来自今天的爱可可AI前沿推介
[CL] Crawling the Internal Knowledge-Base of Language Models
R Cohen, M Geva, J Berant, A Globerson
[Tel Aviv University & Allen Institute for AI]
爬取语言模型内在知识库
要点:
-
提出一种从语言模型中提取结构化知识图谱的方法; -
使用专门设计的提示来控制提取过程中的精度和召回率; -
在GPT-3上进行了评估,显示了高精确度的结果。
一句话总结:
提出一种从语言模型中提取结构化知识图谱的方法,用GPT-3的高精度结果证明了其有效性。
摘要:
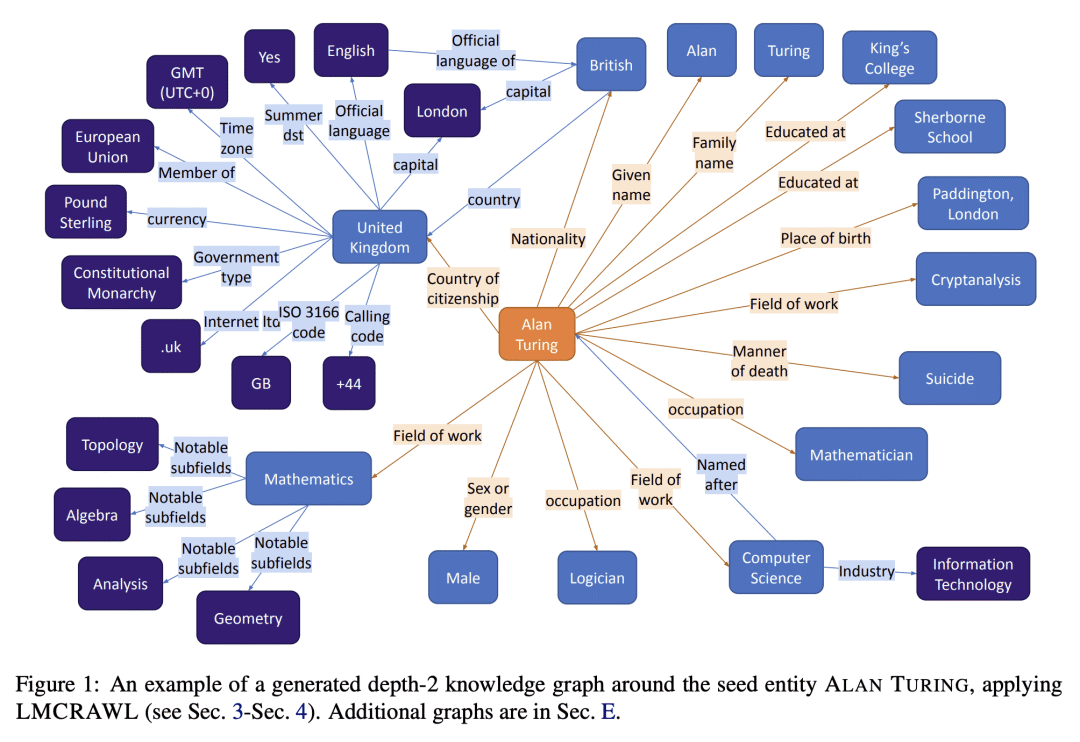
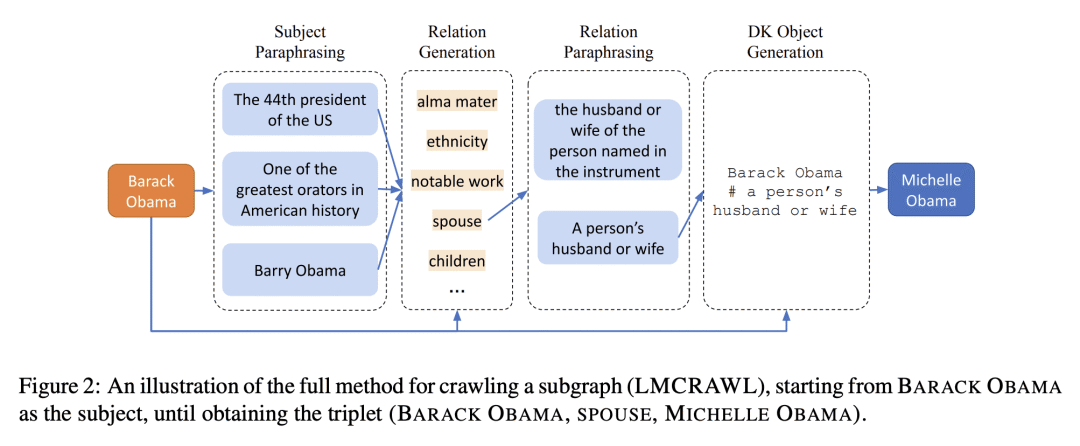
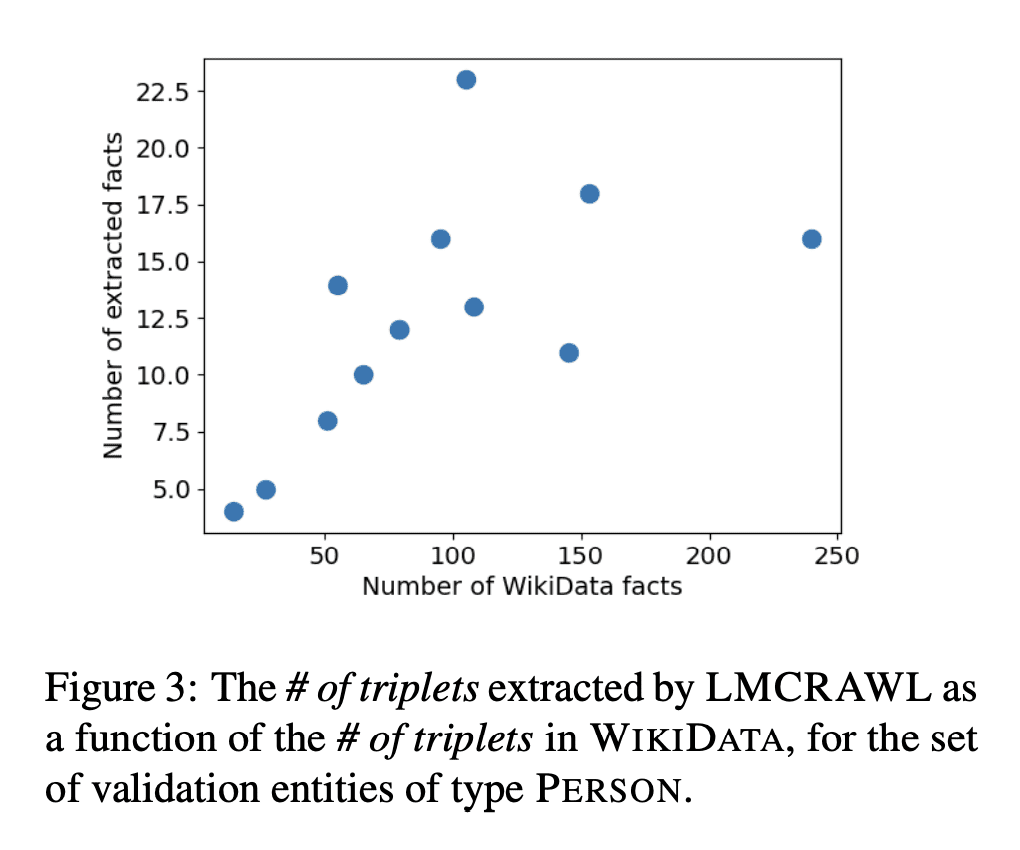
语言模型是在大量文本上训练出来的,因此它们的参数可能包含大量的事实性知识。由这些模型执行的任何下游任务都隐含地建立在这些事实的基础上,因此,非常希望有办法以可解释的方式表示这个知识体系。然而,目前还没有这样的表述机制。本文建议通过从一个给定的语言模型中提取事实的知识图谱来实现这一目标。本文描述了一个"爬取"语言模型内部知识库的程序。具体来说,给定一个种子实体,围绕它展开一个知识图谱。爬取程序被分解为子任务,通过特别设计的提示来实现,这些提示控制了精确度(即没有产生错误的事实)和召回率(即产生的事实的数量)。本文对从几十个种子实体开始抓取的图谱进行了评估,结果显示其产生了高精确度的图谱(82-92%),同时每个实体产生了合理数量的事实。
Language models are trained on large volumes of text, and as a result their parameters might contain a significant body of factual knowledge. Any downstream task performed by these models implicitly builds on these facts, and thus it is highly desirable to have means for representing this body of knowledge in an interpretable way. However, there is currently no mechanism for such a representation. Here, we propose to address this goal by extracting a knowledge-graph of facts from a given language model. We describe a procedure for "crawling" the internal knowledge-base of a language model. Specifically, given a seed entity, we expand a knowledge-graph around it. The crawling procedure is decomposed into sub-tasks, realized through specially designed prompts that control for both precision (i.e., that no wrong facts are generated) and recall (i.e., the number of facts generated). We evaluate our approach on graphs crawled starting from dozens of seed entities, and show it yields high precision graphs (82-92%), while emitting a reasonable number of facts per entity.
论文链接:https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.12810
内容中包含的图片若涉及版权问题,请及时与我们联系删除



评论
沙发等你来抢