来自今日爱可可的前沿推介
推荐理由:通过收敛分析,深入了解该算法的有效性和实际成功,为QTD算法奠定了坚实的理论基础。
An Analysis of Quantile Temporal-Difference Learning
M Rowland, R Munos, M G Azar, Y Tang, G Ostrovski, A Harutyunyan, K Tuyls, M G. Bellemare, W Dabney
[DeepMind]
分位数时间差分学习分析
要点:
-
本文为分位数时间差分(QTD)提供了收敛性分析,QTD是一种流行而有效的分布式强化学习算法; -
在QTD和非线性动态规划之间建立了联系; -
与经典TD学习相比,收敛的证明在较弱条件下成立,为QTD提供了坚实的理论基础。
摘要:
本文分析了分位数时间差分学习(QTD),QTD是一种分布式强化学习算法,已在几个成功的大规模强化学习应用中证明是关键组成部分。尽管有这些经验成功,但直到现在QTD的理论理解仍然难以捉摸。与经典TD学习不同,TD可以用标准随机近似工具分析,QTD更新不近似收缩映射,高度非线性,可能有多个定点。本文的核心结果是证明了一类相关动态规划的定点的收敛性具有概率1,将QTD置于坚实的理论基础上。通过随机近似理论和非光滑分析,证明建立了QTD与非线性微分不等式之间的联系。
We analyse quantile temporal-difference learning (QTD), a distributional reinforcement learning algorithm that has proven to be a key component in several successful large-scale applications of reinforcement learning. Despite these empirical successes, a theoretical understanding of QTD has proven elusive until now. Unlike classical TD learning, which can be analysed with standard stochastic approximation tools, QTD updates do not approximate contraction mappings, are highly non-linear, and may have multiple fixed points. The core result of this paper is a proof of convergence to the fixed points of a related family of dynamic programming procedures with probability 1, putting QTD on firm theoretical footing. The proof establishes connections between QTD and non-linear differential inclusions through stochastic approximation theory and non-smooth analysis.
https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.04462
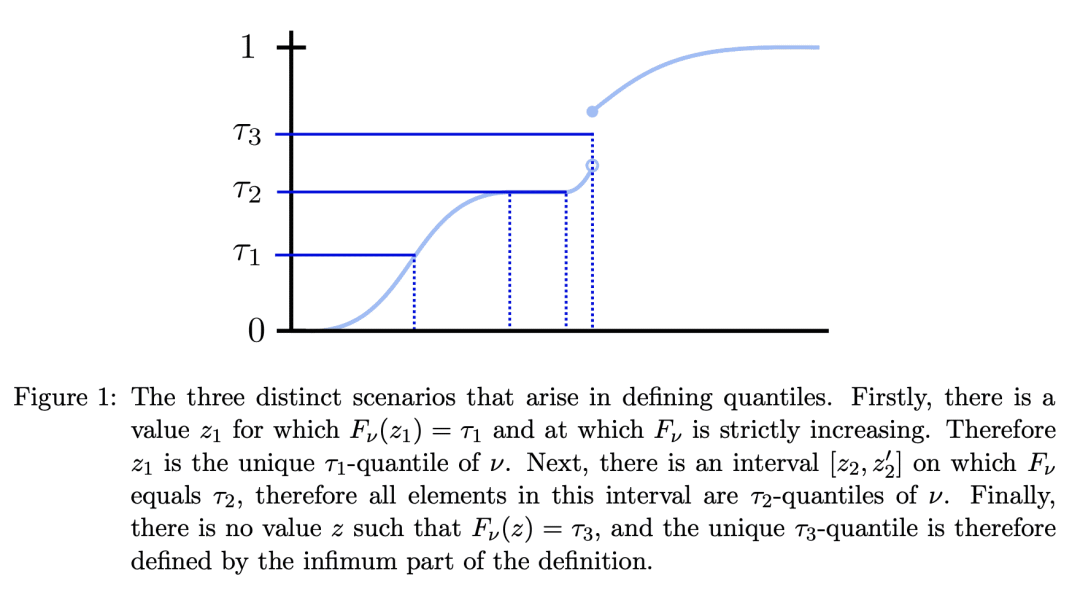
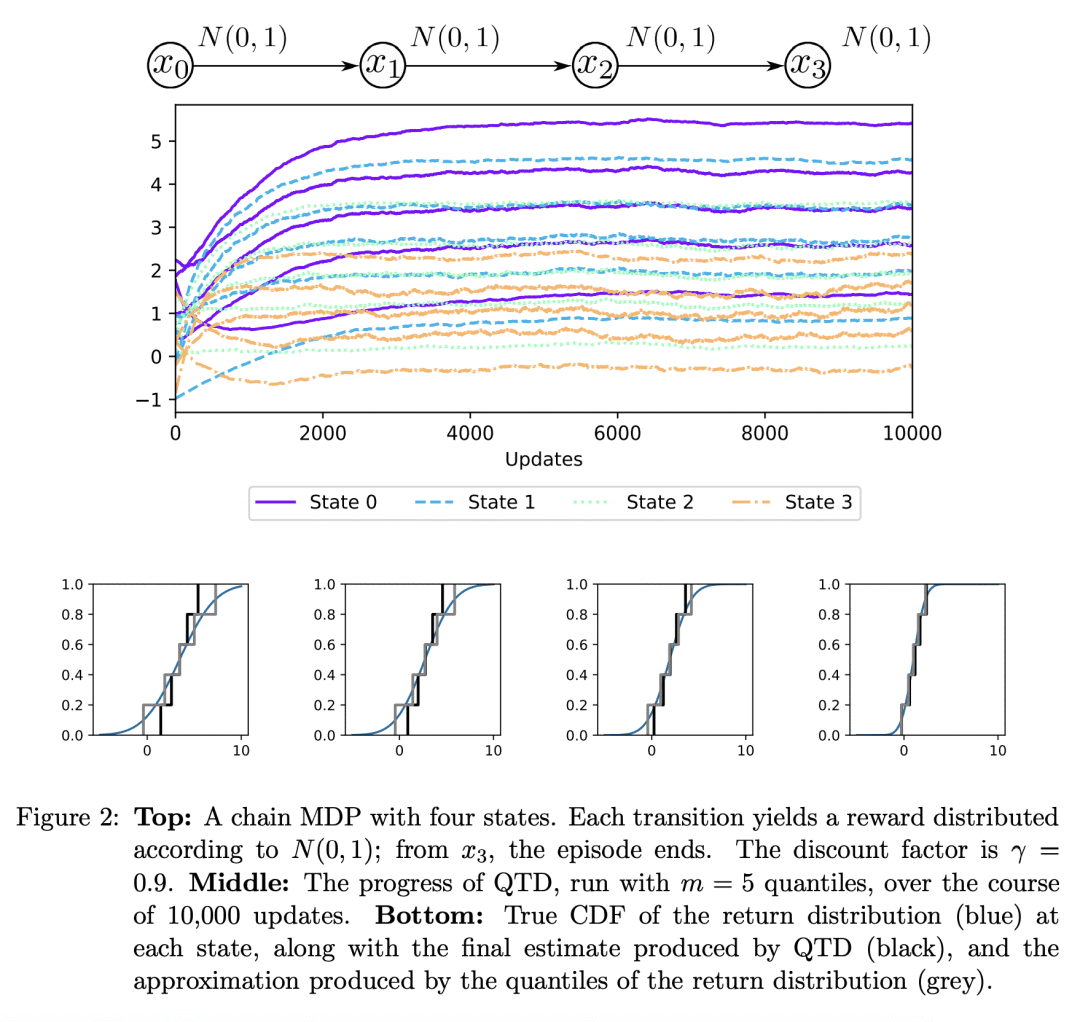
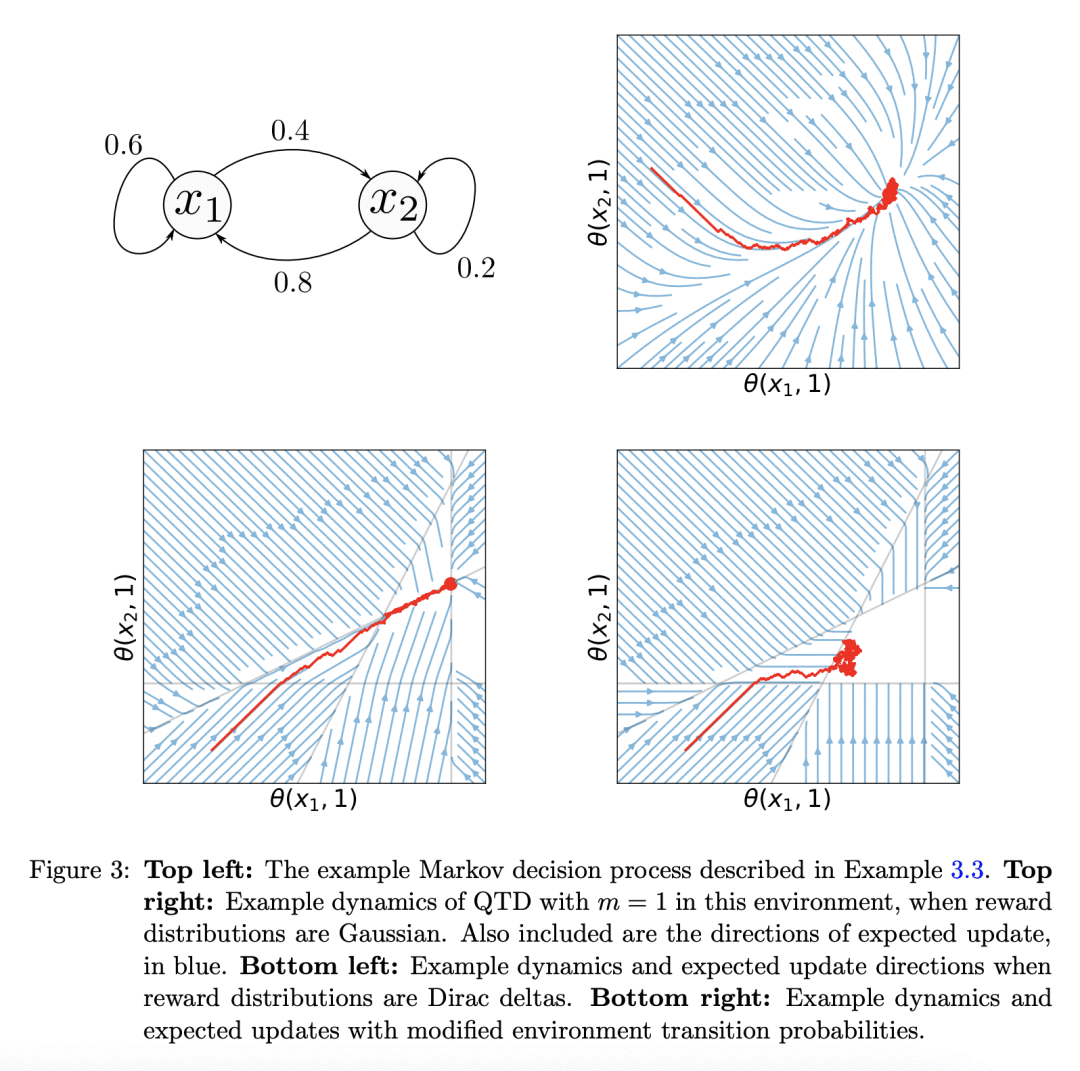
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢