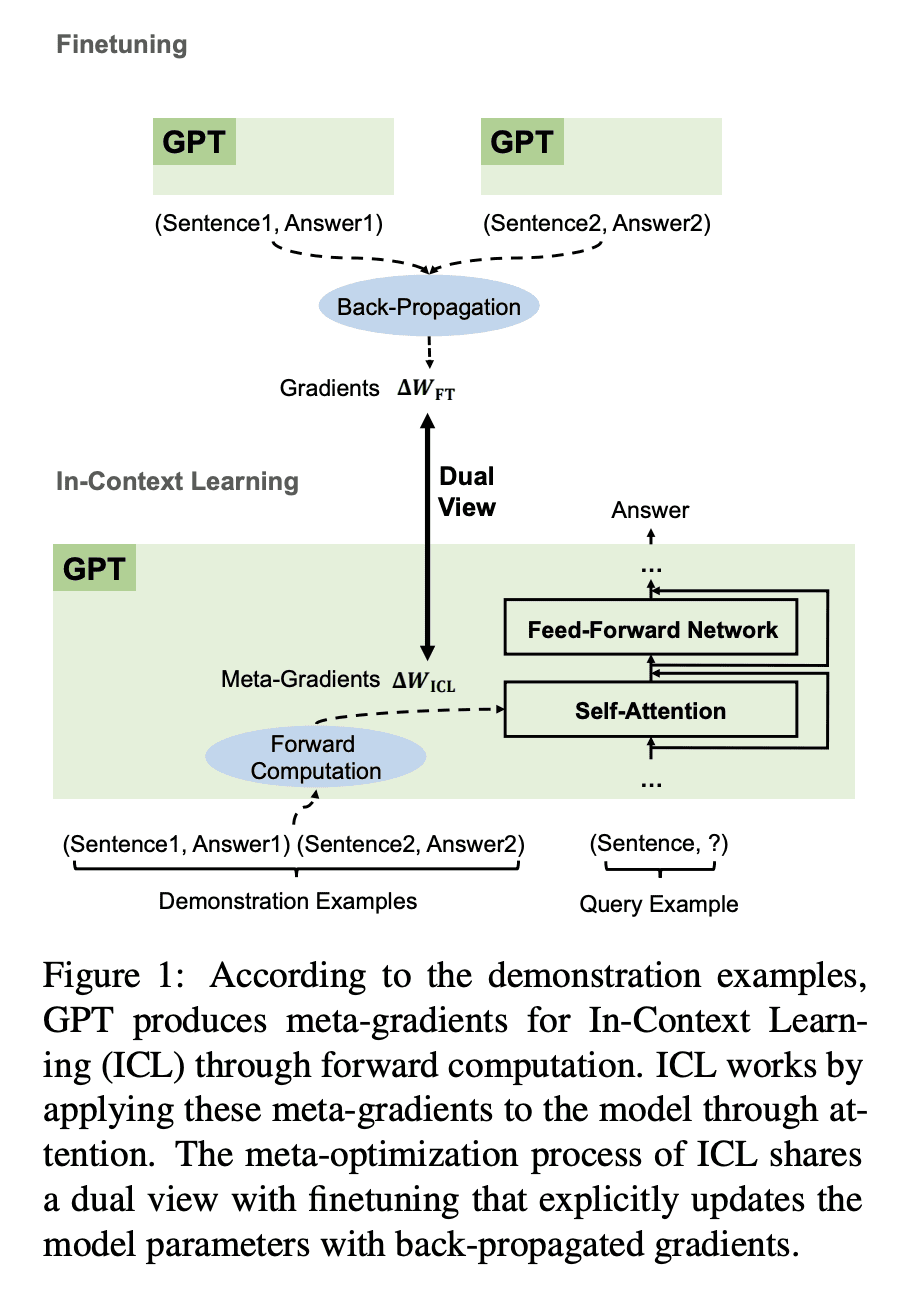
大型预训练语言模型表现出令人惊讶的上下文学习(ICL)能力。通过几个演示输入标签对,可以预测未见输入标签,无需额外的参数更新。尽管在性能方面取得了巨大成功,但ICL的工作机制仍然是一个悬而未决的问题。为了更好地了解ICL的工作原理,本文将语言模型解释为元优化器,并将ICL理解为一种隐式微调。从理论上,发现Transformer注意力具有基于梯度下降优化的双重形式。除此之外,对ICL的理解如下:GPT首先根据演示示例生成元梯度,然后将这些元梯度应用于原始GPT以构建ICL模型。在实验中,根据实际任务全面比较了ICL的行为和显式微调,以提供支持以上理解的经验证据。结果表明,ICL的行为类似于预测级、表示级和注意力行为级的显式微调。此外,受对元优化的理解的启发,通过与基于动量的梯度下降算法进行类比,设计了基于动量的注意力,其总是比vanilla注意力更好的性能支持再次从另一个方面理解,更重要的是,它显示了利用以上理解进行未来模型设计的潜力。
Large pretrained language models have shown surprising In-Context Learning (ICL) ability. With a few demonstration input-label pairs, they can predict the label for an unseen input without additional parameter updates. Despite the great success in performance, the working mechanism of ICL still remains an open problem. In order to better understand how ICL works, this paper explains language models as meta-optimizers and understands ICL as a kind of implicit finetuning. Theoretically, we figure out that the Transformer attention has a dual form of gradient descent based optimization. On top of it, we understand ICL as follows: GPT first produces meta-gradients according to the demonstration examples, and then these meta-gradients are applied to the original GPT to build an ICL model. Experimentally, we comprehensively compare the behavior of ICL and explicit finetuning based on real tasks to provide empirical evidence that supports our understanding. The results prove that ICL behaves similarly to explicit finetuning at the prediction level, the representation level, and the attention behavior level. Further, inspired by our understanding of meta-optimization, we design a momentum-based attention by analogy with the momentum-based gradient descent algorithm. Its consistently better performance over vanilla attention supports our understanding again from another aspect, and more importantly, it shows the potential to utilize our understanding for future model designing.
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.10559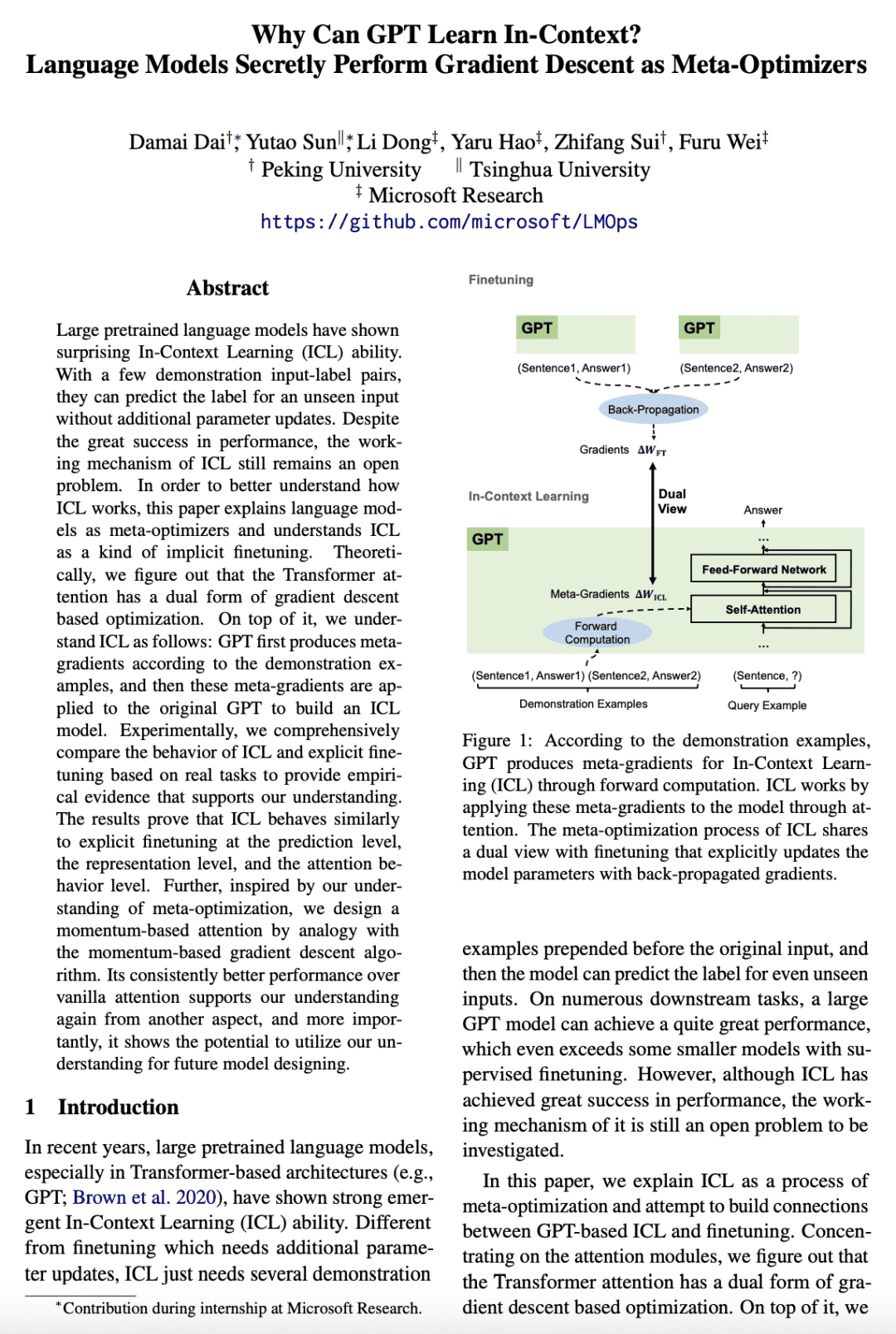
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢