来自今天的爱可可AI前沿推介
[CL] Curriculum Script Distillation for Multilingual Visual Question Answering
K R Chandu, A Geramifard
[Meta & Allen Institute of AI]
多语种视觉问答的课程文字蒸馏
要点:
-
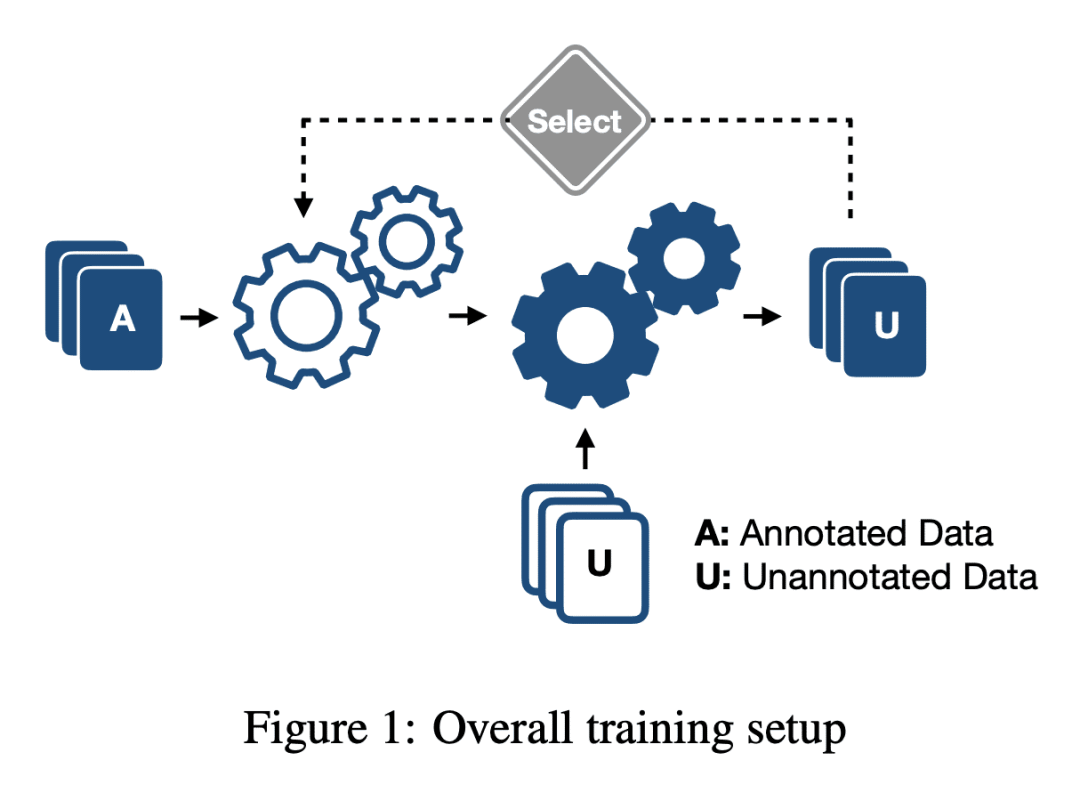
提出课程学习策略,以模拟多语言问题,以单一语言访问黄金标注数据,在多个微调阶段在源和目标之间调度不同的语言; -
表明模型在与英语具有相同字母系统的目标语言中表现相对较好,如罗马文字,与具有不同字母系统的语言相比; -
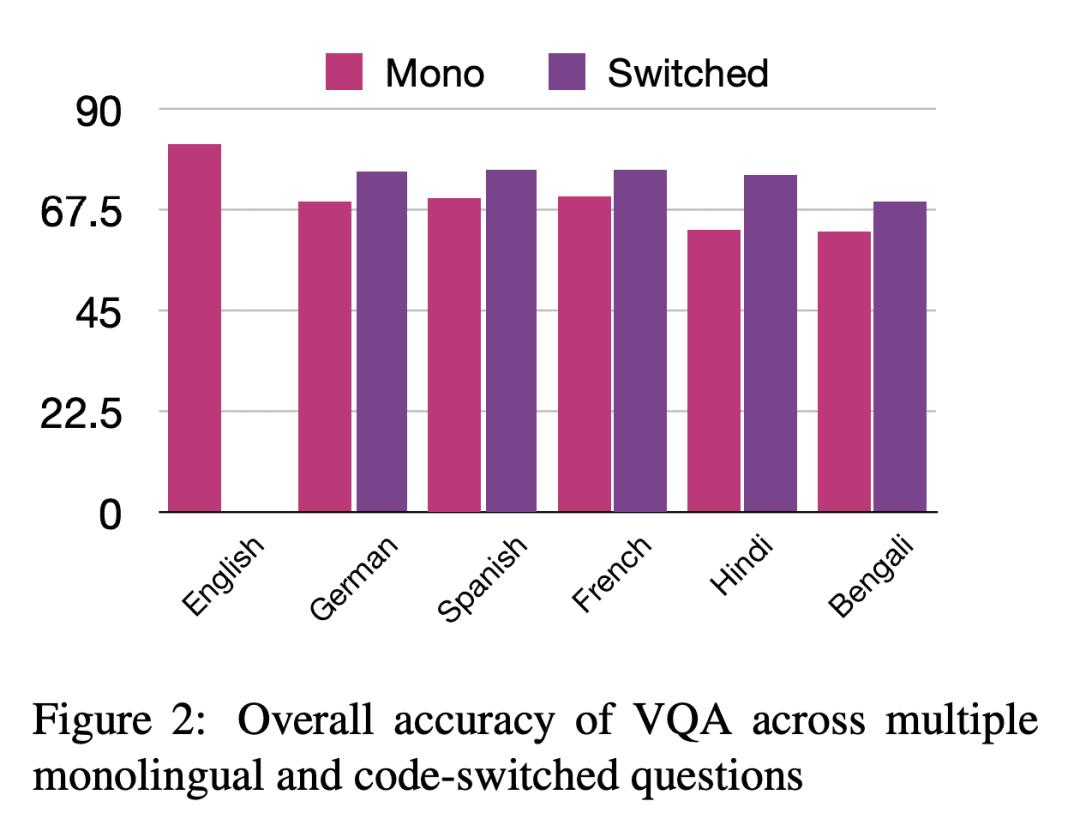
与单语上下文相比,代码交换情况下的部分罗马文字上下文有助于提高性能。
一句话总结:
提出一种多语言 VQA 课程学习策略,该策略在微调期间用语言基于字母系统的调度,有效提高了具有类似字母系统和部分罗马字符化代码交换语言的目标语言性能,还探索了混合脚本用于训练多语言模型的潜力。
摘要:
基于双编码器和交叉编码器的预训练模型,在视觉问答(VQA)中提升视觉和语言的多项任务方面取得了显著成功。然而,由于它们受到黄金标注数据要求的限制,因此大多数这些进步很少迁移到英语以外的其他语言。本文的目标是通过引入基于源语言和目标语言翻译的课程来解决该问题,以微调下游任务的预训练模型。实验结果表明,字母系统在这些模型的性能中起着至关重要的作用。本文表明,共享相同字母系统的目标语言比其他语言表现更好 (~6%),混合字母系统代码切换语言的表现优于对应语言 (~5-12%)。
Pre-trained models with dual and cross encoders have shown remarkable success in propelling the landscape of several tasks in vision and language in Visual Question Answering (VQA). However, since they are limited by the requirements of gold annotated data, most of these advancements do not see the light of day in other languages beyond English. We aim to address this problem by introducing a curriculum based on the source and target language translations to finetune the pre-trained models for the downstream task. Experimental results demonstrate that script plays a vital role in the performance of these models. Specifically, we show that target languages that share the same script perform better (~6%) than other languages and mixed-script code-switched languages perform better than their counterparts (~5-12%).
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.07227
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢