来自今天的爱可可AI前沿推介
[LG] Imitating Human Behaviour with Diffusion Models
T Pearce, T Rashid, A Kanervisto, D Bignell, M Sun, R Georgescu, S V Macua, S Z Tan, I Momennejad, K Hofmann, S Devlin
[Microsoft Research]
基于扩散模型的人类行为模仿
要点:
-
研究了用扩散模型作为观察-到-行动的模型,来模仿连续环境中的人类行为; -
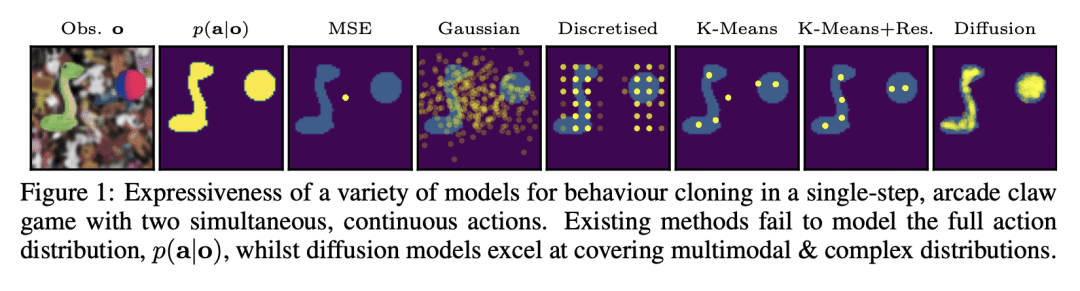
扩散模型很适合模仿人类行为,因为其在联合行动空间上学习到一种表达式分布,与行为克隆中的许多现有建模选择不同; -
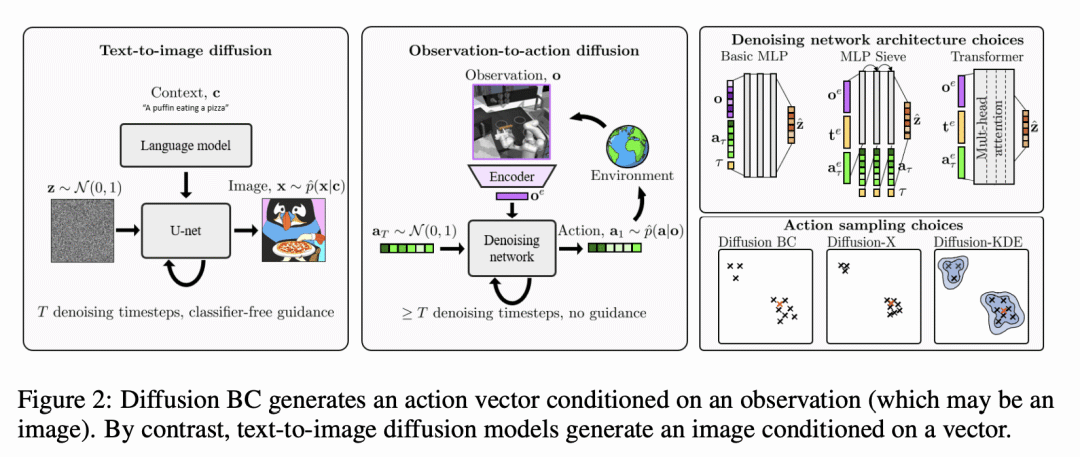
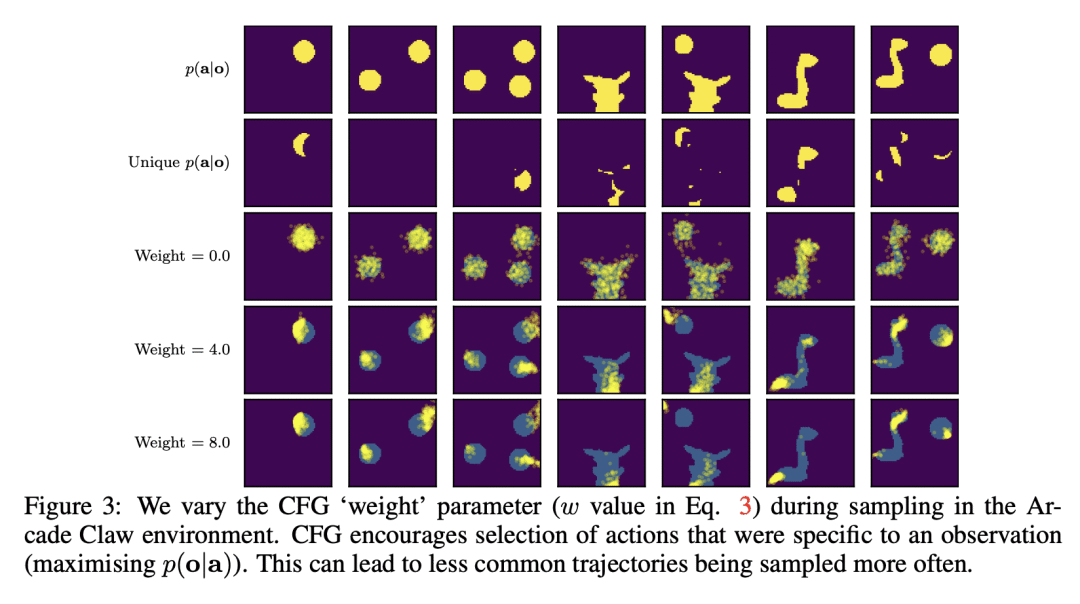
提出了使扩散模型适应观察-到-行动领域的几个创新,如合适的架构、指导和采样策略。
一句话总结:
研究了用扩散模型作为观察-到-行动的模型,来模仿连续环境中的人类行为,并提出一些创新,以使扩散模型适应该领域,从而比现有的方法提高了性能,并有可能将模型应用于复杂的真实世界环境。
摘要:
扩散模型作为强大的生成模型,在文本-到-图像领域崭露头角。本文研究了其作为观察-到-行动模型在连续环境中模仿人类行为的应用。人类行为是随机的和多模态的,行动维度之间有结构化的关联。同时,行为克隆中的标准建模选择,在其表现力方面是有限的,并可能将偏差引入克隆策略中。本文指出这些选择的局限性,提出扩散模型是模仿人类行为的最佳选择,因为其在联合行动空间中学到了一种表达式分布。本文引入了一些创新,使扩散模型适用于连续环境;设计合适的架构,调研指导的作用,并开发可靠的采样策略。在实验中,扩散模型与人类在模拟机器人控制任务和现代 3D 游戏环境中的表现相匹配。
Diffusion models have emerged as powerful generative models in the text-to-image domain. This paper studies their application as observation-to-action models for imitating human behaviour in sequential environments. Human behaviour is stochastic and multimodal, with structured correlations between action dimensions. Meanwhile, standard modelling choices in behaviour cloning are limited in their expressiveness and may introduce bias into the cloned policy. We begin by pointing out the limitations of these choices. We then propose that diffusion models are an excellent fit for imitating human behaviour, since they learn an expressive distribution over the joint action space. We introduce several innovations to make diffusion models suitable for sequential environments; designing suitable architectures, investigating the role of guidance, and developing reliable sampling strategies. Experimentally, diffusion models closely match human demonstrations in a simulated robotic control task and a modern 3D gaming environment.
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.10677

内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢