Extracting Training Data from Diffusion Models
N Carlini, J Hayes, M Nasr, M Jagielski, V Sehwag, F Tramèr, B Balle, D Ippolito, E Wallace
[Google & DeepMind & ETHZ & Princeton & UC Berkeley]
从扩散模型提取训练数据
要点:
-
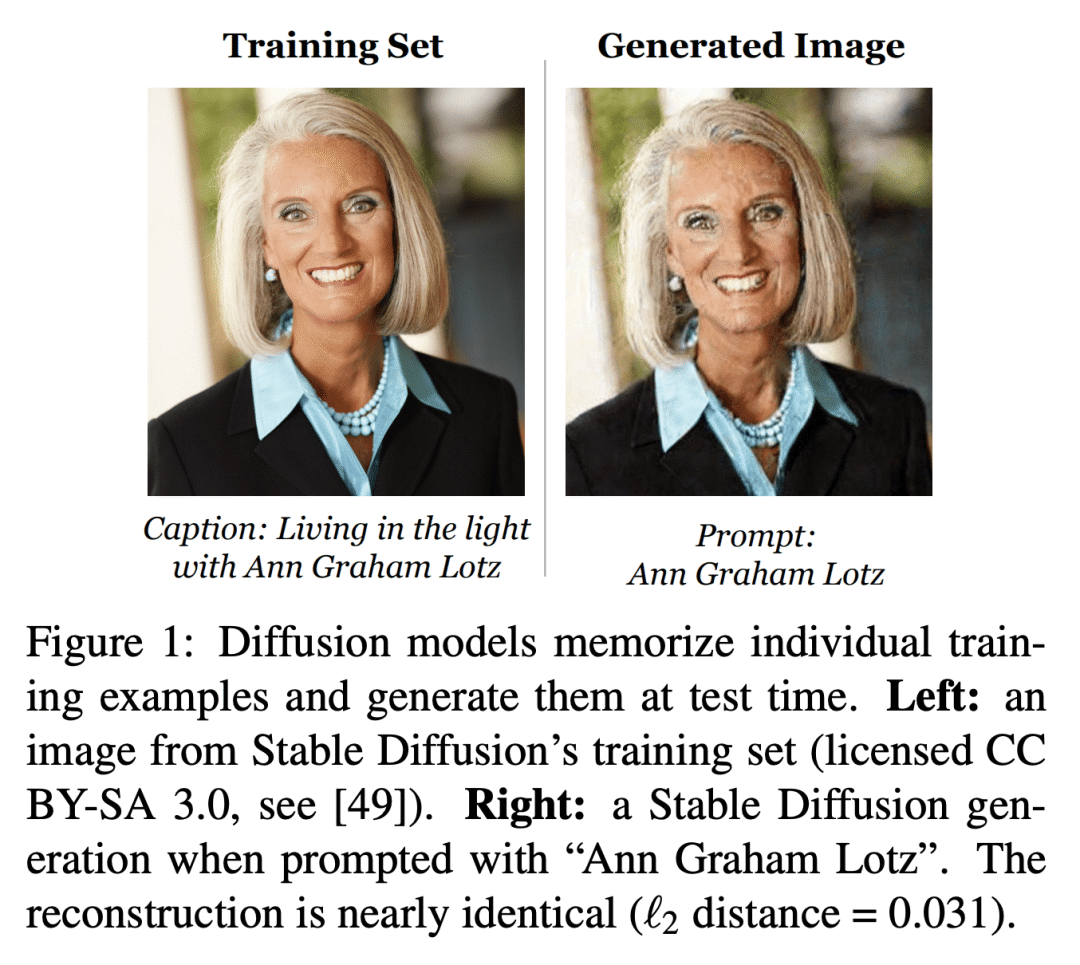
最先进的扩散模型(如DALL-E 2、Imagen和Stable Diffusion)容易受到记忆攻击,并在生成时吐出记忆的单个训练图像; -
提出并实现了图像模型中记忆的新定义,并演示了一种数据提取攻击; -
分析了模型精度、超参数、增强和重复数据删除对隐私的影响,发现扩散模型是最不私密的图像模型形式,泄露的训练数据是 GAN 的两倍以上。
一句话总结:
本文证明,最先进的扩散模型容易受到记忆攻击,并吐出记忆的个人训练图像,突出了强大的生成模型和数据隐私之间的矛盾。
论文地址:https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.13188
摘要:
图像扩散模型,如DALL-E 2、Imagen 和 Stable Diffusion,由于其生成高质量合成图像的能力而引起了极大的关注。本文展示了扩散模型从其训练数据中记忆单个图像,并在生成时将其吐出。通过生成-过滤管道,从最先进的模型中提取了一千多个训练样本,从个人照片到公司注册Logo。本文还在不同的环境中训练了数百个扩散模型,以分析不同的建模和数据决定如何影响隐私。本文结果表明,扩散模型的隐私性远远低于之前的生成模型,如GAN,并且减轻这些漏洞可能需要在保护隐私的训练方面取得新的进展。
Image diffusion models such as DALL-E 2, Imagen, and Stable Diffusion have attracted significant attention due to their ability to generate high-quality synthetic images. In this work, we show that diffusion models memorize individual images from their training data and emit them at generation time. With a generate-and-filter pipeline, we extract over a thousand training examples from state-of-the-art models, ranging from photographs of individual people to trademarked company logos. We also train hundreds of diffusion models in various settings to analyze how different modeling and data decisions affect privacy. Overall, our results show that diffusion models are much less private than prior generative models such as GANs, and that mitigating these vulnerabilities may require new advances in privacy-preserving training.



内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢