来自今天的爱可可AI前沿推介
【CV] Designing BERT for Convolutional Networks: Sparse and Hierarchical Masked Modeling
K Tian, Y Jiang, Q Diao, C Lin, L Wang, Z Yuan
[Peking University & Bytedance Inc & University of Oxford]
卷积网络的BERT预训练方法设计:稀疏和分层掩码建模
要点:
-
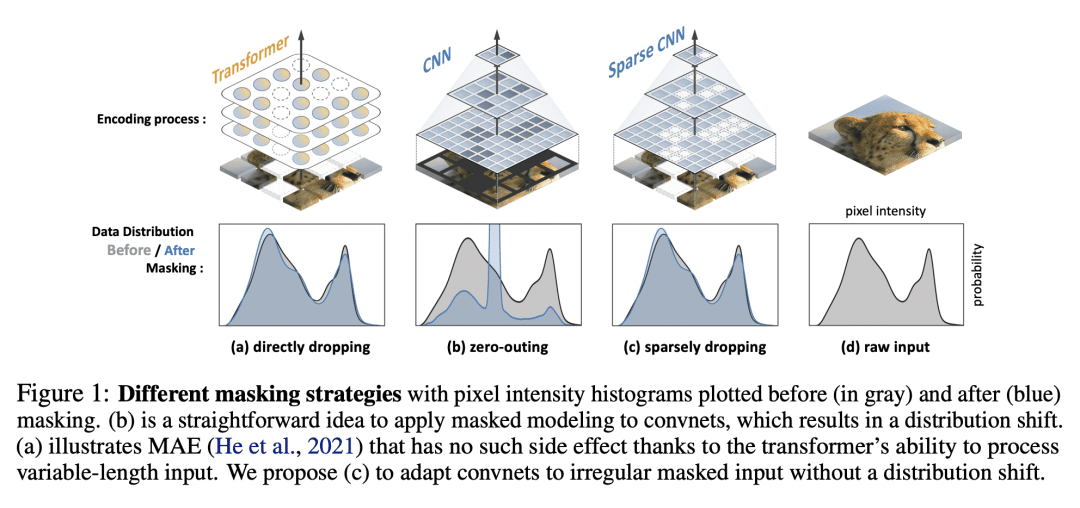
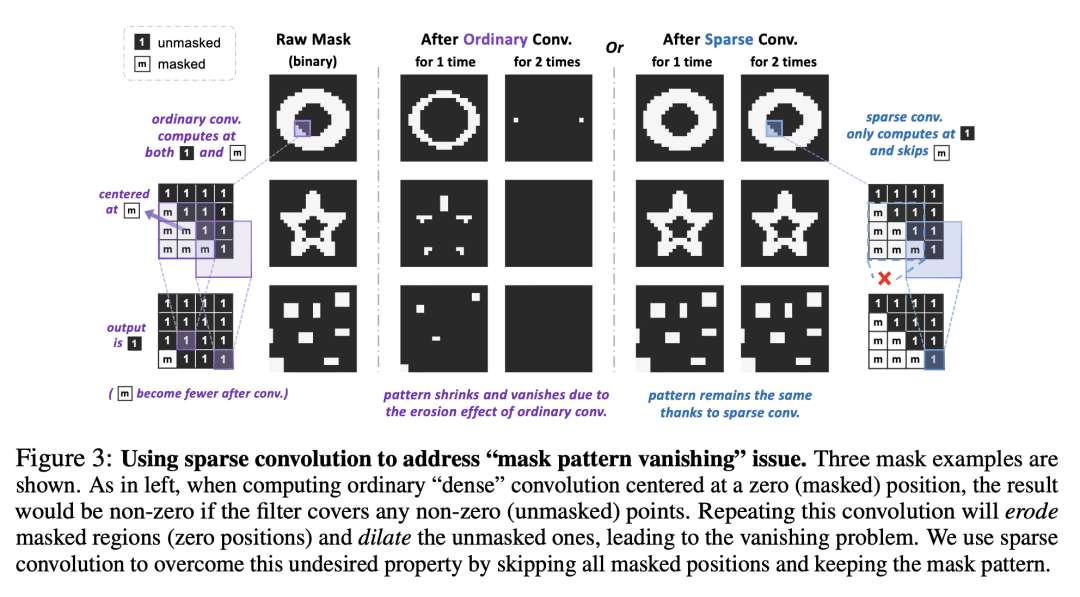
提出可以直接在任意卷积网络上使用、无需修改骨干的BERT风格预训练方法,克服其无法处理不规则掩码输入的问题; -
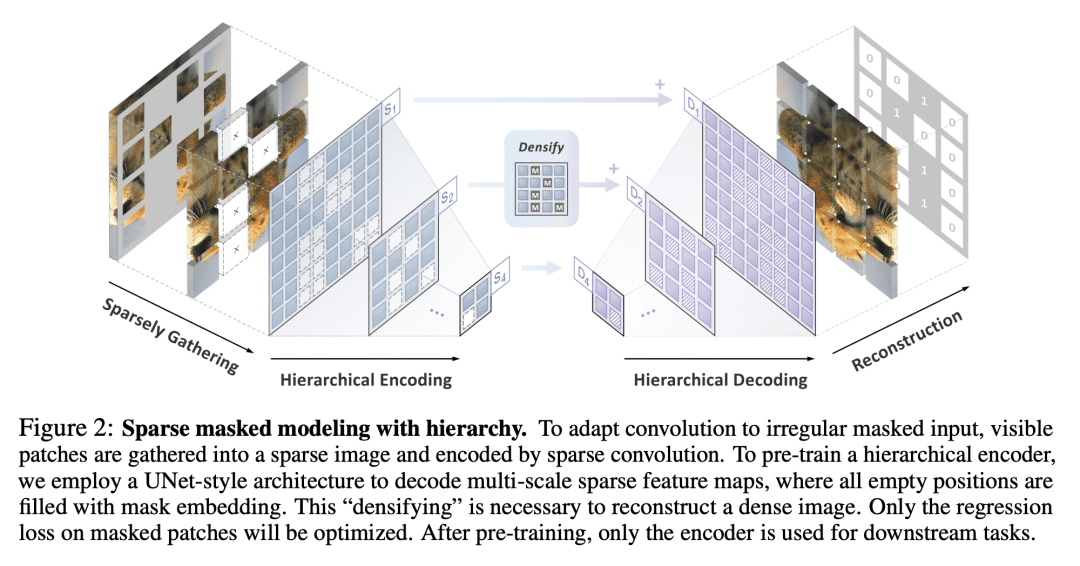
对卷积网络生成式预训练的设计洞察:掩码图像建模中稀疏卷积的使用,以及BERT风格预训练的分层设计; -
在下游任务上卷积网络性能的大幅提高(高达+3.5分),表明了将 Transformer 的预训练-微调范式扩展到卷积网络的前景。
一句话总结:
SparK是一种BERT风格的预训练方法,可以直接应用于任意卷积网络,用稀疏卷积来处理不规则的掩码输入图像,用分层解码器来利用卷积网络的分层结构,能显著提高下游任务的性能。
摘要:
本文分析并克服了将BERT风格预训练或掩码图像建模的成功扩展到卷积网络(convnet)的两个关键障碍:(i) 卷积操作无法处理不规则的随机掩码输入图像;(ii) BERT 预训练的单尺度性质与 convnet 的层次结构不一致。对于(i),将未掩码的像素视为3D点云的稀疏体素,用稀疏卷积进行编码。这是首次使用稀疏卷积进行二维掩码建模。对于(ii),本文提出一个分层解码器,以从多尺度编码特征重建图像。称为Sparse masKed建模(SparK)的方法很通用:可以直接用于任意卷积模型,而无需进行骨干修改。在经典(ResNet)和现代(ConvNeXt)模型上验证了它:在三个下游任务中,它以类似的大幅度(约+1.0%)超越了最先进的对比学习和基于 Transformer 的掩码建模。目标检测和实例分割的改进更加显著(高达+3.5%),验证了所学特征的强大可迁移性。本文还通过在更大模型上观察到更多收益,发现其有利的缩放行为。所有这些证据都揭示了在convnets上进行生成式预训练的有希望的未来。
We identify and overcome two key obstacles in extending the success of BERT-style pre-training, or the masked image modeling, to convolutional networks (convnets): (i) convolution operation cannot handle irregular, random-masked input images; (ii) the single-scale nature of BERT pre-training is inconsistent with convnet's hierarchical structure. For (i), we treat unmasked pixels as sparse voxels of 3D point clouds and use sparse convolution to encode. This is the first use of sparse convolution for 2D masked modeling. For (ii), we develop a hierarchical decoder to reconstruct images from multi-scale encoded features. Our method called Sparse masKed modeling (SparK) is general: it can be used directly on any convolutional model without backbone modifications. We validate it on both classical (ResNet) and modern (ConvNeXt) models: on three downstream tasks, it surpasses both state-of-the-art contrastive learning and transformer-based masked modeling by similarly large margins (around +1.0%). Improvements on object detection and instance segmentation are more substantial (up to +3.5%), verifying the strong transferability of features learned. We also find its favorable scaling behavior by observing more gains on larger models. All this evidence reveals a promising future of generative pre-training on convnets.
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.03580
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢