来自今天的爱可可AI前沿推介
大型语言模型已通过 In-context Learning 在各种复杂任务上展现出卓越的性能,并且无需针对特定任务进行训练或微调,近期 prompt 和解码方面取得的进展也使大型语言模型解决复杂推理任务变成了现实。
但大型语言模型可能会存储过时、不全面或不正确的知识,要将大型语言模型成功部署到实际应用中,外部知识来源(例如维基百科)至关重要。此前,人们尝试将知识用于较小的语言模型 (LM),例如 T5、BERT 和 RoBERTa,但这些方法通常需要额外的训练或微调,成本高昂,对于大型语言模型来说完全不切实际。
基于此,来自罗彻斯特大学、腾讯 AI Lab 和宾夕法尼亚大学的研究者联合提出了一种称为 Rethinking with Retrieval (RR) 的后处理方法,以在大型语言模型中利用外部知识。
Rethinking with Retrieval: Faithful Large Language Model Inference
H He, H Zhang, D Roth
[University of Rochester & Tencent AI Lab & University of Pennsylvania]
基于检索的再思考: 忠实的大型语言模型推断
要点:
-
当前将外部知识纳入LLM的方法通常需要额外的训练或微调,可能成本高昂,对LLM也许不可行;
-
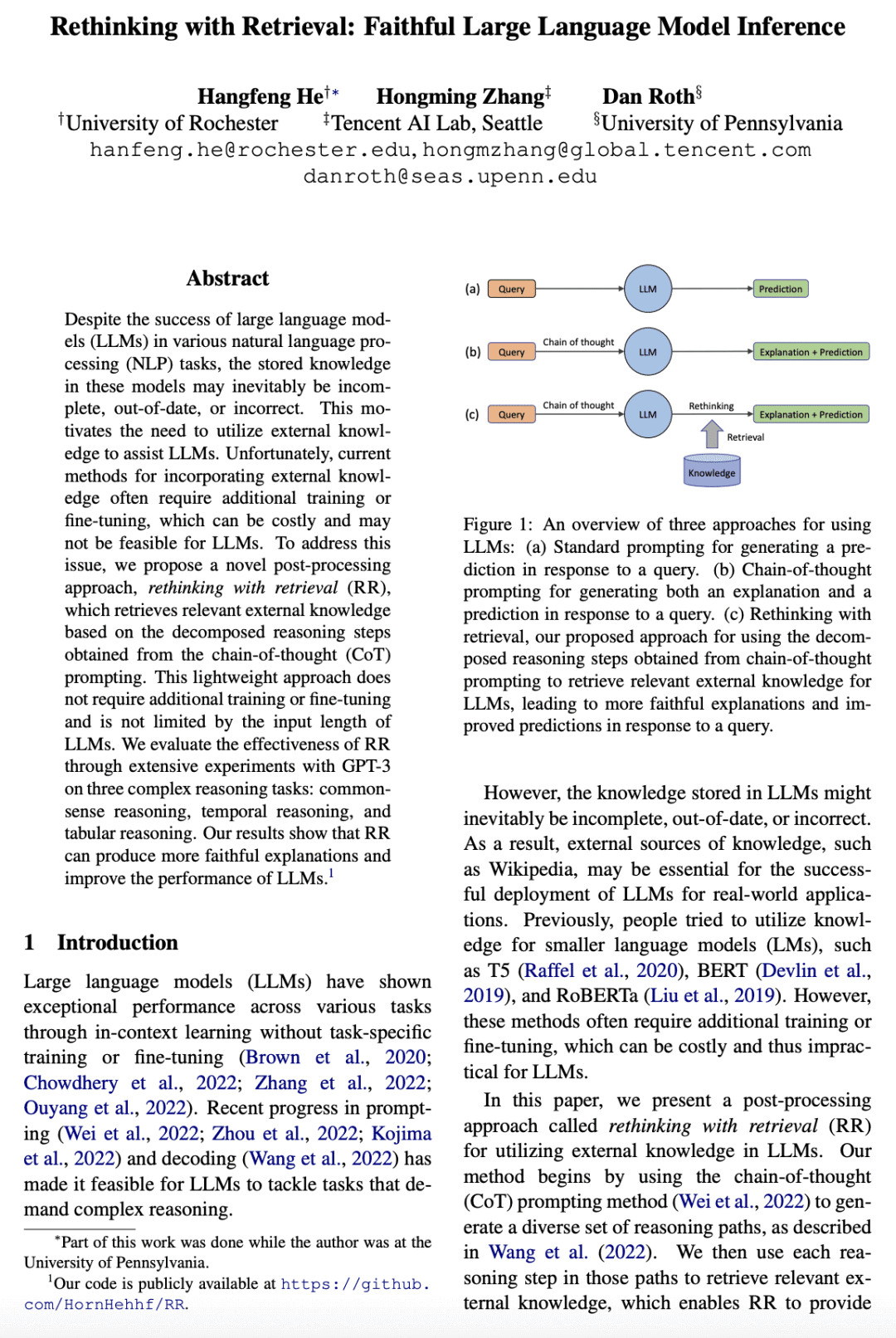
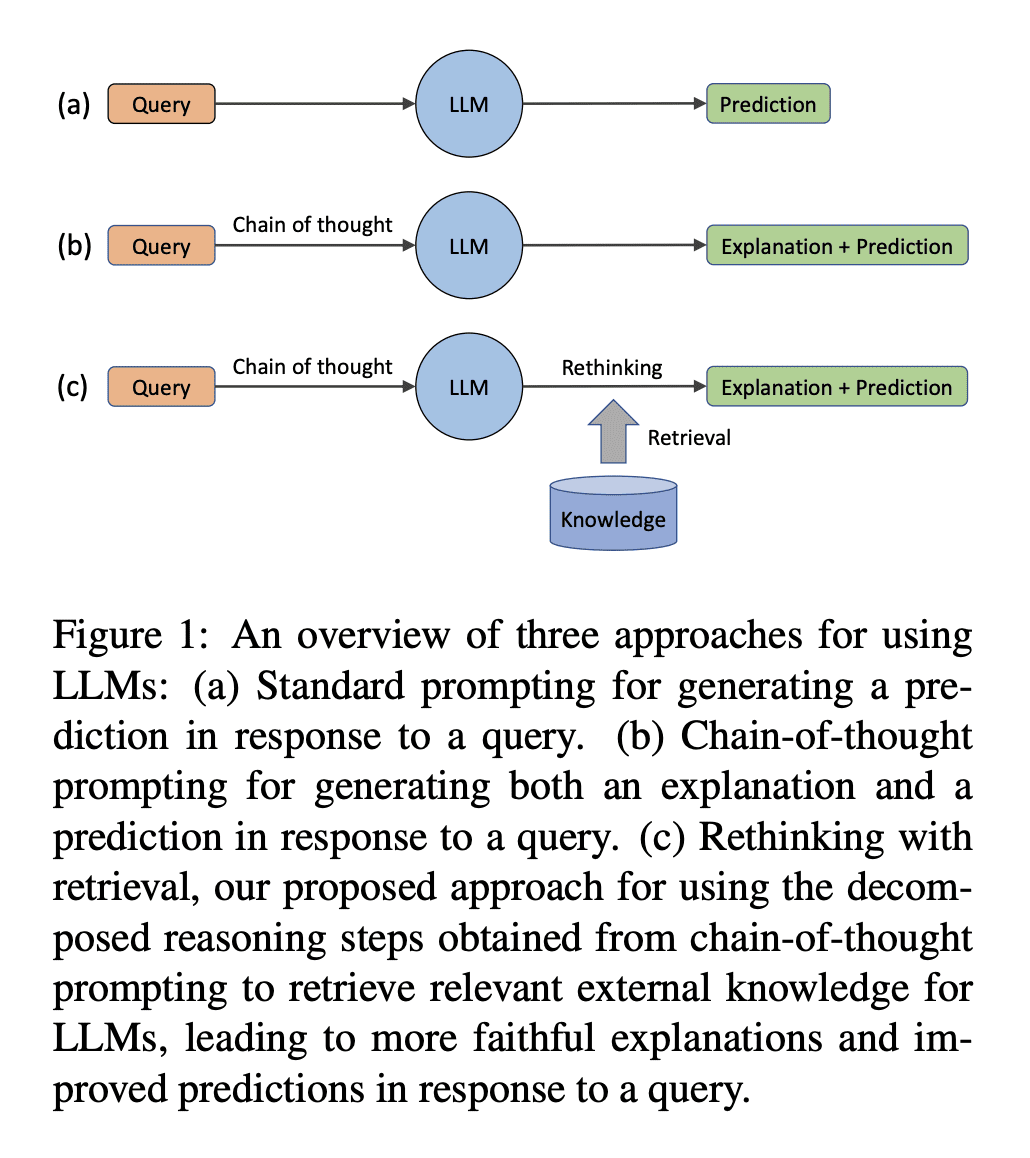
提出一种新的后处理方法“基于检索的再思考(RR)”,基于从“思维链(CoT)”提示获得的分解推理步骤检索相关外部知识;
-
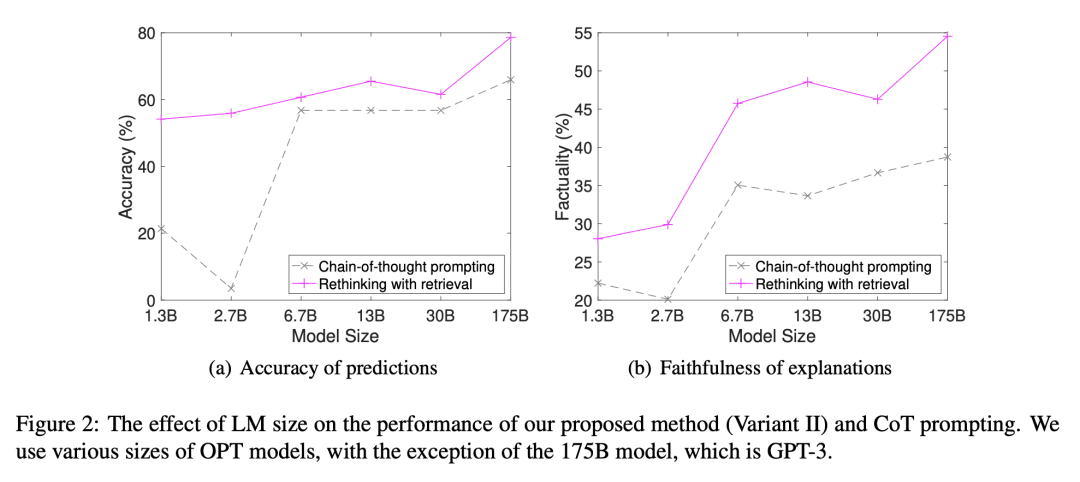
RR不需要额外的训练或微调,也不受LLM输入长度限制,在常识推理、时间推理和表格推理任务中均能显著提高LLM性能。
摘要:
尽管大型语言模型(LLM)在各种自然语言处理(NLP)任务中取得了成功,但这些模型中存储的知识可能不完整,过时或不正确。这促使我们使用外部知识来协助LLM。不幸的是,当前将外部知识纳入LLM的方法通常需要额外的训练或微调,这可能成本高昂,对LLM或许不可行。为了解决该问题,本文提出了一种新的后处理方法“基于检索的再思考(RR)”,基于从“思维链(CoT)”提示获得的分解推理步骤检索相关的外部知识。这种轻量方法不需要额外的训练或微调,也不受LLM输入长度的限制。
通过用GPT-3在三个复杂的推理任务:常识推理,时间推理和表格推理上进行大量实验来评估RR的有效性。结果表明,RR可以产生更忠实的解释,并提高LLM的性能。
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.00303
Despite the success of large language models (LLMs) in various natural language processing (NLP) tasks, the stored knowledge in these models may inevitably be incomplete, out-of-date, or incorrect. This motivates the need to utilize external knowledge to assist LLMs. Unfortunately, current methods for incorporating external knowledge often require additional training or fine-tuning, which can be costly and may not be feasible for LLMs. To address this issue, we propose a novel post-processing approach, rethinking with retrieval (RR), which retrieves relevant external knowledge based on the decomposed reasoning steps obtained from the chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting. This lightweight approach does not require additional training or fine-tuning and is not limited by the input length of LLMs. We evaluate the effectiveness of RR through extensive experiments with GPT-3 on three complex reasoning tasks: commonsense reasoning, temporal reasoning, and tabular reasoning. Our results show that RR can produce more faithful explanations and improve the performance of LLMs.
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢