论文名称:DetectGPT: Zero-Shot Machine-Generated Text Detection using Probability Curvature
作者:Eric Mitchell, Yoonho Lee, Alexander Khazatsky, Christopher D. Manning, Chelsea Finn
摘要
大型语言模型 (LLM) 的流畅性和事实知识,相应系统检测一段文本是否为机器编写的需求越来越多。 例如,学生可能会使用 LLM 来完成书面作业,从而使教师无法准确评估学生的学习情况。 在本文中,我们首先证明从 LLM 采样的文本倾向于占据模型对数概率函数的负曲率区域。 利用这一观察结果,我们随后定义了一个新的基于曲率的标准来判断一段文章是否从给定的 LLM 生成。 名为 DetectGPT 的方法不需要训练单独的分类器、收集真实或生成的段落的数据集,或显式地为生成的文本加水印。 它仅使用感兴趣模型计算的对数概率和来自另一个通用预训练语言模型(例如 T5)段落的随机扰动。 我们发现 DetectGPT 比现有的模型样本检测零样本方法更具辨别力,将 20B 参数 GPT-NeoX 生成的假新闻文章的检测从最强零样本基线的 0.81 AUROC 显著提高到 DetectGPT 的 0.95 AUROC。 有关代码、数据和其他项目信息,请访问: https://ericmitchell.ai/detectgpt/ 。
The fluency and factual knowledge of large language models (LLMs) heightens the need for corresponding systems to detect whether a piece of text is machine-written. For example, students may use LLMs to complete written assignments, leaving instructors unable to accurately assess student learning. In this paper, we first demonstrate that text sampled from an LLM tends to occupy negative curvature regions of the model's log probability function. Leveraging this observation, we then define a new curvature-based criterion for judging if a passage is generated from a given LLM. This approach, which we call DetectGPT, does not require training a separate classifier, collecting a dataset of real or generated passages, or explicitly watermarking generated text. It uses only log probabilities computed by the model of interest and random perturbations of the passage from another generic pre-trained language model (e.g, T5). We find DetectGPT is more discriminative than existing zero-shot methods for model sample detection, notably improving detection of fake news articles generated by 20B parameter GPT-NeoX from 0.81 AUROC for the strongest zero-shot baseline to 0.95 AUROC for DetectGPT. See this https URL for code, data, and other project information.
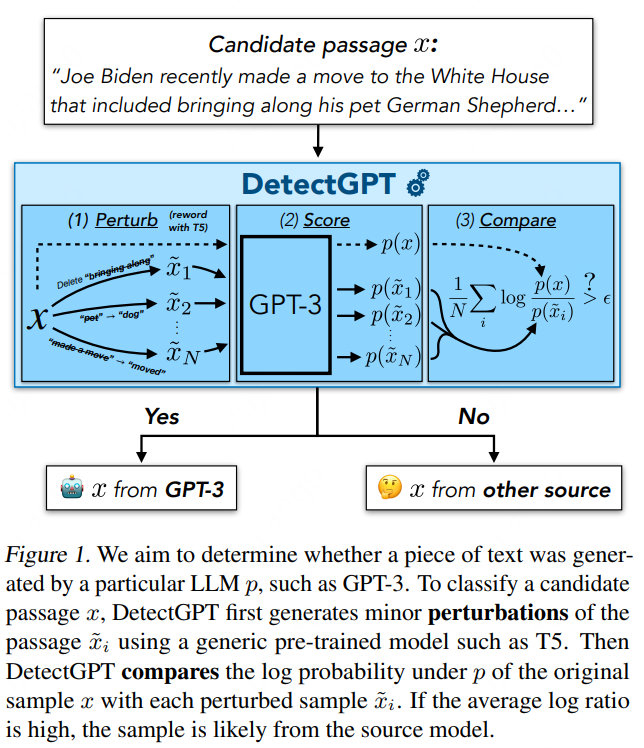
论文中最核心的说明思路的图:
参考
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢