来自今天的爱可可AI前沿推介
[CV] SemPPL: Predicting pseudo-labels for better contrastive representations
M Bošnjak, P H. Richemond, N Tomasev, F Strub, J C. Walker, F Hill, L H Buesing, R Pascanu, C Blundell, J Mitrovic
[DeepMind]
SemPPL: 面向更好对比性表示的伪标签预测
要点:
-
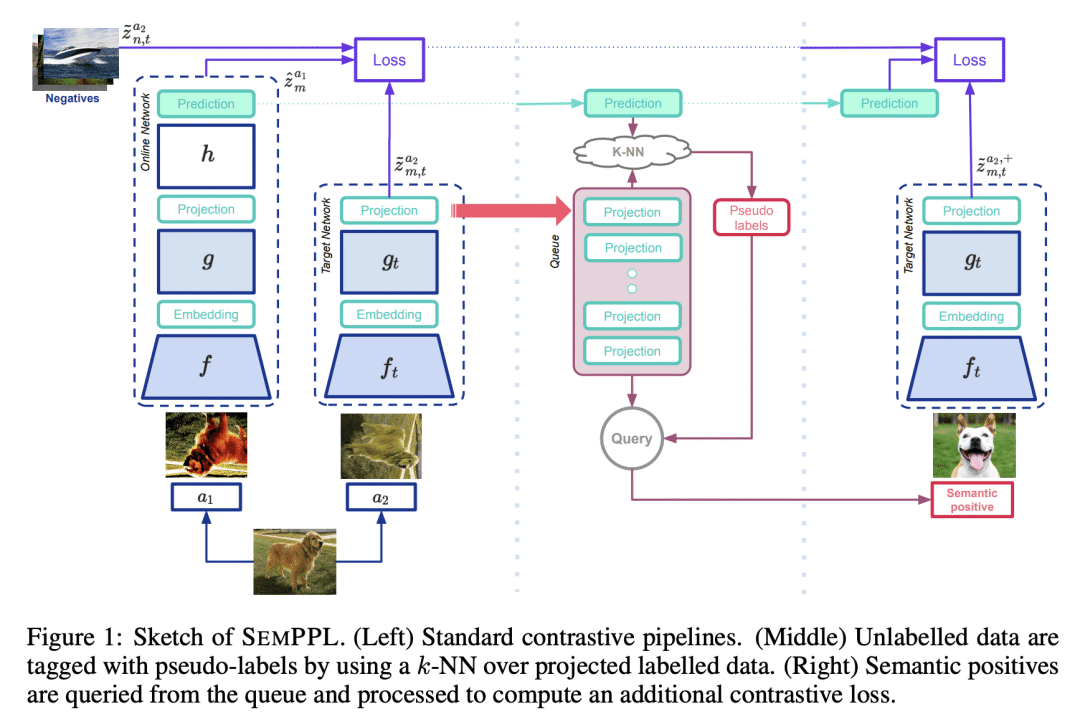
提出一种新的半监督学习方法,Semantic Positives via Pseudo-Labels (SemPPL),结合标记和无标记的数据来学习信息性表示; -
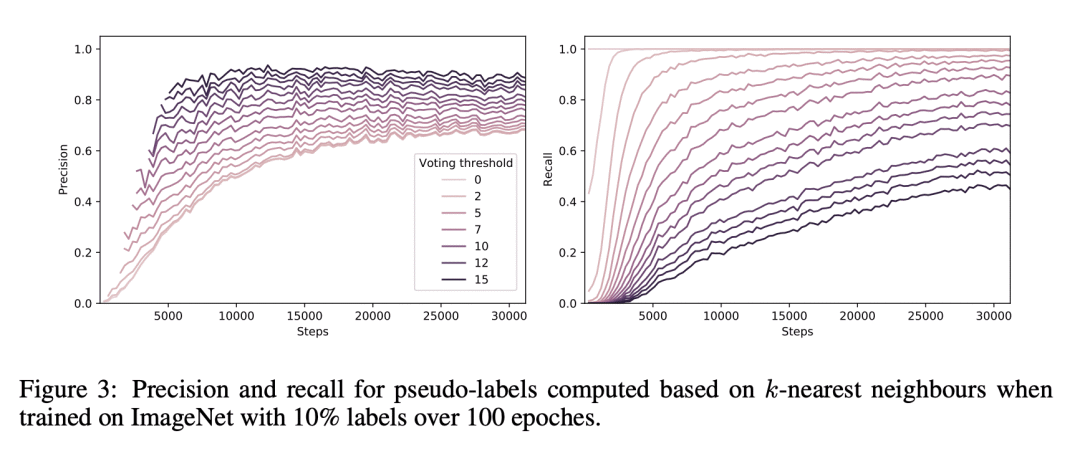
通过使用k近邻分类器来扩展自监督对比学习,以预测缺失标签(伪标签),用具有相同伪标签(语义正样本)的数据点丰富一组正样本; -
联合学习表示和预测 bootstrapped 伪标签,从而提高与竞争的半监督方法相比的性能。
一句话总结:
提出一种新的半监督学习方法Semantic Positives via Pseudo-Labels (SemPPL),结合了标记和未标记数据,通过预测缺失标签来学习信息丰富的表示,在 ImageNet 数据集上取得了新的最佳性能。
摘要:
从大量非监督数据和少量监督中学习,是计算机视觉中的一个重要开放问题。本文提出一种新的半监督学习方法,Semantic Positives via Pseudo-Labels (SemPPL)),结合了标记和无标记数据来学习信息性表示。该方法扩展了自监督对比学习——通过区分两个样本是否代表相同的底层基准(正性)来塑造表示——并采用一种选择正样本的新方法。为了丰富一组正样本,利用现有的少数真实标签,通过k近邻分类器,用标记数据的习得嵌入来预测缺失标签。用具有相同伪标签的数据点扩展正样本,叫做语义正样本。联合学习表征和预测 bootstrapped 伪标签。这创造了一个强化循环。强大的初始表示可以实现更好的伪标签预测,从而改善语义正样本的选择,并导致更好的表示。
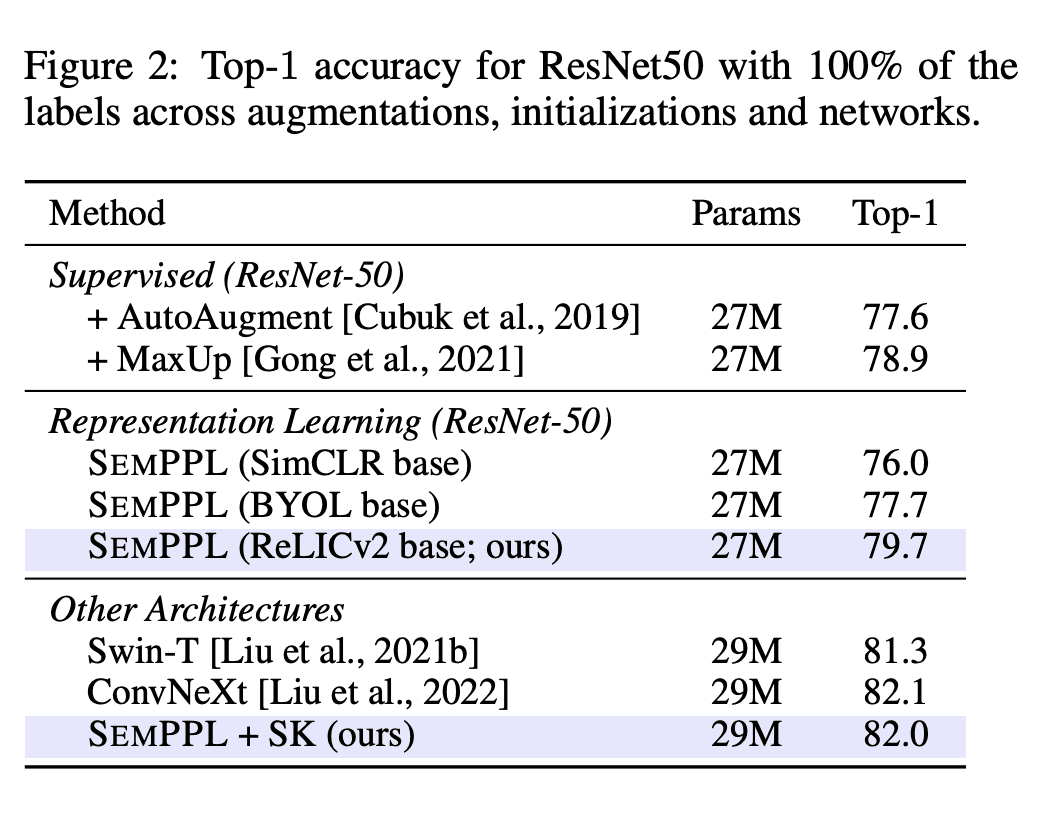
Learning from large amounts of unsupervised data and a small amount of supervision is an important open problem in computer vision. We propose a new semi-supervised learning method, Semantic Positives via Pseudo-Labels (SemPPL), that combines labelled and unlabelled data to learn informative representations. Our method extends self-supervised contrastive learning -- where representations are shaped by distinguishing whether two samples represent the same underlying datum (positives) or not (negatives) -- with a novel approach to selecting positives. To enrich the set of positives, we leverage the few existing ground-truth labels to predict the missing ones through a k-nearest neighbours classifier by using the learned embeddings of the labelled data. We thus extend the set of positives with datapoints having the same pseudo-label and call these semantic positives. We jointly learn the representation and predict bootstrapped pseudo-labels. This creates a reinforcing cycle. Strong initial representations enable better pseudo-label predictions which then improve the selection of semantic positives and lead to even better representations. SemPPL outperforms competing semi-supervised methods setting new state-of-the-art performance of 68.5% and 76% top-1 accuracy when using a ResNet-50 and training on 1% and 10% of labels on ImageNet, respectively. Furthermore, when using selective kernels, SemPPL significantly outperforms previous state-of-the-art achieving 72.3% and 78.3% top-1 accuracy on ImageNet with 1% and 10% labels, respectively, which improves absolute +7.8% and +6.2% over previous work. SemPPL also exhibits state-of-the-art performance over larger ResNet models as well as strong robustness, out-of-distribution and transfer performance.
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.05158
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢