近十年深度学习迅猛发展,但是仍有许多问题亟待解决,例如将知识迁移到新问题上的能力。许多关键问题都可以归结为OOD(out-of-distribution)问题。因为统计学习模型需要独立同分布(i.i.d.)假设,若测试数据与训练数据来自不同的分布,统计学习模型往往会出错。然而在很多情况下,i.i.d.的假设是不成立的。
表征学习(Representation Learning)是机器学习中的重要问题,良好的表征是机器学习算法成功的重要条件;正因如此,近十年来深度学习借助神经网络强大的表达能力、海量的数据以及强大的算力,自动地从数据中学习表征,取代了传统的人工制作的特征,取得了瞩目的成就。
因果推断所研究的正是这样的情形:如何学习一个可以在不同分布下工作、蕴含因果机制的因果模型 (Causal Model),并使用因果模型进行干预或反事实推断。然而现实没有这么容易。因果模型往往处理的是结构化的数据,并不能处理机器学习中常见的高维的低层次的原始数据,例如图像。
自然地,是否会有一种方法可以将图像这样的原始数据转化为可用于因果模型的结构化变量,从而能将因果推断和深度学习的优势更好的结合起来?
因果表征学习应运而生,这是一个非常新兴且前沿的研究方向,也是机器学习和人工智能的基本问题之一,它在解决机器学习和人工智能中两个长期未解决的问题:可解释性和可泛化性方面起着关键作用。
随着“因果革命”在人工智能与大数据领域徐徐展开,作为连接因果科学与深度学习桥梁的因果表征学习,成为备受关注的前沿方向。以往的深度表征学习在数据降维中保留信息并过滤噪音,新兴的因果科学则形成了因果推理与发现的一系列方法。随着二者结合,因果表征学习有望催生更强大的新一代AI。
因果表征学习,即从低水平的观察中发现高水平的因果变量。因果表征学习就是连接因果科学、机器学习与复杂系统的桥梁,解决因果表征学习及相关问题,就可以很好的将因果推断与机器学习结合起来,构建下一代更强大的AI。并且因果表征学习作为因果科学的前沿方法,与复杂系统中的因果涌现问题有异曲同工之妙,是研究复杂系统中涌现问题的重要方法之一,涌现是从微观到宏观的产生过程, 这与因果表征学习恰好对应。因果表征学习也是一个从微观到宏观的学习过程,它从一些微观的信息(比如图像或者音频) 中可以学到宏观的、可解释的因果变量,这也有望解决复杂系统中定量刻画涌现现象等问题。

因此,特此推荐因果表征领域的一系列经典、前沿文献,供大家学习参考,讨论交流,也可前往集智斑图查看论文详细信息。
主题1:因果表征学习导论
这是第一篇因果表征学习的研究综述,很好地阐释了因果表征学习的基本问题、基础假设、技术框架、和未来可能的研究方向。
-
Bernhard Schölkopf, Francesco Locatello, Stefan Bauer, Nan Rosemary Ke, Nal Kalchbrenner, Anirudh Goyal, Yoshua Bengio: Towards Causal Representation Learning. CoRR abs/2102.11107 (2021)
主题2:因果表征学习理论基础
独立成分分析
这是第一篇从独立成分分析理论的角度,探索解决变分自编码器中表征学习可识别性问题的论文,其证明的框架和思想启发了许多这个方向的研究。
-
Ilyes Khemakhem, Diederik P. Kingma, Ricardo Pio Monti, Aapo Hyvärinen: Variational Autoencoders and Nonlinear ICA: A Unifying Framework. AISTATS 2020: 2207-2217
-
Luigi Gresele, Paul K. Rubenstein, Arash Mehrjou, Francesco Locatello, Bernhard Schölkopf:The Incomplete Rosetta Stone problem: Identifiability results for Multi-view Nonlinear ICA. UAI 2019: 217-227
独立因果机制
这是第一篇在统计上为独立因果机制建立形式化定义的论文。
这是第一篇将独立因果机制应用于不变性模型预测的论文,启发了包括不变风险最小化(Invariant Risk Minimization)在内的大量研究。
这是第一篇分析思考机器学习和因果建模关系的论文,为后续因果机器学习的研究奠定了基础。这篇论文今年也获得了机器学习顶会ICML的时间检验奖荣誉提名(Test of Time Honorable Mention)。
稀疏因果机制偏移
这是第一篇从稀疏因果机制偏移假设出发,通过在不同分布变化数据上的学习速度,进行二元因果发现的论文。
-
Yoshua Bengio, Tristan Deleu, Nasim Rahaman, Nan Rosemary Ke, Sébastien Lachapelle, Olexa Bilaniuk, Anirudh Goyal, Christopher J. Pal:A Meta-Transfer Objective for Learning to Disentangle Causal Mechanisms. ICLR 2020
-
Ronan Perry, Julius von Kügelgen, Bernhard Schölkopf:Causal Discovery in Heterogeneous Environments Under the Sparse Mechanism Shift Hypothesis. CoRR abs/2206.02013 (2022)
因果变量学习
这是第一篇从理论和大规模试验上证明了好的解耦表征学习需要归纳偏见和监督信息指导。这篇论文获得了机器学习顶会ICML 2019的最佳论文奖。
-
Francesco Locatello, Stefan Bauer, Mario Lucic, Gunnar Rätsch, Sylvain Gelly, Bernhard Schölkopf, Olivier Bachem:Challenging Common Assumptions in the Unsupervised Learning of Disentangled Representations. ICML 2019: 4114-4124
-
Raphael Suter, Ðorðe Miladinovic, Bernhard Schölkopf, Stefan Bauer:Robustly Disentangled Causal Mechanisms: Validating Deep Representations for Interventional Robustness. ICML 2019: 6056-6065
因果机制学习
这篇论文提出一种基于专家竞争的方式来学习独立因果机制的算法。
-
Giambattista Parascandolo, Niki Kilbertus, Mateo Rojas-Carulla, Bernhard Schölkopf:Learning Independent Causal Mechanisms. ICML 2018: 4033-4041
-
Martín Arjovsky, Léon Bottou, Ishaan Gulrajani, David Lopez-Paz:Invariant Risk Minimization. CoRR abs/1907.02893 (2019)
因果结构学习
这篇论文提出了一种从视频数据中进行因果发现的框架。
-
Yunzhu Li, Antonio Torralba, Anima Anandkumar, Dieter Fox, Animesh Garg:Causal Discovery in Physical Systems from Videos. NeurIPS 2020
-
Weiran Yao, Yuewen Sun, Alex Ho, Changyin Sun, Kun Zhang:Learning Temporally Causal Latent Processes from General Temporal Data. ICLR 2022
主题4:因果表征学习在机器学习中的应用
因果推断
这是第一篇基于深度表征学习对治疗组和对照组协变量进行筛选和表征,从而预测缺失的潜在结果的文章,并且在线性假设下证明了估计的条件平均因果效应的泛化误差界。
1. Johansson, Fredrik, Uri Shalit, and David Sontag. "Learning representations for counterfactual inference." In International conference on machine learning, pp. 3020-3029. PMLR, 2016.
考虑到只有一些基于观察到的协变量X的因素有助于选择治疗T,只有一些因素有助于确定结果Y,这篇文章提出了一种新算法来对观察变量进行解藕:(1)从任何给定的观察数据集D中识别上述基本因素的分解表示;(2)利用这种知识来减少选择偏差对估计D中治疗效果的负面影响。
因果生成模型
这篇文章首次基于变分自编码器(VAE),同时估计混杂因素和因果效应的未知潜空间,从而估计ITE。
1. Louizos, Christos, Uri Shalit, Joris M. Mooij, David Sontag, Richard Zemel, and Max Welling. "Causal effect inference with deep latent-variable models." Advances in neural information processing systems 30 (2017).
-
Zhang, Weijia, Lin Liu, and Jiuyong Li. "Treatment effect estimation with disentangled latent factors." In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 35, no. 12, pp. 10923-10930. 2021.
因果公平性
-
Kusner, Matt J., Joshua Loftus, Chris Russell, and Ricardo Silva. "Counterfactual fairness." Advances in neural information processing systems 30 (2017).
-
Chiappa, Silvia. "Path-specific counterfactual fairness." In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, vol. 33, no. 01, pp. 7801-7808. 2019.
-
Wu, Yongkai, Lu Zhang, Xintao Wu, and Hanghang Tong. "Pc-fairness: A unified framework for measuring causality-based fairness." Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32 (2019).
-
Kilbertus, Niki, Mateo Rojas Carulla, Giambattista Parascandolo, Moritz Hardt, Dominik Janzing, and Bernhard Schölkopf. "Avoiding discrimination through causal reasoning." Advances in neural information processing systems 30 (2017).
因果强化学习
这篇文章提出了一个赌博机 Agents 应该追求的优化指标(同时采用实验分布和观察分布),并阐释了其相较于传统算法的优势。
-
Bareinboim, Elias, Andrew Forney, and Judea Pearl. "Bandits with unobserved confounders: A causal approach." Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 28 (2015).
-
Biwei Huang, Fan Feng, Chaochao Lu, Sara Magliacane, Kun Zhang. "AdaRL: What, Where, and How to Adapt in Transfer Reinforcement Learning." International Conference on Learning Representation (2022).
-
De Haan, Pim, Dinesh Jayaraman, and Sergey Levine. "Causal confusion in imitation learning." Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 32 (2019).
-
Bottou, Léon, Jonas Peters, Joaquin Quiñonero-Candela, Denis X. Charles, D. Max Chickering, Elon Portugaly, Dipankar Ray, Patrice Simard, and Ed Snelson. "Counterfactual Reasoning and Learning Systems: The Example of Computational Advertising." Journal of Machine Learning Research 14, no. 11 (2013).
-
Buesing, Lars, Theophane Weber, Yori Zwols, Sebastien Racaniere, Arthur Guez, Jean-Baptiste Lespiau, and Nicolas Heess. "Woulda, coulda, shoulda: Counterfactually-guided policy search." arXiv preprint arXiv:1811.06272 (2018).
-
Pitis, Silviu, Elliot Creager, and Animesh Garg. "Counterfactual data augmentation using locally factored dynamics." Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 33 (2020): 3976-3990.
这篇文章将外生状态的变量和奖励形式化,并且确定了具有外生状态的MDP(马尔科夫决策过程)可以被分解为只包含了一个外生状态+奖励的外生马尔可夫奖励过程,和一个仅针对内生奖励定义的内生马尔可夫决策过程的条件。
-
Zhang, Amy, Clare Lyle, Shagun Sodhani, Angelos Filos, Marta Kwiatkowska, Joelle Pineau, Yarin Gal, and Doina Precup. "Invariant causal prediction for block mdps." In International Conference on Machine Learning, pp. 11214-11224. PMLR, 2020.
主题5:因果表征学习在工业场景中的应用
因果推荐系统
这篇文章提供了一个正式的因果分析框架来综述和统一现有的因果启发的推荐方法,它可以适应推荐系统中不同的场景。此外,这篇文章提出了一个新的分类法,并从违反因果假设的角度给出了推荐系统中各种偏差的正式因果定义。
-
Wu, Peng, Haoxuan Li, Yuhao Deng, Wenjie Hu, Quanyu Dai, Zhenhua Dong, Jie Sun, Rui Zhang, and Xiao-Hua Zhou. "On the opportunity of causal learning in recommendation systems: Foundation, estimation, prediction and challenges." In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Vienna, Austria, pp. 23-29. 2022.
-
Gao, Chen, Yu Zheng, Wenjie Wang, Fuli Feng, Xiangnan He, and Yong Li. "Causal Inference in Recommender Systems: A Survey and Future Directions." arXiv preprint arXiv:2208.12397 (2022).
因果自然语言处理
这是一篇因果自然语言处理的研究综述,很好地阐释了因果自然语言处理的基本问题、任务分类、技术框架、和未来可能的研究方向。
-
Keith, Katherine A., David Jensen, and Brendan O'Connor. "Text and causal inference: A review of using text to remove confounding from causal estimates." arXiv preprint arXiv:2005.00649 (2020).
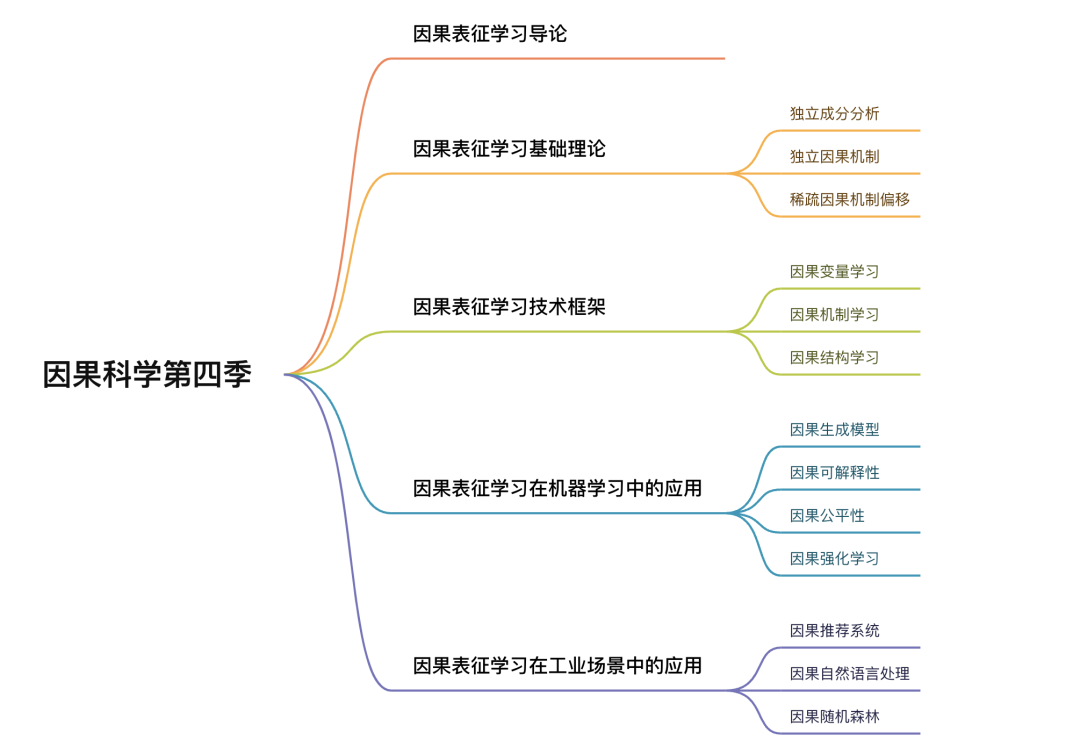
如何能更好的将因果关系和机器学习结合,将因果表征学习更好的应用于实际的复杂系统中,为具体的决策提供科学依据,构建下一代更通用的AI是因果与机器学习链接的重要问题,因此集智俱乐部因果科学社区举办了以“因果表征学习”为主题的因果科学与CausalAI系列读书会第四季(2022年12月27日开始,每周六晚20:00-22:00)。如果你对上述论文感兴趣,欢迎扫描文末二维码进行报名。
围绕更好的梳理因果表征学习的相关问题出发,从因果表征学习的理论基础、技术框架,到因果表征学习最新的前沿应用,包括但不限于因果生成模型、因果可解释性、因果公平性等问题,以及因果在工业界中的具体的落地中去深度探讨,更好的梳理因果表征学习这个领域并促进相关的研究。
感兴趣的朋友可以扫码了解详情,报名参与,加入主题社区进行学习交流。

第一期分享将围绕以下大纲展开(2022年12月31日),在集智俱乐部视频号同步直播,欢迎关注:
-
引言 Preliminaries
-
统计学习理论 Statistical Learning Theory
-
从统计学到因果模型 From Statistical to Causal Models
-
因果建模框架 Causal Modeling Frameworks
-
独立因果机制 Independent Causal Mechanisms
-
因果建模层级 Levels of Causal Modeling
-
因果发现 Causal Discovery
-
对机器学习的意义 Implications for Machine Learning
-
半监督学习 Semi-Supervised Learning
-
不变性和鲁棒性 Invariance and Robustness
-
因果推断 Causal Reasoning
-
研究现状和公开问题 Current Research and Open Problems
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢