来自今天的爱可可AI前沿推介
[CV] Scale-MAE: A Scale-Aware Masked Autoencoder for Multiscale Geospatial Representation Learning
C J. Reed, R Gupta, S Li, S Brockman, C Funk...
[Berkeley AI Research & Meta AI & Kitware Inc]
Scale-MAE: 面向多尺度地理空间表示学习的尺度感知掩码自编码器
要点:
-
提出Scale-MAE,一种预训练方法,可以在多种空间尺度上提供更强大的遥感数据表示; -
Scale-MAE的两个关键:尺度感知位置编码和拉普拉斯金字塔解码器,可多尺度解码低频和高频特征; -
Scale-MAE在八个遥感数据集上比目前最先进的技术实现了5.0%的非参数kNN分类提升。
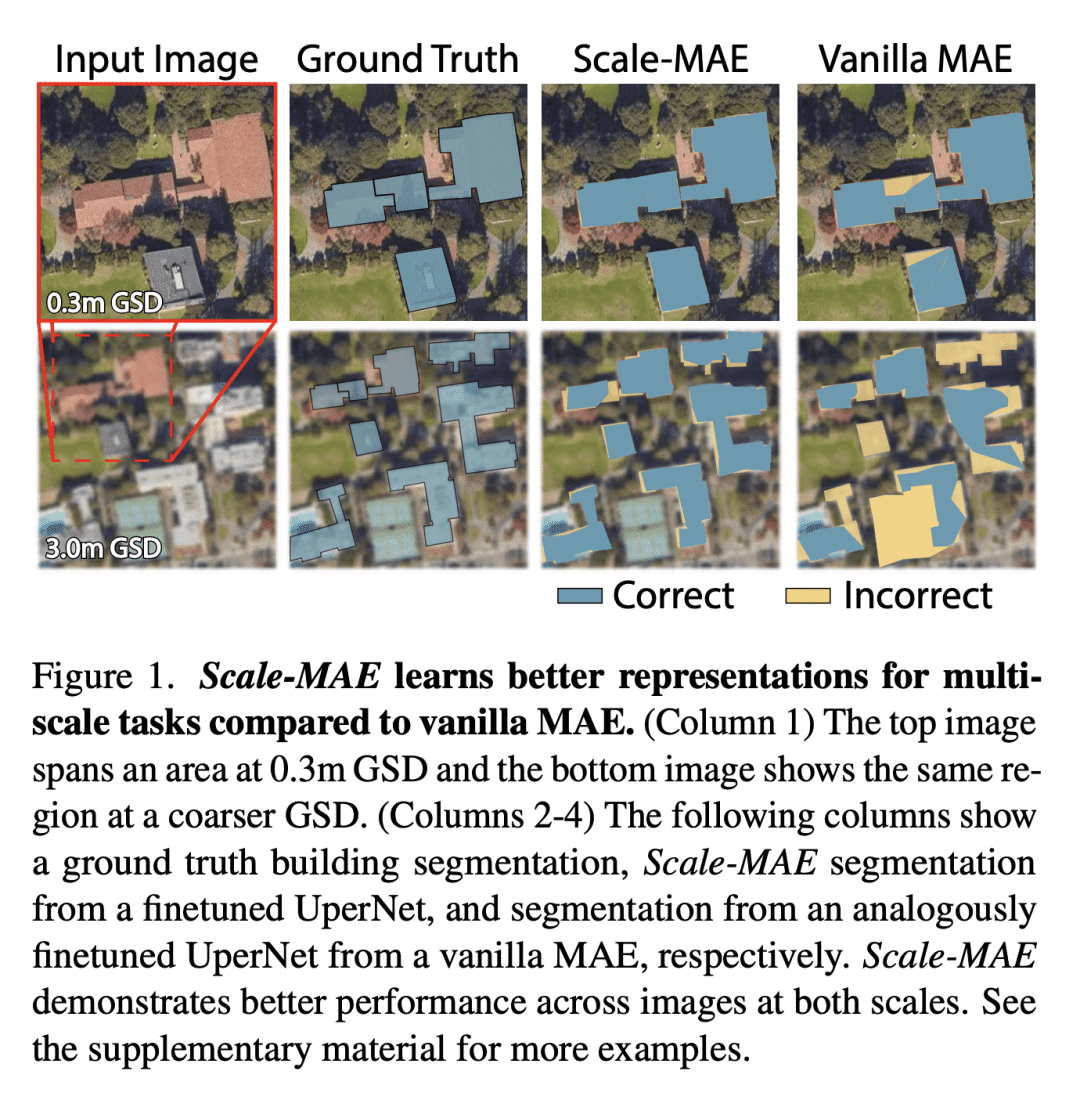
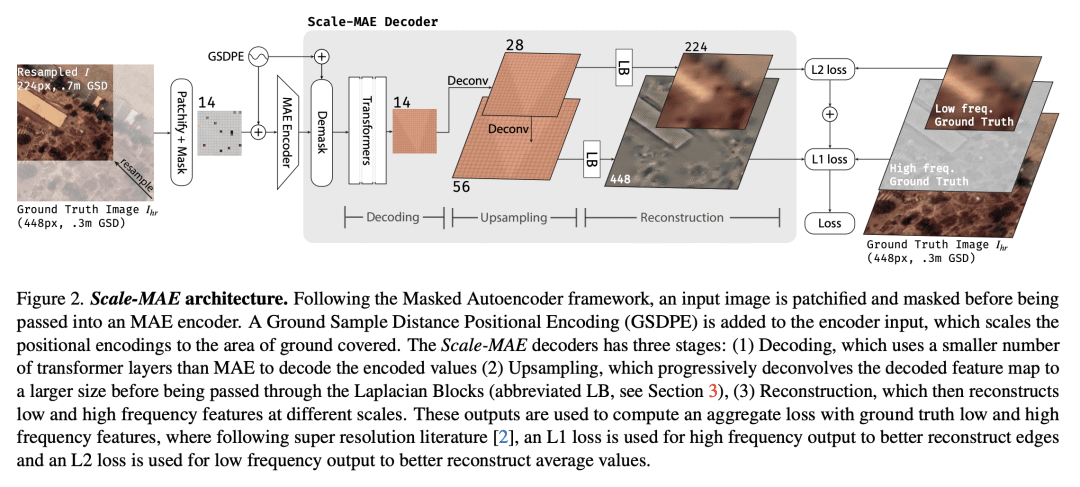
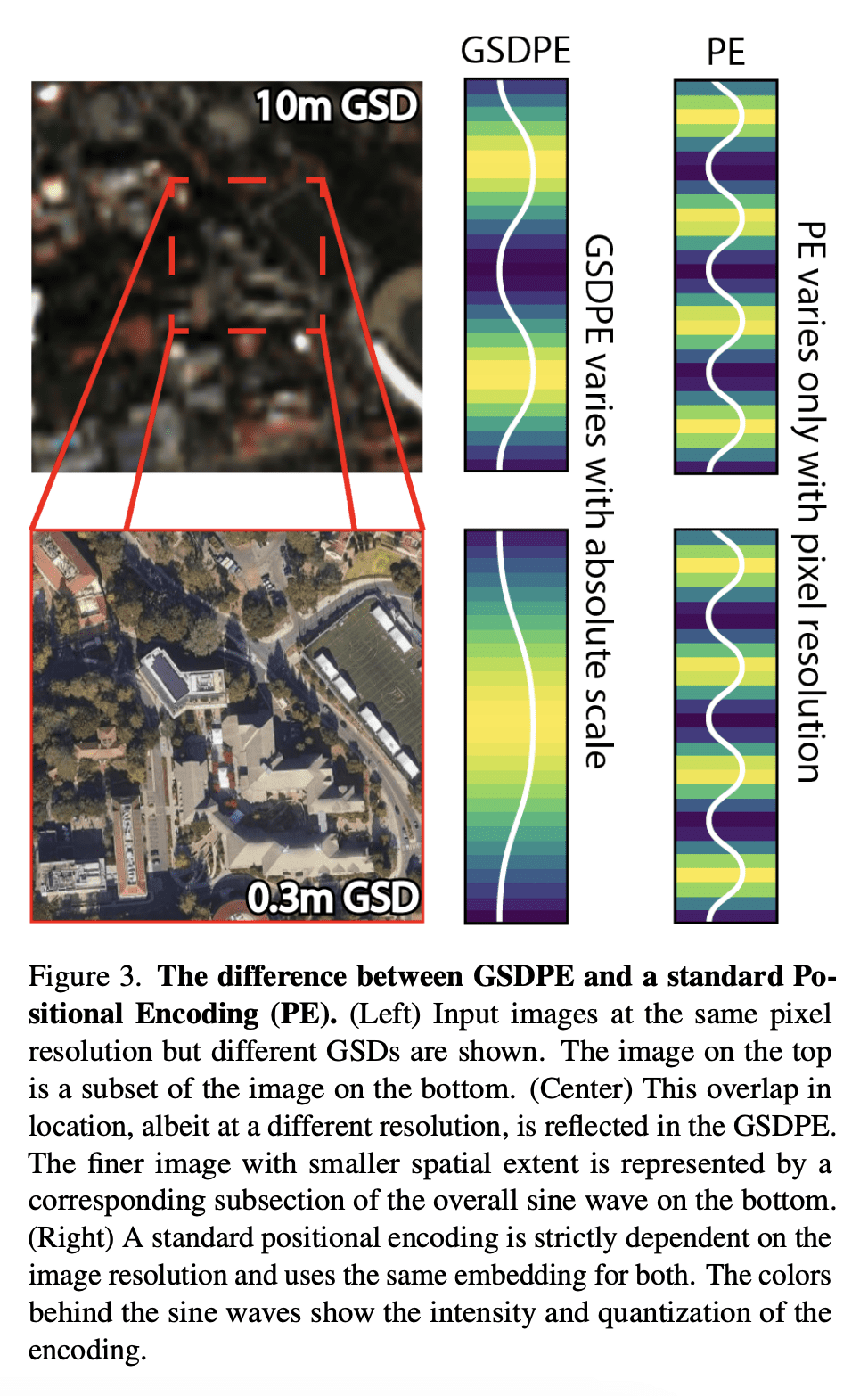
摘要: 遥感图像提供了地球的全面视图,不同的传感器在不同的空间尺度上收集补充数据。大型预训练模型通常用大量增强的图像进行微调,以模仿不同的条件和尺度,由此产生的模型用于各种空间尺度图像任务。这类模型忽略了数据中特定于尺度的信息。本文提出Scale-MAE,一种预训练方法,在整个预训练过程中明确学习不同已知尺度数据间的关系。Scale-MAE通过在已知输入尺度上掩码输入图像来预训练网络,其中图像覆盖的地球面积决定了ViT位置编码的尺度,而不是图像分辨率。Scale-MAE使用标准ViT主干对掩码图像进行编码,然后通过带通滤波器解码掩码图像,以重建低/高比例的低/高频图像。将网络用于低频/高频图像重建可以为遥感图像提供强大的多尺度表示。与当前最先进技术相比,Scale-MAE在八个遥感数据集上平均实现了5.0%的非参数kNN分类改进,并在一系列评估尺度的SpaceNet建筑分割传输任务上获得了0.9 mIoU至3.8 mIoU的改进。
Remote sensing imagery provides comprehensive views of the Earth, where different sensors collect complementary data at different spatial scales. Large, pretrained models are commonly finetuned with imagery that is heavily augmented to mimic different conditions and scales, with the resulting models used for various tasks with imagery from a range of spatial scales. Such models overlook scale-specific information in the data. In this paper, we present Scale-MAE, a pretraining method that explicitly learns relationships between data at different, known scales throughout the pretraining process. Scale-MAE pretrains a network by masking an input image at a known input scale, where the area of the Earth covered by the image determines the scale of the ViT positional encoding, not the image resolution. Scale-MAE encodes the masked image with a standard ViT backbone, and then decodes the masked image through a bandpass filter to reconstruct low/high frequency images at lower/higher scales. We find that tasking the network with reconstructing both low/high frequency images leads to robust multiscale representations for remote sensing imagery. Scale-MAE achieves an average of a 5.0% non-parametric kNN classification improvement across eight remote sensing datasets compared to current state-of-the-art and obtains a 0.9 mIoU to 3.8 mIoU improvement on the SpaceNet building segmentation transfer task for a range of evaluation scales.
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.14532
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢