来自今天的爱可可AI前沿推介
[LG] Improved visualization of high-dimensional data using the distance-of-distance transformation
J Liu ,M Vinck
用距离之距离变换改进高维数据可视化
要点:
-
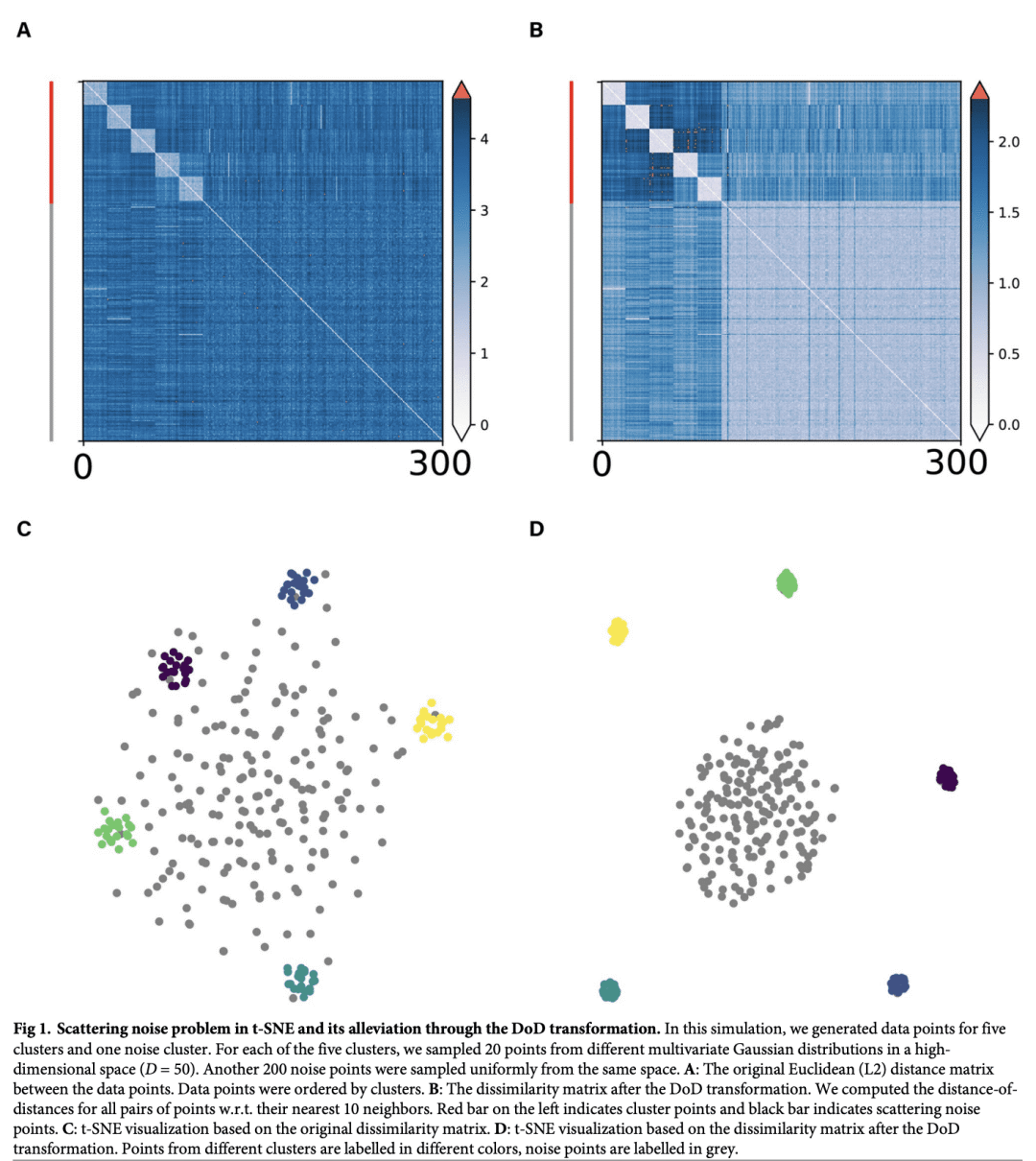
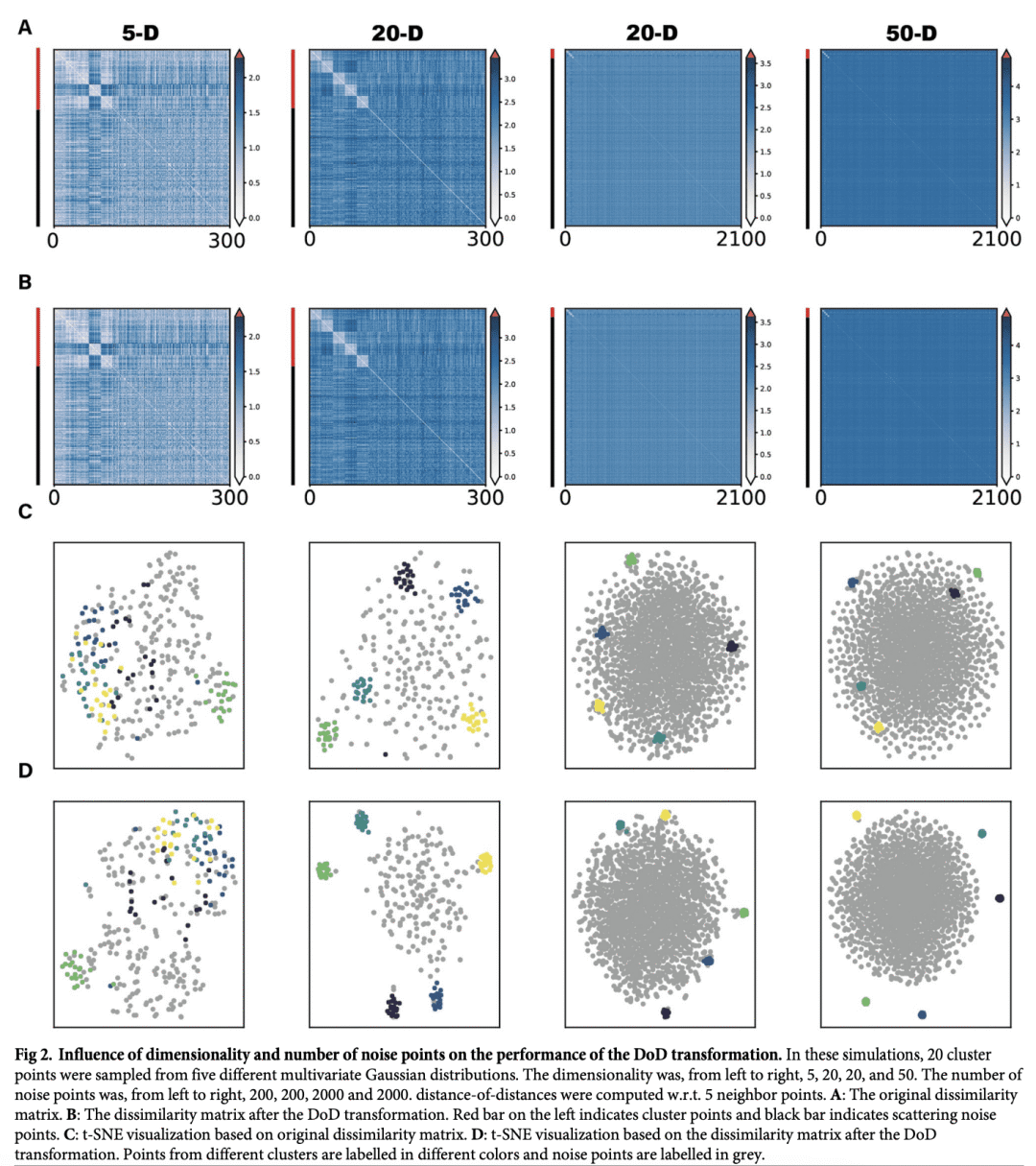
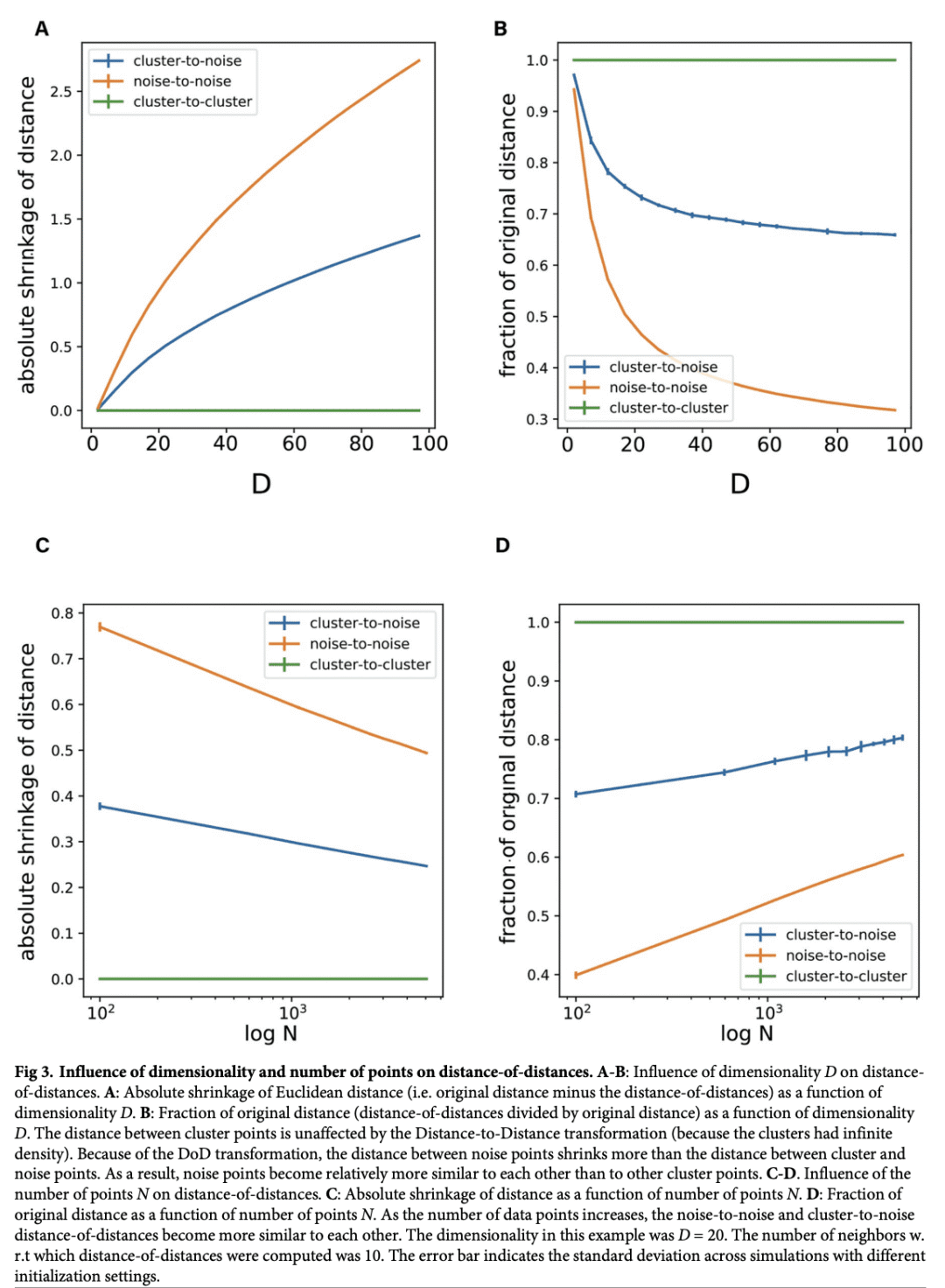
当数据包含高维空间随机分散的噪点时,低维嵌入会出现“散射噪声问题”; -
数据点之间相异度矩阵的距离之距离(DoD)变换能有效消除散射噪声的影响; -
改进了几种高维数据集的低维嵌入,如自然图像的卷积神经网络表示或视觉刺激神经元群表示。
一句话总结:
提出一种更好的含噪高维数据可视化技术,用距离之距离变换来降低噪声并改善低维嵌入,有效消除散射噪声的影响。
摘要:
t-SNE和UMAP等降维工具被广泛用于高维数据分析。本文表明,当数据包括随机分散在高维空间中的噪声点时,噪声点与聚类点重叠的低维嵌入中会出现“散射噪声问题”。通过计算近邻距离间距离的距离矩阵进行简单变换即可缓解该问题,并将噪声点识别为单独的群。将该技术应用于高维神经元尖峰序列,以及卷积神经网络单元对自然图像的表示,发现构建的低维嵌入有所改进。本文进而提出一种改进的包含噪点的高维数据降维技术。
Dimensionality reduction tools like t-SNE and UMAP are widely used for high-dimensional data analysis. For instance, these tools are applied in biology to describe spiking patterns of neuronal populations or the genetic profiles of different cell types. Here, we show that when data include noise points that are randomly scattered within a high-dimensional space, a “scattering noise problem” occurs in the low-dimensional embedding where noise points overlap with the cluster points. We show that a simple transformation of the original distance matrix by computing a distance between neighbor distances alleviates this problem and identifies the noise points as a separate cluster. We apply this technique to high-dimensional neuronal spike sequences, as well as the representations of natural images by convolutional neural network units, and find an improvement in the constructed low-dimensional embedding. Thus, we present an improved dimensionality reduction technique for high-dimensional data containing noise points.
论文链接:https://journals.plos.org/ploscompbiol/article?id=10.1371/journal.pcbi.1010764
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢