Multimodal Chain-of-Thought Reasoning in Language Models
Z Zhang, A Zhang, M Li, H Zhao, G Karypis, A Smola
[Shanghai Jiao Tong University & Amazon Web Services]
要点:
-
多模态思维链推理问题的正式研究;
-
提出了一种两阶段框架,用于微调语言模型以纳入视觉信号;
-
在ScienceQA基准上取得新的最先进性能。
提出一种新方法——多模态CoT,通过对基于视觉和语言特征的小型语言模型进行微调,在多模态中进行思维链(CoT)推理,从而在ScienceQA基准上获得最先进的性能。
Github地址:https://github.com/amazon-science/mm-cot
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2302.00923
摘要:
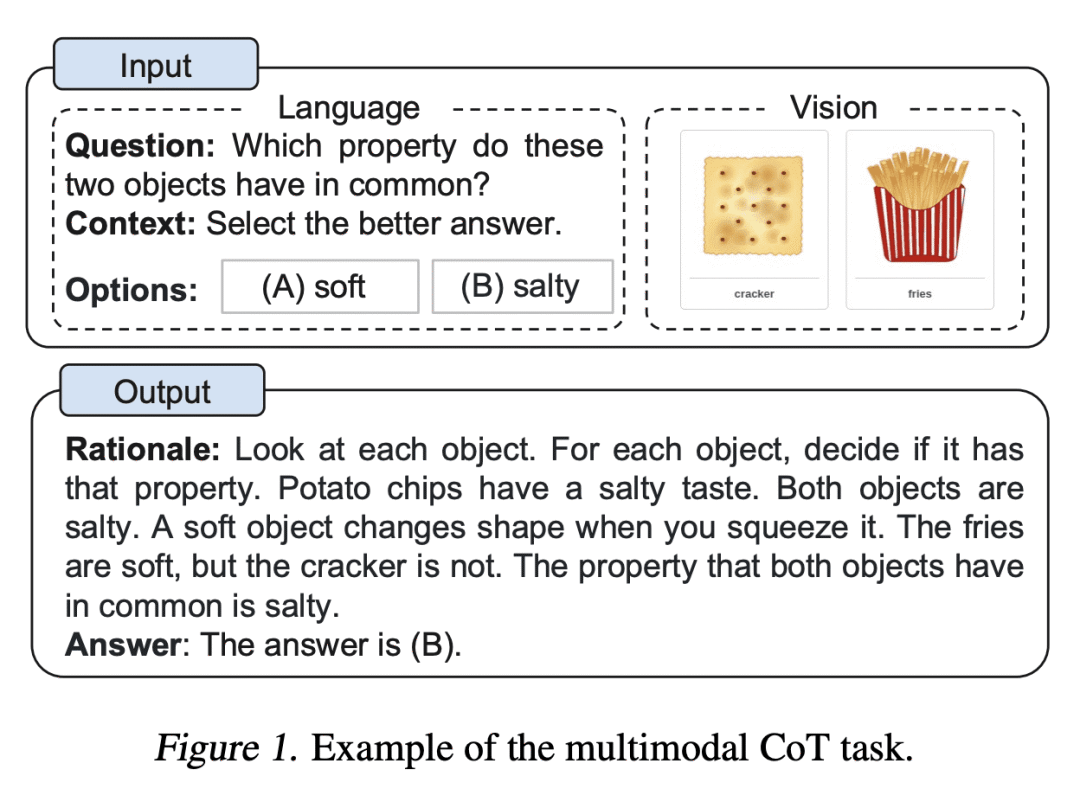
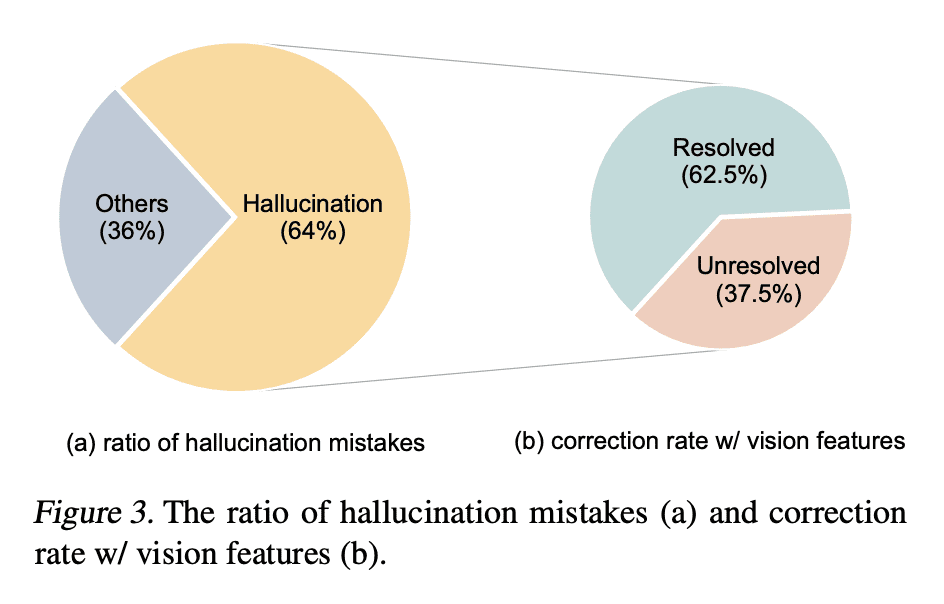
大型语言模型(LLM)通过利用思维链(CoT)提示,生成中间推理链作为推断答案的依据,在复杂推理上表现出令人印象深刻的性能。然而,现有的CoT研究大多是隔离在LLM语言模态下,LLM很难部署。为了在多模态中引出CoT推理,一个可能的解决方案是通过融合视觉和语言特征来微调小的语言模型来进行CoT推理。关键的挑战是,这些语言模型往往会产生幻觉推理链,误导答案推理。为了减轻这种错误的影响,本文提出多模态CoT,在一个解耦的训练框架中加入了视觉特征。该框架将原理生成和答案推理分成两个阶段。通过将视觉特征纳入这两个阶段,该模型能生成有助于答案推理的有效理由。通过Multimodal-CoT,所提出模型在10亿个参数下比以前最先进的LLM(GPT-3.5)在ScienceQA基准上的表现高出16%(75.17%->91.68%),甚至超过了人类的表现。
Large language models (LLMs) have shown impressive performance on complex reasoning by leveraging chain-of-thought (CoT) prompting to generate intermediate reasoning chains as the rationale to infer the answer. However, existing CoT studies are mostly isolated in the language modality with LLMs, where LLMs are hard to deploy. To elicit CoT reasoning in multimodality, a possible solution is to fine-tune small language models by fusing the vision and language features to perform CoT reasoning. The key challenge is that those language models tend to generate hallucinated reasoning chains that mislead the answer inference. To mitigate the effect of such mistakes, we propose Multimodal-CoT that incorporates vision features in a decoupled training framework. The framework separates the rationale generation and answer inference into two stages. By incorporating the vision features in both stages, the model is able to generate effective rationales that contribute to answer inference. With Multimodal-CoT, our model under 1 billion parameters outperforms the previous state-of-the-art LLM (GPT-3.5) by 16% (75.17%->91.68%) on the ScienceQA benchmark and even surpasses human performance.


内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢