来自今天的爱可可AI前沿推介
[CV] Leveraging the Third Dimension in Contrastive Learning
S Aithal, A Goyal, A Lamb, Y Bengio, M Mozer
[Universite de Montreal & Microsoft Research & Google Research]
在对比学习中利用第三维度
要点:
-
提出两种不同的方法来改善单目 RGB 图像的深度信号自监督学习(SSL); -
第一种方法将深度图和图像级联起来,产生 RGB+D 输入到SSL。第二种方法从深度信号中生成 3D 视图,用于对比学习; -
两种方法都提高了3种对比学习方法(BYOL、SimSiam和SwAV)在ImageNette、ImageNet-100和ImageNet-1k 数据集上的性能。
一句话总结:
提出两种方法,用从单目RGB图像中提取的含噪深度信号来改善自监督学习(SSL),用三种不同的 SSL 方法提高了多个数据集的准确性和鲁棒性。
摘要:
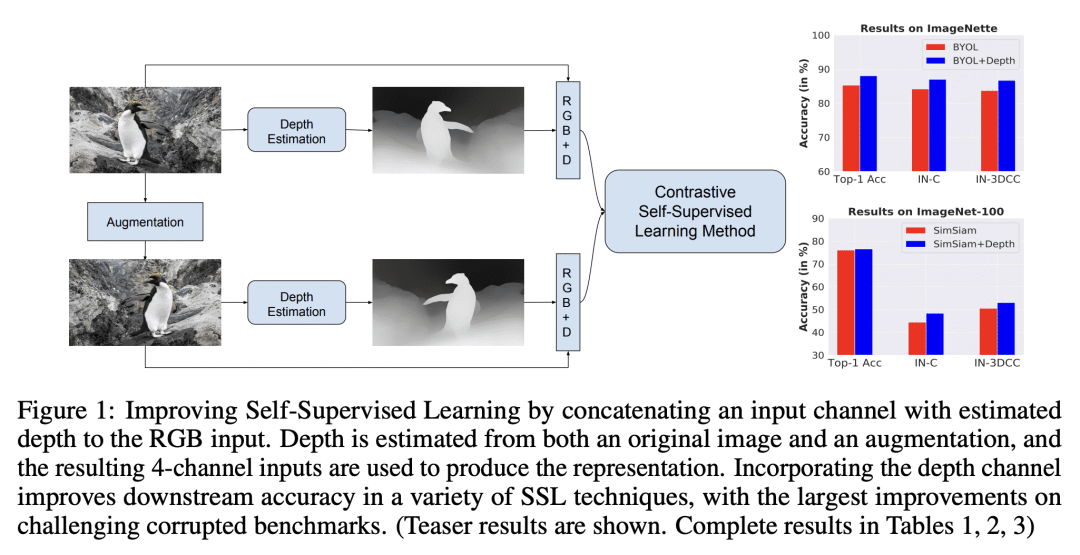
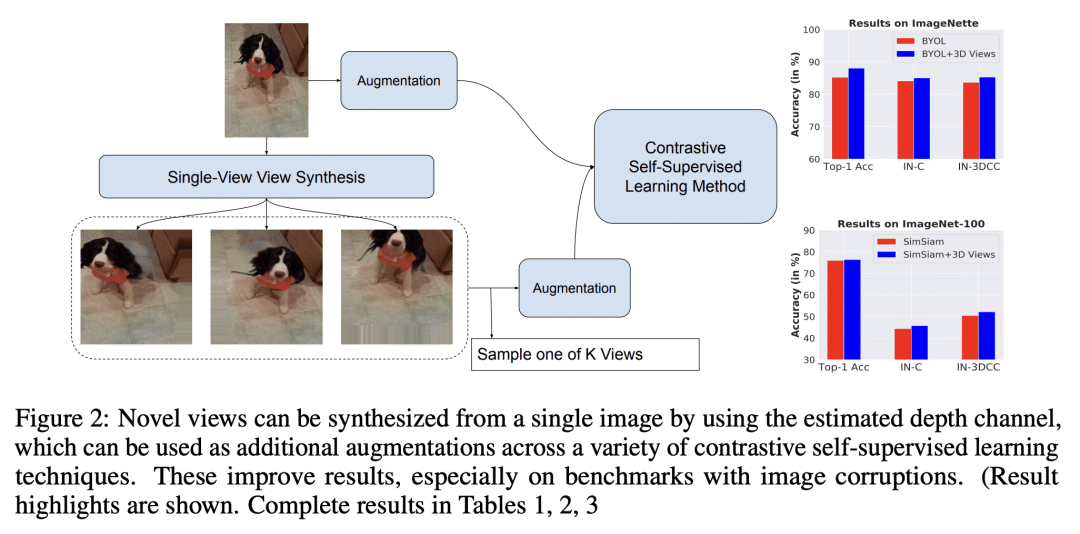
自监督学习(SSL)方法对无标记数据进行操作,以学习对下游任务有用的鲁棒表示。大多数SSL方法依赖于通过变换 2D 图像像素图获得的增强。这些增强方法忽略了这样一个事实,即生物视觉是在一个沉浸式的 3D 的、时间上连续的环境中进行的,而低层次的生物视觉在很大程度上依赖于深度线索。利用预训练好的最先进的单目 RGB-到-深度模型(Depth Prediction Transformer)提供的信号,本文探索了两种不同的方法,将深度信号纳入 SSL 框架。评估了使用 RGB+深度输入表示的对比学习。使用深度信号从稍微不同的相机位置生成新视图,从而为对比学习产生一个 3D 增强。用ImageNette(ImageNet的10类子集)、ImageNet-100和ImageNet-1k数据集对三种不同的SSL方法——BYOL、SimSiam和SwAV——进行评估。发现纳入深度信号的两种方法,都提高了基线 SSL 方法的鲁棒性和泛化性,第一种方法(有深度通道连接)更有优势。例如,带有额外深度通道的 BYOL 实现了下游分类精度的提高,在ImageNette上从85.3%提高到88.0%,在ImageNet-C上从84.1%提高到87.0%。
Self-Supervised Learning (SSL) methods operate on unlabeled data to learn robust representations useful for downstream tasks. Most SSL methods rely on augmentations obtained by transforming the 2D image pixel map. These augmentations ignore the fact that biological vision takes place in an immersive three-dimensional, temporally contiguous environment, and that low-level biological vision relies heavily on depth cues. Using a signal provided by a pretrained state-of-the-art monocular RGB-to-depth model (the \emph{Depth Prediction Transformer}, Ranftl et al., 2021), we explore two distinct approaches to incorporating depth signals into the SSL framework. First, we evaluate contrastive learning using an RGB+depth input representation. Second, we use the depth signal to generate novel views from slightly different camera positions, thereby producing a 3D augmentation for contrastive learning. We evaluate these two approaches on three different SSL methods -- BYOL, SimSiam, and SwAV -- using ImageNette (10 class subset of ImageNet), ImageNet-100 and ImageNet-1k datasets. We find that both approaches to incorporating depth signals improve the robustness and generalization of the baseline SSL methods, though the first approach (with depth-channel concatenation) is superior. For instance, BYOL with the additional depth channel leads to an increase in downstream classification accuracy from 85.3% to 88.0% on ImageNette and 84.1% to 87.0% on ImageNet-C.
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.11790
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢