来自今天的爱可可AI前沿推介
[LG] Wasserstein t-SNE
F Bachmann, P Hennig, D Kobak
[University of Hamburg & University of Tubingen]
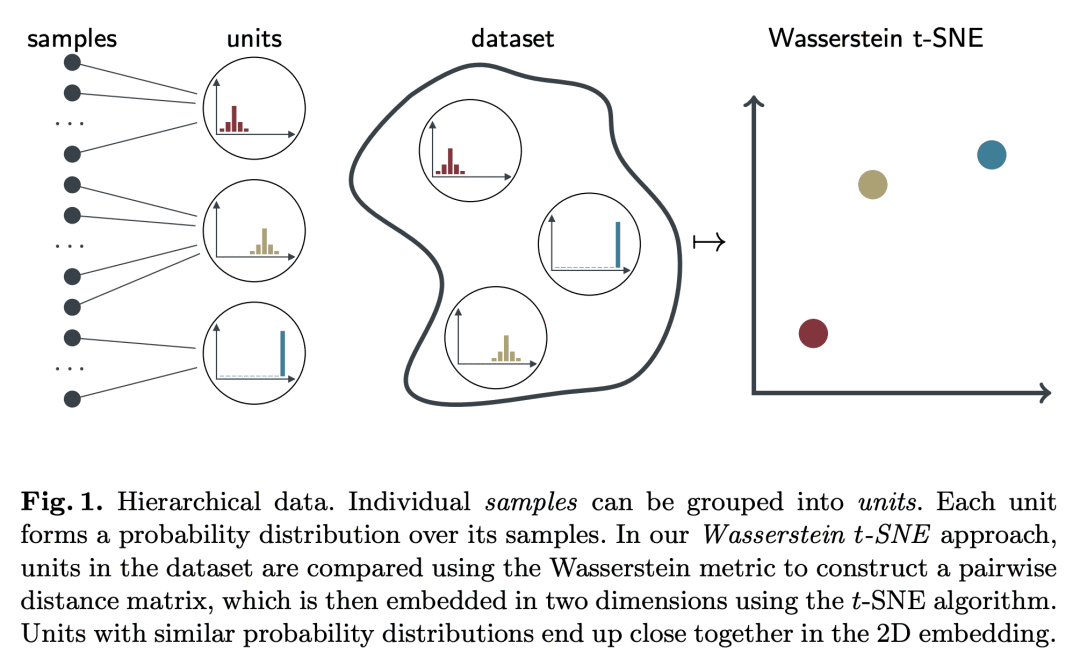
Wasserstein t-SNE聚类
要点:
-
科学数据集通常具有层次结构,样本在更高级别(单位)上分组; -
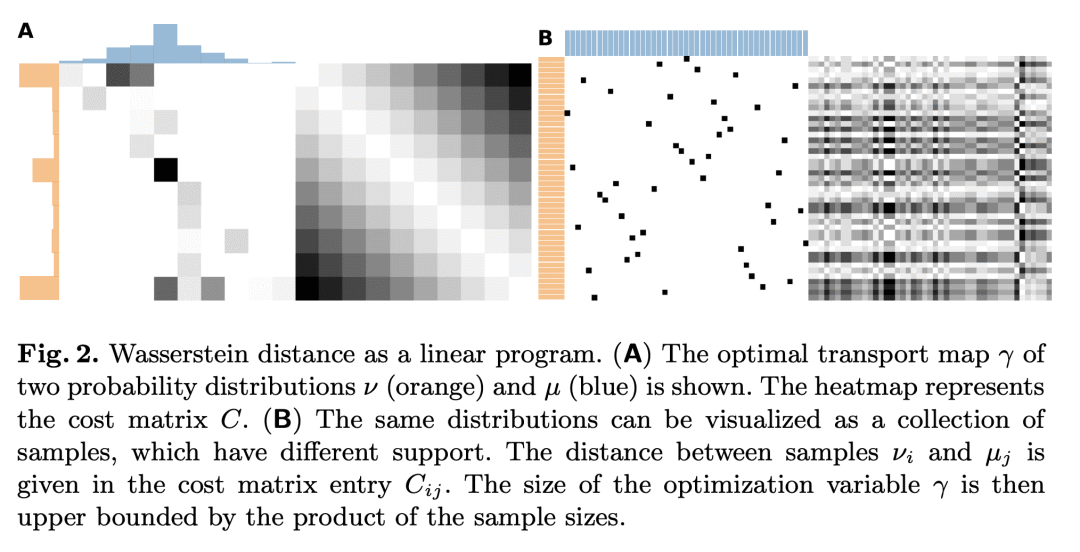
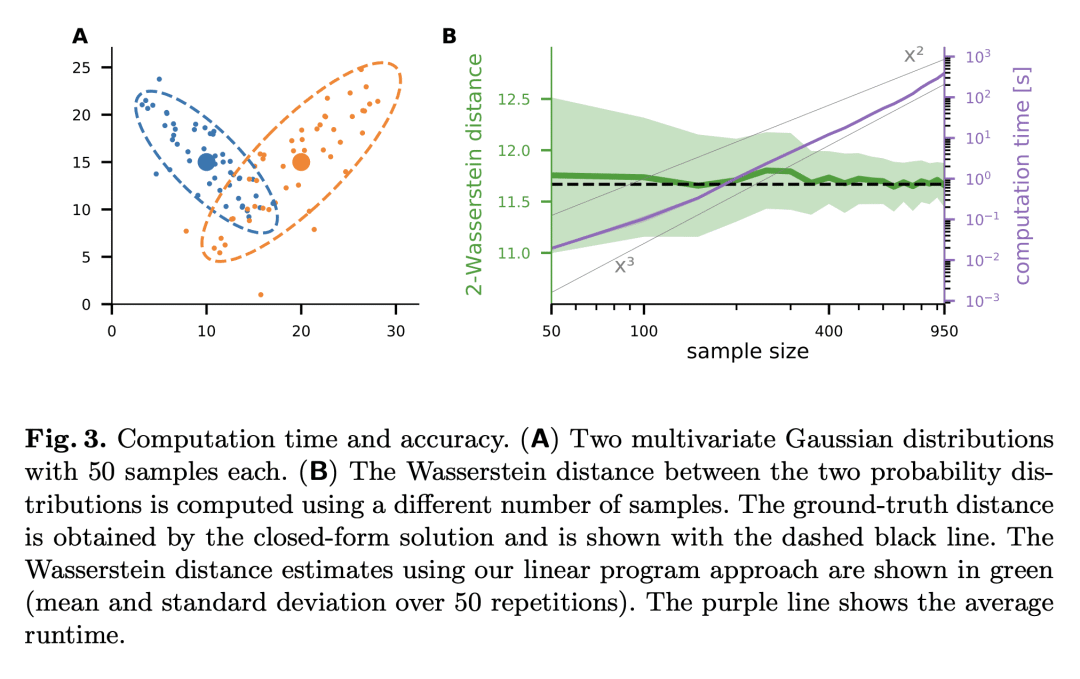
Wasserstein距离度量用来探索层次数据集,因为它考虑到了单元内分布的形状,用t-SNE根据样本间的成对Wasserstein距离矩阵构建单元的2D嵌入; -
将Wasserstein t-SNE应用于2017年德国议会选举的数据,由此产生的嵌入在数据中发现了有意义的结构。
摘要:
科学数据集通常具有层次结构:例如,在调查中,单个参与者(样本)可能会被分组到更高的级(单位),例如他们的地理区域。在这些设置中,人们的兴趣往往是在单元层级而不是样本层级探索结构。单位可以根据其平均值之间的距离进行比较,但这忽略了样品的单位内分布。本文开发了一种使用Wasserstein距离度量对层次数据集进行探索性分析的方法,该指标考虑到单元内分布的形状。使用t-SNE根据它们之间的成对Wasserstein距离矩阵构建单元的2D嵌入。通过用高斯分布近似每个单位,可以有效地计算距离矩阵,本文提供了一种可扩展的方法来计算精确的Wasserstein距离。使用合成数据来证明我们的Wasserstein t-SNE的有效性,并将其应用于2017年德国议会选举的数据,将投票站视为样本,投票区作为单位。由此产生的嵌入揭示了数据中有意义的结构。
Scientific datasets often have hierarchical structure: for example, in surveys, individual participants (samples) might be grouped at a higher level (units) such as their geographical region. In these settings, the interest is often in exploring the structure on the unit level rather than on the sample level. Units can be compared based on the distance between their means, however this ignores the within-unit distribution of samples. Here we develop an approach for exploratory analysis of hierarchical datasets using the Wasserstein distance metric that takes into account the shapes of within-unit distributions. We use t-SNE to construct 2D embeddings of the units, based on the matrix of pairwise Wasserstein distances between them. The distance matrix can be efficiently computed by approximating each unit with a Gaussian distribution, but we also provide a scalable method to compute exact Wasserstein distances. We use synthetic data to demonstrate the effectiveness of our Wasserstein t-SNE, and apply it to data from the 2017 German parliamentary election, considering polling stations as samples and voting districts as units. The resulting embedding uncovers meaningful structure in the data.
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2205.07531
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢